Molecular Studies of HTLV-1 Replication: An Update
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. HTLV-1 Infectious Replication Cycle
2.1. Attachment and Fusion
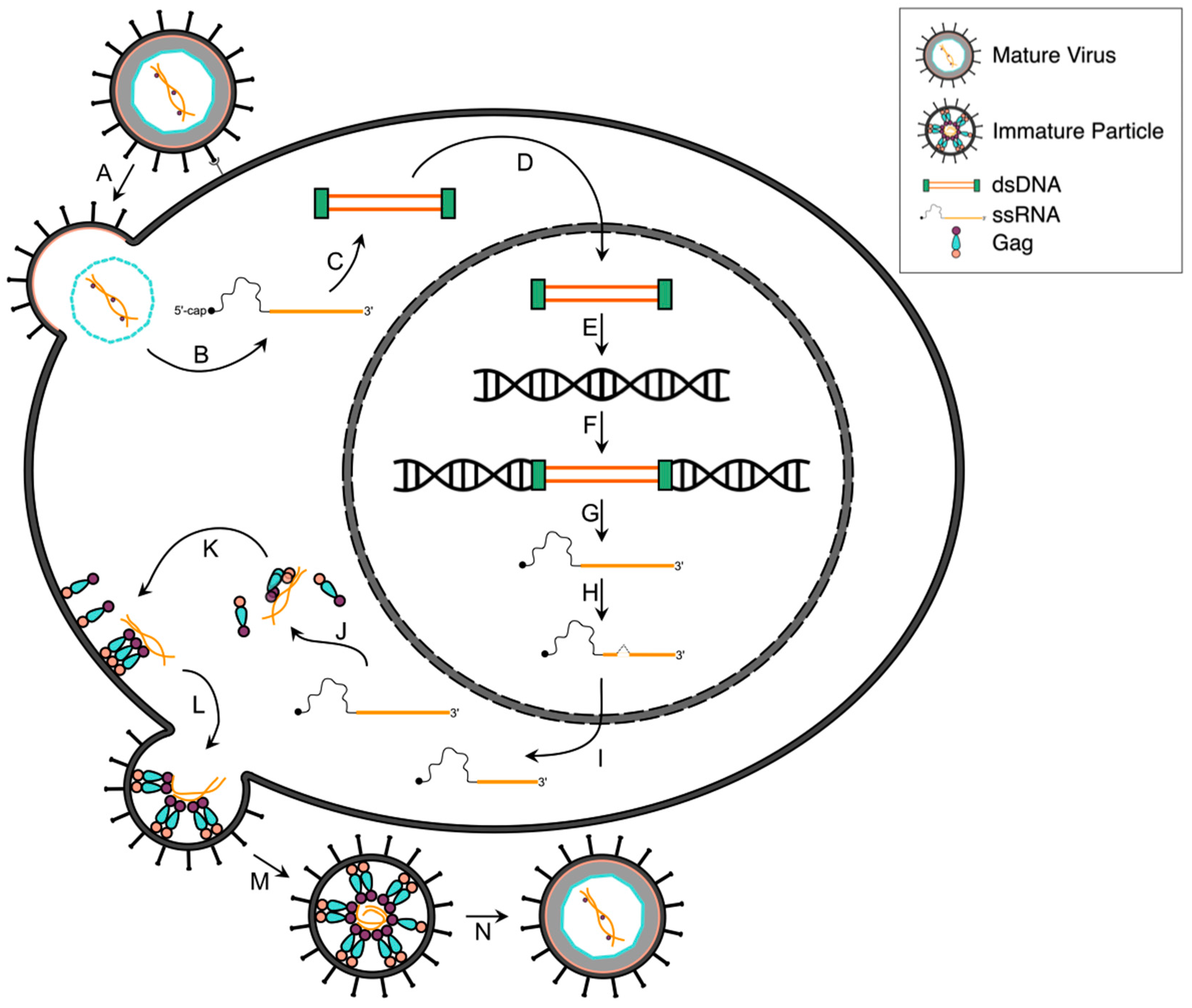
2.2. Reverse Transcription, Nuclear Transport and Integration
2.3. Viral Gene Transcription
2.4. Post-Transcriptional Regulation
2.5. Viral Protein Translation
2.6. Gag and Viral RNA Trafficking
2.7. Assembly, Budding and Maturation
3. HTLV-1 Transmission
3.1. Inter-Host Transmission
3.2. Cell-to-Cell Transmission
3.3. Virological Synapses

3.4. Viral Biofilms
4. Monoclonal Expansion of HTLV-1 Infected Cells and Leukemogenesis
4.1. Tax
4.2. Tax and Canonical NF-κB Signaling
4.3. Tax and Non-Canonical NF-κB Signaling
4.4. Tax and Other Cell Proliferative Pathways
4.5. Tax Downregulation
4.6. HBZ
5. Conclusions and Future Directions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Poiesz, B.J.; Ruscetti, F.W.; Gazdar, A.F.; Bunn, P.A.; Minna, J.D.; Gallo, R.C. Detection and isolation of type C retrovirus particles from fresh and cultured lymphocytes of a patient with cutaneous T-cell lymphoma. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1980, 77, 7415–7419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshida, M.; Miyoshi, I.; Hinuma, Y. Isolation and characterization of retrovirus from cell lines of human adult t-cell leukemia and its implication in the disease. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1982, 79, 2031–2035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gallo, R.C. History of the discoveries of the first human retroviruses: HTLV-1 and HTLV-2. Oncogene 2005, 24, 5926–5930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalyanaraman, V.S.; Sarngadharan, M.G.; Robert-Guroff, M.; Miyoshi, I.; Golde, D.; Gallo, R.C. A new subtype of human T-cell leukemia virus (HTLV-II) associated with a T-cell variant of hairy cell leukemia. Science 1982, 218, 571–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caron, C.; Rousset, R.; Beraud, C.; Moncollin, V.; Egly, J.M.; Jalinot, P. Functional and biochemical interaction of the HTLV-I Tax1 transactivator with tbp. EMBO J. 1993, 12, 4269–4278. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Proietti, F.A.; Carneiro-Proietti, A.B.; Catalan-Soares, B.C.; Murphy, E.L. Global epidemiology of HTLV-I infection and associated diseases. Oncogene 2005, 24, 6058–6068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gessain, A.; Cassar, O. Epidemiological aspects and world distribution of HTLV-1 infection. Front. Microbiol. 2012, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calattini, S.; Chevalier, S.A.; Duprez, R.; Bassot, S.; Froment, A.; Mahieux, R.; Gessain, A. Discovery of a new human T-cell lymphotropic virus (HTLV-3) in central africa. Retrovirology 2005, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wolfe, N.D.; Heneine, W.; Carr, J.K.; Garcia, A.D.; Shanmugam, V.; Tamoufe, U.; Torimiro, J.N.; Prosser, A.T.; Lebreton, M.; Mpoudi-Ngole, E.; et al. Emergence of unique primate T-lymphotropic viruses among central african bushmeat hunters. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 7994–7999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshida, M.; Seiki, M.; Yamaguchi, K.; Takatsuki, K. Monoclonal integration of human T-cell leukemia provirus in all primary tumors of adult T-cell leukemia suggests causative role of human T-cell leukemia virus in the disease. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1984, 81, 2534–2537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murphy, E.L.; Figueroa, J.P.; Gibbs, W.N.; Brathwaite, A.; Holding-Cobham, M.; Waters, D.; Cranston, B.; Hanchard, B.; Blattner, W.A. Sexual transmission of human T-lymphotropic virus type I (HTLV-I). Ann. Int. Med. 1989, 111, 555–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaplan, J.E.; Osame, M.; Kubota, H.; Igata, A.; Nishitani, H.; Maeda, Y.; Khabbaz, R.F.; Janssen, R.S. The risk of development of HTLV-I-associated myelopathy/tropical spastic paraparesis among persons infected with HTLV-I. J. Acquir. Immune Defic. Syndr. 1990, 3, 1096–1101. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hisada, M.; Stuver, S.O.; Okayama, A.; Li, H.C.; Sawada, T.; Hanchard, B.; Mueller, N.E. Persistent paradox of natural history of human T lymphotropic virus type I: Parallel analyses of Japanese and Jamaican carriers. J. Infect. Dis. 2004, 190, 1605–1609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsukasaki, K.; Hermine, O.; Bazarbachi, A.; Ratner, L.; Ramos, J.C.; Harrington, W., Jr.; O'Mahony, D.; Janik, J.E.; Bittencourt, A.L.; Taylor, G.P.; et al. Definition, prognostic factors, treatment, and response criteria of adult T-cell leukemia-lymphoma: A proposal from an international consensus meeting. J. Clin. Oncol. 2009, 27, 453–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanosaki, R.; Uike, N.; Utsunomiya, A.; Saburi, Y.; Masuda, M.; Tomonaga, M.; Eto, T.; Hidaka, M.; Harada, M.; Choi, I.; et al. Allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation using reduced-intensity conditioning for adult T cell leukemia/lymphoma: Impact of antithymocyte globulin on clinical outcome. J. Am. Soc. Blood Marrow Transplant. 2008, 14, 702–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsukasaki, K.; Utsunomiya, A.; Fukuda, H.; Shibata, T.; Fukushima, T.; Takatsuka, Y.; Ikeda, S.; Masuda, M.; Nagoshi, H.; Ueda, R.; et al. VCAP-AMP-VECP compared with biweekly CHOP for adult T-cell leukemia-lymphoma: Japan clinical oncology group study JCOG9801. J. Clin. Oncol. 2007, 25, 5458–5464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamamoto, K.; Utsunomiya, A.; Tobinai, K.; Tsukasaki, K.; Uike, N.; Uozumi, K.; Yamaguchi, K.; Yamada, Y.; Hanada, S.; Tamura, K. Phase I study of KW-0761, a defucosylated humanized anti-CCR4 antibody, in relapsed patients with adult T-cell leukemia-lymphoma and peripheral T-cell lymphoma. J. Clin. Oncol. 2010, 28, 1591–1598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bazarbachi, A.; Plumelle, Y.; Carlos Ramos, J.; Tortevoye, P.; Otrock, Z.; Taylor, G.; Gessain, A.; Harrington, W.; Panelatti, G.; Hermine, O. Meta-analysis on the use of zidovudine and interferon-alfa in adult T-cell leukemia/lymphoma showing improved survival in the leukemic subtypes. J. Clin. Oncol. 2010, 28, 4177–4183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kinpara, S.; Kijiyama, M.; Takamori, A.; Hasegawa, A.; Sasada, A.; Masuda, T.; Tanaka, Y.; Utsunomiya, A.; Kannagi, M. Interferon-α (IFN-α) suppresses HTLV-1 gene expression and cell cycling, while IFN-α combined with zidovudine induces p53 signaling and apoptosis in HTLV-1-infected cells. Retrovirology 2013, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meekings, K.N.; Leipzig, J.; Bushman, F.D.; Taylor, G.P.; Bangham, C.R. HTLV-1 integration into transcriptionally active genomic regions is associated with proviral expression and with HAM/TSP. PLoS Pathog. 2008, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagai, M.; Usuku, K.; Matsumoto, W.; Kodama, D.; Takenouchi, N.; Moritoyo, T.; Hashiguchi, S.; Ichinose, M.; Bangham, C.R.; Izumo, S.; et al. Analysis of HTLV-I proviral load in 202 HAM/TSP patients and 243 asymptomatic HTLV-I carriers: High proviral load strongly predisposes to HAM/TSP. J. Neurovirol. 1998, 4, 586–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oh, U.; Jacobson, S. Treatment of HTLV-I-associated myelopathy/tropical spastic paraparesis: Toward rational targeted therapy. Neurol. Clin. 2008, 26, 781–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamamoto, N.; Matsumoto, T.; Koyanagi, Y.; Tanaka, Y.; Hinuma, Y. Unique cell lines harbouring both epstein-barr virus and adult T-cel lleukaemia virus, established from leukaemia patients. Nature 1982, 299, 367–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ho, D.D.; Rota, T.R.; Hirsch, M.S. Infection of human endothelial cells by human T-lymphotropic virus type I. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1984, 81, 7588–7590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Longo, D.L.; Gelmann, E.P.; Cossman, J.; Young, R.A.; Gallo, R.C.; O’Brien, S.J.; Matis, L.A. Isolation of HTLV-transformed B-lymphocyte clone from a patient with HTLV-associated adult T-cell leukaemia. Nature 1984, 310, 505–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshikura, H.; Nishida, J.; Yoshida, M.; Kitamura, Y.; Takaku, F.; Ikeda, S. Isolation of HTLV derived from Japanese adult T-cell leukemia patients in human diploid fibroblast strain IMR90 and the biological characters of the infected cells. Int. J. Cancer 1984, 33, 745–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koyanagi, Y.; Itoyama, Y.; Nakamura, N.; Takamatsu, K.; Kira, J.; Iwamasa, T.; Goto, I.; Yamamoto, N. In vivo infection of human T-cell leukemia virus type I in non-T cells. Virology 1993, 196, 25–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manel, N.; Kim, F.J.; Kinet, S.; Taylor, N.; Sitbon, M.; Battini, J.L. The ubiquitous glucose transporter GLUT-1 is a receptor for HTLV. Cell 2003, 115, 449–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, K.S.; Petrow-Sadowski, C.; Bertolette, D.C.; Huang, Y.; Ruscetti, F.W. Heparan sulfate proteoglycans mediate attachment and entry of human T-cell leukemia virus type 1 virions into CD4+ T cells. J. Virol. 2005, 79, 12692–12702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghez, D.; Lepelletier, Y.; Lambert, S.; Fourneau, J.M.; Blot, V.; Janvier, S.; Arnulf, B.; van Endert, P.M.; Heveker, N.; Pique, C.; et al. Neuropilin-1 is involved in human T-cell lymphotropic virus type 1 entry. J. Virol. 2006, 80, 6844–6854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, K.S.; Petrow-Sadowski, C.; Huang, Y.K.; Bertolette, D.C.; Ruscetti, F.W. Cell-free HTLV-1 infects dendritic cells leading to transmission and transformation of CD4+ T cells. Nat. Med. 2008, 14, 429–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, Q.; Agrawal, L.; VanHorn-Ali, Z.; Alkhatib, G. Infection of CD4+ T lymphocytes by the human T cell leukemia virus type 1 is mediated by the glucose transporter glut-1: Evidence using antibodies specific to the receptor’s large extracellular domain. Virology 2006, 349, 184–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aiken, C.; Konner, J.; Landau, N.R.; Lenburg, M.E.; Trono, D. Nef induces CD4 endocytosis: Requirement for a critical dileucine motif in the membrane-proximal CD4 cytoplasmic domain. Cell 1994, 76, 853–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Margottin, F.; Bour, S.P.; Durand, H.; Selig, L.; Benichou, S.; Richard, V.; Thomas, D.; Strebel, K.; Benarous, R. A novel human WD protein, H-β TRCP, that interacts with HIV-1 VPU connects CD4 to the ER degradation pathway through an F-box motif. Mol. Cell 1998, 1, 565–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maeda, Y.; Terasawa, H.; Tanaka, Y.; Mitsuura, C.; Nakashima, K.; Yusa, K.; Harada, S. Separate cellular localizations of human T-lymphotropic virus 1 (HTLV-1) Env and glucose transporter type 1 (glut1) are required for HTLV-1 Env-mediated fusion and infection. J. Virol. 2015, 89, 502–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Macintyre, A.N.; Gerriets, V.A.; Nichols, A.G.; Michalek, R.D.; Rudolph, M.C.; Deoliveira, D.; Anderson, S.M.; Abel, E.D.; Chen, B.J.; Hale, L.P.; et al. The glucose transporter glut1 is selectively essential for CD4 T cell activation and effector function. Cell Metab. 2014, 20, 61–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Temin, H.M.; Mizutani, S. RNA-dependent DNA polymerase in virions of Rous sarcoma virus. Nature 1970, 226, 1211–1213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baltimore, D. RNA-dependent DNA polymerase in virions of RNA tumour viruses. Nature 1970, 226, 1209–1211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hulme, A.E.; Perez, O.; Hope, T.J. Complementary assays reveal a relationship between HIV-1 uncoating and reverse transcription. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 9975–9980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tekeste, S.S.; Wilkinson, T.A.; Weiner, E.M.; Xu, X.; Miller, J.T.; Le Grice, S.F.; Clubb, R.T.; Chow, S.A. Interaction between reverse transcriptase and integrase is required for reverse transcription during HIV-1 replication. J. Virol. 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Desrames, A.; Cassar, O.; Gout, O.; Hermine, O.; Taylor, G.P.; Afonso, P.V.; Gessain, A. Northern African strains of human T-lymphotropic virus type 1 arose from a recombination event. J. Virol. 2014, 88, 9782–9788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ooms, M.; Krikoni, A.; Kress, A.K.; Simon, V.; Munk, C. APOBEC3A, APOBEC3B, and APOBEC3H haplotype 2 restrict human T-lymphotropic virus type 1. J. Virol. 2012, 86, 6097–6108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, J.; Ma, G.; Nosaka, K.; Tanabe, J.; Satou, Y.; Koito, A.; Wain-Hobson, S.; Vartanian, J.P.; Matsuoka, M. APOBEC3G generates nonsense mutations in human T-cell leukemia virus type 1 proviral genomes in vivo. J. Virol. 2010, 84, 7278–7287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Derse, D.; Hill, S.A.; Princler, G.; Lloyd, P.; Heidecker, G. Resistance of human T cell leukemia virus type 1 to APOBEC3G restriction is mediated by elements in nucleocapsid. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 2915–2920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coffin, J.M.; Hughes, S.H.; Varmus, H.E. The interactions of retroviruses and their hosts. In Retroviruses; Cold Spring Harbor: NY, USA, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Kitamura, Y.; Lee, Y.M.; Coffin, J.M. Nonrandom integration of retroviral DNA in vitro: Effect of CPG methylation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1992, 89, 5532–5536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doi, K.; Wu, X.; Taniguchi, Y.; Yasunaga, J.; Satou, Y.; Okayama, A.; Nosaka, K.; Matsuoka, M. Preferential selection of human T-cell leukemia virus type I provirus integration sites in leukemic versus carrier states. Blood 2005, 106, 1048–1053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holman, A.G.; Coffin, J.M. Symmetrical base preferences surrounding HIV-1, avian sarcoma/leukosis virus, and murine leukemia virus integration sites. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 6103–6107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, Y.; Moressi, C.J.; Scheetz, T.E.; Xie, L.; Tran, D.T.; Casavant, T.L.; Ak, P.; Benham, C.J.; Davidson, B.L.; McCray, P.B., Jr. Integration site choice of a feline immunodeficiency virus vector. J. Virol. 2006, 80, 8820–8823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Derse, D.; Crise, B.; Li, Y.; Princler, G.; Lum, N.; Stewart, C.; McGrath, C.F.; Hughes, S.H.; Munroe, D.J.; Wu, X. Human T-cell leukemia virus type 1 integration target sites in the human genome: Comparison with those of other retroviruses. J. Virol. 2007, 81, 6731–6741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gillet, N.A.; Cook, L.; Laydon, D.J.; Hlela, C.; Verdonck, K.; Alvarez, C.; Gotuzzo, E.; Clark, D.; Farre, L.; Bittencourt, A.; et al. Strongyloidiasis and infective dermatitis alter human T lymphotropic virus-1 clonality in vivo. PLoS Pathog. 2013, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cook, L.B.; Melamed, A.; Niederer, H.; Valganon, M.; Laydon, D.; Foroni, L.; Taylor, G.P.; Matsuoka, M.; Bangham, C.R. The role of HTLV-1 clonality, proviral structure, and genomic integration site in adult T-cell leukemia/lymphoma. Blood 2014, 123, 3925–3931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niederer, H.A.; Laydon, D.J.; Melamed, A.; Elemans, M.; Asquith, B.; Matsuoka, M.; Bangham, C.R. HTLV-1 proviral integration sites differ between asymptomatic carriers and patients with HAM/TSP. J. Virol. 2014, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kashanchi, F.; Brady, J.N. Transcriptional and post-transcriptional gene regulation of HTLV-1. Oncogene 2005, 24, 5938–5951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeang, K.T.; Boros, I.; Brady, J.; Radonovich, M.; Khoury, G. Characterization of cellular factors that interact with the human T-cell leukemia virus type I p40x-responsive 21-base-pair sequence. J. Virol. 1988, 62, 4499–4509. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Baranger, A.M.; Palmer, C.R.; Hamm, M.K.; Giebler, H.A.; Brauweiler, A.; Nyborg, J.K.; Schepartz, A. Mechanism of DNA-binding enhancement by the human T-cell leukaemia virus transactivator Tax. Nature 1995, 376, 606–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adya, N.; Giam, C.Z. Distinct regions in human T-cell lymphotropic virus type I Tax mediate interactions with activator protein CREB and basal transcription factors. J. Virol. 1995, 69, 1834–1841. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Adya, N.; Zhao, L.J.; Huang, W.; Boros, I.; Giam, C.Z. Expansion of CREB’S DNA recognition specificity by Tax results from interaction with Ala-Ala-Arg at positions 282–284 near the conserved DNA-binding domain of CREB. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1994, 91, 5642–5646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goren, I.; Semmes, O.J.; Jeang, K.T.; Moelling, K. The amino terminus of Tax is required for interaction with the cyclic AMP response element binding protein. J. Virol. 1995, 69, 5806–5811. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Tie, F.; Adya, N.; Greene, W.C.; Giam, C.Z. Interaction of the human T-lymphotropic virus type 1 Tax dimer with CREB and the viral 21-base-pair repeat. J. Virol. 1996, 70, 8368–8374. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zhao, L.J.; Giam, C.Z. Human T-cell lymphotropic virus type I (HTLV-I) transcriptional activator, Tax, enhances CREB binding to HTLV-I 21-base-pair repeats by protein-protein interaction. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1992, 89, 7070–7074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ching, Y.P.; Chun, A.C.; Chin, K.T.; Zhang, Z.Q.; Jeang, K.T.; Jin, D.Y. Specific TATAA and bZIP requirements suggest that HTLV-I Tax has transcriptional activity subsequent to the assembly of an initiation complex. Retrovirology 2004, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seiki, M.; Inoue, J.; Takeda, T.; Yoshida, M. Direct evidence that p40x of human T-cell leukemia virus type I is a trans-acting transcriptional activator. EMBO J. 1986, 5, 561–565. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Giebler, H.A.; Loring, J.E.; van Orden, K.; Colgin, M.A.; Garrus, J.E.; Escudero, K.W.; Brauweiler, A.; Nyborg, J.K. Anchoring of CREB binding protein to the human T-cell leukemia virus type 1 promoter: A molecular mechanism of Tax transactivation. Mol. Cell. Biol. 1997, 17, 5156–5164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Kwok, R.P.; Laurance, M.E.; Lundblad, J.R.; Goldman, P.S.; Shih, H.; Connor, L.M.; Marriott, S.J.; Goodman, R.H. Control of CAMP-regulated enhancers by the viral transactivator Tax through CREB and the co-activator CBP. Nature 1996, 380, 642–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, H.; Lu, H.; Schiltz, R.L.; Pise-Masison, C.A.; Ogryzko, V.V.; Nakatani, Y.; Brady, J.N. PCAF interacts with Tax and stimulates Tax transactivation in a histone acetyltransferase-independent manner. Mol. Cell. Biol. 1999, 19, 8136–8145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrod, R.; Kuo, Y.L.; Tang, Y.; Yao, Y.; Vassilev, A.; Nakatani, Y.; Giam, C.Z. P300 and p300/CAMP-responsive element-binding protein associated factor interact with human T-cell lymphotropic virus type-1 Tax in a multi-histone acetyltransferase/activator-enhancer complex. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 11852–11857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bex, F.; Yin, M.J.; Burny, A.; Gaynor, R.B. Differential transcriptional activation by human T-cell leukemia virus type 1 Tax mutants is mediated by distinct interactions with CREB binding protein and p300. Mol. Cell. Biol. 1998, 18, 2392–2405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, G.; Yasunaga, J.; Akari, H.; Matsuoka, M. Tcf1 and LEF1 act as T-cell intrinsic HTLV-1 antagonists by targeting Tax. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 2216–2221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zou, T.; Yang, Y.; Xia, F.; Huang, A.; Gao, X.; Fang, D.; Xiong, S.; Zhang, J. Resveratrol inhibits CD4+ T cell activation by enhancing the expression and activity of Sirt1. PloS ONE 2013, 8, e75139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, H.M.; Gao, W.W.; Chan, C.P.; Cheng, Y.; Deng, J.J.; Yuen, K.S.; Iha, H.; Jin, D.Y. Sirt1 suppresses human T-cell leukemia virus type 1 transcription. J. Virol. 2015, 89, 8623–8631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, H.; Santoso, N.; Power, D.; Simpson, S.; Dieringer, M.; Miao, H.; Gurova, K.; Giam, C.Z.; Elledge, S.; Zhu, J. Fact proteins, SUPT16H and SSRP1, are transcriptional suppressors of HIV-1 and HTLV-1 that facilitate viral latency. J. Biol. Chem. 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Green, P.L.; Chen, I.S. Regulation of human T cell leukemia virus expression. FASEB J. 1990, 4, 169–175. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hidaka, M.; Inoue, J.; Yoshida, M.; Seiki, M. Post-transcriptional regulator (Rex) of HTLV-1 initiates expression of viral structural proteins but suppresses expression of regulatory proteins. EMBO J. 1988, 7, 519–523. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bogerd, H.P.; Huckaby, G.L.; Ahmed, Y.F.; Hanly, S.M.; Greene, W.C. The type I human T-cell leukemia virus (HTLV-I) Rex trans-activator binds directly to the HTLV-I Rex and the type 1 human immunodeficiency virus Rev RNA response elements. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1991, 88, 5704–5708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nosaka, T.; Siomi, H.; Adachi, Y.; Ishibashi, M.; Kubota, S.; Maki, M.; Hatanaka, M. Nucleolar targeting signal of human T-cell leukemia virus type I Rex-encoded protein is essential for cytoplasmic accumulation of unspliced viral mrna. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1989, 86, 9798–9802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rehberger, S.; Gounari, F.; DucDodon, M.; Chlichlia, K.; Gazzolo, L.; Schirrmacher, V.; Khazaie, K. The activation domain of a hormone inducible HTLV-1 Rex protein determines colocalization with the nuclear pore. Exp. Cell Res. 1997, 233, 363–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palmeri, D.; Malim, M.H. The human T-cell leukemia virus type 1 posttranscriptional trans-activator Rex contains a nuclear export signal. J. Virol. 1996, 70, 6442–6445. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bai, X.T.; Sinha-Datta, U.; Ko, N.L.; Bellon, M.; Nicot, C. Nuclear export and expression of human T-cell leukemia virus type 1 Tax/Rex mRNA are Rxre/Rex dependent. J. Virol. 2012, 86, 4559–4565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rende, F.; Cavallari, I.; Andresen, V.; Valeri, V.W.; D'Agostino, D.M.; Franchini, G.; Ciminale, V. Identification of novel monocistronic HTLV-1 mrnas encoding functional Rex isoforms. Retrovirology 2015, 12, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Butsch, M.; Boris-Lawrie, K. Destiny of unspliced retroviral RNA: Ribosome and/or virion? J. Virol. 2002, 76, 3089–3094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hellen, C.U.; Sarnow, P. Internal ribosome entry sites in eukaryotic mRNA molecules. Genes Dev. 2001, 15, 1593–1612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarnow, P.; Cevallos, R.C.; Jan, E. Takeover of host ribosomes by divergent IRES elements. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 2005, 33, 1479–1482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jackson, R.J. Alternative mechanisms of initiating translation of mammalian mrnas. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 2005, 33, 1231–1241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Attal, J.; Theron, M.C.; Taboit, F.; Cajero-Juarez, M.; Kann, G.; Bolifraud, P.; Houdebine, L.M. The RU5 (“R”) region from human leukaemia viruses (HTLV-1) contains an internal ribosome entry site (IRES)-like sequence. FEBS Let. 1996, 392, 220–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bolinger, C.; Yilmaz, A.; Hartman, T.R.; Kovacic, M.B.; Fernandez, S.; Ye, J.; Forget, M.; Green, P.L.; Boris-Lawrie, K. RNA helicase a interacts with divergent lymphotropic retroviruses and promotes translation of human T-cell leukemia virus type 1. Nucleic Acids Res. 2007, 35, 2629–2642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olivares, E.; Landry, D.M.; Caceres, C.J.; Pino, K.; Rossi, F.; Navarrete, C.; Huidobro-Toro, J.P.; Thompson, S.R.; Lopez-Lastra, M. The 5’ untranslated region of the human T-cell lymphotropic virus type 1 mRNA enables cap-independent translation initiation. J. Virol. 2014, 88, 5936–5955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fogarty, K.H.; Chen, Y.; Grigsby, I.F.; Macdonald, P.J.; Smith, E.M.; Johnson, J.L.; Rawson, J.M.; Mansky, L.M.; Mueller, J.D. Characterization of cytoplasmic Gag-gag interactions by dual-color z-scan fluorescence fluctuation spectroscopy. Biophys. J. 2011, 100, 1587–1595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ritchie, C.; Cylinder, I.; Platt, E.J.; Barklis, E. Analysis of HIV-1 Gag protein interactions via biotin ligase tagging. J. Virol. 2015, 89, 3988–4001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barnard, A.L.; Igakura, T.; Tanaka, Y.; Taylor, G.P.; Bangham, C.R. Engagement of specific T-cellsurface molecules regulates cytoskeletal polarization in HTLV-1-infected lymphocytes. Blood 2005, 106, 988–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qualley, D.F.; Stewart-Maynard, K.M.; Wang, F.; Mitra, M.; Gorelick, R.J.; Rouzina, I.; Williams, M.C.; Musier-Forsyth, K. C-terminal domain modulates the nucleic acid chaperone activity of human T-cell leukemia virus type 1 nucleocapsid protein via an electrostatic mechanism. J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 295–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, M.; Grigsby, I.F.; Gorelick, R.J.; Mansky, L.M.; Musier-Forsyth, K. Retrovirus-specific differences in matrix and nucleocapsid protein-nucleic acid interactions: Implications for genomic RNA packaging. J. Virol. 2014, 88, 1271–1280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Grunwald, D.; Sardo, L.; Galli, A.; Plisov, S.; Nikolaitchik, O.A.; Chen, D.; Lockett, S.; Larson, D.R.; Pathak, V.K.; et al. Cytoplasmic HIV-1 RNA is mainly transported by diffusion in the presence or absence of gag protein. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, E5205–E5213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.; Cao, S.; Martin, J.L.; Mueller, J.D.; Mansky, L.M. Morphology and ultrastructure of retrovirus particles. AIMS Biophys. 2015, 2, 343–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gamble, T.R.; Yoo, S.; Vajdos, F.F.; von Schwedler, U.K.; Worthylake, D.K.; Wang, H.; McCutcheon, J.P.; Sundquist, W.I.; Hill, C.P. Structure of the carboxyl-terminal dimerization domain of the HIV-1 capsid protein. Science 1997, 278, 849–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rayne, F.; Bouamr, F.; Lalanne, J.; Mamoun, R.Z. The NH2-terminal domain of the human T-cell leukemia virus type 1 capsid protein is involved in particle formation. J. Virol. 2001, 75, 5277–5287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ganser-Pornillos, B.K.; von Schwedler, U.K.; Stray, K.M.; Aiken, C.; Sundquist, W.I. Assembly properties of the human immunodeficiency virus type 1 CA protein. J. Virol. 2004, 78, 2545–2552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ako-Adjei, D.; Johnson, M.C.; Vogt, V.M. The retroviral capsid domain dictates virion size, morphology, and coassembly of gag into virus-like particles. J. Virol. 2005, 79, 13463–13472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hogue, I.B.; Hoppe, A.; Ono, A. Quantitative fluorescence resonance energy transfer microscopy analysis of the human immunodeficiency virus type 1 Gag-gag interaction: Relative contributions of the CA and NC domains and membrane binding. J. Virol. 2009, 83, 7322–7336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lingappa, J.R.; Reed, J.C.; Tanaka, M.; Chutiraka, K.; Robinson, B.A. How HIV-1 Gag assembles in cells: Putting together pieces of the puzzle. Virus research 2014, 193, 89–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maldonado, J.O.; Martin, J.L.; Mueller, J.D.; Zhang, W.; Mansky, L.M. New insights into retroviral Gag-gag and Gag-membrane interactions. Frontiers Microbiol. 2014, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lingwood, D.; Kaiser, H.J.; Levental, I.; Simons, K. Lipid rafts as functional heterogeneity in cell membranes. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 2009, 37, 955–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ono, A. HIV-1 assembly at the plasma membrane: Gag trafficking and localization. Futur. Virol. 2009, 4, 241–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sonnino, S.; Prinetti, A. Membrane domains and the “lipid raft” concept. Curr. Med. Chem. 2013, 20, 4–21. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Inlora, J.; Collins, D.R.; Trubin, M.E.; Chung, J.Y.; Ono, A. Membrane binding and subcellular localization of retroviral Gag proteins are differentially regulated by MA interactions with phosphatidylinositol-(4,5)-bisphosphate and RNA. mBio 2014, 5, e02202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Demirov, D.G.; Freed, E.O. Retrovirus budding. Virus Res. 2004, 106, 87–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morita, E.; Sundquist, W.I. Retrovirus budding. Ann. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol. 2004, 20, 395–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le Blanc, I.; Grange, M.P.; Delamarre, L.; Rosenberg, A.R.; Blot, V.; Pique, C.; Dokhelar, M.C. HTLV-1 structural proteins. Virus Res. 2001, 78, 5–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konvalinka, J.; Krausslich, H.G.; Muller, B. Retroviral proteases and their roles in virion maturation. Virology 2015, 479–480, 403–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goncalves, D.U.; Proietti, F.A.; Ribas, J.G.; Araujo, M.G.; Pinheiro, S.R.; Guedes, A.C.; Carneiro-Proietti, A.B. Epidemiology, treatment, and prevention of human T-cell leukemia virus type 1-associated diseases. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2010, 23, 577–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wiktor, S.Z.; Pate, E.J.; Murphy, E.L.; Palker, T.J.; Champegnie, E.; Ramlal, A.; Cranston, B.; Hanchard, B.; Blattner, W.A. Mother-to-child transmission of human T-cell lymphotropic virus type I (HTLV-I) in Jamaica: Association with antibodies to envelope glycoprotein (gp46) epitopes. J. Acquir. Immune Defic. Syndr. 1993, 6, 1162–1167. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Takahashi, K.; Takezaki, T.; Oki, T.; Kawakami, K.; Yashiki, S.; Fujiyoshi, T.; Usuku, K.; Mueller, N.; Osame, M.; Miyata, K.; et al. Inhibitory effect of maternal antibody on mother-to-child transmission of human T-lymphotropic virus type I. The mother-to-child transmission study group. Int. J. Cancer 1991, 49, 673–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nyambi, P.N.; Ville, Y.; Louwagie, J.; Bedjabaga, I.; Glowaczower, E.; Peeters, M.; Kerouedan, D.; Dazza, M.; Larouze, B.; van der Groen, G.; et al. Mother-to-child transmission of human T-cell lymphotropic virus types I and II (HTLV-I/II) in Gabon: A prospective follow-up of 4 years. J. Acquir. Immune Defic. Syndr. 1996, 12, 187–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.C.; Biggar, R.J.; Miley, W.J.; Maloney, E.M.; Cranston, B.; Hanchard, B.; Hisada, M. Provirus load in breast milk and risk of mother-to-child transmission of human T lymphotropic virus type I. J. Infec. Dis. 2004, 190, 1275–1278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin-Latil, S.; Gnadig, N.F.; Mallet, A.; Desdouits, M.; Guivel-Benhassine, F.; Jeannin, P.; Prevost, M.C.; Schwartz, O.; Gessain, A.; Ozden, S.; et al. Transcytosis of HTLV-1 across a tight human epithelial barrier and infection of subepithelial dendritic cells. Blood 2012, 120, 572–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kinlock, B.L.; Wang, Y.; Turner, T.M.; Wang, C.; Liu, B. Transcytosis of HIV-1 through vaginal epithelial cells is dependent on trafficking to the endocytic recycling pathway. PloS ONE 2014, 9, e96760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alfsen, A.; Yu, H.; Magerus-Chatinet, A.; Schmitt, A.; Bomsel, M. HIV-1-infected blood mononuclear cells form an integrin- and agrin-dependent viral synapse to induce efficient HIV-1 transcytosis across epithelial cell monolayer. Mol. Biol. Cell 2005, 16, 4267–4279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Filippone, C.; Betsem, E.; Tortevoye, P.; Cassar, O.; Bassot, S.; Froment, A.; Fontanet, A.; Gessain, A. A severe bite from a nonhuman primate is a major risk factor for HTLV-1 infection in hunters from central Africa. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2015, 60, 1667–1676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kazanji, M.; Mouinga-Ondeme, A.; Lekana-Douki-Etenna, S.; Caron, M.; Makuwa, M.; Mahieux, R.; Gessain, A. Origin of HTLV-1 in hunters of nonhuman primates in central Africa. J. Infect. Dis. 2015, 211, 361–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- LeBreton, M.; Switzer, W.M.; Djoko, C.F.; Gillis, A.; Jia, H.; Sturgeon, M.M.; Shankar, A.; Zheng, H.; Nkeunen, G.; Tamoufe, U.; et al. A gorilla reservoir for human T-lymphotropic virus type 4. Emerg. Microbes Infect. 2014, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miura, M.; Yasunaga, J.; Tanabe, J.; Sugata, K.; Zhao, T.; Ma, G.; Miyazato, P.; Ohshima, K.; Kaneko, A.; Watanabe, A.; et al. Characterization of simian T-cell leukemia virus type 1 in naturally infected Japanese macaques as a model of HTLV-1 infection. Retrovirology 2013, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, K.J.; Nerurkar, V.R.; Saitou, N.; Lazo, A.; Blakeslee, J.R.; Miyoshi, I.; Yanagihara, R. Genetic analysis and molecular phylogeny of simian T-cell lymphotropic virus type I: Evidence for independent virus evolution in Asia and Africa. Virology 1994, 199, 56–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, N.; Gavalchin, J.; Paul, B.; Wells, K.H.; Lane, M.J.; Poiesz, B.J. Infection of peripheral blood mononuclear cells and cell lines by cell-free human T-cell lymphoma/leukemia virus type I. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1992, 30, 905–910. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Igakura, T.; Stinchcombe, J.C.; Goon, P.K.; Taylor, G.P.; Weber, J.N.; Griffiths, G.M.; Tanaka, Y.; Osame, M.; Bangham, C.R. Spread of HTLV-I between lymphocytes by virus-induced polarization of the cytoskeleton. Science 2003, 299, 1713–1716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Majorovits, E.; Nejmeddine, M.; Tanaka, Y.; Taylor, G.P.; Fuller, S.D.; Bangham, C.R. Human T-lymphotropic virus-1 visualized at the virological synapse by electron tomography. PLoS ONE 2008, 3, e2251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nejmeddine, M.; Negi, V.S.; Mukherjee, S.; Tanaka, Y.; Orth, K.; Taylor, G.P.; Bangham, C.R. HTLV-1-Tax and ICAM-1 act on T-cellsignal pathways to polarize the microtubule-organizing center at the virological synapse. Blood 2009, 114, 1016–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nejmeddine, M.; Barnard, A.L.; Tanaka, Y.; Taylor, G.P.; Bangham, C.R. Human T-lymphotropic virus, type 1, Tax protein triggers microtubule reorientation in the virological synapse. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 29653–29660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chevalier, S.A.; Turpin, J.; Cachat, A.; Afonso, P.V.; Gessain, A.; Brady, J.N.; Pise-Masison, C.A.; Mahieux, R. Gem-induced cytoskeleton remodeling increases cellular migration of HTLV-1-infected cells, formation of infected-to-target T-cellconjugates and viral transmission. PLoS Pathog. 2014, 10, e1003917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fukudome, K.; Furuse, M.; Fukuhara, N.; Orita, S.; Imai, T.; Takagi, S.; Nagira, M.; Hinuma, Y.; Yoshie, O. Strong induction of ICAM-1 in human T cells transformed by human T-cell-leukemia virus type 1 and depression of ICAM-1 or LFA-1 in adult T-cell-leukemia-derived cell lines. Int. J. Cancer. 1992, 52, 418–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dimitrov, D.S.; Willey, R.L.; Sato, H.; Chang, L.J.; Blumenthal, R.; Martin, M.A. Quantitation of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 infection kinetics. J. Virol. 1993, 67, 2182–2190. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Mazurov, D.; Ilinskaya, A.; Heidecker, G.; Lloyd, P.; Derse, D. Quantitative comparison of HTLV-1 and HIV-1 cell-to-cell infection with new replication dependent vectors. PLoS Pathog. 2010, 6, e1000788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, A.P.; Jiang, J.F.; Guo, M.G.; Jin, Y.M.; Li, Y.Y.; Wang, J.H. Human blood-circulating basophils capture HIV-1 and mediate viral trans-infection of CD4+ T cells. J. Virol. 2015, 89, 8050–8062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pais-Correia, A.M.; Sachse, M.; Guadagnini, S.; Robbiati, V.; Lasserre, R.; Gessain, A.; Gout, O.; Alcover, A.; Thoulouze, M.I. Biofilm-like extracellular viral assemblies mediate HTLV-1 cell-to-cell transmission at virological synapses. Nat. Med. 2010, 16, 83–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tarasevich, A.; Filatov, A.; Pichugin, A.; Mazurov, D. Monoclonal antibody profiling of cell surface proteins associated with the viral biofilms on HTLV-1 transformed cells. Acta Virol. 2015, 59, 247–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alais, S.; Mahieux, R.; Dutartre, H. Viral source-independent high susceptibility of dendritic cells to human T-cell leukemia virus type 1 infection compared to that of T lymphocytes. J. Virol. 2015, 89, 10580–10590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gessain, A.; Gallo, R.C.; Franchini, G. Low degree of human T-cell leukemia/lymphoma virus type I genetic drift in vivo as a means of monitoring viral transmission and movement of ancient human populations. J. Virol. 1992, 66, 2288–2295. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Van Dooren, S.; Pybus, O.G.; Salemi, M.; Liu, H.F.; Goubau, P.; Remondegui, C.; Talarmin, A.; Gotuzzo, E.; Alcantara, L.C.; Galvao-Castro, B.; et al. The low evolutionary rate of human T-cell lymphotropic virus type-1 confirmed by analysis of vertical transmission chains. Mol. Biol. Evolut. 2004, 21, 603–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mansky, L.M. In vivo analysis of human T-cell leukemia virus type 1 reverse transcription accuracy. J. Virol. 2000, 74, 9525–9531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mansky, L.M.; Temin, H.M. Lower in vivo mutation rate of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 than that predicted from the fidelity of purified reverse transcriptase. J. Virol. 1995, 69, 5087–5094. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Taylor, G.P.; Goon, P.; Furukawa, Y.; Green, H.; Barfield, A.; Mosley, A.; Nose, H.; Babiker, A.; Rudge, P.; Usuku, K.; et al. Zidovudine plus lamivudine in human T-lymphotropic virus type-I-associated myelopathy: A randomised trial. Retrovirology 2006, 3, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miyazato, P.; Yasunaga, J.; Taniguchi, Y.; Koyanagi, Y.; Mitsuya, H.; Matsuoka, M. De novo human T-cell leukemia virus type 1 infection of human lymphocytes in NOD-SCID, common γ-chain knockout mice. J. Virol. 2006, 80, 10683–10691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seiki, M.; Eddy, R.; Shows, T.B.; Yoshida, M. Nonspecific integration of the HTLV provirus genome into adult T-cell leukaemia cells. Nature 1984, 309, 640–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohshima, K.; Ohgami, A.; Matsuoka, M.; Etoh, K.; Utsunomiya, A.; Makino, T.; Ishiguro, M.; Suzumiya, J.; Kikuchi, M. Random integration of HTLV-1 provirus: Increasing chromosomal instability. Cancer Lett. 1998, 132, 203–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wattel, E.; Vartanian, J.P.; Pannetier, C.; Wain-Hobson, S. Clonal expansion of human T-cell leukemia virus type I-infected cells in asymptomatic and symptomatic carriers without malignancy. J. Virol. 1995, 69, 2863–2868. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Etoh, K.; Tamiya, S.; Yamaguchi, K.; Okayama, A.; Tsubouchi, H.; Ideta, T.; Mueller, N.; Takatsuki, K.; Matsuoka, M. Persistent clonal proliferation of human T-lymphotropic virus type I-infected cells in vivo. Cancer Res. 1997, 57, 4862–4867. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Cavrois, M.; Gessain, A.; Wain-Hobson, S.; Wattel, E. Proliferation of HTLV-1 infected circulating cells in vivo in all asymptomatic carriers and patients with TSP/HAM. Oncogene 1996, 12, 2419–2423. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zhao, T.; Satou, Y.; Matsuoka, M. Development of t cell lymphoma in HTLV-1 bZIP factor and Tax double transgenic mice. Archives Virol. 2014, 159, 1849–1856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oeckinghaus, A.; Hayden, M.S.; Ghosh, S. Crosstalk in NF-κB signaling pathways. Nat. Immunol. 2011, 12, 695–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peloponese, J.M., Jr.; Jeang, K.T. Role for Akt/protein kinase B and activator protein-1 in cellular proliferation induced by the human T-cell leukemia virus type 1 Tax oncoprotein. J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 281, 8927–8938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, X.; Sun, S.C. Retroviral oncoprotein Tax deregulates NF-κB by activating Tak1 and mediating the physical association of tak1-IKK. EMBO Rep. 2007, 8, 510–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Avesani, F.; Romanelli, M.G.; Turci, M.; Di Gennaro, G.; Sampaio, C.; Bidoia, C.; Bertazzoni, U.; Bex, F. Association of HTLV Tax proteins with Tak1-binding protein 2 and RelA in calreticulin-containing cytoplasmic structures participates in Tax-mediated NF-κB activation. Virology 2010, 408, 39–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, Y.B.; Harhaj, E.W. HTLV-1 Tax stabilizes mcl-1 via traf6-dependent k63-linked polyubiquitination to promote cell survival and transformation. PLoS Pathog. 2014, 10, e1004458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, M.J.; Christerson, L.B.; Yamamoto, Y.; Kwak, Y.T.; Xu, S.; Mercurio, F.; Barbosa, M.; Cobb, M.H.; Gaynor, R.B. HTLV-I Tax protein binds to mekk1 to stimulate IκB kinase activity and NF-κB activation. Cell 1998, 93, 875–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harhaj, E.W.; Sun, S.C. Ikkγ serves as a docking subunit of the IκB kinase (Ikk) and mediates interaction of IKK with the human T-cell leukemia virus Tax protein. J. Biol. Chem. 1999, 274, 22911–22914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shembade, N.; Harhaj, N.S.; Yamamoto, M.; Akira, S.; Harhaj, E.W. The human T-cell leukemia virus type 1 Tax oncoprotein requires the ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme UBC13 for NF-κB activation. J. Virol. 2007, 81, 13735–13742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Israel, A. The IKK complex, a central regulator of NF-κB activation. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2010, 2, a000158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kray, A.E.; Carter, R.S.; Pennington, K.N.; Gomez, R.J.; Sanders, L.E.; Llanes, J.M.; Khan, W.N.; Ballard, D.W.; Wadzinski, B.E. Positive regulation of IκB kinase signaling by protein serine/threonine phosphatase 2A. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 35974–35982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, D.X.; Kuo, Y.L.; Liu, B.Y.; Jeang, K.T.; Giam, C.Z. Human T-lymphotropic virus type I Tax activates I-κB kinase by inhibiting I-κB kinase-associated serine/threonine protein phosphatase 2A. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 1487–1493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, S.; Wang, L.C.; Gao, X.; Kuo, Y.L.; Liu, B.; Merling, R.; Kung, H.J.; Shih, H.M.; Giam, C.Z. Heptad repeats regulate protein phosphatase 2A recruitment to I-κB kinase γ/NF-κB essential modulator and are targeted by human T-lymphotropic virus type 1 Tax. J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, 12119–12126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Azran, I.; Jeang, K.T.; Aboud, M. High levels of cytoplasmic HTLV-1 Tax mutant proteins retain a Tax-NF-κB-CBP ternary complex in the cytoplasm. Oncogene 2005, 24, 4521–4530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lamsoul, I.; Lodewick, J.; Lebrun, S.; Brasseur, R.; Burny, A.; Gaynor, R.B.; Bex, F. Exclusive ubiquitination and sumoylation on overlapping lysine residues mediate NF-κB activation by the human T-cell leukemia virus Tax oncoprotein. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2005, 25, 10391–10406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petropoulos, L.; Lin, R.; Hiscott, J. Human T cell leukemia virus type 1 Tax protein increases NF-κB dimer formation and antagonizes the inhibitory activity of the IκBα regulatory protein. Virology 1996, 225, 52–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shembade, N.; Harhaj, N.S.; Parvatiyar, K.; Copeland, N.G.; Jenkins, N.A.; Matesic, L.E.; Harhaj, E.W. The E3 ligase ITCH negatively regulates inflammatory signaling pathways by controlling the function of the ubiquitin-editing enzyme A20. Nat. Immunol. 2008, 9, 254–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pujari, R.; Hunte, R.; Thomas, R.; van der Weyden, L.; Rauch, D.; Ratner, L.; Nyborg, J.K.; Ramos, J.C.; Takai, Y.; Shembade, N. Human T-cell leukemia virus type 1 (HTLV-1) Tax requires CADM1/TSLC1 for inactivation of the NF-κB inhibitor A20 and constitutive NF-κB signaling. PLoS Pathog. 2015, 11, e1004721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, J.; Qu, Z.; Yan, P.; Ishikawa, C.; Aqeilan, R.I.; Rabson, A.B.; Xiao, G. The tumor suppressor gene WWOX links the canonical and noncanonical NF-κB pathways in HTLV-I Tax-mediated tumorigenesis. Blood 2011, 117, 1652–1661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Higuchi, M.; Tsubata, C.; Kondo, R.; Yoshida, S.; Takahashi, M.; Oie, M.; Tanaka, Y.; Mahieux, R.; Matsuoka, M.; Fujii, M. Cooperation of NF-κB2/p100 activation and the PDZ domain binding motif signal in human T-cell leukemia virus type 1 (HTLV-1) Tax1 but not HTLV-2 Tax2 is crucial for interleukin-2-independent growth transformation of a T-cell line. J. Virol. 2007, 81, 11900–11907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, G.; Cvijic, M.E.; Fong, A.; Harhaj, E.W.; Uhlik, M.T.; Waterfield, M.; Sun, S.C. Retroviral oncoprotein Tax induces processing of NF-κB2/p100 in T cells: Evidence for the involvement of IKKα. EMBO J. 2001, 20, 6805–6815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fraedrich, K.; Muller, B.; Grassmann, R. The HTLV-1 Tax protein binding domain of cyclin-dependent kinase 4 (CDK4) includes the regulatory pstaire helix. Retrovirology 2005, 2, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suzuki, T.; Yoshida, M. HTLV-1 Tax protein interacts with cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor p16INK4A and counteracts its inhibitory activity to CDK4. Leukemia 1997, 11 (Suppl. 3), 14–16. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Yamakuchi, M.; Masuda, S.; Tokioka, T.; Yamaoka, S.; Maruyama, I.; Kitajima, I. Phosphoinositide-3 kinase-PKB/Akt pathway activation is involved in fibroblast Rat-1 transformation by human T-cell leukemia virus type I Tax. Oncogene 2001, 20, 2514–2526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.J.; Kehrl, J.H.; Burton, J.; Tendler, C.L.; Jeang, K.T.; Danielpour, D.; Thevenin, C.; Kim, K.Y.; Sporn, M.B.; Roberts, A.B. Transactivation of the transforming growth factor β 1 (TGF-β1) gene by human T lymphotropic virus type 1 Tax: A potential mechanism for the increased production of TGF-β 1 in adult T cell leukemia. J. Exp. Med. 1990, 172, 121–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moriuchi, M.; Moriuchi, H. Transforming growth factor-β enhances human T-cell leukemia virus type I infection. J. Med. Virol. 2002, 67, 427–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ariumi, Y.; Kaida, A.; Lin, J.Y.; Hirota, M.; Masui, O.; Yamaoka, S.; Taya, Y.; Shimotohno, K. HTLV-1 Tax oncoprotein represses the p53-mediated trans-activation function through coactivator CBP sequestration. Oncogene 2000, 19, 1491–1499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suzuki, T.; Uchida-Toita, M.; Yoshida, M. Tax protein of HTLV-1 inhibits CBP/p300-mediated transcription by interfering with recruitment of CBP/p300 onto DNA element of E-box or p53 binding site. Oncogene 1999, 18, 4137–4143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zane, L.; Yasunaga, J.; Mitagami, Y.; Yedavalli, V.; Tang, S.W.; Chen, C.Y.; Ratner, L.; Lu, X.; Jeang, K.T. WIP1 and p53 contribute to HTLV-1 Tax-induced tumorigenesis. Retrovirology 2012, 9, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harashima, N.; Kurihara, K.; Utsunomiya, A.; Tanosaki, R.; Hanabuchi, S.; Masuda, M.; Ohashi, T.; Fukui, F.; Hasegawa, A.; Masuda, T.; et al. Graft-versus-Tax response in adult T-cell leukemia patients after hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Cancer Res. 2004, 64, 391–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rowan, A.G.; Suemori, K.; Fujiwara, H.; Yasukawa, M.; Tanaka, Y.; Taylor, G.P.; Bangham, C.R. Cytotoxic T lymphocyte lysis of HTLV-1 infected cells is limited by weak HBZ protein expression, but non-specifically enhanced on induction of Tax expression. Retrovirology 2014, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takeda, S.; Maeda, M.; Morikawa, S.; Taniguchi, Y.; Yasunaga, J.; Nosaka, K.; Tanaka, Y.; Matsuoka, M. Genetic and epigenetic inactivation of Tax gene in adult T-cell leukemia cells. Int. J. Cancer 2004, 109, 559–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Furukawa, Y.; Kubota, R.; Tara, M.; Izumo, S.; Osame, M. Existence of escape mutant in HTLV-I Tax during the development of adult T-cell leukemia. Blood 2001, 97, 987–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tamiya, S.; Matsuoka, M.; Etoh, K.; Watanabe, T.; Kamihira, S.; Yamaguchi, K.; Takatsuki, K. Two types of defective human T-lymphotropic virus type I provirus in adult T-cell leukemia. Blood 1996, 88, 3065–3073. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Koiwa, T.; Hamano-Usami, A.; Ishida, T.; Okayama, A.; Yamaguchi, K.; Kamihira, S.; Watanabe, T. 5’-long terminal repeat-selective CPG methylation of latent human T-cell leukemia virus type 1 provirus in vitro and in vivo. J. Virol. 2002, 76, 9389–9397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaudray, G.; Gachon, F.; Basbous, J.; Biard-Piechaczyk, M.; Devaux, C.; Mesnard, J.M. The complementary strand of the human T-cell leukemia virus type 1 RNA genome encodes a bZIP transcription factor that down-regulates viral transcription. J. Virol. 2002, 76, 12813–12822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Satou, Y.; Yasunaga, J.; Yoshida, M.; Matsuoka, M. HTLV-I basic leucine zipper factor gene mRNA supports proliferation of adult T cell leukemia cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 720–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitobe, Y.; Yasunaga, J.; Furuta, R.; Matsuoka, M. HTLV-1 bZIP factor rna and protein impart distinct functions on T-cellproliferation and survival. Cancer Res. 2015, 75, 4143–4152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lemasson, I.; Lewis, M.R.; Polakowski, N.; Hivin, P.; Cavanagh, M.H.; Thebault, S.; Barbeau, B.; Nyborg, J.K.; Mesnard, J.M. Human T-cell leukemia virus type 1 (HTLV-1) bZIP protein interacts with the cellular transcription factor CREB to inhibit HTLV-1 transcription. J. Virol. 2007, 81, 1543–1553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hagiya, K.; Yasunaga, J.; Satou, Y.; Ohshima, K.; Matsuoka, M. ATF3, an HTLV-1 bZip factor binding protein, promotes proliferation of adult T-cell leukemia cells. Retrovirology 2011, 8, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, Y.; Zheng, S.; Wang, Y.; Zang, W.; Li, M.; Wang, N.; Li, P.; Jin, J.; Dong, Z.; Zhao, G. The HTLV-1 HBZ protein inhibits cyclin D1 expression through interacting with the cellular transcription factor CREB. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2013, 40, 5967–5975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wurm, T.; Wright, D.G.; Polakowski, N.; Mesnard, J.M.; Lemasson, I. The HTLV-1-encoded protein HBZ directly inhibits the acetyl transferase activity of p300/CBP. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012, 40, 5910–5925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borowiak, M.; Kuhlmann, A.S.; Girard, S.; Gazzolo, L.; Mesnard, J.M.; Jalinot, P.; Dodon, M.D. HTLV-1 bZIP factor impedes the menin tumor suppressor and upregulates JunD-mediated transcription of the Htert gene. Carcinogenesis 2013, 34, 2664–2672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hivin, P.; Basbous, J.; Raymond, F.; Henaff, D.; Arpin-Andre, C.; Robert-Hebmann, V.; Barbeau, B.; Mesnard, J.M. The HBZ-SP1 isoform of human T-cell leukemia virus type I represses JunB activity by sequestration into nuclear bodies. Retrovirology 2007, 4, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thebault, S.; Basbous, J.; Hivin, P.; Devaux, C.; Mesnard, J.M. HBZ interacts with JunD and stimulates its transcriptional activity. FEBS Lett. 2004, 562, 165–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugata, K.; Yasunaga, J.I.; Mitobe, Y.; Miura, M.; Miyazato, P.; Kohara, M.; Matsuoka, M. Protective effect of cytotoxic T lymphocytes targeting HTLV-1 bZIP factor. Blood 2015, 126, 1095–1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons by Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Martin, J.L.; Maldonado, J.O.; Mueller, J.D.; Zhang, W.; Mansky, L.M. Molecular Studies of HTLV-1 Replication: An Update. Viruses 2016, 8, 31. https://doi.org/10.3390/v8020031
Martin JL, Maldonado JO, Mueller JD, Zhang W, Mansky LM. Molecular Studies of HTLV-1 Replication: An Update. Viruses. 2016; 8(2):31. https://doi.org/10.3390/v8020031
Chicago/Turabian StyleMartin, Jessica L., José O. Maldonado, Joachim D. Mueller, Wei Zhang, and Louis M. Mansky. 2016. "Molecular Studies of HTLV-1 Replication: An Update" Viruses 8, no. 2: 31. https://doi.org/10.3390/v8020031
APA StyleMartin, J. L., Maldonado, J. O., Mueller, J. D., Zhang, W., & Mansky, L. M. (2016). Molecular Studies of HTLV-1 Replication: An Update. Viruses, 8(2), 31. https://doi.org/10.3390/v8020031








