Embryo Development, Seed Germination, and the Kind of Dormancy of Ginkgo biloba L.
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Morphological Characteristics of Seeds and Variation of Embryo Length
2.2. Determination of Moisture Content (MC)
2.3. Seed Germination Characteristics
2.3.1. In Vitro Embryo Culture
2.3.2. Germination Test
2.3.3. Effect of Temperature on Seed Germination
2.4. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Embryo Development
3.2. Seed Dispersal
3.3. In Vitro Embryo Culture
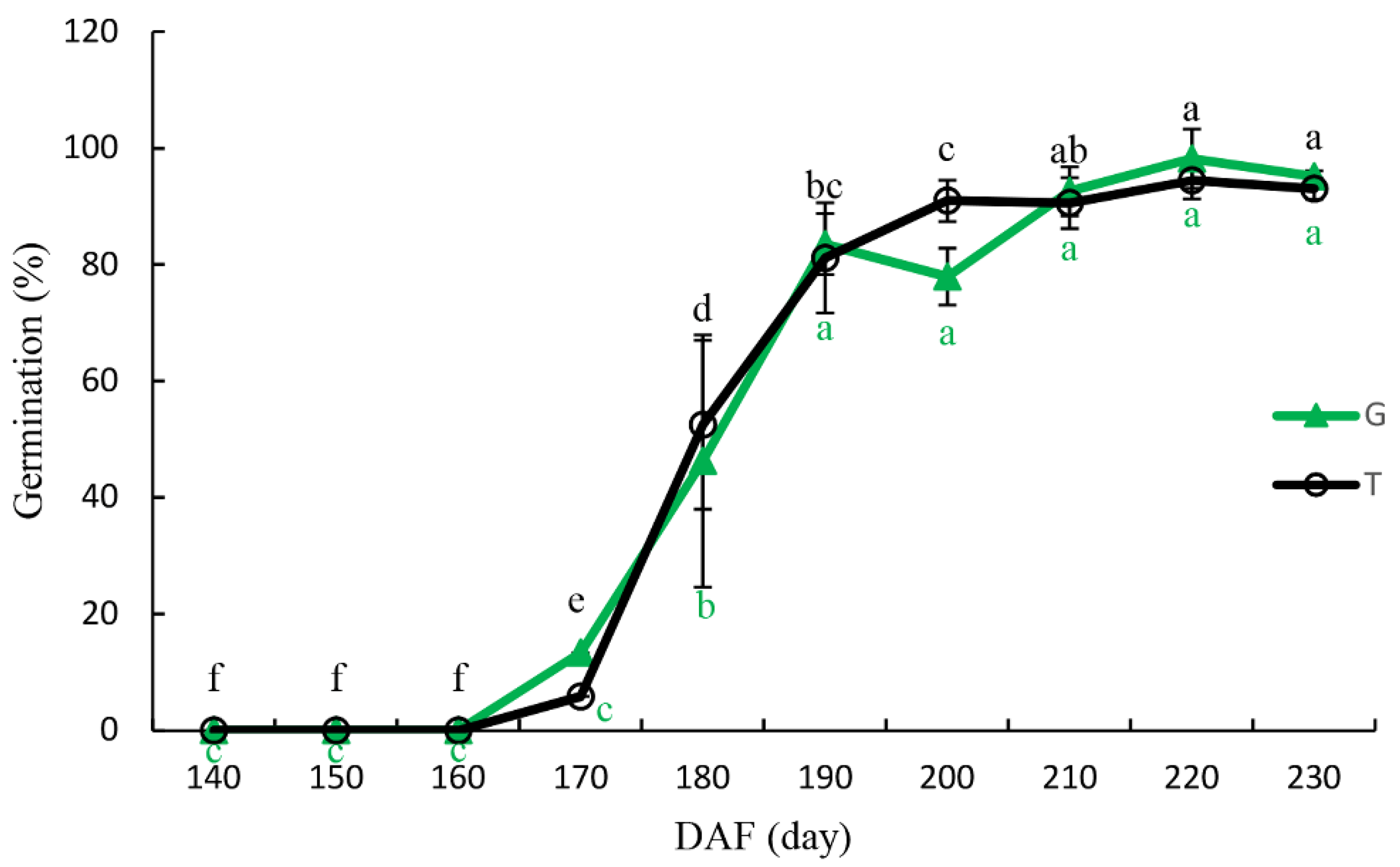
3.4. Seed Germination
3.5. Effect of Temperature on Germination
4. Discussion
4.1. Morphological Changes in Seed Development of G. biloba
4.2. Seed Maturation and Dispersal
4.3. Seed Germination and Isolated Embryo
4.4. Effect of Temperature on Seed Germination
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fenner, M.; Thompson, K. The Ecology of Seeds; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2005; pp. 1–29. [Google Scholar]
- Fenner, M. Seeds: The Ecology of Regeneration in Plant Communities, 2nd ed.; CABI Publishing: Wallingford, UK, 2002; pp. 331–361. [Google Scholar]
- Del Tredici, P. The phenology of sexual reproduction in Ginkgo biloba: Ecological and evolutionary implications. Bot. Rev. 2007, 73, 267–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, B.; Cai, C. Advances in Physiology of Ginkgo Seeds. Shandong Agric. Sci. 2001, 1, 40–42. [Google Scholar]
- Men, X. Structure and developmental rhythm of Ginkgo biloba seeds. Deciduous Fruits 1989, 1, 20–22. [Google Scholar]
- West, W.C.; Frattarelli, F.J.; Russin, K.J. Effect of Stratification and Gibberellin on Seed Germination in Ginkgo biloba. Bull. Torrey Bot. Club 1970, 97, 380–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, M.I.; Wickliff, J.L. Seed germination in Ginkgo biloba LI Influences of cold treatment, gibberellic acid and red light. J. Ark. Acad. Sci. 1974, 28, 34–36. [Google Scholar]
- Nikolaeva, M.G. Factors controlling the seed dormancy pattern. In The Physiology and Biochemistry of Seed Dormancy and Germination; Khan, A.A., Ed.; North-Holland Pub. Co.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1977; pp. 51–74. [Google Scholar]
- Baskin, J.M.; Baskin, C.C. A classification system for seed dormancy. Seed Sci. Res. 2004, 14, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willis, C.G.; Baskin, C.C.; Baskin, J.M.; Auld, J.R.; Venable, D.L.; Cavender-Bares, J.; Donohue, K.; Rubio de Casas, R. The evolution of seed dormancy: Environmental cues, evolutionary hubs, and diversification of the seed plants. New phytol. 2014, 203, 300–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Forbis, T.A.; Floyd, S.K.; de Queiroz, A. The evolution of embryo size in angiosperms and other seed plants: Implications for the evolution of seed dormancy. Evolution 2002, 56, 2112–2125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, T.T.; Chen, S. Temperature and the development of Ginkgo embryo. Sci. Rep. Natl. Tsing Hua Univ. 1934, 2, 37–39. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z. Plant Physiology; China Agriculture Press: Beijing, China, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, B.; Cai, C.; Mu, H. Post-maturity Physiology of the Ginkgo Seed Nuts. Econ. For. Res. 2002, 20, 22–23. [Google Scholar]
- Qin, X.S.; Yan, L.U.; Wan-Wen, Y.U.; Cao, F.L. Study on Tissue Culture of Ginkgo Embryos from Different Developing Stages. North. Hortic. 2014, 23, 87–90. [Google Scholar]
- ISTA. International Rules for Seed Testing; The International Seed Testing Association (ISTA): Bassersdorf, Switzerland, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Duclos, D.V.; Ray, D.T.; Johnson, D.J.; Taylor, A.G. Investigating seed dormancy in switchgrass (Panicum virgatum L.): Understanding the physiology and mechanisms of coat-imposed seed dormancy. Ind. Crops Prod. 2013, 45, 377–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellis, R.H.; Roberts, E.H. The quantification of ageing and survival in orthodox seeds. Seed Sci. Technol. 1981, 9, 373–409. [Google Scholar]
- Maguire, J.D. Speed of germination—Aid in selection and evaluation for seedling emergence and vigor. Crop. Sci. 1962, 2, 176–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laurain, D.; Tremouillaux-Guiller, J.; Chenieux, J.C. Embryogenesis from microspores of Ginkgo biloba L., a medicinal woody species. Plant Cell Rep. 1993, 12, 501–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, C.L. Recent Advances (1949–1959) in Morphology, Anatomy and Cytology of Ginkgo bilola L. (I). Acta Bot. Sin. 1959, 8, 262–270. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L.; Lu, Y.; Jin, B.; Lin, M.; Chen, P. Gametophyte development and embryogenesis in Ginkgo biloba: A current view. Chin. Bull. Bot. 2010, 45, 119–127. [Google Scholar]
- Ball, E. Growth of the embryo of Ginkgo Biloba under experimental conditions. I. Origin of the first root of the seedling in vitro. Am. J. Bot. 1956, 43, 488–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.H.; Chen, T.K. Experimental studies of young Ginkgo embryos—The effect of coconut milk on the embryos cultured in vitro. Acta Bot. Sin. 1965, 13, 224–231. [Google Scholar]
- Del Tredici, P. The evolution, ecology, and cultivation of Ginkgo biloba. In Ginkgo Biloba; Harwood Academic Publishers: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2000; pp. 7–23. [Google Scholar]
- Bonner, F.T.; Karrfalt, R.P. The Woody Plant Seed Manual; Forest Service: Washington, DC, USA, 2008; pp. 23–25. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, F.; Chen, Z.; Li, X. Experimental studies of young Ginkgo embryos I. The effect of the bee royal jelly on the embryo growth. Acta Bot. Sin. 1963, 11, 217–224. [Google Scholar]
- Li, T.T. The development of Ginkgo embryo in vitro. Sci. Rep. Natl. Tsing Hua Univ. 1934, 7, 169–174. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, G. Seeds of Ginkgo biloba. Plants 1996, 7, 28–29. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, F.; Chen, Z. A contribution to the embryology of Ginkgo with a discussion on the affinity of the Ginkgoales. Acta Bot. Sin. 1983, 25, 199–207. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, B.; Zhu, G.; An, L. Cytological studies on the structure of spermatozoid and fertilization in Ginkgo biloba (Ginkgoaceae). Acta Bot. Yunnanica 2009, 31, 513–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, J.; Shen, Y.; Shi, F.; Li, C. Changes in Seed Germination Ability, Lipid Peroxidation and Antioxidant Enzyme Activities of Ginkgo biloba Seed during Desiccation. Forests 2017, 8, 286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghildiyal, S.K.; Sharma, C.M. Effect of Seed Size and Temperature Treatments on Germination of Various Seed Sources of Pinus wallichiana and Pinus roxburghii from Garhwal Mmalaya. Indian For. 2005, 131, 56–65. [Google Scholar]
- Mayer, A.M.; Poljakoff-Mayber, A. The Germination of Seeds, 3rd ed.; Pergamon Press: London, UK, 1982; pp. 182–185. [Google Scholar]
- Bewley, J.D.; Bradford, K.; Hilhorst, H.; Nonogaki, H. Seeds: Physiology of Development, Germination and Dormancy, 3rd ed.; Plenum Press: New York, NY, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Mattana, E.; Picciau, R.; Puddu, S.; Cuena Lombraña, A.; Bacchetta, G. Effect of temperature and cold stratification on seed germination of the Mediterranean wild aromatic Clinopodium sandalioticum (Lamiaceae). Plant. Biosyst. Int. J. Deal. All Asp. Plant. Biol. 2016, 150, 846–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitelock, L.M. The Cycads; Timber Press: Portland, OR, USA, 2002; p. 374. [Google Scholar]
- Grobbelaar, N. Cycads, with Special Reference to the Southern African Species; Nat Grobbelaar: Pretoria, South Africa, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, W.; Cao, F.; Wang, G.; Zhang, W. Seed Germination Physiology of Different Ginkgo Strains under Two Temperatures. J. Northeast For. Univ. 2008, 36, 1–2. [Google Scholar]
- Xia, Q.; Zhang, M. Preliminary study on germination characteristics of Ginkgo seed. J. Huazhong Agric. Univ. 1995, 14, 93–96. [Google Scholar]
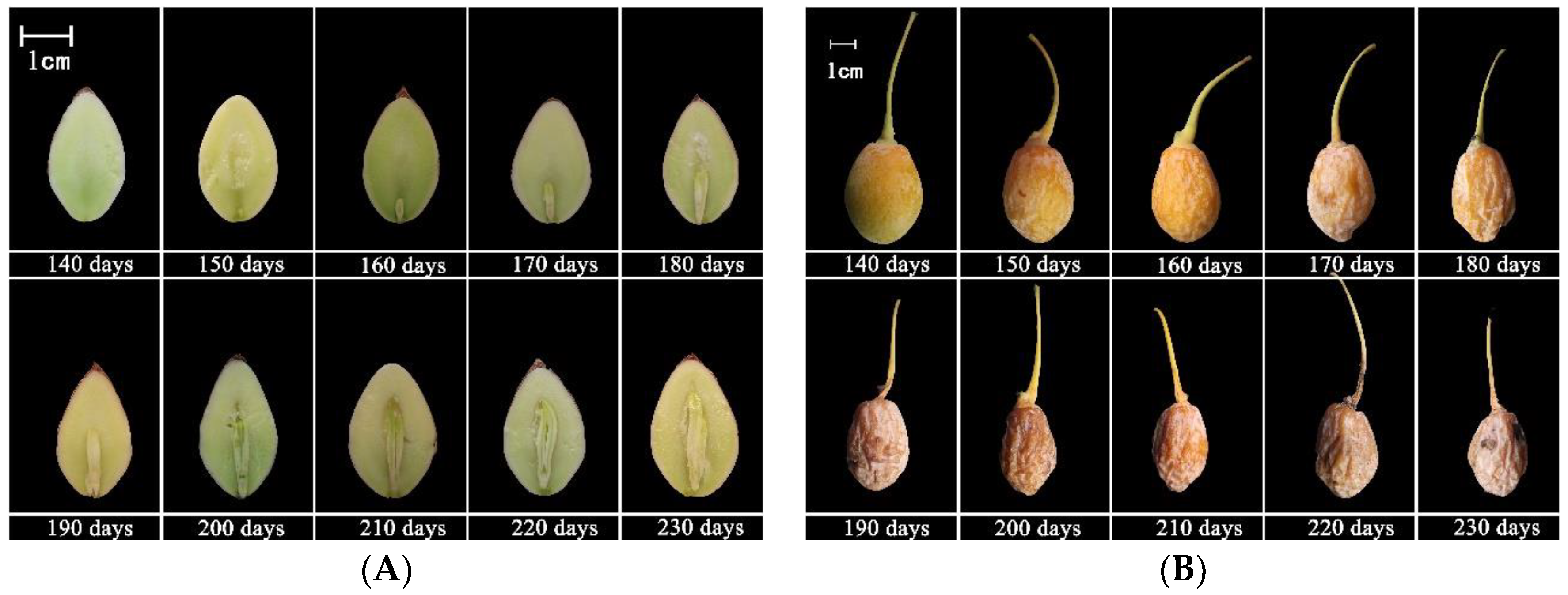
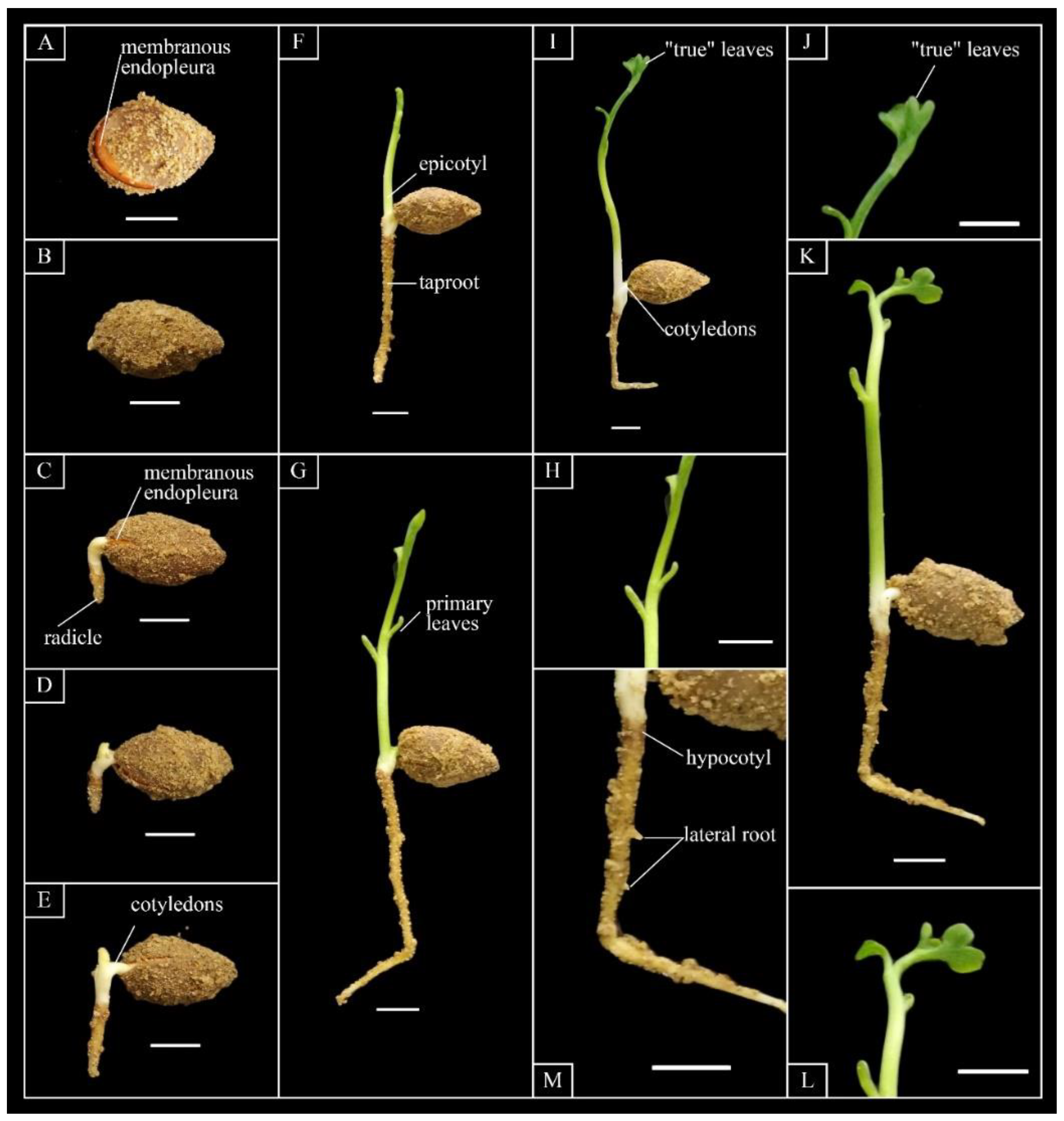

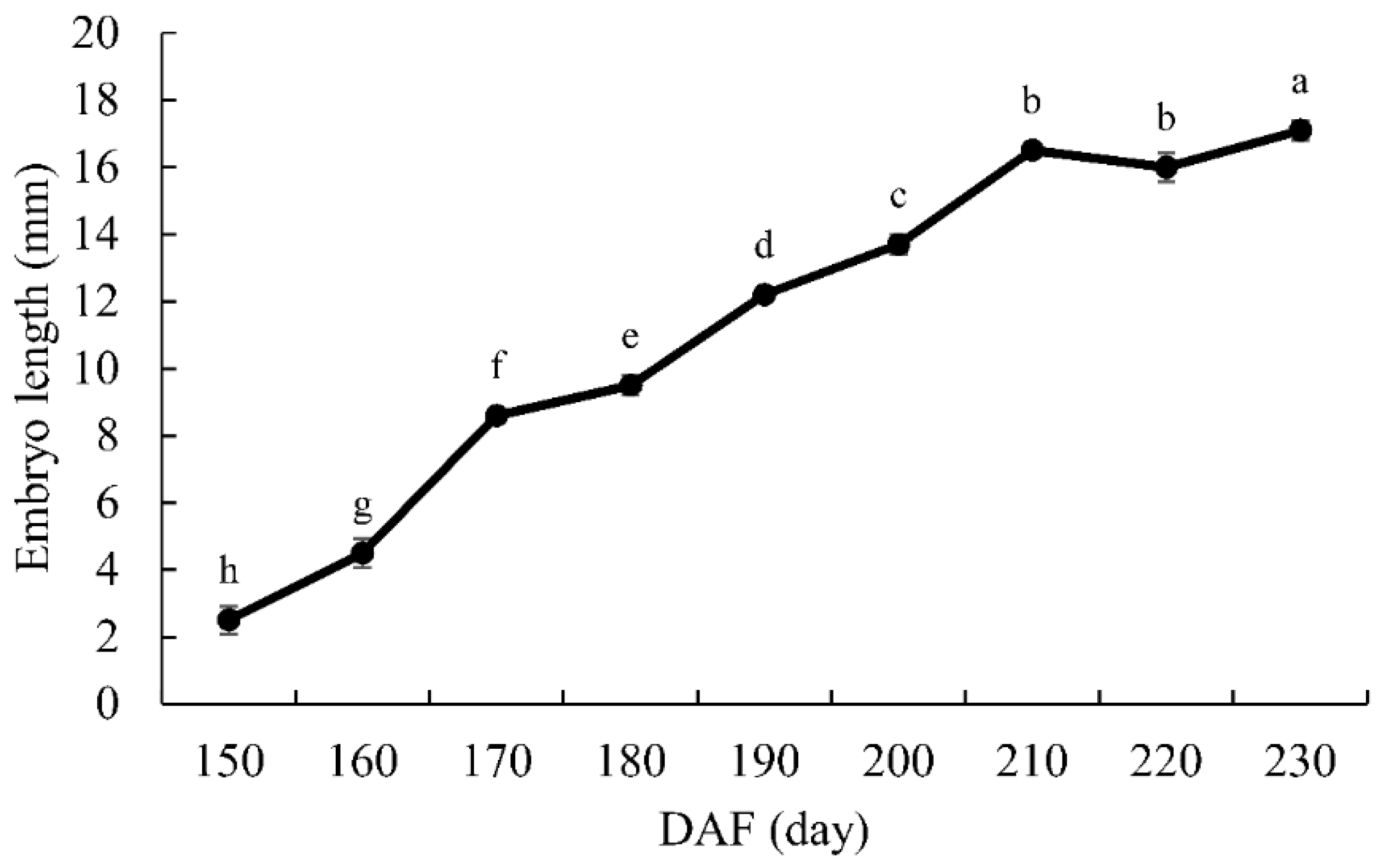



| DAF | Date | Fresh Weight (g) | Water Content (%) | Vertical Diameter (mm) | Transverse Diameter (mm) | Embryo Length (mm) | Features |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 150 | 18 September 2017 | 10.10 ± 1.00 a | 64.27 ± 0.33 ab | 31.18 ± 0.17 a | 22.86 ± 0.30 a | 2.5 ± 0.40 h | Orange-yellow, slightly wrinkled |
| 160 | 28 September 2017 | 10.09 ± 0.33 a | 65.49 ± 0.55 a | 31.35 ± 0.24 a | 22.33 ± 0.27 b | 4.5 ± 0.44 g | idem |
| 170 | 8 October 2017 | 9.17 ± 0.32 ab | 63.67 ± 0.96 b | 30.78 ± 0.92 ab | 21.83 ± 0.29 c | 8.6 ± 0.40 f | idem |
| 180 | 18 October 2017 | 8.50 ± 0.14 bcd | 61.63 ± 0.72 c | 30.87 ± 0.22 ab | 20.83 ± 0.30 d | 9.5 ± 0.11 e | Yellowish-brown, wrinkled |
| 190 | 28 October 2017 | 8.58 ± 0.85 bc | 61.46 ± 0.90 c | 30.20 ± 0.27 bc | 20.57 ± 0.16 de | 12.2 ± 0.64 d | Brown, covered with white powder, wrinkled, stem shrank |
| 200 | 7 November 2017 | 7.44 ± 0.30 cd | 58.36 ± 0.76 d | 31.51 ± 0.73 a | 20.61 ± 0.41 de | 13.7 ± 0.50 c | idem |
| 210 | 17 November 2017 | 7.38 ± 0.40 d | 58.27 ± 1.53 d | 30.86 ± 0.35 ab | 20.30 ± 0.10 e | 16.5 ± 0.61 ab | idem |
| 220 | 27 November 2017 | 7.71 ± 0.34 cd | 57.35 ± 1.03 d | 29.87 ± 0.20 c | 19.61 ± 0.30 f | 16.0 ± 0.70 b | idem |
| 230 | 7 December 2017 | 7.62 ± 1.05 cd | 56.97 ± 1.03 d | 30.13 ± 0.35 bc | 19.54 ± 0.21 f | 17.1 ± 0.66 a | Grayish-brown, covered with white powder, wrinkled, fruit stalk shrank |
| Indicators | Embryo Length | Transverse Diameter | Vertical Diameter | Water Content | Fresh Weight |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Embryo Length | 1 | –0.942 ** | –0.464 * | –0.908 ** | –0.865 ** |
| Sig. (two-tailed) | 0.000 | 0.015 | 0.000 | 0.000 | |
| Transverse Diameter | 1 | 0.564 ** | 0.898 ** | 0.779 ** | |
| Sig. (two-tailed) | 0.002 | 0.000 | 0.000 | ||
| Vertical Diameter | 1 | 0.423 * | 0.275 | ||
| Sig. (two-tailed) | 0.028 | 0.165 | |||
| Water Content | 1 | 0.809 ** | |||
| Sig. (two-tailed) | 0.000 | ||||
| Fresh Weight | 1 |
| Time (Day) | Germination (%) | |
|---|---|---|
| T | G | |
| 200 DAF | 59.33 ± 8.14b | 57.03 ± 10.90b |
| 210 DAF | 55.00 ± 5.00b | 56.51 ± 10.25b |
| 220 DAF | 80.68 ± 9.03a | 71.96 ± 5.57b |
| 230 DAF | 81.30 ± 3.95a | 82.57 ± 5.32a |
| Source | Sum of Squares | df | Mean Square | F | p |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Corrected Model | 3727.075 a | 7 | 532.439 | 9.029 | 0.000 |
| Intercept | 113,324.925 | 1 | 11,3324.925 | 1921.645 | 0.000 |
| Methods | 3.150 | 1 | 3.150 | 0.053 | 0.820 |
| Time | 3535.747 | 3 | 1178.582 | 19.985 | 0.000 * |
| Methods × Time | 188.178 | 3 | 62.726 | 1.064 | 0.392 |
| Error | 943.566 | 16 | 58.973 | ||
| Total | 117,995.566 | 24 | |||
| Corrected Total | 4670.641 | 23 |
| Temperature (°C) | Germination (%) | Mean Germination Time (MGT) (day) | Speed of Germination (SG) (%) | Rot Rate (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 15 | 16.59 ± 11.87 b | 26.93 ± 0.53 a | 0.27 ± 0.21 c | 0.00 ± 0.00 c |
| 25 | 82.57 ± 7.67 a | 17.57 ± 0.85 b | 2.18 ± 0.22 b | 3.00 ± 2.58 bc |
| 30 | 84.82 ± 1.69 a | 14.05 ± 1.28 c | 3.10 ± 0.47 a | 9.50 ± 4.12 b |
| 35 | 73.73 ± 9.81 a | 13.14 ± 0.42 c | 2.98 ± 0.43 a | 19.00 ± 7.39 a |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Feng, J.; Shen, Y.; Shi, F.; Li, C. Embryo Development, Seed Germination, and the Kind of Dormancy of Ginkgo biloba L. Forests 2018, 9, 700. https://doi.org/10.3390/f9110700
Feng J, Shen Y, Shi F, Li C. Embryo Development, Seed Germination, and the Kind of Dormancy of Ginkgo biloba L. Forests. 2018; 9(11):700. https://doi.org/10.3390/f9110700
Chicago/Turabian StyleFeng, Jing, Yongbao Shen, Fenghou Shi, and Chengzhong Li. 2018. "Embryo Development, Seed Germination, and the Kind of Dormancy of Ginkgo biloba L." Forests 9, no. 11: 700. https://doi.org/10.3390/f9110700
APA StyleFeng, J., Shen, Y., Shi, F., & Li, C. (2018). Embryo Development, Seed Germination, and the Kind of Dormancy of Ginkgo biloba L. Forests, 9(11), 700. https://doi.org/10.3390/f9110700





