Of Keeping and Tipping the Balance: Host Regulation and Viral Modulation of IRF3-Dependent IFNB1 Expression
Abstract
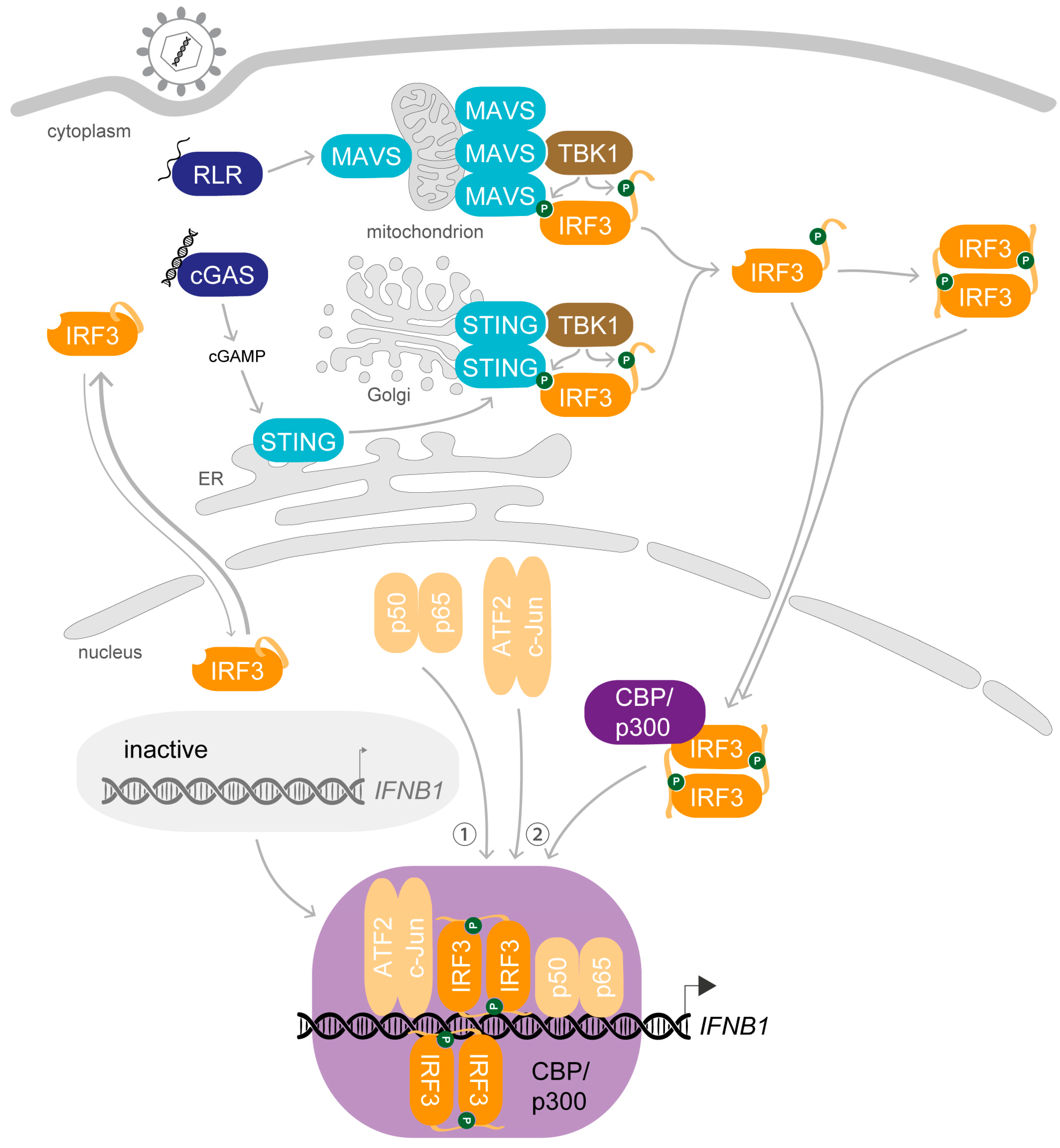
1. Synopsis—IRF3 Activation Induces Transcription of IFNB1 upon Viral Infection
1.1. The Name Says It All—Interferons Counter Infections
1.2. The Setting—Cytosolic Nucleic Acids Stimulate Activation of Specific Transcription Factors
1.3. Meet the Lead—IRF3 and IRF7, the “Masters” of Type I IFN Transcription
2. Preparation Is Everything—The Key Steps Enabling the Biological Role of IRF3
2.1. Dress up—Phosphorylation of IRF3 Enables Protein–Protein Interactions
2.2. Join Forces—Dimerisation and Interaction with Coactivators Is Required for DNA-Binding of IRF3
2.3. Enter the Final Scene—Protein–Protein Interactions Retain IRF3 in the Nucleus after Stimulation
2.4. Leave Room for Improvement—IRF3 Activity Comes in Different Ranges
3. A Complex Performance—Stimulus-Induced Assembly of the IFNβ Enhanceosome
3.1. The Preface—The DNA Blueprint for Inducible IFNB1 Expression
3.2. On the Marks—Assembly of the IFNβ Enhanceosome
3.3. Get Ready and Go—Initiation of IFNB1 Transcription
3.4. The Run-Through—Basal Transcription of IFNB1
3.5. Backstage—Long-Range Modulation of IFNB1 Expression
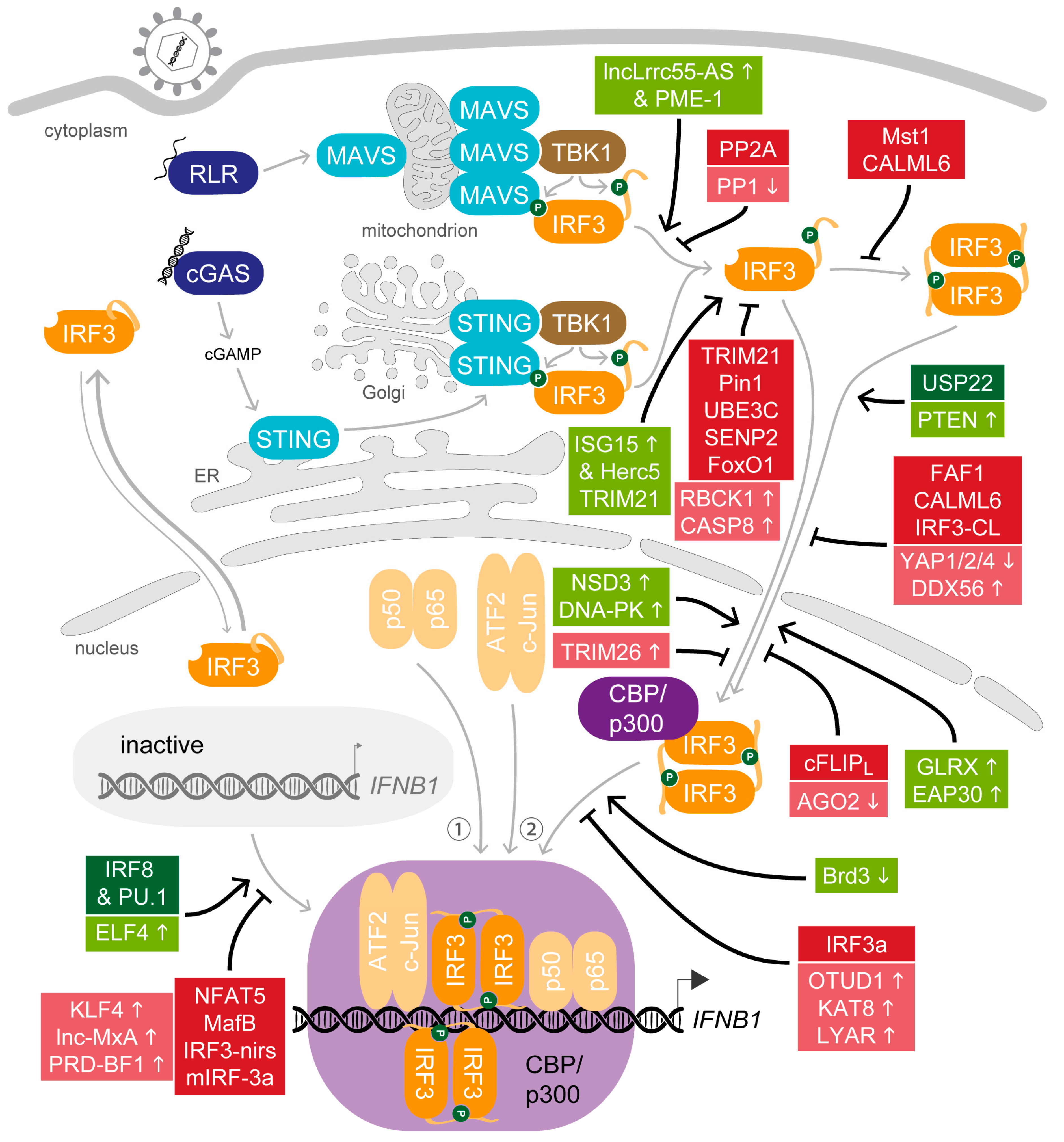
4. All in Moderation—The Many Ways to Adjust IRF3 Activity
4.1. Support for the Key Actor—Host Factors that Promote IRF3 Activity after Viral Stimulation
4.2. Balance Is Key—Host Factors That Attenuate IRF3 Activity
4.3. The Curtain Drops—Host Factors that Terminate IRF3 Activity after Viral Stimulation
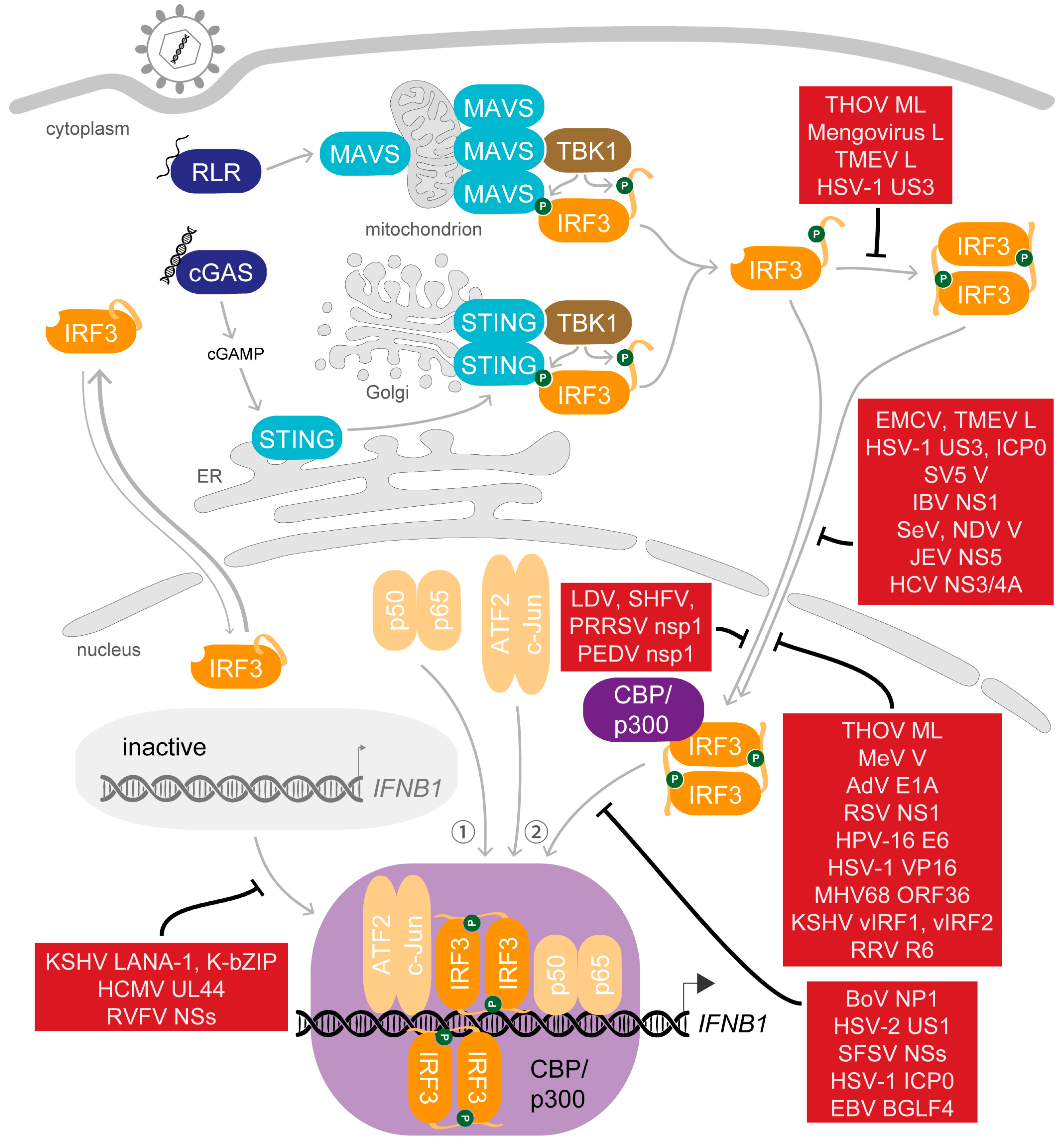
5. Saboteurs of the Main Act—Viral Modulation of Activated IRF3
5.1. Dispersing the Winning Team—Inhibition of Dimerisation
5.2. Selected Cast Only—Inhibition of Nuclear Translocation
5.3. Gate-Crashers Barge in—Inhibition of the IRF3-CBP/p300 Holocomplex Formation
5.4. At the Eleventh Hour—Inhibition of DNA Binding
6. To Be Continued—Perspective
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
References
- Isaacs, A.; Lindenmann, J. Virus interference. I. The interferon. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. B Biol. Sci. 1957, 147, 258–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, B.X.; Fish, E.N. Global virus outbreaks: Interferons as 1st responders. Semin. Immunol. 2019, 43, 101300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.; Gong, M.; Zhao, F.; Shao, J.; Xie, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Chang, H. Type I Interferons: Distinct Biological Activities and Current Applications for Viral Infection. Cell Physiol. Biochem. 2018, 51, 2377–2396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, A.J.; Ashkar, A.A. The Dual Nature of Type I and Type II Interferons. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 2061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazear, H.M.; Schoggins, J.W.; Diamond, M.S. Shared and Distinct Functions of Type I and Type III Interferons. Immunity 2019, 50, 907–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, L.; Schnepf, D.; Staeheli, P. Interferon-λ orchestrates innate and adaptive mucosal immune responses. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2019, 19, 614–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chasset, F.; Arnaud, L. Targeting interferons and their pathways in systemic lupus erythematosus. Autoimmun. Rev. 2018, 17, 44–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mancino, A.; Natoli, G. Specificity and Function of IRF Family Transcription Factors: Insights from Genomics. J. Interferon Cytokine Res. 2016, 36, 462–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jensen, K.E.; Neal, A.L.; Owens, R.E.; Warren, J. Interferon Response of Chicken Embryo Fibroblasts to Nucleic Acids and Related Compounds. Nature 1963, 200, 433–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rotem, Z.; Cox, R.A.; Isaacs, A. Inhibition of virus multiplication by foreign nucleic acid. Nature 1963, 197, 564–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janeway, C.A., Jr. Approaching the asymptote? Evolution and revolution in immunology. Cold Spring Harb. Symp. Quant. Biol. 1989, 54, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roers, A.; Hiller, B.; Hornung, V. Recognition of Endogenous Nucleic Acids by the Innate Immune System. Immunity 2016, 44, 739–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, X.; Sun, L.; Chen, J.; Chen, Z.J. Detection of Microbial Infections Through Innate Immune Sensing of Nucleic Acids. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 2018, 72, 447–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miyake, K.; Shibata, T.; Ohto, U.; Shimizu, T.; Saitoh, S.I.; Fukui, R.; Murakami, Y. Mechanisms controlling nucleic acid-sensing Toll-like receptors. Int. Immunol. 2018, 30, 43–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Napetschnig, J.; Wu, H. Molecular basis of NF-κB signaling. Annu. Rev. Biophys. 2013, 42, 443–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karin, M. The regulation of AP-1 activity by mitogen-activated protein kinases. Philos Trans. R. Soc. Lond. B Biol. Sci. 1996, 351, 127–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ford, E.; Thanos, D. The transcriptional code of human IFN-beta gene expression. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2010, 1799, 328–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Au, W.C.; Moore, P.A.; Lowther, W.; Juang, Y.T.; Pitha, P.M. Identification of a member of the interferon regulatory factor family that binds to the interferon-stimulated response element and activates expression of interferon-induced genes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1995, 92, 11657–11661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, R.; Mamane, Y.; Hiscott, J. Structural and functional analysis of interferon regulatory factor 3: Localization of the transactivation and autoinhibitory domains. Mol. Cell. Biol. 1999, 19, 2465–2474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, B.Y.; Liu, C.; Lam, S.S.; Srinath, H.; Delston, R.; Correia, J.J.; Derynck, R.; Lin, K. Crystal structure of IRF-3 reveals mechanism of autoinhibition and virus-induced phosphoactivation. Nat. Struct. Biol. 2003, 10, 913–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoneyama, M.; Suhara, W.; Fukuhara, Y.; Fukuda, M.; Nishida, E.; Fujita, T. Direct triggering of the type I interferon system by virus infection: Activation of a transcription factor complex containing IRF-3 and CBP/p300. Embo J. 1998, 17, 1087–1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, K.P.; McBride, K.M.; Weaver, B.K.; Dingwall, C.; Reich, N.C. Regulated nuclear-cytoplasmic localization of interferon regulatory factor 3, a subunit of double-stranded RNA-activated factor 1. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2000, 20, 4159–4168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, M.; Fang, T.; Li, S.; Meng, K.; Guo, D. Bipartite Nuclear Localization Signal Controls Nuclear Import and DNA-Binding Activity of IFN Regulatory Factor 3. J. Immunol. 2015, 195, 289–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Au, W.C.; Yeow, W.S.; Pitha, P.M. Analysis of functional domains of interferon regulatory factor 7 and its association with IRF-3. Virology 2001, 280, 273–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakaya, T.; Sato, M.; Hata, N.; Asagiri, M.; Suemori, H.; Noguchi, S.; Tanaka, N.; Taniguchi, T. Gene induction pathways mediated by distinct IRFs during viral infection. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2001, 283, 1150–1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Royer, W.E., Jr. Structural insights into interferon regulatory factor activation. Cell Signal. 2010, 22, 883–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Honda, K.; Yanai, H.; Negishi, H.; Asagiri, M.; Sato, M.; Mizutani, T.; Shimada, N.; Ohba, Y.; Takaoka, A.; Yoshida, N.; et al. IRF-7 is the master regulator of type-I interferon-dependent immune responses. Nature 2005, 434, 772–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ning, S.; Pagano, J.S.; Barber, G.N. IRF7: Activation, regulation, modification and function. Genes Immun. 2011, 12, 399–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swiecki, M.; Colonna, M. The multifaceted biology of plasmacytoid dendritic Cells. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2015, 15, 471–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Au, W.-C.; Moore, P.A.; LaFleur, D.W.; Tombal, B.; Pitha, P.M. Characterization of the Interferon Regulatory Factor-7 and Its Potential Role in the Transcription Activation of Interferon A Genes. J. Biol. Chem. 1998, 273, 29210–29217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, M.; Hata, N.; Asagiri, M.; Nakaya, T.; Taniguchi, T.; Tanaka, N. Positive feedback regulation of type I IFN genes by the IFN-inducible transcription factor IRF-7. FEBS Lett. 1998, 441, 106–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marie, I.; Durbin, J.E.; Levy, D.E. Differential viral induction of distinct interferon-alpha genes by positive feedback through interferon regulatory factor-7. Embo J. 1998, 17, 6660–6669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, R.; Genin, P.; Mamane, Y.; Hiscott, J. Selective DNA binding and association with the CREB binding protein coactivator contribute to differential activation of alpha/beta interferon genes by interferon regulatory factors 3 and 7. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2000, 20, 6342–6353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sato, M.; Suemori, H.; Hata, N.; Asagiri, M.; Ogasawara, K.; Nakao, K.; Nakaya, T.; Katsuki, M.; Noguchi, S.; Tanaka, N.; et al. Distinct and essential roles of transcription factors IRF-3 and IRF-7 in response to viruses for IFN-alpha/beta gene induction. Immunity 2000, 13, 539–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michalska, A.; Blaszczyk, K.; Wesoly, J.; Bluyssen, H.A.R. A Positive Feedback Amplifier Circuit That Regulates Interferon (IFN)-Stimulated Gene Expression and Controls Type I and Type II IFN Responses. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 1135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, M.; Tanaka, N.; Hata, N.; Oda, E. Taniguchi T. Involvement of the IRF family transcription factor IRF-3 in virus-induced activation of the IFN-beta gene. FEBS Lett. 1998, 425, 112–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, R.; Heylbroeck, C.; Pitha, P.M.; Hiscott, J. Virus-dependent phosphorylation of the IRF-3 transcription factor regulates nuclear translocation, transactivation potential, and proteasome-mediated degradation. Mol. Cell. Biol. 1998, 18, 2986–2996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wathelet, M.G.; Lin, C.H.; Parekh, B.S.; Ronco, L.V.; Howley, P.M.; Maniatis, T. Virus infection induces the assembly of coordinately activated transcription factors on the IFN-beta enhancer in vivo. Mol. Cell 1998, 1, 507–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Servant, M.J.; ten Oever, B.; LePage, C.; Conti, L.; Gessani, S.; Julkunen, I.; Lin, R.; Hiscott, J. Identification of distinct signaling pathways leading to the phosphorylation of interferon regulatory factor 3. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 355–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, Y.; Chen, Z.J. STING specifies IRF3 phosphorylation by TBK1 in the cytosolic DNA signaling pathway. Sci. Signal. 2012, 5, ra20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Cai, X.; Wu, J.; Cong, Q.; Chen, X.; Li, T.; Du, F.; Ren, J.; Wu, Y.T.; Grishin, N.V.; et al. Phosphorylation of innate immune adaptor proteins MAVS, STING, and TRIF induces IRF3 activation. Science 2015, 347, aaa2630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, B.; Shu, C.; Gao, X.; Sankaran, B.; Du, F.; Shelton, C.L.; Herr, A.B.; Ji, J.Y.; Li, P. Structural basis for concerted recruitment and activation of IRF-3 by innate immune adaptor proteins. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, E3403–E3412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fitzgerald, K.A.; McWhirter, S.M.; Faia, K.L.; Rowe, D.C.; Latz, E.; Golenbock, D.T.; Coyle, A.J.; Liao, S.M. Maniatis, T. IKKepsilon and TBK1 are essential components of the IRF3 signaling pathway. Nat. Immunol. 2003, 4, 491–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, S.; tenOever, B.R.; Grandvaux, N.; Zhou, G.P.; Lin, R.; Hiscott, J. Triggering the interferon antiviral response through an IKK-related pathway. Science 2003, 300, 1148–1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panne, D.; McWhirter, S.M.; Maniatis, T.; Harrison, S.C. Interferon regulatory factor 3 is regulated by a dual phosphorylation-dependent switch. J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, 22816–22822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, B.Y.; Liu, C.; Srinath, H.; Lam, S.S.; Correia, J.J.; Derynck, R.; Lin, K. Crystal structure of IRF-3 in complex with CBP. Structure 2005, 13, 1269–1277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Servant, M.J.; Grandvaux, N.; tenOever, B.R.; Duguay, D.; Lin, R.; Hiscott, J. Identification of the minimal phosphoacceptor site required for in vivo activation of interferon regulatory factor 3 in response to virus and double-stranded RNA. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 9441–9447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clément, J.F.; Bibeau-Poirier, A.; Gravel, S.P.; Grandvaux, N.; Bonneil, E.; Thibault, P.; Meloche, S.; Servant, M.J. Phosphorylation of IRF-3 on Ser 339 generates a hyperactive form of IRF-3 through regulation of dimerization and CBP association. J. Virol. 2008, 82, 3984–3996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahasi, K.; Horiuchi, M.; Fujii, K.; Nakamura, S.; Noda, N.N.; Yoneyama, M.; Fujita, T.; Inagaki, F. Ser386 phosphorylation of transcription factor IRF-3 induces dimerization and association with CBP/p300 without overall conformational change. Genes Cells 2010, 15, 901–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mori, M.; Yoneyama, M.; Ito, T.; Takahashi, K.; Inagaki, F.; Fujita, T. Identification of Ser-386 of interferon regulatory factor 3 as critical target for inducible phosphorylation that determines activation. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 9698–9702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Srinath, H.; Lam, S.S.; Schiffer, C.A.; Royer, W.E., Jr.; Lin, K. Contribution of Ser386 and Ser396 to activation of interferon regulatory factor 3. J. Mol. Biol. 2008, 379, 251–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weaver, B.K.; Kumar, K.P.; Reich, N.C. Interferon regulatory factor 3 and CREB-binding protein/p300 are subunits of double-stranded RNA-activated transcription factor DRAF1. Mol. Cell. Biol. 1998, 18, 1359–1368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suhara, W.; Yoneyama, M.; Iwamura, T.; Yoshimura, S.; Tamura, K.; Namiki, H.; Aimoto, S.; Fujita, T. Analyses of virus-induced homomeric and heteromeric protein associations between IRF-3 and coactivator CBP/p300. J. Biochem. 2000, 128, 301–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Suhara, W.; Yoneyama, M.; Kitabayashi, I.; Fujita, T. Direct involvement of CREB-binding protein/p300 in sequence-specific DNA binding of virus-activated interferon regulatory factor-3 holocomplex. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 22304–22313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Lin, C.H.; Ma, G.; Orr, M.; Baffi, M.O.; Wathelet, M.G. Transcriptional activity of interferon regulatory factor (IRF)-3 depends on multiple protein-protein interactions. Eur. J. Biochem. 2002, 269, 6142–6151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dyson, H.J.; Wright, P.E. Role of Intrinsic Protein Disorder in the Function and Interactions of the Transcriptional Coactivators CREB-binding Protein (CBP) and p300. J. Biol. Chem. 2016, 291, 6714–6722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bedford, D.C.; Kasper, L.H.; Fukuyama, T.; Brindle, P.K. Target gene context influences the transcriptional requirement for the KAT3 family of CBP and p300 histone acetyltransferases. Epigenetics 2010, 5, 9–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos, Y.F.; Hestand, M.S.; Verlaan, M.; Krabbendam, E.; Ariyurek, Y.; van Galen, M.; van Dam, H.; van Ommen, G.J.; den Dunnen, J.T.; Zantema, A.; et al. Genome-wide assessment of differential roles for p300 and CBP in transcription regulation. Nucleic Acids Res. 2010, 38, 5396–5408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lipinski, M.; Del Blanco, B.; Barco, A. CBP/p300 in brain development and plasticity: Disentangling the KAT’s cradle. Curr. Opin. Neurobiol. 2019, 59, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Z.; Zhang, M.X.; Tang, Z.; Zhang, Q.; Ye, J.; Xiong, T.C.; Zhang, Z.D.; Zhong, B. USP22 promotes IRF3 nuclear translocation and antiviral responses by deubiquitinating the importin protein KPNA2. J. Exp. Med. 2020, 217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortega, E.; Rengachari, S.; Ibrahim, Z.; Hoghoughi, N.; Gaucher, J.; Holehouse, A.S.; Khochbin, S.; Panne, D. Transcription factor dimerization activates the p300 acetyltransferase. Nature 2018, 562, 538–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noyce, R.S.; Collins, S.E.; Mossman, K.L. Differential modification of interferon regulatory factor 3 following virus particle entry. J. Virol. 2009, 83, 4013–4022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spiegel, M.; Pichlmair, A.; Martinez-Sobrido, L.; Cros, J.; Garcia-Sastre, A.; Haller, O.; Weber, F. Inhibition of Beta interferon induction by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus suggests a two-step model for activation of interferon regulatory factor 3. J. Virol. 2005, 79, 2079–2086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grandvaux, N.; Servant, M.J.; tenOever, B.; Sen, G.C.; Balachandran, S.; Barber, G.N.; Lin, R.; Hiscott, J. Transcriptional profiling of interferon regulatory factor 3 target genes: Direct involvement in the regulation of interferon-stimulated genes. J. Virol. 2002, 76, 5532–5539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Ji, J.; Peng, D.; Ma, F.; Cheng, G.; Qin, F.X. Complex Regulation Pattern of IRF3 Activation Revealed by a Novel Dimerization Reporter System. J. Immunol. 2016, 196, 4322–4330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maniatis, T.; Falvo, J.V.; Kim, T.H.; Kim, T.K.; Lin, C.H.; Parekh, B.S.; Wathelet, M.G. Structure and function of the interferon-beta enhanceosome. Cold Spring Harb. Symp Quant. Biol. 1998, 63, 609–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merika, M.; Thanos, D. Enhanceosomes. Curr. Opin. Genet. Dev. 2001, 11, 205–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panne, D. The enhanceosome. Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 2008, 18, 236–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thanos, D.; Maniatis, T. Virus induction of human IFN beta gene expression requires the assembly of an enhanceosome. Cell 1995, 83, 1091–1100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munshi, N.; Agalioti, T.; Lomvardas, S.; Merika, M.; Chen, G.; Thanos, D. Coordination of a transcriptional switch by HMGI(Y) acetylation. Science 2001, 293, 1133–1136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agalioti, T.; Lomvardas, S.; Parekh, B.; Yie, J.; Maniatis, T.; Thanos, D. Ordered recruitment of chromatin modifying and general transcription factors to the IFN-beta promoter. Cell 2000, 103, 667–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imbalzano, A.N.; Kwon, H.; Green, M.R.; Kingston, R.E. Facilitated binding of TATA-binding protein to nucleosomal DNA. Nature 1994, 370, 481–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lomvardas, S.; Thanos, D. Modifying gene expression programs by altering core promoter chromatin architecture. Cell 2002, 110, 261–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrilenas, K.K.; Ramlall, V.; Kurland, J.; Leung, B.; Harbaugh, A.G.; Siggers, T. DNA-binding landscape of IRF3, IRF5 and IRF7 dimers: Implications for dimer-specific gene regulation. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018, 46, 2509–2520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, W.; Maniatis, T. An ATF/CREB binding site is required for virus induction of the human interferon beta gene [corrected]. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1992, 89, 2150–2154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrillo, R.J.; Dragan, A.I.; Privalov, P.L. Stability and DNA-binding ability of the bZIP dimers formed by the ATF-2 and c-Jun transcription factors. J. Mol. Biol. 2010, 396, 431–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hiscott, J.; Alper, D.; Cohen, L.; Leblanc, J.F.; Sportza, L.; Wong, A.; Xanthoudakis, S. Induction of human interferon gene expression is associated with a nuclear factor that interacts with the NF-kappa B site of the human immunodeficiency virus enhancer. J. Virol. 1989, 63, 2557–2566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lenardo, M.J.; Fan, C.M.; Maniatis, T.; Baltimore, D. The involvement of NF-kappa B in beta-interferon gene regulation reveals its role as widely inducible mediator of signal transduction. Cell 1989, 57, 287–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Visvanathan, K.V.; Goodbourn, S. Double-stranded RNA activates binding of NF-kappa B to an inducible element in the human beta-interferon promoter. Embo J. 1989, 8, 1129–1138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujii, Y.; Shimizu, T.; Kusumoto, M.; Kyogoku, Y.; Taniguchi, T.; Hakoshima, T. Crystal structure of an IRF-DNA complex reveals novel DNA recognition and cooperative binding to a tandem repeat of core sequences. Embo J. 1999, 18, 5028–5041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panne, D.; Maniatis, T.; Harrison, S.C. An atomic model of the interferon-beta enhanceosome. Cell 2007, 129, 1111–1123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Csumita, M.; Csermely, A.; Horvath, A.; Nagy, G.; Monori, F.; Goczi, L.; Orbea, H.A.; Reith, W.; Szeles, L. Specific enhancer selection by IRF3, IRF5 and IRF9 is determined by ISRE half-sites, 5′ and 3′ flanking bases, collaborating transcription factors and the chromatin environment in a combinatorial fashion. Nucleic Acids Res. 2020, 48, 589–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Apostolou, E.; Thanos, D. Virus Infection Induces NF-kappaB-dependent interchromosomal associations mediating monoallelic IFN-beta gene expression. Cell 2008, 134, 85–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nikopoulou, C.; Panagopoulos, G.; Sianidis, G.; Psarra, E.; Ford, E.; Thanos, D. The Transcription Factor ThPOK Orchestrates Stochastic Interchromosomal Interactions Required for IFNB1 Virus-Inducible Gene Expression. Mol. Cell 2018, 71, 352–3561.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thanos, D.; Maniatis, T. The high mobility group protein HMG I(Y) is required for NF-kappa B-dependent virus induction of the human IFN-beta gene. Cell 1992, 71, 777–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falvo, J.V.; Thanos, D.; Maniatis, T. Reversal of intrinsic DNA bends in the IFN beta gene enhancer by transcription factors and the architectural protein HMG I(Y). Cell 1995, 83, 1101–1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, T.K.; Maniatis, T. The mechanism of transcriptional synergy of an in vitro assembled interferon-beta enhanceosome. Mol. Cell 1997, 1, 119–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yie, J.; Merika, M.; Munshi, N.; Chen, G.; Thanos, D. The role of HMG I(Y) in the assembly and function of the IFN-beta enhanceosome. Embo J. 1999, 18, 3074–3089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, W.; Thanos, D.; Maniatis, T. Mechanisms of transcriptional synergism between distinct virus-inducible enhancer elements. Cell 1993, 74, 887–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merika, M.; Williams, A.J.; Chen, G.; Collins, T.; Thanos, D. Recruitment of CBP/p300 by the IFN beta enhanceosome is required for synergistic activation of transcription. Mol. Cell 1998, 1, 277–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujita, T.; Kimura, Y.; Miyamoto, M.; Barsoumian, E.L.; Taniguchi, T. Induction of endogenous IFN-alpha and IFN-beta genes by a regulatory transcription factor, IRF-1. Nature 1989, 337, 270–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujita, T.; Sakakibara, J.; Sudo, Y.; Miyamoto, M.; Kimura, Y.; Taniguchi, T. Evidence for a nuclear factor(s), IRF-1, mediating induction and silencing properties to human IFN-beta gene regulatory elements. Embo J. 1988, 7, 3397–3405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reis, L.F.; Harada, H.; Wolchok, J.D.; Taniguchi, T.; Vilcek, J. Critical role of a common transcription factor, IRF-1, in the regulation of IFN-beta and IFN-inducible genes. Embo J. 1992, 11, 185–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miyamoto, M.; Fujita, T.; Kimura, Y.; Maruyama, M.; Harada, H.; Sudo, Y.; Miyata, T.; Taniguchi, T. Regulated expression of a gene encoding a nuclear factor, IRF-1, that specifically binds to IFN-beta gene regulatory elements. Cell 1988, 54, 903–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuyama, T.; Kimura, T.; Kitagawa, M.; Pfeffer, K.; Kawakami, T.; Watanabe, N.; Kündig, T.M.; Amakawa, R.; Kishihara, K.; Wakeham, A.; et al. Targeted disruption of IRF-1 or IRF-2 results in abnormal type I IFN gene induction and aberrant lymphocyte development. Cell 1993, 75, 83–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reis, L.F.; Ruffner, H.; Stark, G.; Aguet, M.; Weissmann, C. Mice devoid of interferon regulatory factor 1 (IRF-1) show normal expression of type I interferon genes. Embo J. 1994, 13, 4798–4806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falvo, J.V.; Parekh, B.S.; Lin, C.H.; Fraenkel, E.; Maniatis, T. Assembly of a functional beta interferon enhanceosome is dependent on ATF-2-c-jun heterodimer orientation. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2000, 20, 4814–4825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panne, D.; Maniatis, T.; Harrison, S.C. Crystal structure of ATF-2/c-Jun and IRF-3 bound to the interferon-beta enhancer. Embo J. 2004, 23, 4384–4393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Escalante, C.R.; Nistal-Villan, E.; Shen, L.; Garcia-Sastre, A.; Aggarwal, A.K. Structure of IRF-3 bound to the PRDIII-I regulatory element of the human interferon-beta enhancer. Mol. Cell 2007, 26, 703–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Y.; Nussinov, R. The role of response elements organization in transcription factor selectivity: The IFN-beta enhanceosome example. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2011, 7, e1002077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, T.K.; Kim, T.H.; Maniatis, T. Efficient recruitment of TFIIB and CBP-RNA polymerase II holoenzyme by an interferon-beta enhanceosome in vitro. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1998, 95, 12191–12196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parekh, B.S.; Maniatis, T. Virus infection leads to localized hyperacetylation of histones H3 and H4 at the IFN-beta promoter. Mol. Cell 1999, 3, 125–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agalioti, T.; Chen, G.; Thanos, D. Deciphering the transcriptional histone acetylation code for a human gene. Cell 2002, 111, 381–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lomvardas, S.; Thanos, D. Nucleosome sliding via TBP DNA binding in vivo. Cell 2001, 106, 685–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cramer, P. Eukaryotic Transcription Turns 50. Cell 2019, 179, 808–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, Y.; Geiger, J.H.; Hahn, S.; Sigler, P.B. Crystal structure of a yeast TBP/TATA-box complex. Nature 1993, 365, 512–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Freaney, J.E.; Zhang, Q.; Yigit, E.; Kim, R.; Widom, J.; Wang, J.P.; Horvath, C.M. High-density nucleosome occupancy map of human chromosome 9p21-22 reveals chromatin organization of the type I interferon gene cluster. J. Interferon Cytokine Res. 2014, 34, 676–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zawatzky, R.; De Maeyer, E.; De Maeyer-Guignard, J. Identification of individual interferon-producing cells by in situ hybridization. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1985, 82, 1136–1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lipniacki, T.; Paszek, P.; Brasier, A.R.; Luxon, B.A.; Kimmel, M. Stochastic regulation in early immune response. Biophys. J. 2006, 90, 725–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Sealfon, S.C.; Hayot, F.; Jayaprakash, C.; Kumar, M.; Pendleton, A.C.; Ganee, A.; Fernandez-Sesma, A.; Moran, T.M.; Wetmur, J.G. Chromosome-specific and noisy IFNB1 transcription in individual virus-infected human primary dendritic Cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 2007, 35, 5232–5241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balachandran, S.; Beg, A.A. Defining emerging roles for NF-kappaB in antivirus responses: Revisiting the interferon-beta enhanceosome paradigm. PLoS Pathog. 2011, 7, e1002165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Senger, K.; Merika, M.; Agalioti, T.; Yie, J.; Escalante, C.R.; Chen, G.; Aggarwal, A.K.; Thanos, D. Gene repression by coactivator repulsion. Mol. Cell 2000, 6, 931–937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, C.S.; Feldman, K.E.; Lee, J.; Verma, S.; Huang, D.B.; Huynh, K.; Chang, M.; Ponomarenko, J.V.; Sun, S.C.; Benedict, C.A.; et al. The specificity of innate immune responses is enforced by repression of interferon response elements by NF-κB p50. Sci. Signal. 2011, 4, ra11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nourbakhsh, M.; Hauser, H. The transcriptional silencer protein NRF: A repressor of NF-kappa B enhancers. Immunobiology 1997, 198, 65–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nourbakhsh, M.; Hauser, H. Constitutive silencing of IFN-beta promoter is mediated by NRF (NF-kappaB-repressing factor), a nuclear inhibitor of NF-kappaB. Embo J. 1999, 18, 6415–6425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Hussain, S.; Wang, E.J.; Wang, X.; Li, M.O.; Garcia-Sastre, A.; Beg, A.A. Lack of essential role of NF-kappa B p50, RelA, and cRel subunits in virus-induced type 1 IFN expression. J. Immunol. 2007, 178, 6770–6776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basagoudanavar, S.H.; Thapa, R.J.; Nogusa, S.; Wang, J.; Beg, A.A.; Balachandran, S. Distinct roles for the NF-kappa B RelA subunit during antiviral innate immune responses. J. Virol. 2011, 85, 2599–2610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Basagoudanavar, S.H.; Wang, X.; Hopewell, E.; Albrecht, R.; García-Sastre, A.; Balachandran, S.; Beg, A.A. NF-kappa B RelA subunit is crucial for early IFN-beta expression and resistance to RNA virus replication. J. Immunol. 2010, 185, 1720–1729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Josse, T.; Mokrani-Benhelli, H.; Benferhat, R.; Shestakova, E.; Mansuroglu, Z.; Kakanakou, H.; Billecocq, A.; Bouloy, M.; Bonnefoy, E. Association of the interferon-β gene with pericentromeric heterochromatin is dynamically regulated during virus infection through a YY1-dependent mechanism. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012, 40, 4396–4411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zan, J.; Zhang, H.; Gu, A.P.; Zhong, K.L.; Lu, M.Y.; Bai, X.X.; Zhang, J.Y.; Cai, J. Yin Yang 1 Dynamically Regulates Antiviral Innate Immune Responses During Viral Infection. Cell Physiol. Biochem. 2017, 44, 607–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klar, M.; Bode, J. Enhanceosome formation over the beta interferon promoter underlies a remote-control mechanism mediated by YY1 and YY2. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2005, 25, 10159–10170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weill, L.; Shestakova, E.; Bonnefoy, E. Transcription factor YY1 binds to the murine beta interferon promoter and regulates its transcriptional capacity with a dual activator/repressor role. J. Virol. 2003, 77, 2903–2914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mokrani, H.; Sharaf el Dein, O.; Mansuroglu, Z.; Bonnefoy, E. Binding of YY1 to the proximal region of the murine beta interferon promoter is essential to allow CBP recruitment and K8H4/K14H3 acetylation on the promoter region after virus infection. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2006, 26, 8551–8561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Banerjee, A.R.; Kim, Y.J.; Kim, T.H. A novel virus-inducible enhancer of the interferon-β gene with tightly linked promoter and enhancer activities. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014, 42, 12537–12554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sin, W.X.; Li, P.; Yeong, J.P.; Chin, K.C. Activation and regulation of interferon-β in immune responses. Immunol. Res. 2012, 53, 25–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; He, C.; Wang, L.; Ge, B. Post-translational regulation of antiviral innate signaling. Eur. J. Immunol. 2017, 47, 1414–1426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, M.; Zhang, T.; lin, W.; Liu, Z.; Lai, R.; Xia, D.; Huang, H.; Wang, X. Protein phosphatase PP1 negatively regulates the Toll-like receptor- and RIG-I-like receptor-triggered production of type I interferon by inhibiting IRF3 phosphorylation at serines 396 and 385 in macrophage. Cell Signal. 2014, 26, 2930–2939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Wang, Q.; Xu, X.; Xie, B.; Zhao, Y.; Li, N.; Cao, X. The methyltransferase NSD3 promotes antiviral innate immunity via direct lysine methylation of IRF3. J. Exp. Med. 2017, 214, 3597–3610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Li, M.; Xue, Y.; Li, Z.; Wen, W.; Liu, X.; Cao, X. Interferon-inducible cytoplasmic lncLrrc55-AS promotes antiviral innate responses by strengthening IRF3 phosphorylation. Cell Res. 2019, 29, 641–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, L.; Deng, Y.; Yao, F.; Guan, D.; Feng, Y.; Jiang, H.; Li, X.; Hu, P.; Lu, X.; Wang, H.; et al. Recruitment of phosphatase PP2A by RACK1 adaptor protein deactivates transcription factor IRF3 and limits type I interferon signaling. Immunity 2014, 40, 515–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Zhang, L.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, H.; Gao, J.; Wang, Q.; Tian, Z.; Xuan, L.; Chen, H.; Wang, Y. PP2A Facilitates Porcine Reproductive and Respiratory Syndrome Virus Replication by Deactivating irf3 and Limiting Type I Interferon Production. Viruses 2019, 11, 948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, G.; Reinert, J.T.; Pitha-Rowe, I.; Okumura, A.; Kellum, M.; Knobeloch, K.P.; Hassel, B.; Pitha, P.M. ISG15 enhances the innate antiviral response by inhibition of IRF-3 degradation. Cell Mol. Biol. (Noisy-le-grand) 2006, 52, 29–41. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, H.X.; Yang, K.; Liu, X.; Liu, X.Y.; Wei, B.; Shan, Y.F.; Zhu, L.H.; Wang, C. Positive regulation of interferon regulatory factor 3 activation by Herc5 via ISG15 modification. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2010, 30, 2424–2436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saitoh, T.; Tun-Kyi, A.; Ryo, A.; Yamamoto, M.; Finn, G.; Fujita, T.; Akira, S.; Yamamoto, N.; Lu, K.P.; Yamaoka, S. Negative regulation of interferon-regulatory factor 3-dependent innate antiviral response by the prolyl isomerase Pin1. Nat. Immunol. 2006, 7, 598–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Xie, F.; Chu, F.; Zhang, Z.; Yang, B.; Dai, T.; Gao, L.; Wang, L.; Ling, L.; Jia, J.; et al. YAP antagonizes innate antiviral immunity and is targeted for lysosomal degradation through IKKɛ-mediated phosphorylation. Nat. Immunol. 2017, 18, 733–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.; Zhu, M.; Pan, R.; Fang, T.; Cao, Y.Y.; Chen, S.; Zhao, X.; Lei, C.Q.; Guo, L.; Chen, Y.; et al. The tumor suppressor PTEN has a critical role in antiviral innate Immunity. Nat. Immunol. 2016, 17, 241–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karpova, A.Y.; Trost, M.; Murray, J.M.; Cantley, L.C.; Howley, P.M. Interferon regulatory factor-3 is an in vivo target of DNA-PK. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 2818–2823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prinarakis, E.; Chantzoura, E.; Thanos, D.; Spyrou, G. S-glutathionylation of IRF3 regulates IRF3-CBP interaction and activation of the IFN beta pathway. Embo J. 2008, 27, 865–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumthip, K.; Yang, D.; Li, N.L.; Zhang, Y.; Fan, M.; Sethuraman, A.; Li, K. Pivotal role for the ESCRT-II complex subunit EAP30/SNF8 in IRF3-dependent innate antiviral defense. PLoS Pathog. 2017, 13, e1006713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Sun, X.; Yi, C.; Zhang, D.; Lin, X.; Sun, X.; Chen, H.; Jin, M. AGO2 Negatively Regulates Type I Interferon Signaling Pathway by Competition Binding IRF3 with CBP/p300. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2017, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, F.; Wang, P.; Yang, L.; Yang, G.; Zhao, Y.O.; Qian, F.; Walker, W.; Sutton, R.; Montgomery, R.; Lin, R.; et al. ELF4 is critical for induction of type I interferon and the host antiviral response. Nat. Immunol. 2013, 14, 1237–1246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Wong, J.J.; Sum, C.; Sin, W.X.; Ng, K.Q.; Koh, M.B.; Chin, K.C. IRF8 and IRF3 cooperatively regulate rapid interferon-beta induction in human blood monocytes. Blood 2011, 117, 2847–2854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, Y.; Hayward, G.S. The ubiquitin E3 ligase RAUL negatively regulates type i interferon through ubiquitination of the transcription factors IRF7 and IRF3. Immunity 2010, 33, 863–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higgs, R.; Ni Gabhann, J.; Ben Larbi, N.; Breen, E.P.; Fitzgerald, K.A.; Jefferies, C.A. The E3 ubiquitin ligase Ro52 negatively regulates IFN-beta production post-pathogen recognition by polyubiquitin-mediated degradation of IRF3. J. Immunol. 2008, 181, 1780–1786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, K.; Shi, H.X.; Liu, X.Y.; Shan, Y.F.; Wei, B.; Chen, S.; Wang, C. TRIM21 is essential to sustain IFN regulatory factor 3 activation during antiviral response. J. Immunol. 2009, 182, 3782–3792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ran, Y.; Liu, T.T.; Zhou, Q.; Li, S.; Mao, A.P.; Li, Y.; Liu, L.J.; Cheng, J.K.; Shu, H.B. SENP2 negatively regulates cellular antiviral response by deSUMOylating IRF3 and conditioning it for ubiquitination and degradation. J. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2011, 3, 283–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kubota, T.; Matsuoka, M.; Chang, T.H.; Tailor, P.; Sasaki, T.; Tashiro, M.; Kato, A.; Ozato, K. Virus infection triggers SUMOylation of IRF3 and IRF7, leading to the negative regulation of type I interferon gene expression. J. Biol. Chem. 2008, 283, 25660–25670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meng, F.; Zhou, R.; Wu, S.; Zhang, Q.; Jin, Q.; Zhou, Y.; Plouffe, S.W.; Liu, S.; Song, H.; Xia, Z.; et al. Mst1 shuts off cytosolic antiviral defense through IRF3 phosphorylation. Genes Dev. 2016, 30, 1086–1100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, S.; Lee, J.J.; Kim, H.J.; Lee, J.Y.; Chang, J.; Lee, K.J. Fas-Associated Factor 1 Negatively Regulates the Antiviral Immune Response by Inhibiting Translocation of Interferon Regulatory Factor 3 to the Nucleus. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2016, 36, 1136–1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, W.; Wang, C.; Wang, Q.; Zhao, D.; Zhao, K.; Sun, D.; Liu, X.; Han, C.; Hou, J.; Li, X.; et al. Bromodomain protein Brd3 promotes Ifnb1 transcription via enhancing IRF3/p300 complex formation and recruitment to Ifnb1 promoter in macrophages. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 39986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Wang, D.; Wang, P.; Zhao, Y.; You, F. OTUD1 Negatively Regulates Type I IFN Induction by Disrupting Noncanonical Ubiquitination of IRF3. J. Immunol. 2020, 204, 1904–1918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huerga Encabo, H.; Traveset, L.; Argilaguet, J.; Angulo, A.; Nistal-Villan, E.; Jaiswal, R.; Escalante, C.R.; Gekas, C.; Meyerhans, A.; Aramburu, J.; et al. The transcription factor NFAT5 limits infection-induced type I interferon responses. J. Exp. Med. 2020, 217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.; Seed, B. The transcription factor MafB antagonizes antiviral responses by blocking recruitment of coactivators to the transcription factor IRF3. Nat. Immunol. 2010, 11, 743–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bibeau-Poirier, A.; Gravel, S.P.; Clément, J.F.; Rolland, S.; Rodier, G.; Coulombe, P.; Hiscott, J.; Grandvaux, N.; Meloche, S.; Servant, M.J. Involvement of the IkappaB kinase (IKK)-related kinases tank-binding kinase 1/IKKi and cullin-based ubiquitin ligases in IFN regulatory factor-3 degradation. J. Immunol. 2006, 177, 5059–5067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, J.; Maniatis, T. Negative Regulation of Interferon-β Gene Expression during Acute and Persistent Virus Infections. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e20681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lei, C.Q.; Zhang, Y.; Xia, T.; Jiang, L.Q.; Zhong, B.; Shu, H.B. FoxO1 negatively regulates cellular antiviral response by promoting degradation of IRF3. J. Biol. Chem. 2013, 288, 12596–12604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, P.; Zhao, W.; Zhao, K.; Zhang, L.; Gao, C. TRIM26 negatively regulates interferon-β production and antiviral response through polyubiquitination and degradation of nuclear IRF3. PLoS Pathog. 2015, 11, e1004726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Tian, Y.; Wang, R.P.; Gao, D.; Zhang, Y.; Diao, F.C.; Chen, D.Y.; Zhai, Z.H.; Shu, H.B. Negative feedback regulation of cellular antiviral signaling by RBCK1-mediated degradation of IRF3. Cell Res. 2008, 18, 1096–1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sears, N.; Sen, G.C.; Stark, G.R.; Chattopadhyay, S. Caspase-8-mediated cleavage inhibits IRF-3 protein by facilitating its proteasome-mediated degradation. J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 33037–33044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, W.W.; Lian, H.; Zhong, B.; Shu, H.B.; Li, S. Krüppel-like factor 4 negatively regulates cellular antiviral immune response. Cell Mol. Immunol. 2016, 13, 65–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huai, W.; Liu, X.; Wang, C.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, X.; Chen, X.; Xu, S.; Thomas, T.; Li, N.; Cao, X. KAT8 selectively inhibits antiviral immunity by acetylating IRF3. J. Exp. Med. 2019, 216, 772–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schoggins, J.W.; Wilson, S.J.; Panis, M.; Murphy, M.Y.; Jones, C.T.; Bieniasz, P.; Rice, C.M. A diverse range of gene products are effectors of the type I interferon antiviral response. Nature 2011, 472, 481–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, D.; Fu, S.; Wu, Z.; Yang, W.; Ru, Y.; Shu, H.; Liu, X.; Zheng, H. DDX56 inhibits type I interferon by disrupting assembly of IRF3-IPO5 to inhibit IRF3 nucleus import. J. Cell Sci. 2019, 133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Liu, X.; Cheng, T.; Xiao, R.; Gao, Q.; Ming, F.; Jin, M.; Chen, H.; Zhou, H. LYAR Suppresses Beta Interferon Induction by Targeting Phosphorylated Interferon Regulatory Factor 3. J. Virol. 2019, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Guo, G.; Lu, M.; Chai, W.; Li, Y.; Tong, X.; Li, J.; Jia, X.; Liu, W.; Qi, D.; et al. Long Noncoding RNA Lnc-MxA Inhibits Beta Interferon Transcription by Forming RNA-DNA Triplexes at Its Promoter. J. Virol. 2019, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gyory, I.; Wu, J.; Fejer, G.; Seto, E.; Wright, K.L. PRDI-BF1 recruits the histone H3 methyltransferase G9a in transcriptional silencing. Nat. Immunol. 2004, 5, 299–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keller, A.D.; Maniatis, T. Identification and characterization of a novel repressor of beta-interferon gene expression. Genes Dev. 1991, 5, 868–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Sheng, C.; Yao, C.; Chen, H.; Wang, D.; Chen, S. The EF-Hand Protein CALML6 Suppresses Antiviral Innate Immunity by Impairing IRF3 Dimerization. Cell Rep. 2019, 26, 1273–1285.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gates, L.T.; Shisler, J.L. cFLIPL Interrupts IRF3-CBP-DNA Interactions To Inhibit IRF3-Driven Transcription. J. Immunol. 2016, 197, 923–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Ma, L.; Chen, X. Interferon regulatory factor 3-CL, an isoform of IRF3, antagonizes activity of IRF3. Cell Mol. Immunol. 2011, 8, 67–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karpova, A.Y.; Ronco, L.V.; Howley, P.M. Functional characterization of interferon regulatory factor 3a (IRF-3a), an alternative splice isoform of IRF-3. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2001, 21, 4169–4176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karpova, A.Y.; Howley, P.M.; Ronco, L.V. Dual utilization of an acceptor/donor splice site governs the alternative splicing of the IRF-3 gene. Genes Dev. 2000, 14, 2813–2818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Marozin, S.; Altomonte, J.; Stadler, F.; Thasler, W.E.; Schmid, R.M.; Ebert, O. Inhibition of the IFN-beta response in hepatocellular carcinoma by alternative spliced isoform of IFN regulatory factor-3. Mol. Ther. 2008, 16, 1789–1797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhai, J.; Gao, D.; Liu, W.; Hong, R.; Qin, Y.; Ouyang, H.; Kong, Y.; Wang, Y.; Xie, Y.; Liu, J. Characterization of a novel isoform of murine interferon regulatory factor 3. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2008, 377, 384–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ronco, L.V.; Karpova, A.Y.; Vidal, M.; Howley, P.M. Human papillomavirus 16 E6 oncoprotein binds to interferon regulatory factor-3 and inhibits its transcriptional activity. Genes Dev. 1998, 12, 2061–2072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Juang, Y.T.; Lowther, W.; Kellum, M.; Au, W.C.; Lin, R.; Hiscott, J.; Pitha, P.M. Primary activation of interferon A and interferon B gene transcription by interferon regulatory factor 3. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1998, 95, 9837–9842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, K.E.; Mossman, K.L. Recent advances in understanding viral evasion of type I interferon. Immunology 2013, 138, 190–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orzalli, M.H.; Knipe, D.M. Cellular sensing of viral DNA and viral evasion mechanisms. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 2014, 68, 477–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coccia, E.M.; Battistini, A. Early IFN type I response: Learning from microbial evasion strategies. Semin. Immunol. 2015, 27, 85–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schulz, K.S.; Mossman, K.L. Viral Evasion Strategies in Type I IFN Signaling-A Summary of Recent Developments. Front. Immunol. 2016, 7, 498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, C.; Anderson, P.; Hahm, B. Viral dedication to vigorous destruction of interferon receptors. Virology 2018, 522, 19–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banete, A.; Seaver, K.; Bakshi, D.; Gee, K.; Basta, S. On taking the STING out of immune activation. J. Leukoc Biol. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abe, T.; Marutani, Y.; Shoji, I. Cytosolic DNA-sensing immune response and viral infection. Microbiol. Immunol. 2019, 63, 51–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, H.C.; Chathuranga, K.; Lee, J.S. Intracellular sensing of viral genomes and viral evasion. Exp. Mol. Med. 2019, 51, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guan, X.; Zhang, M.; Fu, M.; Luo, S.; Hu, Q. Herpes Simplex Virus Type 2 Immediate Early Protein ICP27 Inhibits IFN-β Production in Mucosal Epithelial Cells by Antagonizing IRF3 Activation. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Z.; Li, P.; Yang, F.; Cao, W.; Zhang, X.; Dang, W.; Ma, X.; Tian, H.; Zhang, K.; Zhang, M.; et al. Peste des Petits Ruminants Virus Nucleocapsid Protein Inhibits Beta Interferon Production by Interacting with IRF3 To Block Its Activation. J. Virol. 2019, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, H.; Zheng, C.; Xing, J.; Wang, S.; Li, S.; Lin, R.; Ma, X.; Tian, H.; Zhang, K.; Zhang, M.; et al. Varicella-zoster virus immediate-early protein ORF61 abrogates the IRF3-mediated innate immune response through degradation of activated IRF3. J. Virol. 2011, 85, 11079–11089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bowie, A.G.; Unterholzner, L. Viral evasion and subversion of pattern-recognition receptor signalling. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2008, 8, 911–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zinzula, L.; Tramontano, E. Strategies of highly pathogenic RNA viruses to block dsRNA detection by RIG-I-like receptors: Hide, mask, hit. Antivir. Res. 2013, 100, 615–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grandvaux, N.; tenOever, B.R.; Servant, M.J.; Hiscott, J. The interferon antiviral response: From viral invasion to evasion. Curr. Opin. Infect. Dis. 2002, 15, 259–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber, F.; Haller, O. Viral suppression of the interferon system. Biochimie 2007, 89, 836–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Randall, R.E.; Goodbourn, S. Interferons and viruses: An interplay between induction, signalling, antiviral responses and virus countermeasures. J. Gen. Virol. 2008, 89, 1–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marsili, G.; Perrotti, E.; Remoli, A.L.; Acchioni, C.; Sgarbanti, M.; Battistini, A. IFN Regulatory Factors and Antiviral Innate Immunity: How Viruses Can Get Better. J. Interferon Cytokine Res. 2016, 36, 414–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garcia-Sastre, A. Ten Strategies of Interferon Evasion by Viruses. Cell Host Microbe 2017, 22, 176–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiang, H.S.; Liu, H.M. The Molecular Basis of Viral Inhibition of IRF- and STAT-Dependent Immune Responses. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 3086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hagmaier, K.; Gelderblom, H.R.; Kochs, G. Functional comparison of the two gene products of Thogoto virus segment 6. J. Gen. Virol. 2004, 85, 3699–3708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jennings, S.; Martinez-Sobrido, L.; Garcia-Sastre, A.; Weber, F.; Kochs, G. Thogoto virus ML protein suppresses IRF3 function. Virology 2005, 331, 63–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Vogt, C.; Preuss, E.; Mayer, D.; Weber, F.; Schwemmle, M.; Kochs, G. The interferon antagonist ML protein of thogoto virus targets general transcription factor IIB. J. Virol. 2008, 82, 11446–11453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haas, D.A.; Meiler, A.; Geiger, K.; Vogt, C.; Preuss, E.; Kochs, G.; Pichlmair, A. Viral targeting of TFIIB impairs de novo polymerase II recruitment and affects antiviral Immunity. PLoS Pathog. 2018, 14, e1006980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lidsky, P.V.; Hato, S.; Bardina, M.V.; Aminev, A.G.; Palmenberg, A.C.; Sheval, E.V.; Polyakov, V.Y.; van Kuppeveld, F.J.; Agol, V.I. Nucleocytoplasmic traffic disorder induced by cardioviruses. J. Virol. 2006, 80, 2705–2717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hato, S.V.; Ricour, C.; Schulte, B.M.; Lanke, K.H.; de Bruijni, M.; Zoll, J.; Melchers, W.J.; Michiels, T.; van Kuppeveld, F.J. The mengovirus leader protein blocks interferon-alpha/beta gene transcription and inhibits activation of interferon regulatory factor 3. Cell Microbiol. 2007, 9, 2921–2930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Delhaye, S.; van Pesch, V.; Michiels, T. The leader protein of Theiler’s virus interferes with nucleocytoplasmic trafficking of cellular proteins. J. Virol. 2004, 78, 4357–4362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ricour, C.; Delhaye, S.; Hato, S.V.; Olenyik, T.D.; Michel, B.; van Kuppeveld, F.J.; Gustin, K.E.; Michiels, T. Inhibition of mRNA export and dimerization of interferon regulatory factor 3 by Theiler’s virus leader protein. J. Gen. Virol. 2009, 90, 177–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Wang, K.; Lin, R.; Zheng, C. Herpes simplex virus 1 serine/threonine kinase US3 hyperphosphorylates IRF3 and inhibits beta interferon production. J. Virol. 2013, 87, 12814–12827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, B.; Paterson, R.G.; Stock, N.; Durbin, J.E.; Durbin, R.K.; Goodbourn, S.; Randall, R.E.; Lamb, R.A. Recovery of paramyxovirus simian virus 5 with a V protein lacking the conserved cysteine-rich domain: The multifunctional V protein blocks both interferon-beta induction and interferon signaling. Virology 2002, 303, 15–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Donelan, N.R.; Dauber, B.; Wang, X.; Basler, C.F.; Wolff, T.; Garcia-Sastre, A. The N- and C-terminal domains of the NS1 protein of influenza B virus can independently inhibit IRF-3 and beta interferon promoter activation. J. Virol. 2004, 78, 11574–11582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paladino, P.; Collins, S.E.; Mossman, K.L. Cellular localization of the herpes simplex virus ICP0 protein dictates its ability to block IRF3-mediated innate immune responses. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e10428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakaguchi, T.; Irie, T.; Kuwayama, M.; Ueno, T.; Yoshida, A.; Kawabata, R. Analysis of interaction of Sendai virus V protein and melanoma differentiation-associated gene 5. Microbiol. Immunol. 2011, 55, 760–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kato, H.; Sato, S.; Yoneyama, M.; Yamamoto, M.; Uematsu, S.; Matsui, K.; Tsujimura, T.; Takeda, K.; Fujita, T.; Takeuchi, O.; et al. Cell type-specific involvement of RIG-I in antiviral response. Immunity 2005, 23, 19–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melchjorsen, J.; Jensen, S.B.; Malmgaard, L.; Rasmussen, S.B.; Weber, F.; Bowie, A.G.; Matikainen, S.; Paludan, S.R. Activation of innate defense against a paramyxovirus is mediated by RIG-I and TLR7 and TLR8 in a cell-type-specific manner. J. Virol. 2005, 79, 12944–12951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kato, H.; Takeuchi, O.; Sato, S.; Yoneyama, M.; Yamamoto, M.; Matsui, K.; Uematsu, S.; Jung, A.; Kawai, T.; Ishii, K.J.; et al. Differential roles of MDA5 and RIG-I helicases in the recognition of RNA Viruses. Nature 2006, 441, 101–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Irie, T.; Kiyotani, K.; Igarashi, T.; Yoshida, A.; Sakaguchi, T. Inhibition of Interferon Regulatory Factor 3 Activation by Paramyxovirus V Protein. J. Virol. 2012, 86, 7136–7145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, J.; Chen, Z.; Li, Y.; Zhao, Z.; He, W.; Zohaib, A.; Song, Y.; Deng, C.; Zhang, B.; Chen, H.; et al. Japanese Encephalitis Virus NS5 Inhibits Type I Interferon (IFN) Production by Blocking the Nuclear Translocation of IFN Regulatory Factor 3 and NF-κB. J. Virol. 2017, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gagne, B.; Tremblay, N.; Park, A.Y.; Baril, M.; Lamarre, D. Importin beta1 targeting by hepatitis C virus NS3/4A protein restricts IRF3 and NF-kappaB signaling of IFNB1 antiviral response. Traffic 2017, 18, 362–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, J.; Liu, T.; Pang, L.; Li, K.; Garofalo, R.P.; Casola, A.; Bao, X. A novel mechanism for the inhibition of interferon regulatory factor-3-dependent gene expression by human respiratory syncytial virus NS1 protein. J. Gen. Virol. 2011, 92, 2153–2159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, D.; Huang, S.M.; Baglia, L.A.; McCance, D.J. The E6 protein of human papillomavirus type 16 binds to and inhibits co-activation by CBP and p300. Embo J. 1999, 18, 5061–5072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, J.; Ni, L.; Wang, S.; Wang, K.; Lin, R.; Zheng, C. Herpes Simplex Virus 1-Encoded Tegument Protein VP16 Abrogates the Production of Beta Interferon (IFN) by Inhibiting NF-κB Activation and Blocking IFN Regulatory Factor 3 To Recruit Its Coactivator CBP. J. Virol. 2013, 87, 9788–9801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, S.; Kim, K.S.; Flano, E.; Wu, T.-T.; Tong, L.M.; Park, A.N.; Song, M.J.; Sanchez, D.J.; O’Connell, R.M.; Cheng, G.; et al. Conserved Herpesviral Kinase Promotes Viral Persistence by Inhibiting the IRF-3-Mediated Type I Interferon Response. Cell Host Microbe 2009, 5, 166–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myoung, J.; Lee, S.A.; Lee, H.R. Beyond Viral Interferon Regulatory Factors: Immune Evasion Strategies. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2019, 29, 1873–1881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burýsek, L.; Yeow, W.S.; Lubyová, B.; Kellum, M.; Schafer, S.L.; Huang, Y.Q.; Pitha, P.M. Functional analysis of human herpesvirus 8-encoded viral interferon regulatory factor 1 and its association with cellular interferon regulatory factors and p300. J. Virol. 1999, 73, 7334–7342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, T.; Lee, D.; Lee, B.; Chung, J.H.; Choe, J. Viral interferon regulatory factor 1 of Kaposi’s sarcoma-associated herpesvirus (human herpesvirus 8) binds to, and inhibits transactivation of, CREB-binding protein. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2000, 270, 23–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, R.; Genin, P.; Mamane, Y.; Sgarbanti, M.; Battistini, A.; Harrington, W.J., Jr.; Barber, G.N.; Hiscott, J. HHV-8 encoded vIRF-1 represses the interferon antiviral response by blocking IRF-3 recruitment of the CBP/p300 coactivators. Oncogene 2001, 20, 800–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fuld, S.; Cunningham, C.; Klucher, K.; Davison, A.J.; Blackbourn, D.J. Inhibition of interferon signaling by the Kaposi’s sarcoma-associated herpesvirus full-length viral interferon regulatory factor 2 protein. J. Virol. 2006, 80, 3092–3097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morin, G.; Robinson, B.A.; Rogers, K.S.; Wong, S.W. A Rhesus Rhadinovirus Viral Interferon (IFN) Regulatory Factor Is Virion Associated and Inhibits the Early IFN Antiviral Response. J. Virol. 2015, 89, 7707–7721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, M.; Kim, C.Y.; Rowland, R.R.; Fang, Y.; Kim, D.; Yoo, D. Biogenesis of non-structural protein 1 (nsp1) and nsp1-mediated type I interferon modulation in arteriviruses. Virology 2014, 458, 136–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, M.; Du, Y.; Song, C.; Yoo, D. Degradation of CREB-binding protein and modulation of type I interferon induction by the zinc finger motif of the porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus nsp1alpha subunit. Virus Res. 2013, 172, 54–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, O.; Sun, Y.; Lai, F.W.; Song, C.; Yoo, D. Modulation of type I interferon induction by porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus and degradation of CREB-binding protein by non-structural protein 1 in MARC-145 and HeLa Cells. Virology 2010, 402, 315–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Shi, K.; Yoo, D. Suppression of type I interferon production by porcine epidemic diarrhea virus and degradation of CREB-binding protein by nsp1. Virology 2016, 489, 252–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Zheng, Z.; Luo, H.; Meng, J.; Li, H.; Li, Q.; Zhang, X.; Ke, X.; Bai, B.; Mao, P.; et al. Human bocavirus NP1 inhibits IFN-β production by blocking association of IFN regulatory factor 3 with IFNB promoter. J. Immunol. 2012, 189, 1144–1153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Liu, Y.; Wang, P.; Guan, X.; He, S.; Luo, S.; Li, C.; Hu, K.; Jin, W.; Du, T.; et al. HSV-2 immediate-early protein US1 inhibits IFN-β production by suppressing association of IRF-3 with IFN-β promoter. J. Immunol. 2015, 194, 3102–3115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wuerth, J.D.; Habjan, M.; Wulle, J.; Superti-Furga, G.; Pichlmair, A.; Weber, F. NSs Protein of Sandfly Fever Sicilian Phlebovirus Counteracts Interferon (IFN) Induction by Masking the DNA-Binding Domain of IFN Regulatory Factor 3. J. Virol. 2018, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Melroe, G.T.; Silva, L.; Schaffer, P.A.; Knipe, D.M. Recruitment of activated IRF-3 and CBP/p300 to herpes simplex virus ICP0 nuclear foci: Potential role in blocking IFN-beta induction. Virology 2007, 360, 305–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Jiang, Y.; Geiser, V.; Zhou, J.; Jones, C. Bovine herpesvirus 1 immediate-early protein (bICP0) interacts with the histone acetyltransferase p300, which stimulates productive infection and gC promoter activity. J. Gen. Virol. 2006, 87, 1843–1851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.T.; Doong, S.L.; Teng, S.C.; Lee, C.P.; Tsai, C.H.; Chen, M.R. Epstein-Barr virus BGLF4 kinase suppresses the interferon regulatory factor 3 signaling pathway. J. Virol. 2009, 83, 1856–1869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cloutier, N.; Flamand, L. Kaposi sarcoma-associated herpesvirus latency-associated nuclear antigen inhibits interferon (IFN) beta expression by competing with IFN regulatory factor-3 for binding to IFNB promoter. J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 7208–7221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, Y.Z.; Su, S.; Zou, H.M.; Guo, Y.; Wang, S.Y.; Li, S.; Luo, M.H.; Wang, Y.Y. Human Cytomegalovirus DNA Polymerase Subunit UL44 Antagonizes Antiviral Immune Responses by Suppressing IRF3- and NF-kappaB-Mediated Transcription. J. Virol. 2019, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lefort, S.; Soucy-Faulkner, A.; Grandvaux, N.; Flamand, L. Binding of Kaposi’s sarcoma-associated herpesvirus K-bZIP to interferon-responsive factor 3 elements modulates antiviral gene expression. J. Virol. 2007, 81, 10950–10960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le May, N.; Mansuroglu, Z.; Léger, P.; Josse, T.; Blot, G.; Billecocq, A.; Flick, R.; Jacob, Y.; Bonnefoy, E.; Bouloy, M. A SAP30 complex inhibits IFN-beta expression in Rift Valley fever virus infected Cells. PLoS Pathog. 2008, 4, e13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwanaszko, M.; Kimmel, M. NF-κB and IRF pathways: Cross-regulation on target genes promoter level. BMC Genom. 2015, 16, 307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marineau, A.; Khan, K.A.; Servant, M.J. Roles of GSK-3 and beta-Catenin in Antiviral Innate Immune Sensing of Nucleic Acids. Cells 2020, 9, 897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Schwanke, H.; Stempel, M.; Brinkmann, M.M. Of Keeping and Tipping the Balance: Host Regulation and Viral Modulation of IRF3-Dependent IFNB1 Expression. Viruses 2020, 12, 733. https://doi.org/10.3390/v12070733
Schwanke H, Stempel M, Brinkmann MM. Of Keeping and Tipping the Balance: Host Regulation and Viral Modulation of IRF3-Dependent IFNB1 Expression. Viruses. 2020; 12(7):733. https://doi.org/10.3390/v12070733
Chicago/Turabian StyleSchwanke, Hella, Markus Stempel, and Melanie M. Brinkmann. 2020. "Of Keeping and Tipping the Balance: Host Regulation and Viral Modulation of IRF3-Dependent IFNB1 Expression" Viruses 12, no. 7: 733. https://doi.org/10.3390/v12070733
APA StyleSchwanke, H., Stempel, M., & Brinkmann, M. M. (2020). Of Keeping and Tipping the Balance: Host Regulation and Viral Modulation of IRF3-Dependent IFNB1 Expression. Viruses, 12(7), 733. https://doi.org/10.3390/v12070733





