Alphaviruses Detected in Mosquitoes in the North-Eastern Regions of South Africa, 2014 to 2018
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
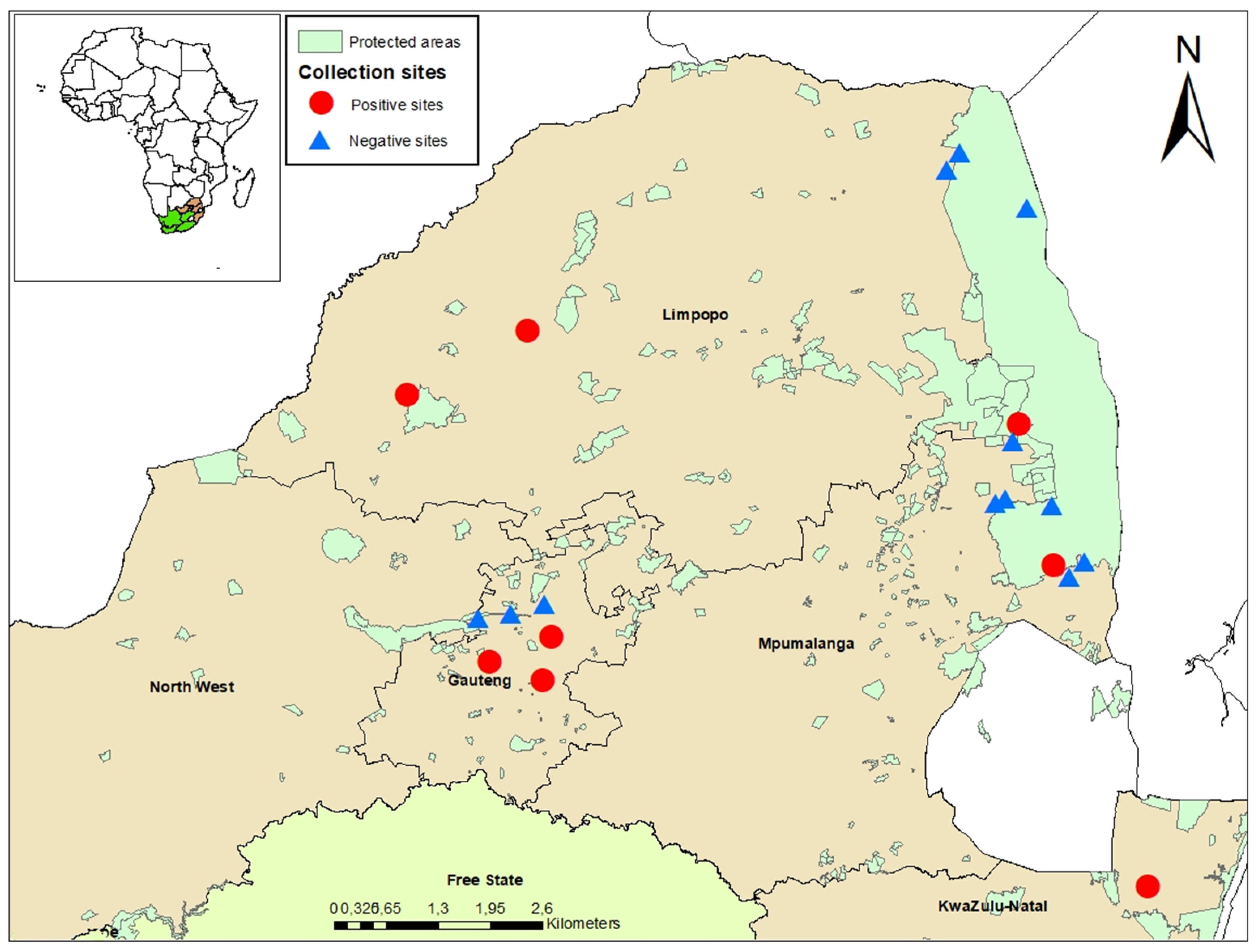
2.1. Study Areas
2.2. Mosquito Processing
2.3. Detection and Analysis by RT-PCR
2.4. Virus Isolation
2.5. Whole Genome Sequencing Using Illumina iSeq
2.6. Molecular Identification of Mosquito Samples
2.7. Gel Electrophoresis and Sequencing
2.8. Data Analysis and Phylogenetic Analysis
3. Results
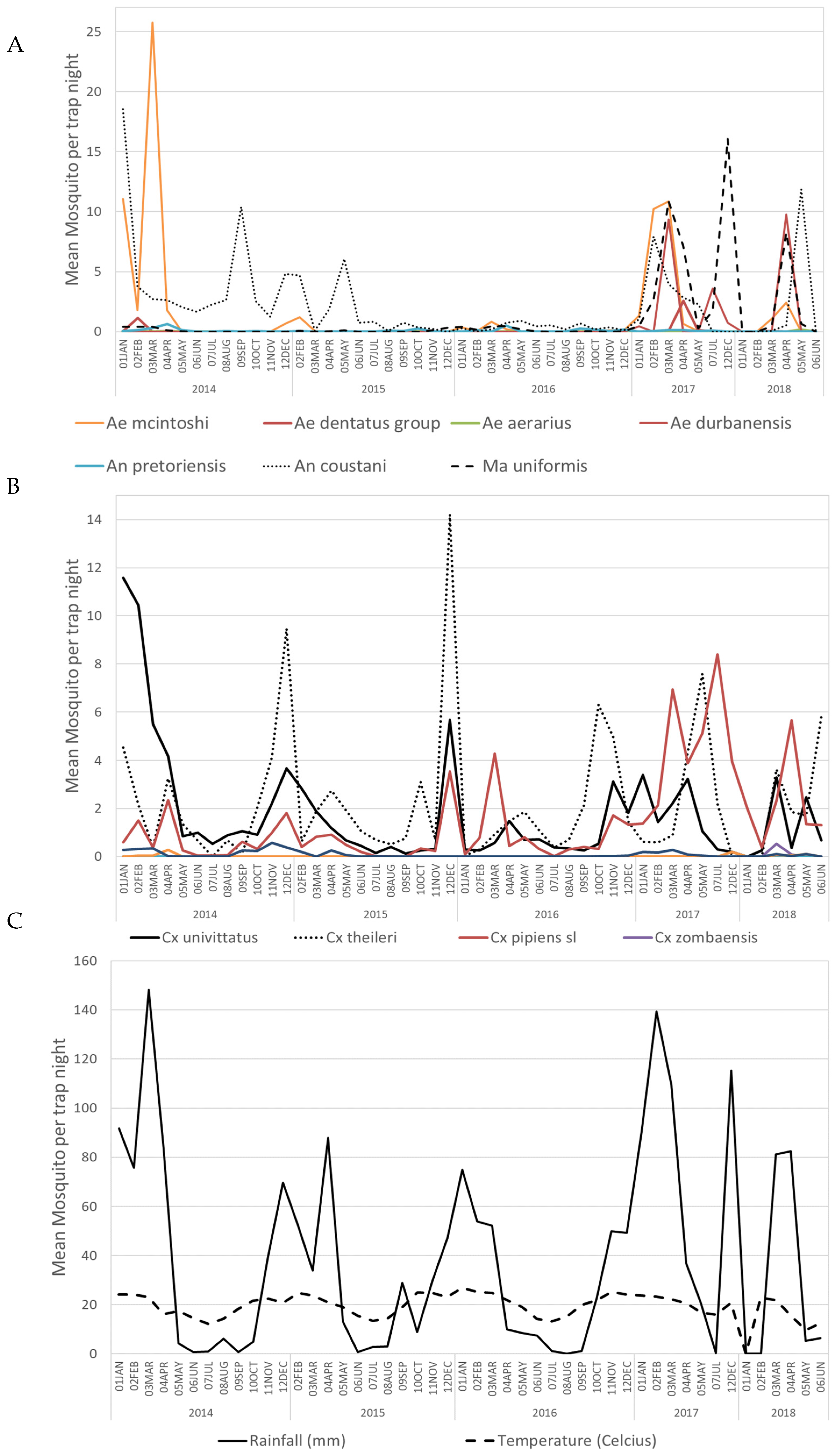
3.1. Mosquito Collection
3.2. Alphavirus Detection
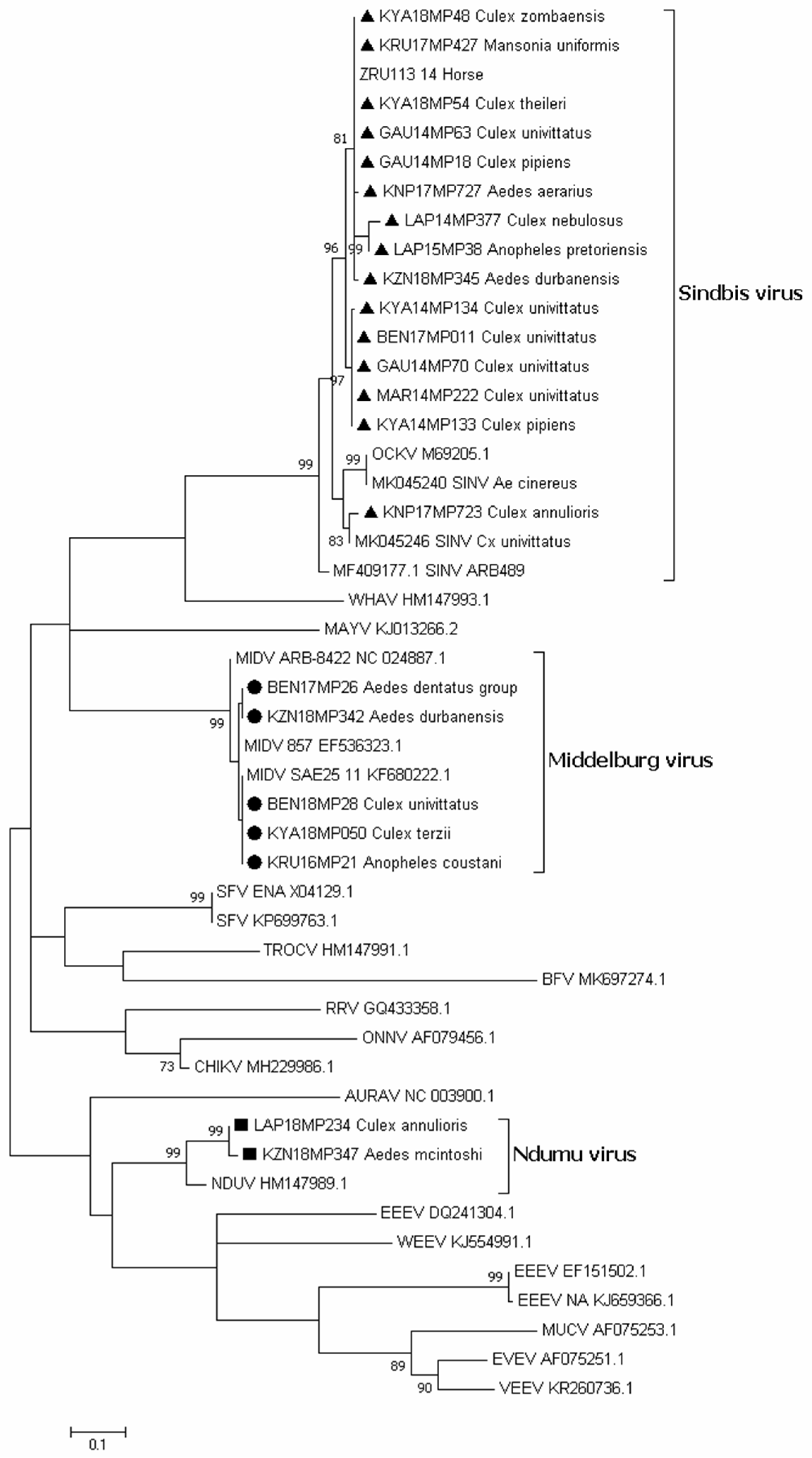
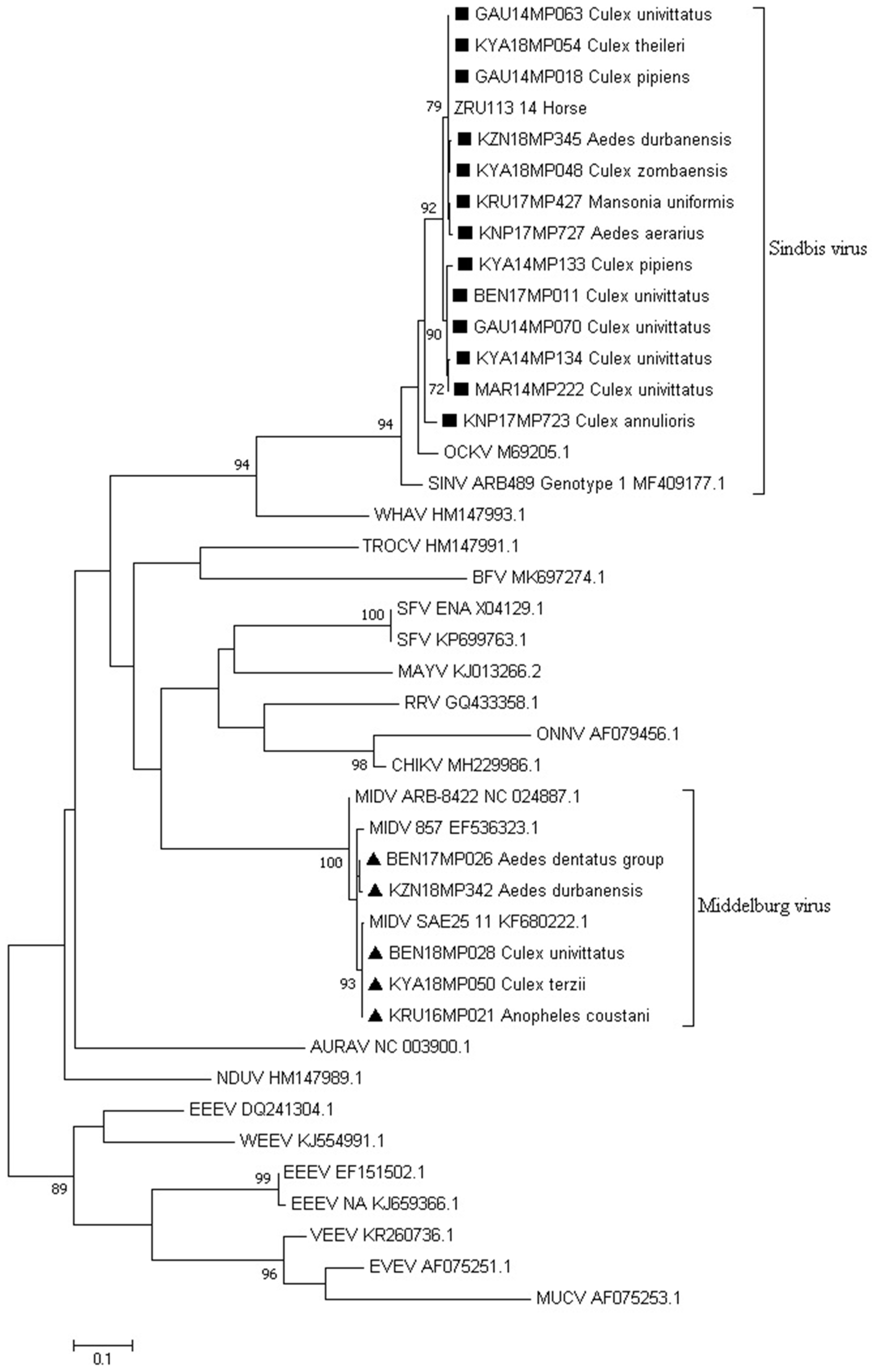
3.3. Virus Isolation
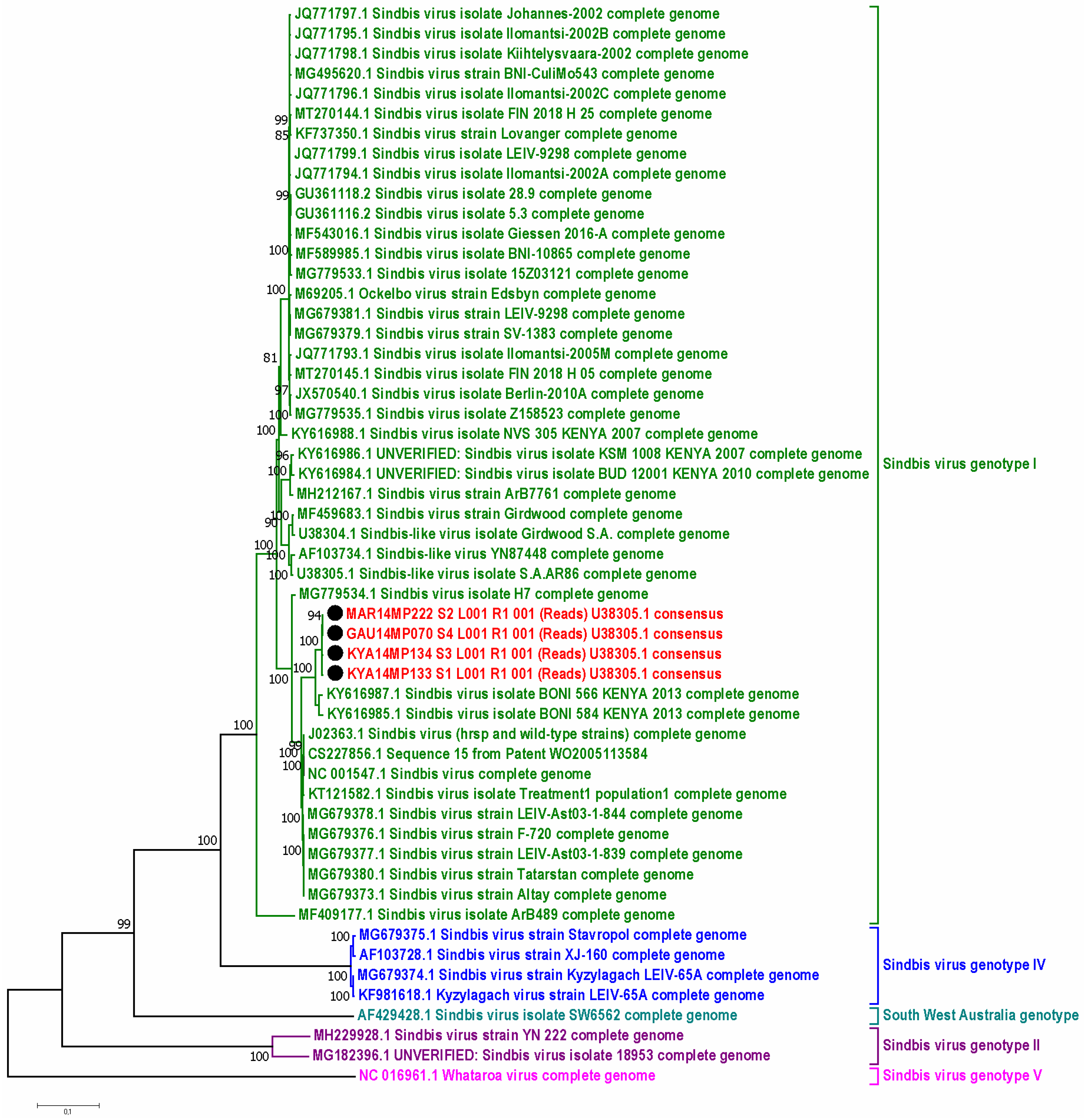
3.4. Whole Genome Sequencing Using Illumina iSeq
3.5. Molecular Identification of Mosquito Samples
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Strauss, J.; Strauss, E.G. The alphaviruses: Gene expression, replication, and evolution. Microbiol. Rev. 1994, 58, 491–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jupp, P.G.; Blackburn, N.K.; Thompson, D.L.; Meenehan, G.M. Sindbis and West Nile virus infections in the Witwatersrand-Pretoria region. S. Afr. Med. J. 1986, 70, 218–220. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ryman, K.D.; Klimstra, W.B. Host responses to alphavirus infection. Immunol. Rev. 2008, 225, 27–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Forrester, N.L.; Palacios, G.; Tesh, R.B.; Savji, N.; Guzman, H.; Sherman, M.; Weaver, S.C.; Lipkin, W.I. Genome-scale phylogeny of the alphavirus genus suggests a marine origin. J. Virol. 2012, 86, 2729–2738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Josseran, L.; Paquet, C.; Zehgnoun, A.; Caillère, N.; le Tertre, A.; Solet, J.-L.; Ledrans, M. Chikungunya disease outbreak, Reunion Island. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2006, 12, 1994–1995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ling, J.; Smura, T.; Lundström, J.O.; Pettersson, J.H.; Sironen, T.; Vapalahti, O.; Lundkvist, Å.; Hesson, J.C. The introduction and dispersal of Sindbis virus from central Africa to Europe. J. Virol. 2019, 93, e00620-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McIntoshi, B.M.; Jupp, P.G.; dos Santos, I.; Meenehan, G.M. Epidemics of West Nile and Sindbis viruses in South Africa with Culex (Culex) univittatus Theobald as vector. S. Afr. J. Sci. 1976, 72, 295–300. [Google Scholar]
- Braack, L.; de Almeida, A.P.G.; Cornel, A.J.; Swanepoel, R.; de Jager, C. Mosquito-borne arboviruses of African origin: Review of key viruses and vectors. Parasites Vectors 2018, 11, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mcintosh, B.M.; Jupp, P.G.; Santos, I.D. Rural epidemic of chikungunya in South Africa with involvement of Aedes furcifer (Diceromyia) (Edwards) and baboons. S. Afr. J. Sci. 1977, 73, 267–269. [Google Scholar]
- Jupp, P.G.; Mcintosh, B.M. Aedes furcifer and other mosquitos as vectors of chikungunya virus at Mica, Northeastern Transvaal, South-Africa. J. Am. Mosq. Contr. 1990, 6, 415–420. [Google Scholar]
- Jupp, P.G. Mosquitoes as vectors of human disease in South Africa. S. Afr. Fam. Pract. 2014, 47, 68–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fourie, I.; Williams, J.; Ismail, A.; van Vuren, P.J.; Stolz, A.; Venter, M. Detection and genome characterization of Middelburg virus strains isolated from CSF and whole blood samples of humans with neurological manifestations in South Africa. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2022, 16, e0010020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meno, K.; Yah, C.; Mendes, A.; Venter, M. Incidence of Sindbis Virus in Hospitalized Patients with Acute Fevers of Unknown Cause in South Africa, 2019–2020. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 12, 798810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Niekerk, S.; Human, S.; Williams, J.; van Wilpe, E.; Pretorius, M.; Swanepoel, R.; Venter, M. Sindbis and Middelburg Old World alphaviruses associated with neurologic disease in horses, South Africa. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2015, 21, 2225–2229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kokernot, R.H.; de Meillon, B.; Paterson, H.E.; Heymann, C.S.; Smithburn, K.C. Middelburg virus; a hitherto unknown agent isolated from Aedes mosquitoes during an epizootic in sheep in the eastern Cape Province. S. Afr. J. Med. Sci. 1957, 22, 145–153. [Google Scholar]
- Hubálek, Z.; Rudolf, I.; Nowotny, N. Arboviruses pathogenic for domestic and wild animals. Adv. Virus Res. 2014, 89, 201–275. [Google Scholar]
- McIntoshi, B.M. Rift Valley Fever. 1. Vectors studies in the field. J. S. Afr. Vet. Assoc. 1972, 43, 391–395. [Google Scholar]
- Worth, C.B.; Paterson, H.E.; de Meillon, B. The incidence of arthropod-borne viruses in a population of culicine mosquitoes in Tongaland, Union of South Africa (January 1956, through April 1960). Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 1961, 10, 583–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Attoui, H.; Sailleau, C.; Jaafar, F.M.; Belhouchet, M.; Biagini, P.; Cantaloube, J.F.; de Micco, P.; Mertens, P.; Zientara, S. Complete nucleotide sequence of Middelburg virus, isolated from the spleen of a horse with severe clinical disease in Zimbabwe. J. Gen. Virol. 2007, 88, 3078–3088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steyn, J. Culicoides midges (Diptera: Ceratopogonidae) as Potential Vectors for Neurological Arboviruses and the Prevalence of Infection at the Wildlife/Livestock/Human Interface. Viruses 2021, 13, 1978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guarido, M.M.; Riddin, M.A.; Johnson, T.; Braack, L.E.O.; Schrama, M.; Gorsich, E.E.; Brooke, B.D.; Almeida, A.P.G.; Venter, M. Aedes species (Diptera: Culicidae) ecological and host feeding patterns in the north-eastern parts of South Africa, 2014–2018. Parasites Vectors 2021, 14, 339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gorsich, E.E.; Beechler, B.R.; van Bodegom, P.M.; Govender, D.; Guarido, M.M.; Venter, M.; Schrama, M. A comparative assessment of adult mosquito trapping methods to estimate spatial patterns of abundance and community composition in southern Africa. Parasites Vectors 2019, 12, 462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edwards, F.W. Mosquitoes of the Ethiopian Region. III—Culicine Adults and Pupae; The Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 1941. [Google Scholar]
- Gillies, M.T.; Coetzee, M. A Supplement to the Anophelinae of South of the Sahara (Afrotropical Region); South African Institute for Medical Research: Johannesburg, South Africa, 1987. [Google Scholar]
- Jupp, P.G. Mosquitoes of Southern Africa. Culicinae and Toxorhynchitinae; Ekogilde Publishers: Hartebeespoort, South Africa, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Service, M.W. Handbook to the Afrotropical Toxorhynchitine and Culicine Mosquitoes, Excepting Aedes and Culex; British Museum (Natural History): London, UK, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Sánchez-Seco, M.P.; Rosario, D.; Quiroz, E.; Guzmán, G.; Tenorio, A. A generic nested-RT-PCR followed by sequencing for detection and identification of members of the alphavirus genus. J. Virol. Methods 2001, 95, 153–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Norder, H.; Lundström, J.O.; Kozuch, O.; Magnius, L.O. Genetic relatedness of Sindbis virus strains from Europe, Middle East, and Africa. Virology 1996, 222, 440–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bryant, J.E.; Crabtree, M.B.; Nan, V.S.; Thi Yen, N.; Duc, H.M.; Miller, B. Isolation of arboviruses from mosquitoes in northern Vietnan. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2005, 73, 470–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Folmer, O.; Black, M.; Hoeh, W.; Lutz, R.; Vrijenhoek, R. DNA primers for amplification of mitochondrial cytochrome c oxidase subunit I from diverse metazoan invertebrate. Mol. Mar. Biol. Biotechnol. 1994, 3, 294–299. [Google Scholar]
- CLC Genomics Workbench 8.0.1: Qiagen Bioinformatics. Available online: https://www.qiagenbioinformatics.com (accessed on 12 July 2020).
- Medicine Nlo. National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI) Bethesda (US). 1988. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov (accessed on 10 June 2020).
- Altschul, S.F.; Gish, W.; Miller, W.; Myers, E.W.; Lipman, D.J. Basic local alignment search tool. J. Mol. Biol. 1990, 215, 403–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ratnasigham, S.; Herbert, P.D.N. BOLD: The Barcode of Life Data System (www.barcodinglife.org). Mol. Ecol. Notes 2007, 7, 355–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katoh, K.; Misawa, K.; Kuma, K.; Miyata, T. MAFFT: A novel method for rapid multiple sequence alignment based on fast Fourier transform. Nucleic Acids Res. 2002, 30, 3059–3066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Stecher, G.; Tamura, K. MEGA7: Molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 7.0 for bigger datasets. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2016, 33, 1870–1874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corporation, M. Microsoft Office Excel; Microsoft Corporation: Redmond, WA, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Nei, M.; Kumar, S. Molecular Evolution and Phylogenetics; Oxford University Press: New York, NY, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Feselsntein, J. Phylogenies and the comparative Method. Am. Nat. 1985, 125, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, F. The Vegetation of Africa; UNESCO: Paris, France, 1983. [Google Scholar]
- Cornel, A.J.; Lee, Y.; Almeida, A.P.G.; Johnson, T.; Mouatcho, J.; Venter, M.; de Jager, C.; Braack, L. Mosquito community composition in South Africa and some neighboring countries. Parasites Vectors 2018, 11, 331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kurkela, S.; Manni, T.; Vaheri, A.; Vapalahti, O. Causative agent of Pogosta disease isolated from blood and skin lesions. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2004, 10, 889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McIntoshi, B.M. A taxonomic revision of certain Aedes species (Diptera: Culicidae) of the subgenus Aedimorphus in southern Africa. J. Entomol. Soc. S. Afr. 1975, 38, 251–287. [Google Scholar]
- Kokernot, R.H.; McIntosh, B.M.; Worth, C.B. Ndumu virus, a hitherto unknown agent, isolated from culicine mosquitoes collected in northern natal, union of South Africa. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 1961, 10, 383–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lutomiah, J.; Ongus, J.; Linthicum, K.J.; Sang, R. Natural vertical transmission of ndumu virus in Culex pipiens (Diptera: Culicidae) mosquitoes collected as larvae. J. Med. Entomol. 2014, 51, 1091–1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masembe, C.; Michuki, G.; Onyango, M.; Rumberia, C.; Norling, M.; Bishop, R.P.; Djikeng, A.; Kemp, S.J.; Orth, A.; Skilton, R.A.; et al. Viral metagenomics demonstrates that domestic pigs are a potential reservoir for Ndumu virus. Virol. J. 2012, 8, 218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO. Arboviruses and Human Diseases; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 1967. [Google Scholar]
- WHO. Arthropod-Borne Viruses; World Health Organization Technical Report Series; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 1961; Volume 219, p. 47. [Google Scholar]
- Jupp, P.G. The taxonomic status of Culex (Culex) univittatus Theobald (Diptera: Cuilicidae) in South Africa. J. Entomol. Soc. S. Afr. 1971, 34, 339–357. [Google Scholar]
- Jupp, P.G. A morphological study of Culex (Culex) univittatus Theobald and Culex (Culex) neavei Theobald from various african countries. Mosq. Syst. 1972, 4, 103–113. [Google Scholar]
- Mixão, V.; Barriga, D.B.; Parreira, R.; Novo, M.T.; Sousa, C.A.; Frontera, E.; Venter, M.; Braack, L.; Almeida, A.P. Comparative morphological and molecular analysis confirms the presence of the West Nile virus mosquito vector Cx univittatus in the Iberian Peninsula. Parasites Vectors 2016, 9, 601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Culicidae Alphaviruses Detected | N Mosq. Assayed | Pools Positive/Pool Tested | Infection Rate * |
|---|---|---|---|
| Middelburg virus | |||
| Ae. dentatus gr. | 471 | 1/21 | 2.1 |
| Ae. durbanensis | 716 | 2/17 | 1.4 |
| An. coustani | 2205 | 1/62 | 0.5 |
| Cx. terzii | 54 | 1/12 | 18.5 |
| Cx. univittatus | 4061 | 1/105 | 0.2 |
| Sindbis virus | |||
| Ae. durbanensis | 716 | 1/17 | 1.4 |
| Ae. Aerarius/tarsalis | 58 | 1/3 | 17.2 |
| Cx. zombaensis | 33 | 1/5 | 30.3 |
| Cx. annulioris | 165 | 1/15 | 6.1 |
| Cx. univittatus | 4061 | 5/105 | 1.2 |
| Cx. pipiens s.l. | 2617 | 2/76 | 0.8 |
| Cx. theileri | 2129 | 1/70 | 0.5 |
| Ma. uniformis | 2472 | 1/67 | 0.4 |
| Ndumu virus | |||
| Ae. mcintoshi | 3653 | 1/17 | 0.3 |
| Cx. annulioris | 165 | 1/15 | 6.1 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Guarido, M.M.; Fourie, I.; Meno, K.; Mendes, A.; Riddin, M.A.; MacIntyre, C.; Manyana, S.; Johnson, T.; Schrama, M.; Gorsich, E.E.; et al. Alphaviruses Detected in Mosquitoes in the North-Eastern Regions of South Africa, 2014 to 2018. Viruses 2023, 15, 414. https://doi.org/10.3390/v15020414
Guarido MM, Fourie I, Meno K, Mendes A, Riddin MA, MacIntyre C, Manyana S, Johnson T, Schrama M, Gorsich EE, et al. Alphaviruses Detected in Mosquitoes in the North-Eastern Regions of South Africa, 2014 to 2018. Viruses. 2023; 15(2):414. https://doi.org/10.3390/v15020414
Chicago/Turabian StyleGuarido, Milehna M., Isabel Fourie, Kgothatso Meno, Adriano Mendes, Megan A. Riddin, Caitlin MacIntyre, Sontaga Manyana, Todd Johnson, Maarten Schrama, Erin E. Gorsich, and et al. 2023. "Alphaviruses Detected in Mosquitoes in the North-Eastern Regions of South Africa, 2014 to 2018" Viruses 15, no. 2: 414. https://doi.org/10.3390/v15020414
APA StyleGuarido, M. M., Fourie, I., Meno, K., Mendes, A., Riddin, M. A., MacIntyre, C., Manyana, S., Johnson, T., Schrama, M., Gorsich, E. E., Brooke, B. D., Almeida, A. P. G., & Venter, M. (2023). Alphaviruses Detected in Mosquitoes in the North-Eastern Regions of South Africa, 2014 to 2018. Viruses, 15(2), 414. https://doi.org/10.3390/v15020414





