The Feat of Packaging Eight Unique Genome Segments
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Nuclear Export of vRNPs
3. Perinuclear vRNP Accumulation at the Microtubule-Organizing Center
4. Rab11GTP-Mediated vRNP Transport Towards the Apical Plasma Membrane
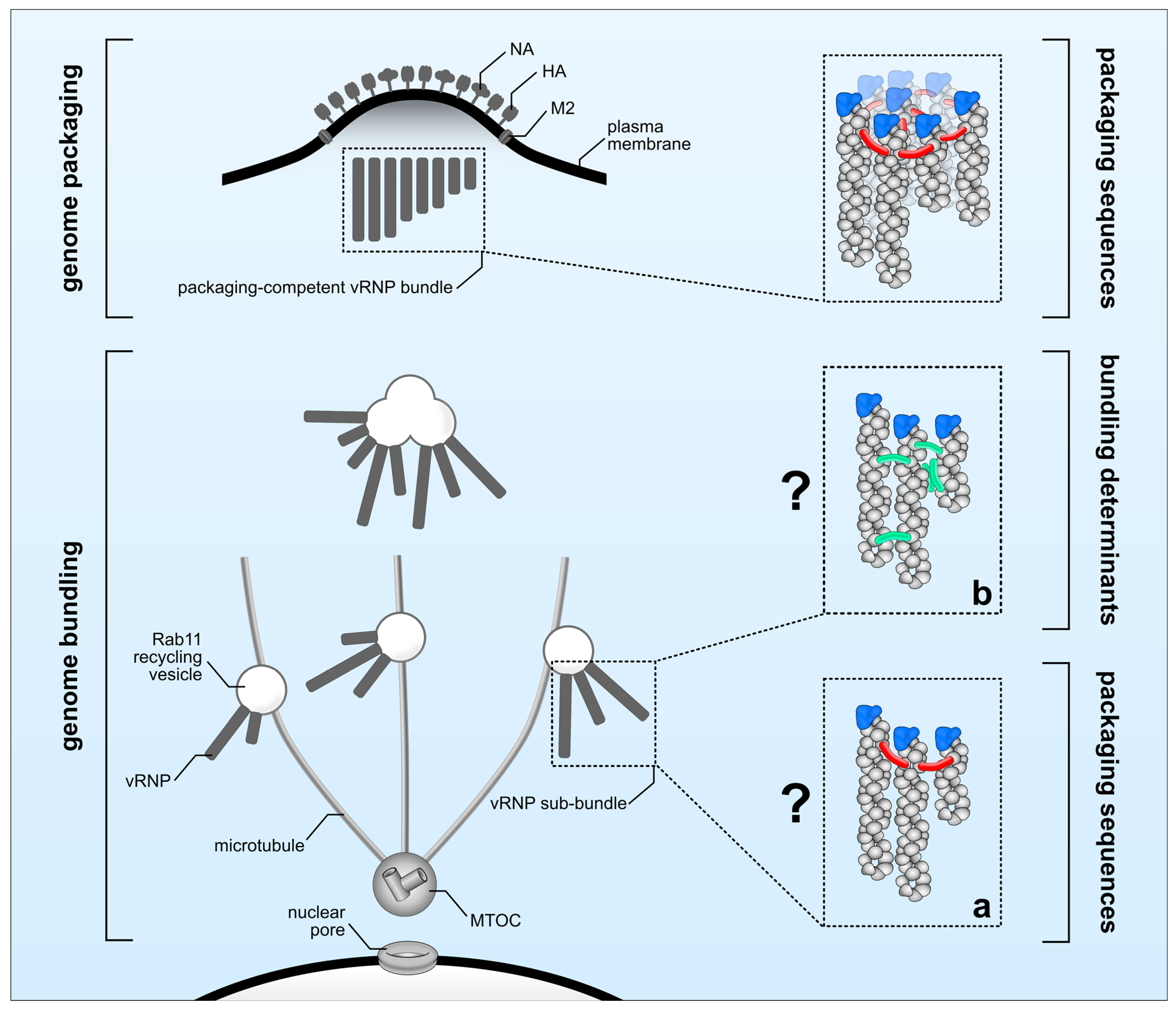
5. Genome Packaging
6. Genome Bundling and Genome Packaging: Interconnected or Not?
Acknowledgment
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Palese, P.; Schulman, J.L. Mapping of the influenza virus genome: identification of the hemagglutinin and the neuraminidase genes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1976, 73, 2142–2146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Compans, R.W.; Content, J.; Duesberg, P.H. Structure of the ribonucleoprotein of influenza virus. J. Virol. 1972, 10, 795–800. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Fodor, E.; Seong, B.L.; Brownlee, G.G. Photochemical cross-linking of influenza A polymerase to its virion RNA promoter defines a polymerase binding site at residues 9 to 12 of the promoter. J. Gen. Virol. 1993, 74 Pt 7, 1327–1333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsu, M.T.; Parvin, J.D.; Gupta, S.; Krystal, M.; Palese, P. Genomic RNAs of influenza viruses are held in a circular conformation in virions and in infected cells by a terminal panhandle. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1987, 84, 8140–8144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garten, R.J.; Davis, C.T.; Russell, C.A.; Shu, B.; Lindstrom, S.; Balish, A.; Sessions, W.M.; Xu, X.; Skepner, E.; Deyde, V.; et al. Antigenic and genetic characteristics of swine-origin 2009 A(H1N1) influenza viruses circulating in humans. Science 2009, 325, 197–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lam, T.T.; Wang, J.; Shen, Y.; Zhou, B.; Duan, L.; Cheung, C.L.; Ma, C.; Lycett, S.J.; Leung, C.Y.; Chen, X.; et al. The genesis and source of the H7N9 influenza viruses causing human infections in China. Nature 2013, 502, 241–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gerber, M.; Isel, C.; Moules, V.; Marquet, R. Selective packaging of the influenza A genome and consequences for genetic reassortment. Trends Microbiol. 2014, 22, 446–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goto, H.; Muramoto, Y.; Noda, T.; Kawaoka, Y. The genome-packaging signal of the influenza A virus genome comprises a genome incorporation signal and a genome-bundling signal. J. Virol. 2013, 87, 11316–11322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hutchinson, E.C.; von Kirchbach, J.C.; Gog, J.R.; Digard, P. Genome packaging in influenza A virus. J. Gen. Virol. 2010, 91, 313–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lakdawala, S.S.; Wu, Y.; Wawrzusin, P.; Kabat, J.; Broadbent, A.J.; Lamirande, E.W.; Fodor, E.; Altan-Bonnet, N.; Shroff, H.; Subbarao, K. Influenza A virus assembly intermediates fuse in the cytoplasm. PLoS Pathog. 2014, 10, e1003971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chou, Y.Y.; Heaton, N.S.; Gao, Q.; Palese, P.; Singer, R.H.; Lionnet, T. Colocalization of different influenza viral RNA segments in the cytoplasm before viral budding as shown by single-molecule sensitivity FISH analysis. PLoS Pathog. 2013, 9, e1003358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O'Neill, R.E.; Jaskunas, R.; Blobel, G.; Palese, P.; Moroianu, J. Nuclear import of influenza virus RNA can be mediated by viral nucleoprotein and transport factors required for protein import. J. Biol. Chem. 1995, 270, 22701–22704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakada, R.; Hirano, H.; Matsuura, Y. Structure of importin-alpha bound to a non-classical nuclear localization signal of the influenza A virus nucleoprotein. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 15055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, W.W.; Sun, Y.H.; Pante, N. Nuclear import of influenza A viral ribonucleoprotein complexes is mediated by two nuclear localization sequences on viral nucleoprotein. Virol J. 2007, 4, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hutchinson, E.C.; Fodor, E. Transport of the influenza virus genome from nucleus to nucleus. Viruses 2013, 5, 2424–2446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dias, A.; Bouvier, D.; Crepin, T.; McCarthy, A.A.; Hart, D.J.; Baudin, F.; Cusack, S.; Ruigrok, R.W. The cap-snatching endonuclease of influenza virus polymerase resides in the PA subunit. Nature 2009, 458, 914–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Plotch, S.J.; Bouloy, M.; Ulmanen, I.; Krug, R.M. A unique cap(m7GpppXm)-dependent influenza virion endonuclease cleaves capped RNAs to generate the primers that initiate viral RNA transcription. Cell 1981, 23, 847–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guilligay, D.; Tarendeau, F.; Resa-Infante, P.; Coloma, R.; Crepin, T.; Sehr, P.; Lewis, J.; Ruigrok, R.W.; Ortin, J.; Hart, D.J.; et al. The structural basis for cap binding by influenza virus polymerase subunit PB2. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2008, 15, 500–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kobayashi, M.; Toyoda, T.; Ishihama, A. Influenza virus PB1 protein is the minimal and essential subunit of RNA polymerase. Arch. Virol. 1996, 141, 525–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toyoda, T.; Kobayashi, M.; Nakada, S.; Ishihama, A. Molecular dissection of influenza virus RNA polymerase: PB1 subunit alone is able to catalyze RNA synthesis. Virus Genes 1996, 12, 155–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biswas, S.K.; Nayak, D.P. Mutational analysis of the conserved motifs of influenza A virus polymerase basic protein 1. J. Virol. 1994, 68, 1819–1826. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ulmanen, I.; Broni, B.A.; Krug, R.M. Role of two of the influenza virus core P proteins in recognizing cap 1 structures (m7GpppNm) on RNAs and in initiating viral RNA transcription. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1981, 78, 7355–7359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jorba, N.; Coloma, R.; Ortin, J. Genetic trans-complementation establishes a new model for influenza virus RNA transcription and replication. PLoS Pathog. 2009, 5, e1000462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vreede, F.T.; Ng, A.K.; Shaw, P.C.; Fodor, E. Stabilization of influenza virus replication intermediates is dependent on the RNA-binding but not the homo-oligomerization activity of the viral nucleoprotein. J. Virol. 2011, 85, 12073–12078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moeller, A.; Kirchdoerfer, R.N.; Potter, C.S.; Carragher, B.; Wilson, I.A. Organization of the influenza virus replication machinery. Science 2012, 338, 1631–1634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akarsu, H.; Burmeister, W.P.; Petosa, C.; Petit, I.; Muller, C.W.; Ruigrok, R.W.; Baudin, F. Crystal structure of the M1 protein-binding domain of the influenza A virus nuclear export protein (NEP/NS2). EMBO J. 2003, 22, 4646–4655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin, K.; Helenius, A. Nuclear transport of influenza virus ribonucleoproteins: the viral matrix protein (M1) promotes export and inhibits import. Cell 1991, 67, 117–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brunotte, L.; Flies, J.; Bolte, H.; Reuther, P.; Vreede, F.; Schwemmle, M. The nuclear export protein of H5N1 influenza A viruses recruits Matrix 1 (M1) protein to the viral ribonucleoprotein to mediate nuclear export. J. Biol. Chem. 2014, 289, 20067–20077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shimizu, T.; Takizawa, N.; Watanabe, K.; Nagata, K.; Kobayashi, N. Crucial role of the influenza virus NS2 (NEP) C-terminal domain in M1 binding and nuclear export of vRNP. FEBS Lett. 2011, 585, 41–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O'Neill, R.E.; Talon, J.; Palese, P. The influenza virus NEP (NS2 protein) mediates the nuclear export of viral ribonucleoproteins. EMBO J. 1998, 17, 288–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elton, D.; Simpson-Holley, M.; Archer, K.; Medcalf, L.; Hallam, R.; McCauley, J.; Digard, P. Interaction of the influenza virus nucleoprotein with the cellular CRM1-mediated nuclear export pathway. J. Virol. 2001, 75, 408–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, K.; Roy, A.M.; Whittaker, G.R. Nuclear export of influenza virus ribonucleoproteins: Identification of an export intermediate at the nuclear periphery. Virology 2001, 282, 215–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, C.Y.; Jeng, K.S.; Lai, M.M. The SUMOylation of matrix protein M1 modulates the assembly and morphogenesis of influenza A virus. J. Virol. 2011, 85, 6618–6628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, W.; Li, J.; Wang, S.; Cao, S.; Jiang, J.; Chen, C.; Ding, C.; Qin, C.; Ye, X.; Gao, G.F.; et al. Phosphorylation controls the nuclear-cytoplasmic shuttling of influenza A virus nucleoprotein. J. Virol. 2015, 89, 5822–5834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reuther, P.; Giese, S.; Gotz, V.; Riegger, D.; Schwemmle, M. Phosphorylation of highly conserved serine residues in the influenza A virus nuclear export protein NEP plays a minor role in viral growth in human cells and mice. J. Virol. 2014, 88, 7668–7673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eisfeld, A.J.; Neumann, G.; Kawaoka, Y. Human immunodeficiency virus Rev-binding protein is essential for influenza A virus replication and promotes genome trafficking in late-stage infection. J. Virol. 2011, 85, 9588–9598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wurzer, W.J.; Planz, O.; Ehrhardt, C.; Giner, M.; Silberzahn, T.; Pleschka, S.; Ludwig, S. Caspase 3 activation is essential for efficient influenza virus propagation. EMBO J. 2003, 22, 2717–2728. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Muhlbauer, D.; Dzieciolowski, J.; Hardt, M.; Hocke, A.; Schierhorn, K.L.; Mostafa, A.; Muller, C.; Wisskirchen, C.; Herold, S.; Wolff, T.; et al. Influenza virus-induced caspase-dependent enlargement of nuclear pores promotes nuclear export of viral ribonucleoprotein complexes. J. Virol. 2015, 89, 6009–6021. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Avilov, S.; Magnus, J.; Cusack, S.; Naffakh, N. Time-Resolved Visualisation of Nearly-Native Influenza A Virus Progeny Ribonucleoproteins and Their Individual Components in Live Infected Cells. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0149986. [Google Scholar]
- Eisfeld, A.J.; Kawakami, E.; Watanabe, T.; Neumann, G.; Kawaoka, Y. RAB11A is essential for transport of the influenza virus genome to the plasma membrane. J. Virol. 2011, 85, 6117–6126. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Amorim, M.J.; Bruce, E.A.; Read, E.K.; Foeglein, A.; Mahen, R.; Stuart, A.D.; Digard, P. A Rab11- and microtubule-dependent mechanism for cytoplasmic transport of influenza A virus viral RNA. J. Virol. 2011, 85, 4143–4156. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Amorim, M.J.; Kao, R.Y.; Digard, P. Nucleozin targets cytoplasmic trafficking of viral ribonucleoprotein-Rab11 complexes in influenza A virus infection. J. Virol. 2013, 87, 4694–4703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawaguchi, A.; Hirohama, M.; Harada, Y.; Osari, S.; Nagata, K. Influenza Virus Induces Cholesterol-Enriched Endocytic Recycling Compartments for Budozone Formation via Cell Cycle-Independent Centrosome Maturation. PLoS Pathog. 2015, 11, e1005284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bruce, E.A.; Digard, P.; Stuart, A.D. The Rab11 pathway is required for influenza A virus budding and filament formation. J. Virol. 2010, 84, 5848–5859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Momose, F.; Sekimoto, T.; Ohkura, T.; Jo, S.; Kawaguchi, A.; Nagata, K.; Morikawa, Y. Apical transport of influenza A virus ribonucleoprotein requires Rab11-positive recycling endosome. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e21123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Avilov, S.V.; Moisy, D.; Naffakh, N.; Cusack, S. Influenza A virus progeny vRNP trafficking in live infected cells studied with the virus-encoded fluorescently tagged PB2 protein. Vaccine 2012, 30, 7411–7417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horgan, C.P.; Oleksy, A.; Zhdanov, A.V.; Lall, P.Y.; White, I.J.; Khan, A.R.; Futter, C.E.; McCaffrey, J.G.; McCaffrey, M.W. Rab11-FIP3 is critical for the structural integrity of the endosomal recycling compartment. Traffic 2007, 8, 414–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Momose, F.; Kikuchi, Y.; Komase, K.; Morikawa, Y. Visualization of microtubule-mediated transport of influenza viral progeny ribonucleoprotein. Microbes Infect 2007, 9, 1422–1433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sherwood, R.K.; Roy, C.R. A Rab-centric perspective of bacterial pathogen-occupied vacuoles. Cell Host Microbe 2013, 14, 256–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawaguchi, A.; Matsumoto, K.; Nagata, K. YB-1 functions as a porter to lead influenza virus ribonucleoprotein complexes to microtubules. J. Virol. 2012, 86, 11086–11095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Welz, T.; Wellbourne-Wood, J.; Kerkhoff, E. Orchestration of cell surface proteins by Rab11. Trends Cell Biol. 2014, 24, 407–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ullrich, O.; Reinsch, S.; Urbe, S.; Zerial, M.; Parton, R.G. Rab11 regulates recycling through the pericentriolar recycling endosome. J. Cell Biol. 1996, 135, 913–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vale-Costa, S.; Alenquer, M.; Sousa, A.L.; Kellen, B.; Ramalho, J.; Tranfield, E.M.; Amorim, M.J. Influenza A virus ribonucleoproteins modulate host recycling by competing with Rab11 effectors. J. Cell Sci. 2016, 129, 1697–1710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heaton, N.S.; Moshkina, N.; Fenouil, R.; Gardner, T.J.; Aguirre, S.; Shah, P.S.; Zhao, N.; Manganaro, L.; Hultquist, J.F.; Noel, J.; et al. Targeting Viral Proteostasis Limits Influenza Virus, HIV, and Dengue Virus Infection. Immunity 2016, 44, 46–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmitt, A.P.; Lamb, R.A. Escaping from the cell: assembly and budding of negative-strand RNA viruses. Curr. Top. Microbiol. Immunol. 2004, 283, 145–196. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hess, S.T.; Kumar, M.; Verma, A.; Farrington, J.; Kenworthy, A.; Zimmerberg, J. Quantitative electron microscopy and fluorescence spectroscopy of the membrane distribution of influenza hemagglutinin. J. Cell Biol. 2005, 169, 965–976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leser, G.P.; Lamb, R.A. Influenza virus assembly and budding in raft-derived microdomains: A quantitative analysis of the surface distribution of HA, NA and M2 proteins. Virology 2005, 342, 215–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Engel, S.; Scolari, S.; Thaa, B.; Krebs, N.; Korte, T.; Herrmann, A.; Veit, M. FLIM-FRET and FRAP reveal association of influenza virus haemagglutinin with membrane rafts. Biochem. J. 2010, 425, 567–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scheiffele, P.; Roth, M.G.; Simons, K. Interaction of influenza virus haemagglutinin with sphingolipid-cholesterol membrane domains via its transmembrane domain. EMBO J. 1997, 16, 5501–5508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scolari, S.; Engel, S.; Krebs, N.; Plazzo, A.P.; De Almeida, R.F.; Prieto, M.; Veit, M.; Herrmann, A. Lateral distribution of the transmembrane domain of influenza virus hemagglutinin revealed by time-resolved fluorescence imaging. J. Biol. Chem. 2009, 284, 15708–15716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohkura, T.; Momose, F.; Ichikawa, R.; Takeuchi, K.; Morikawa, Y. Influenza A virus hemagglutinin and neuraminidase mutually accelerate their apical targeting through clustering of lipid rafts. J. Virol. 2014, 88, 10039–10055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rossman, J.S.; Jing, X.; Leser, G.P.; Lamb, R.A. Influenza virus M2 protein mediates ESCRT-independent membrane scission. Cell 2010, 142, 902–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thaa, B.; Siche, S.; Herrmann, A.; Veit, M. Acylation and cholesterol binding are not required for targeting of influenza A virus M2 protein to the hemagglutinin-defined budozone. FEBS Lett. 2014, 588, 1031–1036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, H.; Leser, G.P.; Zhang, J.; Lamb, R.A. Influenza virus hemagglutinin and neuraminidase cytoplasmic tails control particle shape. EMBO J. 1997, 16, 1236–1247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCown, M.F.; Pekosz, A. Distinct domains of the influenza a virus M2 protein cytoplasmic tail mediate binding to the M1 protein and facilitate infectious virus production. J. Virol. 2006, 80, 8178–8189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Pekosz, A.; Lamb, R.A. Influenza virus assembly and lipid raft microdomains: a role for the cytoplasmic tails of the spike glycoproteins. J. Virol. 2000, 74, 4634–4644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Wit, E.; Spronken, M.I.; Rimmelzwaan, G.F.; Osterhaus, A.D.; Fouchier, R.A. Evidence for specific packaging of the influenza A virus genome from conditionally defective virus particles lacking a polymerase gene. Vaccine 2006, 24, 6647–6650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujii, Y.; Goto, H.; Watanabe, T.; Yoshida, T.; Kawaoka, Y. Selective incorporation of influenza virus RNA segments into virions. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 2002–2007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marsh, G.A.; Hatami, R.; Palese, P. Specific residues of the influenza A virus hemagglutinin viral RNA are important for efficient packaging into budding virions. J. Virol. 2007, 81, 9727–9736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ozawa, M.; Victor, S.T.; Taft, A.S.; Yamada, S.; Li, C.; Hatta, M.; Das, S.C.; Takashita, E.; Kakugawa, S.; Maher, E.A.; et al. Replication-incompetent influenza A viruses that stably express a foreign gene. J. Gen. Virol. 2011, 92, 2879–2888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hutchinson, E.C.; Curran, M.D.; Read, E.K.; Gog, J.R.; Digard, P. Mutational analysis of cis-acting RNA signals in segment 7 of influenza A virus. J. Virol. 2008, 82, 11869–11879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, Y.; Hong, Y.; Parslow, T.G. cis-Acting packaging signals in the influenza virus PB1, PB2, and PA genomic RNA segments. J. Virol. 2005, 79, 10348–10355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fournier, E.; Moules, V.; Essere, B.; Paillart, J.C.; Sirbat, J.D.; Cavalier, A.; Rolland, J.P.; Thomas, D.; Lina, B.; Isel, C.; et al. Interaction network linking the human H3N2 influenza A virus genomic RNA segments. Vaccine 2012, 30, 7359–7367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fournier, E.; Moules, V.; Essere, B.; Paillart, J.C.; Sirbat, J.D.; Isel, C.; Cavalier, A.; Rolland, J.P.; Thomas, D.; Lina, B.; et al. A supramolecular assembly formed by influenza A virus genomic RNA segments. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012, 40, 2197–2209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gavazzi, C.; Isel, C.; Fournier, E.; Moules, V.; Cavalier, A.; Thomas, D.; Lina, B.; Marquet, R. An in vitro network of intermolecular interactions between viral RNA segments of an avian H5N2 influenza A virus: comparison with a human H3N2 virus. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013, 41, 1241–1254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noda, T.; Sagara, H.; Yen, A.; Takada, A.; Kida, H.; Cheng, R.H.; Kawaoka, Y. Architecture of ribonucleoprotein complexes in influenza A virus particles. Nature 2006, 439, 490–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noda, T.; Sugita, Y.; Aoyama, K.; Hirase, A.; Kawakami, E.; Miyazawa, A.; Sagara, H.; Kawaoka, Y. Three-dimensional analysis of ribonucleoprotein complexes in influenza A virus. Nat. Commun. 2012, 3, 639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sugita, Y.; Sagara, H.; Noda, T.; Kawaoka, Y. Configuration of viral ribonucleoprotein complexes within the influenza A virion. J. Virol. 2013, 87, 12879–12884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCown, M.F.; Pekosz, A. The influenza A virus M2 cytoplasmic tail is required for infectious virus production and efficient genome packaging. J. Virol. 2005, 79, 3595–3605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baudin, F.; Petit, I.; Weissenhorn, W.; Ruigrok, R.W. In vitro dissection of the membrane and RNP binding activities of influenza virus M1 protein. Virology 2001, 281, 102–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, T.; Muller, J.; Ye, Z. Association of influenza virus matrix protein with ribonucleoproteins may control viral growth and morphology. Virology 2002, 304, 89–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, Z.; Liu, T.; Offringa, D.P.; McInnis, J.; Levandowski, R.A. Association of influenza virus matrix protein with ribonucleoproteins. J. Virol. 1999, 73, 7467–7473. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Harris, A.; Cardone, G.; Winkler, D.C.; Heymann, J.B.; Brecher, M.; White, J.M.; Steven, A.C. Influenza virus pleiomorphy characterized by cryoelectron tomography. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 19123–19127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gavazzi, C.; Yver, M.; Isel, C.; Smyth, R.P.; Rosa-Calatrava, M.; Lina, B.; Moules, V.; Marquet, R. A functional sequence-specific interaction between influenza A virus genomic RNA segments. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 16604–16609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- York, A.; Hengrung, N.; Vreede, F.T.; Huiskonen, J.T.; Fodor, E. Isolation and characterization of the positive-sense replicative intermediate of a negative-strand RNA virus. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, E4238–E4245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, W.; Olson, J.; Vakharia, V.; Tao, Y.J. The crystal structure and RNA-binding of an orthomyxovirus nucleoprotein. PLoS Pathog. 2013, 9, e1003624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marsh, G.A.; Rabadan, R.; Levine, A.J.; Palese, P. Highly conserved regions of influenza a virus polymerase gene segments are critical for efficient viral RNA packaging. J. Virol. 2008, 82, 2295–2304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Giese, S.; Bolte, H.; Schwemmle, M. The Feat of Packaging Eight Unique Genome Segments. Viruses 2016, 8, 165. https://doi.org/10.3390/v8060165
Giese S, Bolte H, Schwemmle M. The Feat of Packaging Eight Unique Genome Segments. Viruses. 2016; 8(6):165. https://doi.org/10.3390/v8060165
Chicago/Turabian StyleGiese, Sebastian, Hardin Bolte, and Martin Schwemmle. 2016. "The Feat of Packaging Eight Unique Genome Segments" Viruses 8, no. 6: 165. https://doi.org/10.3390/v8060165
APA StyleGiese, S., Bolte, H., & Schwemmle, M. (2016). The Feat of Packaging Eight Unique Genome Segments. Viruses, 8(6), 165. https://doi.org/10.3390/v8060165





