PRMT5 Is Upregulated in HTLV-1-Mediated T-Cell Transformation and Selective Inhibition Alters Viral Gene Expression and Infected Cell Survival
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cell Lines and Culture
2.2. Plasmids and Cloning
2.3. Immunoblotting
2.4. Quantitative RT-PCR
2.5. Co-Culture Immortalization Assays
2.6. Packaging and Infection of Lentivirus Vectors
2.7. PRMT5i Treatment
2.8. HIV-1 Gene Expression in Chronically Infected Cells
2.9. Transient Transfections, Reporter Assays, and p19 Gag ELISA
2.10. Annexin V Staining
2.11. ChIP Assays
3. Results
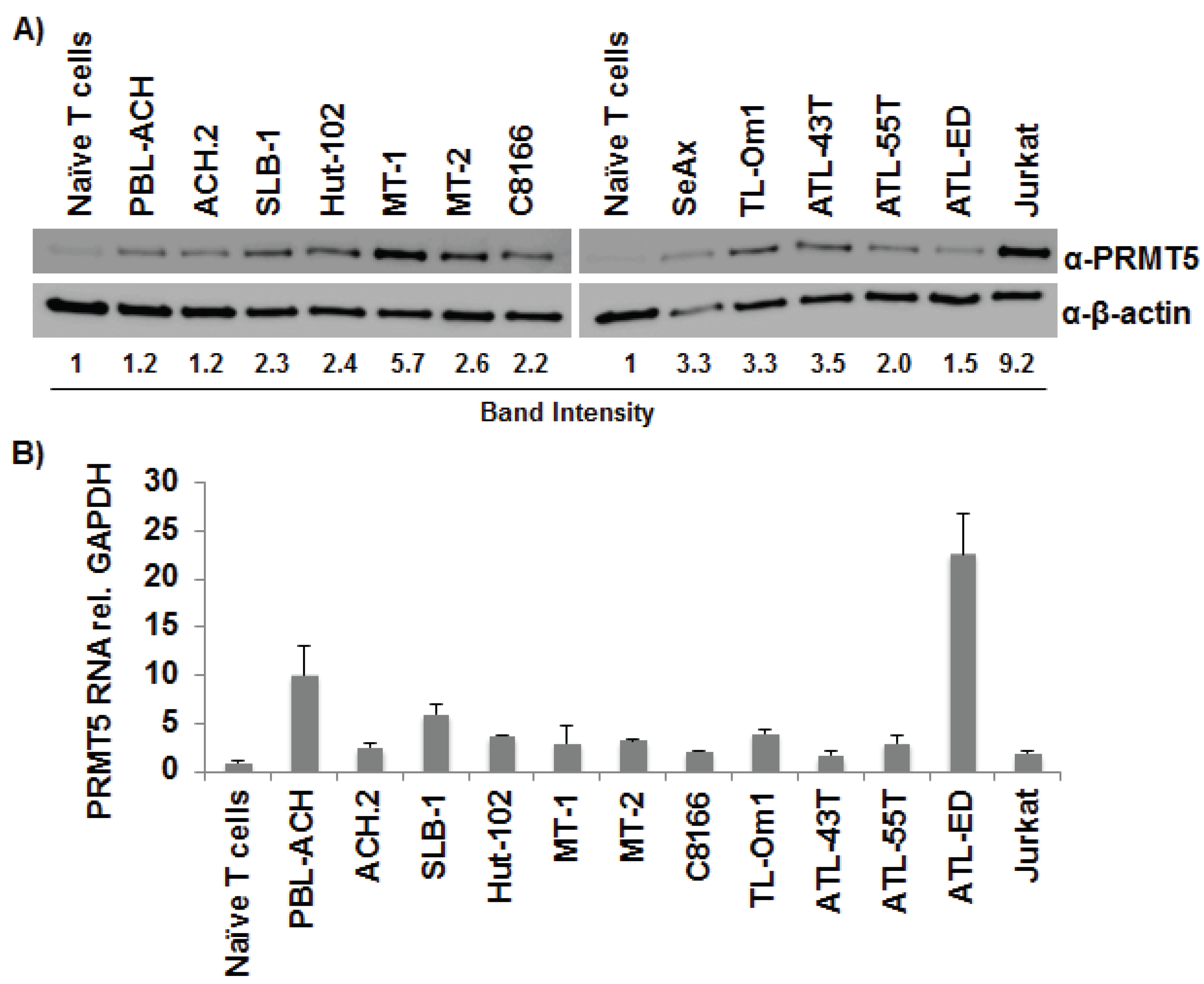
3.1. PRMT5 Was Upregulated in T-Cell Leukemia/Lymphoma Cells

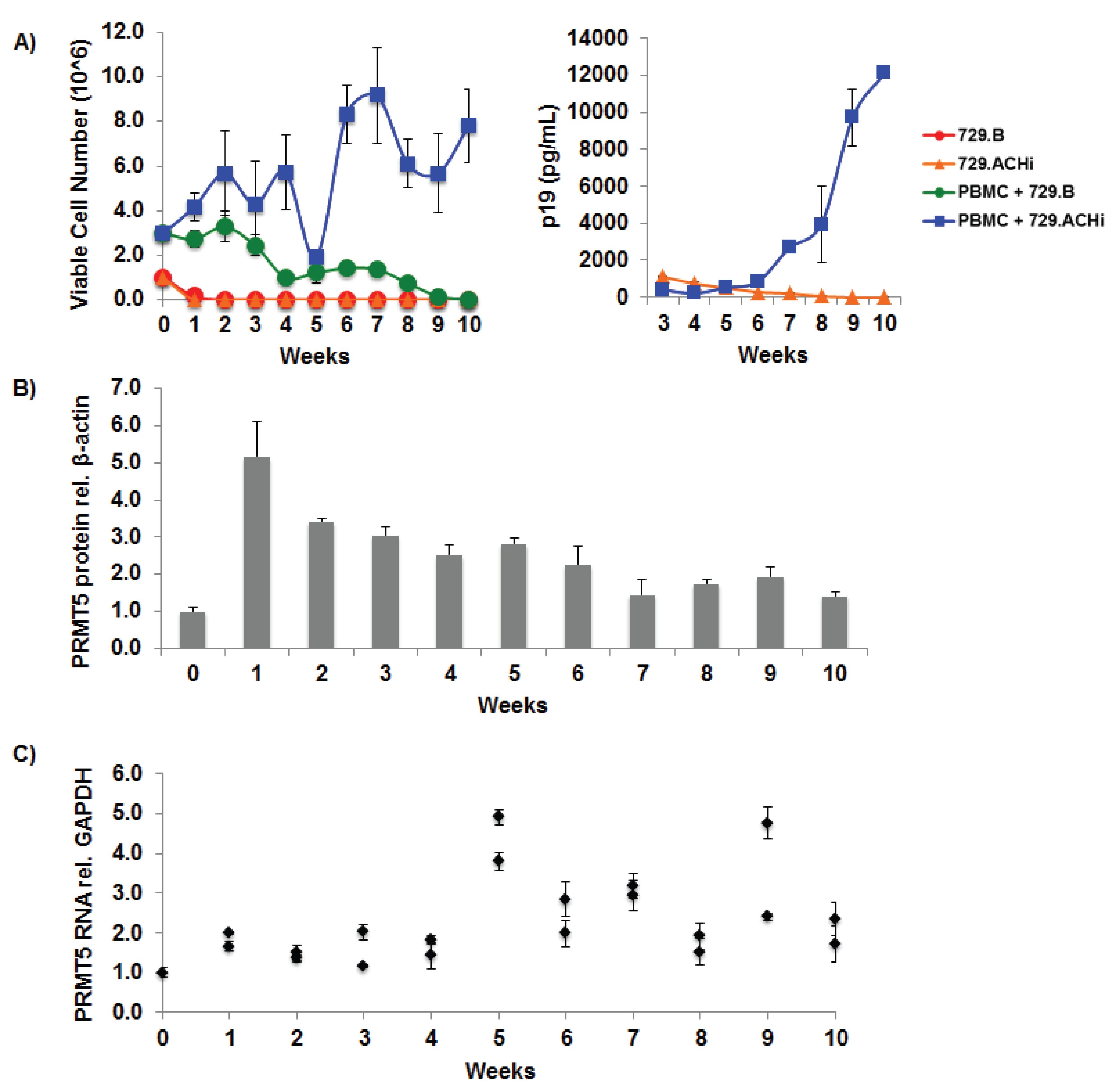
3.2. PRMT5 Levels Were Elevated during HTLV-1-Mediated Cellular Transformation
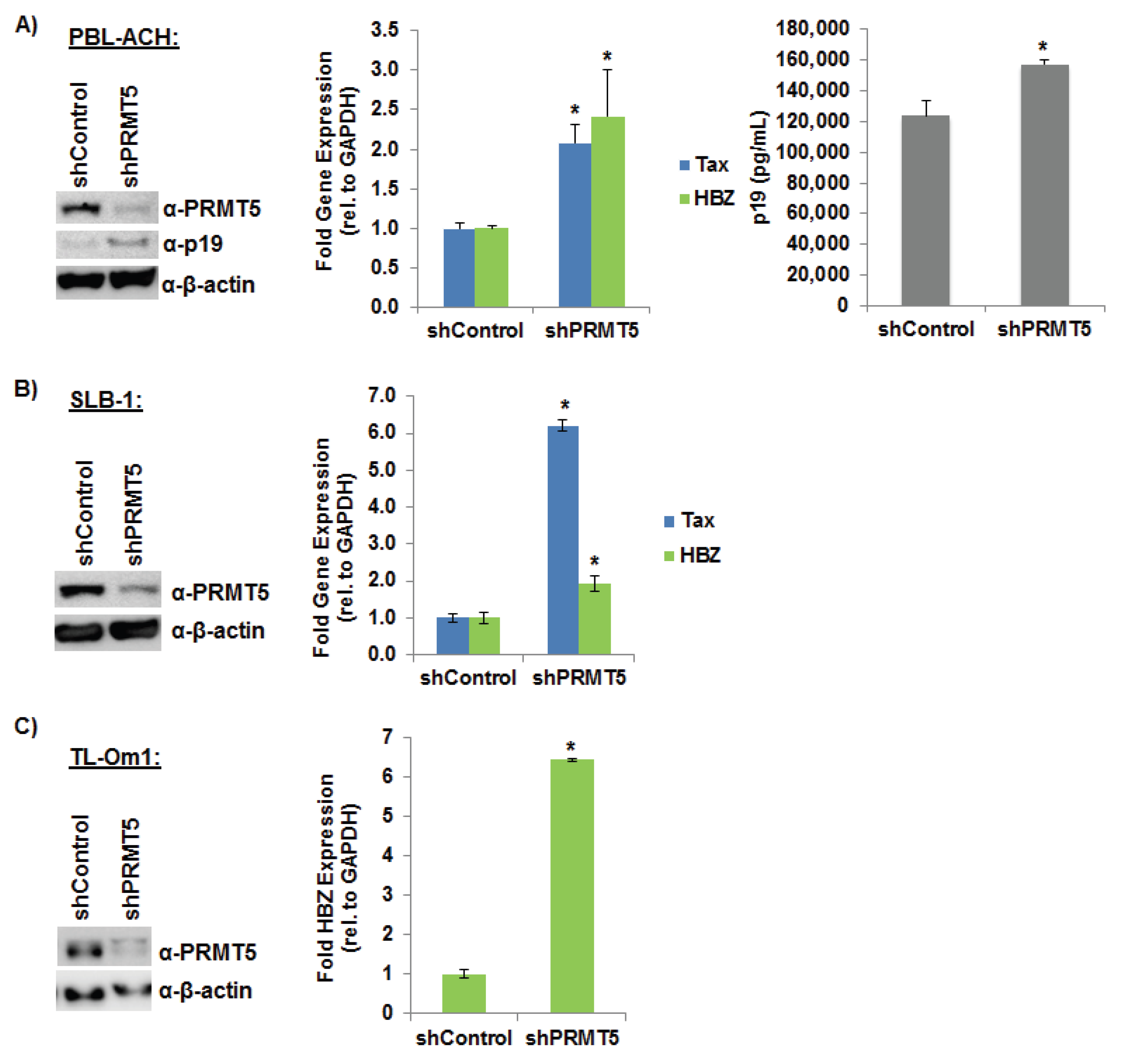
3.3. Loss of Endogenous PRMT5 Increased HTLV-1 Gene Expression
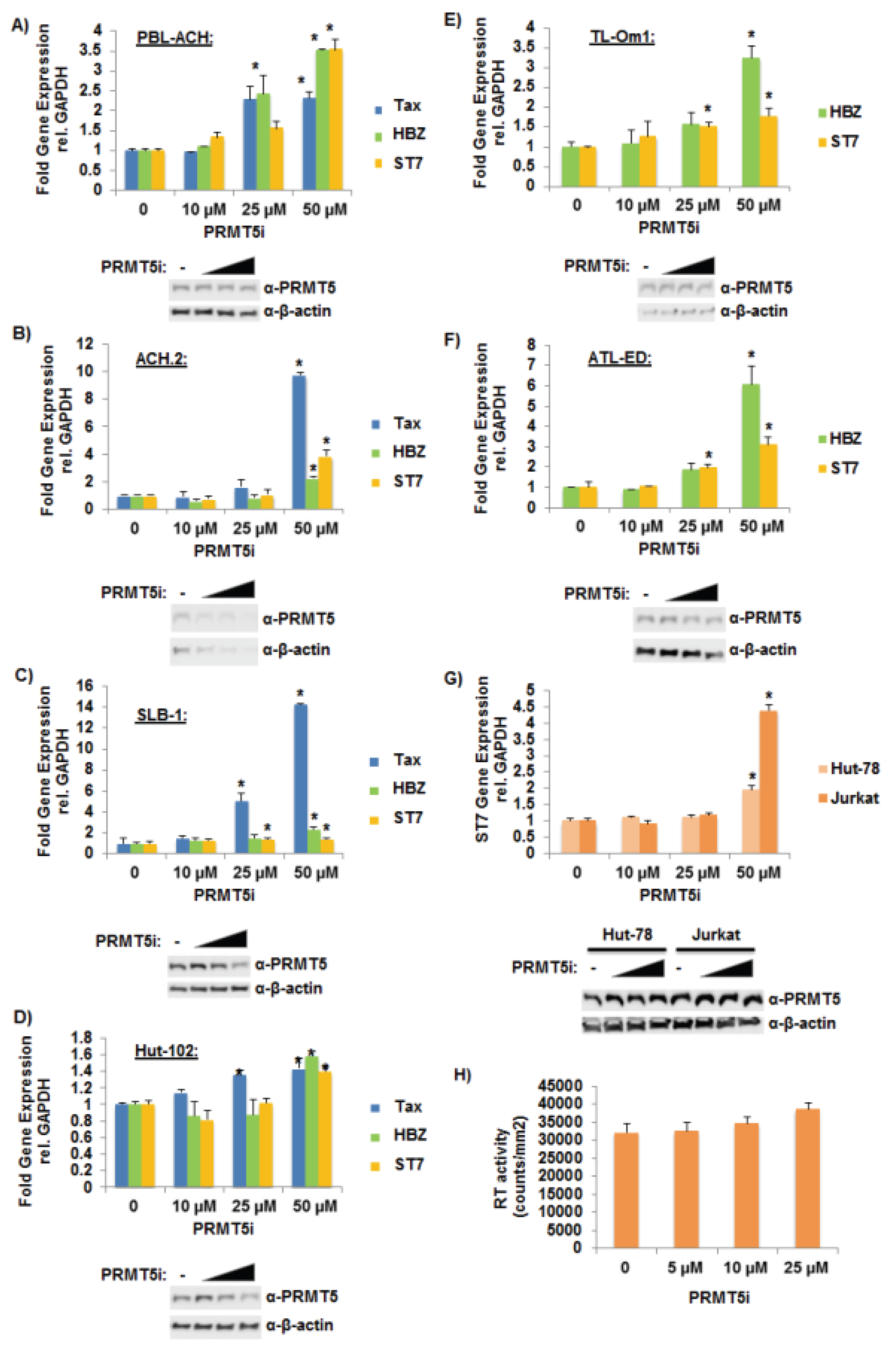
3.4. Selective Inhibition of PRMT5 Enhanced HTLV-1 Gene Expression
3.5. Selective Inhibition of PRMT5 Decreased Cell Proliferation and Viability

3.6. PRMT5 Negatively Regulated HTLV-1 Gene Expression
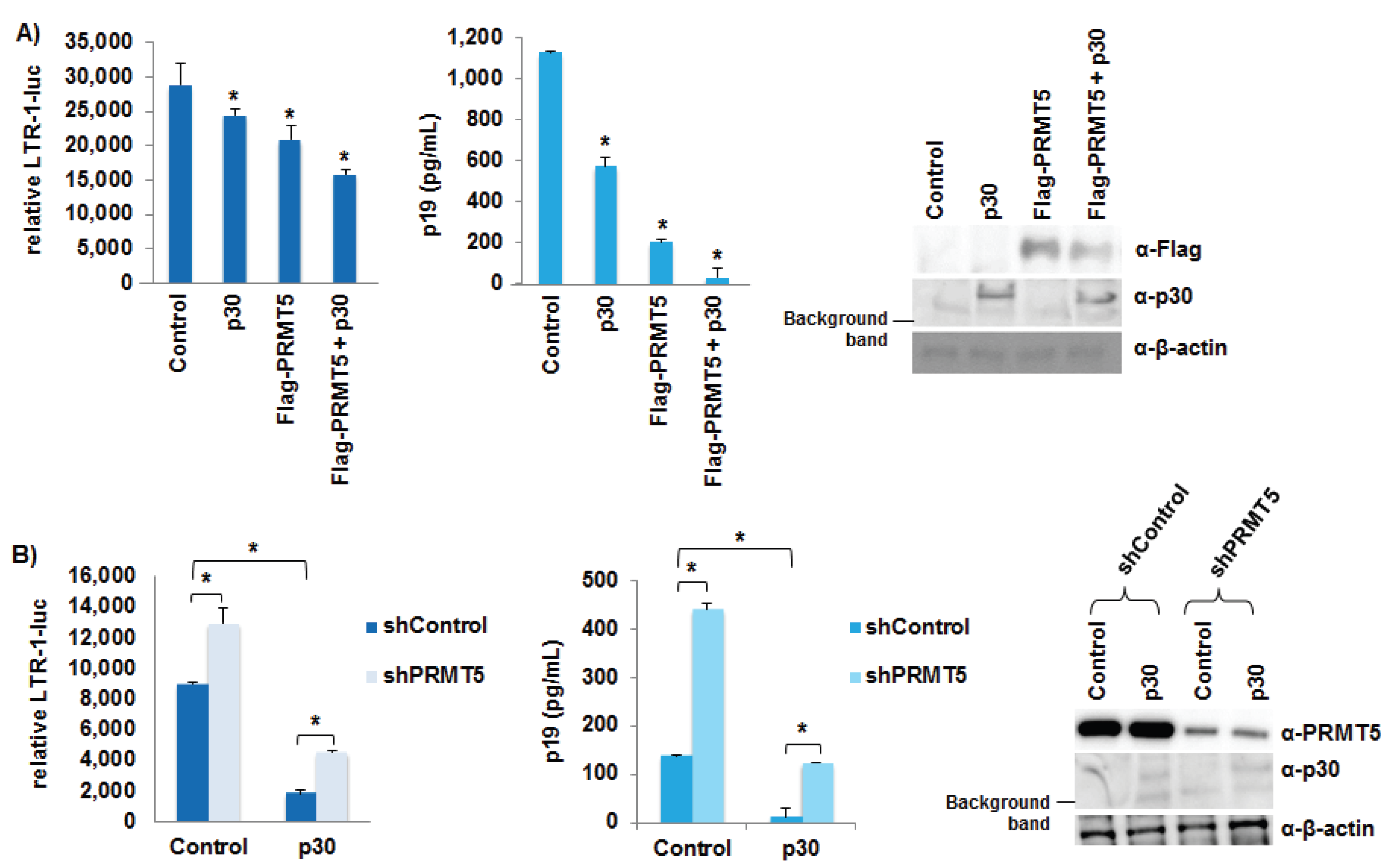
3.7. PRMT5 Did Not Affect Tax Transcriptional Function
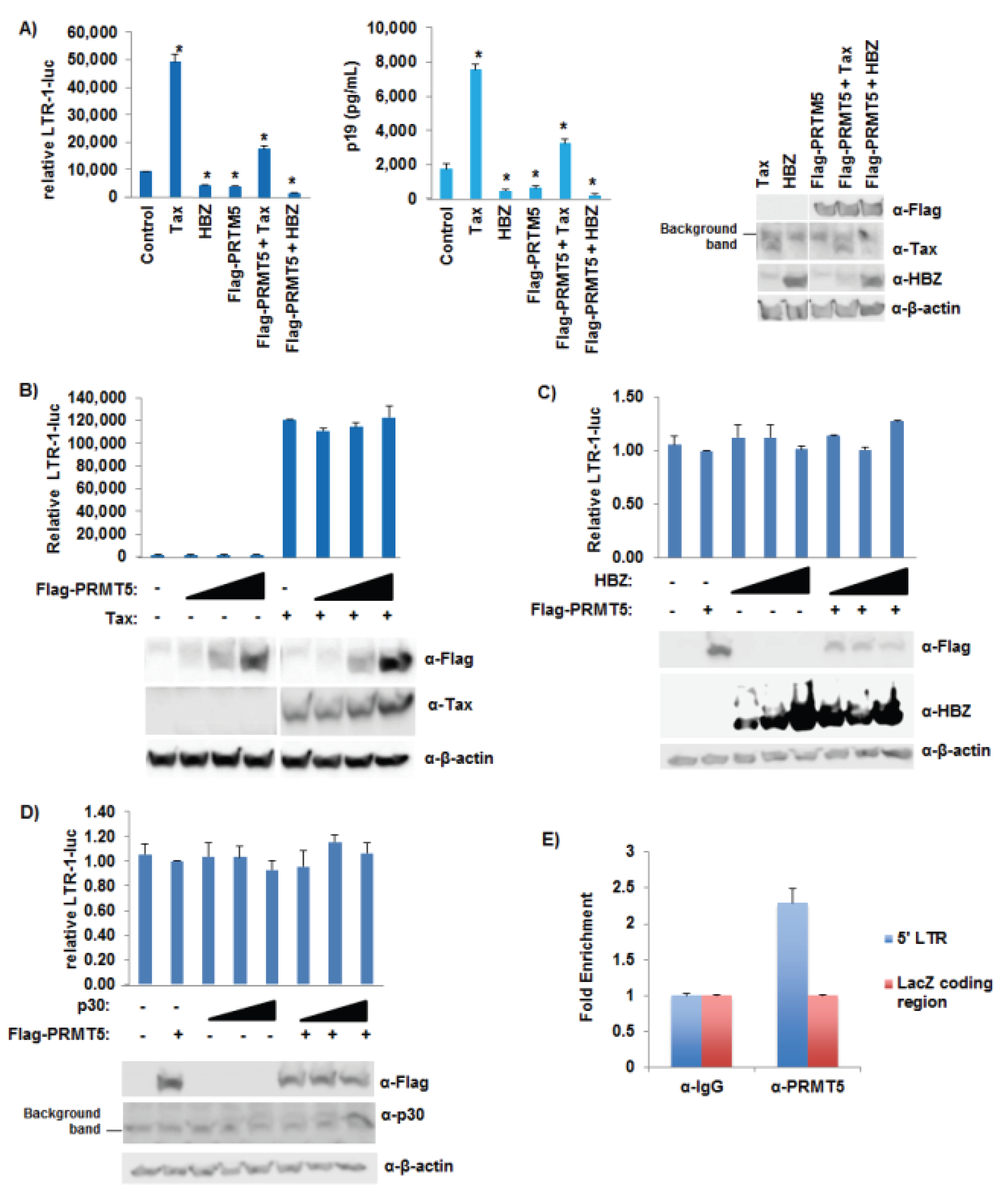
4. Discussion
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Proietti, F.A.; Carneiro-Proietti, A.B.; Catalan-Soares, B.C.; Murphy, E.L. Global epidemiology of HTLV-I infection and associated diseases. Oncogene 2005, 24, 6058–6068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poiesz, B.J.; Ruscetti, F.W.; Gazdar, A.F.; Bunn, P.A.; Minna, J.D.; Gallo, R.C. Detection and isolation of type C retrovirus particles from fresh and cultured lymphocytes of a patient with cutaneous T-cell lymphoma. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1980, 77, 7415–7419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshida, M.; Miyoshi, I.; Hinuma, Y. Isolation and characterization of retrovirus from cell lines of human adult T-cell leukemia and its implication in the disease. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1982, 79, 2031–2035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hinuma, Y.; Nagata, K.; Hanaoka, M.; Nakai, M.; Matsumoto, T.; Kinoshita, K.-I.; Shirakawa, S.; Miyoshi, I. Adult T-cell leukemia: Antigen in an ATL cell line and detection of antibodies to the antigen in human sera. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1981, 78, 6476–6480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Osame, M.; Izumo, S.; Igata, A.; Matsumoto, M.; Matsumoto, T.; Sonoda, S.; Tara, M.; Shibata, Y. Blood transfusion with HTLV-I associated myelopathy. Lancet 1986, 2, 104–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gessain, A.; Barin, F.; Vernant, J.C.; Gout, O.; Maurs, L.; Calender, A.; de The, G. Antibodies to human T-lymphotropic virus type-I in patients with tropical spastic paraparesis. Lancet 1985, 2, 407–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, G.P. Editorial commentary: Human T-cell lymphotropic virus type 1 (HTLV-1) and HTLV-1-associated myelopathy/tropical spastic paraparesis. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2015, 61, 57–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Utsunomiya, A.; Choi, I.; Chihara, D.; Seto, M. Recent advances in the treatment of adult T-cell leukemia-lymphomas. Cancer Sci. 2015, 106, 344–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, H.; Ren, T.; Sun, S.C. New insight into the oncogenic mechanism of the retroviral oncoprotein Tax. Protein Cell 2012, 3, 581–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Matsuoka, M.; Green, P.L. The HBZ gene, a key player in HTLV-1 pathogenesis. Retrovirology 2009, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grassmann, R.; Aboud, M.; Jeang, K.T. Molecular mechanisms of cellular transformation by HTLV-1 Tax. Oncogene 2005, 24, 5976–5985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bex, F.; Gaynor, R.B. Regulation of gene expression by HTLV-I Tax protein. Methods 1998, 16, 83–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arima, N.; Tei, C. HTLV-I Tax related dysfunction of cell cycle regulators and oncogenesis of adult T cell leukemia. Leuk. Lymphoma 2001, 40, 267–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Satou, Y.; Yasunaga, J.; Yoshida, M.; Matsuoka, M. HTLV-I basic leucine zipper factor gene mRNA supports proliferation of adult t cell leukemia cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 720–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arnold, J.; Zimmerman, B.; Li, M.; Lairmore, M.D.; Green, P.L. Human T-cell leukemia virus type-1 antisense-encoded gene, HBZ, promotes T lymphocyte proliferation. Blood 2008, 112, 3788–3797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arnold, J.; Yamamoto, B.; Li, M.; Phipps, A.J.; Younis, I.; Lairmore, M.D.; Green, P.L. Enhancement of infectivity and persistence in vivo by HBZ, a natural antisense coded protein of HTLV-1. Blood 2006, 107, 3976–3982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clerc, I.; Polakowski, N.; Andre-Arpin, C.; Cook, P.; Barbeau, B.; Mesnard, J.M.; Lemasson, I. An interaction between the human T cell leukemia virus type 1 basic leucine zipper factor (HBZ) and the KIX domain of p300/CBP contributes to the down-regulation of Tax-dependent viral transcription by HBZ. J. Biol. Chem. 2008, 283, 23903–23913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaudray, G.; Gachon, F.; Basbous, J.; Biard-Piechaczyk, M.; Devaux, C.; Mesnard, J. The complementary strand of the human T-cell leukemia virus type 1 RNA genome encodes a bZIP transcription factor that down-regulates viral transcription. J. Virol. 2002, 76, 12813–12822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lemasson, I.; Lewis, M.R.; Polakowski, N.; Hivin, P.; Cavanagh, M.H.; Thebault, S.; Barbeau, B.; Nyborg, J.K.; Mesnard, J.M. Human T-cell leukemia virus type 1 (HTLV-1) bZIP protein interacts with the cellular transcription factor CREB to inhibit HTLV-1 transcription. J. Virol. 2007, 81, 1543–1553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thebault, S.; Basbous, J.; Hivin, P.; Devaux, C.; Mesnard, J.M. HBZ interacts with JunD and stimulates its transcriptional activity. FEBS Lett. 2004, 562, 165–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basbous, J.; Arpin, C.; Gaudray, G.; Piechaczyk, M.; Devaux, C.; Mesnard, J. HBZ factor of HTLV-1 dimerizes with transcription factors JunB and c-Jun and modulates their transcriptional activity. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 43620–43627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsumoto, J.; Ohshima, T.; Isono, O.; Shimotohno, K. HTLV-1 HBZ suppresses AP-1 activity by impairing both the DNA-binding ability and the stability of c-Jun protein. Oncogene 2005, 24, 1001–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsuoka, M.; Jeang, K.T. Human T-cell leukaemia virus type 1 (HTLV-1) infectivity and cellular transformation. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2007, 7, 270–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Egger, G.; Liang, G.; Aparicio, A.; Jones, P.A. Epigenetics in human disease and prospects for epigenetic therapy. Nature 2004, 429, 457–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ganesan, A.; Nolan, L.; Crabb, S.J.; Packham, G. Epigenetic therapy: Histone acetylation, DNA methylation and anti-cancer drug discovery. Curr. Cancer Drug Targets 2009, 9, 963–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poke, F.S.; Qadi, A.; Holloway, A.F. Reversing aberrant methylation patterns in cancer. Curr. Med. Chem. 2010, 17, 1246–1254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Majumder, S.; Alinari, L.; Roy, S.; Miller, T.; Datta, J.; Sif, S.; Baiocchi, R.; Jacob, S.T. Methylation of histone H3 and H4 by PRMT5 regulates ribosomal RNA gene transcription. J. Cell. Biochem. 2010, 109, 553–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pal, S.; Baiocchi, R.A.; Byrd, J.C.; Grever, M.R.; Jacob, S.T.; Sif, S. Low levels of miR-92b/96 induce PRMT5 translation and H3R8/H4R3 methylation in mantle cell lymphoma. EMBO J. 2007, 26, 3558–3569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pal, S.; Vishwanath, S.N.; Erdjument-Bromage, H.; Tempst, P.; Sif, S. Human SWI/SNF-associated PRMT5 methylates histone H3 arginine 8 and negatively regulates expression of ST7 and NM23 tumor suppressor genes. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2004, 24, 9630–9645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Pal, S.; Sif, S. Protein arginine methyltransferase 5 suppresses the transcription of the RB family of tumor suppressors in leukemia and lymphoma cells. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2008, 28, 6262–6277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alinari, L.; Mahasenan, K.V.; Yan, F.; Karkhanis, V.; Chung, J.H.; Smith, E.M.; Quinion, C.; Smith, P.L.; Kim, L.; Patton, J.T.; et al. Selective inhibition of protein arginine methyltransferase 5 blocks initiation and maintenance of B-cell transformation. Blood 2015, 125, 2530–2543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chung, J.; Karkhanis, V.; Tae, S.; Yan, F.; Smith, P.; Ayers, L.W.; Agostinelli, C.; Pileri, S.; Denis, G.V.; Baiocchi, R.A.; et al. Protein arginine methyltransferase 5 (PRMT5) inhibition induces lymphoma cell death through reactivation of the retinoblastoma tumor suppressor pathway and polycomb repressor complex 2 (PRC2) silencing. J. Biol. Chem. 2013, 288, 35534–35547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karkhanis, V.; Hu, Y.J.; Baiocchi, R.A.; Imbalzano, A.N.; Sif, S. Versatility of PRMT5-induced methylation in growth control and development. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2011, 36, 633–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rank, G.; Cerruti, L.; Simpson, R.J.; Moritz, R.L.; Jane, S.M.; Zhao, Q. Identification of a PRMT5-dependent repressor complex linked to silencing of human fetal globin gene expression. Blood 2010, 116, 1585–1592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, C.; Lim, Y.; Yoo, B.C.; Won, N.H.; Kim, S.; Kim, G. Regulation of post-translational protein arginine methylation during HeLa cell cycle. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2010, 1800, 977–985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ancelin, K.; Lange, U.C.; Hajkova, P.; Schneider, R.; Bannister, A.J.; Kouzarides, T.; Surani, M.A. Blimp1 associates with Prmt5 and directs histone arginine methylation in mouse germ cells. Nat. Cell Biol. 2006, 8, 623–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doueiri, R.; Anupam, R.; Kvaratskhelia, M.; Green, K.B.; Lairmore, M.D.; Green, P.L. Comparative host protein interactions with HTLV-1 p30 and HTLV-2 p28: Insights into difference in pathobiology of human retroviruses. Retrovirology 2012, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koralnik, I.J.; Gessain, A.; Klotman, M.E.; lo Monico, A.; Berneman, Z.N.; Franchini, G. Protein isoforms encoded by the pX region of human T-cell leukemia/lymphotropic virus type I. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1992, 89, 8813–8817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lairmore, M.D.; Albrecht, B.; D’Souza, C.; Nisbet, J.W.; Ding, W.; Bartoe, J.T.; Green, P.L.; Zhang, W. In vitro and in vivo functional analysis of human T cell lymphotropic virus type 1 pX open reading frames I and II. AIDS Res. Hum. Retrovir. 2000, 16, 1757–1764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.; Nisbet, J.W.; Albrecht, B.; Ding, W.; Kashanchi, F.; Bartoe, J.T.; Lairmore, M.D. Human T-lymphotropic virus type 1 p30II regulates gene transcription by binding CREB binding protein/p300. J. Virol. 2001, 75, 9885–9895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Younis, I.; Khair, L.; Dundr, M.; Lairmore, M.D.; Franchini, G.; Green, P.L. Repression of human T-cell leukemia virus type 1 and 2 replication by a viral mRNA-encoded posttranscriptional regulator. J. Virol. 2004, 78, 11077–11083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nicot, C.; Dundr, J.M.; Johnson, J.R.; Fullen, J.R.; Alonzo, N.; Fukumoto, R.; Princler, G.L.; Derse, D.; Misteli, T.; Franchini, G. HTLV-1-encoded p30II is a post-transcriptional negative regulator of viral replication. Nat. Med. 2004, 10, 197–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anderson, M.D.; Ye, J.; Xie, L.; Green, P.L. Transformation studies with a human T-cell leukemia virus type 1 molecular clone. J. Virol. Methods 2004, 116, 195–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, M.; Green, P.L. Detection and quantitation of HTLV-1 and HTLV-2 mRNA species by real-time RT-PCR. J. Virol. Methods 2007, 142, 159–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Green, P.L.; Ross, T.M.; Chen, I.S.Y.; Pettiford, S. Human T-cell leukemia virus type II nucleotide sequences between env and the last exon of tax/rex are not required for viral replication or cellular transformation. J. Virol. 1995, 69, 387–394. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Astier-Gin, T.; Portail, J.P.; Lafond, F.; Guillemain, B. Identification of HTLV-I- or HTLV-II-producing cells by cocultivation with BHK-21 cells stably transfected with a LTR-lacZ gene construct. J. Virol. Methods 1995, 51, 19–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Livak, K.J.; Schmittgen, T.D. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2−ΔΔCT method. Methods 2001, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shilo, K.; Wu, X.; Sharma, S.; Welliver, M.; Duan, W.; Villalona-Calero, M.; Fukuoka, J.; Sif, S.; Baiocchi, R.; Hitchcock, C.L.; et al. Cellular localization of protein arginine methyltransferase-5 correlates with grade of lung tumors. Diagn. Pathol. 2013, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, F.; Alinari, L.; Lustberg, M.E.; Martin, L.K.; Cordero-Nieves, H.M.; Banasavadi-Siddegowda, Y.; Virk, S.; Barnholtz-Sloan, J.; Bell, E.H.; Wojton, J.; et al. Genetic validation of the protein arginine methyltransferase PRMT5 as a candidate therapeutic target in glioblastoma. Cancer Res. 2014, 74, 1752–1765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nicholas, C.; Yang, J.; Peters, S.B.; Bill, M.A.; Baiocchi, R.A.; Yan, F.; Sif, S.; Tae, S.; Gaudio, E.; Wu, X.; et al. PRMT5 is upregulated in malignant and metastatic melanoma and regulates expression of MITF and p27(Kip1.). PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e74710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhi, H.; Yang, L.; Kuo, Y.L.; Ho, Y.K.; Shih, H.M.; Giam, C.Z. Nf-κb hyper-activation by HTLV-1 Tax induces cellular senescence, but can be alleviated by the viral anti-sense protein HBZ. PLoS Pathog. 2011, 7, e1002025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krause, C.D.; Yang, Z.H.; Kim, Y.S.; Lee, J.H.; Cook, J.R.; Pestka, S. Protein arginine methyltransferases: Evolution and assessment of their pharmacological and therapeutic potential. Pharmacol. Ther. 2007, 113, 50–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aggarwal, P.; Vaites, L.P.; Kim, J.K.; Mellert, H.; Gurung, B.; Nakagawa, H.; Herlyn, M.; Hua, X.; Rustgi, A.K.; McMahon, S.B.; et al. Nuclear cyclin D1/CDK4 kinase regulates CUL4 expression and triggers neoplastic growth via activation of the PRMT5 methyltransferase. Cancer Cell 2010, 18, 329–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2015 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons by Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Panfil, A.R.; Al-Saleem, J.; Howard, C.M.; Mates, J.M.; Kwiek, J.J.; Baiocchi, R.A.; Green, P.L. PRMT5 Is Upregulated in HTLV-1-Mediated T-Cell Transformation and Selective Inhibition Alters Viral Gene Expression and Infected Cell Survival. Viruses 2016, 8, 7. https://doi.org/10.3390/v8010007
Panfil AR, Al-Saleem J, Howard CM, Mates JM, Kwiek JJ, Baiocchi RA, Green PL. PRMT5 Is Upregulated in HTLV-1-Mediated T-Cell Transformation and Selective Inhibition Alters Viral Gene Expression and Infected Cell Survival. Viruses. 2016; 8(1):7. https://doi.org/10.3390/v8010007
Chicago/Turabian StylePanfil, Amanda R., Jacob Al-Saleem, Cory M. Howard, Jessica M. Mates, Jesse J. Kwiek, Robert A. Baiocchi, and Patrick L. Green. 2016. "PRMT5 Is Upregulated in HTLV-1-Mediated T-Cell Transformation and Selective Inhibition Alters Viral Gene Expression and Infected Cell Survival" Viruses 8, no. 1: 7. https://doi.org/10.3390/v8010007
APA StylePanfil, A. R., Al-Saleem, J., Howard, C. M., Mates, J. M., Kwiek, J. J., Baiocchi, R. A., & Green, P. L. (2016). PRMT5 Is Upregulated in HTLV-1-Mediated T-Cell Transformation and Selective Inhibition Alters Viral Gene Expression and Infected Cell Survival. Viruses, 8(1), 7. https://doi.org/10.3390/v8010007




