Combination Antiretroviral Therapy and Immunophenotype of Feline Immunodeficiency Virus
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
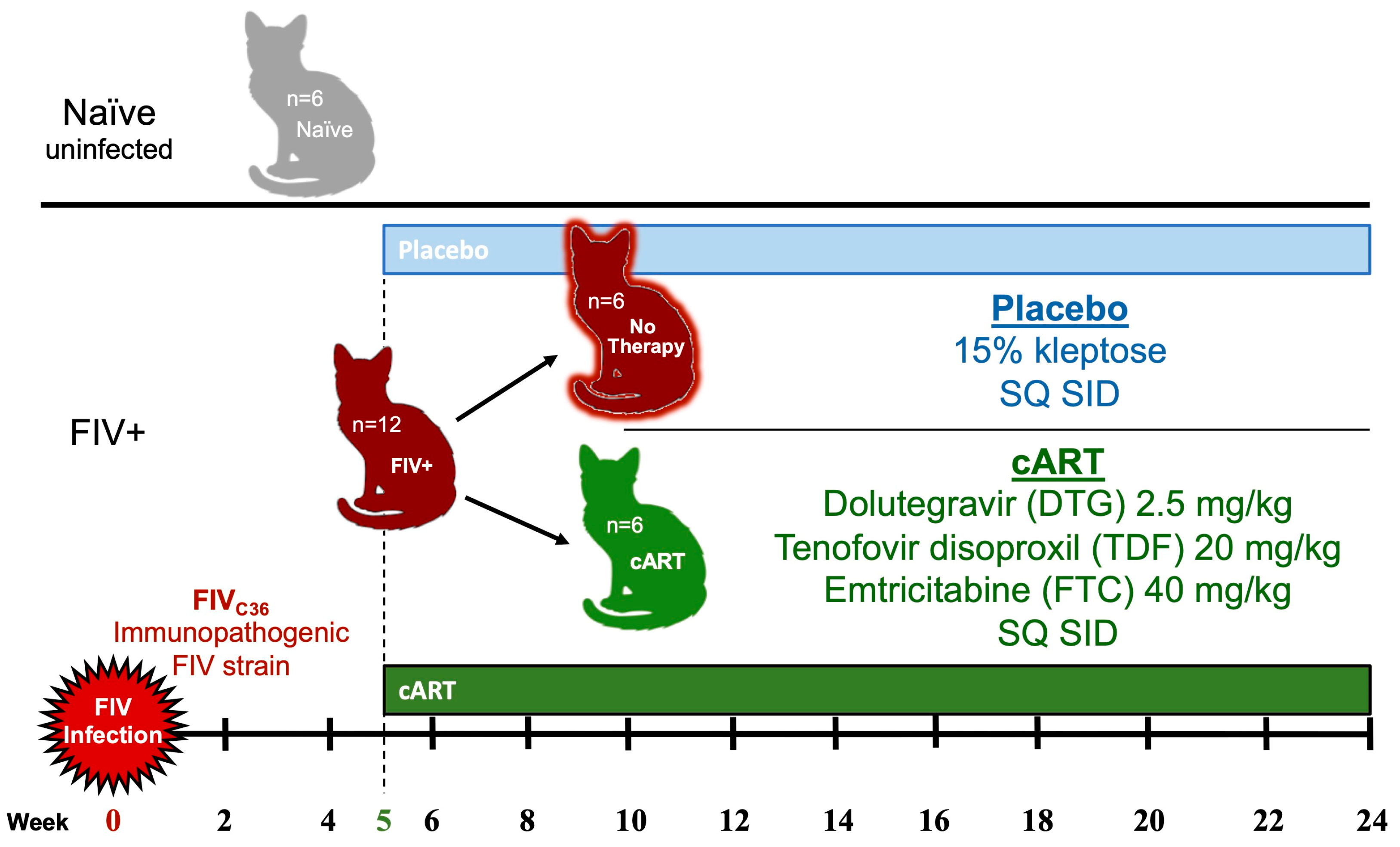
2.1. In Vivo Protocol
2.2. Blood and Saliva Collection
2.3. Viral RNA and Proviral DNA Extractions
2.4. Viral and Proviral Quantification
2.5. Flow Cytometry
2.6. Pharmacokinetics
2.7. Ethics Statement
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
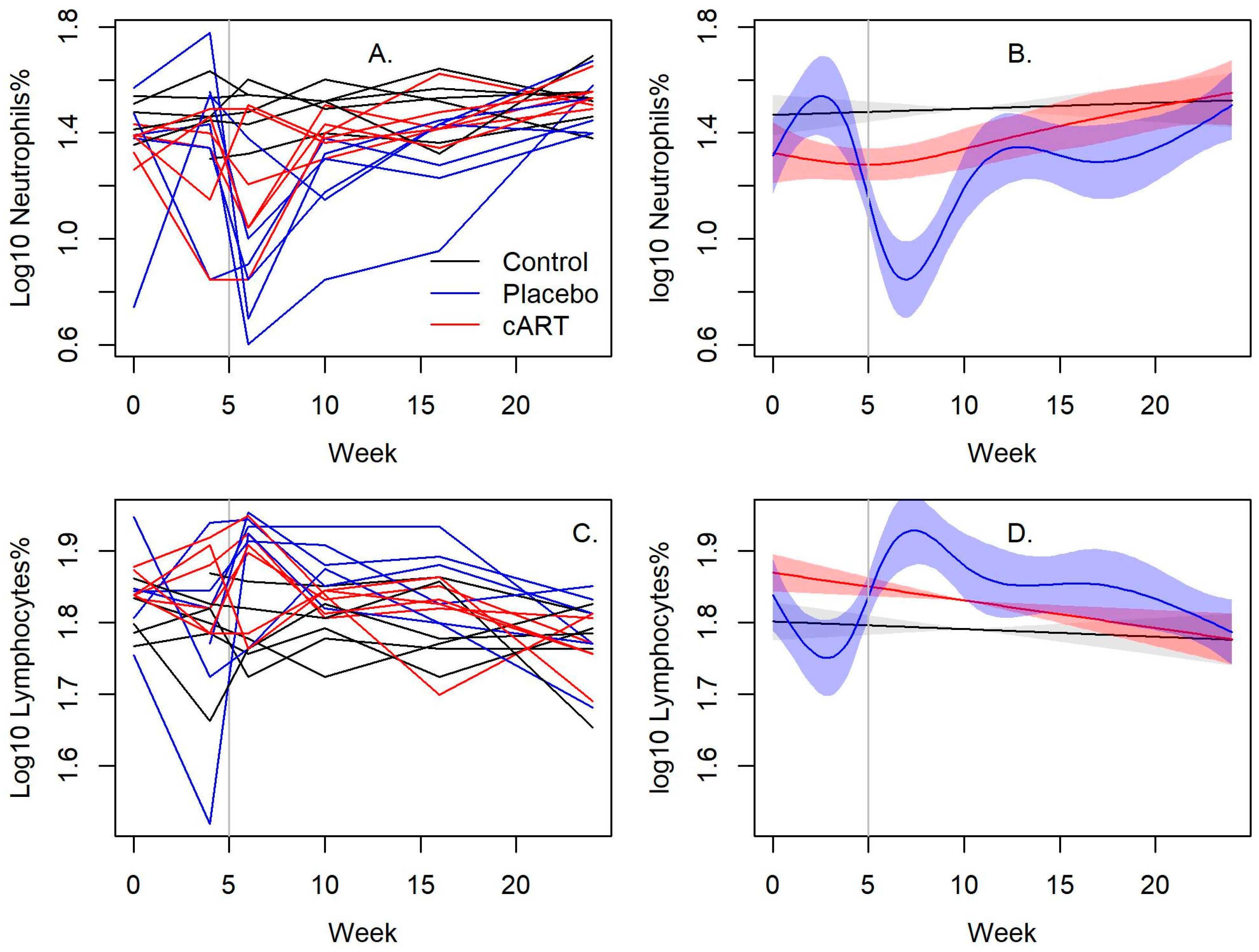
3.1. cART Improves the Hematologic Impact of FIV-C Infection
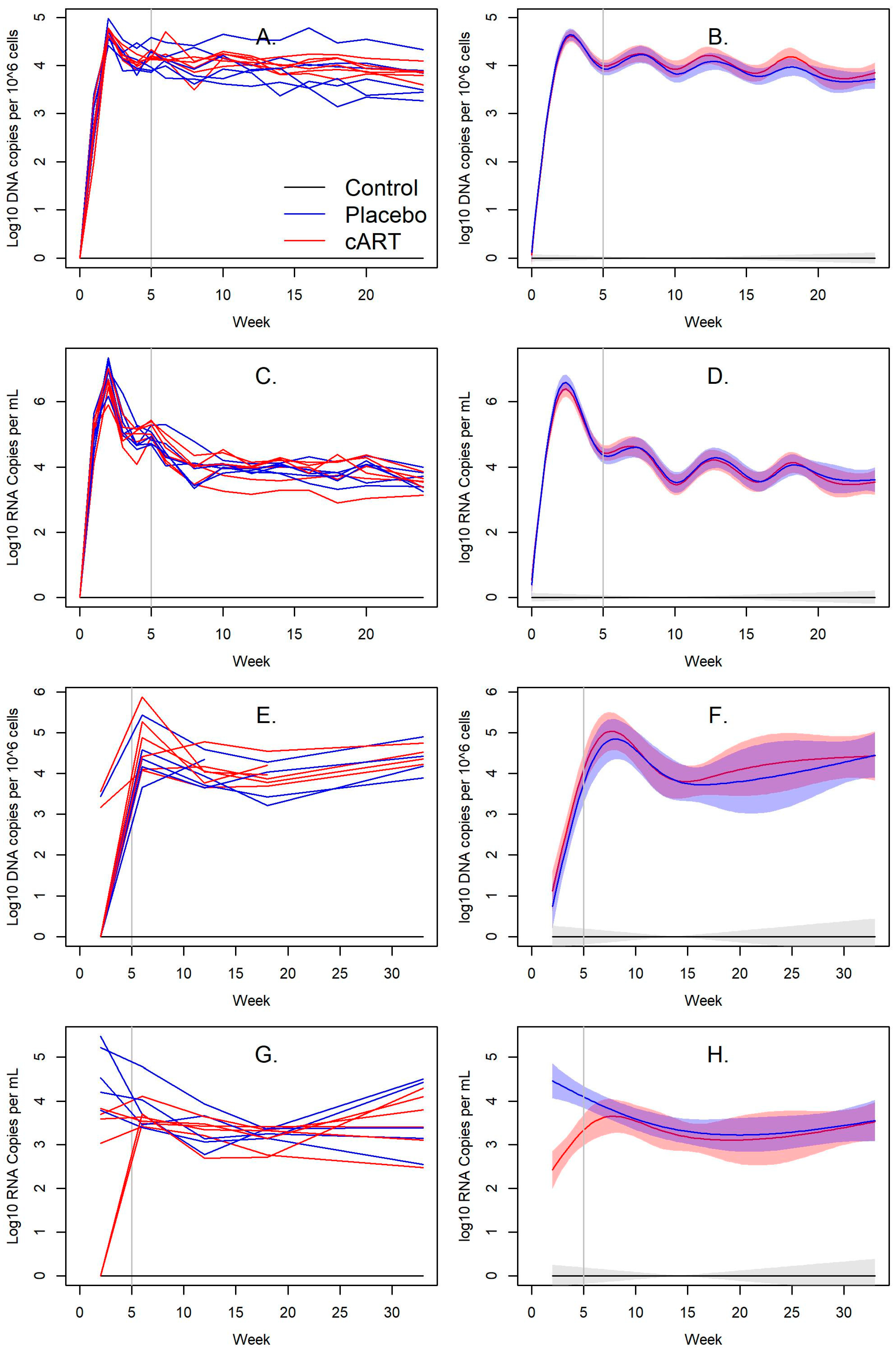
3.2. Impact of cART on FIV Viral and Proviral Loads
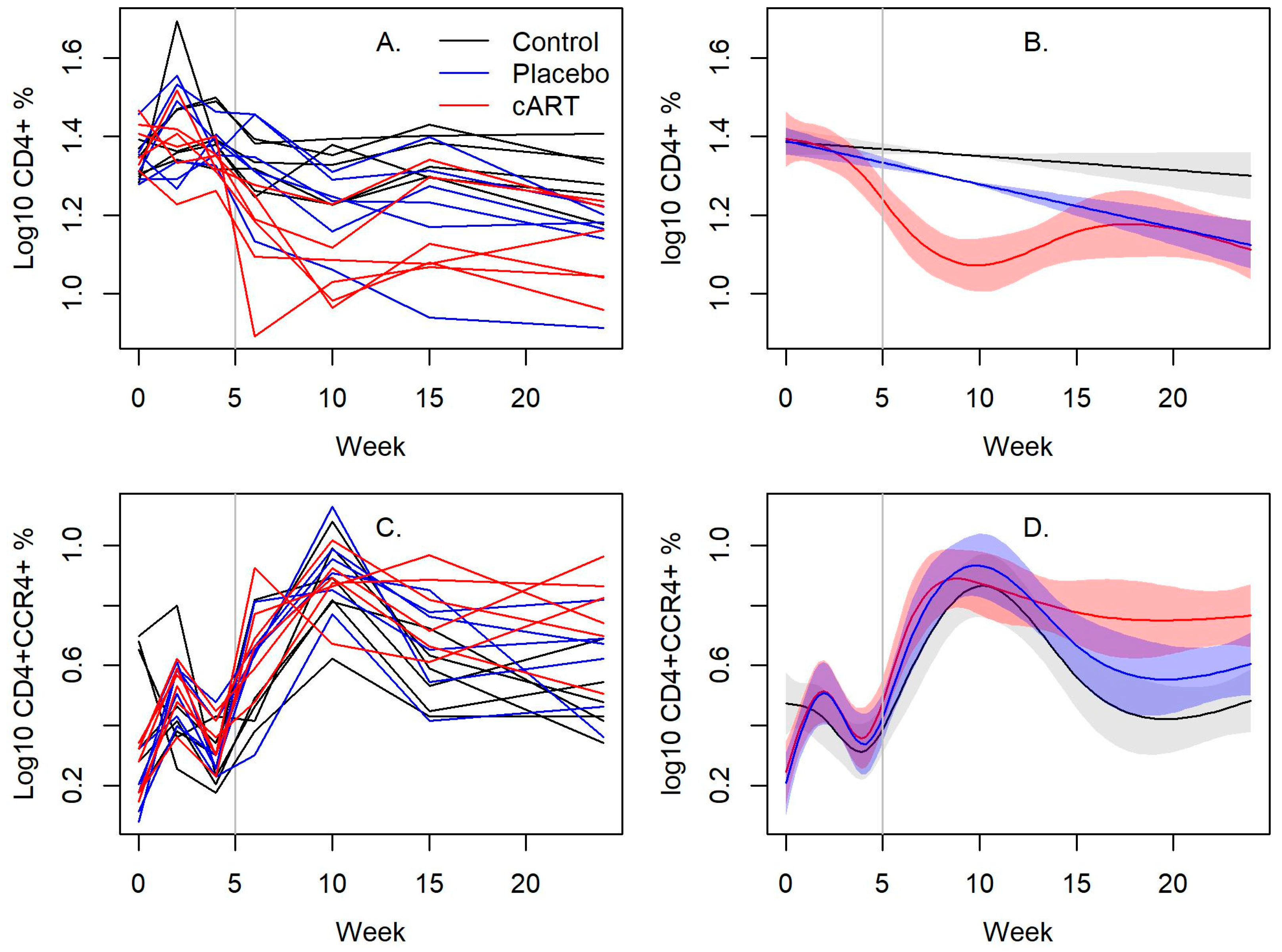
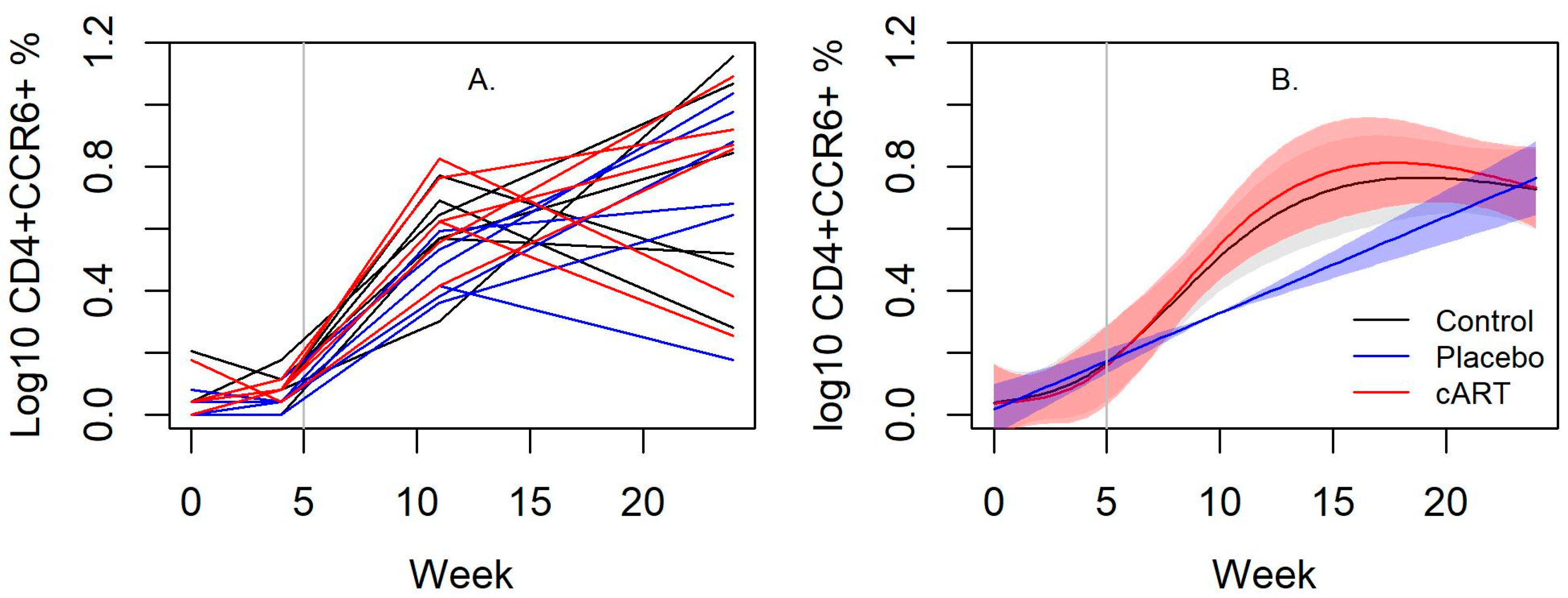
3.3. cART Impacts on Lineage and Activation Markers
3.4. Pharmacokinetics
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A. Clinical Impacts of FIV-C Infection
References
- Hartmann, K. Feline Immunodeficiency Virus Infection: An Overview. Vet. J. 1998, 155, 123–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hopper, C.; Sparkes, A.; Gruffydd-Jones, T.; Crispin, S.; Muir, P.; Harbour, D.; Stokes, C. Clinical and Laboratory Findings in Cats Infected with Feline Immunodeficiency Virus. Vet. Rec. 1989, 125, 341–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hart, S.W.; Nolte, I. Hemostatic Disorders in Feline Immunodeficiency Virus-Seropositive Cats. J. Vet. Intern. Med. 1994, 8, 355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujino, Y.; Liao, C.P.; Zhao, Y.S.; Pan, J.; Mathes, L.E.; Hayes, K.A.; Ohno, K.; Tsujimoto, H.; Roy-Burman, P. Identification of a Novel Common Proviral Integration Site, Flit-1, in Feline Leukemia Virus Induced Thymic Lymphoma. Virology 2009, 386, 16–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gleich, S.; Hartmann, K. Hematology and Serum Biochemistry of Feline Immunodeficiency Virus-Infected and Feline Leukemia Virus-Infected Cats. J. Vet. Intern. Med. 2009, 23, 552–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hartmann, K. Clinical Aspects of Feline Retroviruses: A Review. Viruses 2012, 4, 2684–2710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedersen, N.C.; Yamamoto, J.K.; Ishida, T.; Hansen, H. Feline Immunodeficiency Virus Infection. Vet. Immunol. Immunopathol. 1989, 21, 111–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beczkowski, P.M.; Litster, A.; Lin, T.L.; Mellor, D.J.; Willett, B.J.; Hosie, M.J. Contrasting Clinical Outcomes in Two Cohorts of Cats Naturally Infected with Feline Immunodeficiency Virus (FIV). Vet. Microbiol. 2015, 176, 50–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diehl, L.J.; Mathiason-Dubard, C.K.; O’Neil, L.L.; Obert, L.A.; Hoover, E.A. Induction of Accelerated Feline Immunodeficiency Virus Disease by Acute-Phase Virus Passage. J. Virol. 1995, 69, 6149–6157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obert, L.A.; Hoover, E.A. Feline Immunodeficiency Virus Clade C Mucosal Transmission and Disease Courses. AIDS Res. Hum. Retrovir. 2000, 16, 677–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Rozières, S.; Mathiason, C.K.; Rolston, M.R.; Chatterji, U.; Hoover, E.A.; Elder, J.H. Characterization of a Highly Pathogenic Molecular Clone of Feline Immunodeficiency Virus Clade C. J. Virol. 2004, 78, 8971–8982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, C.; Abdo, Z.; Ericsson, A.; Elder, J.; VandeWoude, S. Applications of the FIV Model to Study HIV Pathogenesis. Viruses 2018, 10, 206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balzarini, J.; Vahlenkamp, T.; Egberink, H.; Hartmann, K.; Witvrouw, M.; Pannecouque, C.; Casara, P.; Navé, J.F.; de Clercq, E. Antiretroviral Activities of Acyclic Nucleoside Phosphonates [9-(2-Phosphonylmethoxyethyl)Adenine, 9-(2-Phosphonylmethoxyethyl)Guanine, (R)-9-(2-Phosphonylmethoxypropyl)Adenine, and MDL 74,968] in Cell Cultures and Murine Sarcoma Virus-Infected Newborn NMRI Mice. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 1997, 41, 611–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vahlenkamp, T.W.; de Ronde, A.; Balzarini, J.; Naesens, L.; de Clercq, E.; van Eijk, M.J.T.; Horzinek, M.C.; Egberink, H.F. (R)-9-(2-Phosphonylmethoxypropyl)-2,6-Diaminopurine Is a Potent Inhibitor of Feline Immunodeficiency Virus Infection. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 1995, 39, 746–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stevenson, M.A.M.C.; McBroom, D.G. In Vitro Characterization of FIV-PPPR, a Pathogenic Molecular Clone of Feline Immunodeficiency Virus, and Two Drug-Resistant Pol Gene Mutants. Am. J. Vet. Res. 2001, 62, 588–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwartz, A.M.; McCrackin, M.A.; Schinazi, R.F.; Hill, P.B.; Vahlenkamp, T.W.; Tompkins, M.B.; Hartmann, K. Antiviral Efficacy of Nine Nucleoside Reverse Transcriptase Inhibitors against Feline Immunodeficiency Virus in Feline Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells. Am. J. Vet. Res. 2014, 75, 273–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, R.A.; Remington, K.M.; Lloyd, R.M.; Schinazi, R.F.; North, T.W. A Novel Met-to-Thr Mutation in the YMDD Motif of Reverse Transcriptase from Feline Immunodeficiency Virus Confers Resistance to Oxathiolane Nucleosides. J. Virol. 1997, 71, 2357–2362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, R.A.; Remington, K.M.; Preston, B.D.; Schinazi, R.F.; North, T.W. A Novel Point Mutation at Position 156 of Reverse Transcriptase from Feline Immunodeficiency Virus Confers Resistance to the Combination of (-)-Beta-2′,3′-Dideoxy-3′-Thiacytidine and 3′-Azido-3′-Deoxythymidine. J. Virol. 1998, 72, 2335–2340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osterholzer, D.A.; Goldman, M. Dolutegravir: A Next-Generation Integrase Inhibitor for Treatment of HIV Infection. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2014, 59, 265–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rathbun, R.C.; Lockhart, S.M.; Miller, M.M.; Liedtke, M.D. Dolutegravir, a Second-Generation Integrase Inhibitor for the Treatment of HIV-1 Infection. Ann. Pharmacother. 2014, 48, 395–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cahn, P.; Pozniak, A.L.; Mingrone, H.; Shuldyakov, A.; Brites, C.; Andrade-Villanueva, J.F.; Richmond, G.; Buendia, C.B.; Fourie, J.; Ramgopal, M.; et al. Dolutegravir versus Raltegravir in Antiretroviral-Experienced, Integrase-Inhibitor-Naive Adults with HIV: Week 48 Results from the Randomised, Double-Blind, Non-Inferiority SAILING Study. Lancet 2013, 382, 700–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCormack, P.L. Dolutegravir: A Review of Its Use in the Management of HIV-1 Infection in Adolescents and Adults. Drugs 2014, 74, 1241–1252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bekerman, E.; Hesselgesser, J.; Carr, B.; Nagel, M.; Hung, M.; Wang, A.; Stapleton, L.; von Gegerfelt, A.; Elyard, H.A.; Lifson, J.D.; et al. PD-1 Blockade and TLR7 Activation Lack Therapeutic Benefit in Chronic Simian Immunodeficiency Virus-Infected Macaques on Antiretroviral Therapy. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2019, 63, e01163-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mavigner, M.; Zanoni, M.; Tharp, G.K.; Habib, J.; Mattingly, C.R.; Lichterfeld, M.; Nega, M.T.; Vanderford, T.H.; Bosinger, S.E.; Chahroudi, A. Pharmacological Modulation of the Wnt/β-Catenin Pathway Inhibits Proliferation and Promotes Differentiation of Long-Lived Memory CD4+ T Cells in Antiretroviral. Am. Soc. Microbiol. 2020, 94, 1094–1113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strongin, Z.; Micci, L.; Fromentin, R.; Harper, J.; McBrien, J.; Ryan, E.; Shenvi, N.; Easley, K.; Chomont, N.; Silvestri, G.; et al. Virologic and Immunologic Features of Simian Immunodeficiency Virus Control Post-ART Interruption in Rhesus Macaques. J. Virol. 2020, 94, e00338-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoang, T.N.; Harper, J.L.; Pino, M.; Wang, H.; Micci, L.; King, C.T.; McGary, C.S.; McBrien, J.B.; Cervasi, B.; Silvestri, G.; et al. Bone Marrow-Derived CD4+ T Cells Are Depleted in Simian Immunodeficiency Virus-Infected Macaques and Contribute to the Size of the Replication-Competent Reservoir. J. Virol. 2019, 93, e01344-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mavigner, M.; Liao, L.E.; Brooks, A.D.; Ke, R.; Mattingly, C.; Schoof, N.; McBrien, J.; Carnathan, D.; Liang, S.; Vanderford, T.H.; et al. CD8 Lymphocyte Depletion Enhances the Latency Reversal Activity of the SMAC Mimetic AZD5582 in ART-Suppressed Simian Immunodeficiency Virus-Infected Rhesus Macaques. J. Virol. 2021, 95, e01429-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McBrien, J.B.; Wong, A.K.H.; White, E.; Carnathan, D.G.; Lee, J.H.; Safrit, J.T.; Vanderford, T.H.; Paiardini, M.; Chahroudi, A.; Silvestri, G. Combination of CD8β Depletion and Interleukin-15 Superagonist N-803 Induces Virus Reactivation in Simian-Human Immunodeficiency Virus-Infected, Long-Term ART-Treated Rhesus Macaques. J. Virol. 2020, 94, 755–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitney, J.B.; Hill, A.L.; Sanisetty, S.; Penaloza-Macmaster, P.; Liu, J.; Shetty, M.; Parenteau, L.; Cabral, C.; Shields, J.; Blackmore, S.; et al. Rapid Seeding of the Viral Reservoir Prior to SIV Viraemia in Rhesus Monkeys. Nature 2014, 512, 74–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beck, S.E.; Queen, S.E.; Metcalf Pate, K.A.; Mangus, L.M.; Abreu, C.M.; Gama, L.; Witwer, K.W.; Adams, R.J.; Zink, M.C.; Clements, J.E.; et al. An SIV/Macaque Model Targeted to Study HIV-Associated Neurocognitive Disorders. J. Neurovirol. 2018, 24, 204–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, N.A.; McBrien, J.B.; Carnathan, D.G.; Mavigner, M.; Mattingly, C.; White, E.R.; Viviano, F.; Bosinger, S.E.; Chahroudi, A.; Silvestri, G.; et al. Antibody-Mediated CD4 Depletion Induces Homeostatic CD4+ T Cell Proliferation without Detectable Virus Reactivation in Antiretroviral Therapy-Treated Simian Immunodeficiency Virus-Infected Macaques. J. Virol. 2018, 92, e01235-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savarino, A.; Pistello, M.; D’Ostilio, D.; Zabogli, E.; Taglia, F.; Mancini, F.; Ferro, S.; Matteucci, D.; de Luca, L.; Barreca, M.L.; et al. Human Immunodeficiency Virus Integrase Inhibitors Efficiently Suppress Feline Immunodeficiency Virus Replication In Vitro and Provide a Rationale to Redesign Antiretroviral Treatment for Feline AIDS. Retrovirology 2007, 4, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van der Meer, F.J.U.M.; Schuurman, N.M.P.; Balzarini, J.; Egberink, H.F. Comparative Evaluation of the Activity of Antivirals towards Feline Immunodeficiency Virus in Different Cell Culture Systems. Antivir. Res. 2007, 76, 198–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Vergote, D.; Pardo, C.; Noorbakhsh, F.; McArthur, J.C.; Hollenberg, M.D.; Overall, C.M.; Power, C. CXCR3 Activation by Lentivirus Infection Suppresses Neuronal Autophagy: Neuroprotective Effects of Antiretroviral Therapy. FASEB J. 2009, 23, 2928–2941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez, N.V.; Fontanals, A.; Castillo, V.; Gisbert, M.A.; Suraniti, A.; Mira, G.; Pisano, P.B. Evaluation of Different Antiretroviral Drug Protocols on Naturally Infected Feline Immunodeficiency Virus (FIV) Cats in the Late Phase of the Asymptomatic Stage of Infection. Viruses 2012, 4, 924–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- TerWee, J.A.; Carlson, J.K.; Sprague, W.S.; Sondgeroth, K.S.; Shropshire, S.B.; Troyer, J.L.; VandeWoude, S. Prevention of Immunodeficiency Virus Induced CD4+ T-Cell Depletion by Prior Infection with a Non-Pathogenic Virus. Virology 2008, 377, 63–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, C.; Powers, J.; Musselman, E.; Mackie, R.; Elder, J.; Vandewoude, S. Immunopathologic Effects of Prednisolone and Cyclosporine A on Feline Immunodeficiency Virus Replication and Persistence. Viruses 2019, 11, 805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, C.; Boegler, K.; Carver, S.; MacMillan, M.; Bielefeldt-Ohmann, H.; VandeWoude, S. Pathogenesis of Oral FIV Infection. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0185138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kao, Y.F.; Peake, B.; Madden, R.; Cowan, S.R.; Scimeca, R.C.; Thomas, J.E.; Reichard, M.V.; Ramachandran, A.; Miller, C.A. A Probe-Based Droplet Digital Polymerase Chain Reaction Assay for Early Detection of Feline Acute Cytauxzoonosis. Vet. Parasitol. 2021, 292, 109413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, J.; MacMillan, M.; Boegler, K.; Wood, C.; Elder, J.H.; VandeWoude, S. Pathogenicity and Rapid Growth Kinetics of Feline Immunodeficiency Virus Are Linked to 3′ Elements. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e24020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, C.; Emanuelli, M.; Fink, E.; Musselman, E.; Mackie, R.; Troyer, R.; Elder, J.; VandeWoude, S. FIV Vaccine with Receptor Epitopes Results in Neutralizing Antibodies but Does Not Confer Resistance to Challenge. NPJ Vaccines 2018, 3, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Del Fierro, G.M.; Meers, J.; Thomas, J.; Chadwick, B.; Park, H.S.; Robinson, W.F. Quantification of Lymphadenopathy in Experimentally Induced Feline Immunodeficiency Virus Infection in Domestic Cats. Vet. Immunol. Immunopathol. 1995, 46, 3–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strain, M.C.; Lada, S.M.; Luong, T.; Rought, S.E.; Gianella, S.; Terry, V.H.; Spina, C.A.; Woelk, C.H.; Richman, D.D. Highly Precise Measurement of HIV DNA by Droplet Digital PCR. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e55943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anderson, E.M.; Maldarelli, F. Quantification of HIV DNA Using Droplet Digital PCR Techniques. Curr. Protoc. Microbiol. 2018, 51, e62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levy, C.N.; Hughes, S.M.; Roychoudhury, P.; Reeves, D.B.; Amstuz, C.; Zhu, H.; Huang, M.L.; Wei, Y.; Bull, M.E.; Cassidy, N.A.J.; et al. A Highly Multiplexed Droplet Digital PCR Assay to Measure the Intact HIV-1 Proviral Reservoir. Cell Rep. Med. 2021, 2, 100243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunay, G.A.; Solomatina, A.; Kummer, S.; Hüfner, A.; Bialek, J.K.; Eberhard, J.M.; Tolosa, E.; Hauber, J.; Schulze zur Wiesch, J. Assessment of the HIV-1 Reservoir in CD4+ Regulatory T Cells by a Droplet Digital PCR Based Approach. Virus Res. 2017, 240, 107–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alteri, C.; Scutari, R.; Stingone, C.; Maffongelli, G.; Brugneti, M.; Falasca, F.; Martini, S.; Bertoli, A.; Turriziani, O.; Sarmati, L.; et al. Quantification of HIV-DNA and Residual Viremia in Patients Starting ART by Droplet Digital PCR: Their Dynamic Decay and Correlations with Immunological Parameters and Virological Success. J. Clin. Virol. 2019, 117, 61–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, S.C.; Laperriere, G.; Germain, H. Droplet Digital PCR versus QPCR for Gene Expression Analysis with Low Abundant Targets: From Variable Nonsense to Publication Quality Data. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 2409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hindson, C.M.; Chevillet, J.R.; Briggs, H.A.; Gallichotte, E.N.; Ruf, I.K.; Hindson, B.J.; Vessella, R.L.; Tewari, M. Absolute Quantification by Droplet Digital PCR versus Analog Real-Time PCR. Nat. Methods 2013, 10, 1003–1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Power, C. Neurologic Disease in Feline Immunodeficiency Virus Infection: Disease Mechanisms and Therapeutic Interventions for NeuroAIDS. J. Neurovirol. 2017, 24, 220–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffmann-Fezer, G.; Mortelbauer, W.; Hartmann, K.; Mysliwietz, J.; Thefeld, S.; Beer, B.; Thum, I.; Kraft, W. Comparison of T-Cell Subpopulations in Cats Naturally Infected with Feline Leukaemia Virus or Feline Immunodeficiency Virus. Res. Vet. Sci. 1996, 61, 222–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ackley, C.D.; Yamamoto, J.K.; Levy, N.; Pedersen, N.C.; Cooper, M.D. Immunologic Abnormalities in Pathogen-Free Cats Experimentally Infected with Feline Immunodeficiency Virus. J. Virol. 1990, 64, 5652–5655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffmann-Fezer, G.; Thum, J.; Ackley, C.; Herbold, M.; Mysliwietz, J.; Thefeld, S.; Hartmann, K.; Kraft, W. Decline in CD4+ Cell Numbers in Cats with Naturally Acquired Feline Immunodeficiency Virus Infection. J. Virol. 1992, 66, 1484–1488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willett, B.; Hosie, M.; Callanan, J.; Neil, J.; Jarrett, O. Infection with Feline Immunodeficiency Virus Is Followed by the Rapid Expansion of a CD8+ Lymphocyte Subset. Immunology 1993, 78, 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Beatty, J.A.; Willett, B.J.; Gault, E.A.; Jarrett, O. A Longitudinal Study of Feline Immunodeficiency Virus-Specific Cytotoxic T Lymphocytes in Experimentally Infected Cats, Using Antigen-Specific Induction. J. Virol. 1996, 70, 6199–6206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedersen, N.C.; Ho, E.W.; Brown, M.L.; Yamamoto, J.K. Isolation of a T-Lymphotropic Virus from Domestic Cats with an Immunodeficiency-like Syndrome. Science 1987, 235, 790–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brenchley, J.M.; Price, D.A.; Douek, D.C. HIV Disease: Fallout from a Mucosal Catastrophe? Nat. Immunol. 2006, 7, 235–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehandru, S.; Poles, M.A.; Tenner-Racz, K.; Horowitz, A.; Hurley, A.; Hogan, C.; Boden, D.; Racz, P.; Markowitz, M. Primary HIV-1 Infection Is Associated with Preferential Depletion of CD4+ T Lymphocytes from Effector Sites in the Gastrointestinal Tract. J. Exp. Med. 2004, 200, 761–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brenchley, J.M.; Price, D.A.; Schacker, T.W.; Asher, T.E.; Silvestri, G.; Rao, S.; Kazzaz, Z.; Bornstein, E.; Lambotte, O.; Altmann, D.; et al. Microbial Translocation Is a Cause of Systemic Immune Activation in Chronic HIV Infection. Nat. Med. 2006, 12, 1365–1371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sallusto, F.; Lanzavecchia, A.; MacKay, C.R. Chemokines and Chemokine Receptors in T-Cell Priming and Th1/Th2-Mediated Responses. Immunol. Today 1998, 19, 568–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acosta-Rodriguez, E.V.; Rivino, L.; Geginat, J.; Jarrossay, D.; Gattorno, M.; Lanzavecchia, A.; Sallusto, F.; Napolitani, G. Surface Phenotype and Antigenic Specificity of Human Interleukin 17–Producing T Helper Memory Cells. Nat. Immunol. 2007, 8, 639–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Groom, J.R.; Luster, A.D. CXCR3 in T Cell Function. Exp. Cell Res. 2011, 317, 620–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sallusto, F. The Role of Chemokine Receptors in Primary, Effector and Memory Immune Response. Exp. Dermatol. 2002, 11, 476–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivino, L.; Messi, M.; Jarrossay, D.; Lanzavecchia, A.; Sallusto, F.; Geginat, J. Chemokine Receptor Expression Identifies Pre–T Helper (Th)1, Pre–Th2, and Nonpolarized Cells among Human CD4+ Central Memory T Cells. J. Exp. Med. 2004, 200, 725–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berger, A. Th1 and Th2 Responses: What Are They? BMJ 2000, 321, 424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuo, H.H.; Banga, R.; Lee, G.Q.; Gao, C.; Cavassini, M.; Corpataux, J.M.; Blackmer, J.E.; zur Wiesch, S.; Yu, X.G.; Pantaleo, G.; et al. Blood and Lymph Node Dissemination of Clonal Genome-Intact Human Immunodeficiency Virus 1 DNA Sequences during Suppressive Antiretroviral Therapy. J. Infect. Dis. 2020, 222, 655–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, V.L.; Boudreaux, C.E.; Lockett, N.N.; Clay, B.T.; Coats, K.S. Cytokine Dysregulation in Early- and Late-Term Placentas from Feline Immunodeficiency Virus (FIV)-Infected Cats. Am. J. Reprod. Immunol. 2011, 65, 480–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tompkins, M.; Tompkins, W. Lentivirus-Induced Immune Dysregulation. Vet. Immunol. Immunopathol. 2008, 123, 45–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aleebrahim-Dehkordi, E.; Molavi, B.; Mokhtari, M.; Deravi, N.; Fathi, M.; Fazel, T.; Mohebalizadeh, M.; Koochaki, P.; Shobeiri, P.; Hasanpour-Dehkordi, A. T Helper Type (Th1/Th2) Responses to SARS-CoV-2 and Influenza A (H1N1) Virus: From Cytokines Produced to Immune Responses. Transpl. Immunol. 2022, 70, 101495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dean, G.A.; Pedersen, N.C. Cytokine Response in Multiple Lymphoid Tissues during the Primary Phase of Feline Immunodeficiency Virus Infection. J. Virol. 1998, 72, 9436–9440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levy, J.K.; Ritchey, J.W.; Rottman, J.B.; Davidson, M.G.; Liang, Y.-H.; Jordan, H.L.; Tompkins, W.A.; Tompkins, M.B. Elevated Interleukin-10-to-Interleukin-12 Ratio in Feline Immunodeficiency Virus-Infected Cats Predicts Loss of Type 1 Immunity to Toxoplasma Gondii. J. Infect. Dis. 1998, 178, 503–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avery, P.R.; Hoover, E.A. Gamma Interferon/Interleukin 10 Balance in Tissue Lymphocytes Correlates with Down Modulation of Mucosal Feline Immunodeficiency Virus Infection. J. Virol. 2004, 78, 4011–4019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ritchey, J.; Levy, J.; Bliss, S.; Tompkins, W.; Tompkins, M. Constitutive Expression of Types 1 and 2 Cytokines by Alveolar Macrophages from Feline Immunodeficiency Virus-Infected Cats. Vet. Immunol. Immunopathol. 2001, 79, 83–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levy, J.; Liang, Y.; Ritchey, J.; Davidson, M.; Tompkins, W.; Tompkins, M. Failure of FIV-Infected Cats to Control Toxoplasma Gondii Correlates with Reduced IL2, IL6, and IL12 and Elevated IL10 Expression by Lymph Node T Cells. Vet. Immunol. Immunopathol. 2004, 98, 101–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, J.L.; Khoury, G.; Fromentin, R.; Solomon, A.; Chomont, N.; Sinclair, E.; Milush, J.M.; Hartogensis, W.; Bacchetti, P.; Roche, M.; et al. Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV)–Infected CCR6+ Rectal CD4+ T Cells and HIV Persistence On Antiretroviral Therapy. J. Infect. Dis. 2020, 221, 744–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.P.; Zhang, H.H.; Foley, J.F.; Hedrick, M.N.; Farber, J.M. Human T Cells That Are Able to Produce IL-17 Express the Chemokine Receptor CCR6. J. Immunol. 2008, 180, 214–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chumbley, L.B.; Boudreaux, C.E.; Coats, K.S. Aberrant Placental Immune Parameters in the Feline Immunodeficiency Virus (FIV)-Infected Cat Suggest Virus-Induced Changes in T Cell Function. Virol. J. 2013, 10, 238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joshi, A.; Vahlenkamp, T.; Garg, H.; Tompkins, W.; Tompkins, M. Preferential Replication of FIV in Activated CD4+ CD25+ T Cells Independent of Cellular Proliferation. Virology 2004, 321, 307–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joshi, A.; Garg, H.; Tompkins, M.B.; Tompkins, W.A. Preferential Feline Immunodeficiency Virus (FIV) Infection of CD4+ CD25+ T-Regulatory Cells Correlates Both with Surface Expression of CXCR4 and Activation of FIV Long Terminal Repeat Binding Cellular Transcriptional Factors. J. Virol. 2005, 79, 4965–4976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conti, H.R.; Shen, F.; Nayyar, N.; Stocum, E.; Sun, J.N.; Lindemann, M.J.; Ho, A.W.; Hai, J.H.; Yu, J.J.; Jung, J.W.; et al. Th17 Cells and IL-17 Receptor Signaling Are Essential for Mucosal Host Defense against Oral Candidiasis. J. Exp. Med. 2009, 206, 299–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barditch-Crovo, P.; Deeks, S.G.; Collier, A.; Safrin, S.; Coakley, D.F.; Miller, M.; Kearney, B.P.; Coleman, R.L.; Lamy, P.D.; Kahn, J.O.; et al. Phase I/II Trial of the Pharmacokinetics, Safety, and Antiretroviral Activity of Tenofovir Disoproxil Fumarate in Human Immunodeficiency Virus-Infected Adults. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2001, 45, 2733–2739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calcagno, A.; Gonzalez De Requena, D.; Simiele, M.; D’Avolio, A.; Tettoni, M.C.; Salassa, B.; Orofino, G.; Bramato, C.; Libanore, V.; Motta, I.; et al. Tenofovir Plasma Concentrations According to Companion Drugs: A Cross-Sectional Study of HIV-Positive Patients with Normal Renal Function. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2013, 57, 1840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cressey, T.R.; Avihingsanon, A.; Halue, G.; Leenasirimakul, P.; Sukrakanchana, P.O.; Tawon, Y.; Jaisieng, N.; Jourdain, G.; Podany, A.T.; Fletcher, C.V.; et al. Plasma and Intracellular Pharmacokinetics of Tenofovir Disoproxil Fumarate 300 Mg Every 48 Hours vs 150 Mg Once Daily in HIV-Infected Adults with Moderate Renal Function Impairment. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2015, 61, 633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dobard, C.W.; Makarova, N.; West-Deadwyler, R.; Taylor, A.; Dinh, C.; Martin, A.; Lipscomb, J.; Mitchell, J.; Khalil, G.; Garcia-Lerma, G.; et al. Efficacy of Vaginally Administered Gel Containing Emtricitabine and Tenofovir against Repeated Rectal Simian Human Immunodeficiency Virus Exposures in Macaques. J. Infect. Dis. 2018, 218, 1284–1290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.H.; Begley, J.; St. Claire, R.L.; Harris, J.; Wakeford, C.; Rousseau, F.S. Pharmacokinetic and Pharmacodynamic Characteristics of Emtricitabine Support Its Once Daily Dosing for the Treatment of HIV Infection. AIDS Res. Hum. Retrovir. 2004, 20, 1173–1182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greener, B.; Patterson, K.; Prince, H.; Sykes, G.; Adams, J.; Dumond, J.; Shaheen, N.; Madanick, R.; Dellon, E.; Cohen, M.; et al. Dolutegravir Pharmacokinetics in the Genital Tract and Colorectum of HIV Negative Men after Single and Multiple Dosing. J. Acquir. Immune Defic. Syndr. 2013, 64, 39–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massud, I.; Martin, A.; Dinh, C.; Mitchell, J.; Jenkins, L.; Heneine, W.; Pau, C.P.; Gerardo Garcí-Lerma, J. Pharmacokinetic Profile of Raltegravir, Elvitegravir and Dolutegravir in Plasma and Mucosal Secretions in Rhesus Macaques. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2015, 70, 1473–1481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Rompay, K.K.A.; Hassounah, S.; Keele, B.F.; Lifson, J.D.; Ardeshir, A.; Watanabe, J.; Pham, H.T.; Chertova, E.; Sowder, R.; Balzarini, J.; et al. Dolutegravir Monotherapy of Simian Immunodeficiency Virus-Infected Macaques Selects for Several Patterns of Resistance Mutations with Variable Virological Outcomes. J. Virol. 2019, 93, e01189-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Hayes, S.; Sadler, B.M.; Minto, I.; Brandt, J.; Piscitelli, S.; Min, S.; Song, I.H. Population Pharmacokinetics of Dolutegravir in HIV-Infected Treatment-Naive Patients. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2015, 80, 502–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, J.L.; Patterson, K.B.; Ma Prince, H.; Sykes, C.; Greener, B.N.; Dumond, J.B.; Dm Kashuba, A. Single and Multiple Dose Pharmacokinetics of Dolutegravir in the Genital Tract of HIV-Negative Women. Antivir. Ther. 2013, 18, 1005–1013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Min, S.; Song, I.; Borland, J.; Chen, S.; Lou, Y.; Fujiwara, T.; Piscitelli, S.C. Pharmacokinetics and Safety of S/GSK1349572, a next-Generation HIV Integrase Inhibitor, in Healthy Volunteers. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2010, 54, 254–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kim, J.; Behzadi, E.S.; Nehring, M.; Carver, S.; Cowan, S.R.; Conry, M.K.; Rawlinson, J.E.; VandeWoude, S.; Miller, C.A. Combination Antiretroviral Therapy and Immunophenotype of Feline Immunodeficiency Virus. Viruses 2023, 15, 822. https://doi.org/10.3390/v15040822
Kim J, Behzadi ES, Nehring M, Carver S, Cowan SR, Conry MK, Rawlinson JE, VandeWoude S, Miller CA. Combination Antiretroviral Therapy and Immunophenotype of Feline Immunodeficiency Virus. Viruses. 2023; 15(4):822. https://doi.org/10.3390/v15040822
Chicago/Turabian StyleKim, Jeffrey, Elisa S. Behzadi, Mary Nehring, Scott Carver, Shannon R. Cowan, Megan K. Conry, Jennifer E. Rawlinson, Sue VandeWoude, and Craig A. Miller. 2023. "Combination Antiretroviral Therapy and Immunophenotype of Feline Immunodeficiency Virus" Viruses 15, no. 4: 822. https://doi.org/10.3390/v15040822
APA StyleKim, J., Behzadi, E. S., Nehring, M., Carver, S., Cowan, S. R., Conry, M. K., Rawlinson, J. E., VandeWoude, S., & Miller, C. A. (2023). Combination Antiretroviral Therapy and Immunophenotype of Feline Immunodeficiency Virus. Viruses, 15(4), 822. https://doi.org/10.3390/v15040822






