Abstract
Human T-cell leukemia virus type 1 (HTLV-1) is a retrovirus associated with human diseases, such as adult T-cell leukemia (ATL) and HTLV-1-associated myelopathy/Tropic spastic paraparesis (HAM/TSP). As a retrovirus, its life cycle includes a step where HTLV-1 is integrated into the host genomic DNA and forms proviral DNA. In the chronic phase of the infection, HTLV‑1 is known to proliferate as a provirus via the mitotic division of the infected host cells. There are generally tens of thousands of infected clones within an infected individual. They exist not only in peripheral blood, but also in various lymphoid organs. Viral proteins encoded in HTLV-1 genome play a role in the proliferation and survival of the infected cells. As is the case with other chronic viral infections, HTLV-1 gene expression induces the activation of the host immunity against the virus. Thus, the transcription from HTLV-1 provirus needs to be controlled in order to evade the host immune surveillance. There should be a dynamic and complex regulation in vivo, where an equilibrium between viral antigen expression and host immune surveillance is achieved. The mechanisms regulating viral gene expression from the provirus are a key to understanding the persistent/latent infection with HTLV-1 and its pathogenesis. In this article, we would like to review our current understanding on this topic.
1. Introduction
It has been estimated that Human T-cell leukemia virus type 1 (HTLV-1) has been infecting humans for several thousand years [1]. In ancient times, prior to the advent of blood transfusions or drug abuse, the virus spread either by vertical transmission, from mother to child via breast-feeding, or by horizontal transmission mainly from man to woman, through sexual intercourse. HTLV-1 generally induces de novo infection not via free viral particles but via cell-to-cell contact between infected and uninfected cells [2,3,4]. The presence of infected lymphocytes in breast milk or sperm is pivotal for de novo infection. In the case of vertical transmission, infected individuals acquire the virus during infancy and need to carry the virus for decades, before they are able to transfer the virus to their children. Also, infected women need to remain healthy for decades in order to become pregnant, in spite of the persistent HTLV-1 infection in their bodies. To achieve such a long-term persistent infection without having severe health problems, HTLV-1 seems to have developed a strategy to achieve an asymptomatic condition by minimizing the effect of viral infection on our vital systems. At the same time, as with other viruses that cause persistent infections, HTLV-1 needs to evade the host immune surveillance [5].
The main routes of de novo HTLV-1 infection are cell-to-cell transmission and/or extracellular biofilm-like-structure-mediated transmission [2,4]. In either case, the virus produces viral proteins that are necessary for reverse transcription and integration of the viral DNA into the host cellular DNA. HTLV-1 is required to keep a latent state in the chronic phase of infection, but it also needs to reactivate viral gene expression for de novo infection. This implies that the virus makes use of a reversible system to switch from the latent phase of infection to the active phase, where viruses are produced. For example, when the infected cells are transferred from mother to child, proviruses in the infected lymphocytes contained in the breast-milk would be transcriptionally reactivated, and producing infectious viral particles or inducing cell-to-cell transmission. Since an anti-virus immunity has not been established yet in the new host during the initial phase of infection, the virus would be able to spread via de novo infection (Figure 1).
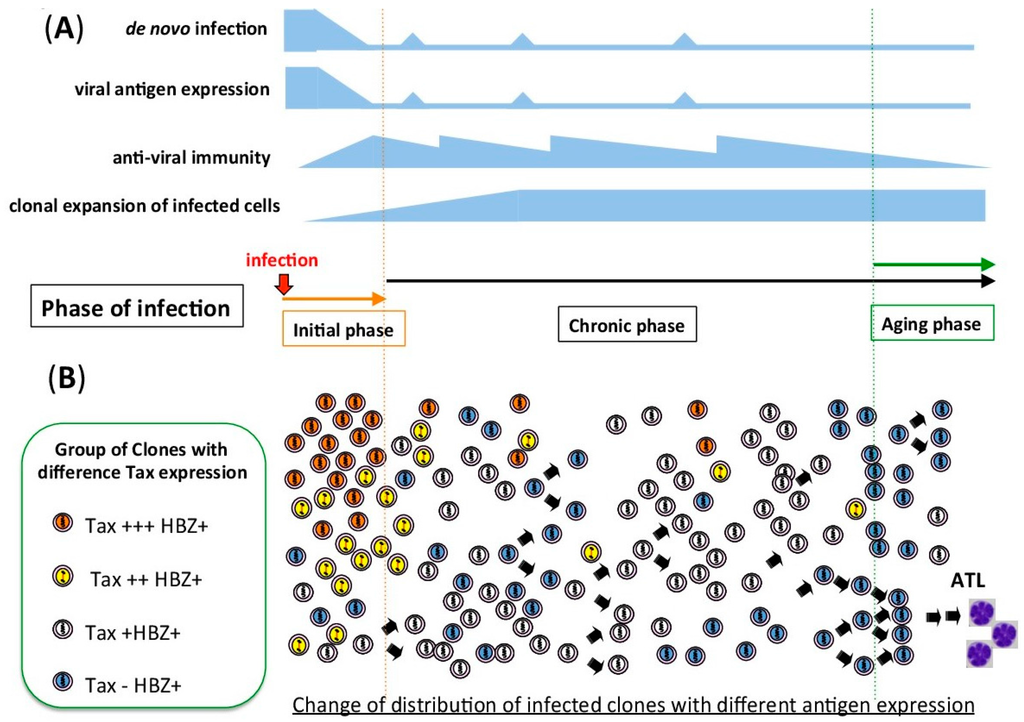
Figure 1.
Schematic figure of Human T-cell leukemia virus type 1 (HTLV-1) infection from the initial to the chronic phase of infection. (A) During the initial phase of infection, before an anti-virus immunity has been established, de novo infection should be more dominant than the clonal expansion of infected cells. In the chronic phase of infection, antiviral immunity removes infected cells with high viral antigen expression. HTLV-1 increases the viral copy number by clonal expansion of the infected cells. There is sporadic viral antigen expression, which should maintain the activity of the anti-viral immunity. (B) Change in the distribution of infected clones with different antigen expression. In the initial phase, the proportion of infected clones with high Tax expression is high, because there is little anti-viral immunity. After the establishment of an anti-viral immunity, clones with high antigen expression are eliminated by the host immune system.
In a typical asymptomatic carrier, approximately 2% of peripheral mononuclear cells are infected with HTLV-1 [6], which is far more frequent when compared with the proviral load of HIV‑1 in patients undergoing anti-retroviral therapy [7]. We can also observe cytotoxic T-lymphocytes (CTLs) specific for HTLV-1 antigens in asymptomatic carriers as well as in HTLV-1-associated myelopathy/Tropic spastic paraparesis (HAM/TSP) patients, suggesting that even in the absence of clinical symptoms there is a balance between the host immune surveillance and the persistent viral infection [8,9]. Therefore, to understand the regulatory mechanisms acting on HTLV-1 provirus integrated within the host genomic DNA is a key to elucidate the virological and pathophysiological aspect of HTLV-1 infection, including the mechanisms leading to transformation of the infected cells or the establishment of chronic inflammatory diseases.
2. Structure of Human T-cell Leukemia Virus Type 1 (HTLV-1)
HTLV-1 is a delta-type retrovirus [10,11]. Viral RNA is reverse-transcribed, integrated into the genomic DNA of the host cell, and thereafter remains as a provirus. The size of the proviral genome is approximately 9000 base pairs (bp) [12]. As is the case with other retroviruses, there are identical sequences, long terminal repeats (LTRs), at both ends of the provirus. The 5′-LTR is the promoter for the transcripts in the sense orientation, whereas the 3′-LTR is the promoter for antisense transcription. Most of the viral structural genes, such as gag, pol, and env are encoded in the 5′ side of the provirus in the sense orientation, as is commonly observed in other retroviruses [13]. However, a unique characteristic of HTLV-1, also shared with the bovine leukemia virus (BLV), another delta-type retrovirus, is the presence of the pX region, which is located in the 3′ side of the provirus. There are two regulatory proteins, Tax and Rex, encoded in the pX region. Tax, the most intensively characterized viral protein, is a strong transactivator of HTLV-1 5′-LTR. Rex is another positive regulator for the expression of viral antigens, which controls the nuclear export of viral mRNAs. There are several accessory proteins also encoded in the sense orientation in the pX region, including p13, p30, p12, p27, p21Rex and p8 [14,15,16,17,18]. In addition, HTLV-1 bZIP factor (HBZ) is encoded in the pX region in the anti-sense orientation [19].
HTLV-1 very efficiently utilizes its small genome via alternative splicing and bidirectional transcription. The regulatory and accessory viral proteins coordinately control viral antigen expression, contributing to achieve a persistent infection with HTLV-1.
3. Regulation of the 5′- and 3′-LTR Promoter Regions of HTLV-1 Provirus
There is sense- and antisense-transcription from HTLV-1 provirus, driven by sequences contained in the LTRs that serve as promoters. The sequence of the 5′- and 3′-LTRs is identical, so the directionality, sense or anti-sense orientation, confers the different promoter activity on the 5′- and 3′-LTRs. There is a DNA sequence found in the promoter region of some genes (TATA-box) in the sense orientation of the LTR, but not in the anti-sense orientation. Promoters containing a TATA-box structure generally exhibit high-plasticity in their promoter activity, whereas TATA-less promoters show low transcriptional plasticity [20,21]. In line with this notion, the plus strand of the 5′-LTR, a TATA-box-containing promoter, shows variable activity, whereas the minus strand of the 3′-LTR, a TATA-less promoter, shows a relatively stable promoter activity [22]. A recent study has shown that HTLV-1 LTR possesses a bidirectional transcriptional activity and that Tax could preferentially activate the sense transcription with no or limited effect on the antisense transcription in a reporter plasmid system [23]. It is well known that the sense transcription from the 5′-LTR is significantly induced in the presence of Tax. There are three copies of imperfect repeats of a 21 bp sequence called TRE (Tax-response element) that is responsive to the transactivation mediated by the viral protein Tax. Tax is a strong positive regulator of sense transcription from the 5′-LTR [12,24,25].
A recent interesting study has further extended our understanding on how both sense and antisense transcriptions are regulated within the provirus. They showed that sense transcription from the 5′-LTR did not interfere with antisense transcription from the 3′-LTR and vice versa [26]. They further showed that the cell cycle arrest induced by Tax expression might inhibit Tax-mediated activation of the sense transcription without affecting antisense transcription. As the authors pointed out, the mechanism may play a role in HTLV-1 latency. The 5′-LTR is regulated by cellular signaling pathways, such as the T-cell receptor (TCR)-mediated one, in addition to the viral regulatory/accessory proteins. TCR stimulation in combination with Tax strongly enhances HTLV-1 gene expression [27].
On the other hand, there are several negative regulatory systems acting on the 5′-LTR during transcription, translation, and even post-translation phases. HTLV-1 p30 has the potential to inhibit the interaction between Tax and p300, resulting in suppression of the 5′-LTR [28,29]. p30 additionally enhances the retention of mRNA in the nucleus and suppresses viral antigen expression [30]. HTLV-1 p13 is also known to exert an inhibitory effect on the physical interaction between Tax and p300 [15]. Furthermore, HBZ competes with Tax for cAMP response element binding (CREB) protein and p300 binding, so HBZ suppresses the 5′-LTR [19,31,32]. The minus strand of the 3′-LTR is the promoter of the spliced form of HBZ [33,34] and is controlled by Sp-1 and Jun-D [22,35]. The unspliced form of HBZ is transcribed from the promoter located within the pX region [22].
In summary, there is convergent transcription, in the sense- and antisense-orientations, and various viral transcripts with alternative splicing within HTLV-1 provirus. Growing evidence so far indicates that HTLV-1 maintains an equilibrium between viral antigen expression and the host immune surveillance by controlling both sense and antisense transcription, viral regulatory and accessory proteins’ expression, and host cellular mechanisms, such as cellular-signaling pathways and cell cycling.
5. Epigenetic Regulation of HTLV-1 Provirus
HTLV-1 provirus is integrated into the cellular DNA, chromatinized, and affected by genomic and epigenomic circumstances nearby the integration site [64,65,66,67]. An important characteristic of epigenetic regulation is that the epigenetic state is generally not static but variable depending on intra-cellular and/or extra-cellular conditions. For example, histone modifications are dynamically laid down and removed by chromatin-modifying enzymes [68,69]. As we discussed above, HTLV-1 has to be transcriptionally repressed but, at the same time, maintaining an ability to reactivate the proviral expression to achieve continuous infection within human beings. HTLV-1 should utilize a reversible epigenetic mechanism of the host cell to achieve a transiently suppressed condition of HTLV-1 provirus.
5.1. DNA Methylation of HTLV-1 Provirus
DNA methylation is a key mechanism to control gene expression of the host cells. Based on sequence analyses, HTLV-1 LTRs contain CpG islands, which are defined based on their high percentage of GC content (a GC percentage greater than 50%) and the length of the region (more than 200 bp) [70]. CpG islands are frequently present in gene promoter regions of the host cells and play a role in nucleosomal positioning and transcriptional regulation. DNA hypermethylation of CpG islands in promoter regions is associated with gene silencing. In the case of HTLV-1, DNA hypermethylation is what controls the activity of the 5′-LTR both in latently infected cell lines and ATL cells [54,71,72]. In contrast, the 3′-LTR is rarely methylated, suggesting that selective DNA methylation occurs in HTLV-1 provirus [41,71,73]. Since the sequence of the 5′- and the 3′-LTRs is identical, there should be some mechanism that induces selective DNA methylation of the 5′-LTR (or selective hypomethylation of 3′-LTR). That is a key question that remains to be answered about HTLV‑1 infection.
5.2. Histone Modifications in HTLV-1 Provirus
The nucleosome is the fundamental unit of chromatin, and it is composed of an octamer of the four core histones (H3, H4, H2A, and H2B). Around 147 bp of DNA wrap around each histone octamer. The histone tails are modified by acetylation, methylation, phosphorylation, and ubiquitylation [68]. These modifications function as platforms for the recruitment of specific effector proteins, such as transcriptional factors, chromatin remodelers and the general transcription apparatus, including RNA Polymerase II (RNA Pol II) [74]. Thus, histone modifications are a critical determinant for gene transcription [69]. The viral protein Tax, together with the phosphorylated CREB, recruits both CBP and p300 to the 5′-LTR [75], resulting in histone acetylation and eviction of nucleosomes, thus contributing to a strong sense transcription from the 5′-LTR [76,77]. Tax also interacts with the chromatin remodeling complex, changes nucleosome positioning, and induces transcriptional activation from the 5′-LTR [78,79]. These findings are thought to be molecular mechanisms inducing strong sense-transcription in in vitro cell cultures, where there is abundant Tax expression. The Tax-mediated strong transcription from the 5′-LTR is the case in vitro but not in vivo, as discussed above.
In order to characterize the pattern of histone modifications in vivo, we have to analyze fresh ATL cells without doing any ex vivo culture. There are some reports on histone acetylation and methylation of ATL cells. The previous data suggested that histone acetylation is detectable both in 5′- and 3′-LTRs [80,81]. We recently demonstrated that H3K9ac is high in the 3′-LTR but very low in the 5′-LTR in the ATL-derived cell line ED [39,67]. Another histone modification, H3K4me3, a mark of active promoter regions, also shows a similar distribution pattern as H3K9ac. In a proportion of fresh ATL cells and ATL cell lines, H3K9ac and H3K4me3 are detectable at the 5′-LTR, although the distribution is limited only to the 5′-LTR. On the other hand, the active histone marks around the 3′LTR are not limited to the LTR region, but extend to the pX region, suggesting different histone modifications between 5′- and 3′-LTRs [67].
In general, there are two categories of promoters, active and poised promoters [82]. Active promoters exhibit active histone marks both on the promoter region and downstream of the transcriptional start site, suggesting the movement of RNA Pol II starts at the promoter and moves into the gene body [74]. In contrast, poised promoters show limited distribution of H3K9ac and H3K4me3 at promoter regions. Taken together these data suggest that RNA Pol II might be present at both 5′- and 3′-LTRs. But, while the 5′-LTR is a poised promoter, the 3′-LTR functions as an active one. This is consistent with the pattern of transcription where the 3′-LTR is constitutively active but the 5′-LTR is generally suppressed. Also, poised RNA Pol II is ready to start transcription. The possibility of a poised RNA Pol II at the 5′-LTR would also explain why fresh PBMCs, isolated from HTLV-1-infected individuals, start to express Tax after a very short time in ex vivo culture.
Most studies on histone modifications of HTLV-1 have, so far, been limited to the promoter regions, 5′- and 3′-LTRs. However transcription is a biological event with multiple steps, including transcriptional initiation, elongation, and termination [83]. To understand the whole picture of transcriptional regulation, we need to analyze all processes of the transcription. Recent technological advances, such as chromatin immunoprecipitation sequencing (ChIP-seq) analysis will be able to provide more evidence on the epigenetic regulation of HTLV-1.
5.3. Insulator Region within HTLV-1 Provirus
As mentioned above, there is a significant difference in the transcriptional activity and the epigenetic characteristics of the 5′ and the 3′ regions of HTLV-1 provirus. Since the size of the provirus is just about 9000 bp, there should be a positive regulatory mechanism to maintain such distinct transcriptional activity within the provirus [67]. We have recently reported that the insulator-binding protein CTCF (CCCTC-binding factor) directly binds to HTLV-1 provirus. Insulator regions are functional genomic regions that delimit an epigenetic border between transcriptionally active and inactive regions [84]. CTCF is also the most characterized insulator-binding protein, which is well conserved from flies to humans, and plays a fundamental role in the higher order chromatin structure of the genome [85,86]. Histone modifications, such as H3K4me3, H3K36me3, and H3K9ac, are significantly changed at the insulator region of HTLV-1. These data suggest that HTLV-1 utilizes this host insulator-binding molecule to maintain the appropriate pattern of proviral transcription to achieve persistent infection in infected individuals (Figure 2).
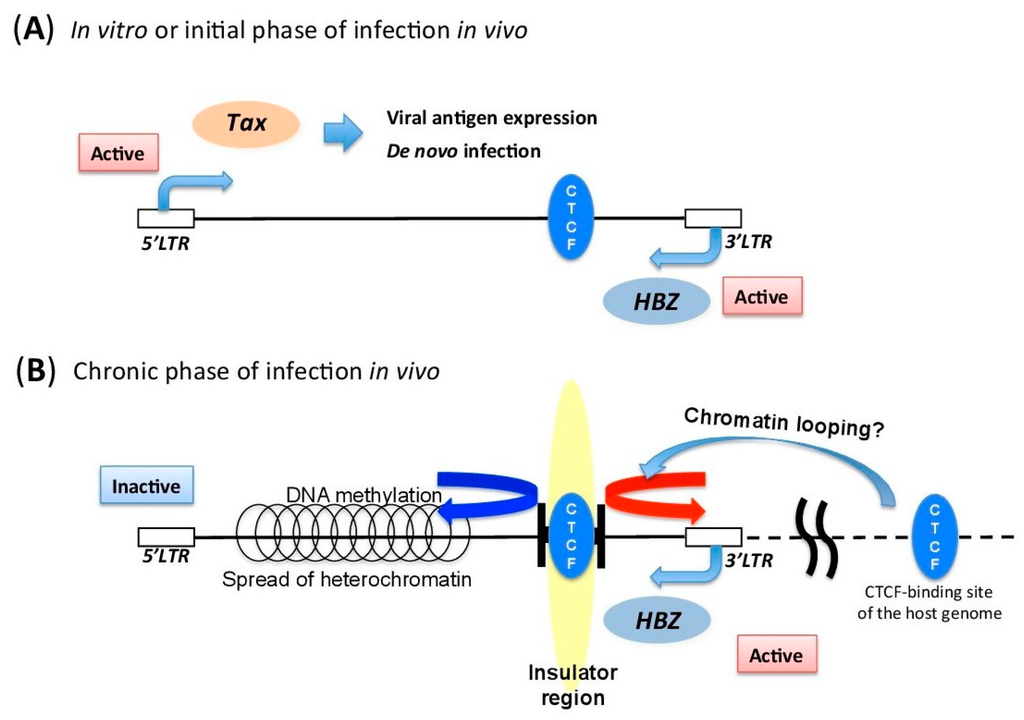
Figure 2.
Schematic figure of mechanisms regulating HTLV-1 provirus, in vitro and in vivo. (A) Schematic figure of HTLV-1 provirus in vitro or during the initial phase of infection in vivo. Tax and viral structural proteins can be expressed, because there is little immune surveillance against the viral antigens. (B) Schematic figure of HTLV-1 provirus during the chronic phase of infection in vivo. HTLV-1 maintains a distinct transcription pattern between 5′ long terminal repeat (LTR) and 3′-LTR by recruiting the host insulator protein CTCF. The insulator region of HTLV-1 provirus is thought to prevent the spread of heterochromatin from 5′-LTR to 3′-LTR. This could also induce chromatin looping with the host’s CTCF-binding sites.
Another function of CTCF is chromatin loop formation by homodimerization [87]. CTCF, in concert with Cohesin, regulates the proximity of promoters and enhancers, and controls the transcriptional activity of genes [88,89,90]. This suggests the possibility that HTLV-1 provirus can form chromatin looping with distant host genomic sites through its CTCF-binding site. Therefore, CTCF‑mediated chromatin looping with the host genome is another possible mechanism to regulate proviral expression. It is very interesting that some gamma herpes viruses, such as Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) and Kaposi’s sarcoma-associated herpesvirus (KSHV), also use CTCF to switch the pattern of viral gene expression [91,92]. As is the case with HTLV-1, EBV is known as a virus with different in vitro and in vivo pattern of viral gene transcription [93]. A previous report demonstrated that CTCF plays a role in determining promoter usage at different latency states in EBV infection [92]. EBV is generally not integrated into the host genome, but HTLV‑1 is integrated as a step of the viral life cycle of retroviruses. Thus integration of HTLV-1 generates ectopic CTCF-binding sites in the human genome. This could induce aberrant chromatin structure and gene transcription of the host genome [67,94].
8. Closing Remarks
Recent HTLV-1 research has made substantial progress in proviral regulation, but there are several issues that remain to be addressed. For example, the evidence we have so far is the result of analyzing a population of infected cells or ATL cells, so we cannot exclude the possibility that a part of the infected cells sporadically expresses plus-strand transcripts like Tax at the single-cell level. Also, it is still unclear how much the maintenance of ATL cells depends on HTLV-1 provirus. It is obvious that genetic and epigenetic alterations associated with oncogenesis in the host genome play a central role in the leukemogenesis of ATL [42,43,44,45,46,47,48,49,50]. Given that the incidence of T-cell malignancy in peripheral CD4 T cell is quite low in the absence of HTLV-1 infection, HTLV-1 does play a role in ATL generation in HTLV-1 infection. Intermittent expression of Tax possibly accelerates genomic and epigenomic abnormalities in the host cellular genome [25,107]. Continuous antisense transcription from the 3′-LTR supports the proliferation of ATL cells [34,52], which gives the host cells more of a chance to accumulate genomic and epigenomic alterations [3,13,61]. A wide variability of leukemogenesis among individual ATL cases is likely to exist. Further investigations are required to elucidate the role of proviral transcription in HTLV-1 pathogenesis.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by grants from the JSPS KAKENHI Grant Number 26461428 (Y.S.), Takeda Science Foundation (Y.S.), the Japan Science of Technology Agency (Y.S.), and JSPS KAKENHI Grant Number 16K19580 (H.K.).
Author Contributions
P.M. and Y.S. wrote the paper; M.M. and H.K. contributed with helpful discussions.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Van Dooren, S.; Salemi, M.; Vandamme, A.M. Dating the origin of the african human T-cell lymphotropic virus type-1 (HTLV-1) subtypes. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2001, 18, 661–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Igakura, T.; Stinchcombe, J.C.; Goon, P.K.; Taylor, G.P.; Weber, J.N.; Griffiths, G.M.; Tanaka, Y.; Osame, M.; Bangham, C.R. Spread of HTLV-1 between lymphocytes by virus-induced polarization of the cytoskeleton. Science 2003, 299, 1713–1716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsuoka, M.; Jeang, K.T. Human T-cell leukaemia virus type 1 (HTLV-1) infectivity and cellular transformation. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2007, 7, 270–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pais-Correia, A.M.; Sachse, M.; Guadagnini, S.; Robbiati, V.; Lasserre, R.; Gessain, A.; Gout, O.; Alcover, A.; Thoulouze, M.I. Biofilm-like extracellular viral assemblies mediate HTLV-1 cell-to-cell transmission at virological synapses. Nat. Med. 2010, 16, 83–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bangham, C.R. CTL quality and the control of human retroviral infections. Eur. J. Immunol. 2009, 39, 1700–1712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iwanaga, M.; Watanabe, T.; Utsunomiya, A.; Okayama, A.; Uchimaru, K.; Koh, K.R.; Ogata, M.; Kikuchi, H.; Sagara, Y.; Uozumi, K.; et al. Human T-cell leukemia virus type I (HTLV-1) proviral load and disease progression in asymptomatic HTLV-1 carriers: A nationwide prospective study in japan. Blood 2010, 116, 1211–1219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruelas, D.S.; Greene, W.C. An integrated overview of HIV-1 latency. Cell 2013, 155, 519–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jacobson, S.; Shida, H.; McFarlin, D.E.; Fauci, A.S.; Koenig, S. Circulating CD8+ cytotoxic T lymphocytes specific for HTLV-1 px in patients with HTLV-1 associated neurological disease. Nature 1990, 348, 245–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kannagi, M.; Harada, S.; Maruyama, I.; Inoko, H.; Igarashi, H.; Kuwashima, G.; Sato, S.; Morita, M.; Kidokoro, M.; Sugimoto, M.; et al. Predominant recognition of human T cell leukemia virus type i (HTLV-1) px gene products by human CD8+ cytotoxic T cells directed against HTLV-1-infected cells. Int. Immunol. 1991, 3, 761–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poiesz, B.J.; Ruscetti, F.W.; Gazdar, A.F.; Bunn, P.A.; Minna, J.D.; Gallo, R.C. Detection and isolation of type C retrovirus particles from fresh and cultured lymphocytes of a patient with cutaneous T-cell lymphoma. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1980, 77, 7415–7419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gallo, R.C. The discovery of the first human retrovirus: HTLV-1 and HTLV-2. Retrovirology 2005, 2, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seiki, M.; Hattori, S.; Hirayama, Y.; Yoshida, M. Human adult T-cell leukemia virus: Complete nucleotide sequence of the provirus genome integrated in leukemia cell DNA. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1983, 80, 3618–3622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, T. The role of HBZ in HTLV-1-induced oncogenesis. Viruses 2016, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valeri, V.W.; Hryniewicz, A.; Andresen, V.; Jones, K.; Fenizia, C.; Bialuk, I.; Chung, H.K.; Fukumoto, R.; Parks, R.W.; Ferrari, M.G.; et al. Requirement of the human T-cell leukemia virus p12 and p30 products for infectivity of human dendritic cells and macaques but not rabbits. Blood 2010, 116, 3809–3817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andresen, V.; Pise-Masison, C.A.; Sinha-Datta, U.; Bellon, M.; Valeri, V.; Washington Parks, R.; Cecchinato, V.; Fukumoto, R.; Nicot, C.; Franchini, G. Suppression of HTLV-1 replication by tax-mediated rerouting of the p13 viral protein to nuclear speckles. Blood 2011, 118, 1549–1559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zazopoulos, E.; Sodroski, J.G.; Haseltine, W.A. P21rex protein of HTLV-1. J. Acquir. Immune Defic. Syndr. 1990, 3, 1135–1139. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Silic-Benussi, M.; Biasiotto, R.; Andresen, V.; Franchini, G.; D’Agostino, D.M.; Ciminale, V. HTLV-1 p13, a small protein with a busy agenda. Mol. Asp. Med. 2010, 31, 350–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silic-Benussi, M.; Cavallari, I.; Vajente, N.; Vidali, S.; Chieco-Bianchi, L.; Di Lisa, F.; Saggioro, D.; D’Agostino, D.M.; Ciminale, V. Redox regulation of T-cell turnover by the p13 protein of human T-cell leukemia virus type 1: Distinct effects in primary versus transformed cells. Blood 2010, 116, 54–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaudray, G.; Gachon, F.; Basbous, J.; Biard-Piechaczyk, M.; Devaux, C.; Mesnard, J.M. The complementary strand of the human T-cell leukemia virus type 1 RNA genome encodes a bZIP transcription factor that down-regulates viral transcription. J. Virol. 2002, 76, 12813–12822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tirosh, I.; Weinberger, A.; Carmi, M.; Barkai, N. A genetic signature of interspecies variations in gene expression. Nat. Genet. 2006, 38, 830–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Landry, C.R.; Lemos, B.; Rifkin, S.A.; Dickinson, W.J.; Hartl, D.L. Genetic properties influencing the evolvability of gene expression. Science 2007, 317, 118–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshida, M.; Satou, Y.; Yasunaga, J.; Fujisawa, J.; Matsuoka, M. Transcriptional control of spliced and unspliced human T-cell leukemia virus type 1 bZIP factor (HBZ) gene. J. Virol. 2008, 82, 9359–9368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arpin-Andre, C.; Laverdure, S.; Barbeau, B.; Gross, A.; Mesnard, J.M. Construction of a reporter vector for analysis of bidirectional transcriptional activity of retrovirus LTR. Plasmid 2014, 74, 45–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujisawa, J.; Seiki, M.; Kiyokawa, T.; Yoshida, M. Functional activation of the long terminal repeat of human T-cell leukemia virus type 1 by a trans-acting factor. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1985, 82, 2277–2281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshida, M. Multiple viral strategies of HTLV-1 for dysregulation of cell growth control. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2001, 19, 475–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laverdure, S.; Polakowski, N.; Hoang, K.; Lemasson, I. Permissive sense and antisense transcription from the 5′ and 3′ long terminal repeats of human T-cell leukemia virus type 1. J. Virol. 2016, 90, 3600–3610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, H.C.; Hickey, M.; Hsu, L.; Medina, D.; Rabson, A.B. Activation of human T cell leukemia virus type 1 LTR promoter and cellular promoter elements by T cell receptor signaling and HTLV-1 tax expression. Virology 2005, 339, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.; Nisbet, J.W.; Bartoe, J.T.; Ding, W.; Lairmore, M.D. Human t-lymphotropic virus type 1 p30(ii) functions as a transcription factor and differentially modulates CREB-responsive promoters. J. Virol. 2000, 74, 11270–11277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.; Nisbet, J.W.; Albrecht, B.; Ding, W.; Kashanchi, F.; Bartoe, J.T.; Lairmore, M.D. Human t-lymphotropic virus type 1 p30(II) regulates gene transcription by binding CREB binding protein/p300. J. Virol. 2001, 75, 9885–9895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nicot, C.; Dundr, M.; Johnson, J.M.; Fullen, J.R.; Alonzo, N.; Fukumoto, R.; Princler, G.L.; Derse, D.; Misteli, T.; Franchini, G. HTLV-1-encoded p30ii is a post-transcriptional negative regulator of viral replication. Nat. Med. 2004, 10, 197–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lemasson, I.; Lewis, M.R.; Polakowski, N.; Hivin, P.; Cavanagh, M.H.; Thebault, S.; Barbeau, B.; Nyborg, J.K.; Mesnard, J.M. Human T-cell leukemia virus type 1 (HTLV-1) bZIP protein interacts with the cellular transcription factor CREB to inhibit HTLV-1 transcription. J. Virol. 2007, 81, 1543–1553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clerc, I.; Polakowski, N.; Andre-Arpin, C.; Cook, P.; Barbeau, B.; Mesnard, J.M.; Lemasson, I. An interaction between the human T cell leukemia virus type 1 basic leucine zipper factor (HBZ) and the KIX domain of p300/CBP contributes to the down-regulation of tax-dependent viral transcription by HBZ. J. Biol. Chem. 2008, 283, 23903–23913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murata, K.; Hayashibara, T.; Sugahara, K.; Uemura, A.; Yamaguchi, T.; Harasawa, H.; Hasegawa, H.; Tsuruda, K.; Okazaki, T.; Koji, T.; et al. A novel alteRNAtive splicing isoform of human T-cell leukemia virus type 1 bZIP factor (HBZ-SI) targets distinct subnuclear localization. J. Virol. 2006, 80, 2495–2505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Satou, Y.; Yasunaga, J.; Yoshida, M.; Matsuoka, M. HTLV-1 basic leucine zipper factor gene mRNA supports proliferation of adult T cell leukemia cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 720–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gazon, H.; Lemasson, I.; Polakowski, N.; Cesaire, R.; Matsuoka, M.; Barbeau, B.; Mesnard, J.M.; Peloponese, J.M., Jr. Human T-cell leukemia virus type 1 (HTLV-1) bZIP factor requires cellular transcription factor jund to upregulate HTLV-1 antisense transcription from the 3′ long terminal repeat. J. Virol. 2012, 86, 9070–9078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grassmann, R.; Berchtold, S.; Radant, I.; Alt, M.; Fleckenstein, B.; Sodroski, J.G.; Haseltine, W.A.; Ramstedt, U. Role of human T-cell leukemia virus type 1 x region proteins in immortalization of primary human lymphocytes in culture. J. Virol. 1992, 66, 4570–4575. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Akagi, T.; Shimotohno, K. Proliferative response of tax1-transduced primary human T cells to anti-cd3 antibody stimulation by an interleukin-2-independent pathway. J. Virol. 1993, 67, 1211–1217. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Akagi, T.; Ono, H.; Shimotohno, K. Characterization of T cells immortalized by tax1 of human T-cell leukemia virus type 1. Blood 1995, 86, 4243–4249. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Maeda, M.; Shimizu, A.; Ikuta, K.; Okamoto, H.; Kashihara, M.; Uchiyama, T.; Honjo, T.; Yodoi, J. Origin of human t-lymphotrophic virus i-positive T cell lines in adult T cell leukemia. Analysis of T cell receptor gene rearrangement. J. Exp. Med. 1985, 162, 2169–2174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Furukawa, Y.; Kubota, R.; Tara, M.; Izumo, S.; Osame, M. Existence of escape mutant in HTLV-1 tax during the development of adult T-cell leukemia. Blood 2001, 97, 987–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takeda, S.; Maeda, M.; Morikawa, S.; Taniguchi, Y.; Yasunaga, J.; Nosaka, K.; Tanaka, Y.; Matsuoka, M. Genetic and epigenetic inactivation of tax gene in adult T-cell leukemia cells. Int. J. Cancer 2004, 109, 559–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nosaka, K.; Maeda, M.; Tamiya, S.; Sakai, T.; Mitsuya, H.; Matsuoka, M. Increasing methylation of the cdkn2a gene is associated with the progression of adult T-cell leukemia. Cancer Res. 2000, 60, 1043–1048. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Yasunaga, J.; Taniguchi, Y.; Nosaka, K.; Yoshida, M.; Satou, Y.; Sakai, T.; Mitsuya, H.; Matsuoka, M. Identification of aberrantly methylated genes in association with adult T-cell leukemia. Cancer Res. 2004, 64, 6002–6009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshida, M.; Nosaka, K.; Yasunaga, J.; Nishikata, I.; Morishita, K.; Matsuoka, M. Aberrant expression of the MEL1S gene identified in association with hypomethylation in adult T-cell leukemia cells. Blood 2004, 103, 2753–2760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hidaka, T.; Nakahata, S.; Hatakeyama, K.; Hamasaki, M.; Yamashita, K.; Kohno, T.; Arai, Y.; Taki, T.; Nishida, K.; Okayama, A.; et al. Down-regulation of TCF8 is involved in the leukemogenesis of adult T-cell leukemia/lymphoma. Blood 2008, 112, 383–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamagishi, M.; Nakano, K.; Miyake, A.; Yamochi, T.; Kagami, Y.; Tsutsumi, A.; Matsuda, Y.; Sato-Otsubo, A.; Muto, S.; Utsunomiya, A.; et al. Polycomb-mediated loss of mir-31 activates nik-dependent nf-kappab pathway in adult T cell leukemia and other cancers. Cancer Cell 2012, 21, 121–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kataoka, K.; Nagata, Y.; Kitanaka, A.; Shiraishi, Y.; Shimamura, T.; Yasunaga, J.; Totoki, Y.; Chiba, K.; Sato-Otsubo, A.; Nagae, G.; et al. Integrated molecular analysis of adult T cell leukemia/lymphoma. Nat. Genet. 2015, 47, 1304–1315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujikawa, D.; Nakagawa, S.; Hori, M.; Kurokawa, N.; Soejima, A.; Nakano, K.; Yamochi, T.; Nakashima, M.; Kobayashi, S.; Tanaka, Y.; et al. Polycomb-dependent epigenetic landscape in adult T-cell leukemia. Blood 2016, 127, 1790–1802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagata, Y.; Kontani, K.; Enami, T.; Kataoka, K.; Ishii, R.; Totoki, Y.; Kataoka, T.R.; Hirata, M.; Aoki, K.; Nakano, K.; et al. Variegated RHOA mutations in adult T-cell leukemia/lymphoma. Blood 2016, 127, 596–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakagawa, M.; Schmitz, R.; Xiao, W.; Goldman, C.K.; Xu, W.; Yang, Y.; Yu, X.; Waldmann, T.A.; Staudt, L.M. Gain-of-function ccr4 mutations in adult T cell leukemia/lymphoma. J. Exp. Med. 2014, 211, 2497–2505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Belrose, G.; Gross, A.; Olindo, S.; Lezin, A.; Dueymes, M.; Komla-Soukha, I.; Smadja, D.; Tanaka, Y.; Willems, L.; Mesnard, J.M.; et al. Effects of valproate on tax and HBZ expression in HTLV-1 and ham/tsp T lymphocytes. Blood 2011, 118, 2483–2491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Usui, T.; Yanagihara, K.; Tsukasaki, K.; Murata, K.; Hasegawa, H.; Yamada, Y.; Kamihira, S. Characteristic expression of HTLV-1 basic zipper factor (HBZ) transcripts in HTLV-1 provirus-positive cells. Retrovirology 2008, 5, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Macnamara, A.; Rowan, A.; Hilburn, S.; Kadolsky, U.; Fujiwara, H.; Suemori, K.; Yasukawa, M.; Taylor, G.; Bangham, C.R.; Asquith, B. Hla class i binding of HBZ determines outcome in HTLV-1 infection. PLoS Pathog. 2010, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clarke, M.F.; Trainor, C.D.; Mann, D.L.; Gallo, R.C.; Reitz, M.S. Methylation of human T-cell leukemia virus proviral DNA and viral RNA expression in short- and long-term cultures of infected cells. Virology 1984, 135, 97–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanon, E.; Hall, S.; Taylor, G.P.; Saito, M.; Davis, R.; Tanaka, Y.; Usuku, K.; Osame, M.; Weber, J.N.; Bangham, C.R. Abundant tax protein expression in CD4+ T cells infected with human T-cell lymphotropic virus type i (HTLV-1) is prevented by cytotoxic T lymphocytes. Blood 2000, 95, 1386–1392. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Satou, Y.; Utsunomiya, A.; Tanabe, J.; Nakagawa, M.; Nosaka, K.; Matsuoka, M. HTLV-1 modulates the frequency and phenotype of foxp3+CD4+ T cells in virus-infected individuals. Retrovirology 2012, 9, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rende, F.; Cavallari, I.; Corradin, A.; Silic-Benussi, M.; Toulza, F.; Toffolo, G.M.; Tanaka, Y.; Jacobson, S.; Taylor, G.P.; D’Agostino, D.M.; et al. Kinetics and intracellular compartmentalization of HTLV-1 gene expression: Nuclear retention of HBZ mRNAs. Blood 2011, 117, 4855–4859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cavallari, I.; Rende, F.; Ciminale, V. Quantitative analysis of human t-lymphotropic virus type 1 (HTLV-1) gene expression using nucleo-cytoplasmic fractionation and splice junction-specific real-time rt-pcr (qrt-pcr). Methods Mol. Biol. 2014, 1087, 325–337. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Cavallari, I.; Rende, F.; Bona, M.K.; Sztuba-Solinska, J.; Silic-Benussi, M.; Tognon, M.; LeGrice, S.F.; Franchini, G.; D’Agostino, D.M.; Ciminale, V. Expression of alternatively spliced human T-cell leukemia virus type 1 mRNAs is influenced by mitosis and by a novel cis-acting regulatory sequence. J. Virol. 2016, 90, 1486–1498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitobe, Y.; Yasunaga, J.; Furuta, R.; Matsuoka, M. HTLV-1 bZIP factor RNA and protein impart distinct functions on T-cell proliferation and survival. Cancer Res. 2015, 75, 4143–4152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Satou, Y.; Matsuoka, M. Implication of the HTLV-1 bZIP factor gene in the leukemogenesis of adult T-cell leukemia. Int. J. Hematol. 2007, 86, 107–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, G.; Yasunaga, J.; Matsuoka, M. Multifaceted functions and roles of HBZ in HTLV-1 pathogenesis. Retrovirology 2016, 13, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cavanagh, M.H.; Landry, S.; Audet, B.; Arpin-Andre, C.; Hivin, P.; Pare, M.E.; Thete, J.; Wattel, E.; Marriott, S.J.; Mesnard, J.M.; et al. HTLV-1 antisense transcripts initiating in the 3′LTR are alternatively spliced and polyadenylated. Retrovirology 2006, 3, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gillet, N.A.; Malani, N.; Melamed, A.; Gormley, N.; Carter, R.; Bentley, D.; Berry, C.; Bushman, F.D.; Taylor, G.P.; Bangham, C.R. The host genomic environment of the provirus determines the abundance of HTLV-1-infected T-cell clones. Blood 2011, 117, 3113–3122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Melamed, A.; Laydon, D.J.; Gillet, N.A.; Tanaka, Y.; Taylor, G.P.; Bangham, C.R. Genome-wide determinants of proviral targeting, clonal abundance and expression in natural HTLV-1 infection. PLoS Pathog. 2013, 9, e1003271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bangham, C.R.; Cook, L.B.; Melamed, A. HTLV-1 clonality in adult T-cell leukaemia and non-malignant HTLV-1 infection. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2014, 26, 89–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Satou, Y.; Miyazato, P.; Ishihara, K.; Yaguchi, H.; Melamed, A.; Miura, M.; Fukuda, A.; Nosaka, K.; Watanabe, T.; Rowan, A.G.; et al. The retrovirus HTLV-1 inserts an ectopic CTCF-binding site into the human genome. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, 3054–3059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kouzarides, T. Chromatin modifications and their function. Cell 2007, 128, 693–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, B.; Carey, M.; Workman, J.L. The role of chromatin during transcription. Cell 2007, 128, 707–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deaton, A.M.; Bird, A. CpG islands and the regulation of transcription. Genes Dev. 2011, 25, 1010–1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kitamura, T.; Takano, M.; Hoshino, H.; Shimotohno, K.; Shimoyama, M.; Miwa, M.; Takaku, F.; Sugimura, T. Methylation pattern of human T-cell leukemia virus in vivo and in vitro: Px and LTR regions are hypomethylated in vivo. Int. J. Cancer 1985, 35, 629–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saggioro, D.; Panozzo, M.; Chieco-Bianchi, L. Human t-lymphotropic virus type i transcriptional regulation by methylation. Cancer Res. 1990, 50, 4968–4973. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Koiwa, T.; Hamano-Usami, A.; Ishida, T.; Okayama, A.; Yamaguchi, K.; Kamihira, S.; Watanabe, T. 5′-long terminal repeat-selective CpG methylation of latent human T-cell leukemia virus type 1 provirus in vitro and in vivo. J. Virol. 2002, 76, 9389–9397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Q.; Li, T.; Price, D.H. RNA polymerase ii elongation control. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2012, 81, 119–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geiger, T.R.; Sharma, N.; Kim, Y.M.; Nyborg, J.K. The human T-cell leukemia virus type 1 Tax protein confers CBP/p300 recruitment and transcriptional activation properties to phosphorylated CREB. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2008, 28, 1383–1392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lemasson, I.; Polakowski, N.J.; Laybourn, P.J.; Nyborg, J.K. Tax-dependent displacement of nucleosomes during transcriptional activation of human T-cell leukemia virus type 1. J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 281, 13075–13082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, N.; Nyborg, J.K. The coactivators CBP/p300 and the histone chaperone nap1 promote transcription-independent nucleosome eviction at the HTLV-1 promoter. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 7959–7963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Easley, R.; Carpio, L.; Guendel, I.; Klase, Z.; Choi, S.; Kehn-Hall, K.; Brady, J.N.; Kashanchi, F. Human t-lymphotropic virus type 1 transcription and chromatin-remodeling complexes. J. Virol. 2010, 84, 4755–4768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lemasson, I.; Polakowski, N.J.; Laybourn, P.J.; Nyborg, J.K. Transcription factor binding and histone modifications on the integrated proviral promoter in human T-cell leukemia virus-i-infected T-cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 49459–49465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lemasson, I.; Polakowski, N.J.; Laybourn, P.J.; Nyborg, J.K. Transcription regulatory complexes bind the human T-cell leukemia virus 5′ and 3′ long terminal repeats to control gene expression. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2004, 24, 6117–6126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taniguchi, Y.; Nosaka, K.; Yasunaga, J.; Maeda, M.; Mueller, N.; Okayama, A.; Matsuoka, M. Silencing of human T-cell leukemia virus type i gene transcription by epigenetic mechanisms. Retrovirology 2005, 2, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barski, A.; Cuddapah, S.; Cui, K.; Roh, T.Y.; Schones, D.E.; Wang, Z.; Wei, G.; Chepelev, I.; Zhao, K. High-resolution profiling of histone methylations in the human genome. Cell 2007, 129, 823–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moore, M.J.; Proudfoot, N.J. Pre-mRNA processing reaches back to transcription and ahead to translation. Cell 2009, 136, 688–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bell, A.C.; Felsenfeld, G. Methylation of a CTCF-dependent boundary controls imprinted expression of the igf2 gene. Nature 2000, 405, 482–485. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hark, A.T.; Schoenherr, C.J.; Katz, D.J.; Ingram, R.S.; Levorse, J.M.; Tilghman, S.M. CTCF mediates methylation-sensitive enhancer-blocking activity at the H19/IGF2 locus. Nature 2000, 405, 486–489. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ong, C.T.; Corces, V.G. CTCF: An architectural protein bridging genome topology and function. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2014, 15, 234–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Wit, E.; Vos, E.S.; Holwerda, S.J.; Valdes-Quezada, C.; Verstegen, M.J.; Teunissen, H.; Splinter, E.; Wijchers, P.J.; Krijger, P.H.; de Laat, W. CTCF binding polarity determines chromatin looping. Mol. Cell 2015, 60, 676–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wendt, K.S.; Yoshida, K.; Itoh, T.; Bando, M.; Koch, B.; Schirghuber, E.; Tsutsumi, S.; Nagae, G.; Ishihara, K.; Mishiro, T.; et al. Cohesin mediates transcriptional insulation by ccctc-binding factor. Nature 2008, 451, 796–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, S.S.; Huntley, M.H.; Durand, N.C.; Stamenova, E.K.; Bochkov, I.D.; Robinson, J.T.; Sanborn, A.L.; Machol, I.; Omer, A.D.; Lander, E.S.; et al. A 3D map of the human genome at kilobase resolution reveals principles of chromatin looping. Cell 2014, 159, 1665–1680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, Z.; Luo, O.J.; Li, X.; Zheng, M.; Zhu, J.J.; Szalaj, P.; Trzaskoma, P.; Magalska, A.; Wlodarczyk, J.; Ruszczycki, B.; et al. CTCF-mediated human 3D genome architecture reveals chromatin topology for transcription. Cell 2015, 163, 1611–1627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, H.; Cho, H.; Sung, G.H.; Lieberman, P.M. CTCF regulates kaposi’s sarcoma-associated herpesvirus latency transcription by nucleosome displacement and RNA polymerase programming. J. Virol. 2013, 87, 1789–1799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tempera, I.; Lieberman, P.M. Epigenetic regulation of ebv persistence and oncogenesis. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2014, 26, 22–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lieberman, P.M. Chromatin structure of epstein-barr virus latent episomes. Curr. Top. Microbiol. Immunol. 2015, 390, 71–102. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kim, T.H.; Abdullaev, Z.K.; Smith, A.D.; Ching, K.A.; Loukinov, D.I.; Green, R.D.; Zhang, M.Q.; Lobanenkov, V.V.; Ren, B. Analysis of the vertebrate insulator protein CTCF-binding sites in the human genome. Cell 2007, 128, 1231–1245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshida, M.; Seiki, M.; Yamaguchi, K.; Takatsuki, K. Monoclonal integration of human T-cell leukemia provirus in all primary tumors of adult T-cell leukemia suggests causative role of human T-cell leukemia virus in the disease. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1984, 81, 2534–2537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Etoh, K.; Tamiya, S.; Yamaguchi, K.; Okayama, A.; Tsubouchi, H.; Ideta, T.; Mueller, N.; Takatsuki, K.; Matsuoka, M. Persistent clonal proliferation of human t-lymphotropic virus type 1-infected cells in vivo. Cancer Res. 1997, 57, 4862–4867. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Doi, K.; Wu, X.; Taniguchi, Y.; Yasunaga, J.; Satou, Y.; Okayama, A.; Nosaka, K.; Matsuoka, M. Preferential selection of human T-cell leukemia virus type 1 provirus integration sites in leukemic versus carrier states. Blood 2005, 106, 1048–1053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meekings, K.N.; Leipzig, J.; Bushman, F.D.; Taylor, G.P.; Bangham, C.R. HTLV-1 integration into transcriptionally active genomic regions is associated with proviral expression and with HAM/TSP. PLoS Pathog. 2008, 4, e1000027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Firouzi, S.; Lopez, Y.; Suzuki, Y.; Nakai, K.; Sugano, S.; Yamochi, T.; Watanabe, T. Development and validation of a new high-throughput method to investigate the clonality of HTLV-1-infected cells based on provirus integration sites. Genome Med. 2014, 6, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gillet, N.A.; Gutierrez, G.; Rodriguez, S.M.; de Brogniez, A.; Renotte, N.; Alvarez, I.; Trono, K.; Willems, L. Massive depletion of bovine leukemia virus proviral clones located in genomic transcriptionally active sites during primary infection. PLoS Pathog. 2013, 9, e1003687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daenke, S.; Nightingale, S.; Cruickshank, J.K.; Bangham, C.R. Sequence variants of human T-cell lymphotropic virus type i from patients with tropical spastic paraparesis and adult T-cell leukemia do not distinguish neurological from leukemic isolates. J. Virol. 1990, 64, 1278–1282. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Konishi, H.; Kobayashi, N.; Hatanaka, M. Defective human T-cell leukemia virus in adult T-cell leukemia patients. Mol. Biol. Med. 1984, 2, 273–283. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Manzari, V.; Wong-Staal, F.; Franchini, G.; Colombini, S.; Gelmann, E.P.; Oroszlan, S.; Staal, S.; Gallo, R.C. Human T-cell leukemia-lymphoma virus (HTLV): Cloning of an integrated defective provirus and flanking cellular sequences. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1983, 80, 1574–1578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tamiya, S.; Matsuoka, M.; Etoh, K.; Watanabe, T.; Kamihira, S.; Yamaguchi, K.; Takatsuki, K. Two types of defective human t-lymphotropic virus type i provirus in adult T-cell leukemia. Blood 1996, 88, 3065–3073. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Miyazaki, M.; Yasunaga, J.; Taniguchi, Y.; Tamiya, S.; Nakahata, T.; Matsuoka, M. Preferential selection of human T-cell leukemia virus type 1 provirus lacking the 5′ long terminal repeat during oncogenesis. J. Virol. 2007, 81, 5714–5723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, J.; Ma, G.; Nosaka, K.; Tanabe, J.; Satou, Y.; Koito, A.; Wain-Hobson, S.; Vartanian, J.P.; Matsuoka, M. Apobec3g generates nonsense mutations in human T-cell leukemia virus type 1 proviral genomes in vivo. J. Virol. 2010, 84, 7278–7287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grassmann, R.; Aboud, M.; Jeang, K.T. Molecular mechanisms of cellular transformation by HTLV-1 tax. Oncogene 2005, 24, 5976–5985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).