Parechovirus A Pathogenesis and the Enigma of Genotype A-3
Abstract
:1. Introduction
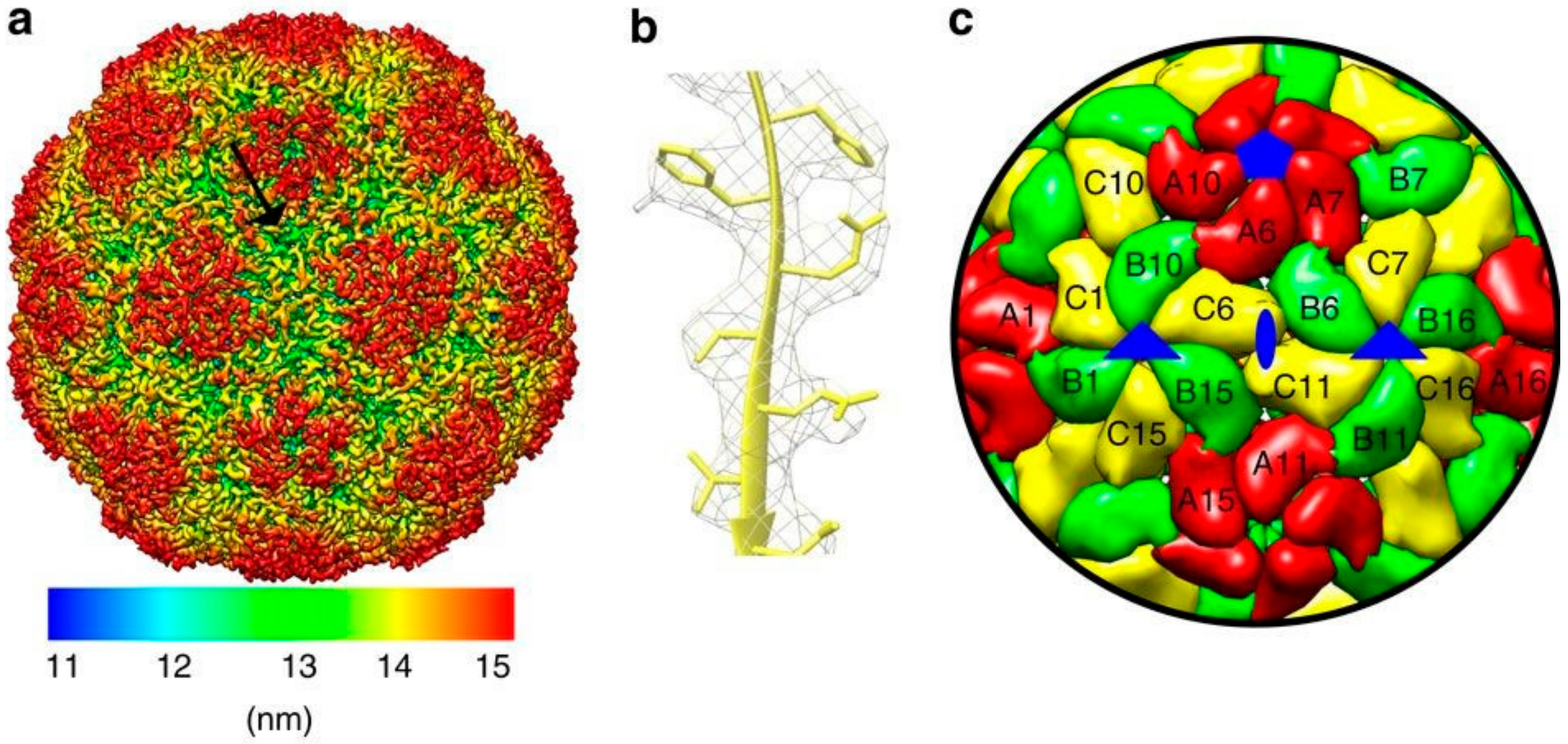
2. Genome and Structure
3. Classification
Evolution
4. Epidemiology
5. Life Cycle
Receptors
6. Pathogenesis
6.1. Clinical Manifestation and Detection
6.2. Immune Response
7. PeV-A3 Stands Out Amongst the PeV-A Genotypes
Host Responses Gone Astray?
8. Treatment
9. Outlook
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| PeV-A | Parechovirus A |
| EV | Enterovirus |
| nt | Nucleotide |
| UTR | Untranslated region |
| CPE | Cytopathogenic effect |
| nAbs | Neutralizing antibodies |
| CV | Coxsackievirus |
| RGD | Arginine-glycine-aspartic acid |
| ITG | Integrin |
| mAbs | Monoclonal antibodies |
| HAE | Human Airway Epithelial |
| HS | Heparin Sulfate |
| β2M | beta-2-microglobulin |
| FcRn | Neonatal Fc receptor |
| NP | nasopharyngeal |
| CNS | Central nervous system |
| CSF | Cerebrospinal fluid |
| TLR | Toll-like receptor |
| IFN | Interferon |
| IVIG | Intravenous immunoglobulin |
| BBB | Blood-brain barrier |
| ITZ | Itraconazole |
References
- Romero, J.R.; Selvarangan, R. The human Parechoviruses: An overview. Adv. Pediatr. 2011, 58, 65–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolthers, K.C.; Benschop, K.S.; Schinkel, J.; Molenkamp, R.; Bergevoet, R.M.; Spijkerman, I.J.; Kraakman, H.C.; Pajkrt, D. Human parechoviruses as an important viral cause of sepsislike illness and meningitis in young children. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2008, 47, 358–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wildenbeest, J.G.; Harvala, H.; Pajkrt, D.; Wolthers, K.C. The need for treatment against human parechoviruses: How, why and when? Expert Rev. Anti Infect. Ther. 2010, 8, 1417–1429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanway, G.; Kalkkinen, N.; Roivainen, M.; Ghazi, F.; Khan, M.; Smyth, M.; Meurman, O.; Hyypia, T. Molecular and biological characteristics of echovirus 22, a representative of a new picornavirus group. J. Virol. 1994, 68, 8232–8238. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, Q.; Hato, S.V.; Langereis, M.A.; Zoll, J.; Virgen-Slane, R.; Peisley, A.; Hur, S.; Semler, B.L.; van Rij, R.P.; van Kuppeveld, F.J. MDA5 detects the double-stranded RNA replicative form in picornavirus-infected cells. Cell Rep. 2012, 2, 1187–1196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shakeel, S.; Westerhuis, B.M.; Domanska, A.; Koning, R.I.; Matadeen, R.; Koster, A.J.; Bakker, A.Q.; Beaumont, T.; Wolthers, K.C.; Butcher, S.J. Multiple capsid-stabilizing interactions revealed in a high-resolution structure of an emerging picornavirus causing neonatal sepsis. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 11387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalynych, S.; Palkova, L.; Plevka, P. The Structure of Human Parechovirus 1 Reveals an Association of the RNA Genome with the Capsid. J. Virol. 2016, 90, 1377–1386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shakeel, S.; Evans, J.D.; Hazelbaker, M.; Kao, C.C.; Vaughan, R.C.; Butcher, S.J. Intrinsically-disordered N-termini in human parechovirus 1 capsid proteins bind encapsidated RNA. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 5820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shakeel, S.; Dykeman, E.C.; White, S.J.; Ora, A.; Cockburn, J.J.B.; Butcher, S.J.; Stockley, P.G.; Twarock, R. Genomic RNA folding mediates assembly of human parechovirus. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandez-Tomas, C.B.; Guttman, N.; Baltimore, D. Morphogenesis of poliovirus 3. Formation of provirion in cell-free extracts. J. Virol. 1973, 12, 1181–1183. [Google Scholar]
- Zell, R.; Delwart, E.; Gorbalenya, A.E.; Hovi, T.; King, A.M.Q.; Knowles, N.J.; Lindberg, A.M.; Pallansch, M.A.; Palmenberg, A.C.; Reuter, G.; et al. ICTV Virus Taxonomy Profile: Picornaviridae. J. Gen. Virol. 2017, 98, 2421–2422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adams, M.J.; Lefkowitz, E.J.; King, A.M.; Harrach, B.; Harrison, R.L.; Knowles, N.J.; Kropinski, A.M.; Krupovic, M.; Kuhn, J.H.; Mushegian, A.R.; et al. Ratificatio n vote on taxonomic proposals to the International Committee on Taxonomy of Viruses. Arch. Virol. 2016, 161, 2921–2949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parechovirus. Available online: http://www.picornaviridae.com/parechovirus/parechovirus.htm (accessed on 10 October 2019).
- Ito, M.; Yamashita, T.; Tsuzuki, H.; Kabashima, Y.; Hasegawa, A.; Nagaya, S.; Kawaguchi, M.; Kobayashi, S.; Fujiura, A.; Sakae, K.; et al. Detection of human parechoviruses from clinical stool samples in Aichi, Japan. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2010, 48, 2683–2688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiang, G.P.K.; Chen, Z.; Chan, M.C.W.; Lee, S.H.M.; Kwok, A.K.; Yeung, A.C.M.; Nelson, E.A.S.; Hon, K.L.; Leung, T.F.; Chan, P.K.S. Clinical features and seasonality of parechovirus infection in an Asian subtropical city, Hong Kong. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0184533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wigand, R.; Sabin, A.B. Properties of ECHO types 22, 23 and 24 viruses. Arch. Gesamte Virusforsch 1961, 11, 224–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oberste, M.S.; Maher, K.; Pallansch, M.A. Complete sequence of echovirus 23 and its relationship to echovirus 22 and other human enteroviruses. Virus Res. 1998, 56, 217–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pulli, T.; Koivunen, E.; Hyypia, T. Cell-surface interactions of echovirus 22. J. Biol. Chem. 1997, 272, 21176–21180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coller, B.A.; Chapman, N.M.; Beck, M.A.; Pallansch, M.A.; Gauntt, C.J.; Tracy, S.M. Echovirus 22 is an atypical enterovirus. J. Virol. 1990, 64, 2692–2701. [Google Scholar]
- Benschop, K.S.; Schinkel, J.; Luken, M.E.; van den Broek, P.J.; Beersma, M.F.; Menelik, N.; van Eijk, H.W.; Zaaijer, H.L.; VandenBroucke-Grauls, C.M.; Beld, M.G.; et al. Fourth human parechovirus serotype. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2006, 12, 1572–1575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, C.H.; Panayiotou, M.; Girling, G.D.; Peard, C.I.; Oikarinen, S.; Hyoty, H.; Stanway, G. Evolution and conservation in human parechovirus genomes. J. Gen. Virol. 2009, 90, 1702–1712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hyypia, T.; Horsnell, C.; Maaronen, M.; Khan, M.; Kalkkinen, N.; Auvinen, P.; Kinnunen, L.; Stanway, G. A distinct picornavirus group identified by sequence analysis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1992, 89, 8847–8851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Souza Luna, L.K.; Baumgarte, S.; Grywna, K.; Panning, M.; Drexler, J.F.; Drosten, C. Identification of a contemporary human parechovirus type 1 by VIDISCA and characterisation of its full genome. Virol. J. 2008, 5, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghazi, F.; Hughes, P.J.; Hyypia, T.; Stanway, G. Molecular analysis of human parechovirus type 2 (formerly echovirus 23). J. Gen. Virol. 1998, 79 Pt 11, 2641–2650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ito, M.; Yamashita, T.; Tsuzuki, H.; Takeda, N.; Sakae, K. Isolation and identification of a novel human parechovirus. J. Gen. Virol. 2004, 85, 391–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watanabe, K.; Oie, M.; Higuchi, M.; Nishikawa, M.; Fujii, M. Isolation and characterization of novel human parechovirus from clinical samples. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2007, 13, 889–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.; Victoria, J.; Kapoor, A.; Naeem, A.; Shaukat, S.; Sharif, S.; Alam, M.M.; Angez, M.; Zaidi, S.Z.; Delwart, E. Genomic characterization of novel human parechovirus type. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2009, 15, 288–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drexler, J.F.; Grywna, K.; Stocker, A.; Almeida, P.S.; Medrado-Ribeiro, T.C.; Eschbach-Bludau, M.; Petersen, N.; da Costa-Ribeiro, H., Jr.; Drosten, C. Novel human parechovirus from Brazil. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2009, 15, 310–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nix, W.A.; Khetsuriani, N.; Penaranda, S.; Maher, K.; Venczel, L.; Cselko, Z.; Freire, M.C.; Cisterna, D.; Lema, C.L.; Rosales, P.; et al. Diversity of picornaviruses in rural Bolivia. J. Gen. Virol. 2013, 94, 2017–2028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benschop, K.; Thomas, X.; Serpenti, C.; Molenkamp, R.; Wolthers, K. High prevalence of human Parechovirus (HPeV) genotypes in the Amsterdam region and identification of specific HPeV variants by direct genotyping of stool samples. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2008, 46, 3965–3970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bottcher, S.; Obermeier, P.E.; Diedrich, S.; Kabore, Y.; D’Alfonso, R.; Pfister, H.; Kaiser, R.; Di Cristanziano, V. Genome Sequence of Novel Human Parechovirus Type 17. Genome Announc. 2017, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graul, S.; Bottcher, S.; Eibach, D.; Krumkamp, R.; Kasmaier, J.; Adu-Sarkodie, Y.; May, J.; Tannich, E.; Panning, M. High diversity of human parechovirus including novel types in stool samples from Ghanaian children. J. Clin. Virol. 2017, 96, 116–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brouwer, L.; Karelehto, E.; Han, A.X.; Thomas, X.V.; Bruning, A.H.L.; Calis, J.C.J.; van Hensbroek, M.B.; Westerhuis, B.M.; Amarthalingam, D.; Koekkoek, S.M.; et al. High frequency and diversity of parechovirus A in a cohort of Malawian children. Arch. Virol. 2019, 164, 799–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faria, N.R.; de Vries, M.; van Hemert, F.J.; Benschop, K.; van der Hoek, L. Rooting human parechovirus evolution in time. BMC Evol. Biol. 2009, 9, 164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benschop, K.S.; Williams, C.H.; Wolthers, K.C.; Stanway, G.; Simmonds, P. Widespread recombination within human parechoviruses: Analysis of temporal dynamics and constraints. J. Gen. Virol. 2008, 89, 1030–1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benschop, K.S.; de Vries, M.; Minnaar, R.P.; Stanway, G.; van der Hoek, L.; Wolthers, K.C.; Simmonds, P. Comprehensive full-length sequence analyses of human parechoviruses: Diversity and recombination. J. Gen. Virol. 2010, 91, 145–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simmonds, P.; Welch, J. Frequency and dynamics of recombination within different species of human enteroviruses. J. Virol. 2006, 80, 483–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Van der Sanden, S.M.; Koopmans, M.P.; van der Avoort, H.G. Detection of human enteroviruses and parechoviruses as part of the national enterovirus surveillance in the Netherlands, 1996–2011. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2013, 32, 1525–1531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khetsuriani, N.; Lamonte, A.; Oberste, M.S.; Pallansch, M. Neonatal enterovirus infections reported to the national enterovirus surveillance system in the United States, 1983–2003. Pediatr. Infect. Dis. J. 2006, 25, 889–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Khetsuriani, N.; Lamonte-Fowlkes, A.; Oberst, S.; Pallansch, M.A.; Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Enterovirus surveillance—United States, 1970–2005. MMWR Surveill. Summ. 2006, 55, 1–20. [Google Scholar]
- Van der Sanden, S.; de Bruin, E.; Vennema, H.; Swanink, C.; Koopmans, M.; van der Avoort, H. Prevalence of human parechovirus in the Netherlands in 2000 to 2007. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2008, 46, 2884–2889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Janes, V.A.; Minnaar, R.; Koen, G.; van Eijk, H.; Dijkman-de Haan, K.; Pajkrt, D.; Wolthers, K.C.; Benschop, K.S. Presence of human non-polio enterovirus and parechovirus genotypes in an Amsterdam hospital in 2007 to 2011 compared to national and international published surveillance data: A comprehensive review. Euro Surveill. 2014, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abedi, G.R.; Watson, J.T.; Nix, W.A.; Oberste, M.S.; Gerber, S.I. Enterovirus and Parechovirus Surveillance—United States, 2014–2016. MMWR Morb. Mortal. Wkly. Rep. 2018, 67, 515–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, Y.M.; Oikarinen, S.; Lehto, K.M.; Nurminen, N.; Juuti, R.; Mangani, C.; Maleta, K.; Hyoty, H.; Ashorn, P. High prevalence of selected viruses and parasites and their predictors in Malawian children. Epidemiol. Infect. 2019, 147, e90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yip, C.C.; Lo, K.L.; Que, T.L.; Lee, R.A.; Chan, K.H.; Yuen, K.Y.; Woo, P.C.; Lau, S.K. Epidemiology of human parechovirus, Aichi virus and salivirus in fecal samples from hospitalized children with gastroenteritis in Hong Kong. Virol. J. 2014, 11, 182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bubba, L.; Martinelli, M.; Pellegrinelli, L.; Primache, V.; Tanzi, E.; Pariani, E.; Binda, S. A 4-year Study on Epidemiologic and Molecular Characteristics of Human Parechoviruses and Enteroviruses Circulating in Children Younger Than 5 Years in Northern Italy. Pediatr. Infect. Dis. J. 2017, 36, 13–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhong, H.; Lin, Y.; Sun, J.; Su, L.; Cao, L.; Yang, Y.; Xu, J. Prevalence and genotypes of human parechovirus in stool samples from hospitalized children in Shanghai, China, 2008 and 2009. J. Med. Virol. 2011, 83, 1428–1434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alam, M.M.; Khurshid, A.; Shaukat, S.; Rana, M.S.; Sharif, S.; Angez, M.; Nisar, N.; Aamir, U.B.; Naeem, M.; Zaidi, S.S. Viral etiologies of acute dehydrating gastroenteritis in pakistani children: Confounding role of parechoviruses. Viruses 2015, 7, 378–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Patil, P.R.; Ganorkar, N.N.; Gopalkrishna, V. Epidemiology and genetic diversity of human parechoviruses circulating among children hospitalised with acute gastroenteritis in Pune, Western India: A 5-years study. Epidemiol. Infect. 2018, 146, 11–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Alam, M.M.; Khurshid, A.; Shaukat, S.; Rana, M.S.; Sharif, S.; Angez, M.; Nisar, N.; Naeem, M.; Zahoor Zaidi, S.S. Human parechovirus genotypes -10, -13 and -15 in Pakistani children with acute dehydrating gastroenteritis. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e78377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolehmainen, P.; Siponen, A.; Smura, T.; Kallio-Kokko, H.; Vapalahti, O.; Jaaskelainen, A.; Tauriainen, S. Intertypic recombination of human parechovirus 4 isolated from infants with sepsis-like disease. J. Clin. Virol. 2017, 88, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohba, K.; Leow, M.K.; Singh, B.K.; Sinha, R.A.; Lesmana, R.; Liao, X.H.; Ghosh, S.; Refetoff, S.; Sng, J.C.; Yen, P.M. Desensitization and Incomplete Recovery of Hepatic Target Genes After Chronic Thyroid Hormone Treatment and Withdrawal in Male Adult Mice. Endocrinology 2016, 157, 1660–1672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fischer, T.K.; Midgley, S.; Dalgaard, C.; Nielsen, A.Y. Human parechovirus infection, Denmark. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2014, 20, 83–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Selvarangan, R.; Nzabi, M.; Selvaraju, S.B.; Ketter, P.; Carpenter, C.; Harrison, C.J. Human parechovirus 3 causing sepsis-like illness in children from midwestern United States. Pediatr. Infect. Dis. J. 2011, 30, 238–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harvala, H.; McLeish, N.; Kondracka, J.; McIntyre, C.L.; McWilliam Leitch, E.C.; Templeton, K.; Simmonds, P. Comparison of human parechovirus and enterovirus detection frequencies in cerebrospinal fluid samples collected over a 5-year period in edinburgh: HPeV type 3 identified as the most common picornavirus type. J. Med. Virol. 2011, 83, 889–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Harvala, H.; Calvert, J.; Van Nguyen, D.; Clasper, L.; Gadsby, N.; Molyneaux, P.; Templeton, K.; McWilliams Leitch, C.; Simmonds, P. Comparison of diagnostic clinical samples and environmental sampling for enterovirus and parechovirus surveillance in Scotland, 2010 to 2012. Euro Surveill. 2014, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Joki-Korpela, P.; Roivainen, M.; Lankinen, H.; Poyry, T.; Hyypia, T. Antigenic properties of human parechovirus 1. J. Gen. Virol. 2000, 81, 1709–1718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tauriainen, S.; Martiskainen, M.; Oikarinen, S.; Lonnrot, M.; Viskari, H.; Ilonen, J.; Simell, O.; Knip, M.; Hyoty, H. Human parechovirus 1 infections in young children—No association with type 1 diabetes. J. Med. Virol. 2007, 79, 457–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Westerhuis, B.; Kolehmainen, P.; Benschop, K.; Nurminen, N.; Koen, G.; Koskiniemi, M.; Simell, O.; Knip, M.; Hyoty, H.; Wolthers, K.; et al. Human parechovirus seroprevalence in Finland and the Netherlands. J. Clin. Virol. 2013, 58, 211–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, S.; Aoki, Y.; Matoba, Y.; Yahagi, K.; Itagaki, T.; Matsuzaki, Y.; Mizuta, K. Seroepidemiology of human parechovirus types 1, 3, and 6 in Yamagata, Japan, in 2014. Microbiol. Immunol. 2016, 60, 854–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, K.; Hirokawa, C.; Tazawa, T. Seropositivity and epidemiology of human parechovirus types 1, 3, and 6 in Japan. Epidemiol. Infect. 2016, 144, 3451–3460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Westerhuis, B.M.; Benschop, K.S.; Koen, G.; Claassen, Y.B.; Wagner, K.; Bakker, A.Q.; Wolthers, K.C.; Beaumont, T. Human Memory B Cells Producing Potent Cross-Neutralizing Antibodies against Human Parechovirus: Implications for Prevalence, Treatment, and Diagnosis. J. Virol. 2015, 89, 7457–7464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Westerhuis, B.M.; Jonker, S.C.; Mattao, S.; Benschop, K.S.; Wolthers, K.C. Growth characteristics of human parechovirus 1 to 6 on different cell lines and cross- neutralization of human parechovirus antibodies: A comparison of the cytopathic effect and real time PCR. Virol. J. 2013, 10, 146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Baggen, J.; Thibaut, H.J.; Strating, J.; van Kuppeveld, F.J.M. The life cycle of non-polio enteroviruses and how to target it. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2018, 16, 368–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, P.; Liu, Y.; Ma, H.C.; Paul, A.V.; Wimmer, E. Picornavirus morphogenesis. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2014, 78, 418–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Limpens, R.W.; van der Schaar, H.M.; Kumar, D.; Koster, A.J.; Snijder, E.J.; van Kuppeveld, F.J.; Barcena, M. The transformation of enterovirus replication structures: A three-dimensional study of single- and double-membrane compartments. MBio 2011, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Krogerus, C.; Egger, D.; Samuilova, O.; Hyypia, T.; Bienz, K. Replication complex of human parechovirus 1. J. Virol. 2003, 77, 8512–8523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gazina, E.V.; Mackenzie, J.M.; Gorrell, R.J.; Anderson, D.A. Differential requirements for COPI coats in formation of replication complexes among three genera of Picornaviridae. J. Virol. 2002, 76, 11113–11122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schultheiss, T.; Emerson, S.U.; Purcell, R.H.; Gauss-Muller, V. Polyprotein processing in echovirus 22: A first assessment. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1995, 217, 1120–1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Z.; Hensley, L.; McKnight, K.L.; Hu, F.; Madden, V.; Ping, L.; Jeong, S.H.; Walker, C.; Lanford, R.E.; Lemon, S.M. A pathogenic picornavirus acquires an envelope by hijacking cellular membranes. Nature 2013, 496, 367–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bird, S.W.; Maynard, N.D.; Covert, M.W.; Kirkegaard, K. Nonlytic viral spread enhanced by autophagy components. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 13081–13086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Robinson, S.M.; Tsueng, G.; Sin, J.; Mangale, V.; Rahawi, S.; McIntyre, L.L.; Williams, W.; Kha, N.; Cruz, C.; Hancock, B.M.; et al. Coxsackievirus B exits the host cell in shed microvesicles displaying autophagosomal markers. PLoS Pathog. 2014, 10, e1004045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Too, I.H.; Yeo, H.; Sessions, O.M.; Yan, B.; Libau, E.A.; Howe, J.L.; Lim, Z.Q.; Suku-Maran, S.; Ong, W.Y.; Chua, K.B.; et al. Enterovirus 71 infection of motor neuron-like NSC-34 cells undergoes a non-lytic exit pathway. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 36983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.H.; Du, W.; Hagemeijer, M.C.; Takvorian, P.M.; Pau, C.; Cali, A.; Brantner, C.A.; Stempinski, E.S.; Connelly, P.S.; Ma, H.C.; et al. Phosphatidylserine vesicles enable efficient en bloc transmission of enteroviruses. Cell 2015, 160, 619–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Plow, E.F.; Haas, T.A.; Zhang, L.; Loftus, J.; Smith, J.W. Ligand binding to integrins. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 21785–21788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Roivainen, M.; Piirainen, L.; Hovi, T.; Virtanen, I.; Riikonen, T.; Heino, J.; Hyypia, T. Entry of coxsackievirus A9 into host cells: Specific interactions with alpha v beta 3 integrin, the vitronectin receptor. Virology 1994, 203, 357–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergelson, J.M.; Shepley, M.P.; Chan, B.M.; Hemler, M.E.; Finberg, R.W. Identification of the integrin VLA-2 as a receptor for echovirus 1. Science 1992, 255, 1718–1720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neff, S.; Sa-Carvalho, D.; Rieder, E.; Mason, P.W.; Blystone, S.D.; Brown, E.J.; Baxt, B. Foot-and-mouth disease virus virulent for cattle utilizes the integrin alpha(v)beta3 as its receptor. J. Virol. 1998, 72, 3587–3594. [Google Scholar]
- Boonyakiat, Y.; Hughes, P.J.; Ghazi, F.; Stanway, G. Arginine-glycine-aspartic acid motif is critical for human parechovirus 1 entry. J. Virol. 2001, 75, 10000–10004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Joki-Korpela, P.; Marjomaki, V.; Krogerus, C.; Heino, J.; Hyypia, T. Entry of human parechovirus 1. J. Virol. 2001, 75, 1958–1967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Triantafilou, K.; Triantafilou, M.; Takada, Y.; Fernandez, N. Human parechovirus 1 utilizes integrins alphavbeta3 and alphavbeta1 as receptors. J. Virol. 2000, 74, 5856–5862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Merilahti, P.; Tauriainen, S.; Susi, P. Human Parechovirus 1 Infection Occurs via alphaVbeta1 Integrin. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0154769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Karelehto, E.; Cristella, C.; Yu, X.; Sridhar, A.; Hulsdouw, R.; de Haan, K.; van Eijk, H.; Koekkoek, S.; Pajkrt, D.; de Jong, M.D.; et al. Polarized Entry of Human Parechoviruses in the Airway Epithelium. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2018, 8, 294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harvala, H.; Wolthers, K.C.; Simmonds, P. Parechoviruses in children: Understanding a new infection. Curr. Opin. Infect. Dis. 2010, 23, 224–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- King, S.L.; Kamata, T.; Cunningham, J.A.; Emsley, J.; Liddington, R.C.; Takada, Y.; Bergelson, J.M. Echovirus 1 interaction with the human very late antigen-2 (integrin alpha2beta1) I domain. Identification of two independent virus contact sites distinct from the metal ion-dependent adhesion site. J. Biol. Chem. 1997, 272, 28518–28522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ylipaasto, P.; Eskelinen, M.; Salmela, K.; Hovi, T.; Roivainen, M. Vitronectin receptors, alpha v integrins, are recognized by several non-RGD-containing echoviruses in a continuous laboratory cell line and also in primary human Langerhans’ islets and endothelial cells. J. Gen. Virol. 2010, 91, 155–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heikkila, O.; Merilahti, P.; Hakanen, M.; Karelehto, E.; Alanko, J.; Sukki, M.; Kiljunen, S.; Susi, P. Integrins are not essential for entry of coxsackievirus A9 into SW480 human colon adenocarcinoma cells. Virol. J. 2016, 13, 171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Merilahti, P.; Karelehto, E.; Susi, P. Role of Heparan Sulfate in Cellular Infection of Integrin-Binding Coxsackievirus A9 and Human Parechovirus 1 Isolates. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0147168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ward, T.; Powell, R.M.; Pipkin, P.A.; Evans, D.J.; Minor, P.D.; Almond, J.W. Role for beta2-microglobulin in echovirus infection of rhabdomyosarcoma cells. J. Virol. 1998, 72, 5360–5365. [Google Scholar]
- Triantafilou, M.; Triantafilou, K.; Wilson, K.M.; Takada, Y.; Fernandez, N.; Stanway, G. Involvement of beta2-microglobulin and integrin alphavbeta3 molecules in the coxsackievirus A9 infectious cycle. J. Gen. Virol. 1999, 80 Pt 10, 2591–2600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Morosky, S.; Wells, A.I.; Lemon, K.; Evans, A.S.; Schamus, S.; Bakkenist, C.J.; Coyne, C.B. The neonatal Fc receptor is a pan-echovirus receptor. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 3758–3763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Benschop, K.; Minnaar, R.; Koen, G.; van Eijk, H.; Dijkman, K.; Westerhuis, B.; Molenkamp, R.; Wolthers, K. Detection of human enterovirus and human parechovirus (HPeV) genotypes from clinical stool samples: Polymerase chain reaction and direct molecular typing, culture characteristics, and serotyping. Diagn. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2010, 68, 166–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Izumita, R.; Deuchi, K.; Aizawa, Y.; Habuka, R.; Watanabe, K.; Otsuka, T.; Saitoh, A. Intrafamilial Transmission of Parechovirus A and Enteroviruses in Neonates and Young Infants. J. Pediatr. Infect Dis. Soc. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aizawa, Y.; Yamanaka, T.; Watanabe, K.; Oishi, T.; Saitoh, A. Asymptomatic children might transmit human parechovirus type 3 to neonates and young infants. J. Clin. Virol. 2015, 70, 105–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wildenbeest, J.G.; Benschop, K.S.; Minnaar, R.P.; Bouma-de Jongh, S.; Wolthers, K.C.; Pajkrt, D. Clinical relevance of positive human parechovirus type 1 and 3 PCR in stool samples. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2014, 20, O640–O647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Khatami, A.; McMullan, B.J.; Webber, M.; Stewart, P.; Francis, S.; Timmers, K.J.; Rodas, E.; Druce, J.; Mehta, B.; Sloggett, N.A.; et al. Sepsis-like disease in infants due to human parechovirus type 3 during an outbreak in Australia. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2015, 60, 228–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- McNeale, D.; Wang, C.Y.T.; Arden, K.E.; Mackay, I.M. HPeV-3 predominated among Parechovirus A positive infants during an outbreak in 2013–2014 in Queensland, Australia. J. Clin. Virol. 2018, 98, 28–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Midgley, C.M.; Jackson, M.A.; Selvarangan, R.; Franklin, P.; Holzschuh, E.L.; Lloyd, J.; Scaletta, J.; Straily, A.; Tubach, S.; Willingham, A.; et al. Severe Parechovirus 3 Infections in Young Infants-Kansas and Missouri, 2014. J. Pediatr. Infect. Dis. Soc. 2018, 7, 104–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Strenger, V.; Diedrich, S.; Boettcher, S.; Richter, S.; Maritschnegg, P.; Gangl, D.; Fuchs, S.; Grangl, G.; Resch, B.; Urlesberger, B. Nosocomial Outbreak of Parechovirus 3 Infection among Newborns, Austria, 2014. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2016, 22, 1631–1634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yamamoto, M.; Abe, K.; Kuniyori, K.; Kunii, E.; Ito, F.; Kasama, Y.; Yoshioka, Y.; Noda, M. Epidemic of human parechovirus type 3 in Hiroshima city, Japan in 2008. Jpn. J. Infect. Dis. 2009, 62, 244–245. [Google Scholar]
- Verboon-Maciolek, M.A.; Groenendaal, F.; Hahn, C.D.; Hellmann, J.; van Loon, A.M.; Boivin, G.; de Vries, L.S. Human parechovirus causes encephalitis with white matter injury in neonates. Ann. Neurol. 2008, 64, 266–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Britton, P.N.; Khandaker, G.; Khatami, A.; Teutsch, S.; Francis, S.; McMullan, B.J.; Jones, C.A. High prevalence of developmental concern amongst infants at 12 months following hospitalised parechovirus infection. J. Paediatr. Child. Health 2018, 54, 289–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berk, M.C.; Bruning, A.H.L.; van Wassenaer-Leemhuis, A.G.; Wolthers, K.C.; Pajkrt, D. Human Parechovirus Meningitis with Adverse Neurodevelopmental Outcome: A Case Report. Pediatr. Infect. Dis. J. 2018, 37, e256–e257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Britton, P.N.; Dale, R.C.; Nissen, M.D.; Crawford, N.; Elliott, E.; Macartney, K.; Khandaker, G.; Booy, R.; Jones, C.A.; Investigators, P.-A. Parechovirus Encephalitis and Neurodevelopmental Outcomes. Pediatrics 2016, 137, e20152848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ferreras Antolin, L.; Kadambari, S.; Braccio, S.; Tang, J.W.; Xerry, J.; Allen, D.J.; Ladhani, S.N.; Parechovirus Surveillance, N. Increased detection of human parechovirus infection in infants in England during 2016: Epidemiology and clinical characteristics. Arch. Dis. Child. 2018, 103, 1061–1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Black, S.; Bradley, C.; Lai, F.Y.; Shenoy, S.; Bandi, S.; Allen, D.J.; Tang, J.W. Comparing the Clinical Severity of Disease Caused by Enteroviruses and Human Parechoviruses in Neonates and Infants. Pediatr. Infect. Dis. J. 2019, 38, e36–e38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kadambari, S.; Braccio, S.; Ribeiro, S.; Allen, D.J.; Pebody, R.; Brown, D.; Cunney, R.; Sharland, M.; Ladhani, S. Enterovirus and parechovirus meningitis in infants younger than 90 days old in the UK and Republic of Ireland: A British Paediatric Surveillance Unit study. Arch. Dis. Child. 2019, 104, 552–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Renna, S.; Bergamino, L.; Pirlo, D.; Rossi, A.; Furione, M.; Piralla, A.; Mascaretti, M.; Cristina, E.; Marazzi, M.G.; Di Pietro, P. A case of neonatal human parechovirus encephalitis with a favourable outcome. Brain Dev. 2014, 36, 70–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mizuta, K.; Kuroda, M.; Kurimura, M.; Yahata, Y.; Sekizuka, T.; Aoki, Y.; Ikeda, T.; Abiko, C.; Noda, M.; Kimura, H.; et al. Epidemic myalgia in adults associated with human parechovirus type 3 infection, Yamagata, Japan, 2008. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2012, 18, 1787–1793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mizuta, K.; Yamakawa, T.; Nagasawa, H.; Itagaki, T.; Katsushima, F.; Katsushima, Y.; Shimizu, Y.; Ito, S.; Aoki, Y.; Ikeda, T.; et al. Epidemic myalgia associated with human parechovirus type 3 infection among adults occurs during an outbreak among children: Findings from Yamagata, Japan, in 2011. J. Clin. Virol. 2013, 58, 188–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, K.L.; Lau, J.S.Y.; Goh, S.M.; Wilson, H.L.; Catton, M.; Korman, T.M. Myocarditis Caused by Human Parechovirus in Adult. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2017, 23, 1571–1573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shinomoto, M.; Kawasaki, T.; Sugahara, T.; Nakata, K.; Kotani, T.; Yoshitake, H.; Yuasa, K.; Saeki, M.; Fujiwara, Y. First report of human parechovirus type 3 infection in a pregnant woman. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2017, 59, 22–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Han, T.H.; Kim, C.H.; Park, S.H.; Chung, J.Y.; Hwang, E.S. Detection of human parechoviruses in children with gastroenteritis in South Korea. Arch. Virol. 2011, 156, 1471–1475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pham, N.T.; Takanashi, S.; Tran, D.N.; Trinh, Q.D.; Abeysekera, C.; Abeygunawardene, A.; Khamrin, P.; Okitsu, S.; Shimizu, H.; Mizuguchi, M.; et al. Human parechovirus infection in children hospitalized with acute gastroenteritis in Sri Lanka. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2011, 49, 364–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Vollbach, S.; Muller, A.; Drexler, J.F.; Simon, A.; Drosten, C.; Eis-Hubinger, A.M.; Panning, M. Prevalence, type and concentration of human enterovirus and parechovirus in cerebrospinal fluid samples of pediatric patients over a 10-year period: A retrospective study. Virol. J. 2015, 12, 199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pellegrinelli, L.; Bubba, L.; Galli, C.; Anselmi, G.; Primache, V.; Binda, S.; Pariani, E. Epidemiology and molecular characterization of influenza viruses, human parechoviruses and enteroviruses in children up to 5 years with influenza-like illness in Northern Italy during seven consecutive winter seasons (2010–2017). J. Gen. Virol. 2017, 98, 2699–2711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mladenova, Z.; Dikova, A.; Thongprachum, A.; Petrov, P.; Pekova, L.; Komitova, R.; Iturriza-Gomara, M.; Ushijima, H. Diversity of human parechoviruses in Bulgaria, 2011: Detection of rare genotypes 8 and 10. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2015, 36, 315–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harvala, H.; Robertson, I.; Chieochansin, T.; McWilliam Leitch, E.C.; Templeton, K.; Simmonds, P. Specific association of human parechovirus type 3 with sepsis and fever in young infants, as identified by direct typing of cerebrospinal fluid samples. J. Infect. Dis. 2009, 199, 1753–1760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harvala, H.; Robertson, I.; McWilliam Leitch, E.C.; Benschop, K.; Wolthers, K.C.; Templeton, K.; Simmonds, P. Epidemiology and clinical associations of human parechovirus respiratory infections. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2008, 46, 3446–3453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Benschop, K.; Molenkamp, R.; van der Ham, A.; Wolthers, K.; Beld, M. Rapid detection of human parechoviruses in clinical samples by real-time PCR. J. Clin. Virol. 2008, 41, 69–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seth, R.B.; Sun, L.; Chen, Z.J. Antiviral innate immunity pathways. Cell Res. 2006, 16, 141–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Triantafilou, K.; Vakakis, E.; Orthopoulos, G.; Ahmed, M.A.; Schumann, C.; Lepper, P.M.; Triantafilou, M. TLR8 and TLR7 are involved in the host’s immune response to human parechovirus 1. Eur. J. Immunol. 2005, 35, 2416–2423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, J.T.; Yang, C.S.; Chen, Y.S.; Chen, B.C.; Chiang, A.J.; Chang, Y.H.; Tsai, W.L.; Lin, Y.S.; Chao, D.; Chang, T.H. Genome and infection characteristics of human parechovirus type 1: The interplay between viral infection and type I interferon antiviral system. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0116158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lin, T.H.; Cheng, C.C.; Su, H.H.; Huang, N.C.; Chen, J.J.; Kang, H.Y.; Chang, T.H. Lipopolysaccharide Attenuates Induction of Proallergic Cytokines, Thymic Stromal Lymphopoietin, and Interleukin 33 in Respiratory Epithelial Cells Stimulated with PolyI:C and Human Parechovirus. Front. Immunol. 2016, 7, 440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Alho, A.; Marttila, J.; Ilonen, J.; Hyypia, T. Diagnostic potential of parechovirus capsid proteins. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2003, 41, 2294–2299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Van de Ven, A.A.; Douma, J.W.; Rademaker, C.; van Loon, A.M.; Wensing, A.M.; Boelens, J.J.; Sanders, E.A.; van Montfrans, J.M. Pleconaril-resistant chronic parechovirus-associated enteropathy in agammaglobulinaemia. Antivir. Ther. 2011, 16, 611–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wildenbeest, J.G.; Wolthers, K.C.; Straver, B.; Pajkrt, D. Successful IVIG treatment of human parechovirus-associated dilated cardiomyopathy in an infant. Pediatrics 2013, 132, e243–e247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shakeel, S.; Westerhuis, B.M.; Ora, A.; Koen, G.; Bakker, A.Q.; Claassen, Y.; Wagner, K.; Beaumont, T.; Wolthers, K.C.; Butcher, S.J. Structural Basis of Human Parechovirus Neutralization by Human Monoclonal Antibodies. J. Virol. 2015, 89, 9571–9580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Aizawa, Y.; Watanabe, K.; Oishi, T.; Hirano, H.; Hasegawa, I.; Saitoh, A. Role of Maternal Antibodies in Infants with Severe Diseases Related to Human Parechovirus Type 3. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2015, 21, 1966–1972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karelehto, E.; Wildenbeest, J.G.; Benschop, K.S.M.; Koen, G.; Rebers, S.; Bouma-de Jongh, S.; Westerhuis, B.M.; de Jong, M.D.; Pajkrt, D.; Wolthers, K.C. Human Parechovirus 1, 3 and 4 Neutralizing Antibodies in Dutch Mothers and Infants and Their Role in Protection Against Disease. Pediatr. Infect. Dis. J. 2018, 37, 1304–1308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Calvert, J.; Chieochansin, T.; Benschop, K.S.; McWilliam Leitch, E.C.; Drexler, J.F.; Grywna, K.; da Costa Ribeiro, H., Jr.; Drosten, C.; Harvala, H.; Poovorawan, Y.; et al. Recombination dynamics of human parechoviruses: Investigation of type-specific differences in frequency and epidemiological correlates. J. Gen. Virol. 2010, 91, 1229–1238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, T.Y.; Chang, L.Y.; Huang, Y.C.; Hsu, K.H.; Chiu, C.H.; Yang, K.D. Different proinflammatory reactions in fatal and non-fatal enterovirus 71 infections: Implications for early recognition and therapy. Acta Paediatr. 2002, 91, 632–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.M.; Lei, H.Y.; Huang, K.J.; Wu, J.M.; Wang, J.R.; Yu, C.K.; Su, I.J.; Liu, C.C. Pathogenesis of enterovirus 71 brainstem encephalitis in pediatric patients: Roles of cytokines and cellular immune activation in patients with pulmonary edema. J. Infect. Dis. 2003, 188, 564–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lin, T.Y.; Hsia, S.H.; Huang, Y.C.; Wu, C.T.; Chang, L.Y. Proinflammatory cytokine reactions in enterovirus 71 infections of the central nervous system. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2003, 36, 269–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Guo, X.J.; Thomas, P.G. New fronts emerge in the influenza cytokine storm. Semin. Immunopathol. 2017, 39, 541–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Channappanavar, R.; Perlman, S. Pathogenic human coronavirus infections: Causes and consequences of cytokine storm and immunopathology. Semin. Immunopathol. 2017, 39, 529–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shane, A.L.; Sanchez, P.J.; Stoll, B.J. Neonatal sepsis. Lancet 2017, 390, 1770–1780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danielski, L.G.; Giustina, A.D.; Badawy, M.; Barichello, T.; Quevedo, J.; Dal-Pizzol, F.; Petronilho, F. Brain Barrier Breakdown as a Cause and Consequence of Neuroinflammation in Sepsis. Mol. Neurobiol. 2018, 55, 1045–1053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barichello, T.; Sayana, P.; Giridharan, V.V.; Arumanayagam, A.S.; Narendran, B.; Della Giustina, A.; Petronilho, F.; Quevedo, J.; Dal-Pizzol, F. Long-Term Cognitive Outcomes After Sepsis: A Translational Systematic Review. Mol. Neurobiol. 2019, 56, 186–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.M.; Lei, H.Y.; Liu, C.C. Cytokine immunopathogenesis of enterovirus 71 brain stem encephalitis. Clin. Dev. Immunol. 2012, 2012, 876241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Harvala, H.; Griffiths, M.; Solomon, T.; Simmonds, P. Distinct systemic and central nervous system disease patterns in enterovirus and parechovirus infected children. J. Infect. 2014, 69, 69–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verboon-Maciolek, M.A.; Krediet, T.G.; Gerards, L.J.; de Vries, L.S.; Groenendaal, F.; van Loon, A.M. Severe neonatal parechovirus infection and similarity with enterovirus infection. Pediatr. Infect. Dis. J. 2008, 27, 241–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Jong, E.P.; van den Beuken, M.G.A.; van Elzakker, E.P.M.; Wolthers, K.C.; Sprij, A.J.; Lopriore, E.; Walther, F.J.; Brus, F. Epidemiology of Sepsis-like Illness in Young Infants: Major Role of Enterovirus and Human Parechovirus. Pediatr. Infect. Dis. J. 2018, 37, 113–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghanem-Zoubi, N.; Shiner, M.; Shulman, L.M.; Sofer, D.; Wolf, D.; Marva, E.; Kra-Oz, Z.; Shachor-Meyouhas, Y.; Averbuch, D.; Bechor-Fellner, A.; et al. Human parechovirus type 3 central nervous system infections in Israeli infants. J. Clin. Virol. 2013, 58, 205–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharp, J.; Harrison, C.J.; Puckett, K.; Selvaraju, S.B.; Penaranda, S.; Nix, W.A.; Oberste, M.S.; Selvarangan, R. Characteristics of young infants in whom human parechovirus, enterovirus or neither were detected in cerebrospinal fluid during sepsis evaluations. Pediatr. Infect. Dis. J. 2013, 32, 213–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Westerhuis, B.M.; Koen, G.; Wildenbeest, J.G.; Pajkrt, D.; de Jong, M.D.; Benschop, K.S.; Wolthers, K.C. Specific cell tropism and neutralization of human parechovirus types 1 and 3: Implications for pathogenesis and therapy development. J. Gen. Virol. 2012, 93, 2363–2370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Karelehto, E.; Brouwer, L.; Benschop, K.; Kok, J.; Basile, K.; McMullan, B.; Rawlinson, W.; Druce, J.; Nicholson, S.; Selvarangan, R.; et al. Seroepidemiology of Parechovirus A3 Neutralizing Antibodies, Australia, the Netherlands, and United States. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2019, 25, 148–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sedmak, G.; Nix, W.A.; Jentzen, J.; Haupt, T.E.; Davis, J.P.; Bhattacharyya, S.; Pallansch, M.A.; Oberste, M.S. Infant deaths associated with human parechovirus infection in Wisconsin. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2010, 50, 357–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Van der Linden, L.; Wolthers, K.C.; van Kuppeveld, F.J. Replication and Inhibitors of Enteroviruses and Parechoviruses. Viruses 2015, 7, 4529–4562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van der Linden, L.; Ulferts, R.; Nabuurs, S.B.; Kusov, Y.; Liu, H.; George, S.; Lacroix, C.; Goris, N.; Lefebvre, D.; Lanke, K.H.; et al. Application of a cell-based protease assay for testing inhibitors of picornavirus 3C proteases. Antivir. Res. 2014, 103, 17–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamm, I.; Eggers, H.J. Differences in the selective virus inhibitory action of 2-(alpha-hydroxybenzyl)-benzimidazole and guanidine HCl. Virology 1962, 18, 439–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rhoden, E.; Nix, W.A.; Weldon, W.C.; Selvarangan, R. Antifungal azoles itraconazole and posaconazole exhibit potent in vitro antiviral activity against clinical isolates of parechovirus A3 (Picornaviridae). Antivir. Res. 2018, 149, 75–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Domanska, A.; Flatt, J.W.; Jukonen, J.J.J.; Geraets, J.A.; Butcher, S.J. A 2.8-Angstrom-Resolution Cryo-Electron Microscopy Structure of Human Parechovirus 3 in Complex with Fab from a Neutralizing Antibody. J. Virol. 2019, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Karelehto, E.; van der Sanden, S.; Geraets, J.A.; Domanska, A.; van der Linden, L.; Hoogendoorn, D.; Koen, G.; van Eijk, H.; Shakeel, S.; Beaumont, T.; et al. Strain-dependent neutralization reveals antigenic variation of human parechovirus 3. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 12075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sato, T.; Vries, R.G.; Snippert, H.J.; van de Wetering, M.; Barker, N.; Stange, D.E.; van Es, J.H.; Abo, A.; Kujala, P.; Peters, P.J.; et al. Single Lgr5 stem cells build crypt-villus structures in vitro without a mesenchymal niche. Nature 2009, 459, 262–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lancaster, M.A.; Knoblich, J.A. Generation of cerebral organoids from human pluripotent stem cells. Nat. Protoc. 2014, 9, 2329–2340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]

| Type | Strain | Reference | Accession |
|---|---|---|---|
| PeV-A1A | Harris | Hyypia et al., 1992 [22] | L02971 |
| PeV-A1B | BNI-788 St | Baumgarte et al., 2008 [23] | EF051629 |
| PeV-A2 | Williamson | Ghazi et al., 1998 [24] | AJ005695 |
| PeV-A3 | A308/99 | Ito et al., 2004 [25] | AB084913 |
| PeV-A4 | K251176-02 | Benschop et al., 2006b [20] | DQ315670 |
| PeV-A5 | CT86-6760 | Oberste et al., 1998 [17] | AF055846 |
| PeV-A6 | NII561-2000 | Watanabe et al., 2007 [26] | AB252582 |
| PeV-A7 | PAK5045 | Li et al., 2009 [27] | EU556224 |
| PeV-A8 | BR/217/2006 | Drexler et al., 2009 [28] | EU716175 |
| PeV-A9 | BAN2004-10902 | Nix et al., 2013 [29] | JX219575 |
| PeV-A10 | BAN2004-10903 | Nix et al., 2013 [29] | JX219568 |
| PeV-A11 | BAN2004-10905 | Nix et al., 2013 [29] | JX219574 |
| PeV-A12 | BAN2004-10904 | Nix et al., 2013 [29] | JX219567 |
| PeV-A13 | BAN2004-10901 | Nix et al., 2013 [29] | JX219579 |
| PeV-A14 | 451564 | Benschop et al., 2008c [30] | FJ373179 |
| PeV-A15 | BAN-11614 | Nix et al., 2013 [29] | JX219573 |
| PeV-A16 | BAN-11615 | Nix et al., 2013 [29] | JX219580 |
| PeV-A17 | M36/CI/2014 | Böttcher et al., 2017 [31] | KT319121 |
| PeV-A18 | GhanaA36 886 | Graul et al., 2017 [32] | KY931660 |
| PeV-A19 | P02-4058 | Brouwer et al., 2019 [33] | MH339678 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sridhar, A.; Karelehto, E.; Brouwer, L.; Pajkrt, D.; Wolthers, K.C. Parechovirus A Pathogenesis and the Enigma of Genotype A-3. Viruses 2019, 11, 1062. https://doi.org/10.3390/v11111062
Sridhar A, Karelehto E, Brouwer L, Pajkrt D, Wolthers KC. Parechovirus A Pathogenesis and the Enigma of Genotype A-3. Viruses. 2019; 11(11):1062. https://doi.org/10.3390/v11111062
Chicago/Turabian StyleSridhar, Adithya, Eveliina Karelehto, Lieke Brouwer, Dasja Pajkrt, and Katja C. Wolthers. 2019. "Parechovirus A Pathogenesis and the Enigma of Genotype A-3" Viruses 11, no. 11: 1062. https://doi.org/10.3390/v11111062
APA StyleSridhar, A., Karelehto, E., Brouwer, L., Pajkrt, D., & Wolthers, K. C. (2019). Parechovirus A Pathogenesis and the Enigma of Genotype A-3. Viruses, 11(11), 1062. https://doi.org/10.3390/v11111062





