Algal Viruses: The (Atomic) Shape of Things to Come
Abstract
1. Introduction
Early Virus Structural Studies
2. Electron Microscopy
2.1. Cryoelectron Microscopy
2.2. Electron Microscopy Viral ‘Dynamics’
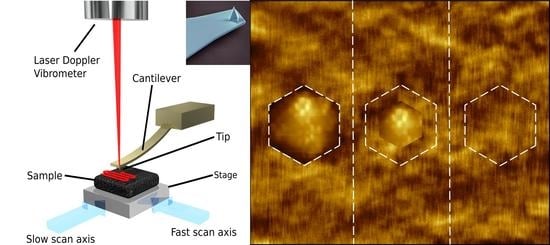
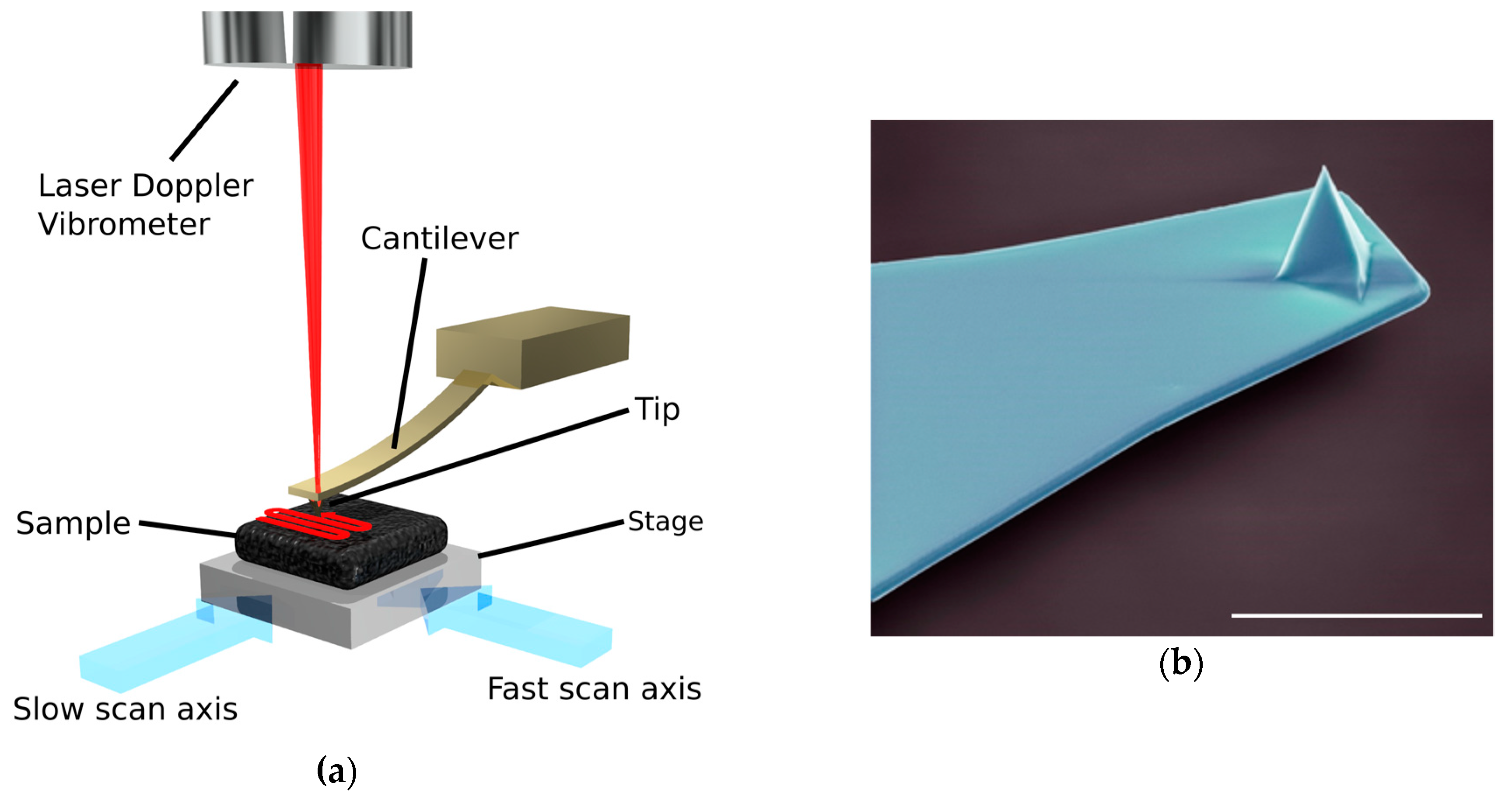
3. Atomic Force Microscopy
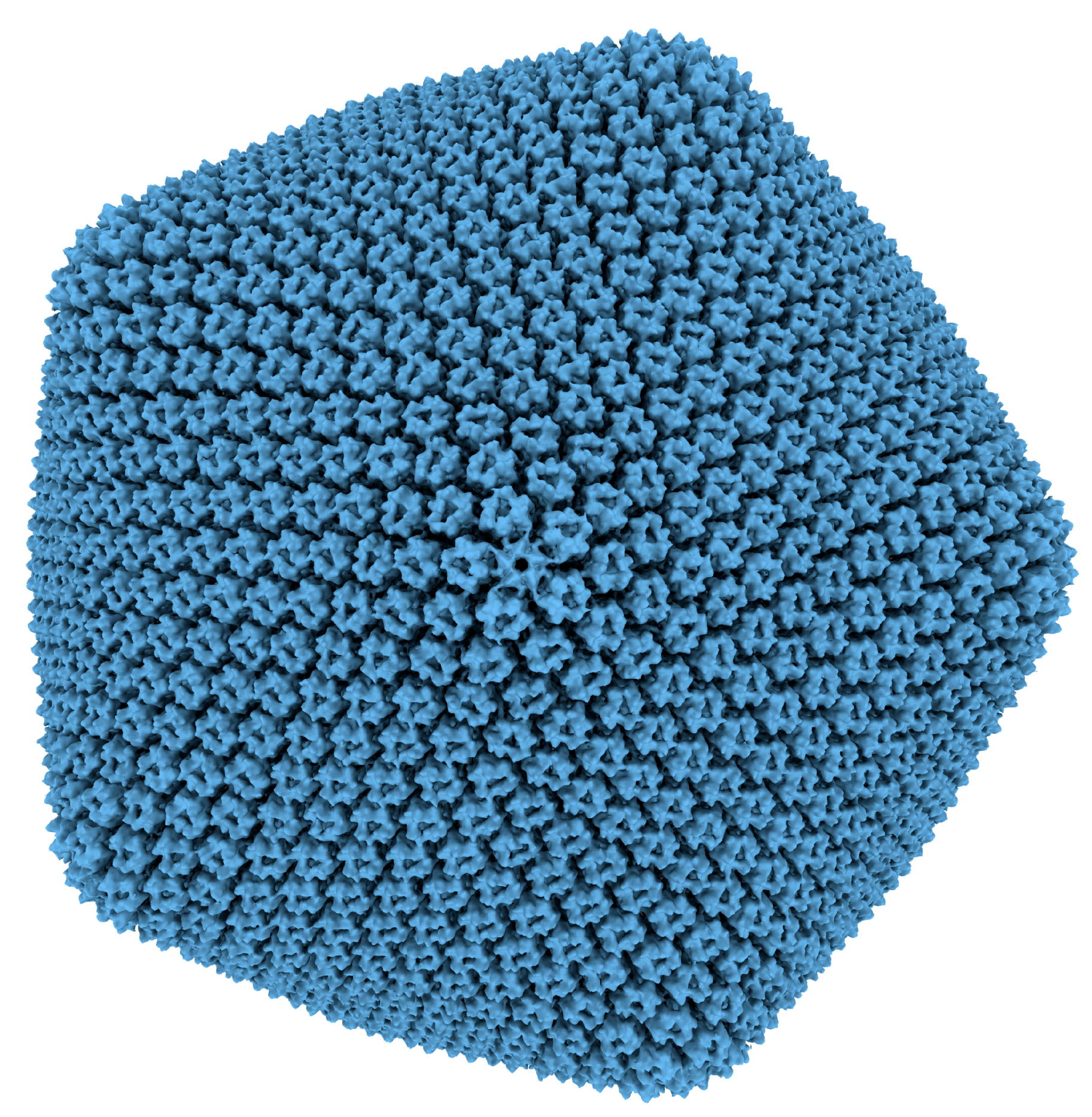
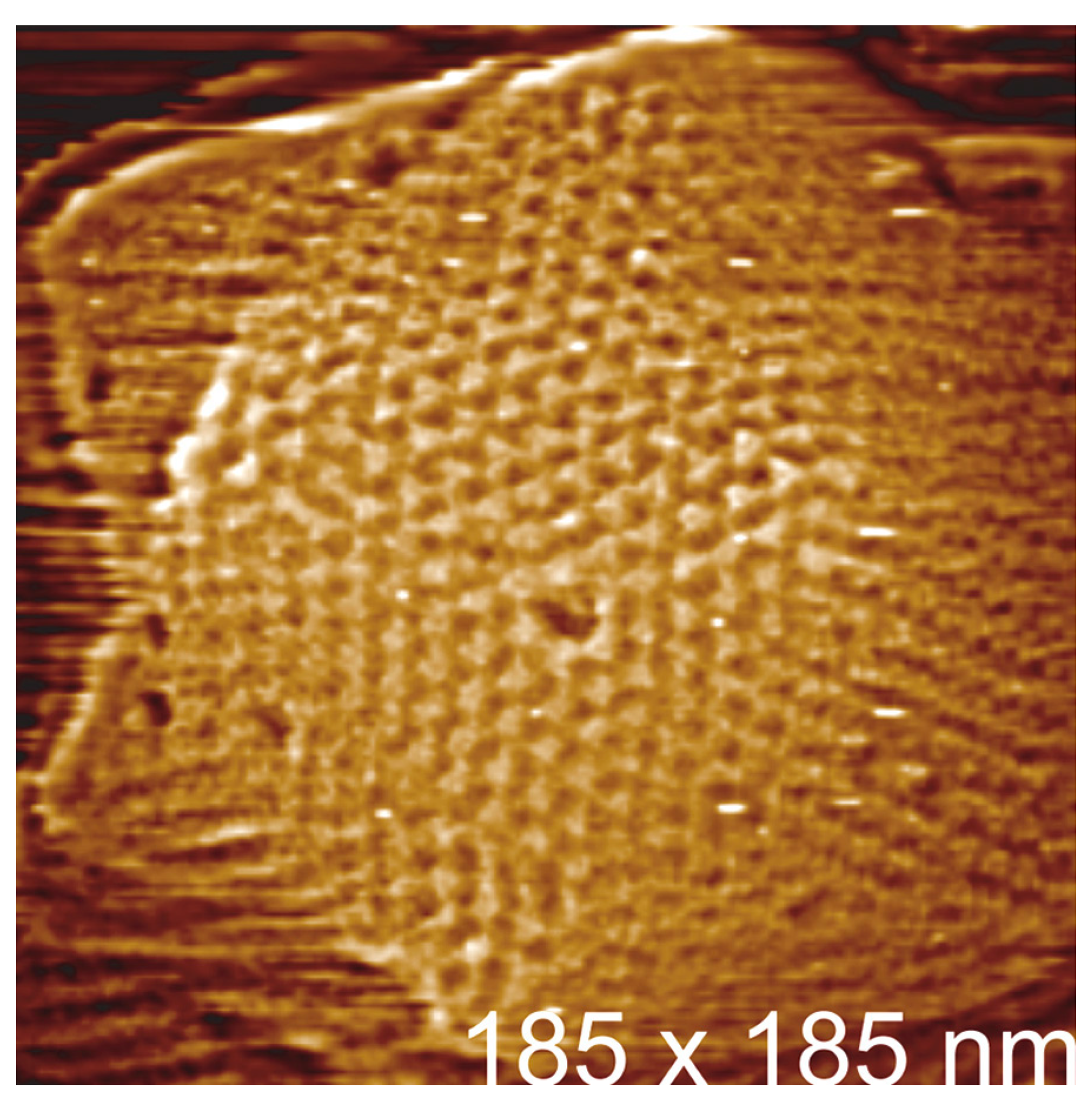
3.1. PBCV-1 Atomic Force Microscopy
3.2. Atomic Force Microscopy Viral ‘Dynamics’
3.3. Improving AFM Speeds
3.4. Force-Distance Curve-Based Atomic Force Microscopy
3.5. Subsurface Atomic Force Microscopy
4. Conclusions and Perspective
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bergh, O.; BOrsheim, K.Y.; Bratbak, G.; Heldal, M. High abundance of viruses found in aquatic environments. Nature 1989, 340, 467–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Breitbart, M.; Thompson, L.; Suttle, C.; Sullivan, M. Exploring the Vast Diversity of Marine Viruses. Oceanography 2007, 20, 135–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guidi, L.; Chaffron, S.; Bittner, L.; Eveillard, D.; Larhlimi, A.; Roux, S.; Darzi, Y.; Audic, S.; Berline, L.; Brum, J.R.; et al. Plankton networks driving carbon export in the oligotrophic ocean. Nature 2016, 532, 465–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Danovaro, R.; Corinaldesi, C.; Dell’Anno, A.; Fuhrman, J.A.; Middelburg, J.J.; Noble, R.T.; Suttle, C.A. Marine viruses and global climate change. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2011, 35, 993–1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crick, F.H.C.; Watson, J.D. Structure of Small Viruses. Nature 1956, 177, 473–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caspar, D.L.D. Structure of small viruses-tomato bushy stunt virus. Nature 1956, 177, 79–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaesberg, P. Structure of Small “Spherical” Viruses. Science 1956, 124, 626–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williams, R.C.; Smith, K.M. The polyhedral form of the Tipula iridescent virus. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1958, 28, 464–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinmann, E. An Eletron Microscope Study of the Structure of Sericesthis Iridescent Virus. J. Gen. Virol. 1969, 5, 123–134. [Google Scholar]
- Vidaver, A.K.; Koski, R.K.; Van Etten, J.L. Bacteriophage phi6: A Lipid-Containing Virus of Pseudomonas phaseolicola. J. Virol. 1973, 11, 799–805. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Dodds, J.A. Viruses of marine algae. Experientia 1979, 35, 440–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Etten, J.L.; Burbank, D.E.; Kuczmarski, D.; Meints, R.H. Virus Infection of Culturable Chlorella-Like Algae and Development of a Plaque Assay. Science 1983, 219, 994–996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Von Ardenne, M.B. Die praktische Ausführung der Elektronensonden-Mikroskope. In Elektronen-Übermikroskopie; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1940. [Google Scholar]
- Mulvey, T. Origins and Historical Development of the Electron Microscope. Br. J. Appl. Phys. 1962, 13, 197–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oatley, C.W. The early history of the scanning electron microscope. J. Appl. Phys. 1982, 53, R1–R13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meints, R.H.; Lee, K.; Burbank, D.E.; van Etten, J.L. Infection of a chlorella-like alga with the virus, PBCV-1: Ultrastructural studies. Virology 1984, 346, 341–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skrdla, M.P.; Burbank, D.E.; Xia, Y.; Meints, R.H.; van Etten, J.L. Structural proteins and lipids in a virus, PBCV-1, which replicates in a Chlorella-like alga. Virology 1984, 135, 308–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gazzarrini, S.; Severino, M.; Lombardi, M.; Morandi, M.; DiFrancesco, D.; Van Etten, J.L.; Thiel, G.; Moroni, A. The viral potassium channel Kcv: Structural and functional features. FEBS Lett. 2003, 552, 12–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adrian, M.; Dubochet, J.; Lepault, J.; McDowall, A.W. Cryo-electron microscopy of viruses. Nature 1984, 308, 32–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- The Nobel Prize in Chemistry 2017-Scientific Background: The Development of Cryo-Electron Microscopy. Available online: http://www.nobelprize.org/nobel_prizes/chemistry/laureates/2017/advanced.html (accessed on 29 July 2018).
- Yan, X.; Olson, N.H.; Etten, J.L.; Van Baker, T.S. Cryo-electron microscopy and image reconstruction of PBCV-1, an algal virus with T = 169 lattice symmetry. Electron. Microsc. 1998, 1, 775–776. [Google Scholar]
- Caspar, D.L.; Klug, A. Physical principles in the construction of regular viruses. Cold Spring Harb. Symp. Quant. Biol. 1962, 27, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Xiang, Y.; Dunigan, D.D.; Klose, T.; Chipman, P.R.; Van Etten, J.L.; Rossmann, M.G. Three-dimensional structure and function of the Paramecium bursaria chlorella virus capsid. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 14837–14842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bushby, A.J.; P’Ng, K.M.Y.; Young, R.D.; Pinali, C.; Knupp, C.; Quantock, A.J. Imaging three-dimensional tissue architectures by focused ion beam scanning electron microscopy. Nat. Protoc. 2011, 6, 845–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aoyama, K.; Takagi, T.; Hirase, A.; Miyazawa, A. STEM tomography for thick biological specimens. Ultramicroscopy 2008, 109, 70–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, C.Y.; Johnson, J.E. Viral life cycles captured in three-dimensions with electron microscopy tomography. Curr. Opin. Virol. 2011, 1, 125–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yashchenko, V.V.; Gavrilova, O.V.; Rautian, M.S.; Jakobsen, K.S. Association of Paramecium bursaria Chlorella viruses with Paramecium bursaria cells: Ultrastructural studies. Eur. J. Protistol. 2012, 48, 149–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thiel, G.; Dunigan, D.; Etten, J.L.; Van Etten, J.L. Van Progress in botany. Nature 1962, 194, 1023. [Google Scholar]
- Meints, R.H.; Lee, K.; Van Etten, J.L. Assembly site of the virus PBCV-1 in a Chlorella-like green alga: Ultrastructural studies. Virology 1986, 154, 240–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milrot, E.; Mutsafi, Y.; Fridmann-Sirkis, Y.; Shimoni, E.; Rechav, K.; Gurnon, J.R.; Van Etten, J.L.; Minsky, A. Virus-host interactions: Insights from the replication cycle of the large Paramecium bursaria chlorella virus. Cell Microbiol. 2016, 18, 3–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murata, K.; Zhang, Q.; Galaz-Montoya, J.M.; Fu, C.; Coleman, M.L.; Osburne, M.S.; Schmid, M.F.; Sullivan, M.B.; Chisholm, S.W.; Chiu, W. Visualizing Adsorption of Cyanophage P-SSP7 onto Marine Prochlorococcus. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeev-Ben-Mordehai, T.; Hagen, C.; Grunewald, K. A cool hybrid approach to the herpesvirus ‘life’ cycle. Curr. Opin. VIrol. 2014, 5, 42–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nandhagopal, N.; Simpson, A.A.; Gurnon, J.R.; Yan, X.; Baker, T.S.; Graves, M.V.; Van Etten, J.L.; Rossmann, M.G. The structure and evolution of the major capsid protein of a large, lipid-containing DNA virus. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 14758–14763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Castro, C.; Klose, T.; Speciale, I.; Lanzetta, R.; Molinaro, A.; Van Etten, J.L.; Rossmann, M.G. Structure of the chlorovirus PBCV-1 major capsid glycoprotein determined by combining crystallographic and carbohydrate molecular modeling approaches. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 115, E44–E52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Romani, G.; Piotrowski, A.; Hillmer, S.; Gurnon, J.; Van Etten, J.L.; Moroni, A.; Thiel, G.; Hertel, B. A virus-encoded potassium ion channel is a structural protein in the chlorovirus Paramecium bursaria chlorella virus 1 virion. J. Gen. Virol. 2013, 94, 2549–2556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thiel, G.; Greiner, T.; Dunigan, D.D.; Moroni, A.; Van Etten, J.L. Large dsDNA chloroviruses encode diverse membrane transport proteins. Virology 2015, 479–480, 38–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, X.; Olson, N.H.; Van Etten, J.L.; Bergoin, M.; Rossmann, M.G.; Baker, T.S. Structure and assembly of large lipid-containing dsDNA viruses. Nat. Struct. Biol. 2000, 7, 101–103. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Binnig, G.; Quate, C.F.; Gerber, C. Atomic Force Microscope. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1986, 56, 930–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kasas, S.; Thomson, N.H.; Smith, B.L.; Hansma, P.K.; Miklossy, J.; Hansma, H.G. Biological applications of the AFM: From single molecules to organs. Int. J. Imaging Syst. Technol. 1997, 8, 151–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Häberle, W.; Hörber, J.K.H.; Ohnesorge, F.; Smith, D.P.E.; Binnig, G. In situ investigations of single living cells infected by viruses. Ultramicroscopy 1992, 42–44, 1161–1167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohnesorge, F.M.; Hörber, J.K.H.; Häberle, W.; Czerny, C.P.; Smith, D.P.E.; Binnig, G. AFM review study on pox viruses and living cells. Biophys. J. 1997, 73, 2183–2194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Payton, O.D.; Picco, L.; Scott, T.B. High-speed atomic force microscopy for materials science. Int. Mater. Rev. 2016, 6608, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.Y.; Sheng, S.T.; Shao, Z.F. Imaging biological structures with the cryo atomic force microscope. Biophys. J. 1996, 71, 2168–2176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Proctor, L.M. Advances in the Study of Marine Viruses. Microsc. Res. Tech. 1997, 37, 136–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malkin, A.J.; Kuznetsov, Y.G.; Lucas, R.W.; McPherson, A. Surface processes in the crystallization of turnip yellow mosaic virus visualized by atomic force microscopy. J. Struct. Biol. 1999, 127, 35–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhong, Q.; Inniss, D.; Kjoller, K.; Elings, V.B. Fractured polymer/silica fiber surface studied by tapping mode atomic force microscopy. Surf. Sci. 1993, 290, L688–L692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansma, P.K.; Cleveland, J.P.; Radmacher, M.; Walters, D.A.; Hillner, P.E.; Bezanilla, M.; Fritz, M.; Vie, D.; Hansma, H.G.; Prater, C.B.; et al. Tapping mode atomic force microscopy in liquids. Appl. Phys. Lett. 1994, 64, 1738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McPherson, A.; Kuznetsov, Y.G. Atomic force microscopy investigation of viruses. Methods Mol. Biol. 2001, 736, 171–195. [Google Scholar]
- Wagner, P. Immobilization strategies for biological scanning probe microscopy. FEBS Lett. 1998, 430, 112–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuznetsov, Y.G.; McPherson, A. Atomic Force Microscopy in Imaging of Viruses and Virus-Infected Cells. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2011, 75, 268–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuznetsov, Y.G.; Gurnon, J.R.; Van Etten, J.L.; McPherson, A. Atomic force microscopy investigation of a chlorella virus, PBCV-1. J. Struct. Biol. 2005, 149, 256–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuznetsov, Y.G.; Datta, S.; Kothari, N.H.; Greenwood, A.; Fan, H.; McPherson, A. Atomic force microscopy investigation of fibroblasts infected with wild-type and mutant murine leukemia virus (MuLV). Biophys. J. 2002, 83, 3665–3674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuznetsov, Y.G.; Victoria, J.G.; Robinson, W.E.; Mcpherson, A. Atomic Force Microscopy Investigation of Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV) and HIV-Infected Lymphocytes. J. Virol. 2003, 77, 11896–11909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Low, A.; Datta, S.; Kuznetsov, Y.; Jahid, S.; Kothari, N.; McPherson, A.; Fan, H. Mutation in the glycosylated gag protein of murine leukemia virus results in reduced in vivo infectivity and a novel defect in viral budding or release. J. Virol. 2007, 81, 3685–3692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gladnikoff, M.; Rousso, I. Directly monitoring individual retrovirus budding events using atomic force microscopy. Biophys. J. 2008, 94, 320–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barrett, R.C.; Quate, C.F. High-speed, large-scale imaging with the atomic force microscope. J. Vac. Sci. Technol. B 1991, 9, 302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viani, M.B.; Schäffer, T.E.; Paloczi, G.T.; Pietrasanta, L.I.; Smith, B.L. Fast imaging and fast force spectroscopy of single biopolymers with a new atomic force microscope designed for small cantilevers. Rev. Sci. 1999, 70, 4300–4303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ando, T.; Kodera, N.; Naito, Y.; Kinoshita, T.; Furuta, K.; Toyoshima, Y.Y. A High-speed Atomic Force Microscope for Studying Biological Macromolecules in Action. ChemPhysChem 2003, 4, 1196–1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Humphris, A.D.L.; Miles, M.J.; Hobbs, J.K. A mechanical microscope: High-speed atomic force microscopy. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2005, 86, 034106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ando, T.; Uchihashi, T.; Fukuma, T. High-speed atomic force microscopy for nano-visualization of dynamic biomolecular processes. Prog. Surf. Sci. 2008, 83, 337–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Picco, L.M.; Dunton, P.G.; Ulcinas, A.; Engledew, D.J.; Hoshi, O.; Ushiki, T.; Miles, M.J. High-speed AFM of human chromosomes in liquid. Nanotechnology 2008, 19, 384018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Picco, L.; Bozec, L.; Ulcinas, A.; Engledew, D.J.; Antognozzi, M.; Horton, M.; Miles, M.J. Breaking the speed limit with atomic force microscopy. Nanotechnology 2007, 18, 044030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kodera, N.; Yamamoto, D.; Ishikawa, R.; Ando, T. Video imaging of walking myosin V by high-speed atomic force microscopy. Nature 2010, 468, 72–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shibata, M.; Nishimasu, H.; Kodera, N.; Hirano, S.; Ando, T.; Uchihashi, T.; Nureki, O. Real-space and real-time dynamics of CRISPR-Cas9 visualized by high-speed atomic force microscopy. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 1430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ando, T.; Uchihashi, T.; Kodera, N.; Yamamoto, D.; Miyagi, A.; Taniguchi, M.; Yamashita, H. High-speed AFM and nano-visualization of biomolecular processes. Pflugers Arch. Eur. J. Physiol. 2008, 456, 211–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ando, T. High-speed atomic force microscopy coming of age. Nanotechnology 2012, 23, 062001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ando, T.; Uchihashi, T.; Kodera, N. High-Speed AFM and Applications to Biomolecular Systems. Annu. Rev. Biophys. 2013, 42, 393–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ando, T. High-speed AFM imaging. Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 2014, 28, 63–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ando, T. Directly watching biomolecules in action by high-speed atomic force microscopy. Biophys. Rev. 2017, 9, 421–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ando, T. High-speed atomic force microscopy and its future prospects. Biophys. Rev. 2018, 10, 285–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hodel, A.W.; Leung, C.; Dudkina, N.V.; Saibil, H.R.; Hoogenboom, B.W. Atomic force microscopy of membrane pore formation by cholesterol dependent cytolysins. Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 2016, 39, 8–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leung, C.; Hodel, A.W.; Brennan, A.J.; Lukoyanova, N.; Tran, S.; House, C.M.; Kondos, S.C.; Whisstock, J.C.; Dunstone, M.A.; Trapani, J.A.; et al. Real-time visualization of perforin nanopore assembly. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2017, 12, 467–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sumino, A.; Uchihashi, T.; Oiki, S. Oriented Reconstitution of the Full-Length KcsA Potassium Channel in a Lipid Bilayer for AFM Imaging. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2017, 8, 785–973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mikheikin, A.; Olsen, A.; Leslie, K.; Mishra, B.; Gimzewski, J.K.; Reed, J. Atomic force microscopic detection enabling multiplexed low-cycle-number quantitative polymerase chain reaction for biomarker assays. Anal. Chem. 2014, 86, 6180–6183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mikheikin, A.; Olsen, A.; Picco, L.; Payton, O.; Mishra, B.; Gimzewski, J.K.; Reed, J. High-Speed Atomic Force Microscopy Revealing Contamination in DNA Purification Systems. Anal. Chem. 2016, 88, 2527–2532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mikheikin, A.; Olsen, A.; Leslie, K.; Russell-Pavier, F.; Yacoot, A.; Picco, L.; Payton, O.; Toor, A.; Chesney, A.; Gimzewski, J.K.; et al. DNA nanomapping using CRISPR-Cas9 as a programmable nanoparticle. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 1665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fritz, M.; Radmacher, M.; Gaub, H.E. Granula Motion and Membrane Spreading during Activation of Human Platelets Imaged by Atomic-Force Microscopy. Biophys. J. 1994, 66, 1328–1334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henderson, E. Imaging of living cells by atomic force microscopy. Prog. Surf. Sci. 1994, 46, 39–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasas, S.; Ikai, A. A method for anchoring round shaped cells for atomic force microscope imaging. Biophys. J. 1995, 68, 1678–1680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Formosa, C.; Pillet, F.; Schiavone, M.; Duval, R.E.; Ressier, L.; Dague, E. Generation of living cell arrays for atomic force microscopy studies. Nat. Protoc. 2015, 10, 199–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gebeshuber, I.C.; Kindt, J.H.; Thomson, J.B.; Del Amo, Y.; Stachelbergers, H.; Brzezinski, M.A.; Stucky, G.D.; Morse, D.E.; Hansma, P.K. Atomic force microscopy study of living diatoms in ambient conditions. J. Microsc. 2003, 212, 292–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luís, A.T.; Hlúbiková, D.; Vaché, V.; Choquet, P.; Hoffmann, L.; Ector, L. Atomic force microscopy (AFM) application to diatom study: Review and perspectives. J. Appl. Phycol. 2017, 29, 2989–3001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Callow, J.A.; Crawford, S.A.; Higgins, M.J.; Mulvaney, P.; Wetherbee, R. The application of atomic force microscopy to topographical studies and force measurements on the secreted adhesive of the green alga Enteromorpha. Planta 2000, 211, 641–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shibata, M.; Uchihashi, T.; Ando, T.; Yasuda, R. Long-tip high-speed atomic force microscopy for nanometer-scale imaging in live cells. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 8724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berquand, A.; Xia, N.; Castner, D.G.; Clare, B.H.; Abbott, N.L.; Dupres, V.; Adriaensen, Y.; Dufrêne, Y.F. Antigen binding forces of single antilysozyme Fv fragments explored by atomic force microscopy. Langmuir 2005, 21, 5517–5523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dufrêne, Y.F. Using nanotechniques to explore microbial surfaces. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2004, 2, 451–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dufrêne, Y.F. Microbial Nanoscopy: Breakthroughs, Challenges, and Opportunities. ACS Nano 2017, 11, 19–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alsteens, D.; Newton, R.; Schubert, R.; Martinez-Martin, D.; Delguste, M.; Roska, B.; Müller, D.J. Nanomechanical mapping of first binding steps of a virus to animal cells. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2016, 12, 177–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sieben, C.; Herrmann, A. Single virus force spectroscopy: The ties that bind. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2017, 12, 102–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agarkova, I.; Hertel, B.; Zhang, X.; Lane, L.; Tchourbanov, A.; Dunigan, D.D.; Thiel, G.; Rossmann, M.G.; Van Etten, J.L. Dynamic attachment of Chlorovirus PBCV-1 to Chlorella variabilis. Virology 2014, 466–467, 95–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dufrêne, Y.F.; Ando, T.; Garcia, R.; Alsteens, D.; Martinez-Martin, D.; Engel, A.; Gerber, C.; Müller, D.J. Imaging modes of atomic force microscopy for application in molecular and cell biology. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2017, 12, 295–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cartagena, A.; Hernando-Pérez, M.; Carrascosa, J.L.; de Pablo, P.J.; Raman, A. Mapping in vitro local material properties of intact and disrupted virions at high resolution using multi-harmonic atomic force microscopy. Nanoscale 2013, 5, 4729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cartagena-Rivera, A.X.; Wang, W.H.; Geahlen, R.L.; Raman, A. Fast, multi-frequency, and quantitative nanomechanical mapping of live cells using the atomic force microscope. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- González-Domínguez, I.; Gutiérrez-Granados, S.; Cervera, L.; Gòdia, F.; Domingo, N. Identification of HIV-1-Based Virus-like Particles by Multifrequency Atomic Force Microscopy. Biophys. J. 2016, 111, 1173–1179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marchetti, M.; Wuite, G.; Roos, W. Atomic force microscopy observation and characterization of single virions and virus-like particles by nano-indentation. Curr. Opin. Virol. 2016, 18, 82–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iwata, F.; Ohashi, Y.; Ishisaki, I.; Picco, L.M.; Ushiki, T. Development of nanomanipulator using a high-speed atomic force microscope coupled with a haptic device. Ultramicroscopy 2013, 133, 88–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koo, H.; Park, I.; Lee, Y.; Kim, H.J.; Jung, J.H.; Lee, J.H.; Kim, Y.; Kim, J.H.; Park, J.W. Visualization and Quantification of MicroRNA in a Single Cell Using Atomic Force Microscopy. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2016, 138, 11664–11671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Plomp, M.; Rice, M.K.; Wagner, E.K.; Mcpherson, A.; Malkin, A.J. Rapid Visualization at High Resolution of Pathogens by Atomic Force Microscopy. Am. J. Pathol. 2002, 160, 1959–1966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malkin, A.J.; McPherson, A.; Gershon, P.D. Structure of intracellular mature vaccinia virus visualized by in situ atomic force microscopy. J. Virol. 2003, 77, 6332–6340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuznetsov, Y.G.; Victoria, J.G.; Low, A.; Robinson, W.E.; Fan, H.; McPherson, A. Atomic force microscopy imaging of retroviruses: Human immunodeficiency virus and murine leukemia virus. Scanning 2004, 26, 209–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuznetsov, Y.G.; McPherson, A. Atomic force microscopy investigation of Turnip Yellow Mosaic Virus capsid disruption and RNA extrusion. Virology 2006, 352, 329–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuznetsov, Y.G.; Daijogo, S.; Zhou, J.; Semler, B.L.; McPherson, A. Atomic force microscopy analysis of icosahedral virus RNA. J. Mol. Biol. 2005, 347, 41–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuznetsov, Y.G.; Dowell, J.J.; Gavira, J.A.; Ng, J.D.; McPherson, A. Biophysical and atomic force microscopy characterization of the RNA from satellite tobacco mosaic virus. Nucleic Acids Res. 2010, 38, 8284–8294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuznetsov, Y.G.; McPherson, A. Identification of DNA and RNA from retroviruses using ribonuclease A. Scanning 2006, 28, 278–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuznetsov, Y.G.; Klose, T.; Rossmann, M.; McPherson, A. Morphogenesis of mimivirus and its viral factories: An atomic force microscopy study of infected cells. J. Virol. 2013, 87, 11200–11213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wulfmeyer, T.; Polzer, C.; Hiepler, G.; Hamacher, K.; Shoeman, R.; Dunigan, D.D.; van Etten, J.L.; Lolicato, M.; Moroni, A.; Thiel, G.; et al. Structural organization of DNA in chlorella viruses. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leung, C.; Bestembayeva, A.; Thorogate, R.; Stinson, J.; Pyne, A.; Marcovich, C.; Yang, J.; Drechsler, U.; Despont, M.; Jankowski, T.; et al. Atomic force microscopy with nanoscale cantilevers resolves different structural conformations of the DNA double helix. Nano Lett. 2012, 12, 3846–3850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, R.Y.-R.; Kudryashev, M.; Li, X.; Egelman, E.H.; Basler, M.; Cheng, Y.; Baker, D.; Dimaio, F. De novo Protein Structure Determination from Near-Atomic Resolution Cryo-EM Maps. Nat. Methods 2015, 12, 335–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gross, L.; Wang, Z.L.; Ugarte, D.; Mohn, F.; Moll, N.; Heer, W.A.; Vincent, P.; Liljeroth, P.; Journet, C.; Meyer, G.; et al. The Chemical Structure of a Molecule Resolved by Atomic Force Microscopy. Science 2009, 325, 1110–1114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Majzik, Z.; Pavliček, N.; Vilas-Varela, M.; Pérez, D.; Moll, N.; Guitián, E.; Meyer, G.; Peña, D.; Gross, L. Studying an antiaromatic polycyclic hydrocarbon adsorbed on different surfaces. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 2–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wastl, D.S.; Weymouth, A.J.; Giessibl, F.J. Atomically resolved graphitic surfaces in air by atomic force microscopy. ACS Nano 2014, 8, 5233–5239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wastl, D.S.; Judmann, M.; Weymouth, A.J.; Giessibl, F.J. Atomic resolution of calcium and oxygen sublattices of calcite in ambient conditions by atomic force microscopy using qPlus sensors with sapphire tips. ACS Nano 2015, 9, 3858–3865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
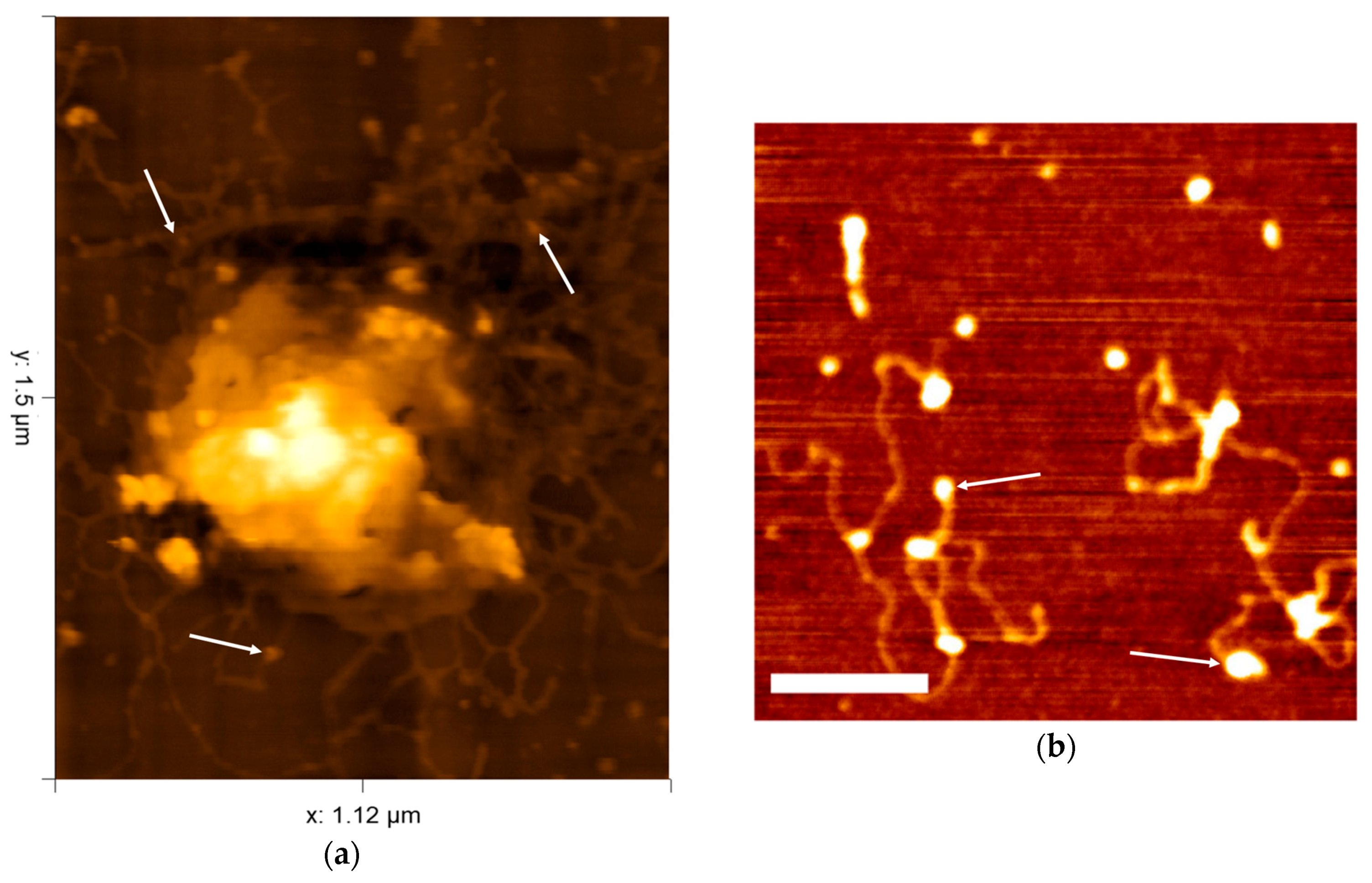
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Evans, C.T.; Payton, O.; Picco, L.; Allen, M.J. Algal Viruses: The (Atomic) Shape of Things to Come. Viruses 2018, 10, 490. https://doi.org/10.3390/v10090490
Evans CT, Payton O, Picco L, Allen MJ. Algal Viruses: The (Atomic) Shape of Things to Come. Viruses. 2018; 10(9):490. https://doi.org/10.3390/v10090490
Chicago/Turabian StyleEvans, Christopher T., Oliver Payton, Loren Picco, and Michael J. Allen. 2018. "Algal Viruses: The (Atomic) Shape of Things to Come" Viruses 10, no. 9: 490. https://doi.org/10.3390/v10090490
APA StyleEvans, C. T., Payton, O., Picco, L., & Allen, M. J. (2018). Algal Viruses: The (Atomic) Shape of Things to Come. Viruses, 10(9), 490. https://doi.org/10.3390/v10090490