Beyond ECMO Survival: Long-Term Symptom Burden and Quality-of-Life Impairment in Hantavirus Cardiopulmonary Syndrome Survivors
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design and Setting
2.2. Participants
2.3. Variables
2.4. Outcomes
2.5. Statistical Analysis and Data Visualization
3. Results
3.1. Participant Characteristics at Admission and Clinical Hospitalization
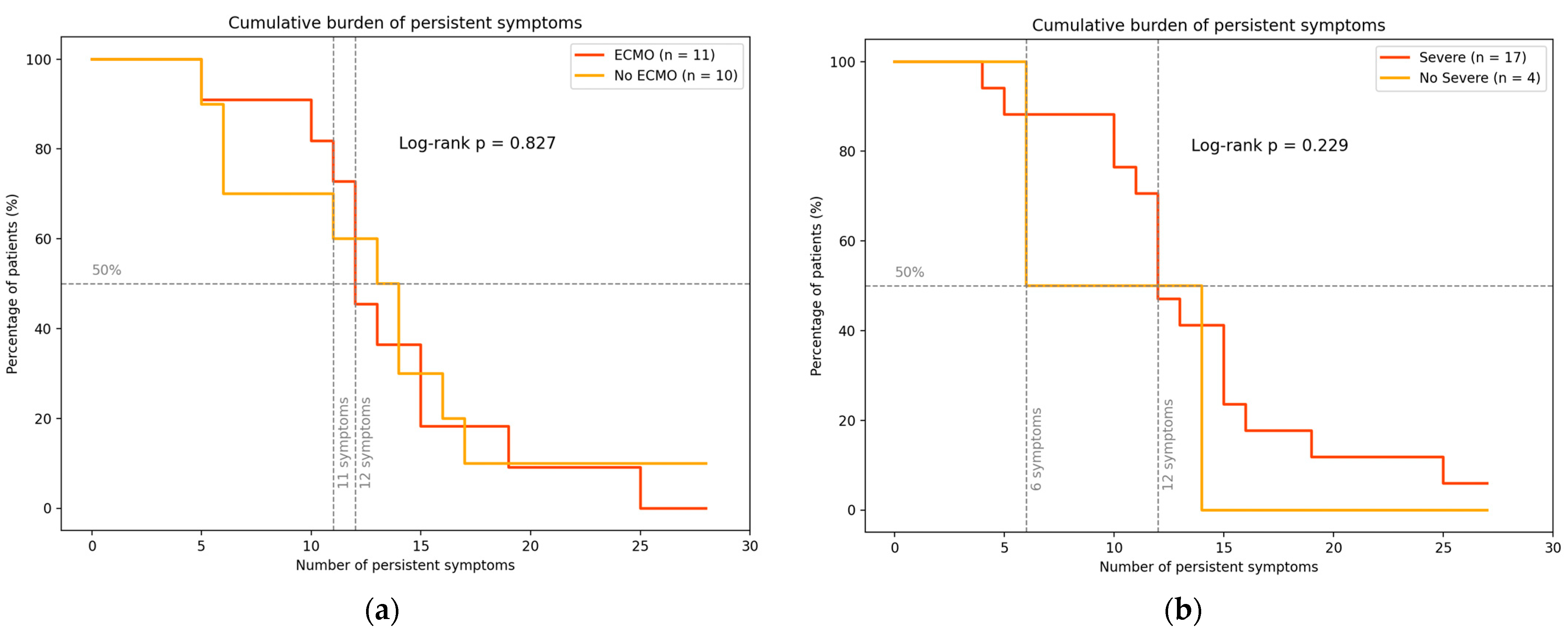
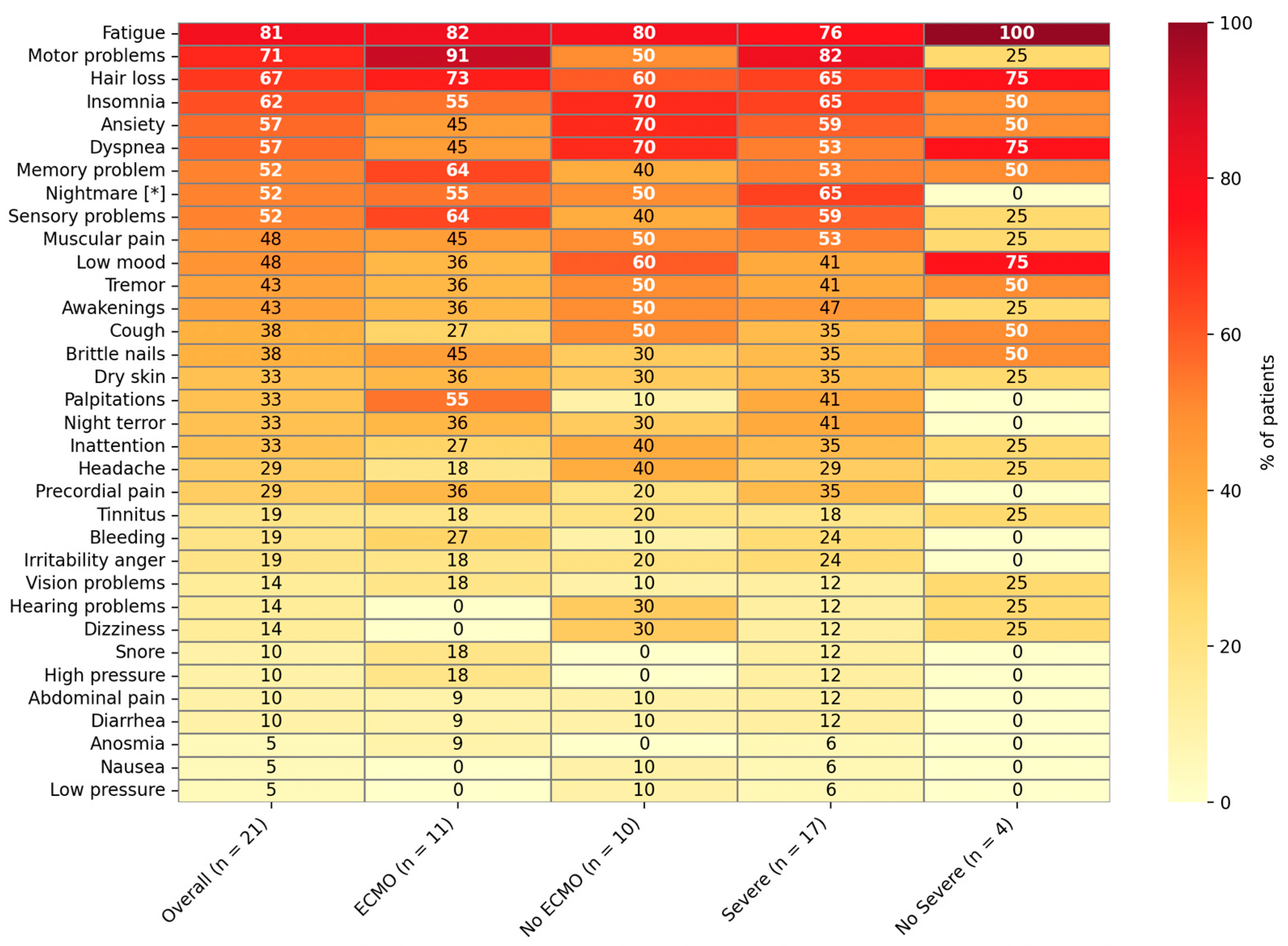
3.2. Recovery and Persistent Symptoms at Convalescence Assessment
3.3. Quality of Life and Functional Status at Follow-Up
3.4. Social and Behavioral Impact
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ANDV | Andes Virus |
| HCPS | Hantavirus Cardiopulmonary Syndrome |
| ECMO | Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation |
| EQ-5D | EuroQol 5 Dimensions Questionnaire |
| HFRS | Hemorrhagic Fever with Renal Syndrome |
| RT-qPCR | Reverse Transcription Quantitative Polymerase Chain Reaction |
| STROBE | Strengthening the Reporting of Observational Studies in Epidemiology |
| REDCap | Research Electronic Data Capture |
| BMI | Body Mass Index |
| WHO | World Health Organization |
| ISARIC WHO | International Severe Acute Respiratory and Emerging Infection Consortium/World Health Organization |
| ICU | Intensive Care Unit |
| EQ-5D-5L | EuroQol 5 Dimensions, 5 Levels (adult version) |
| EQ-5D-Y | EuroQol 5 Dimensions, Youth version |
| IQR | Interquartile Range |
References
- Vial, P.A.; Ferrés, M.; Vial, C.; Klingström, J.; Ahlm, C.; López, R.; Mertz, G.J. Hantavirus in humans: A review of clinical aspects and management. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2023, 23, e371–e382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jonsson, C.B.; Figueiredo, L.T.; Vapalahti, O. A global perspective on hantavirus ecology, epidemiology, and disease. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2010, 23, 412–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medina, R.A.; Torres-Perez, F.; Galeno, H.; Navarrete, M.; Vial, P.A.; Palma, R.E.; Ferres, M.; Cook, J.A.; Hjelle, B. Ecology, genetic diversity, and phylogeographic structure of Andes virus in humans and rodents in Chile. J. Virol. 2009, 83, 2446–2459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Figueiredo, L.T.M.; Souza, W.M.; Ferrés, M.; Enria, D.A. Hantaviruses and cardiopulmonary syndrome in South America. Virus Res. 2014, 187, 43–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ministerio de Salud de Chile. Guía Clínica: Prevención, Diagnóstico y Tratamiento del Síndrome Cardiopulmonar por Hantavirus; MINSAL: Santiago, Chile, 2013. Available online: https://saludresponde.minsal.cl/wp-content/uploads/2022/11/Guia-Clinica-de-prevencion-diag-y-trat-sindrome-CP-por-HV.pdf (accessed on 31 August 2025).
- Vial, P.A.; Valdivieso, F.; Mertz, G.J.; Castillo, C.; Belmar, E.; Delgado, I.; Tapia, M.; Ferrés, M. Incubation period of hantavirus cardiopulmonary syndrome. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2006, 12, 1271–1273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ulloa-Morrison, R.; Pavez, N.; Parra, E.; Lopez, R.; Mondaca, R.; Fernandez, P.; Kraunik, D.; Sanhueza, C.; Bravo, S.; Cornu, M.G.; et al. Critical Care Management of Hantavirus Cardiopulmonary Syndrome: A Narrative Review. J. Crit. Care 2024, 84, 154867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mustonen, J.; Vaheri, A.; Pörsti, I.; Mäkelä, S. Long-term consequences of Puumala hantavirus infection. Viruses 2022, 14, 598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mustonen, J.; Mäkelä, S.; Outinen, T.; Laine, O.; Jylhävä, J.; Arstila, P.T.; Hurme, M.; Vaheri, A. The pathogenesis of nephropathia epidemica: New knowledge and unanswered questions. Antivir. Res. 2013, 100, 589–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sotomayor, P.V.; Olea, N.A.M.; Labraña, A.M.; Castillo, H.C.; Ortega, R.C.; Riquelme, O.R.; Tapia, G.M.; Tomicic, F.V.; Vial, C.P.; Valdivieso, R.F.; et al. Diagnóstico y manejo del síndrome cardiopulmonar por hantavirus: Chile–2007. Rev. Chil. Infect. 2009, 26, 68–86. [Google Scholar]
- Pergam, S.A.; Schmidt, D.W.; Nofchissey, R.A.; Hunt, W.C.; Harford, A.H.; Goade, D.E. Potential renal sequelae in survivors of hantavirus cardiopulmonary syndrome. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2009, 80, 279–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gracia, F.; Armien, B.; Simpson, S.Q.; Munoz, C.; Broce, C.; Pascale, J.M.; Koster, F. Convalescent pulmonary dysfunction following hantavirus pulmonary syndrome in Panama and the USA. Lung 2010, 188, 387–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carlile, O.; Briggs, A.; Henderson, A.D.; Butler-Cole, B.F.C.; Tazare, J.; Tomlinson, L.A.; Marks, M.; Jit, M.; Lin, L.-Y.; Bates, C.; et al. Impact of long COVID on health-related quality-of-life: An OpenSAFELY population cohort study using patient-reported outcome measures (OpenPROMPT). Lancet Reg. Health Eur. 2024, 40, 100908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-de-Las-Peñas, C.; Rodríguez-Jiménez, J.; Moro-López-Menchero, P.; Cancela-Cilleruelo, I.; Pardo-Hernández, A.; Hernández-Barrera, V.; Gil-de-Miguel, Á. Psychometric properties of the Spanish version of the EuroQol-5D-5Lin previously hospitalized COVID-19 survivors with long COVID. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 12605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keshani; Kanwar, S.S. The negative sense RNA hantavirus: A threat to the modern world. Asian Pac. J. Health Sci. 2020, 7, 50–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Needham, D.M.; Davidson, J.; Cohen, H.; Hopkins, R.O.; Weinert, C.; Wunsch, H.; Zawistowski, C.; Bemis-Dougherty, A.; Berney, S.C.; Bienvenu, O.J.; et al. Improving long-term outcomes after discharge from intensive care unit: Report from a stakeholders’ conference. Crit Care Med. 2012, 40, 502–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ISARIC. COVID-19 Long Term Follow Up Study; ISARIC: Oxford, UK, 2020; Available online: https://isaric.org/research/covid-19-clinical-research-resources/covid-19-long-term-follow-up-study/ (accessed on 23 June 2025).
- ISARIC. ISARIC/WHO Core- and Rapid-COVID-19 Case Report Forms; ISARIC: Oxford, UK, 2020; Available online: https://isaric.org/research/covid-19-clinical-research-resources/covid-19-crf/ (accessed on 23 June 2025).
- von Elm, E.; Altman, D.G.; Egger, M.; Pocock, S.J.; Gøtzsche, P.C.; Vandenbroucke, J.P.; STROBE Initiative. The Strengthening the Reporting of Observational Studies in Epidemiology (STROBE) statement: Guidelines for reporting observational studies. Lancet 2007, 370, 1453–1457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vial, C.; Martinez-Valdebenito, C.; Rios, S.; Martinez, J.; Vial, P.A.; Ferres, M.; Rivera, J.C.; Perez, R.; Valdivieso, F. Molecular method for the detection of Andes hantavirus infection: Validation for clinical diagnostics. Diagn. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2016, 84, 36–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrés, M.; Martínez-Valdebenito, C.; Henriquez, C.; Marco, C.; Angulo, J.; Barrera, A.; Palma, C.; Barriga Pinto, G.; Cuiza, A.; Ferreira, L.; et al. Viral shedding and viraemia of Andes virus during acute hantavirus infection: A prospective study. Lancet Infect Dis. 2024, 24, 775–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- FDA. Clinical Trials: Guidance for Industry and Food and Drug Administration Staff; FDA: Silver Spring, MD, USA, 2016. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/regulatory-information/search-fda-guidance-documents/collection-race-and-ethnicity-data-clinical-trials-and-clinical-studies-fda-regulated-medical (accessed on 26 June 2025).
- Tudor-Locke, C.; Bassett, D.R., Jr. How many steps/day are enough? Preliminary pedometer indices for public health. Sports Med. 2004, 34, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Organization. Obesity: Preventing and managing the global epidemic. In Report of a WHO Consultation; WHO Technical Report Series 894; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- World Health Organization. WHO Child Growth Standards: Length/Height-for-Age, Weight-for-Age, Weight-for-Length, Weight-for-Height and Body Mass Index-for-Age: Methods and Development; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2006.
- Weiss, S.L.; Peters, M.J.; Alhazzani, W.; Agus, M.S.D.; Flori, H.R.; Inwald, D.P.; Nadel, S.; Schlapbach, L.J.; Tasker, R.C.; Argent, A.C.; et al. Surviving Sepsis Campaign International Guidelines for the Management of Septic Shock and Sepsis-Associated Organ Dysfunction in Children. Intensive Care Med. 2020, 46 (Suppl. 1), 10–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sigfrid, L.; Drake, T.M.; Pauley, E.; Jesudason, E.C.; Olliaro, P.; Lim, W.S.; Gillesen, A.; Berry, C.; Lowe, D.J.; McPeake, J.; et al. Long COVID in adults discharged from UK hospitals after COVID-19: A prospective, multicentre cohort study using the ISARIC WHO Clinical Characterisation Protocol. Lancet Reg. Health Eur. 2021, 8, 100186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ministerio de Salud, Departamento de Epidemiología. Boletín Epidemiológico: Hantavirus, Semana Epidemiológica 23, año 2025; MINSAL: Santiago, Chile, 2025. Available online: https://epi.minsal.cl/hantavirus-situacion-epidemiologica/ (accessed on 24 June 2025).
- Smith, M.P.; Sharpe, H.; Damant, R.W.; Ferrara, G.; Lim, R.K.; Stickland, M.K.; Lam, G.Y. Factors associated with phenotypes of dyspnea in post-COVID-19 condition: A cross-sectional study. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 13387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marjenberg, Z.; Leng, S.; Tascini, C.; Garg, M.; Misso, K.; El Guerche Seblain, C.; Shaikh, N. Risk of long COVID main symptoms after SARS-CoV-2 infection: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 15332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herridge, M.S.; Cheung, A.M.; Tansey, C.M.; Matte-Martyn, A.; Diaz-Granados, N.; Al-Saidi, F.; Cooper, A.B.; Guest, C.B.; Mazer, C.D.; Mehta, S.; et al. One-year outcomes in survivors of the acute respiratory distress syndrome. N Engl. J. Med. 2003, 348, 683–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valenzuela, G.; Alarcón-Andrade, G.; Schulze-Schiapacasse, C.; Rodríguez, R.; García-Salum, T.; Pardo-Roa, C.; Levican, J.; Serrano, E.; Avendaño, M.J.; Gutiérrez, M.; et al. Short-term complications and post-acute sequelae in hospitalized paediatric patients with COVID-19 and obesity: A multicenter cohort study. Pediatr. Obes. 2023, 18, e12980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Fan, E.; Cheek, F.; Chlan, L.; Gosselink, R.; Hart, N.; Denehy, L.; Herridge, M.S.; Hopkins, R.O.; Hough, C.L.; Kress, J.P.; et al. An official American Thoracic Society Clinical Practice guideline: The diagnosis of intensive care unit–acquired weakness in adults. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2014, 190, 1437–1446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herridge, M.S.; Azoulay, É. Outcomes after Critical Illness. N Engl. J. Med. 2023, 388, 913–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeon, J.J.; Kim, Y.H.; Kang, H.; Ha, M.C.; Jung, S.W.; Son, H.; Kim, M.H.; Lee, W.S.; Lee, S. Global epidemiology of telogen effluvium after the COVID-19 pandemic: A systematic review and modeling study. JAAD Int. 2024, 18, 24–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Rybak, L.P.; Ramkumar, V. Ototoxicity. Kidney Int. 2007, 72, 931–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, D.; Liu, H.; Qi, W.; Jiang, H.; Li, Y.; Wu, X.; Sun, H.; Gross, K.; Salvi, R. Ototoxic effects and mechanisms of loop diuretics. J. Otol. 2016, 11, 145–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Porter, L.L.; Simons, K.S.; Corsten, S.; Westerhof, B.; Rettig, T.C.D.; Ewalds, E.; Janssen, I.; Jacobs, C.; van Santen, S.; Slooter, A.J.C.; et al. Changes in quality of life 1 year after intensive care: A multicenter prospective cohort of ICU survivors. Crit. Care 2024, 28, 255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kapfhammer, H.P.; Rothenhäusler, H.B.; Krauseneck, T.; Stoll, C.; Schelling, G. Posttraumatic stress disorder and health-related quality of life in long-term survivors of acute respiratory distress syndrome. Am. J. Psychiatry 2004, 161, 45–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Myhren, H.; Ekeberg, Ø.; Stokland, O. Health-related quality of life and return to work after critical illness in general intensive care unit patients: A 1-year follow-up study. Crit. Care Med. 2010, 38, 1554–1561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Variable | Overall (n = 21) | ECMO, n (%) (n = 11) | No ECMO, n (%) (n = 10) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Demographic features | |||
| Age, years, median (IQR) | 30.2 (13.2–38.4) | 31.3 (25.1–38.4) | 20.7 (11.5–45.8) |
| Male, n (%) | 11 (52.4) | 5 (45.5) | 6 (60.0) |
| Hispanic, n (%) | 18 (85.7) | 10 (90.9) | 8 (80.0) |
| Comorbidities (e.g., obesity, asthma), n (%) a | 5 (23.8) | 3 (27.3) | 2 (20.0) |
| Malnutrition by excess, n (%) b | 12 (57.1) | 7 (63.6) | 5 (50.0) |
| Smoking history, n (%) | 7 (33.3) | 6 (54.1) | 1 (10.0) |
| Sedentary lifestyle, n (%) c | 7 (33.3) | 4 (36.4) | 3 (30.0) |
| Acute clinical course | |||
| ICU admission, n (%) | 21 (100.0) | 11 (100.0) | 10 (100.0) |
| Invasive MV, n (%) | 16 (76.2) | 11 (100.0) | 5 (50.0) |
| VAD, n (%) | 15 (71.4) | 11 (100.0) | 5 (50.0) |
| ANDV immune plasma infusion, n (%) | 17 (81.1) | 11 (100.0) | 6 (60.0) |
Severity, n (%) d
| 4 (19.0) 17 (81.0) | 0 (0) 11 (100.0) | 4 (40.0) 6 (60.0) |
| BMI reduction, median (IQR) | 2.3 (3.1–3.9) | 3.6 (3.0–4.1) | 2.3 (2.1–3.4) |
| Length of stay, days | 16 (13.0–27.0) | 27 (22.5–32.5) | 13 (9.3–15.5) |
| Referral at discharge | |||
| General practitioner/pediatrician, n (%) | 14 (66.7) | 7 (63.6) | 7 (70.0) |
| Physical therapy, n (%) | 11 (52.4) | 8 (72.7) | 3 (30.0) |
| Respiratory therapy, n (%) | 5 (23.8) | 4 (36.4) | 1 (10.0) |
| Dietetics, n (%) | 5 (23.8) | 4 (36.4) | 1 (10.0) |
| Mental health services, n (%) | 4 (19.0) | 3 (27.3) | 0 (0) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Valenzuela, G.; Barahona, K.; Rojas, C.; Barrera, A.; Henríquez, C.; Martínez-Valdebenito, C.; Potin, M.; Bedregal, P.; Ferrés, M. Beyond ECMO Survival: Long-Term Symptom Burden and Quality-of-Life Impairment in Hantavirus Cardiopulmonary Syndrome Survivors. Viruses 2025, 17, 1241. https://doi.org/10.3390/v17091241
Valenzuela G, Barahona K, Rojas C, Barrera A, Henríquez C, Martínez-Valdebenito C, Potin M, Bedregal P, Ferrés M. Beyond ECMO Survival: Long-Term Symptom Burden and Quality-of-Life Impairment in Hantavirus Cardiopulmonary Syndrome Survivors. Viruses. 2025; 17(9):1241. https://doi.org/10.3390/v17091241
Chicago/Turabian StyleValenzuela, Gonzalo, Katherine Barahona, Camila Rojas, Aldo Barrera, Carolina Henríquez, Constanza Martínez-Valdebenito, Marcela Potin, Paula Bedregal, and Marcela Ferrés. 2025. "Beyond ECMO Survival: Long-Term Symptom Burden and Quality-of-Life Impairment in Hantavirus Cardiopulmonary Syndrome Survivors" Viruses 17, no. 9: 1241. https://doi.org/10.3390/v17091241
APA StyleValenzuela, G., Barahona, K., Rojas, C., Barrera, A., Henríquez, C., Martínez-Valdebenito, C., Potin, M., Bedregal, P., & Ferrés, M. (2025). Beyond ECMO Survival: Long-Term Symptom Burden and Quality-of-Life Impairment in Hantavirus Cardiopulmonary Syndrome Survivors. Viruses, 17(9), 1241. https://doi.org/10.3390/v17091241






