A Phylogeographic Investigation of African Monkeypox
Abstract
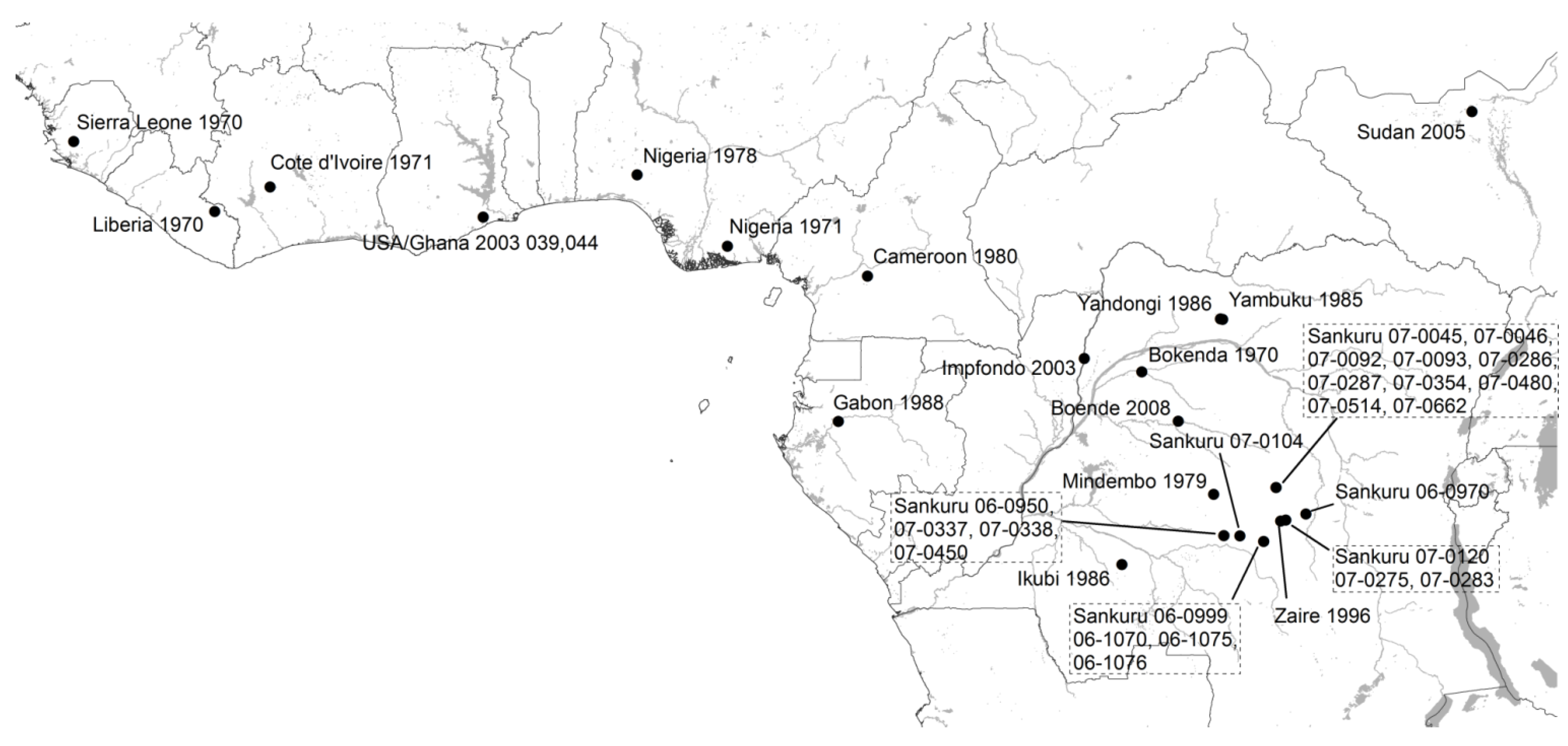
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Genetic Data and Analysis
2.2. Ecological Niche Models
3. Results
3.1. Phylogenetic Analysis
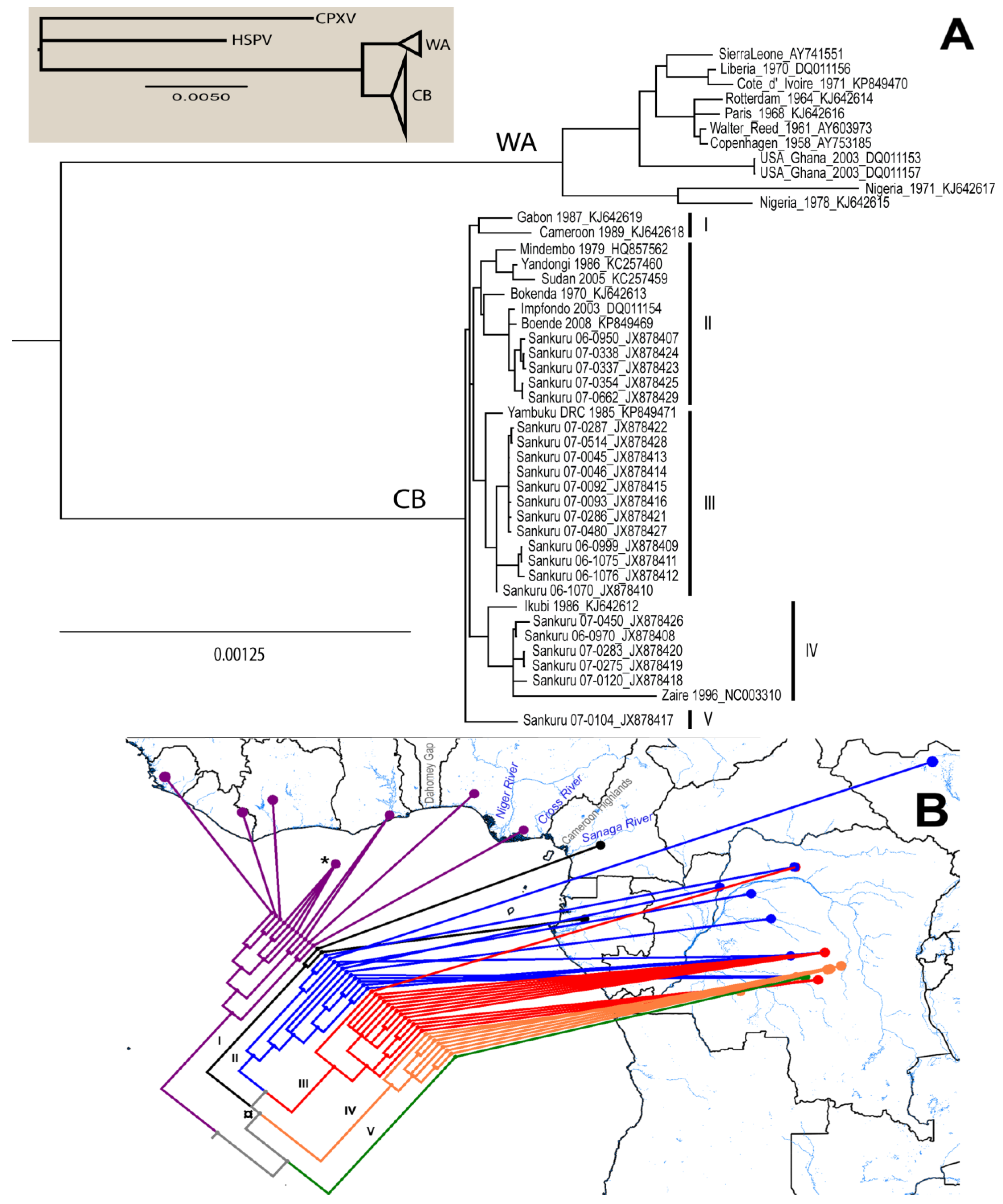
| Isolate Name | Location | Source | Accession # |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ikubi 1986 (IV) | Ikubi, DRC (Zaire) | [4] | KJ642612 |
| **++ Zaire 1996 (IV) | Akungula, DRC (Zaire) | [5] | NC_003310 |
| Yambuku DRC 1985 (III) | Yambuku, DRC (Zaire) | [56] | KP849471 |
| **++ Mindembo 1979 (II) | Mindembo, DRC (Zaire) | [3] | HQ857562 |
| Yandongi 1986 (II) | Yandongi, DRC | [4] | KC257460 |
| Bokenda 1970 (II) | Bokenda, DRC (Zaire) | [1] | KJ642613 |
| Boende 2008 (II) | Boende, DRC | Unpublished | KP849469 |
| **++ Impfondo 2003 (II) | Impfondo, ROC | [6] | DQ011154 |
| Sudan 2005 (II) | Nuria, South Sudan | [57] | KC257459 |
| Cameroon 1989 (I) | Ekoumdouma, Cameroon | [58] | KJ642618 |
| Gabon 1987 (I) | Gabon | [59] | KJ642619 |
| Nigeria 1971 | Ihie, Nigeria | [16] | KJ642617 |
| Nigeria 1978 | Omifunfun, Nigeria | [3] | KJ642615 |
| ++ USA/Ghana 2003_039 | Ghana | [7] | DQ011157 |
| **++ USA/Ghana 2003_044 | Ghana | [7] | DQ011153 |
| ++ Copenhagen 1958 | Copenhagen | [60] | AY753185 |
| ++ Walter Reed 1961 | Walter Reed | [61] | AY603973 |
| Paris 1968 | Paris | [62] | KJ642616 |
| Rotterdam 1965 | Rotterdam | [63] | KJ642614 |
| Cote d’Ivoire 1971 | Cote d’Ivoire | [64] | KP849470 |
| **++ Liberia 1970 | Liberia | [16] | DQ011156 |
| ++ Sierra Leone 1970 | Sierra Leone | [16] | AY741551 |
| ++ Sankuru 06-0950 (II) | Kole Health Zone, DRC | [31] | JX878407 |
| ++ Sankuru 07-0337 (II) | Kole Health Zone, DRC | [31] | JX878423 |
| ++ Sankuru 07-0338 (II) | Kole Health Zone, DRC | [31] | JX878424 |
| ++ Sankuru 07-0450 (IV) | Kole Health Zone, DRC | [31] | JX878426 |
| ++ Sankuru 06-0999 (III) | Vangakete Health Zone, DRC | [31] | JX878409 |
| ++ Sankuru 06-1075 (III) | Vangakete Health Zone, DRC | [31] | JX878411 |
| ++ Sankuru 06-1076 (III) | Vangakete Health Zone, DRC | [31] | JX878412 |
| ++ Sankuru 06-1070 (III) | Vangakete Health Zone, DRC | [31] | JX878410 |
| ++ Sankuru 07-0045 (III) | Lomela Health Zone, DRC | [31] | JX878413 |
| ++ Sankuru 07-0046 (III) | Lomela Health Zone, DRC | [31] | JX878414 |
| ++ Sankuru 07-0092 (III) | Lomela Health Zone, DRC | [31] | JX878415 |
| ++ Sankuru 07-0093 (III) | Lomela Health Zone, DRC | [31] | JX878416 |
| ++ Sankuru 07-0286 (III) | Lomela Health Zone, DRC | [31] | JX878421 |
| ++ Sankuru 07-0480 (III) | Lomela Health Zone, DRC | [31] | JX878427 |
| ++ Sankuru 07-0514 (III) | Lomela Health Zone, DRC | [31] | JX878428 |
| ++ Sankuru 07-0287 (III) | Lomela Health Zone, DRC | [31] | JX878422 |
| ++ Sankuru 07-0354 (II) | Lomela Health Zone, DRC | [31] | JX878425 |
| ++ Sankuru 07-0662 (II) | Lomela Health Zone, DRC | [31] | JX878429 |
| ++ Sankuru 06-0970 (IV) | Katako Kombe Health Zone, DRC | [31] | JX878408 |
| ++Sankuru 07-0120 (IV) | Djalo-Ndjeka Health Zone, DRC | [31] | JX878418 |
| ++Sankuru 07-0275 (IV) | Djalo-Ndjeka Health Zone, DRC | [31] | JX878419 |
| ++Sankuru 07-0283 (IV) | Djalo-Ndjeka Health Zone, DRC | [31] | JX878420 |
| ++Sankuru 07-0104 (V) | Bena-Dibele Health Zone, DRC | [31] | JX878417 |
3.2. Ecological Niche Model
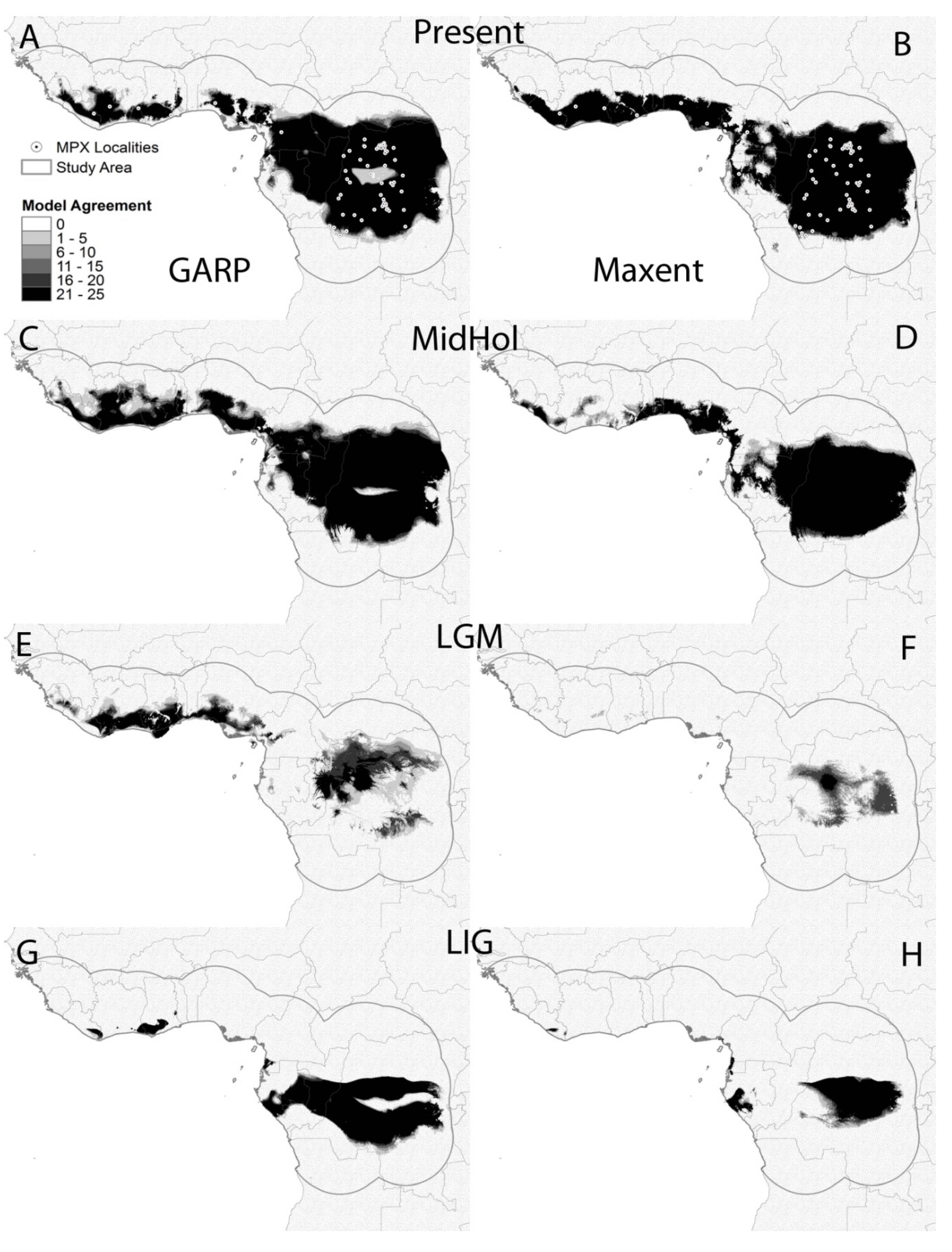
4. Discussion
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
Disclaimer
References
- Ladnyj, I.D.; Ziegler, P.; Kima, E. A human infection caused by monkeypox virus in Basankusu Territory, Democratic Republic of the Congo. Bull. World Health Organ. 1972, 46, 593–597. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Jezek, Z.; Marennikova, S.S.; Mutumbo, M.; Nakano, J.H.; Paluku, K.M.; Szczeniowski, M. Human monkeypox: A study of 2,510 contacts of 214 patients. J. Infect. Dis. 1986, 154, 551–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Breman, J.G.; Ruti, K.; Steniowski, M.V.; Zanotto, E.; Gromyko, A.I.; Arita, I. Human Monkeypox, 1970–79. Bull. World Health Organ. 1980, 58, 165–182. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Jezek, Z. Smallpox and its post-eradication surveillance. Bull. World. Health. Organ. 1987, 65, 425–434. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hutin, Y.J.F.; Williams, R.J.; Mailfait, P.; Pebody, R.; Loparev, V.N.; Ropp, S.L.; Rodriguez, M.; Knight, J.C.; Tshioko, F.K.; Khan, A.S.; et al. Outbreak of human monkeypox, Democratic Republic of Congo, 1996–1997. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2001, 7, 434–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Learned, L.A.; Reynolds, M.G.; Wassa-Wassa, D.; Li, Y.; Olson, V.A.; Karem, K.L.; Stempora, L.L.; Braden, Z.H.; Kline, R.; Likos, A.M.; et al. Extended interhuman transmission of monkeypox in a hospital community in the Republic of the Congo, 2003. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2005, 73, 428–434. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Reed, K.D.; Melski, J.W.; Graham, M.B.; Regnery, R.L.; Sotir, M.J.; Wegner, M.V.; Kazmierczak, J.J.; Stratman, E.J.; Li, Y.; Fairley, J.A.; et al. The detection of monkeypox in humans in the Western Hemisphere. N. Engl. J. Med. 2004, 350, 342–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- MacNeil, A.; Reynolds, M.G.; Carroll, D.S.; Karem, K.L.; Braden, Z.; Lash, R.R.; Moundeli, A.; Mombouli, J.-V.; Jumaan, A.O.; Schmid, D.S.; et al. Monkeypox or varicella? Lessons from a rash outbreak investigation in the Republic of the Congo. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2009, 80, 503–507. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Meyer, H.; Perrichot, M.; Stemmler, M.; Emmerich, P.; Schmitz, H.; Varaine, F.; Shungu, R.; Tshioko, F.; Formenty, P. Outbreaks of disease suspected of being due to monkeypox virus infection in the Democratic Republic of Congo in 2001. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2002, 40, 2919–2921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bass, J.; Tack, D.M.; McCollum, A.M.; Kabamba, J.; Pakuta, E.; Malekani, J.; Nguete, B.; Monroe, B.P.; Doty, J.B.; Karhemere, S.; et al. Enhancing health care worker ability to detect and care for patients with monkeypox in the Democratic Republic of the Congo. Int. Health 2013, 5, 237–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rimoin, A.W.; Kisalu, N.; Kebela-Ilunga, B.; Mukaba, T.; Wright, L.L.; Formenty, P.; Wolfe, N.D.; Shongo, R.L.; Tshioko, F.; Okitolonda, E.; et al. Endemic human monkeypox, Democratic Republic of Congo, 2001–2004. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2007, 13, 934–937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fuller, T.; Thomassen, H.A.; Mulembakani, P.M.; Johnston, S.C.; Lloyd-Smith, J.O.; Kisalu, N.K.; Lutete, T.K.; Blumberg, S.; Fair, J.N.; Wolfe, N.D.; et al. Using remote sensing to map the risk of human monkeypox virus in the Congo Basin. EcoHealth 2011, 8, 14–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Likos, A.M.; Sammons, S.A.; Olson, V.A.; France, M.A.; Li, Y.; Olsen-Rasmussen, M.A.; Davidson, W.; Galloway, R.; Khristova, M.L.; Reynolds, M.G.; et al. A tale of two clades: Monkeypox viruses. J. Gen. Virol. 2005, 86, 2661–2672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Esposito, J.J.; Knight, J.C. Orthopoxvirus DNA: A comparison of restriction profiles and maps. Virology 1985, 143, 230–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mackett, M.; Archard, L.C. Conservation and variation in orthopoxvirus genome structure. J. Gen. Virol. 1979, 45, 683–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foster, S.O.; Brink, E.W.; Hutchins, D.L.; Pifer, J.M.; Lourie, B.; Moser, C.R.; Cummings, E.C.; Kuteyi, O.E.K.; Eke, R.E.A.; Titus, J.B.; et al. Human Monkeypox. Bull. World. Health. Organ. 1972, 46, 569–576. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Waltari, E.; Hijmans, R.J.; Peterson, A.T.; Nyári, Á.S.; Perkins, S.L.; Guralnick, R. Locating Pleistocene refugia: Comparing phylogeographic and ecological niche model predictions. PLoS ONE 2007, 2, e563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonaccorso, E.; Koch, I.; Peterson, A.T. Pleistocene fragmentation of Amazon species’ ranges. Divers. Distrib. 2006, 12, 157–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Svenning, J.-C.; Fløjgaard, C.; Marske, K.A.; Nogués-Bravo, D.; Normand, S. Applications of species distribution modeling to paleobiology. Quaternary Sci. Rev. 2011, 30, 2930–2947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lima-Ribeiro, M.S.; Diniz-Filho, J.A.F. Modelando a distribuição geográfica das espécies no passado: Uma abordagem promissora em paleoecologia. Rev. Brasileira Paleontol. 2012, 15, 371–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varela, S.; Lobo, J.M.; Rodríguez, J.; Batra, P. Were the Late Pleistocene climatic changes responsible for the disappearance of the European spotted hyena populations? Hindcasting a spcies geographic distributions across time. Quat. Sci. Rev. 2010, 29, 2027–2035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González, C.; Wang, O.; Strutz, S.E.; González-Salazar, C.; Sánchez-Cordero, V.; Sarkar, S. Climate change and risk of leishmaniasis in North America: Predictions from ecological niche models of vector and reservoir species. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2010, 4, e585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holt, A.C.; Sealkeld, D.J.; Fritz, C.L.; Tucker, J.R.; Gong, P. Spatial analysis of plague in California: Niche modeling predictions of the current distribution and potential response to climate change. Int. J. Health Geogr. 2009, 8, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Komar, O.; Robbins, M.B.; Klenk, K.; Blitvich, B.J.; Marlenee, N.L.; Burkhalter, K.L.; Gubler, D.J.; Gonzálvez, G.; Peña, C.J.; Peterson, A.T.; et al. West Nile virus transmission in resident birds, Dominican Republic. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2003, 9, 1299–1302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ellis, C.K.; Carroll, D.S.; Lash, R.R.; Peterson, A.T.; Damon, I.K.; Malekani, J.M.; Formenty, P. Ecology and geography of human monkeypox case occurrences across Africa. J. Wildl. Dis. 2012, 48, 335–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakazawa, Y.; Williams, R.; Peterson, A.T.; Mead, P.; Staples, E.; Gage, K.L. Climate change effects on plague and tularemia in the United States. Vector-Borne Zoonotic Dis. 2007, 7, 529–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haffer, J. Speciation in Amazonian forest birds. Science 1969, 195, 131–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haffer, J. Alternative models of vertebrate speciation in Amazonia: An overview. Biodivers. Conserv. 1997, 6, 451–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Endler, J. Pleistocene forest refuges: Fact or fancy? In Biological Diversification in the Tropics; Prance, G.T., Ed.; Columbia University Press: New York, NY, USA, 1982; pp. 179–200. [Google Scholar]
- Ježek, Z.; Fenner, F. Human Monkeypox; Karger: New York, NY, USA, 1988. [Google Scholar]
- Kugelman, J.R.; Johnson, S.C.; Mulembakani, P.M.; Kisalu, N.; Lee, M.S.; Koroleva, G.; McCarthy, S.E.; Gestole, M.C.; Wolfe, N.D.; Fair, J.N.; et al. Genomic variability of monkeypox virus among humans, Democratic Republic of the Congo. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2014, 20, 232–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katoh, K.; Toh, H. Recent developments in the MAFFT multiple sequence alignment program. Brief. Bioinform. 2008, 9, 286–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huelsenbeck, J.P.; Ronquist, F.; Nielsen, R.; Bollback, J.P. Bayesian inference of phylogeny and its impact on evolutionary biology. Science 2001, 294, 2310–2314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ronquist, F.; Huelsenbeck, J.P. MBAYES 3: Bayesian phylogenetic inference under mixed models. Bioinformatics 2003, 19, 1572–1574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- R Development Core Team. R: A language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing, v3.1.1: Vienna, Austria, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Tamura, K.; Stecher, G.; Peterson, D.; Filipski, A.; Kumar, S. MEGA6: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis Version 6.0. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2013, 30, 2725–2729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiménez-Valverde, A.; Nakazawa, Y.; Lira-Noriega, A.; Peterson, A.T. Environmental correlation structure and ecological niche model projections. Biodivers. Inf. 2009, 6, 28–35. [Google Scholar]
- Hijmans, R.J.; Cameron, S.E.; Parra, J.L.; Jones, P.G.; Jarvis, A. Very high resolution interpolated climate surfaces for global land areas. Int. J. Climatol. 2005, 25, 1965–1978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lash, R.R.; Carroll, D.S.; Hughes, C.M.; Nakazawa, Y.; Karem, K.L.; Damon, I.K.; Peterson, A.T. Effects of georeferencing effort on mapping monkeypox case distributions and transmission risk. Int. J. Health Geogr. 2012, 11, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Otto-Bliesner, B.L.; Marshall, S.J.; Overpeck, J.T.; Miller, G.H.; Hu, A. CAPE Last Interglacial Project members, Simulating arctic climate warmth and icefield retreat in the Last Interglaciation. Science 2006, 311, 1751–1753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chapman, A.D.; Wieczorek, J. Guide to Best Practices for Georeferencing; Global Biodiversity Information Facility: Copenhagen, Denmark, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Peterson, A.T.; Sánchez-Cordero, V.; Beard, C.B.; Ramsey, J.M. Ecologic niche modeling and potential reservoirs for Chagas disease, Mexico. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2002, 8, 662–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peterson, A.T.; Martínez-Campos, C.; Nakazawa, Y.; Martínez-Meyer, E. Time-specific ecological niche modeling predicts spatial dynamics of vector insects and human dengue cases. Trans. R. Soc. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2005, 99, 647–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peterson, A.T.; Bauer, J.T.; Mills, J.N. Ecologic and geographic distribution of filovirus disease. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2004, 10, 40–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakazawa, Y.; Williams, R.A.J.; Peterson, A.T.; Mead, P.S.; Kugeler, K.J.; Petersen, J.M. Ecological niche modeling of Francisella tularensis subspecies and clades in the United States. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2010, 82, 912–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peterson, A.T.; Benz, B.W.; Papeş, M. Highly pathogenic H5N1 avian influenza: Entry pathways into North America via bird migration. PLoS ONE 2007, 2, e261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williams, R.A.J.; Peterson, A.T. Ecology and geography of avian influenza (HPAI H5N1) transmission in the Middle East and northeastern Africa. Int. J. Health Geogr. 2009, 8, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elith, J.; Graham, C.H.; Anderson, R.P.; Dudik, M.; Ferrier, S.; Guisan, A.; Hijmans, R.J.; Huettman, F.; Leathwick, J.R.; Lehmann, A.; et al. Novel methods improve prediction of species' distributions from occurrence data. Ecography 2006, 29, 129–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peterson, A.T.; Papeş, M.; Eaton, M. Transferability and model evaluation in ecological niche modeling: A comparison of GARP and Maxent. Ecography 2007, 30, 550–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stockwell, D. The GARP modelling system: Problems and solutions to automated spatial prediction. Int. J. Geogr. Inf. Sci. 1999, 13, 143–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stockwell, D.R.B.; Noble, I.R. Introduction of sets of rules from animal distribution data: A robust and informative method of data analysis. Math. Comput. Simulat. 1992, 33, 385–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, R.P.; Lew, D.; Peterson, A.T. Evaluating predictive models of speciesʼ distributions: Criteria for selecting optimal models. Ecol. Model. 2003, 162, 211–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peterson, A.T.; Papeş, M.; Soberón, J. Rethinking receiver operating characteristic analysis applications in ecological niche modeling. Ecol. Model. 2008, 213, 63–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phillips, S.J.; Anderson, R.P.; Schapire, R.E. Maximum entropy modeling of species geographic distributions. Ecol. Model. 2006, 190, 231–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phillips, S.J.; Dudik, M.; Schapire, R.E. A maximum Entropy Approach to Species Distribution Modeling. In Proceedings of the 21st International Conference on Machine Learning, Banff, Canada, July 2004.
- Khodakevich, L.; Ježek, Z.; Kinzanzka, K. Isolation of monkeypox virus from wild squirrel infected in nature. Lancet 1986, 1, 98–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakazawa, Y.; Emerson, G.L.; Zhao, H.; Li, Y.; Carroll, D.S.; Reynolds, M.G.; Karem, K.L.; Olson, V.A.; Lash, R.R.; Davidson, W.B.; et al. Phylogenetic and ecologic perspectives of a monkeypox outbreak, southern Sudan, 2005. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2013, 19, 237–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tchokoteu, P.F.; Kago, I.; Tetanye, E.; Ndoumbe, P.; Pignon, D.; Mbede, J. Variola or a severe case of varicella? A case of human variola due to monkeypox virus in a child from the Cameroon. Ann. Soc. Belg. Med. Trop. 1991, 71, 123–128. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Müller, G.; Meyer, A.; Gras, F.; Emmerich, P.; Kolakowski, T.; Esposito, J.J. Monkeypox virus in liver and spleen of child in Gabon. Lancet 1988, 331, 769–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arita, I.; Henderson, D.A. Smallpox and monkeypox in non-human primates. Bull. World Health Organ. 1968, 39, 277–283. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- McConnell, S.J.; Herman, Y.F.; Mattson, D.E.; Erickson, L. Monkey pox disease in irradiated cynomologous monkeys. Nature 1962, 195, 1128–1129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milhaud, C.; Klein, M.; Virat, J. Analyse dʼun cas de variole du singe (monkeypox) chez le chimpanzé (Pan troglogdytes). Exp. Anim. 1969, 2, 121–135. [Google Scholar]
- Peters, J.C. An epizootic of monkey pox at Rotterdam Zoo. Int. Zoo Yearb. 1966, 6, 274–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arita, I.; Henderson, D.A. Monkeypox and whitepox viruses in West and Central Africa. Bull. World Health Organ. 1976, 53, 347–353. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Gonder, M.K.; Disotell, T.R.; Oates, J.F. New genetic evidence on the evolution of chimpanzee populations and implications for taxinomy. Int. J. Primatol. 2006, 27, 1103–1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schunke, A.C.; Hutterer, R. The variance of variation: Geographic patters of coat colouration in Anomalurops and Anomalurus (Mammalia, Rodentia, Anomalouridae). Bonn. Zool. Beitr. 2004, 53, 169–185. [Google Scholar]
- Nicolas, V.; Missoup, A.D.; Denys, C.; Kerbis Peterhans, J.; Katuala, P.; Couloux, A.; Colyn, M. The roles of rivers and Pleistocene refugia in shaping genetic diversity in Praomys misonnei in tropical Africa. J. Biogeogr. 2011, 38, 191–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olson, D.M.; Dinerstein, E.; Wikramanayake, E.D.; Burgess, N.D.; Powell, G.V.N.; Underwood, E.C.; DʼAmico, J.; Itoua, I.; Strand, H.E.; Morrison, J.C.; et al. Terrestrial ecorregions of the world: A new map of life on Earth. Bioscience 2001, 51, 933–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salzmann, U.; Hoelzmann, P. The Dahomey Gap: An abrupt climatically induced rain forest fragmentation in West Africa during the late Holocene. Holocene 2005, 15, 190–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Booth, A.H. The Niger, the Volta and teh Dahomey Gap as geographic barriers. Evolution 1958, 12, 48–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicolas, V.; Quérouil, S.; Verheyen, E.; Verheyen, W.; Mboumba, J.F.; Dillen, M.; Colyn, M. Mitochondrial phylogeny of African wood mice, genus Hylomyscus (Rodentia, Muridae): Implications for their taxonomy and biogeography. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2006, 38, 779–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rimoin, A.W.; Mulembakani, P.M.; Johnston, S.C.; Lloyd Smith, J.O.; Kisalu, N.K.; Kinkela, T.L.; Blumberg, S.; Thomassen, H.A.; Pike, B.L.; Fair, J.N.; et al. Major increase in human monkeypox incidence 30 years after smallpox vaccination campaigns cease in the Democratic Republic of Congo. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 16262–16267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jezek, Z.; Fenner, F. Human Monkeypox. In Monographs in Virology; S. Karger AG: Basel, Switzerland, 1988; Volume 14, pp. 1–140. [Google Scholar]
- Mayr, E.; O’Hara, R.J. The biogeographic evidence supporting the Pleistocene forest refuge hypothesis. Evolution 1986, 40, 55–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plana, V. Mechanisms and tempo of evolution in the African Guineo-Congolian rainforest. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. B 2004, 359, 1585–1594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2015 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nakazawa, Y.; Mauldin, M.R.; Emerson, G.L.; Reynolds, M.G.; Lash, R.R.; Gao, J.; Zhao, H.; Li, Y.; Muyembe, J.-J.; Kingebeni, P.M.; et al. A Phylogeographic Investigation of African Monkeypox. Viruses 2015, 7, 2168-2184. https://doi.org/10.3390/v7042168
Nakazawa Y, Mauldin MR, Emerson GL, Reynolds MG, Lash RR, Gao J, Zhao H, Li Y, Muyembe J-J, Kingebeni PM, et al. A Phylogeographic Investigation of African Monkeypox. Viruses. 2015; 7(4):2168-2184. https://doi.org/10.3390/v7042168
Chicago/Turabian StyleNakazawa, Yoshinori, Matthew R. Mauldin, Ginny L. Emerson, Mary G. Reynolds, R. Ryan Lash, Jinxin Gao, Hui Zhao, Yu Li, Jean-Jacques Muyembe, Placide Mbala Kingebeni, and et al. 2015. "A Phylogeographic Investigation of African Monkeypox" Viruses 7, no. 4: 2168-2184. https://doi.org/10.3390/v7042168
APA StyleNakazawa, Y., Mauldin, M. R., Emerson, G. L., Reynolds, M. G., Lash, R. R., Gao, J., Zhao, H., Li, Y., Muyembe, J.-J., Kingebeni, P. M., Wemakoy, O., Malekani, J., Karem, K. L., Damon, I. K., & Carroll, D. S. (2015). A Phylogeographic Investigation of African Monkeypox. Viruses, 7(4), 2168-2184. https://doi.org/10.3390/v7042168






