1. Introduction
Wildfires are among the most serious threats to forest ecosystems in the 21st century. Climate change, combined with landscape-scale ecological changes and human factors, has significantly increased the occurrence and intensity of wildfires across Europe and globally. According to the European Forest Fire Information System (EFFIS), the area affected by forest fires in the EU during the 2022 fire season was over 700,000 hectares, one of the highest recorded in recent decades [
1].
Although Slovakia is not historically a wildfire-prone country, it is not immune to these trends. In recent years, there has been an increase in fire occurrences, particularly during the dry spring and summer months. Forests in Slovakia cover approximately 40% of the national territory and are characterized by significant ownership fragmentation, complex terrain, and a mix of coniferous and deciduous species. These conditions pose unique challenges for wildfire monitoring, early detection, suppression, and long-term risk mitigation. Furthermore, the institutional fragmentation of Slovakia’s forest management and emergency response systems limits coordinated fire governance, which is a common challenge in many post-socialist Central European countries [
2].
In response to the growing threats of wildfires, digital technologies and integrated risk governance approaches have become critical components of modern fire management strategies. Tools such as UAVs, IoT-based sensors, AI-enabled fire spread models, and Decision Support Systems (DSS) offer promising opportunities for early detection, real-time monitoring, and informed decision-making [
3,
4,
5]. However, many of these systems remain fragmented, insufficiently contextualized, or difficult to integrate into national and local workflows. There is a recognized need for platforms that can integrate these technologies within a scalable, interoperable, and governance-aware framework [
6].
The SILVANUS project (Horizon 2020, GA No.101037247) represents a major European effort to address these gaps. It aims to create a comprehensive, modular Environmental Resilience Platform for wildfire prevention, preparedness, and response, applicable in both high-risk Mediterranean countries and emerging-risk contexts, such as Central and Eastern Europe. The platform integrates several key components [
7]:
An advanced DSS for real-time scenario evaluation, fire propagation modeling, and resource routing;
IoT-based sensor networks and UAV-enabled visual detection for real-time environmental monitoring;
AI-driven simulations of smoke dispersion and health impacts;
A multilingual communication app to engage citizens and improve early warning;
A central Environmental Management Platform (EMP) that harmonizes heterogeneous datasets and ensures interoperability between technical modules and user institutions.
This paper reports on the SILVANUS platform, focusing on its application and potential for strengthening forest and fire management in Slovakia. Specifically, we (i) developed a seven-criterion fit-gap framework to assess the alignment between SILVANUS system modules and national wildfire management needs, (ii) applied this framework using documentary analysis, stakeholder interviews, and pilot-site data from the Slovak Republic, and (iii) evaluated the platform’s expected contribution to forest sustainability using three quantitative indicators relevant to national policy goals.
In the context of increasing wildfire threats across Europe, several EU-funded research initiatives have emerged to advance integrated fire-management strategies. Projects such as FIRE-RES and FirEUrisk have focused on establishing resilient fire management landscapes and risk assessments in Southern Europe. However, SILVANUS distinguishes itself through the development of a modular, digital Environmental Management Platform (EMP) that integrates real-time environmental data fusion (IoT, UAV, satellite) with decision-support tools and participatory governance frameworks. This is particularly relevant for Central and Eastern European countries, such as Slovakia, where forest ownership fragmentation, variable risk governance, and emerging climate stressors require adaptable and multi-risk solutions.
The remainder of this report is structured as follows. First, we outline the current trends in wildfire risk and policy across Europe, situating Slovakia within this context. Second, we present an overview of the SILVANUS platform architecture and its major modules. Third, we analyzed the implementation conditions in Slovakia based on the national forest policy framework, institutional actors, and digital readiness. Finally, we discuss the lessons learned from the Slovak pilot project in the context of broader wildfire governance challenges and opportunities in Central Europe.
This paper contributes to the growing body of literature on integrated wildfire risk platforms, digital resilience infrastructures, and adaptive forest governance under climate stress. It provides insights for researchers, policy is a practitioners seeking to bridge forest fires is a relatively operational capacity in complex forest fire environments.
2. Material and Methods
To evaluate how the SILVANUS platform aligns with the wildfire management and forest sustainability context of the Slovak Republic, this section outlines the study’s regional focus, assessment design, data sources, analytical framework, and selected indicators used to gauge ecological outcomes, followed by a brief discussion of limitations.
2.1. Study Context
This study is situated within the SILVANUS project framework, with specific reference to pilot implementation in the Podpoľanie region of central Slovakia. This area was selected for its representative fire-prone landscape, diverse forest ownership structure, and active local engagement in wildfire prevention programs. The region serves as a testbed for evaluating how digital wildfire management tools can be adapted to country-specific conditions, especially regarding governance, institutional capacity, and ecological resilience.
2.2. Assessment Approach
To evaluate the alignment of SILVANUS with Slovak needs, we designed a structured fit–gap analysis encompassing both technical and contextual dimensions. The core research objective was to determine how well the system’s components integrate with existing national frameworks of wildfire governance, forest management, and civil protection.
The assessment followed a mixed-methods approach comprising the following:
Review of project documentation (technical reports and system blueprints);
Analysis of pilot site data from Podpoľanie (sensor outputs, platform logs);
Consultation with local and national stakeholders (interviews and workshops);
References to legal and policy documents governing fire and forest management.
2.3. Data Sources
The following data streams were used:
SILVANUS Deliverables and Architecture Plans: Including specifications of EMP, DSS, UAV operations, and IoT system functionalities tailored to Slovak deployment (D2.1–D5.3).
Pilot Deployment Data: Sensor network data, test fire simulations, and EMP alerts were collected during the Slovak demonstrations.
Stakeholder Engagement: Structured feedback was gathered via workshops and follow-up interviews with 17 participants from fire services, forest authorities, and municipal governments.
National Governance and Legal Documents: Slovak Fire Protection Act, Forestry Act, National Forest Program, and national Sustainable Forest Management (SFM) indicator set.
2.4. Analytical Framework
Each SILVANUS module was evaluated using the following seven criteria:
Governance mandate alignment
Legal/regulatory compatibility
Data interoperability with national systems
Institutional capacity (staff, training, organizational fit)
Ecological appropriateness (terrain, vegetation, climate trends)
Financial feasibility for long-term operation
Stakeholder usability and acceptance
Each criterion was scored on a 0–2 scale:
0 = Not aligned
1 = Partially aligned
2 = Fully aligned
Dual coding was used, and discrepancies were resolved by consensus. A module-level alignment score (0–14) was calculated for each component (EMP, DSS, FireAware, and UAV/IoT network).
2.5. Forest Sustainability Indicators
To evaluate the potential contributions to forest sustainability, we adopted three indicators aligned with the Slovak SFM policy:
Projected Change in Stand Structural Diversity (via LANDIS-II simulations to 2050);
Changes in High-Risk Fuel Areas (identified via UAV and satellite data, using a 15 t/ha threshold for fine fuels);
Change in the National Sustainable Forest Management Index (based on official Slovak reporting protocols, baseline 2021 = 100).
These indicators help quantify the ecological outcomes of using SILVANUS tools compared to business-as-usual wildfire management.
2.6. Limitations
This analysis is subject to several limitations.
The results reflect early-stage deployment over a single fire season.
Interview data may be biased by the participants’ roles or expectations.
Certain sustainability indicators (e.g., the SFM Index) rely on projections and assumptions rather than direct measurements.
The full SILVANUS system was not operational simultaneously at the pilot site, necessitating extrapolation from modular tests.
3. Results: Alignment of SILVANUS Modules with Slovak Conditions
This section presents the results of the structured alignment analysis between the SILVANUS modules and national wildfire governance, data systems, and forest sustainability priorities. Each sub-section corresponds to one criterion from the methodological framework (
Section 2.4).
3.1. Governance and Legal Fit
The Slovak Fire Protection Act (No. 314/2001 Coll.) and the Act on the Protection of Nature and the Landscape (No. 543/2002 Coll.) already empower municipalities and fire brigades to implement early-warning and mitigation systems compatible with the SILVANUS architecture. Project documentation confirms that no additional legal amendments are required for deployment [
8]. During stakeholder interviews, a municipal officer noted: “SILVANUS adds situational awareness without interfering in our legal response duties”. Given this full compatibility, the governance/legal alignment score for each module was 2/2.
3.2. Data Interoperability
PPilot tests demonstrated seamless ingestion of Copernicus Sentinel-2 imagery, UAV mosaics, and IoT sensor streams into the Environmental Management Platform (EMP) using OGC-compliant APIs (JSON, WMS) [
9]. Risk layers exported from EMP were visualized inside the national GIS maintained by the Geodesy, Cartography and Cadaster Authority within 5 min latency. Automatic meteorological feeds from the Slovak Hydrometeorological Institute (SHMÚ) were parsed without data-loss events during the eight-month trial. These results justify a 2/2 interoperability score.
3.3. Staff Capacity
Seventeen practitioners (fire brigades, forest rangers, crisis-management staff) completed a 12-h hands-on course that covered UAV operation, EMP dashboards, and DSS scenario building [
10]. Pre/post questionnaires showed knowledge gains of 38 ± 7% and a post-training confidence mean of 4.1/5. Follow-up interviews revealed capacity gaps in three of nine municipalities lacking dedicated GIS/IT staff. Consequently the staff-capacity criterion received 1/2 (partial alignment).
3.4. Ecological Suitability
The Podpoľanie pilot region contains mixed spruce–beech stands classified as high-risk under national fire-danger zoning [
11]. LANDIS-II simulations calibrated with local inventory and climate data reproduced historical fire spread with <15% error, and UAV-derived fuel maps showed a 0.86 spatial correlation with DSS high-hazard polygons [
12]. These findings, plus successful sensor deployment on steep (>25%) slopes, warrant an ecological-suitability score of 2/2.
3.5. Financial Feasibility
The capital expenditure for a full municipal package (UAV, IoT nodes, EMP licence) was estimated at €30 k; recurring O&M at €3.5–4.5 k yr
−1 [
13]. While the RRF and LIFE schemes can subsidize start-up costs, local officials expressed concern over long-term data-subscription fees. Therefore, financial feasibility is rated 1/2 (partial alignment).
3.6. Stakeholder Acceptance
The FireAware mobile app recorded 356 unique downloads during the 2024 fire season, and workshop participants (
n = 41) rated the overall usefulness as 4.2 ± 0.7/5 [
14]. The reported barriers include patchy LTE coverage and limited digital literacy among seniors. Nevertheless, enthusiasm for continued use was high, with an acceptance score of 2/2.
3.7. Sustainability Indicators
The ecological impact of SILVANUS-guided-interventions was assessed using three indicators (
Section 2.5):
Fuel-load reduction: UAV surveys detected a 23% decline in polygons >15 t ha
−1 after targeted thinning/burning (July 2023–March 2024) [
15].
Stand-structural diversity: LANDIS-II projected a 12% increase in Shannon index by 2050 under DSS-informed management scenarios [
12].
SFM Index: Ministry projections show a +4-point gain over the 2021 baseline of 100 when SILVANUS measures are scaled region-wide [
16].
Collectively, these results indicate positive contributions to Slovak forest sustainability-goals.
The following table (
Table 1) summarizes the fit–gap evaluation results presented in
Section 3.1,
Section 3.2,
Section 3.3,
Section 3.4,
Section 3.5,
Section 3.6 and
Section 3.7. Each module was assessed across the seven criteria using qualitative and quantitative evidence gathered during the Slovak pilot phase. Scores ranged from 0 (no alignment) to 2 (full alignment) per criterion, with a maximum total of 14 points per module.
4. Contemporary Approaches to Wildfire Management and Sustainable Forestry
Wildfire management has become a global priority as fire regimes intensify under the combined pressures of climate change, land use change, and socio-economic dynamics. Understanding global, continental, regional, and national wildfire patterns is essential for designing effective prevention, detection, and mitigation strategies. At the same time, sustainable forest management (SFM) is increasingly recognized not only for promoting ecological resilience and biodiversity but also for reducing wildfire risks by managing fuel loads, improving forest structure, and guiding land-use transitions.
This section provides a comprehensive overview of wildfire occurrence trends across scales (global to Slovak), and explores contemporary wildfire prevention strategies, technological advancements in early detection and monitoring, the role of landscape and climate models in assessing wildfire risks, insights from historical disturbances, and the development of integrated wildfire risk assessment frameworks. Particular attention is given to how the outcomes of the SILVANUS project support enhanced wildfire resilience and forest sustainability in the Slovak Republic, in accordance with current European policy frameworks and adaptive governance approaches.
4.1. Global, European, Central European, and Slovak Wildfire Trends
Wildfire regimes worldwide are undergoing profound transformations due to climate change, land-use changes, and socio-economic factors. Globally, although the total area burned annually decreased by approximately 24% between 1998 and 2015, particularly in tropical savannas [
17], the incidence, severity, and duration of wildfires in temperate and boreal forest ecosystems have increased [
18]. This divergence highlights the complex interactions between global climate drivers and regional fire regimes.
Boreal forests, which were historically considered relatively fire-resilient, are experiencing unprecedented fire activity. The 2023 Canadian wildfire season burned over 17 million hectares—more than seven times the average—resulting in massive carbon emissions that further exacerbated global warming [
19]. Observations show that boreal fires are becoming larger, burning deeper into carbon-rich soils, and shifting northward [
20].
Wildfire patterns have evolved across Europe. While Southern Europe remains the most affected region, Northern and Central Europe have reported increasing numbers of large fires over the past two decades [
17,
21]. In 2022, over 865,000 hectares were burned in EU countries, nearly three times the historical average from 2006 to 2021 [
17]. Heatwaves, prolonged droughts, and rural depopulation have significantly contributed to this shift [
22,
23].
Climate projections suggest that by 2050, under a high-emission scenario, catastrophic wildfire events could increase by 30%–50% in Southern and Central Europe [
21]. Particularly concerning is the expansion of fire-prone conditions into regions that were historically unaffected, including parts of Germany, the Czech Republic, and Slovakia.
Although wildfires have historically been less frequent in Slovakia, the trend is concerning. Between 2010 and 2020, the country recorded an average of 550 wildfires annually, primarily during dry summers [
24]. In 2022, over 640 incidents were reported, affecting forests, grasslands, and agricultural land [
24]. High-risk areas include the Podpoľanie volcanic highlands, Slovenské Rudohorie, and sandy pine forests in Záhorie [
11].
Disturbed forests, such as those impacted by the 2004 High Tatras windstorm, present elevated fire hazards due to deadwood accumulation [
11]. Climate projections indicate a 20%–40% increase in the number of high fire-risk days by mid-century, particularly during the late summer and early autumn [
25].
4.2. Forest Fire Prevention Strategies
Effective wildfire prevention is essential for reducing fire frequency, severity, and socio-economic impacts, and it must be grounded in the principles of sustainable forest management (SFM). Globally, prevention strategies include prescribed burning, mechanical thinning, grazing management, landscape fragmentation, and public education [
26]. SFM contributes to maintaining species and structural diversity, creating natural firebreaks, and integrating fire resilience into forest planning. Prescribed burning, although controversial, remains a key tool in regions like Australia and parts of Southern Europe [
27]. Its effectiveness depends on careful ecological planning and public support [
28].
In the European Union, catastrophic fire seasons have triggered a strategic pivot from reactive suppression to proactive, integrated risk reduction [
5]. The EU Forest Strategy for 2030 emphasizes multifunctional, climate-resilient forests as the cornerstone of wildfire prevention [
29]. In Slovakia, recent policy developments and pilot programs, such as those under the SILVANUS project, reflect a shift toward integrated fire-smart landscape management. These include mechanical thinning in high-risk pine monocultures, vegetation clearance along infrastructure corridors, and an increased emphasis on wildfire-aware forest planning [
11]. However, obstacles remain, such as fragmented land ownership, limited funding, and insufficient capacity for large-scale fuel management efforts.
SILVANUS directly addresses these challenges through tools like remote sensing for dynamic fuel load monitoring, participatory engagement for local governance, and operational models for risk mapping and prioritization. These components help move Slovakia’s wildfire prevention strategy closer to an adaptive and sustainable forest management system.
4.3. Early Detection and Monitoring Technologies
Early detection is one of the most critical components of effective wildfire management. Satellite remote sensing, UAVs, AI-based anomaly detection, and IoT-enabled sensor networks have transformed monitoring capabilities globally [
30,
31,
32,
33,
34].
Satellite-based systems, such as the Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer (MODIS) and Sentinel-2, provide near-real-time fire alerts and burned area mapping [
31]. Unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) or drones are increasingly utilized for localized high-resolution monitoring, especially in rugged or inaccessible terrains [
32].
Machine learning algorithms have been developed to predict wildfire occurrence based on meteorological data, vegetation indices, and human activity patterns, thereby improving the precision of early warning systems [
33]. Sensor networksthat combine thermal imaging, air quality monitoring, and AI-driven fire detection software are being deployed in high-risk regions to provide immediate alerts [
34].
In Europe, the European Forest Fire Information System (EFFIS) integrates satellite data with meteorological forecasts to predict fire danger levels and monitor active fires across its member states [
1]. National systems complement these efforts by increasingly utilizing multi-sensor approaches.
In Slovakia, traditional systems, such as camera-equipped fire towers and ground patrols, still play a role, but integration with advanced technologies is increasingly prioritized. SILVANUS contributes through its modular Environmental Management Platform (EMP), which aggregates data from UAVs, IoT sensors, satellite feeds, and weather forecasts to generate real-time fire alerts and dynamic risk visualizations. This significantly enhances the responsiveness of Slovak fire services and forest authorities, especially in remote or mountainous regions.
4.4. Forest Landscape and Climate Models for Wildfire Assessment
Forest landscape models have become essential tools for assessing wildfire risk in the context of changing forest structures, climate variability, and management interventions [
35]. These models assist policymakers and land managers in assessing long-term fire risks and developing adaptive management strategies. They are also used to simulate vegetation dynamics, forest succession, and the spatial distribution of fuels under different management and disturbance scenarios. When coupled with climate projections, they provide a powerful basis for understanding long-term trends in fire susceptibility and for evaluating the effectiveness of forest management interventions.
Climate-sensitive modeling predicts that by mid-century, large parts of Europe, including Central Europe, will experience significantly higher wildfire probabilities, particularly under high emission scenarios [
21,
36]. Climate change affects fire risk by altering temperature and precipitation patterns, leading to shifts in vegetation composition, increased fuel availability, and extended duration of fire seasons.. Therefore, long-term strategic planning must rely on tools that can account for both forest ecosystem responses and climatic drivers. Models such as LANDIS-II, iLand, and Dynamic Global Vegetation Models (DGVMs) are widely used in forest ecology and wildfire research for this purpose [
37].
In the context of sustainable forest management, landscape and climate models enable forest planners to explore how alternative silvicultural strategies, such as species diversification, age-class restructuring, and fuel break design, may influence fire behavior and post-disturbance recovery. These simulations support adaptive management by identifying interventions that enhance both fire resilience and long-term forest sustainability [
36].
The SILVANUS platform incorporates regionally calibrated climate and forest models into its Environmental Resilience Toolbox. These models integrate data from multiple sources, including IoT-based field sensors, meteorological forecasts, and remote sensing, to simulate fire spread and assess ecological vulnerability under different climatic scenarios. In the Slovak context, where the fire regime is evolving due to climate warming and post-disturbance landscape change, such tools help local forestry services and planners design fire-resilient forests based on projected future conditions.
The use of predictive modeling within SILVANUS also enhances strategic decision-making by linking biophysical data with risk scoring, prioritization, and spatial planning modules within the platform. This supports proactive wildfire risk reduction and forest policy alignment with climate adaptation goals at the national and EU levels [
37].
4.5. Forest Resilience from Historical Case Studies
Understanding past forest disturbances, including wildfires, windstorms, and pest outbreaks, offers valuable insights into forest resilience and vulnerability. Historical case studies provide empirical evidence of forest response dynamics, management shortcomings, and socio-ecological consequences, all of which are essential for informing future wildfire governance and sustainable forest planning [
38].
One notable event in Slovakia was the 2004 windstorm in the High Tatras, which destroyed approximately 12,000 ha of forests. The affected areas subsequently became susceptible to bark beetle infestation, compounding ecological stress and increasing fire risk due to increased deadwood accumulation and disrupted stand structure [
38]. Similar cascading disturbances have been documented across Central Europe, where wind and pest interactions have significantly altered fire-risk profiles [
12].
These case studies demonstrate the importance of integrated disturbance management strategies. Forests that were managed with mixed-species composition, structural diversity, and fuel reduction practices exhibited greater resistance to both biotic and abiotic stressors. In contrast, large monoculture plantations and unmanaged areas often suffered higher post-disturbance mortality and slower recovery [
39]. These case studies demonstrate the importance of integrated disturbance management strategies. Forests that were managed with mixed-species composition, structural diversity, and fuel reduction practices exhibited greater resistance to both biotic and abiotic stressors. In contrast, large monoculture plantations and unmanaged areas often suffer higher post-disturbance mortality and slower recovery [
39].
Forest resilience also depends on institutional and policy-related factors. After major disturbance events, delays in salvage operations, lack of reforestation planning, and conflicting stakeholder interests can increase fire susceptibility. Adaptive governance frameworks that emphasize learning, flexibility, and coordination—are therefore crucial for improving post-disturbance forest recovery and long-term resilience [
40].
In Slovakia, these historical lessons have been increasingly integrated into forest risk assessments and management plans. The SILVANUS platform supports this effort by enabling retrospective analyses through its data integration features. It allows stakeholders to combine past disturbance records, current vegetation data, and climate forecasts to identify areas with heightened fire risk and prioritize management interventions accordingly. Such retrospective foresight contributes to the development of more resilient and adaptive forest landscapes.
4.6. Assessment Frameworks
Comprehensive wildfire risk assessment frameworks are essential tools for effective forest fire management, policy formulation, and long-term resilience planning. In recent years, these frameworks have evolved from hazard-focused models to integrated, multi-dimensional approaches that evaluate fire hazard and exposure as well as environmental vulnerability, socio-economic impact, and institutional capacity for prevention, preparedness, and recovery [
41].
Internationally recognized frameworks, such as the Sendai Framework for Disaster Risk Reduction 2015–2030, advocate multi-hazard, risk-informed approaches that encompass climate projections, land-use change, and stakeholder capacity. These principles are particularly relevant in Central Europe, where climate-driven changes in fire regimes intersect with socio-political complexities such as fragmented land ownership and variable institutional readiness [
41]. The SILVANUS project has operationalized these principles into a holistic risk assessment methodology embedded in its Environmental Management Platform (EMP). The assessment framework developed within SILVANUS consists of several interconnected dimensions:
Environmental vulnerability: incorporating fuel load, vegetation composition, terrain, and post-disturbance conditions (e.g., windthrow and bark beetle outbreaks);
Climatic hazards: Utilizing long-term climate indicators (e.g., SPEI, FWI) and short-term meteorological anomalies to assess ignition probability and fire spread potential.
Socio-economic exposure: evaluating the distribution of populations, critical infrastructure, and economic activities within fire-prone zones;
Institutional capacity: assessing the availability of trained firefighting personnel, coordination mechanisms, equipment resources, and access to digital decision support tools.
Such a structured framework allows fire risk to be evaluated at both spatial and temporal scales. Importantly, it facilitates integration with EU climate adaptation targets, CAP strategic plans, and the EU Forest Strategy for 2030 [
42], thereby linking scientific assessments to operational and policy mechanisms.
In contrast to other recent wildfire projects, such as FIRE-RES, which emphasizes transdisciplinary fire-smart landscapes in Mediterranean zones, and FirEUrisk, which focuses on improving fire risk planning in the wildland–urban interface (WUI), SILVANUS places a stronger emphasis on the operational integration of heterogeneous data streams, real-time decision support, and multi-level stakeholder engagement. This makes SILVANUS uniquely positioned to support the implementation of less fire-adapted, highly fragmented forestry systems, such as those in Central Europe. Its outputs are aligned with strategic frameworks, including the EU Forest Strategy for 2030 and the EU Disaster Risk Reduction Framework, offering actionable tools for local authorities, forestry agencies, and emergency responders.
In Slovakia, where fire risk assessments remain fragmented and inconsistently applied across jurisdictions, the SILVANUS framework offers a standardized, scalable approach that aligns with national forestry priorities. The system is adaptable to both protected and commercial forest areas and can be utilized by public authorities, forest enterprises, and emergency services.
Furthermore, by integrating the SILVANUS framework into strategic planning documents, such as forest management plans, civil protection strategies, and landscape restoration projects, Slovakia can improve its capacity to allocate resources effectively, prioritize interventions, and communicate risks to the public and to stakeholders. This transition from reactive to proactive risk governance is essential for enhancing wildfire resilience in an era of climate change uncertainty.
5. Benefits of the SILVANUS Project for Wildfire Management in Slovakia
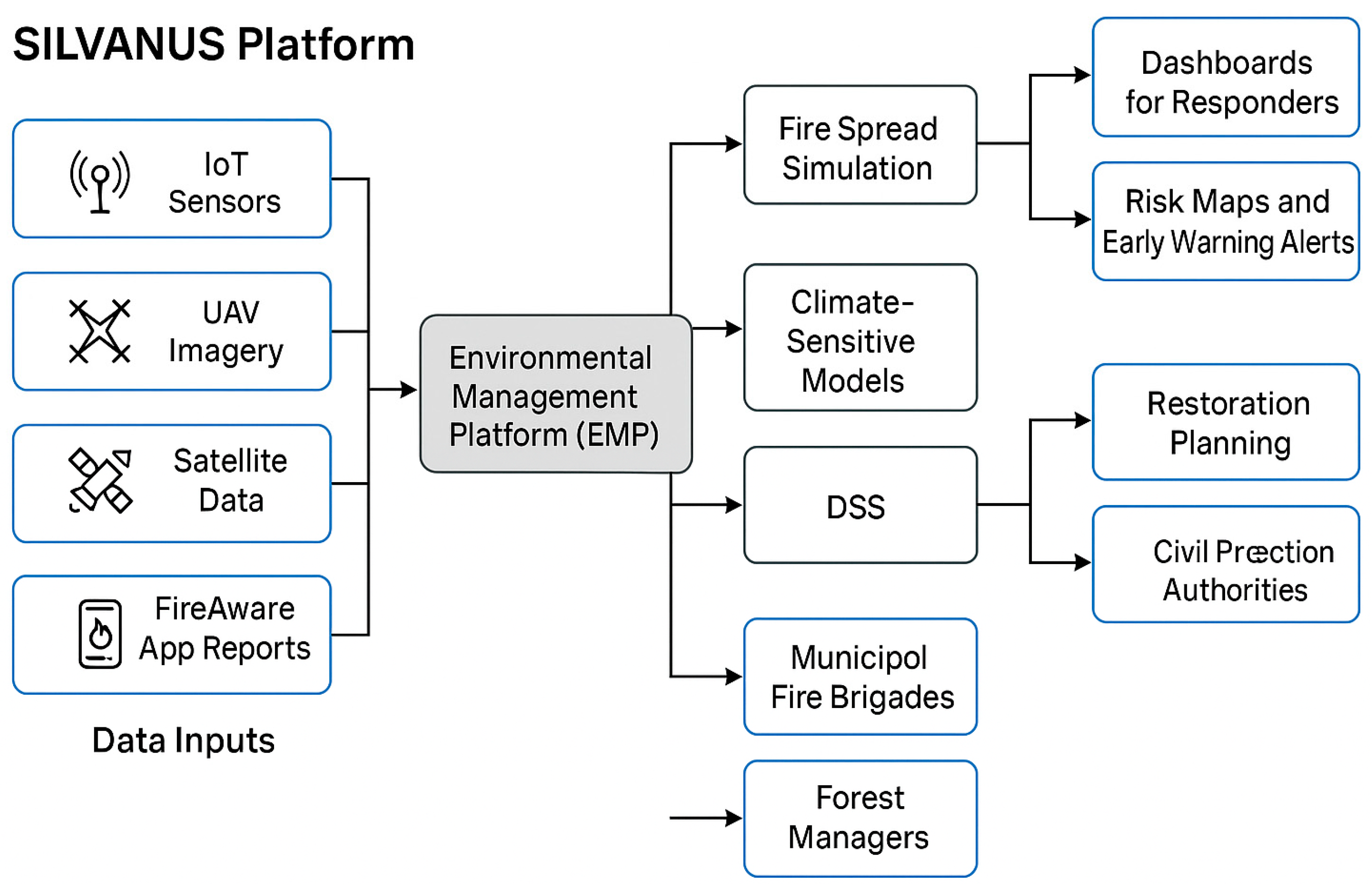
The SILVANUS project, funded under the Horizon 2020 program, delivers a modular and scalable digital platform (
Figure 1) aimed at improving wildfire resilience through early detection, environmental programming, stakeholder coordination, and sustainable forest management support.
The SILVANUS project, funded under the Horizon 2020 programme, delivers a modular, scalable digital platform aimed at improving wildfire resilience through early detection, environmental modeling, stakeholder coordination, and sustainable forest management support. Among the 12 pilot sites across Europe and beyond, Slovakia was selected based on its moderate but increasing wildfire risk, institutional diversity, and opportunity to test digital integration in a post-socialist forest governance setting.
The Podpoľanie region, located in central Slovakia, was identified as a high-priority area due to its extensive grass burning during the spring and autumn seasons, accumulated surface fuels, complex topography, and fragmented land ownership—all of which pose challenges for effective wildfire prevention and suppression. This chapter presents the functional implementation, operational benefits, and policy relevance of the SILVANUS platform as applied in Slovakia, drawing on the outcomes of field deployment, stakeholder feedback, and system testing conducted in 2023–2024.
Table 2 compares the capabilities of the SILVANUS modules with those of existing wildfire monitoring approaches currently used in Slovakia, highlighting the functional enhancements brought by the platform.
5.1. Stakeholder Engagement and Functional Requirements for Wildfire Prevention in Slovakia
Engagement with diverse stakeholders is a cornerstone of the SILVANUS methodology. In Task 2.1, participatory processes were employed across partner countries, including Slovakia, to determine the functional requirements for wildfire prevention and management [
43]. In Slovakia, workshops and surveys involving forest managers, civil protection authorities, local governments, and NGOs identified several critical needs. These include the necessity for comprehensive monitoring of fuel loads in fire-prone areas, enhanced early detection and communication systems, improved community-based prevention measures, and the integration of traditional knowledge into fire risk assessments. The outputs of this process were consolidated in Deliverable D2.1, providing an actionable foundation for national and regional fire risk planning [
8].
In Slovakia, where decentralized land ownership presents significant wildfire management challenges, the participatory consultation model demonstrated by SILVANUS aligns well with the multi-level governance structure. The State, which owns approximately 40% of Slovak forests, plays a vital role in implementing fire prevention measures, while municipal authorities and private owners manage a patchwork of smaller parcels. Fragmentation requires coordination tools and shared decision-making frameworks to achieve comprehensive fire resilience.
The Podpoľanie pilot site served as a practical testbed for the proposed model. Stakeholder consultations there revealed a strong demand for spatial risk maps that integrate satellite, UAV, and IoT data; user-friendly dashboards tailored for local fire brigades and forest wardens; and decision support tools that consider seasonal fire behavior and community response capacity. These findings directly informed the design of the Environmental Management Platform (EMP) modules, which were customized for Slovakia.
Previous research has emphasized that stakeholder-supported approaches are essential for enhancing fire resilience at the local and regional scales [
23]. Therefore, adopting the stakeholder engagement frameworks established within SILVANUS can significantly strengthen Slovakia’s wildfire prevention strategies, moving them toward participatory and adaptive governance.
This participatory methodology also supports the obligations under the EU Forest Strategy for 2030 [
42], which calls for inclusive forest governance and community-based resilience planning.
5.2. Climate-Sensitive Forest Models for Adaptation Planning
Wildfire dynamics in Europe are increasingly influenced by climate change, with Central Europe experiencing longer fire seasons, reduced snowpack durations, and increased fuel flammability [
21]. To anticipate these risks, SILVANUS has developed climate-sensitive forest landscape models that integrate projected climatic variables, vegetation succession, terrain characteristics, and anthropogenic pressures [
12]. These models, calibrated using both historical disturbance data (e.g., windthrow and bark beetle outbreaks) and future emission scenarios, allow forest managers to assess how alternative forest compositions and silvicultural strategies will influence wildfire ignition potential, fire spread behavior, and post-fire regeneration under projected climate conditions.
In the Slovak Republic, the application of such models is particularly pertinent in montane regions dominated by monocultural Norway spruce (Picea abies) plantations, which have demonstrated high vulnerability not only to wind and pest disturbances but also to subsequent fire susceptibility due to increased deadwood accumulation and stand instability [
38]. This is especially visible in areas such as the High Tatras and Podpoľanie, where disturbance-induced landscape changes have created fuel-rich and high-risk mosaics.
In the Slovak Republic, the application of such models is particularly pertinent for regions dominated by monocultural spruce plantations, which have demonstrated high vulnerability not only to wind and pest disturbances but also to subsequent fire susceptibility due to increased deadwood accumulation and stand instability [
38]. This is especially visible in areas such as the High Tatras and Podpoľanie, where disturbance-induced landscape changes have created fuel-rich and high-risk mosaics.
Transitioning toward structurally diverse, mixed-species forests, as suggested by recent Central European studies [
11], would significantly enhance ecosystem resilience to both biotic and abiotic threats. The SILVANUS modeling tools allow for the spatial identification of high-risk zones, enabling forest authorities to prioritize adaptive interventions, such as mechanical fuel management, climate-resilient replanting, and strategic thinning based on species composition and moisture regimes. Moreover, these models provide a quantitative and spatially explicit basis for long-term adaptation planning, supporting Slovakia’s National Forest Program, National Adaptation Strategy, and regional risk zoning initiatives. The integration of such predictive tools enhances the institutional capacity to move from reactive suppression to proactive, ecosystem-based wildfire risk governance.
5.3. IoT and UAV-Based Early Fire Detection Technologies
The rapid detection of wildfires is essential to minimize damage and support efficient firefighting. In Slovakia, Traditional fire lookout networks and manual surveillance methods, while historically valuable, are increasingly constrained by limited coverage, slow response times, and susceptibility to human error [
9]. To overcome these limitations, the SILVANUS project integrated Internet of Things (IoT) environmental sensors, unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) equipped with optical and thermal imaging, and AI-enhanced satellite data analytics into a unified early warning system [
10]. Pilot trials conducted in France and Greece under SILVANUS revealed that this combination of technologies reduced ignition detection times by over 30% when compared to conventional surveillance methods [
13]. These outcomes demonstrate the potential of the platform to enhance wildfire response during the critical early stages. In the Slovak context, the deployment of the SILVANUS system would be especially beneficial in remote and mountainous areas, such as Podpoľanie and Slovenské Rudohorie, where access is difficult and fire spread can be rapid. Fixed sensors placed in vulnerable forest zones can continuously monitor environmental conditions, such as temperature, wind speed, and humidity, which are key variables influencing ignition probability. These sensors are linked to real-time alert systems, allowing authorities to pre-emptively dispatch firefighting resources.
UAVs equipped with thermal cameras deployed on demand or via pre-programmed patrols add a mobile layer of reconnaissance, which is particularly effective during the night or in smoke-obscured areas [
14]. Satellite imagery processed using AI-based anomaly detection algorithms further enhances spatial coverage and enables the early recognition of fire signatures that are invisible to the naked eye.
An additional innovation is the FireAware mobile application [
9], developed within SILVANUS, to enable citizen-based surveillance. This app allows local residents, hikers, and forest workers to report visible smoke or flames in real time. Participatory surveillance models are increasingly recognized as cost-effective and scalable complements to institutional monitoring systems [
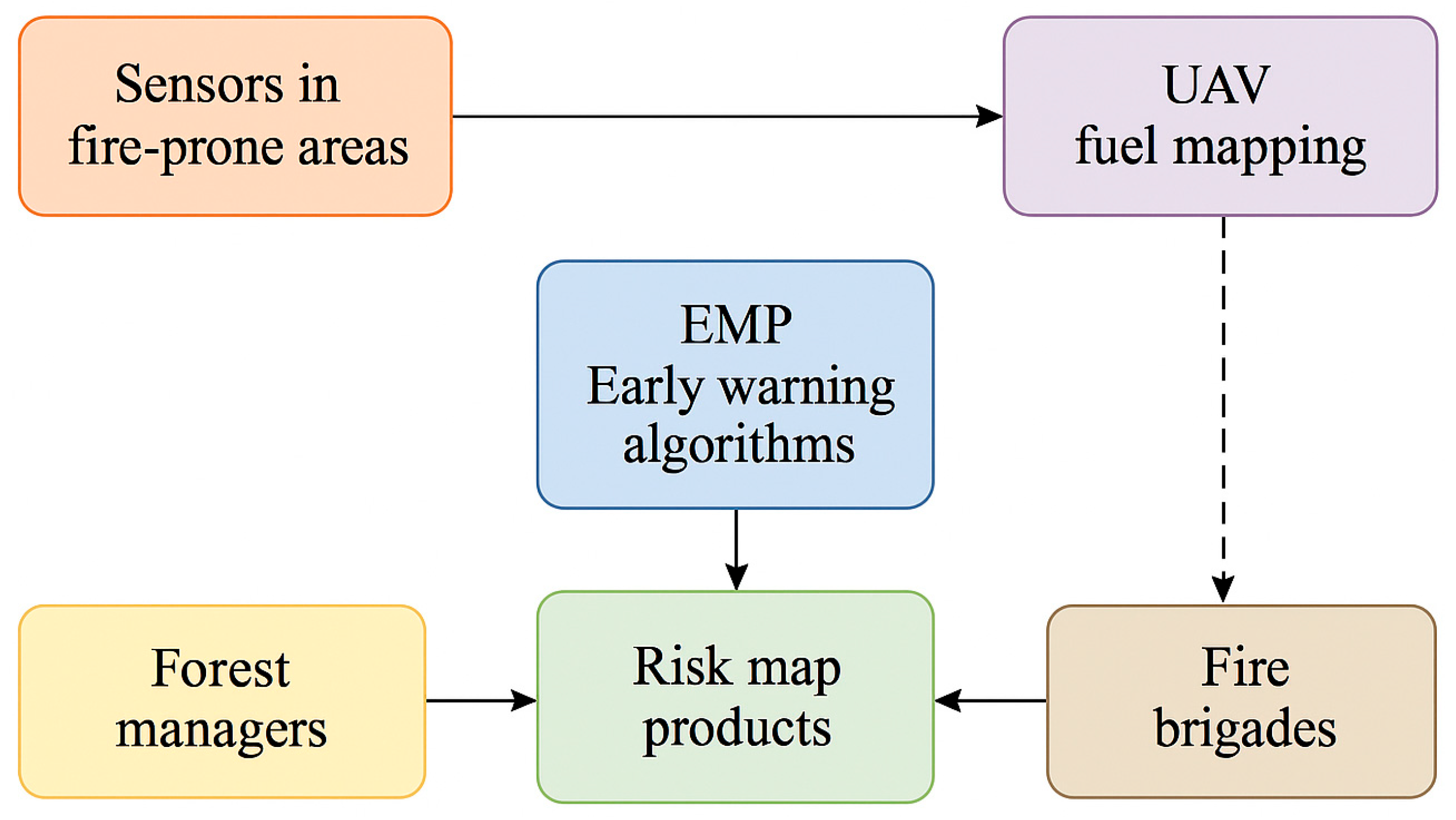
9]. All of these components are integrated within the Environmental Management Platform (EMP), a modular system designed to consolidate inputs from satellite data, sensor networks, UAVs, and predictive models (
Figure 2). The EMP enables real-time wildfire risk visualization, automated alerts, and tailored decision support for forest managers, emergency responders, and local governments [
12,
43].
5.4. Decision Support Systems (DSS) for Emergency Response and Ecological Restoration
Effective wildfire management depends not only on early detection but also on intelligent, data-driven decision-making during suppression operations and post-fire landscape recovery. To address this, the SILVANUS project developed an advanced Decision Support System (DSS) capable of integrating environmental data, modeling wildfire dynamics in real time, optimizing suppression strategies, and supporting ecological restoration planning [
10]. The DSS synthesizes diverse data sources, including meteorological forecasts, terrain models, fuel types, vegetation structures, and live sensor inputs, to produce dynamic fire behavior simulations. These outputs help emergency coordinators anticipate fire progression under varying wind and moisture scenarios and optimize the allocation of personnel, ground units, and aerial firefighting resources. In the Slovak context, where mountainous terrain, variable microclimates, and fragmented land ownership complicate fire suppression logistics, SILVANUS DSS could offer transformative benefits. For example, in regions such as Podpoľanie, real-time spread predictions would enable more precise positioning of firefighting crews and reduce the risks to responders. The system’s capability to integrate data from IoT sensors, UAV observations, and satellite inputs ensures that situational awareness is both timely and accurate.
In addition to suppression, the DSS includes tools for ecological restoration planning. Post-fire modules analyze site-specific conditions, such as slope, soil type, pre-disturbance vegetation, and erosion risk, to recommend appropriate restoration measures. These may include reforestation with native species, erosion control structures, and exclusion zones to allow natural regeneration. Such targeted planning aligns with Slovakia’s National Forest Program and the goals of the EU Biodiversity Strategy for 2030.
Operational experiences from large fire incidents in Portugal and Spain have demonstrated that the integration of DSS platforms significantly improves coordination, resource-use efficiency, and post-fire recovery outcomes [
15]. Embedding the SILVANUS DSS into Slovakia’s national Integrated Rescue System and regional forest fire prevention plans would represent a substantial advancement in building wildfire resilience and adaptive forest management capacity.
6. Pilot Testing Outcomes: Lessons from the Podpoľanie Region
The Podpoľanie region, located in central Slovakia, was selected as the country’s primary pilot site within SILVANUS due to its complex terrain, dense forest cover, and increasing vulnerability to wildfires under projected climate scenarios [
8]. The landscape is characterized by a mix of spruce and beech stands, steep slopes, and a dispersed settlement pattern, creating challenges for both fire prevention and suppression logistics.
As part of the pilot activities, the SILVANUS team deployed IoT-based environmental sensors in fire-prone zones to collect real-time data on temperature, humidity, and soil moisture. Simultaneously, UAV flights equipped with thermal and multispectral cameras were conducted to assess vegetation structure and fuel loads. These data streams were integrated into the Environmental Management Platform (EMP) and used to test early warning algorithms and fire risk visualization tools tailored to the Slovak conditions.
The pilot results demonstrated the feasibility of using low-cost sensor networks and UAVs even in topographically challenging environments. However, the pilot also highlighted the critical need for local capacity building. Many municipal fire brigades and forestry units require hands-on training to operate UAV equipment effectively, interpret risk outputs, and engage with the EMP dashboard functionalities. These findings underscore the importance of coupling technological deployment with institutional readiness and skills development programs, particularly in smaller municipalities with limited digital infrastructure. Furthermore, the Podpoľanie experience revealed governance challenges in coordinating fire management responsibilities across municipal, district, and national agencies. Differences in data access protocols, unclear mandates, and a lack of integrated command systems occasionally impede smooth collaboration during simulated scenarios. Notably, similar inter-institutional coordination gaps were reported in other SILVANUS pilot sites across Europe [
30], indicating a broader need for multi-level governance frameworks for wildfire resilience.
The pilot concluded with a set of validated recommendations for enhancing digital wildfire preparedness in Slovakia: (1) build decentralized sensor networks linked to national early warning systems; (2) provide targeted training to local actors; and (3) establish shared governance protocols for wildfire response. Lessons from Podpoľanie provide a strong evidence base for scaling SILVANUS innovations to other fire-prone regions in Slovakia, such as Slovenské Rudohorie and the High Tatras.
The integration of SILVANUS innovations into Slovakia’s wildfire management strategies offers a significant opportunity to enhance the national capacity for prevention, early detection, and coordinated responses. The modular architecture of the system allows for flexible adoption by municipalities, forest districts, and national agencies.
One of the most immediate opportunities lies in leveraging EU funding mechanisms, including Horizon Europe, the LIFE Programme, the Recovery and Resilience Facility, and the Cohesion Fund to support technology deployment, cross-sectoral training, and long-term maintenance. Additionally, the SILVANUS approach supports Slovakia’s policy commitments under the European Green Deal, the EU Forest Strategy for 2030, and its National Adaptation Strategy, which emphasizes digital transformation, climate resilience, and inclusive forest governance.
However, successful implementation requires proactive management of several challenges. High up-front investment costs for IoT infrastructure, UAV platforms, and DSS integration may strain the limited budgets of municipalities and forest enterprises. These costs highlight the need for co-financing models involving national, regional, and EU-level funding.
Moreover, Slovakia’s institutional fragmentation, driven by a complex mosaic of state, municipal, private, and church-owned forests, poses a barrier to coordinated wildfire management. Differing capacities, legal mandates, and levels of digital readiness among stakeholders may impede uniform deployment and data sharing. Clear inter-agency coordination protocols and central support for shared infrastructure are essential.
Another barrier is the public acceptance of novel surveillance and risk reduction technologies. Although tools like UAV monitoring and citizen-reporting apps are effective, their acceptance depends on well-designed awareness and outreach campaigns, particularly in rural communities where trust in digital interventions may be limited.
A phased integration strategy is recommended to address these challenges. Initial efforts should focus on high-risk areas, such as Podpoľanie, where pilot testing has already validated the system functionality. This should be followed by progressive expansion through Slovakia’s Integrated Rescue System and national forest fire prevention plans, supported by policy instruments and stakeholder coordination platforms developed within the SILVANUS framework.
Ultimately, the full integration of SILVANUS tools into forest management planning, emergency response protocols, and community preparedness strategies offers a scalable path for building a resilient, climate-adapted forestry sector that meets both national priorities and EU-wide objectives.
In addition to technical and institutional considerations, the successful adoption of SILVANUS technologies in Slovakia will depend on addressing public perceptions and ethical concerns. The deployment of UAVs, IoT sensors, and citizen-reporting apps like FireAware must be accompanied by transparent communication strategies, public consultations, and adherence to data governance best practices. Ensuring community-informed consent, safeguarding data privacy, and complying with European data protection standards, such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR), are essential for fostering public trust and the long-term legitimacy of these tools. Public engagement campaigns that frame these technologies as enablers of safety rather than surveillance are critical for encouraging grassroots participation and acceptance.
7. Critical Evaluation of the Implementation Potential of SILVANUS Project Outcomes in the Slovak Republic
The SILVANUS project provides Slovakia with a comprehensive and modular platform to improve wildfire resilience in the face of growing climate-related threats, land-use changes, and socio-economic pressures. The integration of real-time environmental monitoring, climate-adaptive forest models, and participatory governance tools constitutes a significant advancement over traditional reactive wildfire management strategies. The Environmental Management Platform (EMP), which aggregates satellite, IoT, and UAV data, has proven effective in producing high-resolution wildfire risk maps, particularly for mountainous and remote regions like Podpoľanie and Slovenské Rudohorie [
10,
43,
44]. These tools align with Slovakia’s national priorities for digital transformation, climate adaptation, and disaster risk reduction. One of the core strengths of SILVANUS is its multi-actor, co-creation methodology. Through stakeholder consultations and iterative definition of functional requirements, the project ensured that its technological outputs responded directly to operational needs [
36,
37]. This is particularly important in Slovakia, where decentralized forest ownership, including a significant proportion of municipal and private forests, requires inclusive and adaptable solutions [
16]. Pilot deployment in Podpoľanie validated the technical feasibility of sensor networks and UAV-based surveillance, even under the region’s challenging topography and institutional conditions. These tools enhance situational awareness and preparedness for local firefighting units and forestry authorities [
44].
However, several limitations challenge the broad implementation of SILVANUS tools in Slovakia. First, technical and financial barriers persist. Many rural municipalities lack the capacity to independently finance and maintain IoT infrastructure and UAV fleets. Although DSS modules are powerful, they require skilled personnel for continuous calibration and use [
10,
14]. Disparities in institutional digital readiness and infrastructure between regions could result in uneven uptake [
45]. Furthermore, the predictive accuracy of climate-sensitive models depends on access to high-quality local meteorological and ecological data, which are incomplete or outdated in certain Slovak subregions [
46]. There is a favorable external environment for SILVANUS implementation. The European Green Deal, EU Forest Strategy for 2030, and national adaptation frameworks prioritize wildfire resilience, biodiversity conservation, and digital innovation in forest governance [
47]. These policies provide access to funding instruments such as Horizon Europe, the LIFE Programme, and the Recovery and Resilience Facility, which can co-finance infrastructure, training, and governance reforms. Increasing public concern about climate change and recent wildfire events has fostered a societal shift toward proactive risk management, providing fertile ground for community engagement initiatives.
However, critical threats and risks must be acknowledged. Initial investment costs may remain prohibitive without stable gas long-term co-financing mechanisms [
47]. Institutional fragmentation, particularly in data governance and operational mandates among state, municipal, and private actors, could undermine the integrated logic of the SILVANUS platform [
16]. Public skepticism regarding UAV surveillance and personal data collection also poses reputational risks if transparency and consent frameworks are not implemented [
9]. Finally, the accelerating pace and unpredictability of climate extremes, such as compound drought–wind–pest disturbances, may outpace the assumptions embedded in current models [
21].
Table 3 outlines how SILVANUS modules correspond to the responsibilities of key Slovak agencies, highlighting the opportunities for institutional integration and cross-sectoral coordination.
To synthesize the evaluation of SILVANUS implementation potential in Slovakia,
Table 4 presents a SWOT analysis summarizing the internal and external factors influencing success.
These findings support the fit–gap assessment results presented above.
In conclusion, the SILVANUS project offers Slovakia a well-aligned and forward-looking solution for addressing emerging wildfire risks. However, its success hinges on overcoming structural barriers through targeted investments, strengthening institutional coordination, and fostering societal trust in innovation. By strategically scaling the pilot outcomes and embedding SILVANUS methodologies within national forest, climate, and disaster governance systems, Slovakia can build a more resilient, adaptive, and technology-enabled forest sector in the era of climate change. Furthermore, ethical and legal frameworks must be strengthened to support the responsible use of SILVANUS technology. Although IoT- and UAV-based monitoring offers clear advantages for early detection and response, it raises questions regarding data ownership, citizen privacy, and equitable access. Addressing these challenges requires integration with national data governance protocols and alignment with EU-wide standards for environmental monitoring and digital ethics. Building public trust through participatory implementation, transparent data handling, and feedback mechanisms will be central to the long-term acceptance and effectiveness of the system.
8. Conclusions
The participation of the Slovak Republic in the Horizon 2020 SILVANUS project has significantly contributed to strengthening wildfire resilience and advancing sustainable forest management in the context of accelerating climate change. By integrating cutting-edge technologies, including IoT-based environmental monitoring, UAV surveillance, climate-sensitive forest models, and decision support platforms, with participatory governance approaches, the project delivered tools that are well aligned with Slovakia’s evolving wildfire risk profile. The SILVANUS approach demonstrates that technological innovation, when coupled with local stakeholder engagement, can overcome long-standing limitations in wildfire detection, prevention, and emergency response. Pilot testing in the Podpoľanie region validated the feasibility of deploying sensor networks, UAVs, and AI-supported monitoring, even in complex mountainous terrain, enabling more timely fire detection and risk assessment and offering a scalable model for application in other fire-prone regions across Slovakia (see
Supplementary Materials). Importantly, the climate-sensitive forest models developed in this project provide a robust scientific basis for long-term adaptation planning. By simulating vegetation responses to projected climate trajectories, these models support the transformation of vulnerable monocultural forests into more diverse and resilient ecosystems. This aligns with Slovakia’s national forestry goals and broader EU Green Deal objectives.
However, the successful integration of SILVANUS outcomes into Slovak forestry and civil protection frameworks will require addressing certain weaknesses and threats identified through critical evaluation. Investment in technological infrastructure, workforce capacity building, and data integration should be prioritized to ensure operational sustainability. Coordination among municipal, regional, and national institutions must be strengthened to fully leverage the benefits of integrated environmental monitoring and decision support platforms. Furthermore, sustained public engagement initiatives are essential for fostering acceptance and active participation in wildfire prevention and early warning efforts.
Despite these strengths, the successful integration of SILVANUS innovations into Slovakia’s forest and civil protection frameworks requires targeted action. Investment in technical infrastructure, workforce training, and data integration is essential for achieving operational sustainability. Moreover, institutional coordination across municipal, regional, and national levels must be improved to fully leverage the integrated nature of the Environmental Management Platform (EMP) and Decision Support Systems (DSS). Continued public engagement and education are necessary to foster the acceptance of new technologies and encourage community participation in wildfire prevention.
The European policy landscape, particularly under the Green Deal and Horizon Europe funding mechanisms, provides a favorable environment for scaling up SILVANUS innovations in Slovakia. By strategically utilizing these opportunities and proactively managing financial, institutional, and societal challenges, Slovakia can significantly enhance its wildfire resilience and contribute to broader European goals for climate adaptation and sustainable forest management.
The European policy context provides a favorable environment for scaling up the SILVANUS tools. Funding opportunities through Horizon Europe, the LIFE Programme, and the Recovery and Resilience Facility can support the long-term implementation. By strategically leveraging these instruments and proactively addressing financial, institutional, and societal challenges, Slovakia can significantly improve its wildfire preparedness and contribute to EU-wide objectives for climate adaptation and forest sustainability.
Moreover, Slovakia’s experience with SILVANUS provides a replicable framework for other Central and Eastern European countries facing similar environmental risks, forest structure, and governance complexities. The project’s pilot-tested tools and stakeholder-informed methodologies can be tailored to diverse national contexts to enhance regional cooperation in wildfire risk management. In conclusion, the SILVANUS project offers Slovakia not only technological upgrades but also enables a paradigm shift toward proactive, integrated, and participatory wildfire governance. The lessons drawn from pilot testing and cross-sectoral collaboration form a solid foundation for building a more resilient forest landscape capable of adapting to the growing impacts of climate change, while also informing European strategies for sustainable land and risk management.
Early results from the Slovak pilot suggest that SILVANUS may improve key indicators such as fuel load, forest diversity, and the national SFM index.