Enhancement of Dimensional Stability, Hydrophobicity, and Mechanical Strength of North American Red Alder Wood Through Silane Impregnation Combined with DES Pretreatment
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials and Chemicals
2.2. Wood DES Pretreatment
2.3. Preparation of the Silane Hydrolysis Solution
2.4. Preparation of Modified Specimens
2.5. Weight Percentage Gain
2.6. Density
2.7. Moisture Absorption and Water Uptake
2.8. Anti-Swelling Efficiency (ASE)
2.9. Hardness of Specimens
2.10. Water Contact Angle
2.11. Fourier-Transform Infrared Spectrometer (FTIR)
2.12. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM)
3. Results and Discussion
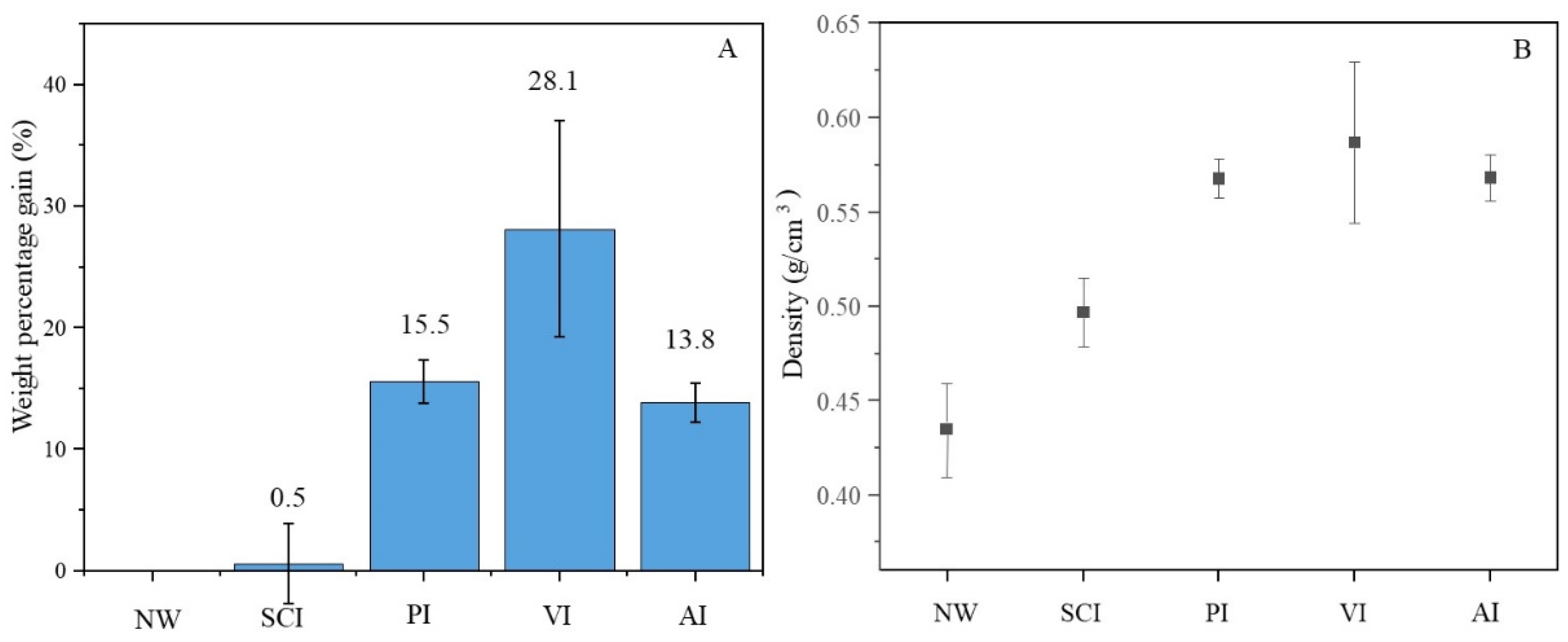
3.1. Weight Percentage Gain and Density
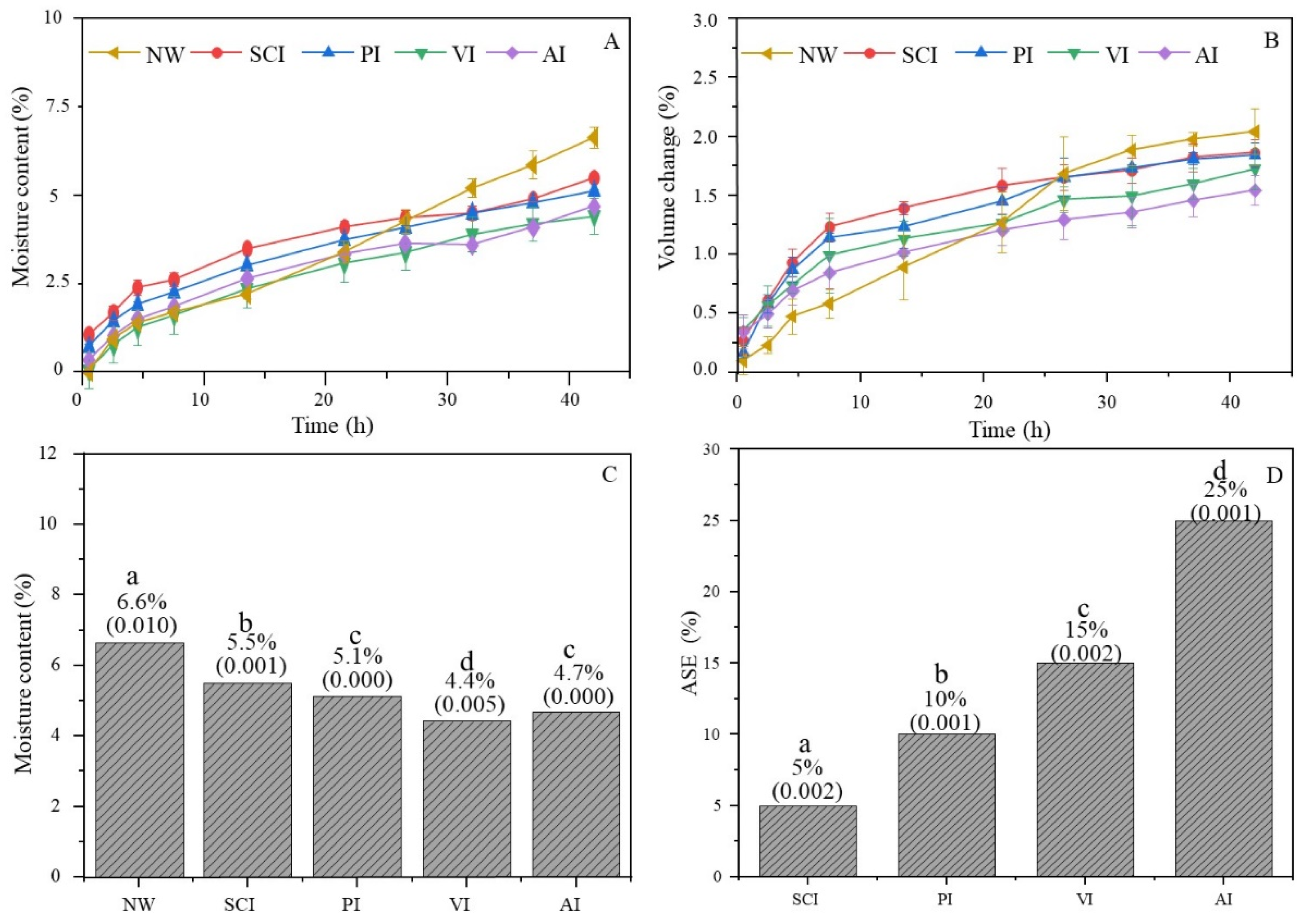
3.2. Moisture Absorption and Dimensional Stability
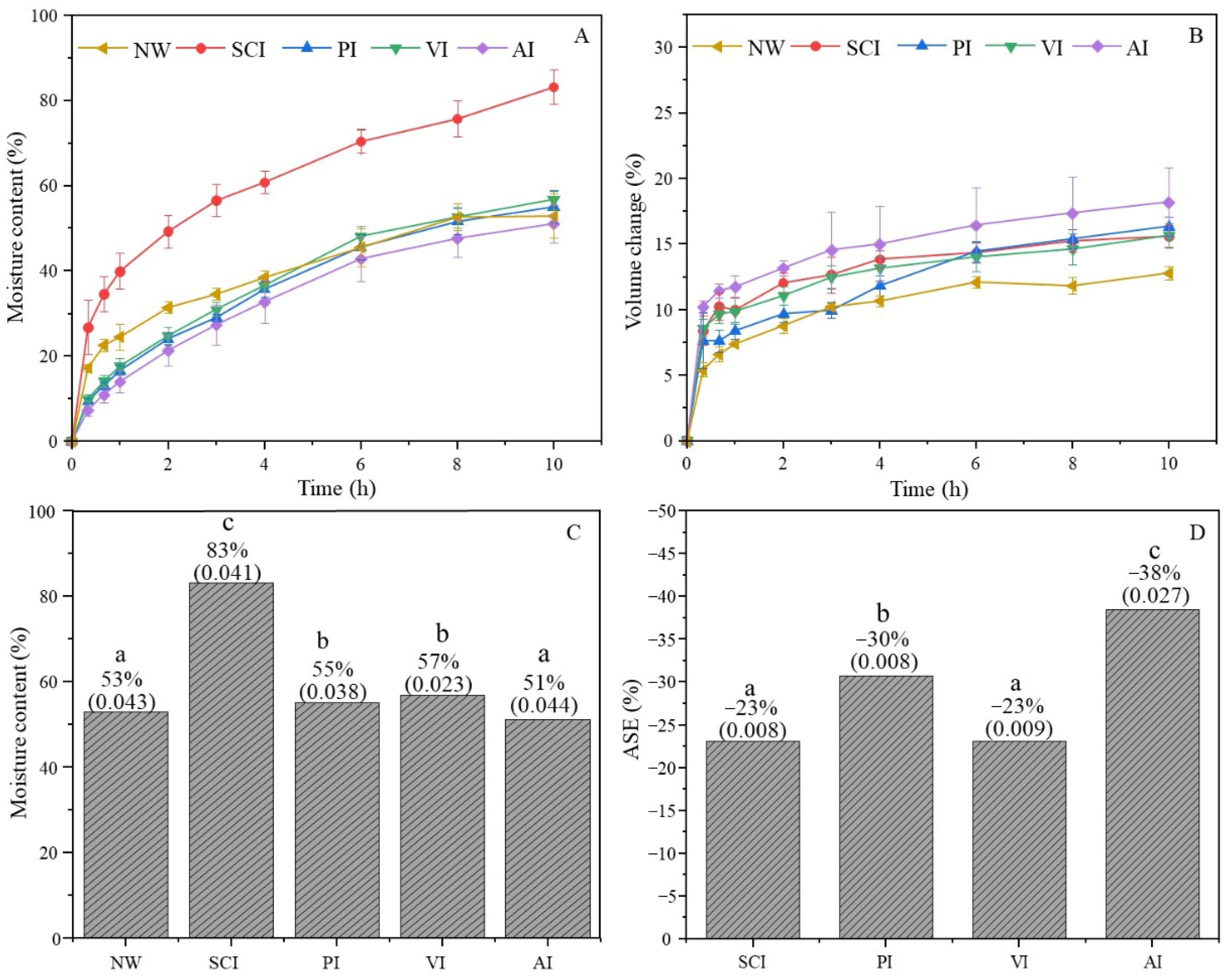
3.3. Water Uptake and Dimensional Stability
3.4. The Effect of Silane Impregnation on the Surface Hardness of Specimens
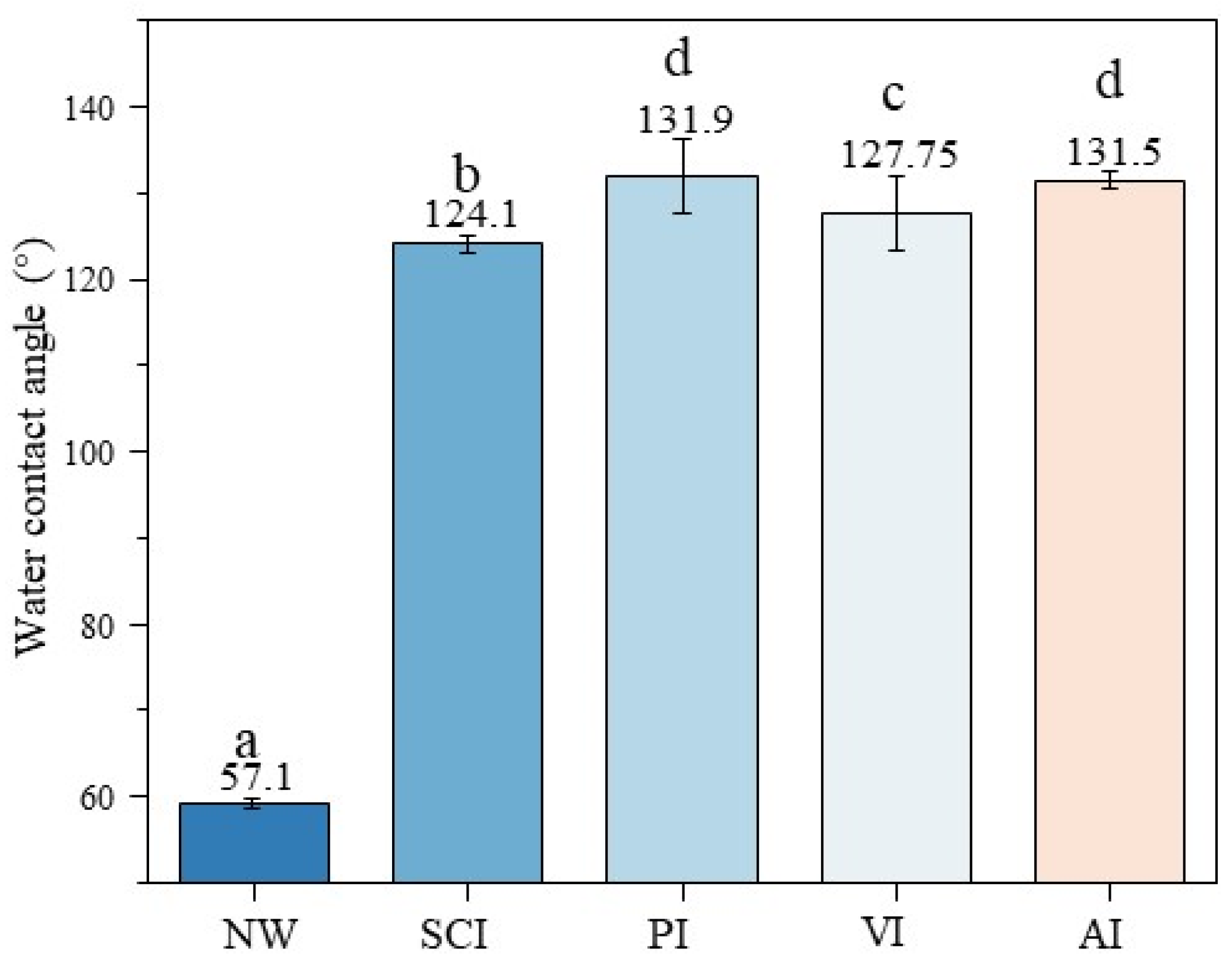
3.5. The Effect of Silane Impregnation on the Water Contact Angle of Specimens
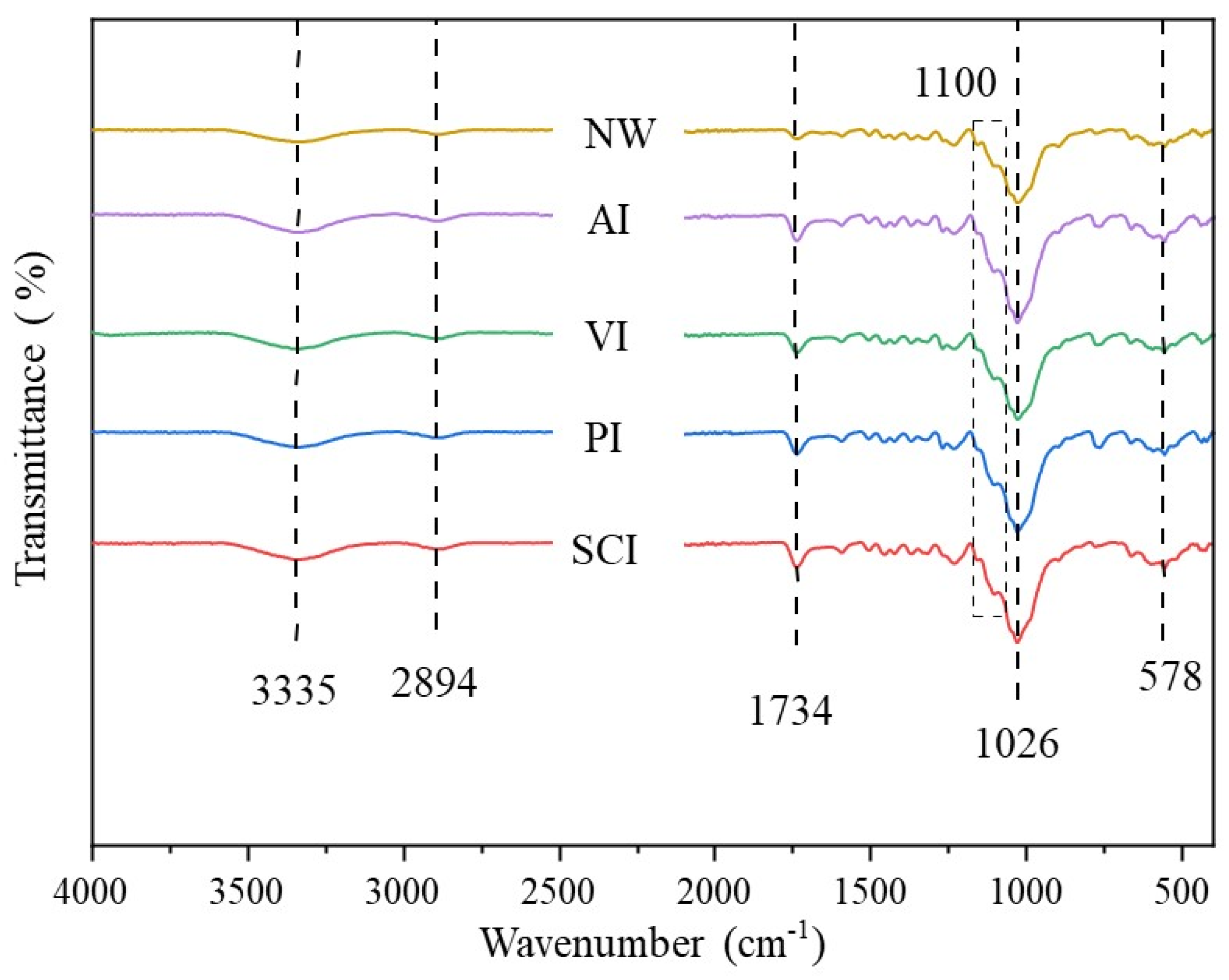
3.6. The Effect of Silane Impregnation on the Chemical Composition of Specimens
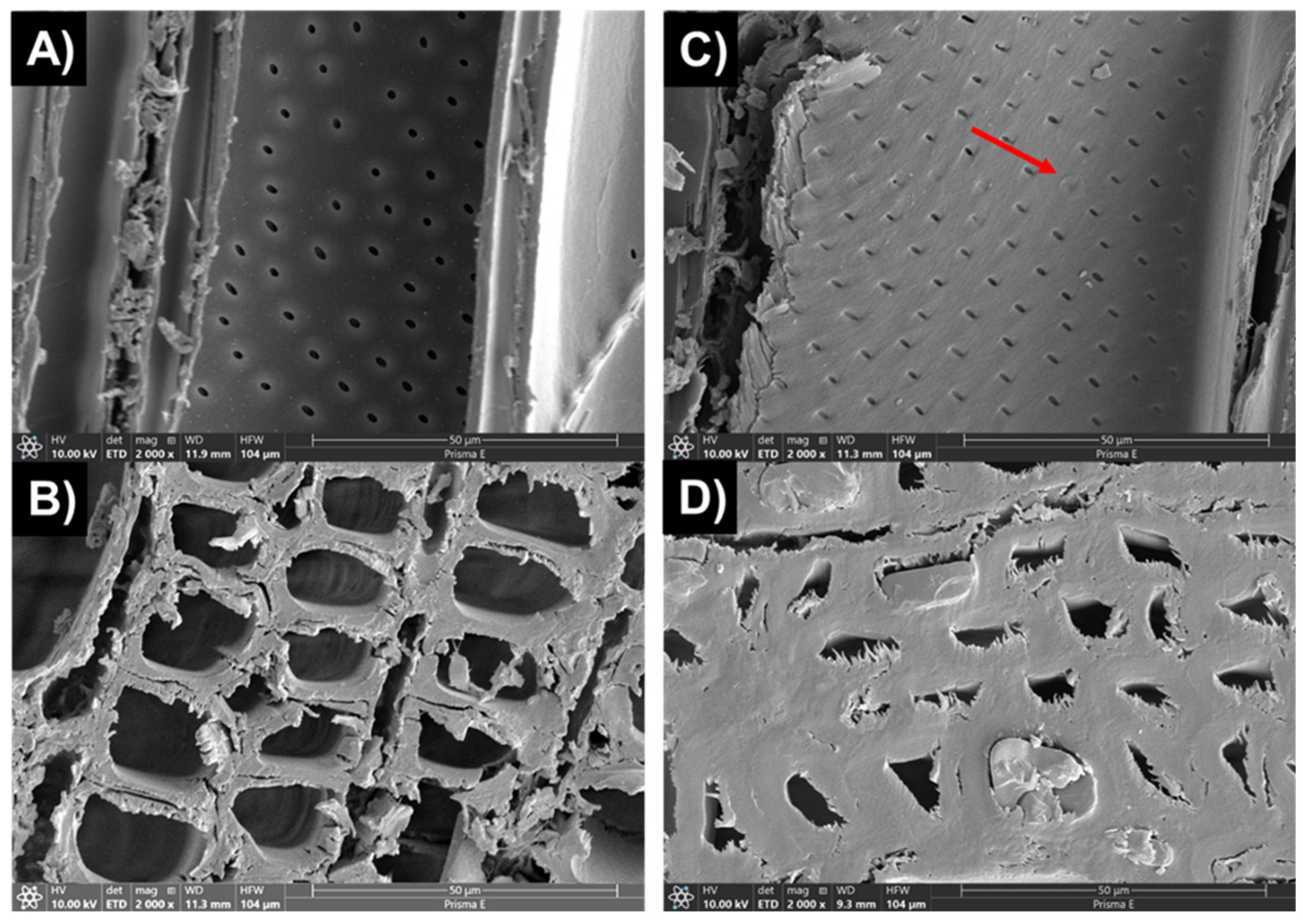
3.7. The Effect of Silane Impregnation on the Microstructure of Specimens
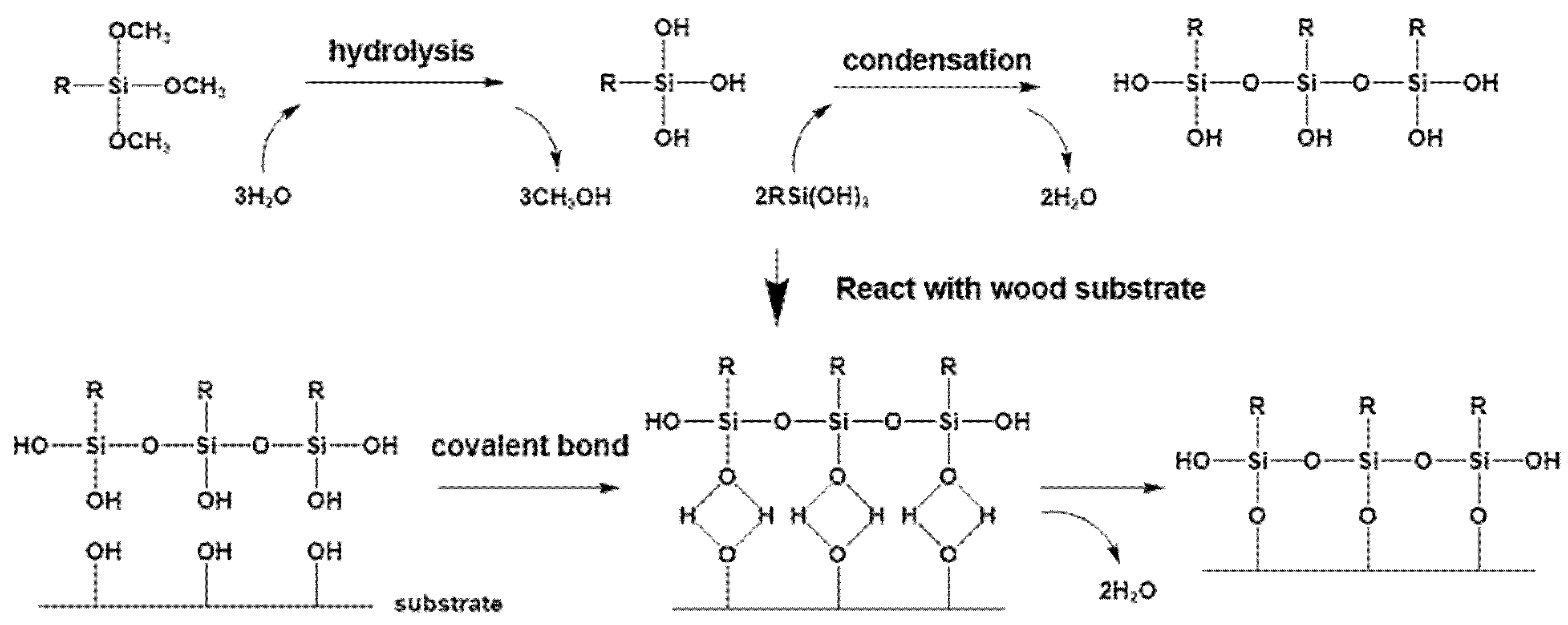
3.8. The Mechanism of Silane Modification on Wood
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yang, L.; Fan, H.; Zheng, J. Effect of Supercritical CO2 Dehydration treatment on the Juglans mandshurica. Wood Res. 2025, 70, 212–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Yang, L. Effect of freezing and freezing-thawing pretreatment on wood properties and drying characteristics of Eucalyptus urophylla × E. grandis. Wood Mater. Sci. Eng. 2024, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Zhao, P.; Yin, Q. Study on The Hydrothermal Treatment of kiln-dried timber of Red Alder. Wood Res. 2025, 70, 224–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, Y.; Zhou, Z.; Xu, R.; Dong, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, M. Effect of NaOH pretreatment on permeability and surface properties of three wood species. ACS Omega 2023, 8, 40362–40374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xue, J.; Xu, W.; Zhou, J.; Mao, W.; Wu, S. Effects of high-temperature heat treatment modification by impregnation on physical and mechanical properties of poplar. Materials 2022, 15, 7334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Li, S.; Han, Y. Effect of pre-freezing treatments on the drying behavior of Eucalyptus platyphylla FV Muell. Drying Technology 2025, 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, N.; Yang, C.; Su, Y.; Lai, C.; Yong, Q. Comparison of effects of carbocation scavengers assisted acid pretreatment on improving enzymatic digestibility of masson pine and poplar. Ind. Crops Prod. 2024, 214, 118603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Xu, W.; Liu, X.; Wang, X. Study on permeability of Cunninghamia lanceolata based on steam treatment and freeze treatment. Wood Res. 2021, 66, 721–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, G.J.; Cho, S.W.; Bandi, R.; Yang, B.S.; Dadigala, R.; Han, S.Y.; Ma, S.Y.; Kim, J.K.; Kim, N.H.; Lee, S.H. Production of lignocellulose nanofibrils by conventional and microwave-assisted deep-eutectic-solvent pretreatments: Mechanical, antioxidant, and UV-blocking properties. Cellulose 2023, 30, 4277–4292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Troter, D.Z.; Todorović, Z.B.; Đokić-Stojanović, D.R.; Stamenković, O.S.; Veljković, V.B. Application of ionic liquids and deep eutectic solvents in biodiesel production: A review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2016, 61, 473–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Yang, L.; Zhou, J.; Yang, F.; Huang, Q.; Cai, Y. Softened wood treated by deep eutectic solvents. ACS Omega 2020, 5, 22163–22170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ran, Y.; Lu, D.; Jiang, J.; Huang, Y.; Wang, W.; Cao, J. Deep eutectic solvents-assisted wood densification: A promising strategy for shape-fixation. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 471, 144476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malaeke, H.; Housaindokht, M.R.; Monhemi, H.; Izadyar, M. Deep eutectic solvent as an efficient molecular liquid for lignin solubilization and wood delignification. J. Mol. Liq. 2018, 263, 193–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Z.; Sun, H.; Zhang, L.; Zhao, X.; Hu, Y. Lightweight, high-strength wood prepared by deep eutectic solvent treatment as a green structural material. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2022, 10, 9600–9611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kroon, M.M.; Francisco Casal, M.M.; Bruinhorst, V.D.A.A. Pretreatment of Lignocellulosic Biomass and Recovery of Substituents Using Natural Deep Eutectic Solvents/Compound Mixtures with Low Transition Temperatures. Patent WO2013153203, 17 October 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Xia, Q.; Chen, C.; Yao, Y.; Li, J.; He, S.; Zhou, Y.; Hu, L. A strong, biodegradable and recyclable lignocellulosic bioplastic. Nat. Sustain. 2021, 4, 627–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamil, M.I.; Ali, A.; Haq, F.; Zhang, Q.; Zhan, X.; Chen, F. Icephobic strategies and materials with superwettability: Design principles and mechanism. Langmuir 2018, 34, 15425–15444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ratajczak, I.; Woźniak, M.; Szentner, K.; Babicka, M.; Jenczyk, J.; Mazela, B. Aminosilane binding to wood substance through an alkyd resin. J. Wood Chem. Technol. 2020, 40, 73–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meints, T.; Hansmann, C.; Gindl-Altmutter, W. Suitability of different variants of polyethylene glycol impregnation for the dimensional stabilization of oak wood. Polymers 2018, 10, 81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donath, S.; Militz, H.; Mai, C. Wood modification with alkoxysilanes. Wood Sci. Technol. 2004, 38, 555–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broda, M.; Mazela, B.; Radka, K. Methyltrimethoxysilane as a stabilising agent for archaeological waterlogged wood differing in the degree of degradation. J. Cult. Herit. 2019, 35, 129–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB/T1933-2009; Method for Determination of the Density of Wood. National Standardization Administration: Beijing, China, 2009.
- GB/T 1931-2009; Method for Determination of the Moisture Content of Wood. National Standardization Administration: Beijing, China, 2009.
- GB/T 1927.19-2021; Test Methods for Physical and Mechanical Properties of Small Clear Wood Specimens—Part 19: Determination of Static Hardness. National Standardization Administration: Beijing, China, 2021.
- Kang, S.M.; Cho, M.W.; Kim, K.M.; Kang, D.Y.; Koo, W.M.; Kim, K.H.; Lee, S.S. Cyproconazole impregnation into wood using sub-and supercritical carbon dioxide. Wood Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 643–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Dang, B.; Luo, X.; Li, W.; Li, J.; Yu, H.; Li, S. Deep eutectic solvent-assisted in situ wood delignification: A promising strategy to enhance the efficiency of wood-based solar steam generation devices. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 26032–26037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabrera-Alvarez, E.N.; Ramos-deValle, L.F.; Sánchez-Valdes, S.; Candia-García, A.; Soriano-Corral, F.; Ramírez-Vargas, E.; Patiño-Soto, P. Study of the silane modification of magnesium hydroxide and their effects on the flame retardant and tensile properties of high density polyethylene nanocomposites. Polym. Compos. 2014, 35, 1060–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schorr, D.; Blanchet, P. Improvement of white spruce wood dimensional stability by organosilanes sol-gel imregnation and heat treatment. Materials 2020, 13, 973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, J.; Xu, X.; Yang, L. Dewatering characteristics of Juglans mandshurica wood using supercritical carbon dioxide: A comparison with conventional drying. Dry. Technol. 2024, 42, 926–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hafezi, S.M.; Doosthoseini, K. The influence of silane coupling agent and poplar particles on the wettability, surface roughness, and hardness of UF-bonded wheat straw (Triticum aestivum L.)/poplar wood particleboard. J. For. Res. 2014, 25, 667–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, G.H.; Chen, R.Y. Anatomical structure and contact angle of Dalbergia latifolia wood. For. Eng. 2023, 39, 85–91. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Liu, M.L.; Zhao, X.F.; Ren, W.B.; Wang, X.W.; Xu, G.F. Modification of Fast-growing Poplar by Ethyl Orthosilicate-KH-570 Composite Impregnation. J. Beihua Univ. (Nat. Sci.) 2020, 21, 416. [Google Scholar]
- Popescu, C.M.; Broda, M. Interactions between different organosilicons and archaeological waterlogged wood evaluated by infrared spectroscopy. Forests 2021, 12, 268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Mao, H.; Wang, C.; Fu, S. Dispersibility and hydrophobicity analysis of titanium dioxide nanoparticles grafted with silane coupling agent. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2011, 50, 11930–11934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parr, L.M.; Finzel, W.A. Water borne silicone alkyds and acrylics. J. Water Borne Coat. 1979, 2, 26–39. [Google Scholar]
- Gogoi, R.; Tyagi, A.K. Surface modification of jute fabric by treating with silane coupling agent for reducing its moisture regain characteristics. J. Nat. Fibers 2021, 18, 803–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meekum, U.; Khongrit, A. Toughening of wood-plastic composites based on silane/peroxide macro crosslink poly (propylene) systems. BioResources 2018, 13, 1678–1695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fathi, B.; Harirforoush, M.; Foruzanmehr, M.; Elkoun, S.; Robert, M. Effect of TEMPO oxidation of flax fibers on the grafting efficiency of silane coupling agents. J. Mater. Sci. 2017, 52, 10624–10636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouyang, L.; Huang, Y.; Cao, J. Hygroscopicity and characterization of wood fibers modified by alkoxysilanes with different chain lengths. BioResources 2014, 9, 7222–7233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
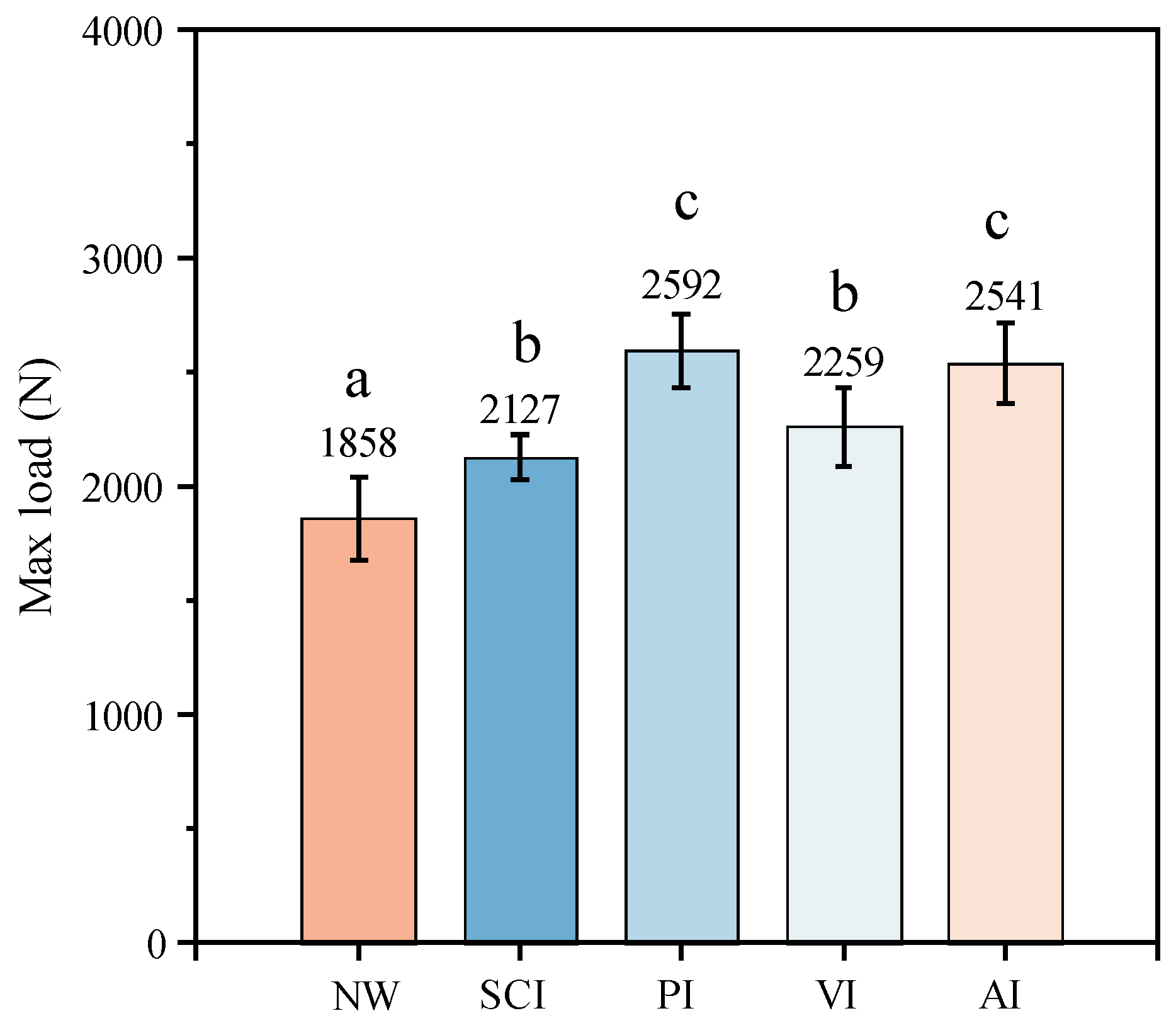
| Groups | Code | DES Pretreatment | Silane Impregnation | Impregnation Conditions |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | NW | No | No | No |
| 1 | SCI | Yes | Supercritical CO2 | 10 MPa/25 °C/4 h |
| 2 | PI | Yes | Pressure | 2.5 MPa/25 °C/4 h |
| 3 | VI | Yes | Vacuum | −0.1 MPa/25 °C/4 h |
| 4 | AI | Yes | Atmospheric | 0.1 MPa/25 °C/4 h |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zheng, Y.; Zhou, T.; Cai, C.; Liu, H. Enhancement of Dimensional Stability, Hydrophobicity, and Mechanical Strength of North American Red Alder Wood Through Silane Impregnation Combined with DES Pretreatment. Forests 2025, 16, 1152. https://doi.org/10.3390/f16071152
Zheng Y, Zhou T, Cai C, Liu H. Enhancement of Dimensional Stability, Hydrophobicity, and Mechanical Strength of North American Red Alder Wood Through Silane Impregnation Combined with DES Pretreatment. Forests. 2025; 16(7):1152. https://doi.org/10.3390/f16071152
Chicago/Turabian StyleZheng, Yang, Ting Zhou, Chenyang Cai, and Honghai Liu. 2025. "Enhancement of Dimensional Stability, Hydrophobicity, and Mechanical Strength of North American Red Alder Wood Through Silane Impregnation Combined with DES Pretreatment" Forests 16, no. 7: 1152. https://doi.org/10.3390/f16071152
APA StyleZheng, Y., Zhou, T., Cai, C., & Liu, H. (2025). Enhancement of Dimensional Stability, Hydrophobicity, and Mechanical Strength of North American Red Alder Wood Through Silane Impregnation Combined with DES Pretreatment. Forests, 16(7), 1152. https://doi.org/10.3390/f16071152






