Anti-CRISPR-Based and CRISPR-Based Genome Editing of Sulfolobus islandicus Rod-Shaped Virus 2
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Strains and Growth Conditions
2.2. Cloning
2.3. Construction of Anti-CRISPR-Based Genome Editing Plasmids
2.4. Construction of CRISPR-Based Genome Editing Plasmids
2.5. Electroporation Procedure
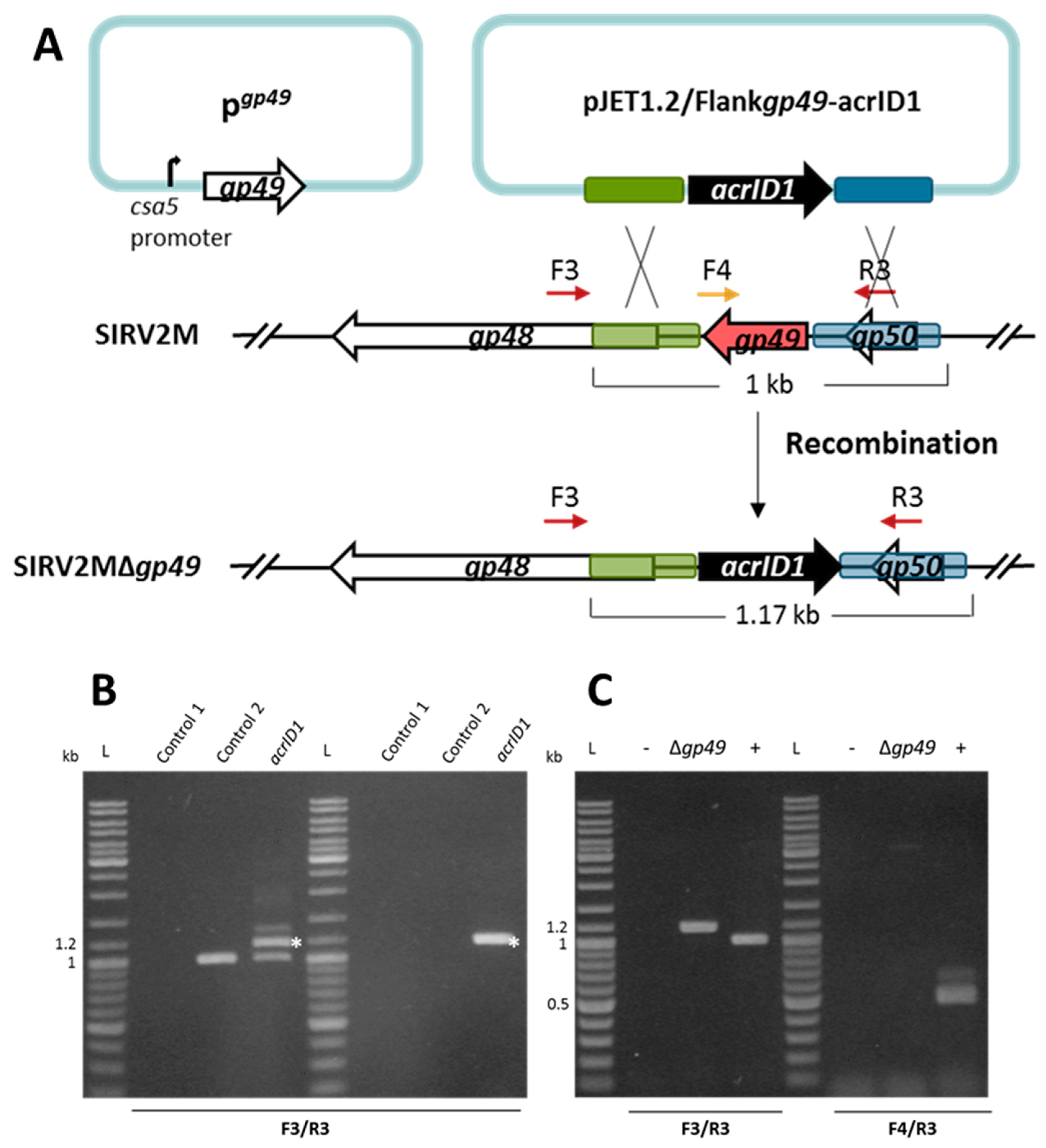
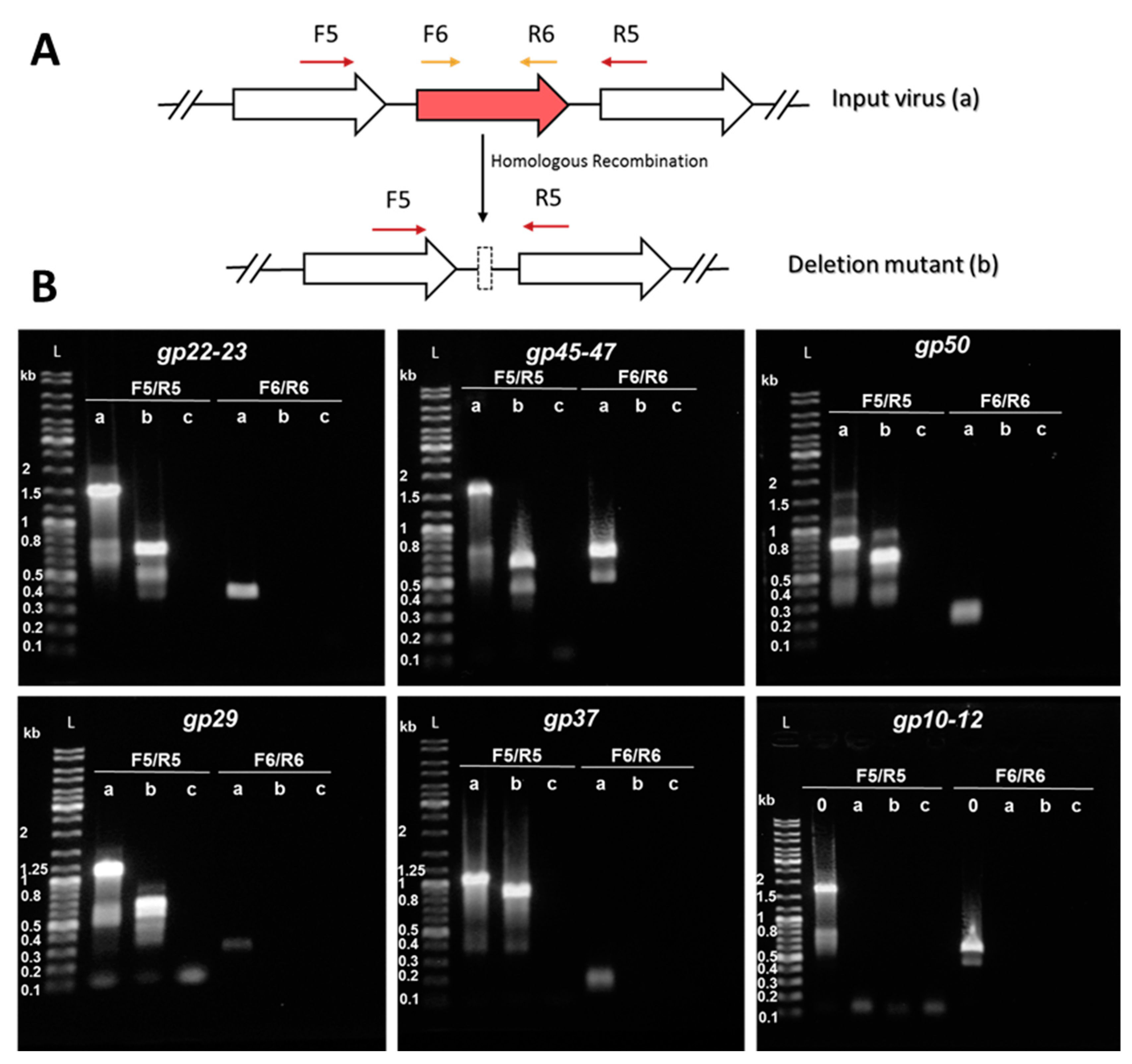
2.6. Construction of Knockout Mutants and Knockout Screening by PCR
2.7. Plaque Assay
3. Results and Discussion
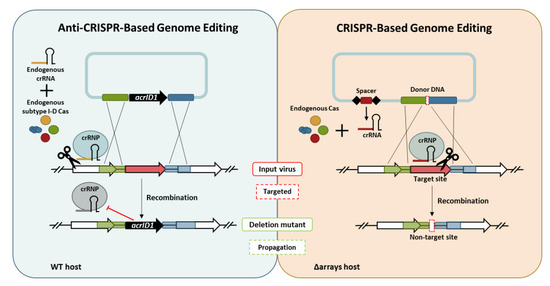
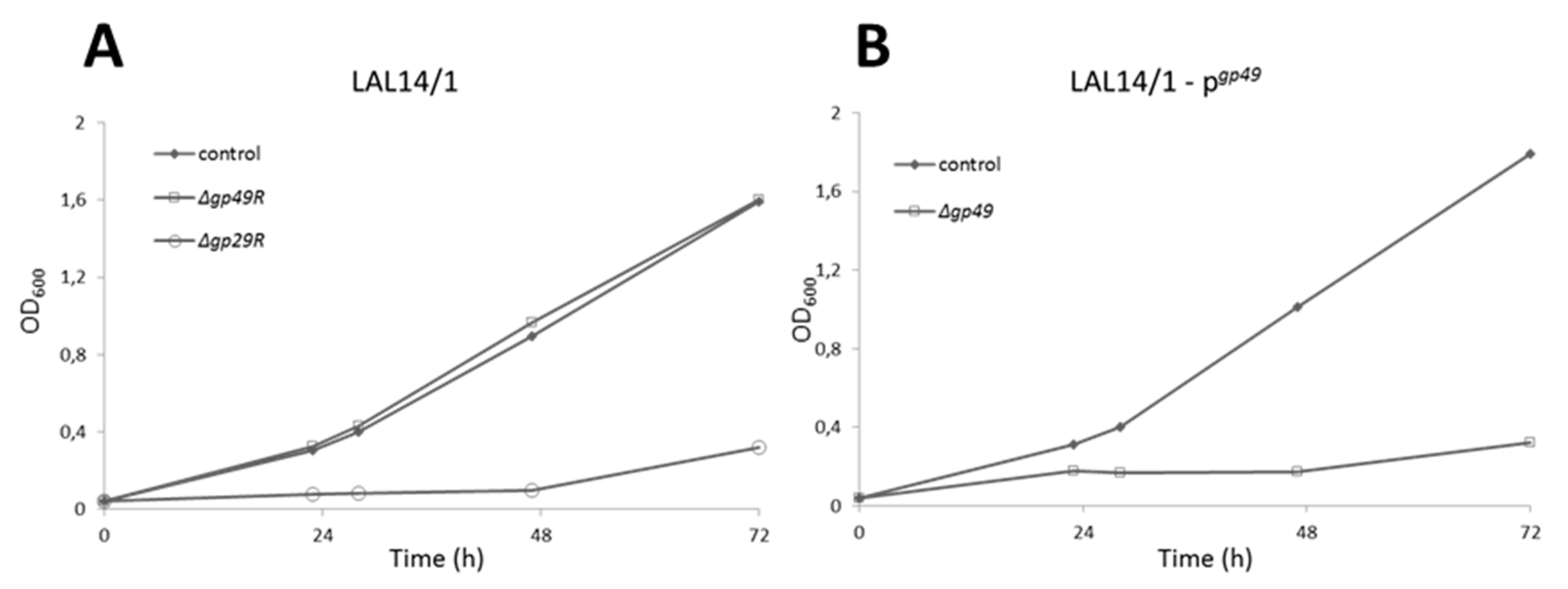
3.1. Knockout of a Non-Essential Gene (SIRV2 Gp29) and an Essential Gene (SIRV2 Gp49) from SIRV2M Genome Using AcrID1 as a Selection Marker
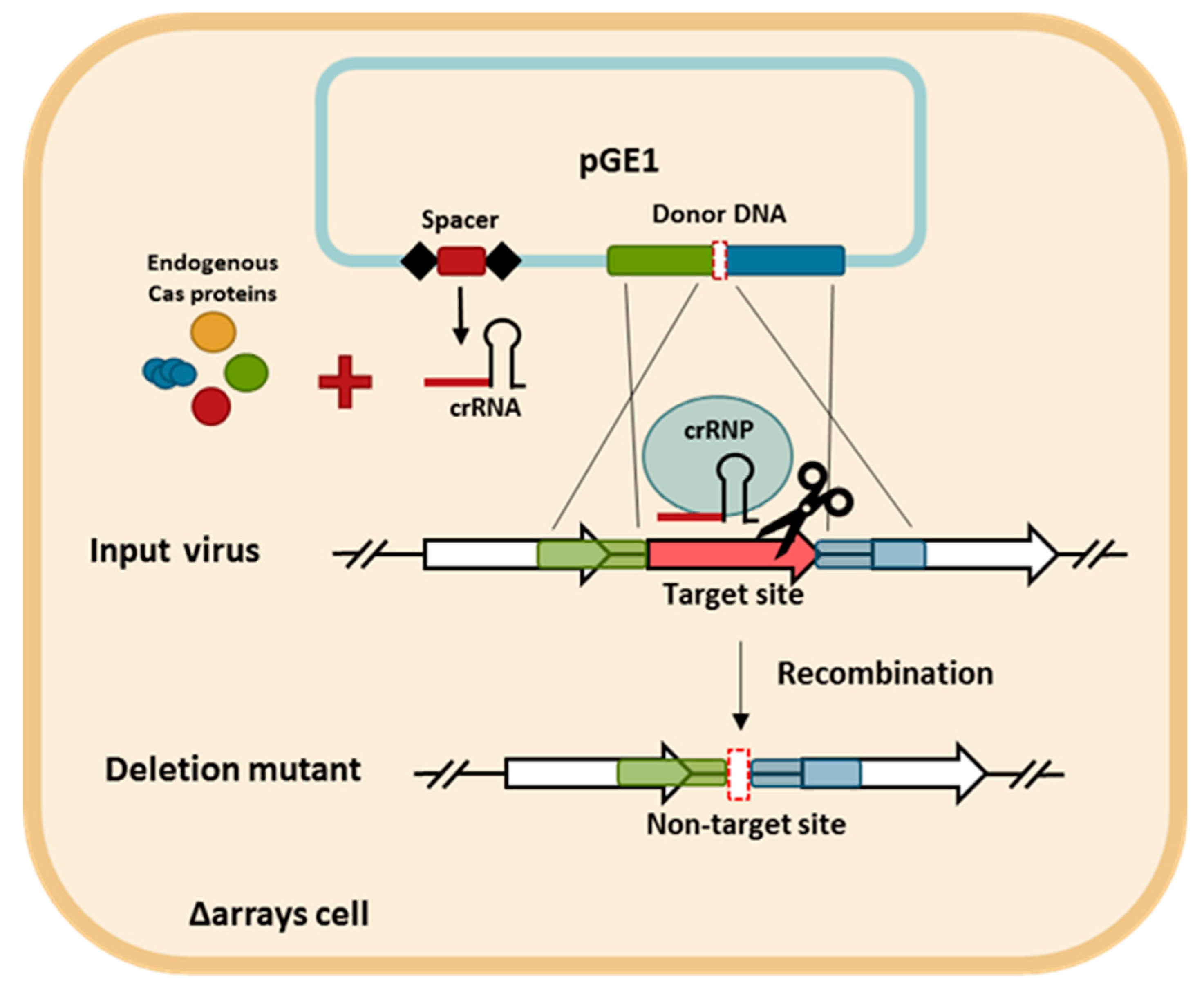
3.2. CRISPR-Based Viral Genome Editing Approach
3.3. Consecutive Knockout of SIRV2 Accessory Genes
3.4. SIRVs’ Core Genome
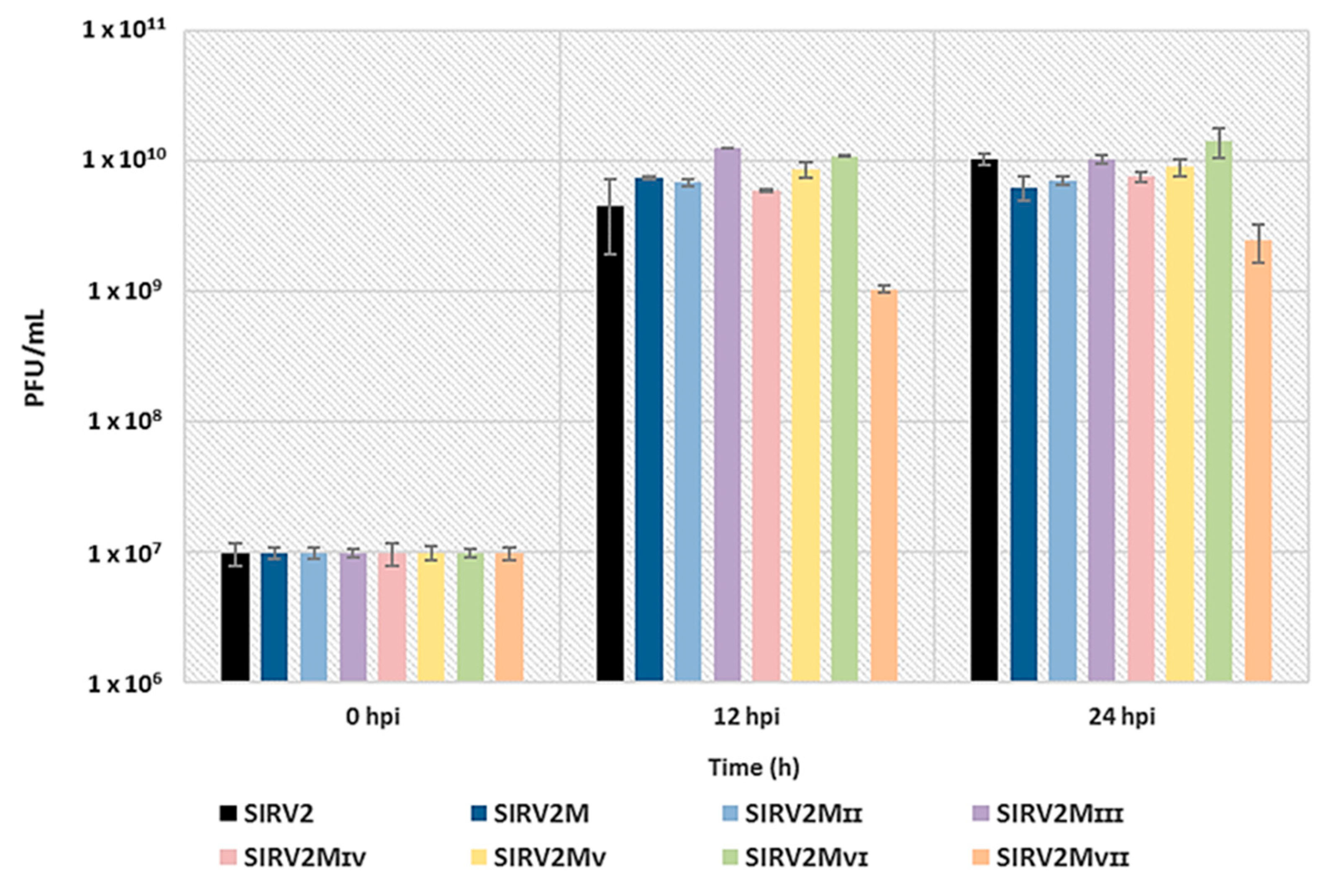
3.5. Assessing the Effect of The Deletions on Viral Infectivity
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hendrix, R.W.; Lawrence, J.G.; Hatfull, G.F.; Casjens, S. The origins and ongoing evolution of viruses. Trends Microbiol. 2000, 8, 504–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suttle, C.A. Marine viruses—Major players in the global ecosystem. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2007, 5, 801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edwards, R.A.; Rohwer, F. Opinion: Viral metagenomics. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2005, 3, 504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Breitbart, M.; Rohwer, F. Here a virus, there a virus, everywhere the same virus? Trends Microbiol. 2005, 13, 278–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mateu, M.G. Structure and Physics of Viruses: An Integrated Textbook; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Qimron, U.; Marintcheva, B.; Tabor, S.; Richardson, C.C. Genomewide screens for Escherichia coli genes affecting growth of T7 bacteriophage. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 19039–19044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marinelli, L.J.; Piuri, M.; Swigoňová, Z.; Balachandran, A.; Oldfield, L.M.; van Kessel, J.C.; Hatfull, G.F. BRED5: A simple and powerful tool for constructing mutant and recombinant bacteriophage genomes. PLoS ONE 2008, 3, e3957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marinelli, L.J.; Hatfull, G.F.; Piuri, M. Recombineering: A powerful tool for modification of bacteriophage genomes. Bacteriophage 2012, 2, 5–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prangishvili, D.; Forterre, P.; Garrett, R.A. Viruses of the Archaea: A unifying view. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2006, 4, 837–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prangishvili, D.; Garrett, R.A.; Koonin, E.V. Evolutionary genomics of archaeal viruses: Unique viral genomes in the third domain of life. Virus Res. 2006, 117, 52–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iverson, E.A.; Goodman, D.A.; Gorchels, M.E.; Stedman, K.M. Extreme Mutation Tolerance: Nearly Half of the Archaeal Fusellovirus Sulfolobus Spindle-Shaped Virus 1 Genes Are Not Required for Virus Function, Including the Minor Capsid Protein Gene vp3. J. Virol. 2017, 91, e02406–e02416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clore, A.J.; Stedman, K.M. The SSV1 viral integrase is not essential. Virology 2007, 361, 103–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iverson, E.; Stedman, K. A genetic study of SSV1, the prototypical fusellovirus. Front. Microbiol. 2012, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goodman, D.A.; Stedman, K.M. Comparative genetic and genomic analysis of the novel fusellovirus Sulfolobus spindle-shaped virus 10. Virus Evol. 2018, 4, vey022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wirth, J.F.; Snyder, J.C.; Hochstein, R.A.; Ortmann, A.C.; Willits, D.A.; Douglas, T.; Young, M.J. Development of a genetic system for the archaeal virus Sulfolobus turreted icosahedral virus (STIV). Virology 2011, 415, 6–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barrangou, R.; Fremaux, C.; Deveau, H.; Richards, M.; Boyaval, P.; Moineau, S.; Romero, D.A.; Horvath, P. CRISPR provides acquired resistance against viruses in prokaryotes. Science 2007, 315, 1709–1712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koonin, E.V.; Makarova, K.S.; Zhang, F. Diversity, classification and evolution of CRISPR-Cas systems. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2017, 37, 67–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wiedenheft, B.; Sternberg, S.H.; Doudna, J.A. RNA-guided genetic silencing systems in bacteria and archaea. Nature 2012, 482, 331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garrett, R.A.; Vestergaard, G.; Shah, S.A. Archaeal CRISPR-based immune systems: Exchangeable functional modules. Trends Microbiol. 2011, 19, 549–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiro, R.; Shitrit, D.; Qimron, U. Efficient engineering of a bacteriophage genome using the type I-E CRISPR-Cas system. RNA Biol. 2014, 11, 42–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, Y.; Sun, L.; Gao, D.; Ding, C.; Li, Z.; Li, Y.; Cun, W.; Li, Q. High-Efficiency Targeted Editing of Large Viral Genomes by RNA-Guided Nucleases. PLoS Pathog. 2014, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martel, B.; Moineau, S. CRISPR-Cas: An efficient tool for genome engineering of virulent bacteriophages. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014, 43, 9504–9513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prangishvili, D.; Arnold, H.P.; Götz, D.; Ziese, U.; Holz, I.; Kristjansson, J.K.; Zillig, W. A novel virus family, the Rudiviridae: Structure, virus-host interactions and genome variability of the sulfolobus viruses SIRV1 and SIRV2. Genetics 1999, 152, 1387–1396. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Peng, X.; Blum, H.; She, Q.; Mallok, S.; Brügger, K.; Garrett, R.A.; Zillig, W.; Prangishvili, D. Sequences and replication of genomes of the archaeal rudiviruses SIRV1 and SIRV2: Relationships to the archaeal lipothrixvirus SIFV and some eukaryal viruses. Virology 2001, 291, 226–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martínez-Alvarez, L.; Bell, S.D.; Peng, X. Multiple consecutive initiation of replication producing novel brush-like intermediates at the termini of linear viral dsDNA genomes with hairpin ends. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016, 44, 8799–8809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pawluk, A.; Bondy-Denomy, J.; Cheung, V.H.W.; Maxwell, K.L.; Davidson, A.R. A new group of phage anti-CRISPR genes inhibits the type I-E CRISPR-Cas system of pseudomonas aeruginosa. mBio 2014, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marino, N.D.; Zhang, J.Y.; Borges, A.L.; Sousa, A.A.; Leon, L.M.; Rauch, B.J.; Walton, R.T.; Berry, J.D.; Joung, J.K.; Kleinstiver, B.P.; et al. Discovery of widespread Type I and Type V CRISPR-Cas inhibitors. Science 2018, 362, 240–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bondy-Denomy, J.; Pawluk, A.; Maxwell, K.L.; Davidson, A.R. Bacteriophage genes that inactivate the CRISPR/Cas bacterial immune system. Nature 2013, 493, 429–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, F.; Bhoobalan-Chitty, Y.; Van, L.B.; Kjeldsen, A.L.; Dedola, M.; Makarova, K.S.; Koonin, E.V.; Brodersen, D.V.; Peng, X. Anti-CRISPR proteins encoded by archaeal lytic viruses inhibit subtype I-D immunity. Nat. Microbiol. 2018, 3, 461–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pawluk, A.; Staals, R.H.J.; Taylor, C.; Watson, B.N.J.; Saha, S.; Fineran, P.C.; Maxwell, K.L.; Davidson, A.R. Inactivation of CRISPR-Cas systems by anti-CRISPR proteins in diverse bacterial species. Nat. Microbiol. 2016, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rauch, B.J.; Silvis, M.R.; Hultquist, J.F.; Waters, C.S.; McGregor, M.J.; Krogan, N.J.; Bondy-Denomy, J. Inhibition of CRISPR-Cas9 with Bacteriophage Proteins. Cell 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hynes, A.P.; Rousseau, G.M.; Lemay, M.L.; Horvath, P.; Romero, D.A.; Fremaux, C.; Moineau, S. An anti-CRISPR from a virulent streptococcal phage inhibits Streptococcus pyogenes Cas9. Nat. Microbiol. 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hynes, A.P.; Rousseau, G.M.; Agudelo, D.; Goulet, A.; Amigues, B.; Loehr, J.; Romero, D.A.; Fremaux, C.; Horvath, P.; Doyon, Y.; Cambillau, C.; Moineau, S. Widespread anti-CRISPR proteins in virulent bacteriophages inhibit a range of Cas9 proteins. Nat. Commun. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pawluk, A.; Amrani, N.; Zhang, Y.; Garcia, B.; Hidalgo-Reyes, Y.; Lee, J.; Edraki, A.; Shah, M.; Sontheimer, E.J.; Maxwell, K.L.; Davidson, A.R. Naturally Occurring Off-Switches for CRISPR-Cas9. Cell 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.; Mir, A.; Edraki, A.; Garcia, B.; Amrani, N.; Lou, H.E.; Gainetdinov, I.; Pawluk, A.; Ibraheim, R.; Gao, X.D.; Liu, P.; Davidson, A.R.; Maxwell, K.L.; Sontheimer, E.J. Potent Cas9 inhibition in bacterial and human cells by new anti-CRISPR protein families. bioRxiv 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watters, K.E.; Fellmann, C.; Bai, H.B.; Ren, S.M.; Doudna, J.A. Systematic discovery of natural CRISPR-Cas12a inhibitors. Science 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bautista, M.A.; Black, J.A.; Youngblut, N.D.; Whitaker, R.J. Differentiation and Structure in Sulfolobus islandicus Rod-Shaped Virus Populations. Viruses 2017, 9, 120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, F.; Vestergaard, G.; Peng, W.; She, Q.; Peng, X. CRISPR-Cas type I-A Cascade complex couples viral infection surveillance to host transcriptional regulation in the dependence of Csa3b. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zillig, W.; Arnold, H.P.; Holz, I.; Prangishvili, D.; Schweier, A.; Stedman, K.; She, Q.; Phan, H.; Garrett, R.; Kristjansson, J.K. Genetic elements in the extremely thermophilic archaeon Sulfolobus. Extremophiles 1998, 2, 131–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gudbergsdottir, S.; Deng, L.; Chen, Z.; Jensen, J.V.K.; Jensen, L.R.; She, Q.; Garrett, R.A. Dynamic properties of the Sulfolobus CRISPR/Cas and CRISPR/Cmr systems when challenged with vector-borne viral and plasmid genes and protospacers. Mol. Microbiol. 2011, 79, 35–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Pan, S.; Zhang, Y.; Ren, M.; Feng, M.; Peng, N.; Chen, L.; Liang, Y.X.; She, Q. Harnessing Type I and Type III CRISPR-Cas systems for genome editing. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016, 44, e34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, N.; Deng, L.; Mei, Y.; Jiang, D.; Hu, Y.; Awayez, M.; Liang, Y.; She, Q. A synthetic arabinose-inducible promoter confers high levels of recombinant protein expression in hyperthermophilic archaeon Sulfolobus islandicus. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horton, R.M.; Cai, Z.; Ho, S.N.; Pease, L.R. Gene splicing by overlap extension: Tailor-made genes using the polymerase chain reaction. Biotechniques 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, L.; Zhu, H.; Chen, Z.; Liang, Y.X.; She, Q. Unmarked gene deletion and host–vector system for the hyperthermophilic crenarchaeon Sulfolobus islandicus. Extremophiles 2009, 13, 735–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- She, Q.; Zhang, C.; Deng, L.; Peng, N.; Chen, Z.; Liang, Y.X. Genetic analyses in the hyperthermophilic archaeon Sulfolobus islandicus. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 2009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quax, T.E.F.; Lucas, S.; Reimann, J.; Pehau-Arnaudet, G.; Prevost, M.-C.; Forterre, P.; Albers, S.-V.; Prangishvili, D. Simple and elegant design of a virion egress structure in Archaea. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bize, A.; Karlsson, E.A.; Ekefjärd, K.; Quax, T.E.F.; Pina, M.; Prevost, M.-C.; Forterre, P.; Tenaillon, O.; Bernander, R.; Prangishvili, D. A unique virus release mechanism in the Archaea. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 11306–11311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, F.; Chen, L.; Peng, X. First experimental evidence for the presence of a CRISPR toxin in Sulfolobus. J. Mol. Biol. 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quax, T.E.F.; Voet, M.; Sismeiro, O.; Dillies, M.; Jagla, B.; Coppee, J.-Y.; Sezonov, G.; Forterre, P.; van der Oost, J.; Lavigne, R.; Prangishvili, D. Massive Activation of Archaeal Defense Genes during Viral Infection. J. Virol. 2013, 87, 8419–8428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okutan, E.; Deng, L.; Mirlashari, S.; Uldahl, K.; Halim, M.; Liu, C.; Garrett, R.A.; She, Q.; Peng, X. Novel insights into gene regulation of the rudivirus SIRV2 infecting Sulfolobus cells. RNA Biol. 2013, 10, 875–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juhala, R.J.; Ford, M.E.; Duda, R.L.; Youlton, A.; Hatfull, G.F.; Hendrix, R.W. Genomic sequences of bacteriophages HK97 and HK022: Pervasive genetic mosaicism in the lambdoid bacteriophages. J. Mol. Biol. 2000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bettstetter, M.; Peng, X.; Garrett, R.A.; Prangishvili, D. AFV1, a novel virus infecting hyperthermophilic archaea of the genus Acidianus. Virology 2003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haring, M.; Rachel, R.; Peng, X.; Garrett, R.A.; Prangishvili, D. Viral Diversity in Hot Springs of Pozzuoli, Italy, and Characterization of a Unique Archaeal Virus, Acidianus Bottle-Shaped Virus, from a New Family, the Ampullaviridae. J. Virol. 2005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khayat, R.; Tang, L.; Larson, E.T.; Lawrence, C.M.; Young, M.; Johnson, J.E. Structure of an archaeal virus capsid protein reveals a common ancestry to eukaryotic and bacterial viruses. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gudbergsdóttir, S.R.; Menzel, P.; Krogh, A.; Young, M.; Peng, X. Novel viral genomes identified from six metagenomes reveal wide distribution of archaeal viruses and high viral diversity in terrestrial hot springs. Environ. Microbiol. 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arnold, H.P.; Zillig, W.; Ziese, U.; Holz, I.; Crosby, M.; Utterback, T.; Weidmann, J.F.; Kristjanson, J.K.; Klenk, H.P.; Nelson, K.E.; Fraser, C.M. A novel lipothrixvirus, SIFV, of the extremely thermophilic crenarchaeon Sulfolobus. Virology 2000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Larson, E.T.; Eilers, B.J.; Reiter, D.; Ortmann, A.C.; Young, M.J.; Lawrence, C.M. A new DNA binding protein highly conserved in diverse crenarchaeal viruses. Virology 2007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keller, J.; Leulliot, N.; Cambillau, C.; Campanacci, V.; Porciero, S.; Prangishvilli, D.; Forterre, P.; Cortez, D.; Quevillon-Cheruel, S.; Van Tilbeurgh, H. Crystal structure of AFV3-109, a highly conserved protein from crenarchaeal viruses. Virol. J. 2007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Virus | Position of New Deletion (bp) | Deletion Size (bp) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| SIRV2 | - | - | |
| SIRV2M: Δgp02–09,51–53 | Δ1491–5474, Δ32426–33939 | 3983, 1513 | [29] |
| SIRV2MII: Δgp02–09,51–53,48,10–14 | Δ30803-31479, Δ5678–8557 | 676, 2879 | Bhoobalan-Chitty unpublished |
| SIRV2MIII: Δgp02–09,51–53,48,10–14,22–23 | Δ12664–13395 | 731 | This work |
| SIRV2MIV: Δgp02–09,51–53,48,10–14,22–23,45–47 | Δ29630–30517 | 888 | This work |
| SIRV2MV: Δgp02–09,51–53,48,10–14,22–23,45–47,50 | Δ32169–32344 | 175 | This work |
| SIRV2MVI: Δgp02–09,51–53,48,10–14,22–23,45–47,50,29 | Δ15827–16366 | 539 | This work |
| SIRV2MVII: Δgp02–09,51–53,48,10–14,22–23,45–47,50,29,37 | Δ19910–20119 | 209 | This work |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mayo-Muñoz, D.; He, F.; Jørgensen, J.B.; Madsen, P.K.; Bhoobalan-Chitty, Y.; Peng, X. Anti-CRISPR-Based and CRISPR-Based Genome Editing of Sulfolobus islandicus Rod-Shaped Virus 2. Viruses 2018, 10, 695. https://doi.org/10.3390/v10120695
Mayo-Muñoz D, He F, Jørgensen JB, Madsen PK, Bhoobalan-Chitty Y, Peng X. Anti-CRISPR-Based and CRISPR-Based Genome Editing of Sulfolobus islandicus Rod-Shaped Virus 2. Viruses. 2018; 10(12):695. https://doi.org/10.3390/v10120695
Chicago/Turabian StyleMayo-Muñoz, David, Fei He, Jacob Bruun Jørgensen, Poul Kári Madsen, Yuvaraj Bhoobalan-Chitty, and Xu Peng. 2018. "Anti-CRISPR-Based and CRISPR-Based Genome Editing of Sulfolobus islandicus Rod-Shaped Virus 2" Viruses 10, no. 12: 695. https://doi.org/10.3390/v10120695
APA StyleMayo-Muñoz, D., He, F., Jørgensen, J. B., Madsen, P. K., Bhoobalan-Chitty, Y., & Peng, X. (2018). Anti-CRISPR-Based and CRISPR-Based Genome Editing of Sulfolobus islandicus Rod-Shaped Virus 2. Viruses, 10(12), 695. https://doi.org/10.3390/v10120695