Nasal Cytokine Profiles of Patients Hospitalised with Respiratory Wheeze Associated with Rhinovirus C
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Cohort and Material Collection
2.2. Nucleic Acid Extraction and PCR and Sequencing
2.3. Cytokine Measurement
2.4. Statistical Analysis
2.5. Ethics
3. Results
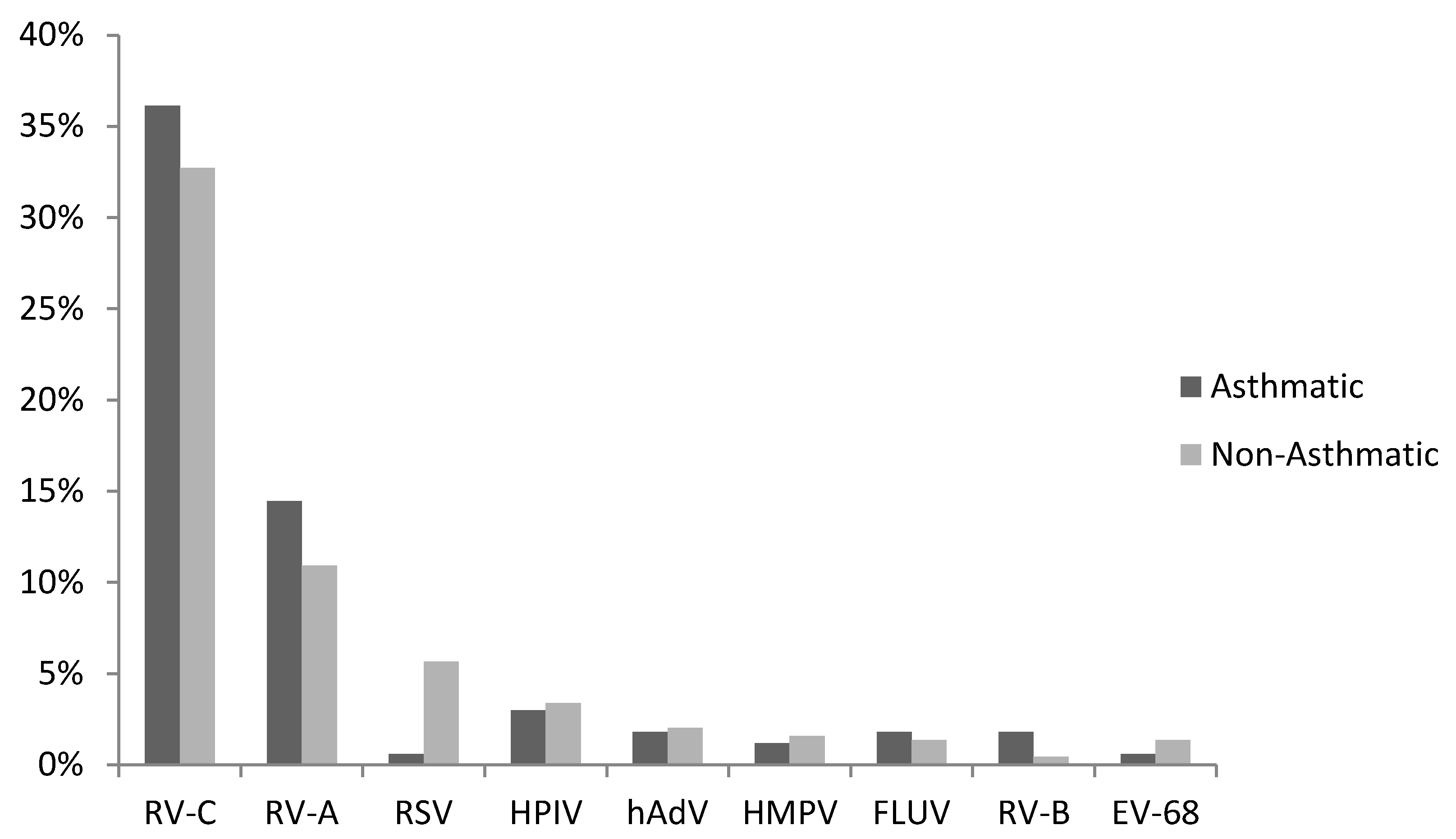
3.1. Virus Detections
3.2. RV-C and Asthma Diagnosis
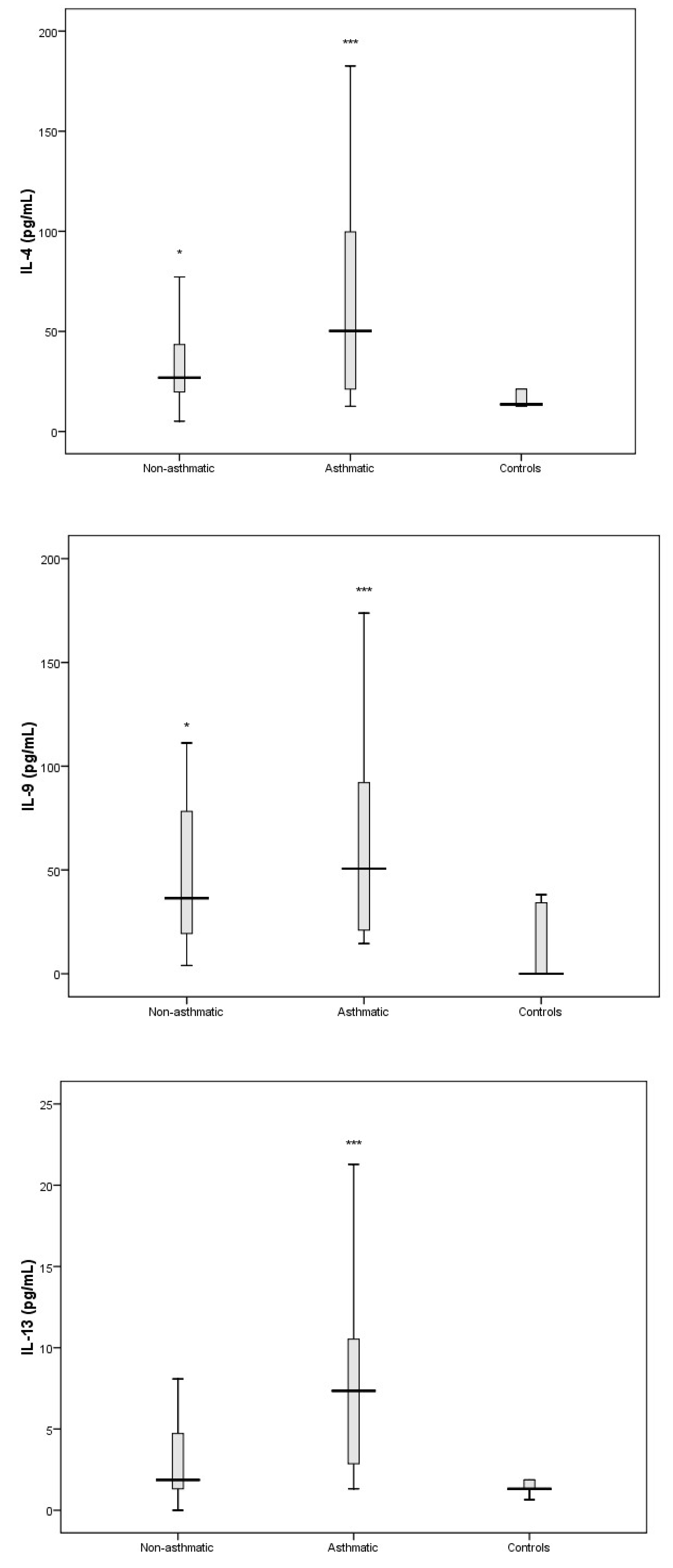
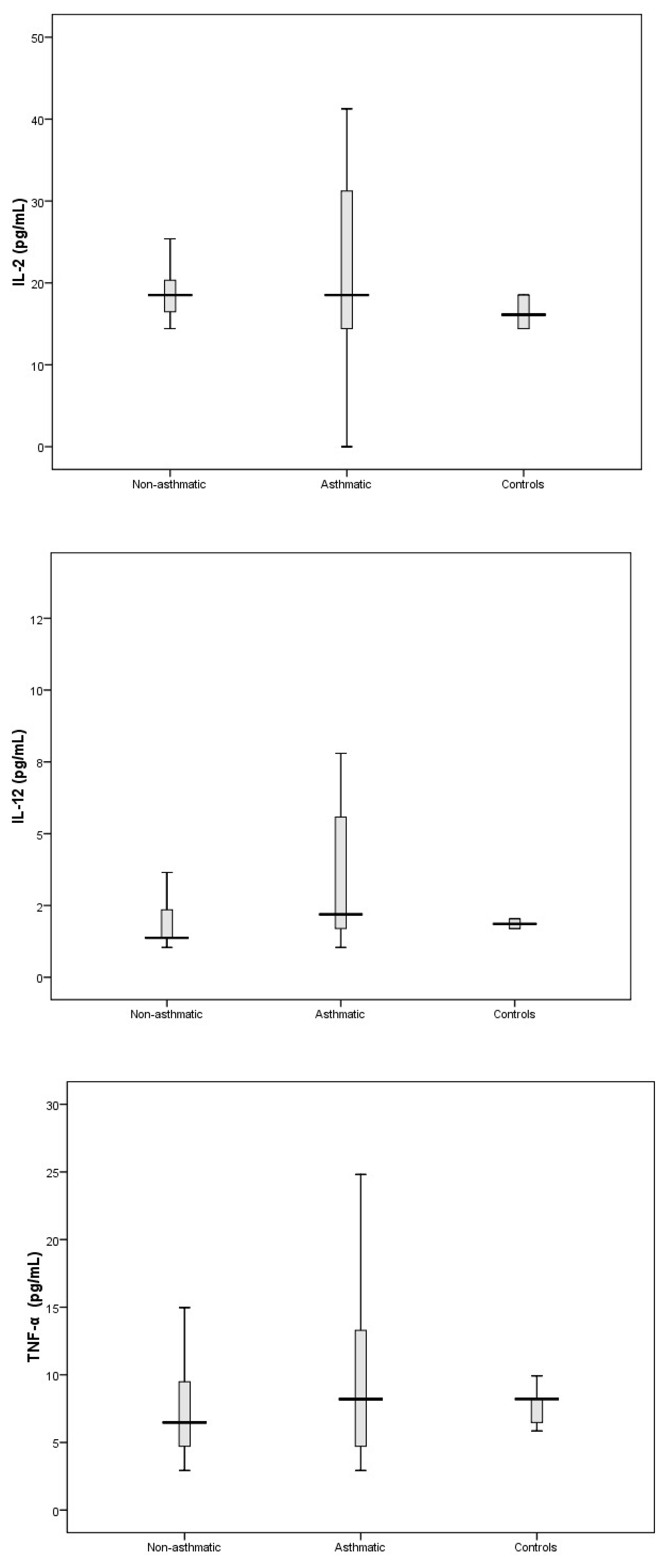
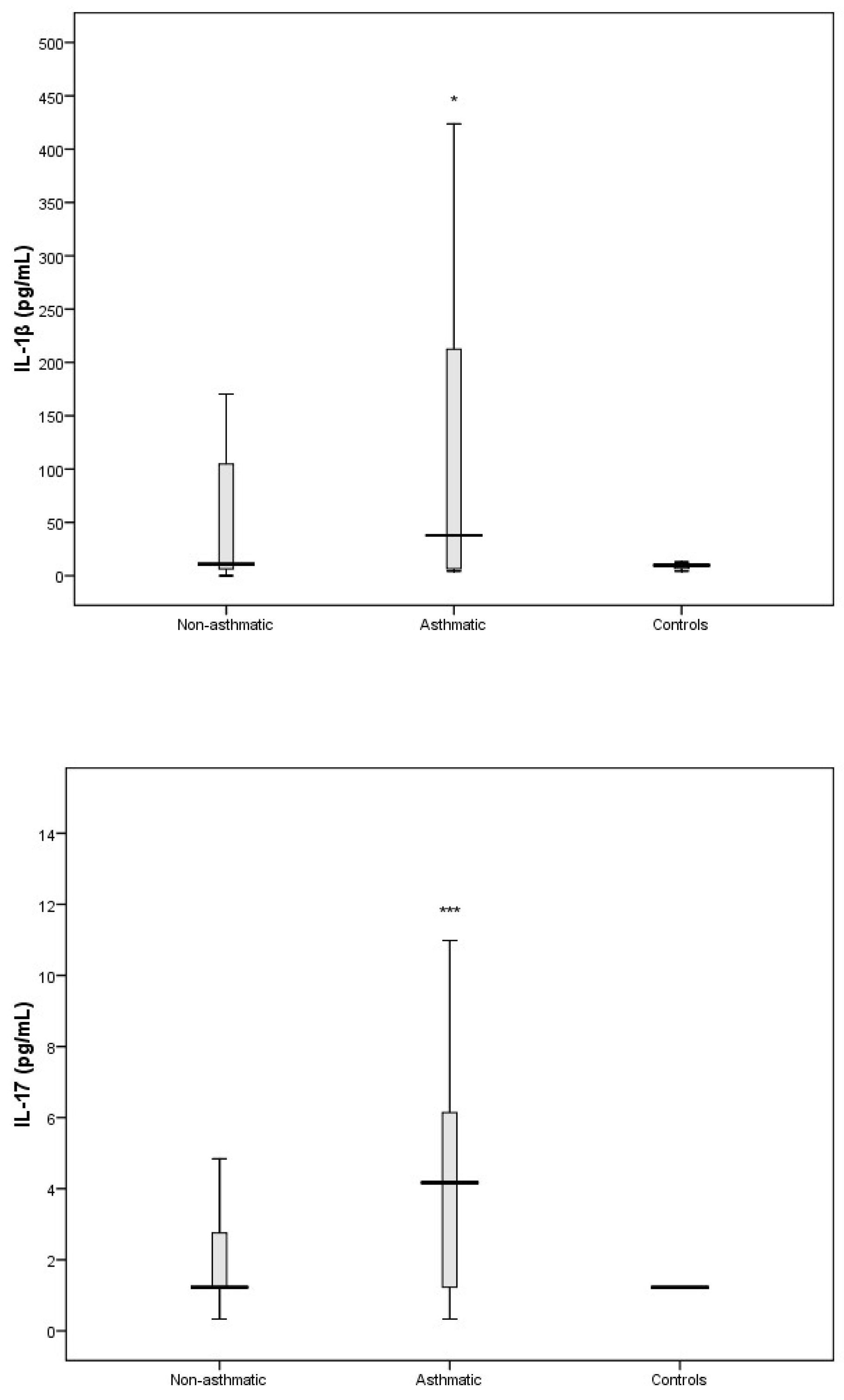
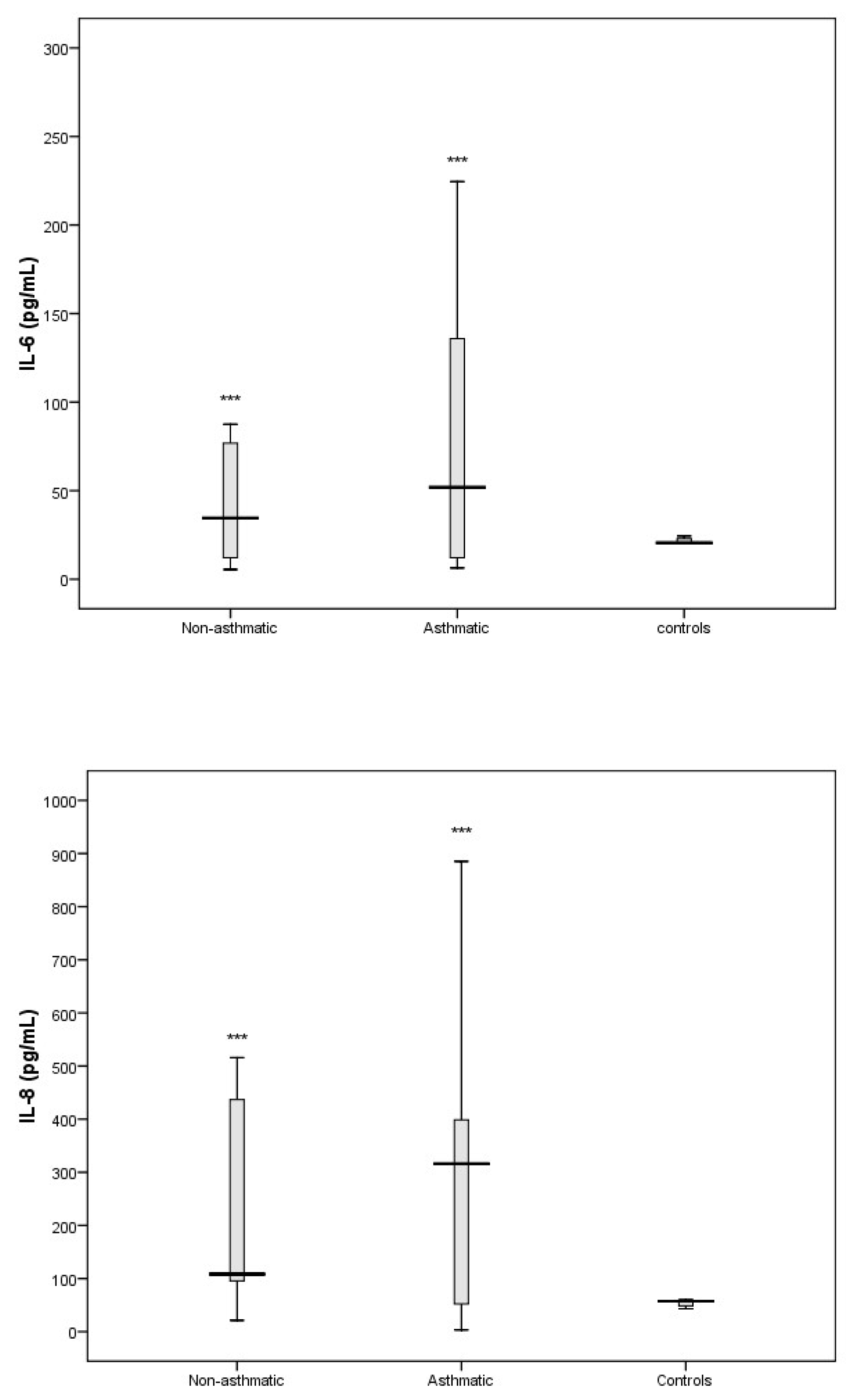
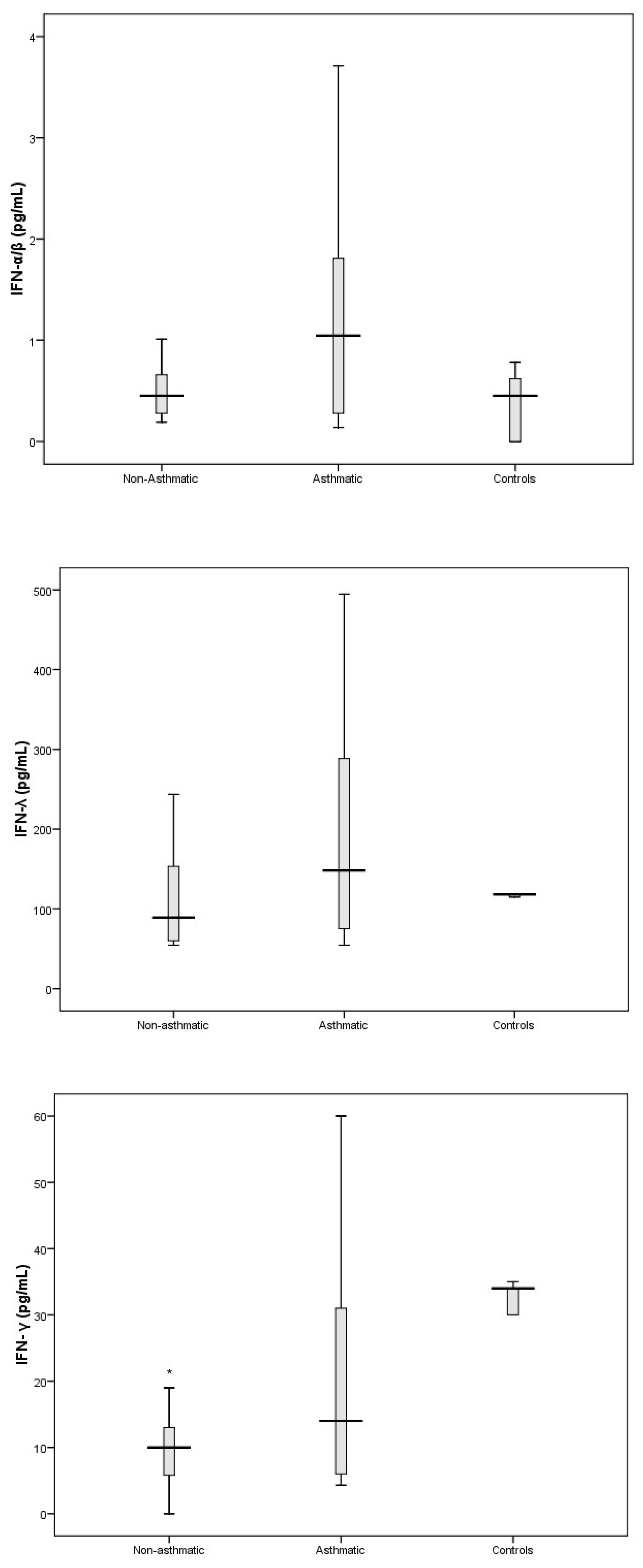
3.3. Cytokine Response Following RV-C Infections
3.4. Relationships Between Cytokines, RV-C Load, and Clinical Outcomes
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cox, D.W.; Bizzintino, J.; Ferrari, G.; Khoo, S.K.; Zhang, G.; Whelan, S.; Lee, W.M.; Bochkov, Y.A.; Geelhoed, G.C.; Goldblatt, J.; et al. Human Rhinovirus Species C Infection in Young Children with Acute Wheeze Is Associated with Increased Acute Respiratory Hospital Admissions. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2013, 188, 1358–1364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Iwane, M.K.; Prill, M.M.; Lu, X.; Miller, E.K.; Edwards, K.M.; Hall, C.B.; Griffin, M.R.; Staat, M.A.; Anderson, L.J.; Williams, J.V.; et al. Human rhinovirus species associated with hospitalizations for acute respiratory illness in young US children. J. Infect. Dis. 2011, 204, 1702–1710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bizzintino, J.; Lee, W.-M.; Laing, I.A.; Vang, F.; Pappas, T.; Zhang, G.; Martin, A.C.; Khoo, S.-K.; Cox, D.W.; Geelhoed, G.C.; et al. Association between human rhinovirus C and severity of acute asthma in children. Eur. Respir. J. 2011, 37, 1037–1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Linsuwanon, P.; Payungporn, S.; Samransamruajkit, R.; Posuwan, N.; Makkoch, J.; Theanboonlers, A.; Poovorawan, Y. High prevalence of human rhinovirus C infection in Thai children with acute lower respiratory tract disease. J. Infect. 2009, 59, 115–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jackson, D.J.; Gangnon, R.E.; Evans, M.D.; Roberg, K.A.; Anderson, E.L.; Pappas, T.E.; Printz, M.C.; Lee, W.M.; Shult, P.A.; Reisdorf, E.; et al. Wheezing rhinovirus illnesses in early life predict asthma development in high-risk children. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2008, 178, 667–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saraya, T.; Kurai, D.; Ishii, H.; Ito, A.; Sasaki, Y.; Niwa, S.; Kiyota, N.; Tsukagoshi, H.; Kozawa, K.; Goto, H.; et al. Epidemiology of virus-induced asthma exacerbations: With special reference to the role of human rhinovirus. Front. Microbiol. 2014, 5, 226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kennedy, J.L.; Shaker, M.; McMeen, V.; Gern, J.; Carper, H.; Murphy, D.; Lee, W.M.; Bochkov, Y.A.; Vrtis, R.F.; Platts-Mills, T.; et al. Comparison of viral load in individuals with and without asthma during infections with rhinovirus. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2014, 189, 532–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pritchard, A.L.; White, O.J.; Burel, J.G.; Upham, J.W. Innate interferons inhibit allergen and microbial specific TH2 responses. Immunol. Cell Biol. 2012, 90, 974–977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quint, J.K. IP-10 as a biomarker for rhinoviral infections in asthma. Thorax 2008, 63, 200. [Google Scholar]
- Peiris, J.S.M.; Hui, K.P.Y.; Yen, H.-L. Host response to Influenza virus: Protection versus immunopathology. Curr. Opin. Immunol. 2010, 22, 475–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansel, T.T.; Tunstall, T.; Trujillo-Torralbo, M.-B.; Shamji, B.; del-Rosario, A.; Dhariwal, J.; Kirk, P.D.W.; Stumpf, M.P.H.; Koopmann, J.; Telcian, A.; et al. A Comprehensive Evaluation of Nasal and Bronchial Cytokines and Chemokines Following Experimental Rhinovirus Infection in Allergic Asthma: Increased Interferons (IFN-γ and IFN-λ) and Type 2 Inflammation (IL-5 and IL-13). EBioMedicine 2017, 19, 128–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kelly, J.T.; Busse, W.W. Host immune responses to rhinovirus: Mechanisms in asthma. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2008, 122, 671–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chidlow, G.R.; Harnett, G.B.; Shellam, G.R.; Smith, D.W. An Economical Tandem Multiplex Real-Time PCR Technique for the Detection of a Comprehensive Range of Respiratory Pathogens. Viruses 2009, 1, 42–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Coiras, M.T.; Aguilar, J.C.; Garcia, M.L.; Casas, I.; Perez-Brena, P. Simultaneous detection of fourteen respiratory viruses in clinical specimens by two multiplex reverse transcription nested-PCR assays. J. Med. Virol. 2004, 72, 484–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sikazwe, C.T.; Chidlow, G.R.; Imrie, A.; Smith, D.W. Reliable quantification of rhinovirus species C using real-time PCR. J. Virol. Methods 2016, 235, 65–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gueudin, M.; Vabret, A.; Petitjean, J.; Gouarin, S.; Brouard, J.; Freymuth, F. Quantitation of respiratory syncytial virus RNA in nasal aspirates of children by real-time RT-PCR assay. J. Virol. Methods 2003, 109, 39–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, B.; Sheng, L.C. Changes in Th1/Th2-producing cytokines during acute exacerbation chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. J. Int. Med. Res. 2018, 46, 3890–3902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnston, N.W.; Johnston, S.L.; Duncan, J.M.; Greene, J.M.; Kebadze, T.; Keith, P.K.; Roy, M.; Waserman, S.; Sears, M.R. The September epidemic of asthma exacerbations in children: A search for etiology. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2005, 115, 132–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, E.K.; Lu, X.; Erdman, D.D.; Poehling, K.A.; Zhu, Y.; Griffin, M.R.; Hartert, T.V.; Anderson, L.J.; Weinberg, G.A.; Hall, C.B.; et al. Rhinovirus-associated hospitalizations in young children. J. Infect. Dis. 2007, 195, 773–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rakes, G.P.; Arruda, E.; Ingram, J.M.; Hoover, G.E.; Zambrano, J.C.; Hayden, F.G.; Platts-Mills, T.A.E.; Heymann, P.W. Rhinovirus and Respiratory Syncytial Virus in Wheezing Children Requiring Emergency Care. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 1999, 159, 785–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasegawa, K.; Mansbach, J.M.; Teach, S.J.; Fisher, E.S.; Hershey, D.; Koh, J.Y.; Clark, S.; Piedra, P.A.; Sullivan, A.F.; Camargo, C.A. Multicenter Study of Viral Etiology and Relapse in Hospitalized Children with Bronchiolitis. Pediatric Infect. Dis. J. 2014, 33, 809–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kau, A.L.; Korenblat, P.E. Anti-Interleukin 4 and 13 for Asthma Treatment in the Era of Endotypes. Curr. Opin. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2014, 14, 570–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kearley, J.; Erjefalt, J.S.; Andersson, C.; Benjamin, E.; Jones, C.P.; Robichaud, A.; Pegorier, S.; Brewah, Y.; Burwell, T.J.; Bjermer, L.; et al. IL-9 governs allergen-induced mast cell numbers in the lung and chronic remodeling of the airways. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2011, 183, 865–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parker, J.C.; Thavagnanam, S.; Skibinski, G.; Lyons, J.; Bell, J.; Heaney, L.G.; Shields, M.D. Chronic IL9 and IL-13 exposure leads to an altered differentiation of ciliated cells in a well-differentiated paediatric bronchial epithelial cell model. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e61023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamada, Y.; Matsumoto, K.; Hashimoto, N.; Saikusa, M.; Homma, T.; Yoshihara, S.; Saito, H. Effect of Th1/Th2 Cytokine Pretreatment on RSV-Induced Gene Expression in Airway Epithelial Cells. Int. Arch. Allergy Immunol. 2011, 154, 185–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Message, S.D.; Laza-Stanca, V.; Mallia, P.; Parker, H.L.; Zhu, J.; Kebadze, T.; Contoli, M.; Sanderson, G.; Kon, O.M.; Papi, A.; et al. Rhinovirus-induced lower respiratory illness is increased in asthma and related to virus load and Th1/2 cytokine and IL-10 production. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 13562–13567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Al-Ramli, W.; Prefontaine, D.; Chouiali, F.; Martin, J.G.; Olivenstein, R.; Lemiere, C.; Hamid, Q. T(H)17-associated cytokines (IL-17A and IL-17F) in severe asthma. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2009, 123, 1185–1187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linden, A. Role of interleukin-17 and the neutrophil in asthma. Int. Arch. Allergy Immunol. 2001, 126, 179–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishnamoorthy, N.; Douda, D.N.; Bruggemann, T.R.; Ricklefs, I.; Duvall, M.G.; Abdulnour, R.E.; Martinod, K.; Tavares, L.; Wang, X.; Cernadas, M.; et al. Neutrophil cytoplasts induce TH17 differentiation and skew inflammation toward neutrophilia in severe asthma. Sci. Immunol. 2018, 3, aao4747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, S.L.; Baker, T.; Lajoie, S.; Richgels, P.K.; Yang, Y.; McAlees, J.W.; van Lier, A.; Wills-Karp, M.; Sivaprasad, U.; Acciani, T.H.; et al. IL-17A enhances IL-13 activity by enhancing IL-13-induced signal transducer and activator of transcription 6 activation. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2017, 139, 462–471.e414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukherjee, S.; Lindell, D.M.; Berlin, A.A.; Morris, S.B.; Shanley, T.P.; Hershenson, M.B.; Lukacs, N.W. IL-17-induced pulmonary pathogenesis during respiratory viral infection and exacerbation of allergic disease. Am. J. Pathol. 2011, 179, 248–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kluijver, J.D.; Grünberg, K.; Pons, D.; Klerk, E.P.A.D.; Dick, C.R.; Sterk, P.J.; Hiemstra, P.S. Interleukin-1β and interleukin--1ra levels in nasal lavages during experimental rhinovirus infection in asthmatic and non--asthmatic subjects. Clin. Exp. Allergy 2003, 33, 1415–1418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Li, S.; Zhang, G.; Nie, G.; Meng, Z.; Mao, D.; Chen, C.; Chen, X.; Zhou, B.; Zeng, G. Genetic variants in IL1A and IL1B contribute to the susceptibility to 2009 pandemic H1N1 influenza A virus. BMC Immunol. 2013, 14, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chidlow, G.R.; Laing, I.A.; Harnett, G.B.; Greenhill, A.R.; Phuanukoonnon, S.; Siba, P.M.; Pomat, W.S.; Shellam, G.R.; Smith, D.W.; Lehmann, D. Respiratory viral pathogens associated with lower respiratory tract disease among young children in the highlands of Papua New Guinea. J. Clin. Virol. 2012, 54, 235–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cox, D.W.; Khoo, S.-K.; Zhang, G.; Lindsay, K.; Keil, A.D.; Knight, G.; Gern, J.E.; Laing, I.A.; Bizzintino, J.; Le Souëf, P.N. Rhinovirus is the most common virus and rhinovirus-C is the most common species in paediatric intensive care respiratory admissions. Eur. Respir. J. 2018, 52, 1800207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, H.; Kim, K.; Kim, D.-W.; Jung, H.-D.; Min Cheong, H.; Kim, K.H.; Soo Kim, D.; Kim, Y.-J. Identification of Recombinant Human Rhinovirus A and C in Circulating Strains from Upper and Lower Respiratory Infections. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e68081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, W.-M.; Lemanske, R.F., Jr.; Evans, M.D.; Vang, F.; Pappas, T.; Gangnon, R.; Jackson, D.J.; Gern, J.E. Human rhinovirus species and season of infection determine illness severity. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2012, 186, 886–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Asthmatic | Non-Asthmatic | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age (mean ± SD) | 2.9 ± 1.2 | 2.8 ± 1 | n.s. # |
| Sex (male %) | 78 | 73 | n.s |
| History of Eczema (%) | 45 | 20 | <0.01 |
| History of Hay Fever | 11 | 0 | <0.0001 |
| Median RV-C Log10 (copies/mL, IQR) | 5.8 (3.1–6.4) | 5.8 (3.8–6.8) | n.s. # |
| Length of Stay (median hours, IQR) | 7 (1–16) | 10 (2–16) | n.s. # |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sikazwe, C.T.; Laing, I.A.; Imrie, A.; Smith, D.W. Nasal Cytokine Profiles of Patients Hospitalised with Respiratory Wheeze Associated with Rhinovirus C. Viruses 2019, 11, 1038. https://doi.org/10.3390/v11111038
Sikazwe CT, Laing IA, Imrie A, Smith DW. Nasal Cytokine Profiles of Patients Hospitalised with Respiratory Wheeze Associated with Rhinovirus C. Viruses. 2019; 11(11):1038. https://doi.org/10.3390/v11111038
Chicago/Turabian StyleSikazwe, Chisha T., Ingrid A. Laing, Allison Imrie, and David W. Smith. 2019. "Nasal Cytokine Profiles of Patients Hospitalised with Respiratory Wheeze Associated with Rhinovirus C" Viruses 11, no. 11: 1038. https://doi.org/10.3390/v11111038
APA StyleSikazwe, C. T., Laing, I. A., Imrie, A., & Smith, D. W. (2019). Nasal Cytokine Profiles of Patients Hospitalised with Respiratory Wheeze Associated with Rhinovirus C. Viruses, 11(11), 1038. https://doi.org/10.3390/v11111038






