Cloning and Expression of the Chitinase Encoded by ChiKJ406136 from Streptomyces Sampsonii (Millard & Burr) Waksman KJ40 and Its Antifungal Effect
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Strains, Plasmids and Plant Samples
2.2. PCR Amplification of the Chitinase Gene
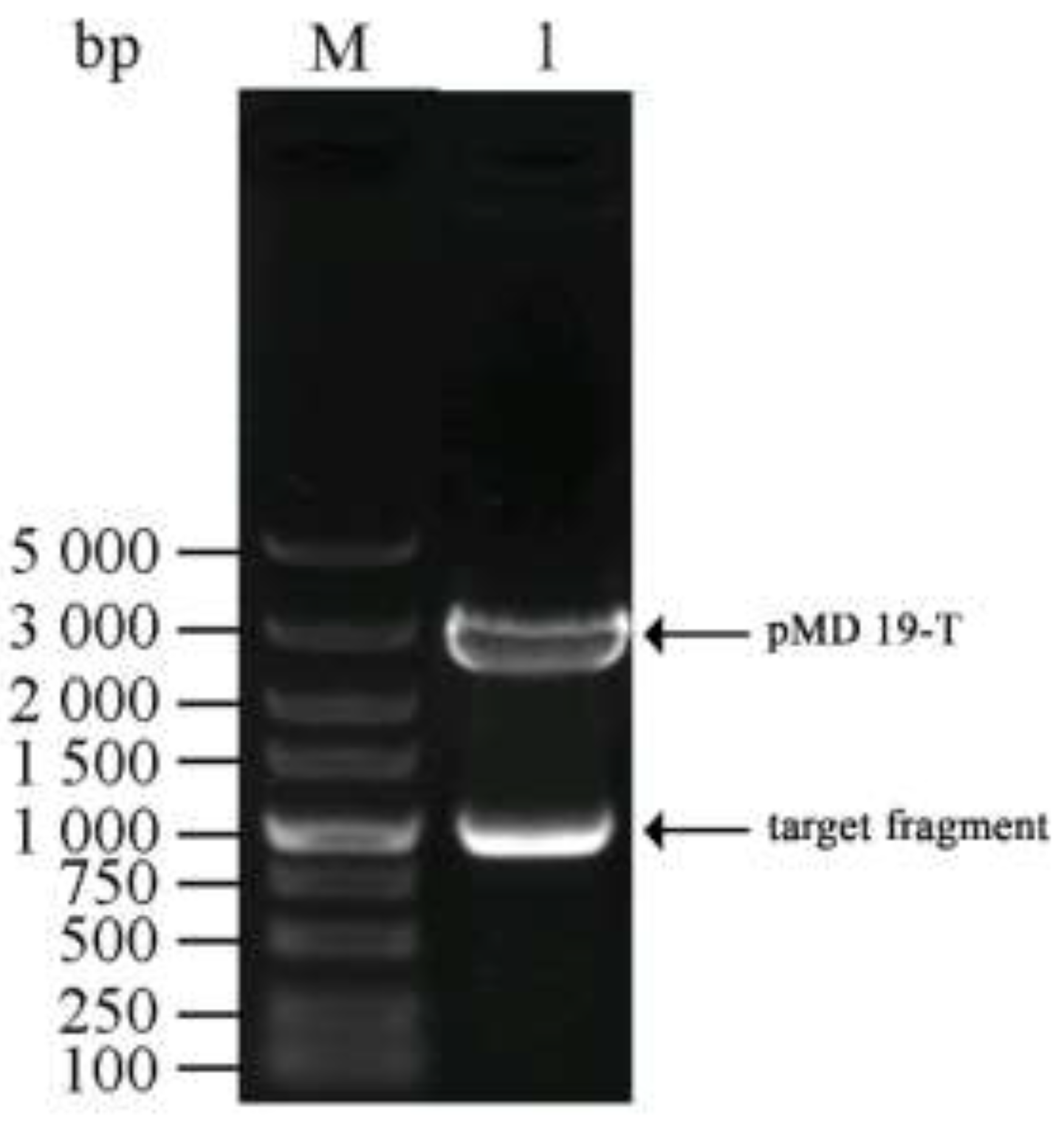
2.3. Construction of a Cloning Vector Harboring the Chitinase Gene
2.4. Gene Sequence and Chitinase Protein Identification
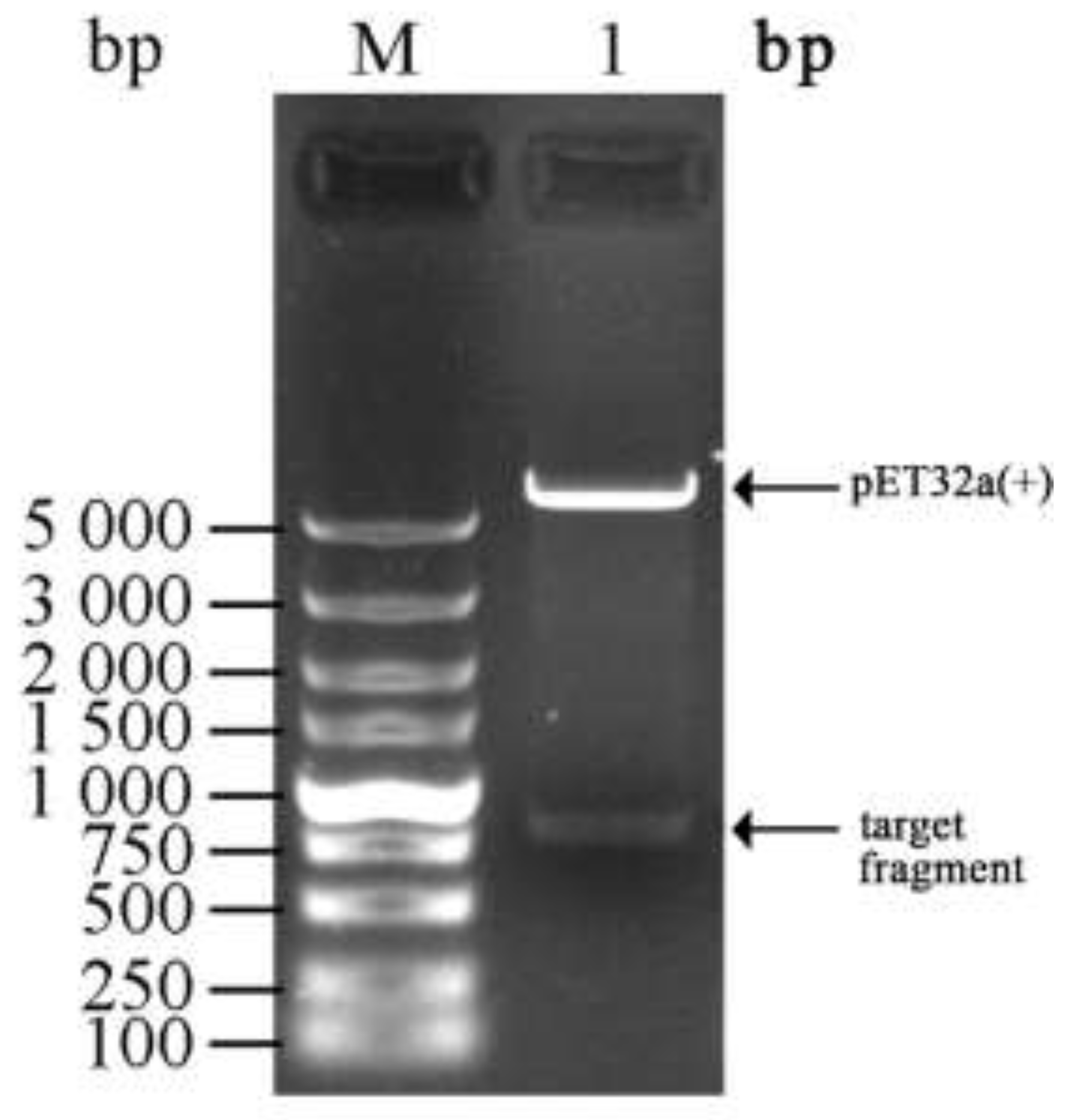
2.5. Construction of the Chitinase Expression Vector
2.6. Induced Expression of the Recombinant Chitinase Gene ChiKJ406136
2.7. Dissolubility Determination and Purification of the Recombinant Chitinase
2.8. Determination of the Concentration and Activity of the Recombinant Chitinase
2.9. Effects of the Recombinant Chitinase on Pathogenic Fungi
2.10. Determination of Biological Control Effects in a Pot Experiment
3. Results
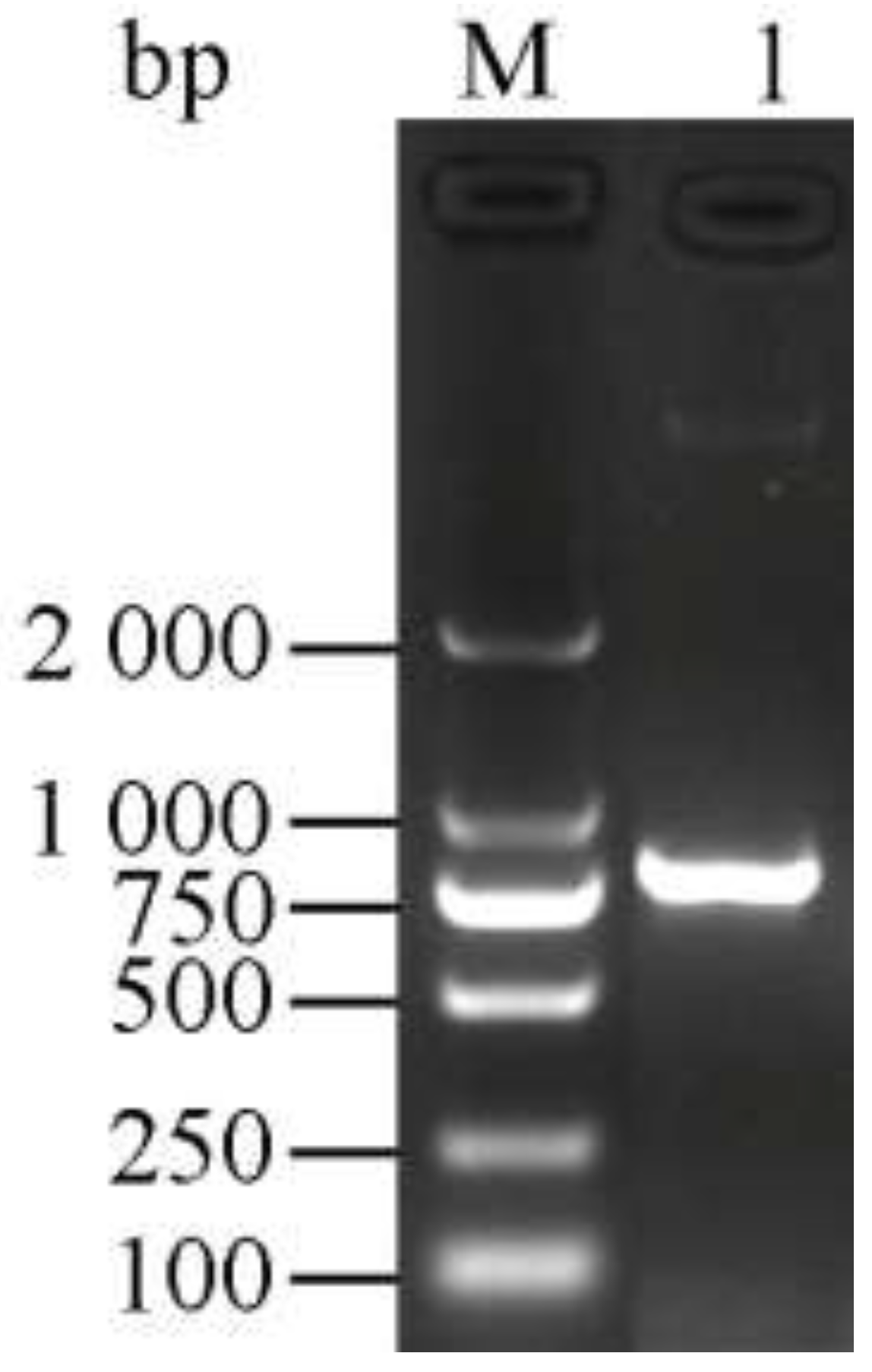
3.1. Cloning and Identification of the Chitinase Gene ChiKJ406136
3.2. Analysis of the ChiKJ406136 Gene Sequence and Protein Bioinformatics
3.3. Induction of Recombinant Chitinase Expression
3.4. Solubility and Purification of the Recombinant Chitinase
3.5. Properties of the Recombinant Chitinase
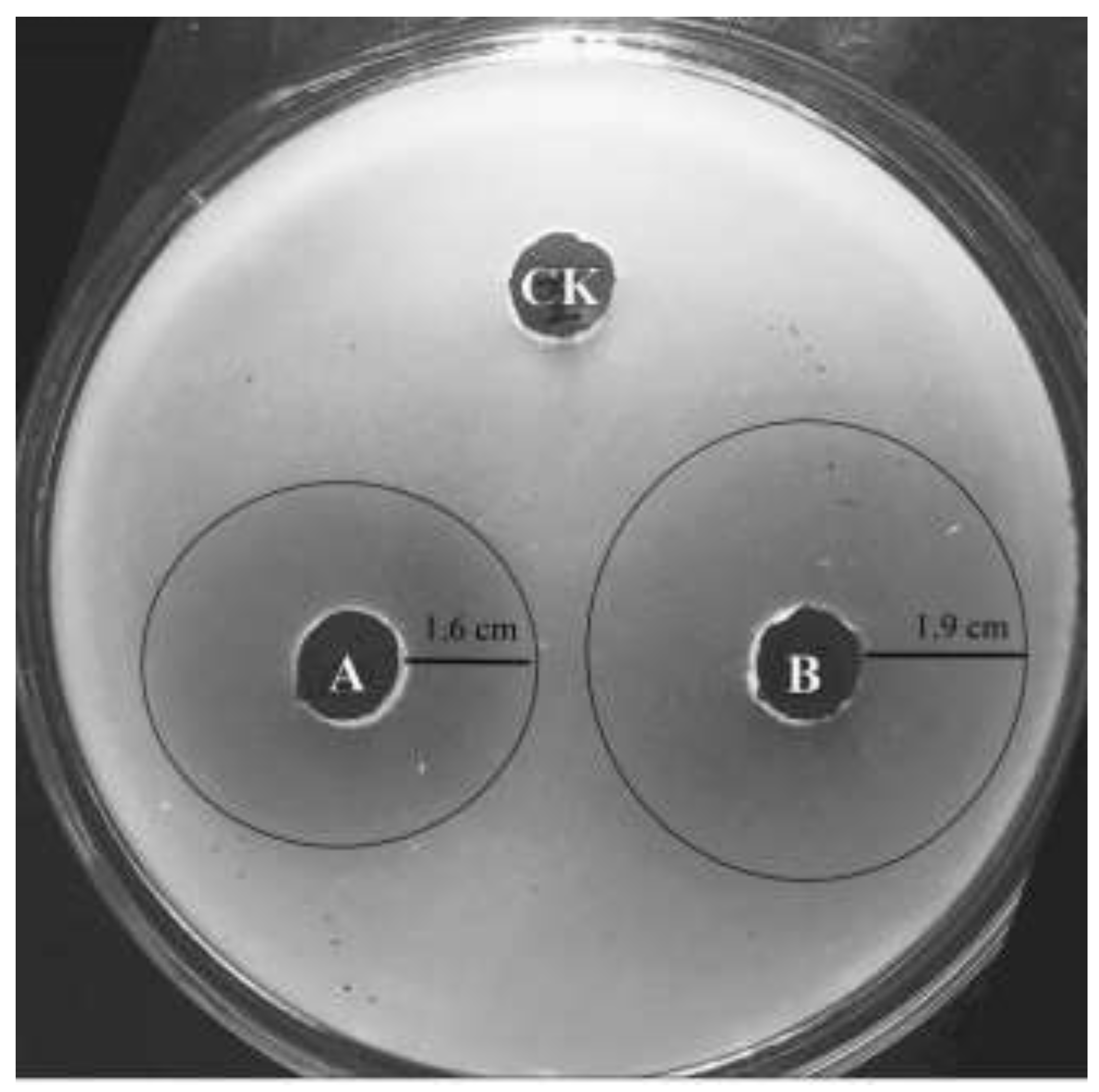
3.6. Effect of the Recombinant Chitinase on Pathogenic Fungi
3.7. Biological Control Effects of Chitinase on Potted Plants
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Flärdh, K.; Buttner, M.J. Streptomyces morphogenetics: Dissecting differentiation in a filamentous bacterium. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2009, 7, 36–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hasani, A.; Kariminik, A.; Issazadeh, K. Streptomycetes: Characteristics and their antimicrobial activities. Int. J. Adv. Biol. Biomed. Res. 2014, 2, 63–75. [Google Scholar]
- Law, J.W.F.; Ser, H.L.; Khan, T.M.; Chuah, L.H.; Pusparajah, P.; Chan, K.G.; Goh, B.H.; Lee, L.H. The potential of Streptomyces as biocontrol agents against the rice blast fungus, Magnaporthe oryzae (Pyricularia oryzae). Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schumacher, R.W.; Talmage, S.C.; Miller, S.A.; Sarris, K.E.; Davidson, B.S.; Goldberg, A. Isolation and structure determination of an antimicrobial ester from a marine sediment-derived bacterium. J. Nat. Prod. 2003, 66, 1291–1293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramesh, S.; Mathivanan, N. Screening of marine actinomycetes isolated from the Bay of Bengal, India for antimicrobial activity and industrial enzymes. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2009, 25, 2103–2111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Lima Procópio, R.E.; da Silva, I.R.; Martins, M.K.; de Azevedo, J.L.; de Araújo, J.M. Antibiotics produced by Streptomyces. Braz. J. Infect. Dis. 2012, 16, 466–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, P.S.; Duraipandiyan, V.; Ignacimuthu, S. Isolation, screening and partial purification of antimicrobial antibiotics from soil Streptomyces sp. SCA 7. Kaohsiung J. Med. Sci. 2014, 30, 435–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, L.H.; Zainal, N.; Azman, A.S.; Eng, S.K.; Ab Mutalib, N.S.; Yin, W.F.; Chan, K.G. Streptomyces pluripotens sp. nov., a bacteriocin-producing streptomycete that inhibits meticillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2014, 64, 3297–3306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ser, H.L.; Law, J.W.F.; Chaiyakunapruk, N.; Jacob, S.A.; Palanisamy, U.D.; Chan, K.G.; Goh, B.H.; Lee, L.H. Fermentation conditions that affect clavulanic acid production in Streptomyces clavuligerus: A systematic review. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lam, K.S. Discovery of novel metabolites from marine actinomycetes. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2006, 9, 245–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ara, I.; Bukhari, N.A.; Aref, N.; Shinwari, M.M.; Bakir, M. Antiviral activities of streptomycetes against tobacco mosaic virus (TMV) in Datura plant: Evaluation of different organic compounds in their metabolites. Afr. J. Biotechnol. 2012, 11, 2130–2138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kino, T.; Hatanaka, H.; Hashimoto, M.; Nishiyama, M.; Goto, T.; Okuhara, M.; Kohsaka, M.; Aoki, H. FK-506, a novel immunosuppressant isolated from a Streptomyces. fermentation, isolation, and physico-chemical and biological characteristics. J. Antibiot. 1987, 40, 1249–1255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ser, H.L.; Ab Mutalib, N.S.; Yin, W.F.; Chan, K.G.; Goh, B.H.; Lee, L.H. Evaluation of antioxidative and cytotoxic activities of Streptomyces pluripotens MUSC 137 isolated from mangrove soil in Malaysia. Front. Microbiol. 2015, 6, 1398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, L.T.H.; Ser, H.L.; Yin, W.F.; Chan, K.G.; Lee, L.H.; Goh, B.H. Investigation of antioxidative and anticancer potentials of Streptomyces sp. MUM256 isolated from Malaysia mangrove soil. Front. Microbiol. 2015, 6, 1316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, L.T.H.; Chan, K.G.; Lee, L.H.; Goh, B.H. Streptomyces bacteria as potential probiotics in aquaculture. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pullen, C.; Schmit, P.; Meurer, K.; Bamberg, D.D.V.; Lohmann, S.; França, S.C.; Groth, I.; Schlegel, B.; Mőllmann, U.; Gollmick, F.; et al. New and bioactive compounds from Streptomyces strains residing in the wood of Celastraceae. Planta 2002, 216, 162–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Imamura, N.; Nishijima, M.; Adachi, K.; Sano, H. Novel antimycin antibiotics, urauchimycins A. and B., produced by marine actinomycete. J. Antibiot. 1993, 46, 241–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jain, P.K.; Jain, P.C. Isolation, characterization and antifungal activity of Streptomyces sampsonii GS 1322. Indian J. Exp. Biol. 2007, 45, 203–206. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Malviya, M.K.; Pandey, A.; Trivedi, P.; Gupta, G.; Kumar, B. Chitinolytic activity of cold tolerant antagonistic species of Streptomyces isolated from glacial sites of Indian Himalaya. Curr Microbiol. 2009, 59, 502–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.J.; Zhu, T.H.; Peng, Y.; Lei, M.Y.; Han, S. Characteristics of chitinase-produced by Streptomycete sampsonii with antimicrobial activity and its biocontrol to Rhizoctonia violacea. J. Northeast. For. Univ. 2014, 42, 116–121. [Google Scholar]
- Charousová, I.; Medo, J.; Halenárová, E.; Maková, J.; Javoreková, S. Effect of fertilization on biological activity of community of soil streptomycetes. J. Cent. Eur. Agr. 2016, 17, 1134–1139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, R.; Jain, A.; Rawat, N.; Nair, M.; Gumashta, R. Feather hydrolysate from Streptomyces sampsonii GS 1322: A potential low cost soil amendment. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 2016, 121, 672–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deepthi, A.R.P. Actinomycete isolates from Arabian Sea and Bay of Bengal: Biochemical, Molecular and Functional Characterization. Ph.D. Thesis, Cochin University of Science and Technology, Kochi, Kerala, India, May 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.D.; Wang, K.Y.; Fan, S.; Yang, Z.Y.; Tian, X.F.; Xu, L.X.; Jin, Y.Y. Isolation of strain producing D-hydantoinase from marine and its simulation analysis of the enzyme catalytic chanel. J. Arg. Biot. 2016, 24, 729–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savi, D.C.; Shaaban, K.A.; Vargas, N.; Ponomarena, L.V.; Possiede, Y.M.; Thorson, J.S.; Glienke, C.; Rohr, J. Microbispora sp. LGMB259 endophytic actinomycete isolated from Vochysia divergens (Pantanal, Brazil) producing β-carbolines and indoles with biological activity. Curr. Microbiol. 2015, 70, 345–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.S.; Kang, S.I.; Kim, J.S.; Lee, Y.S.; Hong, S.H.; Naing, K.W.; Kim, K.Y. Biological control of root-knot nematode by Streptomyces sampsonii KK1024. Korean J. Soil. Sci. Fert. 2011, 44, 1150–1157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, H.; Hu, L.; Xu, Y. Influence of geosmin-producing Streptomyces on the growth and volatile metabolites of yeasts during Chinese liquor fermentation. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2015, 63, 290–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, F.; Ding, Y.Q.; Ding, W.; Reddy, M.S.; Fernando, W.G.D.; Du, B.H. Genetic diversity and phylogeny of antagonistic bacteria against Phytophthora nicotianae isolated from tobacco rhizosphere. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2011, 12, 3055–3071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dalisay, D.S.; Williams, D.E.; Wang, X.L.; Centko, R.; Chen, J.; Andersen, R.J. Marine sediment-derived Streptomyces bacteria from British Columbia, Canada are a promising microbiota resource for the discovery of antimicrobial natural products. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e77078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pesic, A.; Baumann, H.I.; Kleinschmidt, K.; Ensle, P.; Wiese, J.; Süssmuth, R.D.; Imhoff, J.F. Champacyclin, a new cyclic octapeptide from Streptomyces strain C42 isolated from the Baltic sea. Mar. Drugs 2013, 11, 4834–4857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El Baz, S.; Baz, M.; Barakate, M.; Hassani, L.; El Gharmali, A.; Imziln, B. Resistance to and accumulation of heavy metals by actinobacteria isolated from abandoned mining areas. Sci. World J. 2015, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lobova, T.I.; Yemelyanova, E.; Andreeva, I.S.; Puchkova, L.I.; Repin, V.Y. Antimicrobial resistance and plasmid profile of bacterial strains isolated from the urbanized eltsovka-1 river (Russia). Microb. Drug Resist. 2015, 21, 477–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rasimus-Sahari, S.; Mikkola, R.; Andersson, M.A.; Jestoi, M.N.; Salkinoja-Salonen, M. Streptomyces strains producing mitochondriotoxic antimycin A found in cereal grains. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2016, 218, 78–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santos, M.C.D.L.; Taulé, C.; Mareque, C.; Beracochea, M.; Battistoni, F. Identification and characterization of the part of the bacterial community associated with field-grown tall fescue (Festuca arundinacea) cv. SFRO Don Tomás in Uruguay. Ann. Microbiol. 2016, 66, 329–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Liang, K.; Duan, B.; Yu, M.D.; Meng, W.; Wang, Q.G.; Yu, Q. A novel insecticidal peptide SLP1 produced by Streptomyces laindensis H008 against Lipaphis erysimi. Molecules 2016, 21, 1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, B.Y.; Zhu, T.H.; Han, S.; Wang, Y.; Li, S.J.; Qiao, T.M. Whole-genome sequencing and analysis of Streptomyces sampsonii KJ40. Microbiol. China 2018, 45, 805–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurita, K. Controlled functionalization of the polysaccharide chitin. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2001, 26, 1921–1971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purwani, E.Y.; Suhartono, M.T.; Rukayadi, Y.; Hwang, J.K.; Pyun, Y.R. Characteristics of thermostable chitinase enzymes from the indonesian Bacillus sp. 13.26. Enzym. Microb. Tech. 2004, 35, 147–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathivanan, N.; Kabilan, V.; Murugesan, K. Purification, characterization, and antifungal activity of chitinase from Fusarium chlamydosporum, a mycoparasite to groundnut rust, Puccinia arachidis. Can. J. Microbiol. 1998, 44, 646–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.G.; Jiang, Z.Q.; Xu, L.P.; Sun, F.F.; Guo, J.H. Characterization of chitinase secreted by Bacillus cereus strain CH2 and evaluation of its efficacy against Verticillium wilt of eggplant. BioControl 2008, 53, 931–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hjort, K.; Presti, I.; Elväng, A.; Marinelli, F.; Sjőling, S. Bacterial chitinase with phytopathogen control capacity from suppressive soil revealed by functional metagenomics. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2014, 98, 2819–2828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baek, J.M.; Howell, C.R.; Kenerley, C.M. The role of an extracellular chitinase from Trichoderma virens Gv29-8 in the biocontrol of Rhizoctonia solani. Curr. Genet. 1999, 35, 41–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kerrn, M.F.; Maraschin, S.D.F.; Endt, D.V.; Schrank, A. Expression of a chitinase gene from Metarhizium anisopliae in tobacco plants confers resistance against Rhizoctonia solani. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2010, 160, 1933–1946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gadelhak, G.G.; El-Tarabily, K.A.; Al-Kaabi, F.K. Insect control using chitinolytic soil actinomycetes as bio control agents. Int. J. Agric. Biol. 2005, 7, 627–633. [Google Scholar]
- Prasad, K.; Bhatnagar-mathur, P.; Waliyar, F.; Sharma, K.K. Overexpression of a chitinase gene in transgenic peanut confers enhanced resistance to major soil borne and foliar fungal pathogens. J. Plant Biochem. Biot. 2013, 22, 222–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gentile, A.; Deng, Z.; La, M.S.; Distefano, G.; Vitale, A.; Polizzi, G.; Lorito, M. Enhanced resistance to Phoma tracheiphila and Botrytis cinerea in transgenic lemon plants expressing a Trichoderma harzianum chitinase gene. Plant Breed. 2007, 126, 146–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, S.; Mackintosh, C.A.; Lewis, J.; Heinen, S.J.; Radmer, L.; Dill-Macky, R.; Baldridge, G.D.; Zeyen, R.J.; Muehlbauer, G.J. Transgenic wheat expressing a barley class II chitinase gene has enhanced resistance against Fusarium graminearum. J. Exp. Bot. 2008, 59, 2371–2378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Owen, W.; Jayaraman, J.; Zamir, P. Comparative resistance to foliar fungal pathogens in transgenic carrot plants expressing genes encoding for chitinase, β-1,3-glucanase and peroxidise. Eur. J. Plant Pathol. 2009, 123, 331–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, S.H.; Koh, L.; Ma, Y.; Huang, Y.; Sim, K.Y. The oil of garlic, Allium sativum L. (Amaryllidaceae), as a potential grain protectant against Tribolium castaneum (Herbst) and Sitophilus zeamais Motsch. Postharvest Biol. Tec. 1996, 9, 41–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sørensen, C.K.; Thach, T.; Hovmøller, M.S. Evaluation of spray and point inoculation methods for the phenotyping of Puccinia striiformis on wheat. Plant Dis. 2016, 100, 1064–1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, J. The proteasome: A suitable antineoplastic target. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2004, 4, 349–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saito, A.; Fujii, T.; Shinya, T.; Shibuya, N.; Ando, A.; Miyashita, K. The msiK gene, encoding the ATP-hydrolysing component of N, N’-diacetylchitobiose ABC transporters, is essential for induction of chitinase production in Streptomyces coelicolor A3(2). Microbiology 2008, 154, 3358–3365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hirano, T.; Kadokura, K.; Ikegami, T.; Shigeta, Y.; Kumaki, Y.; Hakamata, W.; Oku, T.; Nishio, T. Heterodisaccharide 4-O-(N-acetyl-β-D-glucosaminyl)-D-glucosamine is a specific inducer of chitinolytic enzyme production in Vibrios harboring chitin oligosaccharide deacetylase genes. Glycobiology 2009, 19, 1046–1053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nothaft, H.; Rigali, S.; Boomsma, B.; Swiatek, M.; McDowall, K.J.; van Wezel, G.P.; Titgemeyer, F. The permease gene nagE2 is the key to N-acetylglucosamine sensing and utilization in Streptomyces coelicolor and is subject to multi-level control. Mol. Microbiol. 2010, 75, 1133–1144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamid, R.; Khan, M.A.; Ahmad, M.; Ahmad, M.M.; Abdin, M.Z.; Musarrat, J.; Javed, S. Chitinases: An update. J. Pharm. Bioallied. Sci. 2013, 5, 21–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohno, T.; Armand, S.; Hata, T.; Nikaidou, N.; Henrissat, B.; Mitsutomi, M.; Watanabe, T. A modular family 19 chitinase found in the prokaryotic organism Streptomyces griseus HUT 6037. J. Bacteriol. 1996, 178, 5065–5070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watanabe, T.; Kanai, R.; Kawase, T.; Tanabe, T.; Mitsutomi, M.; Sakuda, S.; Miyashita, K. Family 19 chitinases of Streptomyces species: Characterization and distribution. Microbiology 1999, 145, 3353–3363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawase, T.; Saito, A.; Sato, T.; Kanai, R.; Fujii, T.; Nikaidou, N.; Miyashita, K.; Watanabe, T. Distribution and phylogenetic analysis of family 19 chitinases in Actinobacteria. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2004, 70, 1135–1144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoell, I.A.; Dalhus, B.; Heggset, E.B.; Aspmo, S.I.; Eijsink, V.G.H. Crystal structure and enzymatic properties of a bacterial family 19 chitinase reveal differences from plant enzymes. FEBS J. 2006, 273, 4889–4900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, L.; Garbulewska, E.; Sato, K.; Kato, Y.; Nogawa, M.; Taguchi, G.; Shimosaka, M. Isolation of genes coding for chitin-degrading enzymes in the novel chitinolytic bacterium, Chitiniphilus shinanonensis, and characterization of a gene coding for a family 19 chitinase. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 2012, 113, 293–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhattacharya, D.; Nagpure, A.; Gupta, R.K. Bacterial chitinases: Properties and potential. Crit. Rev. Biotechnol. 2007, 27, 21–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Terpe, K. Overview of bacterial expression systems for heterologous protein production: From molecular and biochemical fundamentals to commercial systems. Appl. Microbiol. Biot. 2006, 72, 211–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ignatova, Z.; Mahsunah, A.; Georgieva, M.; Kasche, V. Improvement of posttranslational bottlenecks in the production of penicillin amidase in recombinant Escherichia coli strains. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2003, 69, 1237–1245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Urban, A.; Aasmant, I.; Motorin, Y. Optimisation of expression and purification of the recombinant Yol066 (Rib2) protein from Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J. Chromatogr. B. 2003, 786, 187–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Fraga, B.; Silva, A.F.D.; Lopez-Seijas, J.; Sieiro, C. A novel family 19 chitinase from the marine-derived Pseudoalteromonas tunicata CCUG 44952T: Heterologous expression, characterization and antifungal activity. Biochem. Eng. J. 2015, 93, 84–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reyes-Ramírez, A.; Escudero-Abarca, B.I.; Aguilar-Uscanga, G.; Hayward-Jones, P.M.; Barboza-Corona, J.E. Antifungal activity of Bacillus thuringiensis chitinase and its potential for the biocontrol of phytopathogenic fungi in soybean seeds. J. Food Sci. 2004, 69, 131–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirubakaran, S.I.; Sakthivel, N. Cloning and overexpression of antifngal barley chitinase gene in Escherichia coil. Protein Expres. Purif. 2007, 52, 159–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, K.Y.; Heo, K.R.; Choi, K.H.; Kong, H.G.; Nam, J.; Yi, Y.B.; Park, S.H.; Lee, S.W.; Moon, B.J. Characterization of a chitinase gene exhibiting antifungal activity from a biocontrol bacterium Bacillus licheniformis N1. Plant Pathol. J. 2009, 25, 344–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viterbo, A.; Haran, S.; Friesem, D.; Ramot, O.; Chet, I. Antifungal activity of a novel endochitinase gene (chit36) from Trichoderma harzianum Rifai TM. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2001, 200, 169–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mincoff, P.C.; Cortez, D.A.G.; Ueda-Nakamura, T.; Nakamura, C.V.; Filho, B.P.D. Isolation and characterization of a 30 kDa antifungal protein from seeds of Sorghum bicolor. Res. Microbio. 2006, 157, 326–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adrangi, S.; Faramarzi, M.A. From bacteria to human: A journey into the world of chitinases. Biotechnol. Adv. 2013, 31, 1786–1795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.J.; Zhu, T.H.; Yu, Q.; Qiao, T.M.; Han, S. Antifungal activity of mutant strains of Streptomyces sampsonii and their control effects on poplar purple root disease in potted experiment. Plant Prot. 2015, 41, 61–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
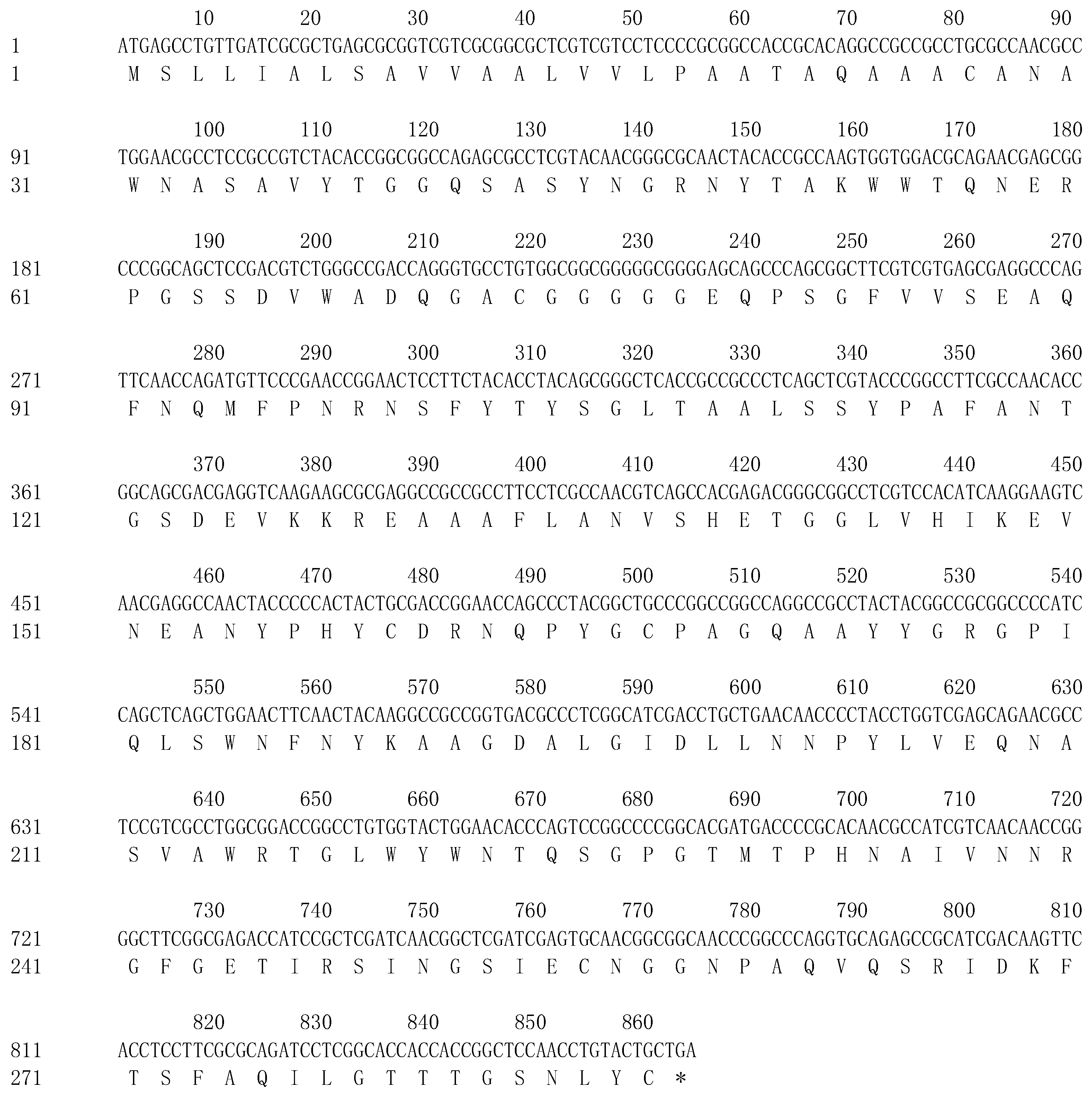





| Purification Procedure | Concentration of Protein (mg/mL) | Chitinase Activity (U/mL) | Specific Activity (U/mg) | Purification Fold | Recovery Rate of Enzyme Activity (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ChiKJ406136-crude protein | 2.06 ± 0.04 a | 0.045 ± 0.010 a | 0.022 ± 0.008 b | 1 b | 100 a |
| ChiKJ406136-purified protein | 0.07 ± 0.01 b | 0.033 ± 0.009 a | 0.471 ± 0.050 a | 21.41 a | 73.33 b |
| Dilutied Solution | Diseases on the Plant Samples | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| E. Robusta Leaf Blight | C. Mollissima Blight | J. Regia Blight | J. Regia Root Rot | |||||||||
| Incidence (%) b | Disease Index c | Control Effect (%) d | Incidence (%) | Disease Index | Control Effect (%) | Incidence (%) | Disease Index | Control Effect (%) | Incidence (%) | Disease Index | Control Effect (%) | |
| – | 9.0 ± 1.0 d | 6.8 ± 0.5 d | 92.7 ± 1.5 a | 12.0 ± 2.0 d | 13.3 ± 1.1 d | 86.1 ± 1.7 a | 8.0 ± 1.5 d | 6.4 ± 0.4 d | 93.5 ± 3.1 a | 10.0 ± 1.0 d | 12.4 ± 0.9 d | 90.4 ± 2.5 a |
| 10-fold | 21.0 ± 2.0 c | 15.9 ± 1.1 c | 79.0 ± 2.3 b | 30.0 ± 2.0 c | 20.2 ± 2.1 c | 70.7 ± 2.0 b | 19.0 ± 1.0 c | 12.3 ± 1.5 c | 80.6 ± 2.8 b | 22.0 ± 1.0 c | 19.0 ± 1.2 c | 75.2 ± 2.2 b |
| 20-fold | 44.0 ± 3.0 b | 33.6 ± 1.6 b | 50.5 ± 2.5 c | 55.0 ± 3.0 b | 41.7 ± 2.4 b | 42.6 ± 2.8 c | 42.0 ± 2.0 b | 31.8 ± 1.9 b | 52.4 ± 2.0 c | 46.5 ± 2.5 b | 38.3 ± 2.5 b | 46.1 ± 1.8 c |
| Control | 92.0 ± 2.0 a | 66.7 ± 2.1 a | – | 90 ± 2.0 a | 70.5 ± 2.3 a | – | 85 ± 2.0 a | 64.9 ± 2.4 a | – | 90 ± 2.0 a | 65.8 ± 2.2 a | – |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, S.; Zhang, B.; Zhu, H.; Zhu, T. Cloning and Expression of the Chitinase Encoded by ChiKJ406136 from Streptomyces Sampsonii (Millard & Burr) Waksman KJ40 and Its Antifungal Effect. Forests 2018, 9, 699. https://doi.org/10.3390/f9110699
Li S, Zhang B, Zhu H, Zhu T. Cloning and Expression of the Chitinase Encoded by ChiKJ406136 from Streptomyces Sampsonii (Millard & Burr) Waksman KJ40 and Its Antifungal Effect. Forests. 2018; 9(11):699. https://doi.org/10.3390/f9110699
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Shujiang, Boyang Zhang, Hanmingyue Zhu, and Tianhui Zhu. 2018. "Cloning and Expression of the Chitinase Encoded by ChiKJ406136 from Streptomyces Sampsonii (Millard & Burr) Waksman KJ40 and Its Antifungal Effect" Forests 9, no. 11: 699. https://doi.org/10.3390/f9110699
APA StyleLi, S., Zhang, B., Zhu, H., & Zhu, T. (2018). Cloning and Expression of the Chitinase Encoded by ChiKJ406136 from Streptomyces Sampsonii (Millard & Burr) Waksman KJ40 and Its Antifungal Effect. Forests, 9(11), 699. https://doi.org/10.3390/f9110699





