Abstract
A virulent recombinant HSV lacking the diploid γ134.5 gene (Δγ134.5) have been investigated over the last two decades both for anti-tumor therapy and as vaccine vectors. The first generation vectors, while safe, are incapable of sustained replication in the majority of treated patients. An interferon inducible host antiviral kinase, protein kinase R (PKR), limits late viral protein synthesis and replication of Δγ134.5 viruses. This review describes the development of new Δγ134.5 vectors, through serial passage selection and direct viral genome engineering, which demonstrate selective PKR evasion in targeted cells and improved viral replication without restoring neurovirulence.
1. Introduction
Serial passage is a time-honored viral laboratory method that has been used to select progeny with attenuating mutations (e.g. OKA vaccine strain from varicella zoster virus). In recent years, serial passaging has been used as a method to identify secondary mutations in attenuated HSV oncolytic vectors that mediate improved viral replication and anti-tumor activity. Additional uses for the serial passaging techniqueinclude: i) the testing of genetic stability of biologic therapeutics and potential pathogenic mutations; ii) identification of cryptic gene functions that may have served evolutionarily distant functions for the virus; and iii) to identify antiviral escape mutations, that can then provide leads to improved drug design.
This review focuses on the interferon-induced, innate antiviral response triggered during viral transcription that limits protein synthesis initiation in the infected cell. In addition to discussing the protein product encoded by the HSV γ134.5 gene that counters this host antiviral response, the review also describes how mutant viruses lacking the γ134.5 gene (Δγ134.5) have been studied as vaccine and anti-tumor therapies because of their safety in humans. While these vectors are safe, their limited late viral protein synthesis and diminished replication limit their efficacy. Serial passage of Δγ134.5 recombinants has been used to identify whether compensatory mutations improve viral replication or the anti-tumor properties of the Δγ134.5 mutants. Current efforts to improve these vectors’ replication are now focused upon engineering a new generation of HSV recombinants based on the earlier serial passage experiments.
3. The HSV-1 γ134.5 Gene
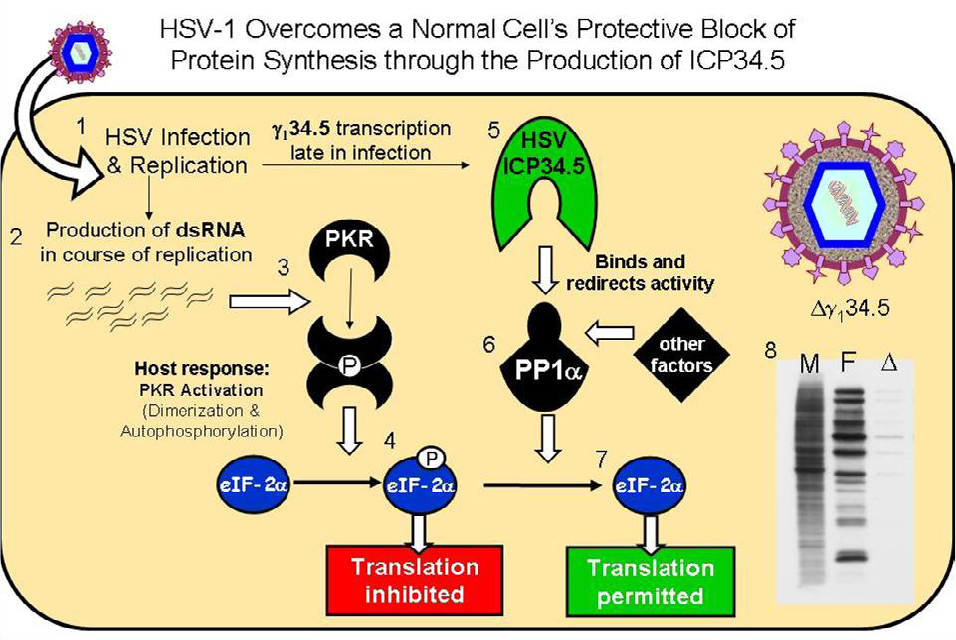
The HSV-1 γ134.5 gene encodes a multifunctional protein called ICP34.5 [11,12]. One function, encoded within the 3’ gene domain, blocks host PKR-mediated protein shutoff during infection thus allowing continued late viral protein synthesis in infected cells [13]. During infection, wild-type HSV-1 produces complementary mRNA transcripts that anneal, forming stable dsRNA, which triggers the dimerization and activation of dsRNA-activated host PKR. The ICP34.5 overcomes this PKR-mediated host protein shutoff by binding and recruiting a host phosphatase that specifically dephosphorylates eIF‑2α, allowing continued viral protein synthesis (hereafter referred to as the HSV wild-type protein synthesis phenotype) in the infected cell (summarized in Figure 1) [14,15].
Recombinant viruses that lack the γ134.5 gene, (Δγ134.5 HSVs) are incapable of maintaining eIF‑2α in an unphosphorylated form and therefore are unable to maintain protein synthesis in the infected cell [16]. Cessation of protein synthesis occurs at the onset of viral DNA synthesis late in infection, essentially eliminating bulk synthesis of viral structural proteins necessary for viral capsid formation [16]. In addition to structural proteins, viral encapsidation, envelopment and maturation are necessary for efficient viral replication. There are examples of Δγ134.5 mutants that are capable of late viral protein synthesis but that cannot negotiate the other steps necessary for viral replication [17]. Evidence suggests that in addition to protein translation, other cellular processes are disrupted in Δγ134.5 infected cells that are critical for viral egress. Consequently, Δγ134.5 HSV replicate inefficiently and produce fewer progeny virions in cells with intact PKR pathways [18]. While the γ134.5 gene product does not interrupt IFN signaling in the infected cell as has been described with the HSV UL13 and UL39 gene products, ICP34.5 is critical for HSV evasion of the IFN inducible gene product, PKR. Consequently, Δγ134.5 viruses are highly sensitive to Type I IFN and replicate poorly in vivo or in IFN treated cells [19,20]. Restoration of the protein synthesis function allows Δγ134.5 HSV to replicate efficiently in the presence of the type l IFN (α or β interferon) response [17].
The γ134.5 gene also encodes a second function, neurovirulence, enabling efficient viral replication in post-mitotic neuronal cells [12-14,21]. The neurovirulence and protein synthesis functions encoded by the γ134.5 gene are discrete and separable. Late viral protein synthesis can be selectively restored without restoring wild-type neurovirulence [17,22,23]. The Δγ134.5 HSV are incapable of efficient replication after direct inoculation in the CNS and do not cause encephalitis [12]. As such, Δγ134.5 HSV vectors have been developed as anti-tumor agents for CNS-based malignancies. Whereas 50-100 PFU of wildtype HSV will lead to encephalitis and death in half of the mice inoculated intracerebrally, more than 1 x 107 PFU are required to produce encephalitis and death with a Δγ134.5 HSV recombinant [12]. Finally, the γ134.5 gene also allows HSV-1 to block autophagy in infected cells [24]. This function contributes to HSV neurovirulence, maps within the 5’ domain of the gene and allows binding and sequestering of beclin-1, a host protein necessary for autophagosome formation [24].
4.γ134.5 HSV as Oncolytic Vectors
Genetically modified HSV are attractive as replication-competent, oncolytic vectors as well as vaccine vectors for a number of reasons: 1) procedures for constructing novel HSV are well established; 2) genetic modifications (insertions or deletions) do not significantly affect virus replication; 3) considerable experience with the biology of HSV and its behavior in humans and nonhuman primates exists; and 4) modified herpesviruses retain sensitivity to standard antiviral drug therapy as a “built-in” safety feature [25-27]. Deletion of the HSV-1 neurovirulence gene, γ134.5, allows the safe administration of recombinant vectors intracranially (for brain tumor therapy) or systemically (for peripheral tumors or as a vaccine vector).
In addition to inhibiting protein synthesis initiation, other viral functions are inhibited as a consequence of this deletional mutation. The Δγ134.5 mutants also demonstrate changes in glycoprotein processing Figure 2). The HSV γ134.5 gene product differs in amino acid sequence between viral strains. Adoptive transfer studies have shown that these ICP34.5 amino acid differences affect glycoprotein processing and plaque phenotype in cell culture [28,29]. In viruses lacking the γ134.5 gene, the differences in glycoprotein processing are even more dramatic. Immunostaining studies show that gD in the Δγ134.5 infected cells exist in a single form after separation using denaturing conditions. In contrast, viruses capable of PKR evasion and late viral protein synthesis exhibit multiple slower migratory forms of the glycoprotein indicative of further glycoprotein processing. In Figure 2 the chimeric HSV, C130, which contains the HCMV PKR-evasion gene TRS1, contains multiple forms of glycoprotein D, similar to that observed for wild-type HSV. Confocal immunofluorescence microscopy further demonstrates differences in glycoprotein trafficking in the infected cell. In tumor cells infected with recombinants capable of late viral protein synthesis, gD accumulates within the trans golgi network (TGN) and late endosomal compartment based upon gD and AP-1 staining and colocalization. In contrast, gD expressed in the Δγ134.5 infected cells does not localize with adaptor protein complex 1 (AP-1) in the TGN. There are also fundamental differences in the appearance of the TGN. In the Δγ134.5 infected cells, the TGN appears disrupted throughout the cytoplasm and does not exhibit the more structured perinuclear aggregates seen in cells capable of continued protein synthesis. The Δγ134.5 recombinants also exhibit differences in protein degradation or autophagy within the infected cell [8]. Improved protein production and processing may may enhance the antitumor capabilities of Δγ134.5 mutants either directly (improved antigen expression and replication) or indirectly by improving the expression and processing of foreign gene inserts in recombinants for gene therapy applications.
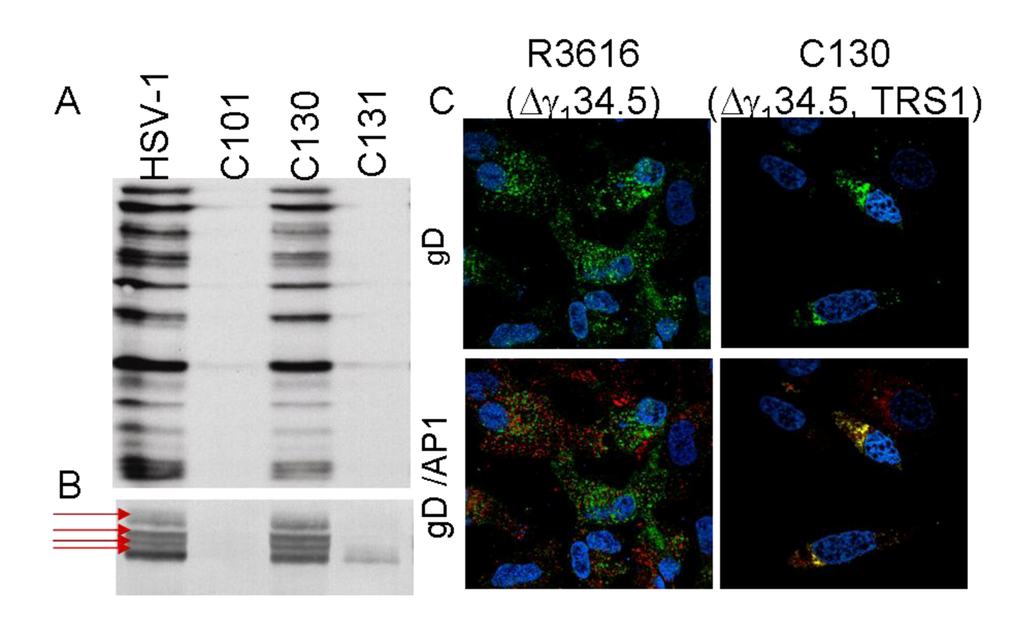
Figure 2.
Glycoprotein processing differences between Δγ134.5 and HSVs capable of PKR evasion and late viral protein synthesis. A) Autoradiograph showing radiolabeled viral proteins produced in infected malignant glioma cells. Viruses capable of PKR evasion (HSV-1 and the chimeric HSV, C130 [discussed in detail in section 6.4]) produce abundant 35S-Methionine-radiolabeled proteins at 12hpi. In contrast, the Δγ134.5 recombinants (C101) and the Chimeric HSV repair virus (C131) have reduced protein synthesis. B) Immunostaining using Ig anti-glycoprotein D (clone H170: SC-69802 Santa Cruz Biotechnology) shows abundant late gene accumulation in the HSV-1 and chimeric HSV (C130) samples as well as multiple migratory gD forms (arrows) indicative of glycoprotein processing in the infected cells. C) Confocal immunofluorescence imaging shows gD (green) distribution in Δγ134.5 (left upper panel) and C130 (right upper panel) -infected U87-MG cells and colocalization with the Transgolgi network marker AP-1 (Sigma). Co-localization detected (yellow) in the chimeric HSV infected samples (lower right panel) but not in the Δγ134.5 infected cells.
In addition to protein processing recent studies also show that the γ134.5 gene product also inhibits IFN response in the cell. ICP34.5 targets the ability of the TANK-binding kinase 1 (TBK1) to activate an antiviral response through interferon regulatory factor 3 (IRF3) and cytokine expression. [30] Phosphorylation and transnuclear translocation of IRF3 as well as expression of downstream genes functioning in antiviral responses are thereby inhibited by the γ134.5 protein product. Suppression of the interferon signaling pathway has consistently been shown to be a major mode of the interaction of HSV with the innate immune system, and its interaction with TBK1 appears to be a novel but critical mechanism to ensure successful and productive HSV infection.
5. Serial Passage and Escape Mutations
5.1. In vitro passage
Attenuated Δγ134.5 recombinants have been engineered for use as antitumor agents. While the vectors are safe and replicate in mitotically active cells, they do not exhibit robust replication. This limited replication and spread is one factor thought to limit their efficacy in vivo. Studies have described acquisition of mutations that overcome certain limitations of the ICP34.5-negative status of attenuated HSV-1 [31]. Mohr and Gluzman reported selection of the SUP-1 mutant after passage of the Δγ134.5 SPBg5e (derived from the Patton HSV-1 strain) in the nonpermissive SK-N-SH human neuroblastoma cell line in vitro [31]. SUP-1 acquired a deletion in the US12 region, resulting in two fundamental changes in the viral phenotype: 1) deletion of US12 results results in greater MHC I expression (as discussed in detail in Section 6), and 2) earlier expression of the US11 gene [31,32]. Later studies using engineered recombinants and recombinant expressed US11 protein in biochemical studies demonstrated that this kinetic shift in US11 expression enabled viral evasion of PKR and late viral protein synthesis [33]. The US11 product, although capable of precluding activated PKR from phosphorylating its target substrate eIF-2α, was much more effective and at lower concentrations at blocking the activation of PKR by dsRNA [32]. Ultimately these escape mutations produced progeny virus capable of continued viral protein translation in infected SK-N-SH cells [33]. Mohr’s mutant SUP-1, while it had a protein synthesis phenotype similar to that of wild-type HSV-1, retained the neurovirulence profile of its Δγ134.5 parent (LD50>6 x105); however, it was engineered in a more neurovirulent strain of HSV-1 which limited maximal LD50 testing [34,35].
R3616, derived from the parent HSV-1 (F) strain, was also sequentially passaged in two different cell lines that restricted Δγ134.5 late viral protein synthesis. Serial passage in HeLa cells produced progeny virus with no compensatory mutations [18]. The parent passage 0 virus and the virus recovered after 8 serial infections in the HeLa cell line both had a Δγ134.5 phenotype. It was concluded that because Δγ134.5 recombinants are capable of modest viral replication in HeLa cells that the selection was not sufficiently rigorous to provide compensatory mutant viruses with a selective advantage. Serial passage in SK-N-SH cells produced progeny that, like SUP-1, were capable of blocking the protein kinase R (PKR)-induced shutoff of protein synthesis [18]. Unlike SUP-1, however, these mutations mapped outside of the US10-12 domain, and at least one isolate had acquired a partially restored neurovirulence profile [18].
5.2. In vivo passage
In vivo passage has also been used to develop improved Δγ134.5 anti-tumor activity. M002, a Δγ134.5 recombinant that expresses murine IL-12, was sequentially passaged in flank tumors of the HSV-1 resistant D54-MG cell line. This study was based on the assumption that the virus would, through selective pressure incurred by the tumor microenvironment, acquire mutations allowing for more efficient replication in the resistant tumor cell line [36]. M002 and its parent virus, R3659 were each sequentially passaged in D54-MG tumor cells in vivo in flank tumors, and in vitro in cell culture [36]. In vitro passage in tissue culture selected for mutants similar to the passaged virus described originally by Mohr. The progeny virus expressed US11 earlier in infection, exhibited a wild-type protein synthesis phenotype, and was found in in vivo studies to partially restore HSV neurotoxicity (LD50 - 5.1x105 – 1.67x106). Interestingly, these secondary mutations did not improve the anti-tumor activity of the Δγ134.5 recombinants. Tumor-bearing animals had similar survival rates irrespective of whether they were administered the parent virus or a serially passaged virus capable of late viral protein synthesis [36].
In contrast, in vivo passage in D54 flank tumors selected for second site Δγ134.5 mutants with different compensatory mutations and a different phenotype. In vivo passaged viruses demonstrated decreased neurovirulence as compared to the non-passaged parent viruses and resulted in significantly improved survival of tumor-bearing mice in two separate murine experimental brain tumor models: human D54-MG intracranial xenografts in SCID mice and murine Neuro-2a neuroblastoma syngeneic tumors in A/J mice. The in vivo passaged virus retained strict γ2 kinetic expression of the US11 gene and Δγ134.5 protein shutoff phenotype. However, the recombinants were more effective in their anti-tumor activity [36]. In contrast to specifically engineered constructs, it can be more difficult to identify the particular mutation(s) responsible for the phenotypic changes seen in passaged viruses, and therefore, their interaction with the host environment more elusive to explain. Currently, the compensatory mutation responsible for this change has not been mapped, re-emphasizing the primary limitation of the serial passage process. In cases where a deletional or insertional mutation is responsible, mapping the mutation can easily be achieved through restriction enzyme digestion and differences in DNA fragment migration in agarose gels. In cases where a point mutation or a small deletion mutation occurs, sequencing of the viral genome or using marker transfer of genetic domains must be used to map the mutation. Thus, these studies emphasize the importance of the in vivo tumor environment for selecting novel oncolytic HSV strains that mediate improved survival in vivo.
6. Engineered Mutations
The serial passaging of many viruses has resulted in selection of novel mutations providing unique insights into the complexity of evasion of PKR by HSV vectors. The findings of these studies have helped investigators specifically engineer viruses with the goal of improving their anti-tumor activity and producing more effective vaccine vectors. Additionally, other strategies have been investigated which involve the engineering of novel viruses to enhance the oncolytic activity of Δγ134.5 HSV oncolytic vectors. These are summarized in the following subsections.
6.1. R8309
One strategy employed replacing the carboxyl terminus of the γ134.5 gene, responsible for blocking host PKR-mediated protein shutoff, with the murine gene encoding myeloid differentiation gene 116 (MyD116), which is homologous to this region [13]. Both MyD116 and the hamster homologue GADD34, are primary response genes in hematopoiesis and expressed during growth arrest and DNA damage. The virus constructed with this substitution in the γ134.5 gene, R8309, does not induce premature host protein shutoff in infected human cells [13]. Treatment of human gliomas established intracranially in SCID mice with R8309 prolonged survival as compared to controls [22].
6.2. GΔ47 – engineering the ΔUS12 αUS11 mutation
Tumor destruction is expected to be determined in part by the properties of the oncolytic virus used, but is also likely strongly influenced by viral-host interaction and induction of an immune response against the tumor. US12 gene expression from HSV-1 functions to inhibit transporter associated with antigen presentation (TAP) of MHC I. When deleted, MHC Class I expression from infected cells is increased. The GΔ47 virus contains an engineered α47 gene deletion in a G207 vector [37]. Like the second site mutants described above, it places US11 gene expression (normally a γ or late gene) under the control of the immediate-early α47 promoter [33]. The authors suggest the combination of early US11 expression (allowing for improved viral replication) along with increased MHC I presentation (allowing enhanced cytopathic effect) result in greater anti-tumor activity of GΔ47 in various animal tumor models, including metastatic breast cancer to the brain [38], prostate adenocarcinoma [39], and schwannomas [40]. These benefits were achieved without increasing the neurovirulence of the vector [37].
6.3. Controlled expression of the γ134.5 gene or tumor targeting of γ134.5 containing HSV
Deletion of the γ134.5 neurovirulence gene allows the safe administration of oncolytic HSV to brain tumors without producing hemorrhagic encephalitis characteristic of wild-type HSV-1 infection. However, since this deletion also diminishes the replicative and cytotoxic abilities of the virus, groups have investigated the targeted expression of the γ134.5 gene to replicating tumors. One method involves placing the γ134.5 gene expression under the control of a tumor specific promoter or enhancer thereby limiting γ134.5 gene expression in complementing tumor cells. One copy of the γ134.5 gene was reintroduced under the control of the cellular B-myb promoter, which responds to E2F regulation [41]. As expected, late viral protein synthesis was maintained after infection with this Myb34.5 virus, which also has a deletion of the ICP6 ribonucleotide reductase gene, and there was greater viral replication. Anti-tumor effect was increased relative to Δγ134.5 HSV-1 in a murine model of liver metastasis [42]. More importantly, the study suggests the potential of regulating γ134.5 gene expression by promoters regulated by the cell-cycle to permit HSV-1 to demonstrate its efficacy within cycling tumor cells yet retaining an advantageous neurovirulence profile. Further development of the targeted expression of the γ134.5 has led to the development of two other conditional expressing HSV recombinants that regulate γ134.5 gene expression using nestin enhancers or musashi promoter (both active in GBM tumors and CNS stem cells) [43,44]. Another method is to limit HSV (γ134.5 +) viral entry to tumor cells. To achieve this, recombinant R5111 was created and replaces the HSV entry molecule gD with a tumor specific fusion entry molecule (gD-IL-13 R α2) [45]. Cell culture studies show that R5111 replicate specifically in tumor [46].
6.4. Chimeric HSV
A different method hypothesized that transfer of the human cytomegalovirus (HCMV) PKR evasion genes TRS1 or IRS1 gene to a Δγ134.5 virus (producing viruses C130 and C134, respectively) would improve viral replication and anti-glioma activity. The TRS1 and IRS1 protein products are HCMV’s tools for blocking the dsRNA-dependent PKR response pathway [47,48]. These “chimeric” HSV vectors expressing HCMV genes improved late viral protein synthesis by preventing the shutdown of protein synthesis after viral infection. This attribute proffers the ability to replicate to wild-type levels in human malignant glioma cells invitro. In vivo, C130 and C134 were found to be aneurovirulent with LD50 measurements from four to over six logs higher than that of wild-type HSV-1 (LD50 = 6.8x105 for C130, >1x107 for C134) [23]. Therefore, despite restoration of late viral protein synthesis and greater replication of progeny virus, expression of TRS1 and IRS1 did not restore wild-type neurovirulence. Indeed, incorporation of TRS1 and IRS1 into the attenuated Δγ134.5 virus produced a more robust vector, permitting more efficient destruction of tumor cells and resulting in enhanced anti-tumor activity. Improved survival was noted in two brain tumor models: a human malignant glioma in severe combined immune deficient (SCID) mice and a syngeneic immunocompetent murine neuroblastoma model [23]. Both chimeric viruses demonstrated enhanced anti-glioma activity compared to their parent Δγ134.5 virus, and performed superiorly at lower doses. A similar greater anti-tumor benefit was seen comparing the viruses against a murine neuroblastoma model [23]. These studies suggest that replication of oncolytic HSV-1 vectors in partially restrictive tumor cells due to anti-viral PKR responses can be significantly improved by encoding PKR-evasion genes from a related herpesvirus.
7. Conclusions
Viral protein synthesis is critical for efficient viral replication. As a consequence, HSV has evolved numerous genes involved in maintaining cellular functions necessary for viral replication. Despite the extensive viral control of the cellular environment, intrinsic intracellular defense systems are nevertheless active and can disrupt viral gene expression. Efforts over the last decade have translated some of the principal work involving HSV innate immune evasion toward development of HSV-1 viral vectors for use as both vaccine and anti-tumor therapy. Fundamental scientific research elucidating these viral mechanisms has made these clinical applications possible.
Acknowledgments
These studies were aided by grants from the Ruth L. Kirschstein NRSA Fellowship 1 F31 NS050924‑01 and Medical Scientist Training Program (ACS), the NIH NCI P01 CA 71933 (JNP), NIH NCI P50 CA-97247 (KAC), NIH-NIAID K08-AI059428-01A2 (MS) and The Research Institute of Alabama Children's Hospital Foundation (KAC, MS).
References and Notes
- Samuel, C.E. Antiviral actions of interferons . Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2001, 14, 778–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katze, M. G. Regulation of the interferon-induced PKR: can viruses cope? Trends Microbiol. 1995, 3, 75–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomis, D.C.; Samuel, C.E. Mechanism of interferon action: evidence for intermolecular autophosphorylation and autoactivation of the interferon-induced, RNA-dependent protein kinase PKR. J. Virol. 1993, 67, 7695–7700. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ortega, L.G.; McCotter, M.D.; Henry, G.L.; McCormack, S.J.; Thomis, D.C.; Samuel, C.E. Mechanism of interferon action. Biochemical and genetic evidence for the intermolecular association of the RNA-dependent protein kinase PKR from human cells. Virology 1996, 215, 31–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williams, B.R. Signal integration via PKR . Sci. STKE 2001, 89, RE2. [Google Scholar]
- Smith, K.D.; Mezhir, J.J.; Bickenbach, K.; Veerapong, J.; Charron, J.; Posner, M.C.; Roizman, B.; Weichselbaum, R.R. Activated MEK suppresses activation of PKR and enables efficient replication and in vivo oncolysis by Deltagamma(1)34.5 mutants of herpes simplex virus 1 . J. Virol. 2006, 80, 1110–1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva, A.M.; Whitmore, M.; Xu, Z.; Jiang, Z.; Li, X.; Williams, B.R. Protein kinase R (PKR) interacts with and activates mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase 6 (MKK6) in response to double-stranded RNA stimulation. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 37670–37676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Talloczy, Z.; Jiang, W.; Virgin, H.W.; Leib, D.A.; Scheuner, D.; Kaufman, R.J.; Eskelinen, E.L.; Levine, B. Regulation of starvation- and virus-induced autophagy by the eIF2alpha kinase signaling pathway . Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U S A 2002, 99, 190–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Franklin, J.L.; Johnson, E.M. Control of neuronal size homeostasis by trophic factor-mediated coupling of protein degradation to protein synthesis. J. Cell Biol. 1998, 142, 1313–1324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williams, B.R. PKR: a sentinel kinase for cellular stress. Oncogene 1999, 18, 6112–6120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chou, J.; Chen, J.J.; Gross, M.; Roizman, B. Association of a M(r) 90,000 phosphoprotein with protein kinase PKR in cells exhibiting enhanced phosphorylation of translation initiation factor eIF-2 alpha and premature shutoff of protein synthesis after infection with gamma 134.5- mutants of herpes simplex virus 1 . Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U S A 1995, 92, 10516–10520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chou, J.Kern. Mapping of herpes simplex virus-1 neurovirulence to gamma 134.5, a gene nonessential for growth in culture. Science 1990, 250, 1262–1266. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- He, B.; Chou, J.; Liebermann, D.A.; Hoffman, B.; Roizman, B. The carboxyl terminus of the murine MyD116 gene substitutes for the corresponding domain of the gamma(1)34.5 gene of herpes simplex virus to preclude the premature shutoff of total protein synthesis in infected human cells. J. Virol. 1996, 70, 84–90. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- He, B.; Gross, M.; Roizman, B. The gamma(1)34.5 protein of herpes simplex virus 1 complexes with protein phosphatase 1alpha to dephosphorylate the alpha subunit of the eukaryotic translation initiation factor 2 and preclude the shutoff of protein synthesis by double-stranded RNA-activated protein kinase. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U S A 1997, 94, 843–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhan, Q.; Lord, K.A.; Alamo, I.; Hollander, M.C.; Carrier, F.; Ron, D.; Kohn, K.W.; Hoffman, B.; Liebermann, D.A.; Fornace, A.J. CarrierF.RonD.KohnK.W.HoffmanB.LiebermannD.A.FornaceA.J.The gadd and MyD genes define a novel set of mammalian genes encoding acidic proteins that synergistically suppress cell growth . Mol. Cell Biol. 1994, 14, 2361–2371. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chou, J.; Roizman, B. The gamma 1(34.5) gene of herpes simplex virus 1 precludes neuroblastoma cells from triggering total shutoff of protein synthesis characteristic of programed cell death in neuronal cells . Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U S A 1992, 89, 3226–3270. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, G.; Yang, K.; He, B. Dephosphorylation of eIF-2alpha mediated by the gamma(1)34.5 protein of herpes simplex virus type 1 is required for viral response to interferon but is not sufficient for efficient viral replication . J. Virol. 2003, 77, 10154–10161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cassady, K.A.; Gross, M.; Gillespie, G.Y.; Roizman, B. Second-site mutation outside of the U(S)10-12 domain of Deltagamma(1)34.5 herpes simplex virus 1 recombinant blocks the shutoff of protein synthesis induced by activated protein kinase R and partially restores neurovirulence . J. Virol. 2002, 76, 942–949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harle, P.; Cull, V.; Agbaga, M.P.; Silverman, R.; Williams, B.R.; James, C.; Carr, D.J. Differential effect of murine alpha/beta interferon transgenes on antagonization of herpes simplex virus type 1 replication. J. Virol. 2002, 76, 6558–6567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yokota, S.; Yokosawa, N.; Okabayashi, T.; Suzutani, T.; Miura, S.; Jimbow, K.; Fujii, N. Induction of suppressor of cytokine signaling-3 by herpes simplex virus type 1 contributes to inhibition of the interferon signaling pathway. J. Virol. 2004, 78, 6282–6286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Markovitz, N.S.; Baunoch, D.; Roizman, B. The range and distribution of murine central nervous system cells infected with the gamma(1)34.5- mutant of herpes simplex virus 1 . J. Virol. 1997, 71, 5560–5569. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Andreansky, S.S.; He, B.; Gillespie, G.Y.; Soroceanu, L.; Markert, J.; Chou, J.; Roizman, B.; Whitley, R.J. The application of genetically engineered herpes simplex viruses to the treatment of experimental brain tumors. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U S A 1996, 93, 11313–11318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shah, A.C.; Parker, J.N.; Gillespie, G.Y.; Lakeman, F.D.; Meleth, S.; Markert, J.M.; Cassady, K.A. Enhanced antiglioma activity of chimeric HCMV/HSV-1 oncolytic viruses. Gene Ther. 2007, 14, 1045–1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orvedahl, A.; Alexander, D.; Talloczy, Z.; Sun, Q.; Wei, Y.; Zhang, W.; Burns, D.; Leib, D.A.; Levine, B. HSV-1 ICP34.5 confers neurovirulence by targeting the Beclin 1 autophagy protein. Cell Host Microbe 2007, 1, 23–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cobbs, C.; Markert, J. Gene Therapy of Glioma: A Review. Perspectives in Neurological Surgery 1999, in press. [Google Scholar]
- Markert, J.M.; Gillespie, G.Y.; Weichselbaum, R.R.; Roizman, B.; Whitley, R.J. Genetically engineered HSV in the treatment of glioma: a review. Rev. Med. Virol. 2000, 10, 17–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rampling, R.; Cruickshank, G.; Papanastassiou, V.; Nicoll, J.; Hadley, D.; Brennan, D.; Petty, R.; MacLean, A.; Harland, J.; McKie, E.; Mabbs, R.; Brown, M. Toxicity evaluation of replication-competent herpes simplex virus (ICP 34.5 null mutant 1716) in patients with recurrent malignant glioma. Gene Ther. 2000, 7, 859–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bower, J.R.; Mao, H.; Durishin, C.; Rozenbom, E.; Detwiler, M.; Rempinski, D.; Karban, T.L.; Rosenthal, K.S. Intrastrain variants of herpes simplex virus type 1 isolated from a neonate with fatal disseminated infection differ in the ICP34.5 gene, glycoprotein processing, and neuroinvasiveness. J. Virol. 1999, 73, 3843–3853. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Mao, H.; Rosenthal, K.S. Strain-dependent structural variants of herpes simplex virus type 1 ICP34.5 determine viral plaque size, efficiency of glycoprotein processing, and viral release and neuroinvasive disease potential . J. Virol. 2003, 77, 3409–3417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verpooten, D.; Ma, Y.; Hou, S.; Yan, Z.; He, B. Control of TANK-binding kinase 1-mediated signaling by the gamma(1)34.5 protein of herpes simplex virus 1 . J. Biol. Chem. 2009, 284, 1097–1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohr, I.; Gluzman, Y. A herpesvirus genetic element which affects translation in the absence of the viral GADD34 function. Embo J. 1996, 15, 4759–4766. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Cassady, K.A.; Gross, M.; Roizman, B. The herpes simplex virus US11 protein effectively compensates for the gamma1(34.5) gene if present before activation of protein kinase R by precluding its phosphorylation and that of the alpha subunit of eukaryotic translation initiation factor 2 . J. Virol. 1998, 72, 8620–8626. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Cassady, K.A.; Gross, M.; Roizman, B. The second-site mutation in the herpes simplex virus recombinants lacking the gamma134.5 genes precludes shutoff of protein synthesis by blocking the phosphorylation of eIF-2alpha. J. Virol. 1998, 72, 7005–7011. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Mohr, I.; Sternberg, D.; Ward, S.; Leib, D.; Mulvey, M.; Gluzman, Y. A herpes simplex virus type 1 gamma34.5 second-site suppressor mutant that exhibits enhanced growth in cultured glioblastoma cells is severely attenuated in animals . J. Virol. 2001, 75, 5189–5196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taneja, S.; MacGregor, J.; Markus, S.; Ha, S.; Mohr, I. Enhanced antitumor efficacy of a herpes simplex virus mutant isolated by genetic selection in cancer cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U S A 2001, 98, 8804–8808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shah, A.C.; Price, K.H.; Parker, J.N.; Samuel, S.L.; Meleth, S.; Cassady, K.A.; Gillespie, G.Y.; Whitley, R.J.; Markert, J.M. Serial passage through human glioma xenografts selects for a Deltagamma134.5 herpes simplex virus type 1 mutant that exhibits decreased neurotoxicity and prolongs survival of mice with experimental brain tumors . J. Virol. 2006, 80, 7308–7315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Todo, T.; Martuza, R.L.; Rabkin, S.D.; Johnson, P.A. Oncolytic herpes simplex virus vector with enhanced MHC class I presentation and tumor cell killing. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U S A 2001, 98, 6396–6401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, R.; Martuza, R.L.; Rabkin, S.D. Intracarotid delivery of oncolytic HSV vector G47Delta to metastatic breast cancer in the brain. Gene Ther. 2005, 12, 647–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fukuhara, H.; Martuza, R.L.; Rabkin, S.D.; Ito, Y.; Todo, T. Oncolytic herpes simplex virus vector g47delta in combination with androgen ablation for the treatment of human prostate adenocarcinoma. Clin. Cancer Res. 2005, 11, 7886–7890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Messerli, S.M.; Prabhakar, S.; Tang, Y.; Mahmood, U.; Giovannini, M.; Weissleder, R.; Bronson, R.; Martuza, R.; Rabkin, S.; Breakefield, X.O. Treatment of schwannomas with an oncolytic recombinant herpes simplex virus in murine models of neurofibromatosis type 2. Hum. Gene Ther. 2006, 17, 20–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chung, R.Y.; Saeki, Y.; Chiocca, E.A. B-myb promoter retargeting of herpes simplex virus gamma34.5 gene- mediated virulence toward tumor and cycling cells . J. Virol. 1999, 73, 7556–7564. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Nakamura, H.; Kasuya, H.; Mullen, J.T.; Yoon, S.S.; Pawlik, T.M.; Chandrasekhar, S.; Donahue, J.M.; Chiocca, E.A.; Chung, R.Y.; Tanabe, K.K. Regulation of herpes simplex virus gamma(1)34.5 expression and oncolysis of diffuse liver metastases by Myb34.5. J. Clin. Invest. 2002, 109, 871–882. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kanai, R.; Tomita, H.; Shinoda, A.; Takahashi, M.; Goldman, S.; Okano, H.; Kawase, T.; Yazaki, T. Enhanced therapeutic efficacy of G207 for the treatment of glioma through Musashi1 promoter retargeting of gamma34.5-mediated virulence. Gene Ther. 2006, 13, 106–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kambara, H.; Okano, H.; Chiocca, E.A.; Saeki, Y. An oncolytic HSV-1 mutant expressing ICP34.5 under control of a nestin promoter increases survival of animals even when symptomatic from a brain tumor . Cancer Res. 2005, 65, 2832–2839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, G.; Ye, G.J.; Debinski, W.; Roizman, B. Engineered herpes simplex virus 1 is dependent on IL13Ralpha 2 receptor for cell entry and independent of glycoprotein D receptor interaction. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U S A 2002, 99, 15124–15129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, G.; Roizman, B. Characterization of a recombinant herpes simplex virus 1 designed to enter cells via the IL13Ralpha2 receptor of malignant glioma cells. J. Virol. 2005, 79, 5272–5277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Child, S.J.; Hakki, M.; De Niro, K.L.; Geballe, A.P. Evasion of cellular antiviral responses by human cytomegalovirus TRS1 and IRS1. J. Virol. 2004, 78, 197–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cassady, K.A. Human cytomegalovirus TRS1 and IRS1 gene products block the double-stranded-RNA-activated host protein shutoff response induced by herpes simplex virus type 1 infection. J. Virol. 2005, 79, 8707–8715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2009 by the authors; licensee Molecular Diversity Preservation International, Basel, Switzerland This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.