Visual and Super-Sensitive Detection of Maize Chlorotic Mottle Virus by Dot-ELISA and Au Nanoparticle-Based Immunochromatographic Test Strip
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Virus Sources, Virion Purification
2.2. Production and Characterization of Anti-MCMV mAbs
2.3. Pretreatment of Maize Leaf Samples
2.4. Development of Dot-ELISA for the Detection of MCMV
2.5. Preparation of AuNP-mAb Conjugate
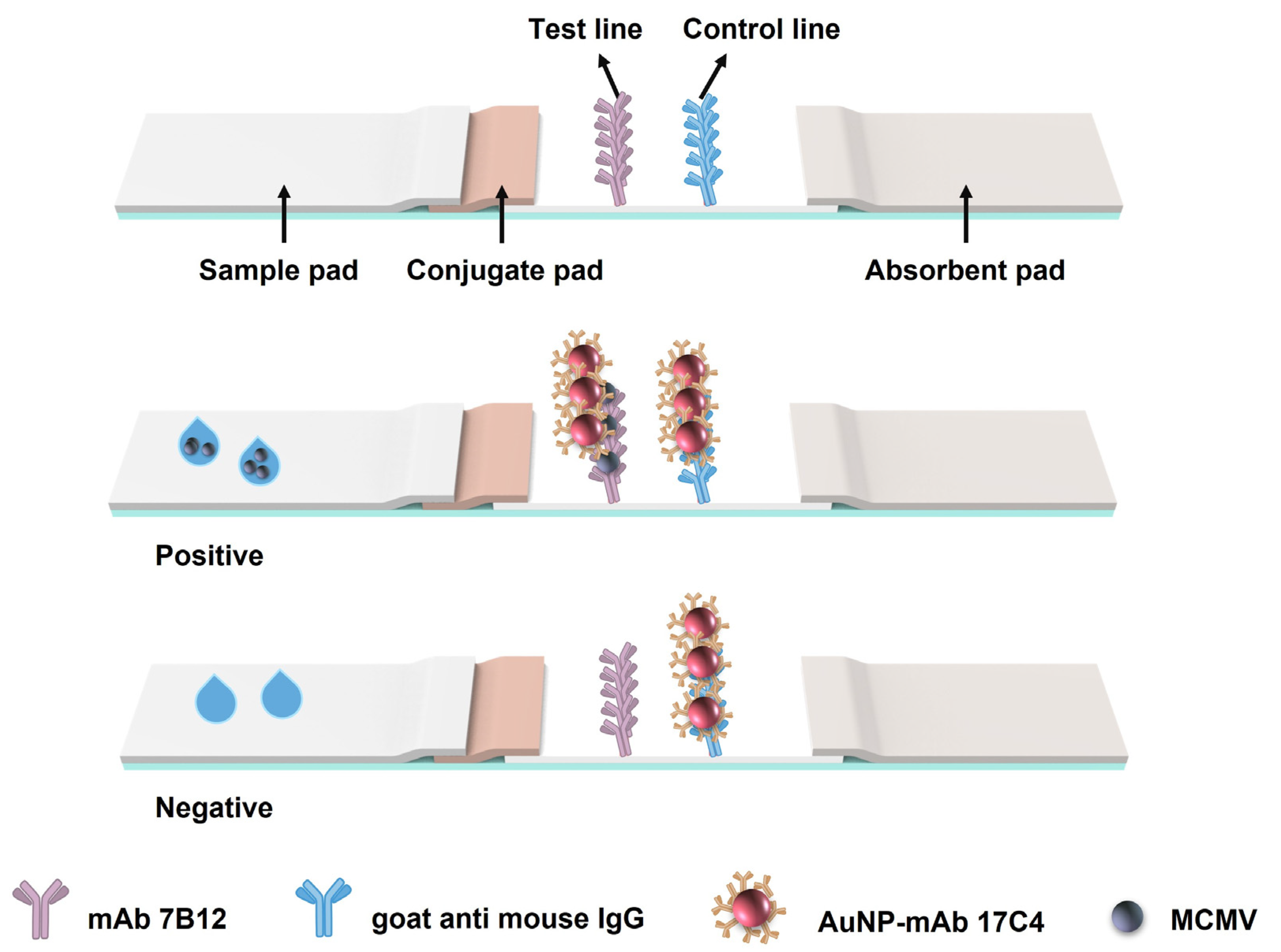
2.6. Fabrication and Principle of the AuNP-ICTS
2.7. Procedure and Characteristics of the AuNP-ICTS for MCMV Detection
2.8. Actual Sample Detection by Dot-ELISA, AuNP-ICTS, and RT-PCR
3. Results
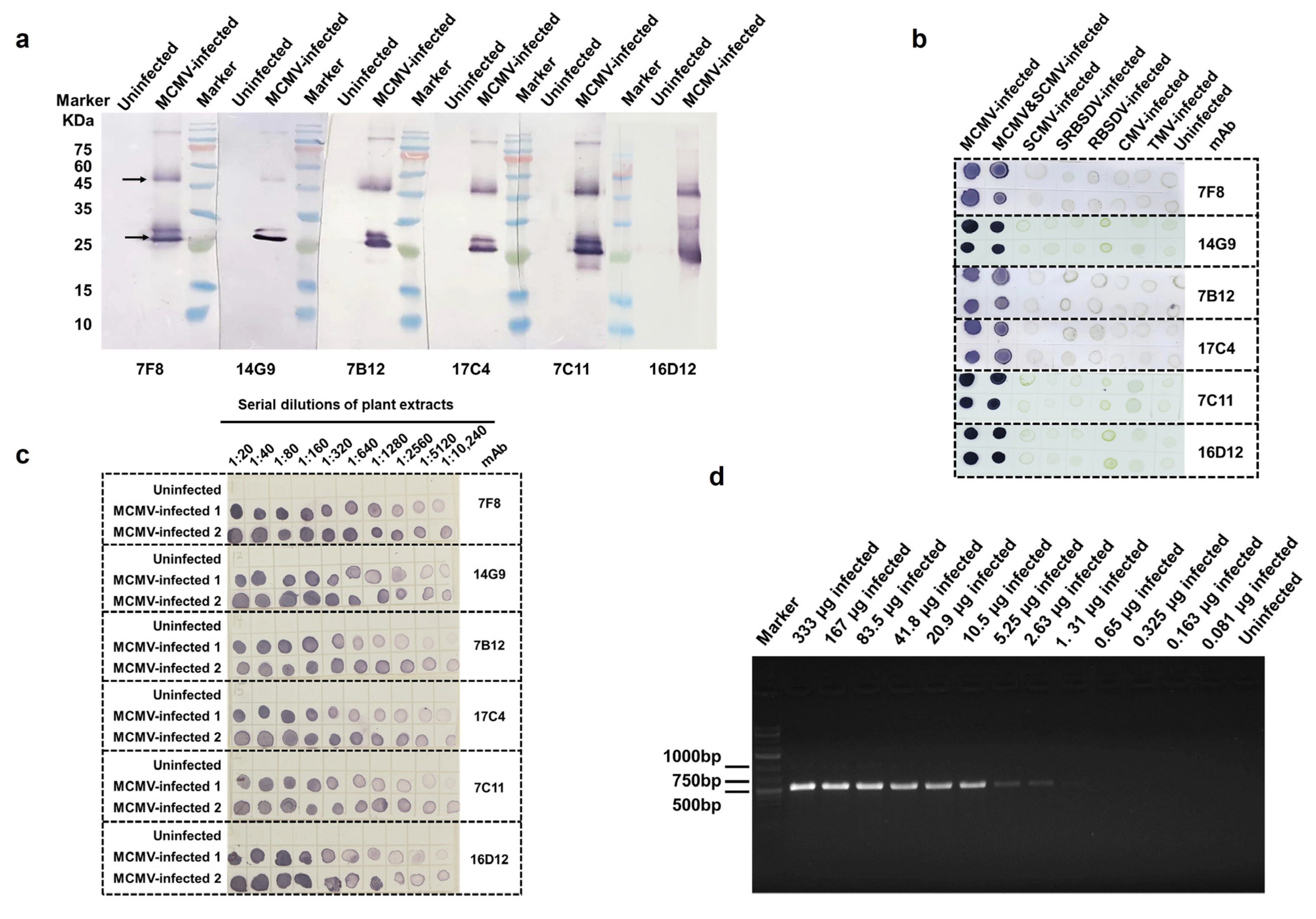
3.1. Preparations of mAbs against MCMV
3.2. Characterization of Six mAbs and MCMV Detection Using Dot-ELISA
3.3. Performance of AuNP-ICTS for MCMV Detection
3.4. Detection Results of Actual Samples by Dot-ELISA, AuNP-ICTS, and RT-PCR
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Castillo, J.; Hebert, T.T. A new virus disease of maize in Peru. Fitopatologia 1974, 9, 79–84. [Google Scholar]
- Scheets, K. Analysis of gene functions in Maize chlorotic mottle virus. Virus Res. 2016, 222, 71–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Redinbaugh, M.G.; Stewart, L.R. Maize Lethal Necrosis: An Emerging, Synergistic Viral Disease. Annu. Rev. Virol. 2018, 5, 301–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kannan, M.; Ismail, I.; Bunawan, H. Maize Dwarf Mosaic Virus: From Genome to Disease Management. Viruses 2018, 10, 492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stewart, L.R.; Willie, K.; Wijeratne, S.; Redinbaugh, M.G.; Massawe, D.; Niblett, C.L.; Kiggundu, A.; Asiimwe, T. Johnsongrass mosaic virus Contributes to Maize Lethal Necrosis in East Africa. Plant Dis. 2017, 101, 1455–1462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiao, Z.; Tian, Y.; Wang, J.; Ismail, R.G.; Bondok, A.; Fan, Z. Advances in research on maize lethal necrosis, a devastating viral disease. Phytopathol. Res. 2022, 4, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fentahun, M.; Feyissa, T.; Abraham, A.; Kwak, H.R. Detection and characterization of Maize chlorotic mottle virus and Sugarcane mosaic virus associated with maize lethal necrosis disease in Ethiopia: An emerging threat to maize production in the region. Eur. J. Plant Pathol. 2017, 149, 1011–1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Zhang, C.; Wang, C.; Qian, Y.; Li, Z.; Hong, J.; Zhou, X. Further characterization of Maize chlorotic mottle virus and its synergistic interaction with Sugarcane mosaic virus in maize. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 39960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, R.A.C.; Vazquez-Iglesias, I.; Hajizadeh, M.; McGreig, S.; Fox, A.; Gibbs, A.J. Phylogenetics and evolution of wheat streak mosaic virus: Its global origin and the source of the Australian epidemic. Plant Pathol. 2022, 71, 1660–1673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awata, L.A.O.; Ifie, B.E.; Tongoona, P.; Danquah, E.; Jumbo, M.B.; Gowda, M.; Marchelo-D’ragga, P.W.; Sitonik, C.; Suresh, L.M. Maize lethal necrosis and the molecular basis of variability in concentrations of the causal viruses in co-infected maize plant. J. Gen. Mol. Virol. 2019, 9, 1–19. [Google Scholar]
- Makone, S.M.; Menge, D.; Basweti, E. Impact of Maize Lethal Necrosis Disease on Maize Yield: A Case of Kisii, Kenya. Int. J. Agr. Exten. 2014, 2, 211–218. [Google Scholar]
- Gordon, D.T.; Bradfute, O.E.; Gingery, R.E.; Nault, L.R.; Uyemoto, J.K. Maize chlorotic mottle virus. In CMI/AAB Description of Plant Viruses; University of Hawaii: Honolulu, HI, USA, 1981. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, L.; Zhang, J.; Wang, Q.; Meng, C.; Hong, J.; Zhou, X. Characterization of Maize Chlorotic Mottle Virus Associated with Maize Lethal Necrosis Disease in China. J. Phytopathol. 2011, 159, 191–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, P.; Qin, Y.; Fan, Z.; Zhou, T.; Guo, S.; Li, Z. Assessment of potential economic loss of maize industry in China caused by maize chlorotic mottle virus using @RISK software. Acta Phy. Sin. 2022, 49, 1377–1382. [Google Scholar]
- Nutter, R.C.; Scheets, K.; Panganiban, L.C.; Lommel, S.A. The complete nucleotide sequence of the maize chlorotic mottle virus genome. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989, 17, 3163–3177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiao, Z.; Tian, Y.; Cao, Y.; Wang, J.; Zhan, B.; Zhao, Z.; Sun, B.; Guo, C.; Ma, W.; Liao, Z.; et al. A novel pathogenicity determinant hijacks maize catalase 1 to enhance viral multiplication and infection. New Phytol. 2021, 230, 1126–1141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.X.; Wang, Q.; Liu, H.; Qian, Y.J.; Xie, Y.; Zhou, X.P. Monoclonal antibody-based serological methods for maize chlorotic mottle virus detection in China. J. Zhejiang Univ.-Sci. B (Biomed. Biotechnol.) 2013, 14, 555–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimani, E.N.; Kiarie, S.M.; Micheni, C.; Muriki, L.G.; Miano, D.W.; Macharia, I.; Munkvold, G.P.; Muiru, W.M.; Prasanna, B.M.; Wangai, A. Maize Seed Contamination and Seed Transmission of Maize Chlorotic Mottle Virus in Kenya. Plant Health Prog. 2021, 22, 496–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, H.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Chen, H.; Gao, B.; Zhu, S. Detection and identification of Maize chlorotic mottle virus from imported maize seeds. Acta Phy. Sin. 2010, 40, 426–429. [Google Scholar]
- Kiarie, S.; Nyasani, J.O.; Gohole, L.S.; Maniania, N.K.; Subramanian, S. Impact of Fungal Endophyte Colonization of Maize (Zea mays L.) on Induced Resistance to Thrips- and Aphid-Transmitted Viruses. Plants 2020, 9, 416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernardo, P.; Frey, T.S.; Barriball, K.; Paul, P.A.; Willie, K.; Mezzalama, M.; Kimani, E.; Mugambi, C.; Wangai, A.; Prasanna, B.M.; et al. Detection of Diverse Maize Chlorotic Mottle Virus Isolates in Maize Seed. Plant Dis. 2021, 105, 1596–1601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhao, W.; Li, M.; Chen, H.; Zhu, S.; Fan, Z. Real-time TaqMan RT-PCR for detection of maize chlorotic mottle virus in maize seeds. J. Virol. Methods 2011, 171, 292–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiao, Y.; Jiang, J.; An, M.; Xia, Z.; Wu, Y. Recombinase polymerase amplification assay for rapid detection of maize chlorotic mottle virus in maize. Arch. Virol. 2019, 164, 2581–2584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Xia, X.; Yang, C.; Huang, J. Colorimetric detection of Maize chlorotic mottle virus by reverse transcription loop-mediated isothermal amplification (RT-LAMP) with hydroxynapthol blue dye. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 73–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Jiao, Z.; Liu, D.; Liu, X.; Xia, Z.; Deng, C.; Zhou, T.; Fan, Z. One-step reverse transcription loop-mediated isothermal amplification for the detection of Maize chlorotic mottle virus in maize. J. Virol. Methods 2017, 240, 49–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adams, I.P.; Miano, D.W.; Kinyua, Z.M.; Wangai, A.; Kimani, E.; Phiri, N.; Reeder, R.; Harju, V.; Glover, R.; Hany, U.; et al. Use of next-generation sequencing for the identification and characterization of Maize chlorotic mottle virus and Sugarcane mosaic virus causing maize lethal necrosis in Kenya. Plant Pathol. 2013, 62, 741–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, X.; Ma, W.; Jiao, Z.; Tian, Y.; Ismail, R.G.; Zhou, T.; Fan, Z. Reverse transcription-recombinase-aided amplification and CRISPR/Cas12a-based visual detection of maize chlorotic mottle virus. Phytopathol. Res. 2022, 4, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bai, F.; Bu, T.; Li, R.; Zhao, S.; He, K.; Li, M.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, L.; Wang, Y.; et al. Rose petals-like Bi semimetal embedded on the zeolitic imidazolate frameworks based-immunochromatographic strip to sensitively detect acetamiprid. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 423, 127202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, F.; Bu, T.; Zhao, S.; He, K.; Zhang, H.; Li, R.; Li, M.; Wang, Y.; Wang, L. Golf-shaped Bi2Se3 microparticles based-immunochromatographic strip for ultrasensitive detection of Acetamiprid. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 433, 128810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ling, S.; Dong, M.; Xu, Y.; Xu, A.; Lin, J.; Lin, M.; Zhao, Q.; Wang, S. Development of sensitive and portable immunosensors based on signal amplification probes for monitoring the mercury (II) ions. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2022, 217, 114676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Zhan, L.; Qin, Z.; Sackrison, J.; Bischof, J.C. Ultrasensitive and Highly Specific Lateral Flow Assays for Point-of-Care Diagnosis. ACS Nano 2021, 15, 3593–3611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Liu, M.; Wang, Z.; Li, S.; Deng, Y.; He, N. Point-of-care diagnostics for infectious diseases: From methods to devices. Nano Today 2021, 37, 101092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, C.; Wang, Y.; Liu, Z.; Bai, M.; Wang, J.; Wang, Y. Nanobody-based immunochromatographic biosensor for colorimetric and photothermal dual-mode detection of foodborne pathogens. Sens. Actuat. B-Chem. 2022, 369, 132371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, D.Q.; Chen, R.; Wang, Y.Q.; Hong, J.; Zhou, X.P.; Wu, J.X. Development of a colloidal gold-based immunochromatographic strip for rapid detection of Rice stripe virus. J. Zhejiang Univ.-Sci. B (Biomed. Biotechnol.) 2019, 20, 343–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Gao, Y.-L.; He, W.-Q.; Wang, Y.-Q.; Qian, Y.-J.; Zhou, X.-P.; Wu, J. Monoclonal antibody-based serological detection of potato virus M in potato plants and tubers. J. Integr. Agr. 2020, 19, 1283–1291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, W.-Q.; Wu, J.-Y.; Ren, Y.-Y.; Zhou, X.-P.; Zhang, S.-B.; Qian, Y.-J.; Li, F.-F.; Wu, J.-X. Highly sensitive serological approaches for Pepino mosaic virus detection. J. Zhejiang Univ.-Sci. B (Biomed. Biotechnol.) 2020, 21, 811–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Yu, C.; Yang, C.; Zhou, X. Monoclonal Antibodies against the Recombinant Nucleocapsid Protein of Tomato spotted wilt virus and its Application in Virus Detection. J. Phytopathol. 2009, 157, 344–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Chen, R.; Zhou, X.; Wu, J. Monoclonal Antibody-Based Serological Detection Methods for Wheat Dwarf Virus. Virol. Sin. 2018, 33, 173–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.-Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zhou, X.-P.; Qian, Y.-J. Three sensitive and reliable serological assays for detection of potato virus A in potato plants. J. Integr. Agr. 2021, 20, 2966–2975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, H.; Xie, Y.; Zhou, X.; Qian, Y.; Wu, J. Monoclonal antibody-based serological methods for detection of Cucumber green mottle mosaic virus. Virol. J. 2011, 8, 228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bu, T.; Huang, Q.; Yan, L.; Huang, L.; Zhang, M.; Yang, Q.; Yang, B.; Wang, J.; Zhang, D. Ultra technically-simple and sensitive detection for Salmonella Enteritidis by immunochromatographic assay based on gold growth. Food Control 2018, 84, 536–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.-X.; Lei, X.-L.; Ye, L.-Y.; Song, S.-S.; Liu, L.-L.; Xu, L.-G.; Xu, C.-L.; Kuang, H. Gold-based paper sensor for sensitive detection of procalcitonin in clinical samples. Chin. J. Anal. Chem. 2022, 50, 100062. [Google Scholar]
- Razo, S.C.; Panferov, V.G.; Safenkova, I.V.; Varitsev, Y.A.; Zherdev, A.V.; Dzantiev, B.B. Double-enhanced lateral flow immunoassay for potato virus X based on a combination of magnetic and gold nanoparticles. Anal. Chim. Acta 2018, 1007, 50–60. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Parolo, C.; Sena-Torralba, A.; Bergua, J.F.; Calucho, E.; Fuentes-Chust, C.; Hu, L.; Rivas, L.; Alvarez-Diduk, R.; Nguyen, E.P.; Cinti, S.; et al. Tutorial: Design and fabrication of nanoparticle-based lateral-flow immunoassays. Nat. Protoc. 2020, 15, 3788–3816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Guo, L.; Guo, M.; Qi, D.; Zhou, X.; Li, F.; Wu, J. Three highly sensitive monoclonal antibody-based serological assays for the detection of tomato mottle mosaic virus. Phytopathol. Res. 2021, 3, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Chen, Z.; Hong, J.; Wang, X.; Zhou, C.; Zhou, X.; Wu, J. Monoclonal antibody-based serological methods for detecting Citrus tristeza virus in citrus groves. Virol. Sin. 2016, 31, 324–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, M.; Qi, D.; Dong, J.; Dong, S.; Yang, X.; Qian, Y.; Zhou, X.; Wu, J. Development of Dot-ELISA and Colloidal Gold Immunochromatographic Strip for Rapid and Super-Sensitive Detection of Plum Pox Virus in Apricot Trees. Viruses 2023, 15, 169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, J.; Ni, Y.; Liu, H.; Rao, L.; Zhou, Y.; Zhou, X. Development and use of three monoclonal antibodies for the detection of rice black-streaked dwarf virus in field plants and planthopper vectors. Virol. J. 2013, 10, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.; Song, X.-J.; Ni, Y.-Q.; Lu, L.-N.; Zhou, X.-P.; Wu, J.-X. Highly Sensitive and Specific Monoclonal Antibody-Based Serological Methods for Rice Ragged Stunt Virus Detection in Rice Plants and Rice Brown Planthopper Vectors. J. Integr. Agr. 2014, 13, 1943–1951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panferov, V.G.; Safenkova, I.V.; Zherdev, A.V.; Dzantiev, B.B. Post-assay growth of gold nanoparticles as a tool for highly sensitive lateral flow immunoassay. Application to the detection of potato virus X. Mikrochim. Acta 2018, 185, 506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivanov, A.V.; Shmyglya, I.V.; Zherdev, A.V.; Dzantiev, B.B.; Safenkova, I.V. The Challenge for Rapid Detection of High-Structured Circular RNA: Assay of Potato Spindle Tuber Viroid Based on Recombinase Polymerase Amplification and Lateral Flow Tests. Plants 2020, 9, 1369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez, E.; Ali, Z.; Islam, T.; Mahfouz, M. A CRISPR-based lateral flow assay for plant genotyping and pathogen diagnostics. Plant Biotechnol. J. 2022, 20, 2418–2429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lei, R.; Kuang, R.; Peng, X.; Jiao, Z.; Zhao, Z.; Cong, H.; Fan, Z.; Zhang, Y. Portable rapid detection of maize chlorotic mottle virus using RT-RAA/CRISPR-Cas12a based lateral flow assay. Front. Plant Sci. 2023, 14, 1088544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| mAbs | Isotypes | Ascites Titer | IgG Yield in Ascites (mg/mL) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 7F8 | IgG1, κ | 10−7 * | 7.18 |
| 14G9 | IgG1, κ | 10−7 | 5.36 |
| 7B12 | IgG1, κ | 10−7 | 3.98 |
| 17C4 | IgG1, κ | 10−7 | 5.09 |
| 7C11 | IgG1, κ | 10−7 | 4.74 |
| 16D12 | IgG2a, κ | 10−7 | 2.30 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, C.; Guo, M.; Dong, J.; Liu, L.; Zhou, X.; Wu, J. Visual and Super-Sensitive Detection of Maize Chlorotic Mottle Virus by Dot-ELISA and Au Nanoparticle-Based Immunochromatographic Test Strip. Viruses 2023, 15, 1607. https://doi.org/10.3390/v15071607
Zhang C, Guo M, Dong J, Liu L, Zhou X, Wu J. Visual and Super-Sensitive Detection of Maize Chlorotic Mottle Virus by Dot-ELISA and Au Nanoparticle-Based Immunochromatographic Test Strip. Viruses. 2023; 15(7):1607. https://doi.org/10.3390/v15071607
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Cui, Mengmeng Guo, Jinxi Dong, Li Liu, Xueping Zhou, and Jianxiang Wu. 2023. "Visual and Super-Sensitive Detection of Maize Chlorotic Mottle Virus by Dot-ELISA and Au Nanoparticle-Based Immunochromatographic Test Strip" Viruses 15, no. 7: 1607. https://doi.org/10.3390/v15071607
APA StyleZhang, C., Guo, M., Dong, J., Liu, L., Zhou, X., & Wu, J. (2023). Visual and Super-Sensitive Detection of Maize Chlorotic Mottle Virus by Dot-ELISA and Au Nanoparticle-Based Immunochromatographic Test Strip. Viruses, 15(7), 1607. https://doi.org/10.3390/v15071607







