Urea Fertilization Buffered Acid-Inhibiting Effect on Litter Decomposition in Subtropical Plantation Forests of Southern China
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Site Description and Litter Collection
2.2. Experimental Design
2.3. Measurements of H+ Content, Mass Loss, Water Content and Fungal Biomass
2.4. Determination of Microbial Respiration and C-Cycling Extracellular Enzyme Activity
2.5. Statistical Analyses
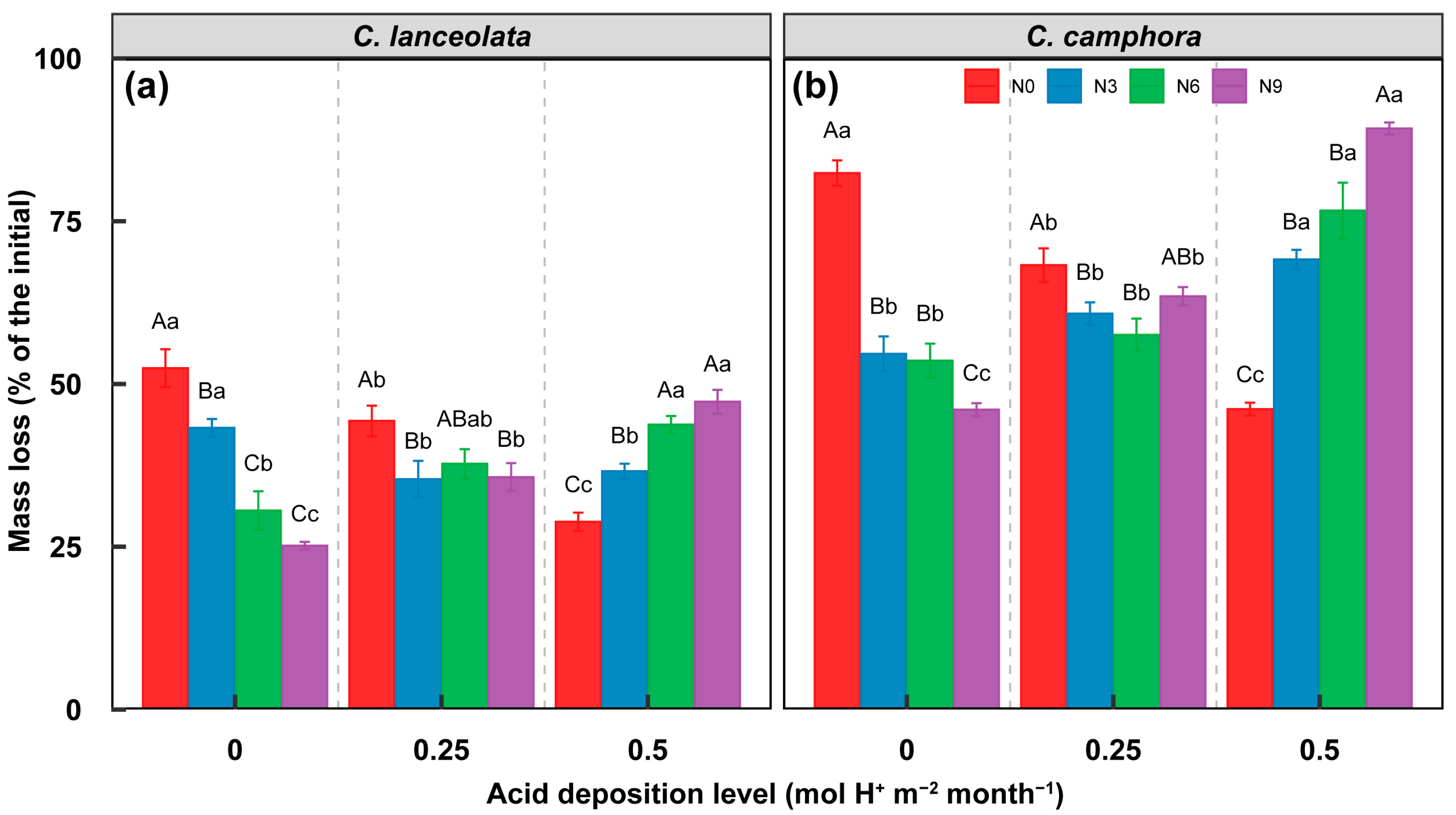
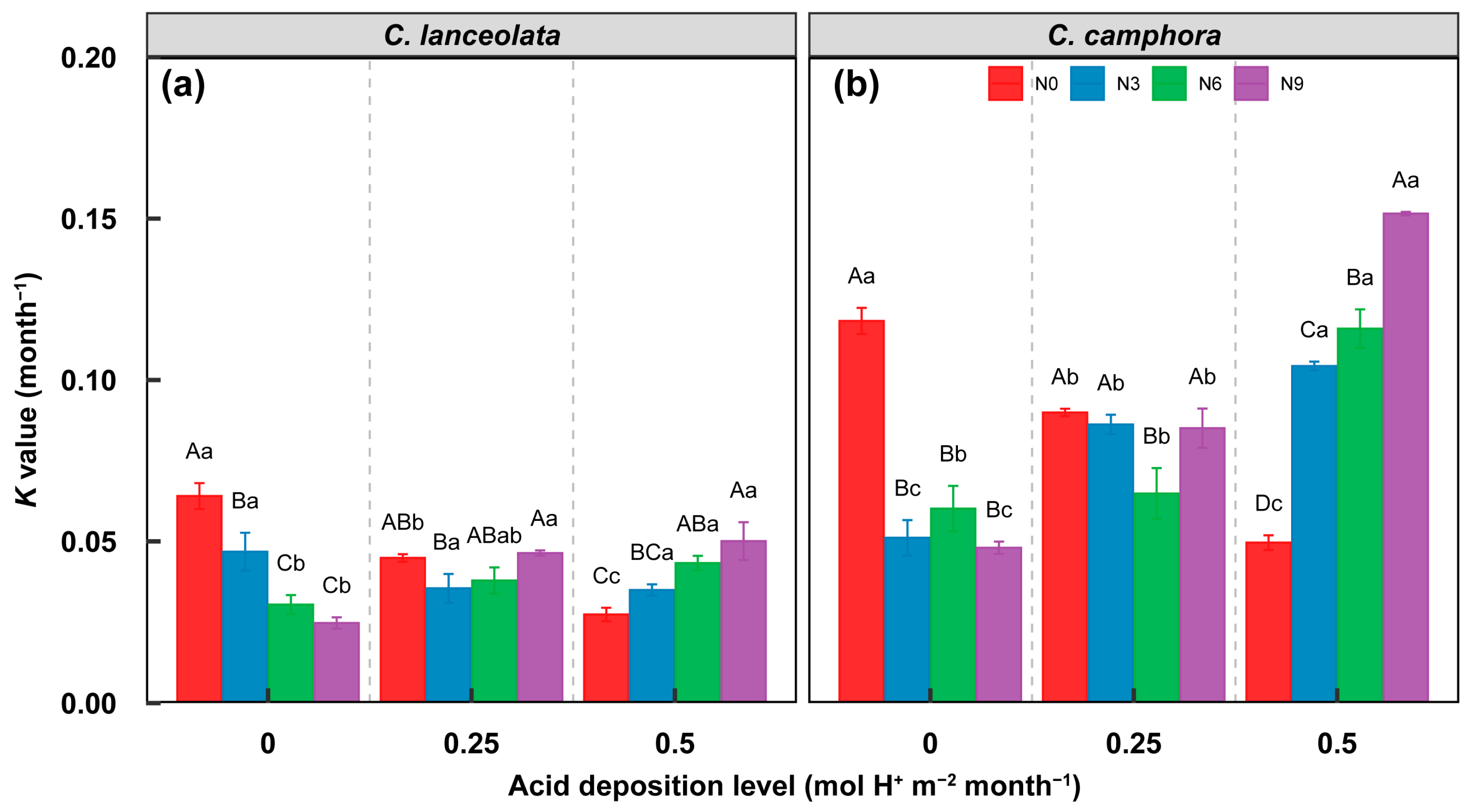
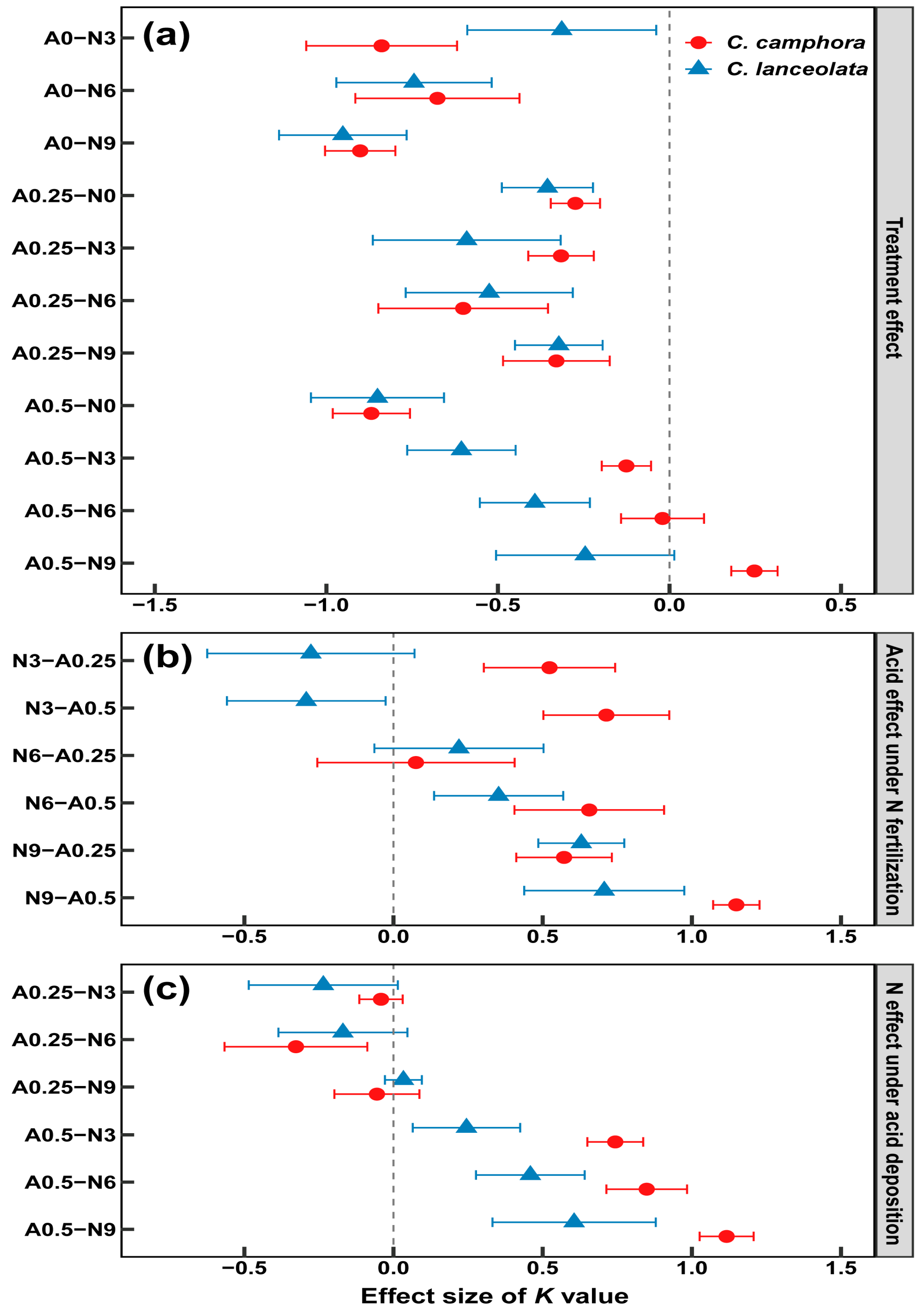
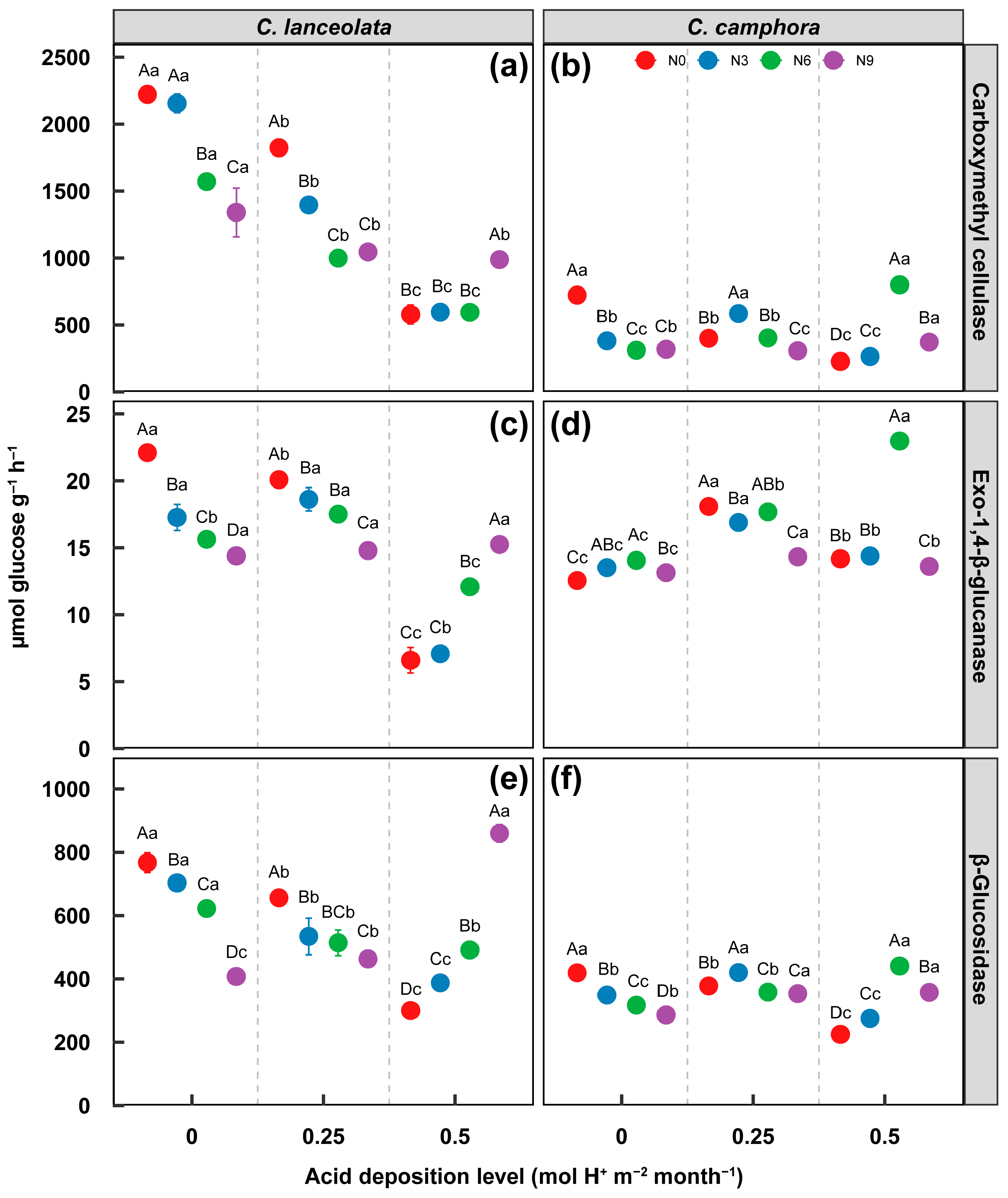
3. Results
3.1. Effect on Litter Decomposition
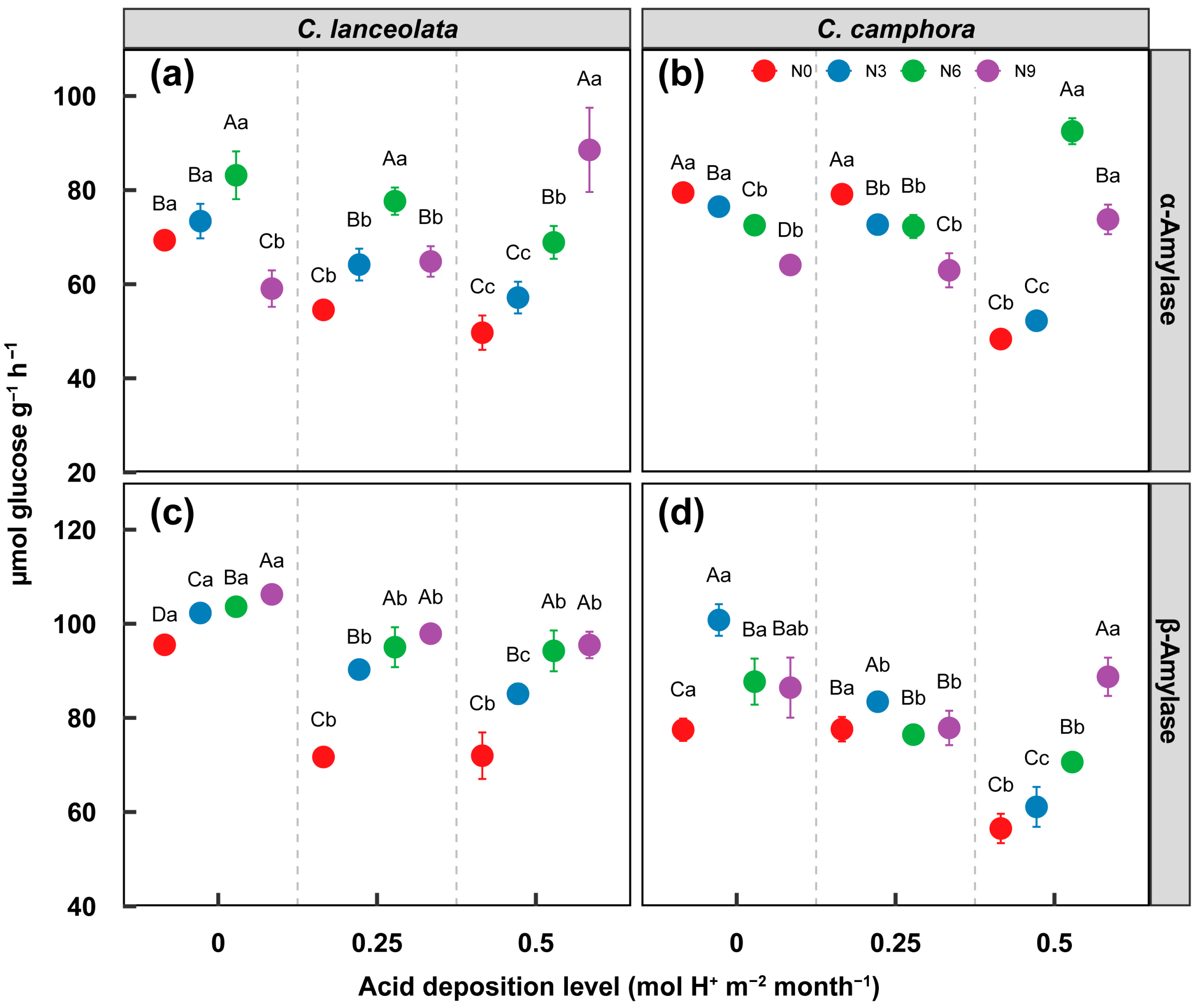
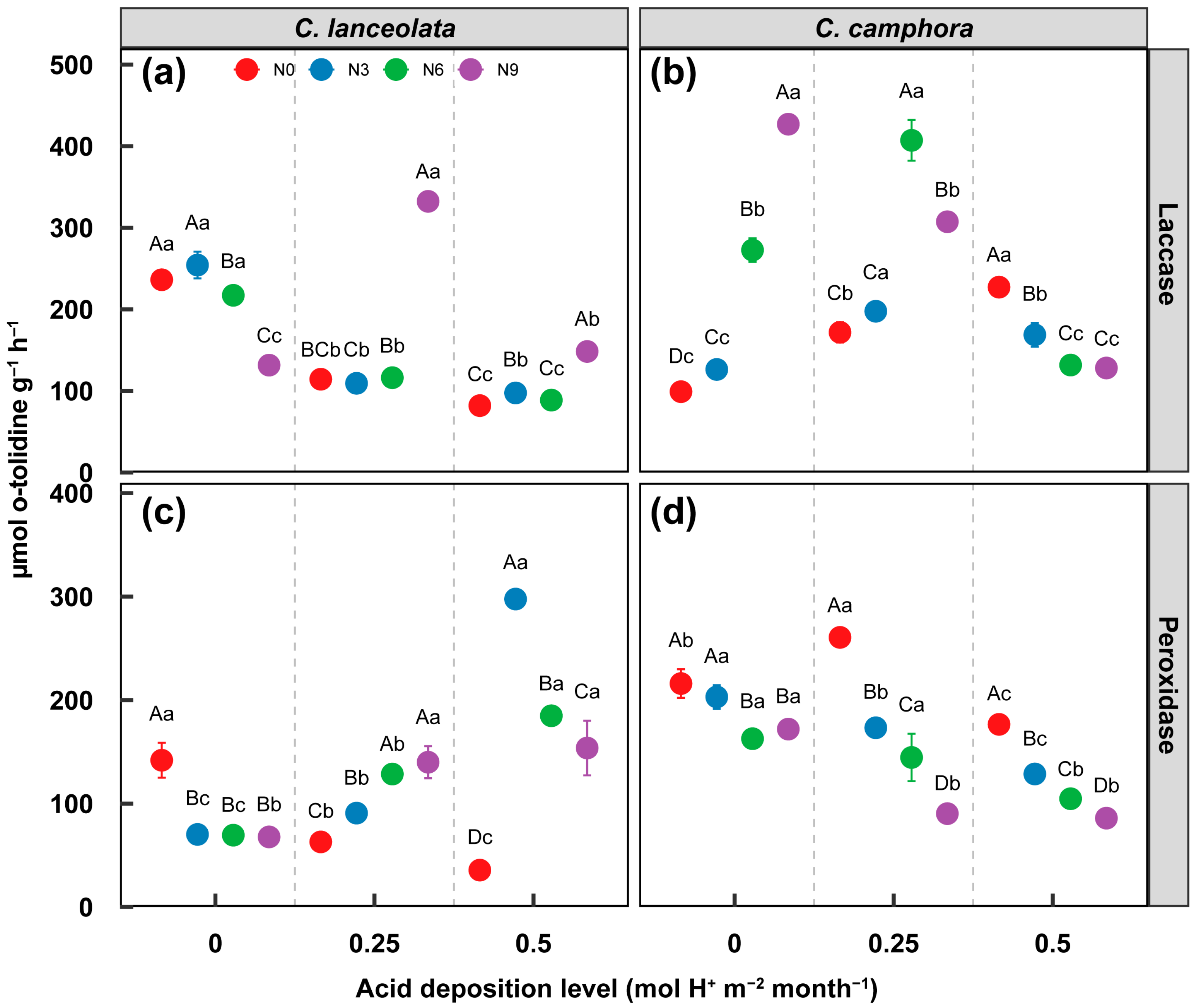
3.2. Effect on Labile and Recalcitrant C Decomposition Enzyme Activity
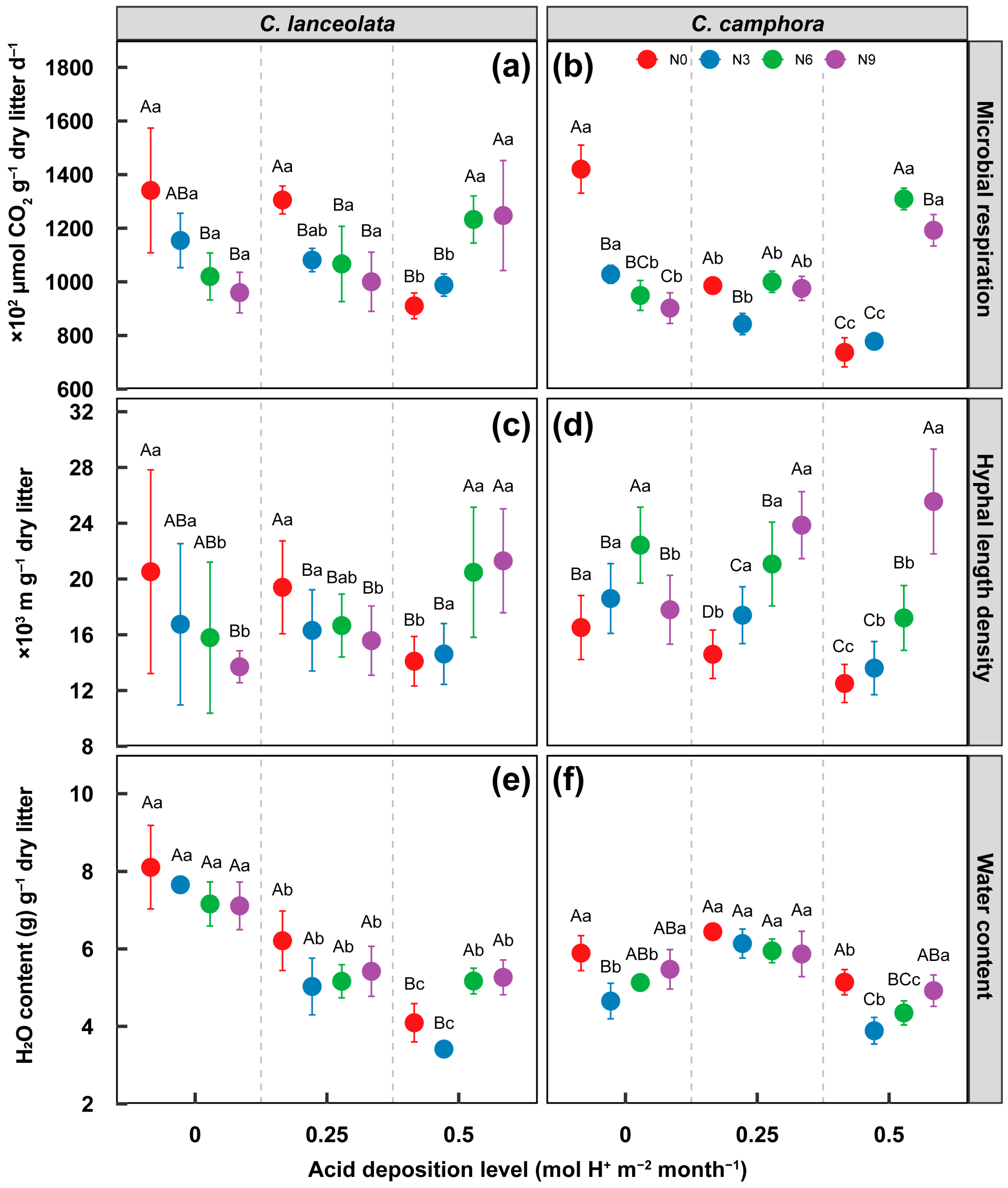
3.3. Effect on Microbial Respiration, Fungal Biomass and Water Content
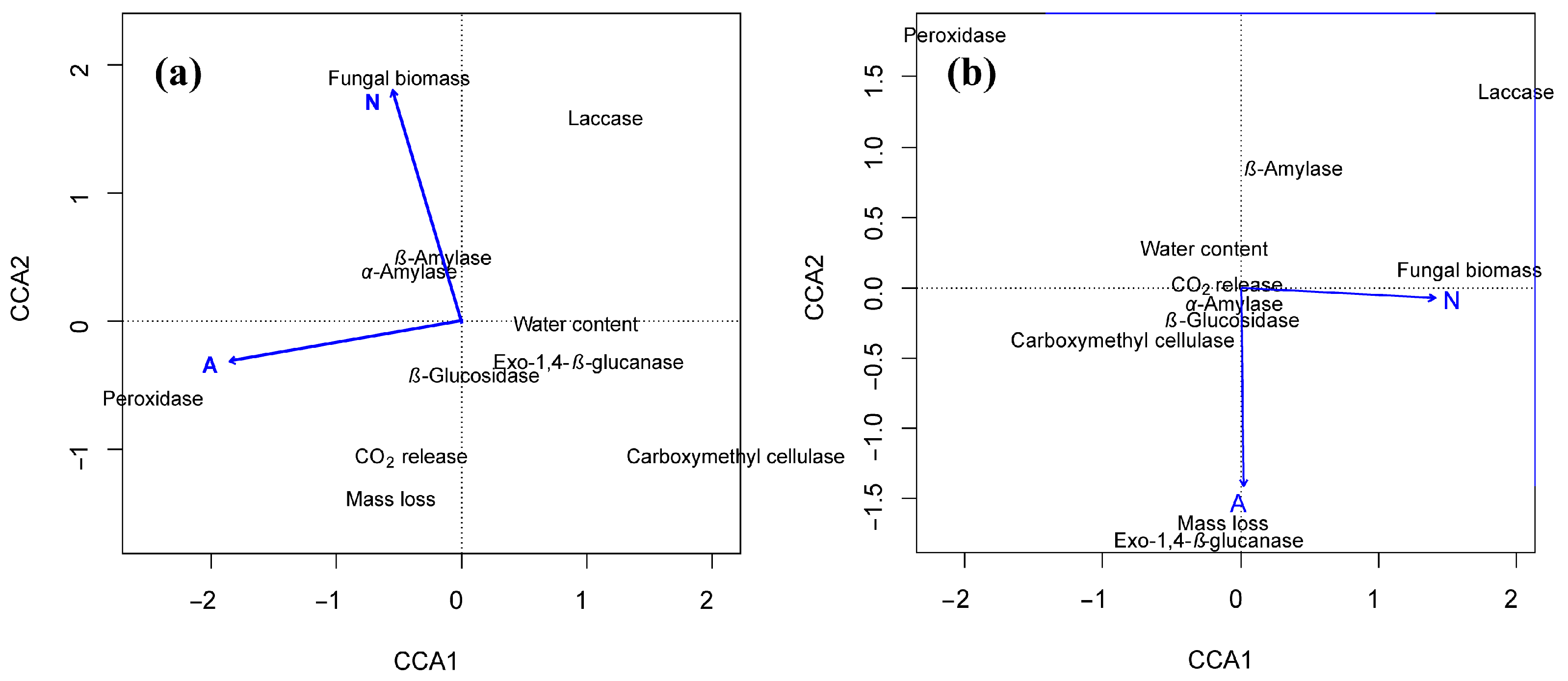
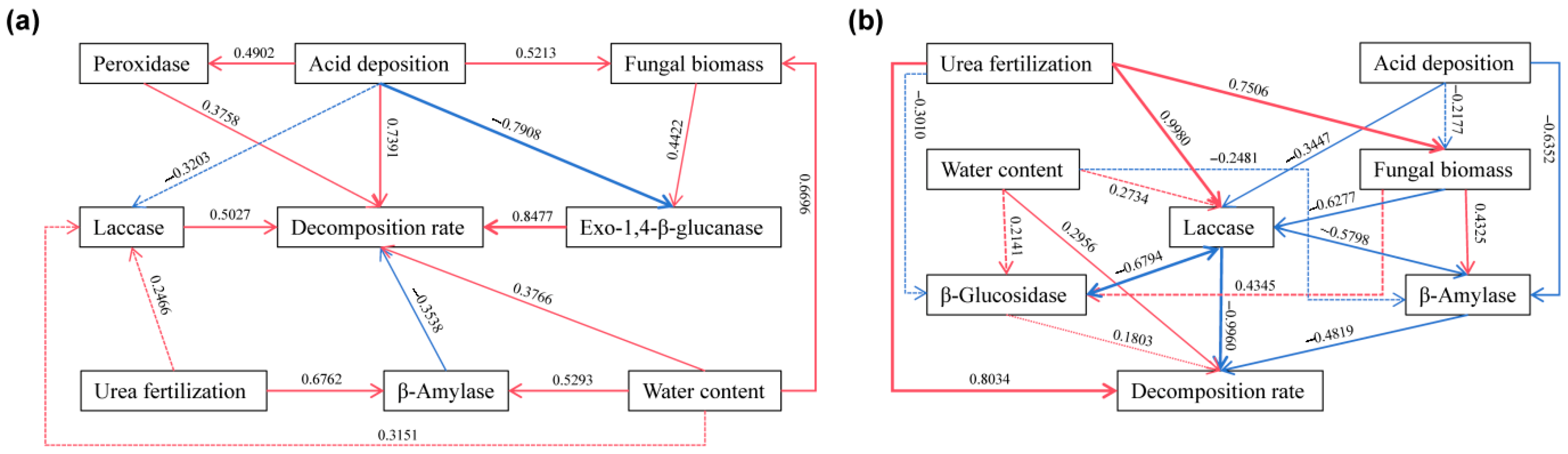
3.4. Relationship of Decomposition Function to Acid Deposition and N Fertilization
4. Discussion
4.1. Acid Deposition Response
4.2. N Fertilization Altered the Acid Deposition Response
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Aas, E.R.; Althuizen, I.; Tang, H.; Geange, S.; Lieungh, E.; Vandvik, V.; Berntsen, T.K. Implications of climate and litter quality for simulations of litterbag decomposition at high latitudes. Biogeosciences 2024, 21, 3789–3817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Bortolli, M.A.; Assmann, T.S.; de Bortolli, B.B.; Macari, M.; Bernardon, A.; Jamhour, J.; Franzluebbers, A.J.; Soares, A.B.; Severo, I.K. Nutrient dynamics in integrated crop-livestock systems: Effects of stocking rates and nitrogen system fertilization on litter decomposition and release. Agronomy 2024, 14, 2009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Shen, X.; Hu, Z.; Chen, H.; Shi, Y.; Liu, Y. Effects of simulated acid rain on soil CO2 emission in a secondary forest in subtropical China. Geoderma 2012, 189–190, 65–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, T.; Liang, X.; Guo, T.; Wu, T.; Chai, B. Bacterial community succession and influencing factors for Imperata cylindrica litter decomposition in a copper tailings area of China. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 815, 152908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Röder, J.; Appelhans, T.; Peters, M.K.; Nauss, T.; Brandl, R. Disturbance can slow down litter decomposition, depending on severity of disturbance and season: An example from Mount Kilimanjaro. Web Ecol. 2024, 21, 11–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keeler, B.L.; Hobbie, S.E.; Kellogg, L.E. Effects of long-term nitrogen addition on microbial enzyme activity in eight forested and grassland sites: Implications for litter and soil organic matter decomposition. Ecosystems 2009, 12, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Itahashi, S.; Ge, B.; Sato, K.; Fu, J.S.; Wang, X.; Yamaji, K.; Nagashima, T.; Li, J.; Kajino, M.; Liao, H.; et al. MICS-Asia III: Overview of model intercomparison and evaluation of acid deposition over Asia. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2020, 20, 2667–2693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, X. Assessment of the maximum allowed acid deposition load at current stage in China. J. Environ. Sci. 2017, 56, 140–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; He, N.; Wang, Q.; Zhu, J.; Gao, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Jia, Y.; Yu, G. Development of atmospheric acid deposition in China from the 1990s to the 2010s. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 231, 182–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Zhou, J.; Li, W.; Xu, J.; Brookes, P.C. The combined effects of urea application and simulated acid rain on soil acidification and microbial community structure. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2014, 21, 6623–6631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, Q.; Wu, J.; Liang, G.; Liu, J.; Chu, G.; Zhou, G.; Zhang, D. Effects of simulated acid rain on soil and soil solution chemistry in a monsoon evergreen broad-leaved forest in southern China. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2015, 187, 272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bouray, M.; Moir, J.L.; Lehto, N.J.; Condron, L.M.; Touhami, D.; Hummel, C. Soil pH effects on phosphorus mobilization in the rhizosphere of Lupinus angustifolius. Plant Soil 2021, 469, 387–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lieb, A.M.; Darrouzet-Nardi, A.; Bowman, W.D. Nitrogen deposition decreases acid buffering capacity of alpine soils in the southern Rocky Mountains. Geoderma 2011, 164, 220–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, J.; Luo, Y.; Tao, Q.; White, P.J.; Sun, G.; Li, M.; Luo, J.; He, Y.; Li, B.; Li, Q.; et al. The exacerbation of soil acidification correlates with structural and functional succession of the soil microbiome upon agricultural intensification. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 828, 154524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujii, K. Soil acidification and adaptations of plants and microorganisms in Bornean tropical forests. Ecol. Res. 2014, 29, 371–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Wei, H.; Zhang, J.; Saleem, M.; He, Y.; Zhong, J.; Ma, R. Seasonality regulates the effects of acid rain on microbial community in a subtropical agricultural soil of Southern China. Ecotox. Environ. Saf. 2021, 224, 112681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, Y.; Wang, C.; Jia, Y.; Wang, W.; Ma, X.; Du, J.; Pu, G.; Tian, X. Effects of sulfuric, nitric, and mixed acid rain on litter decomposition, soil microbial biomass, and enzyme activities in subtropical forests of China. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2014, 79, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, G.; Liu, X.; Chen, X.; Qiu, Q.; Zhang, D.; Chu, G.; Liu, J.; Liu, S.; Zhou, G. Response of soil respiration to acid rain in forests of different maturity in southern China. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e62207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bewley, R.J.F.; Stotzky, G. Simulated acid rain (H2SO4) and microbial activity in soil. Soil Biol. Biochem. 1983, 15, 425–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanhala, P.; Fritze, H.; Neuvonen, S. Prolonged simulated acid rain treatment in the subarctic: Effect on the soil respiration rate and microbial biomass. Biol. Fert. Soils 1996, 23, 7–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheu, S.; Wolters, V. Buffering of the effect of acid rain on decomposition of 14C-labelled beech leaf litter by saprophagous invertebrates. Biol. Fert. Soils 1991, 11, 285–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cha, S.; Lim, S.M.; Amirasheba, B.; Shim, J.K. The effect of simulated acid rain on microbial community structure in decomposing leaf litter. J. Ecol. Environ. 2013, 36, 223–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, X.; Zhou, G.; Gu, H.; Qi, L. Management practices amplify the effects of N deposition on leaf litter decomposition of the Moso bamboo forest. Plant Soil 2015, 395, 391–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Zhang, W.; Sun, T.; Chen, L.; Pang, X.; Wang, Y.; Xiao, F. N and P fertilization reduced soil autotrophic and heterotrophic respiration in a young Cunninghamia lanceolata forest. Agric. Forest Meteorol. 2017, 232, 66–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mo, J.M.; Li, D.J.; Gudersen, P. Seedling growth response of two tropical tree species to nitrogen deposition in sourthern China. Eur. J. Forest Res. 2008, 127, 275–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alster, C.J.; German, D.P.; Lu, Y.; Allison, S.D. Microbial enzymatic responses to drought and to nitrogen addition in a southern California grassland. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2013, 64, 68–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, H.; You, C.; Gao, J. Effects of fertilization on litter decomposition dynamics and nutrient release in orchard systems. Front. Plant Sci. 2024, 15, 1467689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keyhani, A.B.; He, W.; Teng, M.; Yan, Z.; Ma, Z.; Xu, J.; Fayaz, M.; Zhou, C.; Wei, P.; Wang, P. Effect of mineral fertilizers on microorganisms community characteristic during leaf litter decomposition under Pinus massoniana in a subtropical forest. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2024, 199, 105421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allison, S.D.; Lu, Y.; Weihe, C.; Goulden, M.L.; Martiny, A.C.; Treseder, K.K.; Martiny, J.B.H. Microbial abundance and composition influence litter decomposition response to environmental change. Ecology 2013, 94, 714–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, L.; Berg, B.; Gu, W.; Wang, Z.; Sun, T. Effects of different forms of nitrogen addition on microbial extracellular enzyme activity in temperate grassland soil. Ecol. Process. 2022, 11, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ling, J.; Dungait, J.A.J.; Delgado-Baquerizo, M.; Cui, Z.; Zhou, R.; Zhang, W.; Gao, Q.; Chen, Y.; Yue, S.; Kuzyakov, Y.; et al. Soil organic carbon thresholds control fertilizer effects on carbon accrual in croplands worldwide. Nat. Commun. 2025, 16, 3009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.B.; Han, G.M.; Lin, Y.H.; Tian, X.J.; Xiang, C.G.; Tian, Q.J.; Wang, F.Y.; He, Z.H. Diversity and decomposition potential of endophytes in leaves of a Cinnamomum camphora plantation in China. Ecol. Res. 2012, 27, 273–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olson, F.C.W. Quantitative estimates of coniferous forests. Trans. Am. Microsc. Soc. 1950, 69, 272–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papa, S.; Pellegrino, A.; Fioretto, A. Microbial activity and quality changes during decomposition of Quercus ilex leaf litter in three Mediterranean woods. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2008, 40, 401–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, G.L. Use of dinitrosalicylic acid reagent for determination of reducing sugar. Anal. Chem. 1959, 31, 426–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fioretto, A.; Papa, S.; Curcio, E.; Sorrentino, G.; Fuggi, A. Enzyme dynamics on decomposing leaf litter of Cistus incanus and Myrtus communis in a Mediterranean ecosystem. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2000, 32, 1847–1855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dilly, O.; Munch, J.C. Litter decomposition and microbial characteristics in agricultural soil in Northern, Central, and Southern Germany. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 2004, 50, 843–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Guo, P.; Han, G.; Feng, X.; Zhang, P.; Tian, X. Effect of simulated acid rain on the litter decomposition of Quercus acutissima and Pinus massoniana in forest soil microcosms and the relationship with soil enzyme activities. Sci. Total Environ. 2010, 408, 2706–2713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, L.; Lin, Y.; He, X.; Han, G. Acid rain decelerates the decomposition of Cunninghamia lanceolata needle and Cinnamomum camphora leaf litters in a karst region in China. Ecol. Res. 2019, 34, 193–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, X.; Zhu, L.; Xu, G.; Zhang, J.; Xu, J.; Yu, S.; Chen, X. Effects of acid deposition on the avoidance behavior of Folsomia candida (Collembola, Isotomidae). Soil Ecol. Lett. 2022, 4, 164–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Recuss, J.O.; Cosbyt, B.J.; Wright, R.F. Chemical processes governing soil and water acidification. Nature 1987, 329, 27–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, H.; Ma, R.; Zhang, J.; Zhou, L.; Liu, Z.; Fan, Z.; Yang, J.; Shan, X.; Xiang, H. Quality dependence of litter decomposition and its carbon, nitrogen and phosphorus release under simulated acid rain treatments. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 19858–19868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, H.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, J.; Li, S.; Zhong, X.; Xiang, H. Leaching of simulated acid rain deteriorates soil physiochemical and mechanical properties in three agricultural soils. Catena 2021, 206, 105485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, L.; Lin, Y.H.; He, X.B. The patterns of responses of litter decomposition of Cunninghamia needles and Cinnamomum leaves to substrate acidolysis. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2017, 37, 6038–6052. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, W. Impact of simulated acid rain on the composition of soil microbial communities and soil respiration in typical subtropical forests in Southwest China. Ecotox. Environ. Safe. 2021, 215, 112512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Shi, Z.; Wei, H.; Zhang, J. Acid rain reduces soil CO2 emission and promotes soil organic carbon accumulation in association with decreasing the biomass and biological activity of ecosystems: A meta-analysis. Catena 2022, 208, 105714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, N.; Qian, S.; Pan, X.; Chen, Y.; Bai, S.; Xu, F. Effects of simulated acid rain and nitrogen deposition on soil bacterial community structure and diversity in the masson pine forest. Environ. Sci. 2023, 44, 2315–2324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Sun, L.; Zhang, X.; Shen, X.; Liu, Y.; Ren, J. Contrasting effects of long-term acid rain simulation on temperature sensitivity of soil respiration and enzymatic activities in a subtropical forest. J. Soils Sediments 2020, 20, 412–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Liang, G.; Hui, D.; Deng, Q.; Xiong, X.; Qiu, Q.; Liu, J.; Chu, G.; Zhou, G.; Zhang, D. Prolonged acid rain facilitates soil organic carbon accumulation in a mature forest in Southern China. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 544, 94–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Zhang, B.; Zhao, W.; Wang, L.; Xie, D.; Hou, W.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, J. Comparative effects of sulfuric and nitric acid rain on litter decomposition and soil microbial community in subtropical plantation of Yangtze River Delta region. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 601–602, 669–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jenkins, G.B.; Woodward, G.; Hildrew, A. Long-term amelioration of acidity accelerates decomposition in headwater streams. Glob. Change Biol. 2013, 19, 1100–1106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, G.; Hui, D.; Wu, X.; Wu, J.; Liu, J.; Zhou, G.; Zhang, D. Effects of simulated acid rain on soil respiration and its components in a subtropical mixed conifer and broadleaf forest in southern China. Environ. Sci. Process. Impacts 2016, 18, 246–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zheng, Y.; Li, Y. Effects of simulated acid eain on soil enzyme activity and related chemical indexes in woodlands. Forests 2022, 13, 860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Xiong, X.; Hui, D.; Zhang, H.; Li, J.; Chang, Z.; Zhang, S.; Su, Y.; Li, X.; Zhang, D.; et al. Soil aggregate size distribution mediates microbial responses to prolonged acid deposition in a subtropical forest in south China. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2024, 198, 109544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falappi, D.; Farini, A.; Ranalli, G.; Sorlini, C. Effects of simulated acid rain on some microbiological parameters of subacid soil. Chemosphere 1994, 28, 1087–1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Bian, H.; Quan, Q.; Xu, L.; Chen, Z.; He, N. Effect of nitrogen and acid deposition on soil respiration in a temperate forest in China. Geoderma 2018, 329, 82–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Růžek, M.; Tahovská, K.; Guggenberger, G.; Oulehle, F. Litter decomposition in European coniferous and broadleaf forests under experimentally elevated acidity and nitrogen addition. Plant Soil 2021, 463, 471–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, S.; Wang, G.G.; Tang, C.; Fang, H.; Duan, J.; Yu, X. Effects of one-year simulated nitrogen and acid deposition on soil respiration in a subtropical plantation in China. Forests 2020, 11, 235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, X.; Chen, J.; Liao, X.; Liu, J.; Wang, D.; Li, J.; Yan, Q. Ecological stoichiometry of Cinnamomum migao leaf litter and soil nutrients under nitrogen deposition in a karst region. Ecosphere 2021, 12, e03738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, M.K.; Ma, S.Q.; Xiong, Y.Y.; Wu, Y.Q.; Wu, S.Q.; Qian, J.Y.; Chen, Y.C.; Cai, Y.J. Impact of litter decomposition driven by nitrogen deposition on the soil organic carbon fractions in a Moso bamboo forest. Chin. J. Appl. Ecol. 2024, 35, 2983–2991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Long, X.; Liao, Y.; Lin, Y.; He, Z.; Kong, Q.; Kong, X.; He, X. Influence of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi on nitrogen dynamics during Cinnamomum camphora litter decomposition. Microorganisms 2025, 13, 151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eisa, M.; Brondi, M.; Williams, C.; Hejl, R.; Baltrusaitis, J. From urea to urea cocrystals: A critical view of conventional and emerging nitrogenous fertilizer materials for improved environmental sustainability. Sustain. Chem. Environ. 2025, 9, 100209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matulich, K.L.; Martiny, J.B.H. Microbial composition alters the response of litter decomposition to environmental change. Ecology 2015, 96, 154–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ping, Q.; Xu, S.; He, X.; Sun, S. Nitrogen addition alters litter chemical traits to regulate decomposition: A meta-analysis. Sci. Total Environ. 2025, 983, 179705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ayres, E.; Steltzer, H.; Simmons, B.L.; Simpson, R.T.; Steinweg, J.M.; Wallenstein, M.D.; Mellor, N.; Parton, W.J.; Moore, J.C.; Wall, D.H. Home-field advantage accelerates leaf litter decomposition in forests. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2009, 41, 606–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, H.; He, Z.; Hao, J.; Tian, K.; Jia, X.; Kong, X.; Akbar, S.; Bei, Z.; Tian, X. Effect of N addition on home-field advantage of litter decomposition in subtropical forests. For. Ecol. Manag. 2017, 398, 216–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gill, A.L.; Adler, P.B.; Borer, E.T.; Buyarski, C.R.; Cleland, E.E.; D’Antonio, C.M.; Davies, K.F.; Gruner, D.S.; Harpole, W.S.; Hofmockel, K.S.; et al. Nitrogen increases early-stage and slows later-stage decomposition across diverse grasslands. J. Ecol. 2022, 110, 1376–1389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Treseder, K.K.; Kivlin, S.N.; Hawkes, C.V. Evolutionary trade-offs among decomposers determine responses to nitrogen enrichment. Ecol. Lett. 2011, 14, 933–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allison, S.D.; Weintraub, M.N.; Gartner, T.B.; Waldrop, M.P. Evolutionary-economic principles as regulators of soil enzyme production and ecosystem function. In Soil Enzymology; Shukla, G.C., Varma, A., Eds.; Spinger: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, X.; Schneider, R.L.; Morreale, S.J.; Wang, H.; Li, J. The impacts of shrub branch shelter and nitrogen addition on soil microbial activity and plant litter decomposition in a desert steppe. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2025, 207, 105956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hovland, J. The effect of artificial acid rain on respiration and cellulase activity in Norway spruce needle litter. Soil Biol. Biochem. 1981, 13, 23–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelly, J.M.; Strickland, R.C. CO2 efflux from deciduous forest litter and soil in response to simulated acid rain treatment. Water Air Soil Poll. 1984, 23, 431–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, H.; Ma, R.; Zhang, J.; Saleem, M.; Liu, Z.; Shan, X.; Yang, J.; Xiang, H. Crop-litter type determines the structure and function of litter-decomposing microbial communities under acid rain conditions. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 713, 136600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Li, D.; Zhang, J.; Saleem, M.; Zhang, Y.; Ma, R.; He, Y.; Yang, J.; Xiang, H.; Wei, H. Effect of simulated acid rain on soil CO2, CH4, and N2O emissions and microbial communities in a agricultural soil. Geoderma 2020, 366, 114222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Wei, H.; Zhang, J.; Wang, T.; He, Y.; Zhong, J.; Ma, R. Increasing acid rain frequency promotes the microbial community dissimilarities of forest soil rather than agricultural soil in southern China. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2022, 230, 113123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Zou, J.; Liu, Z.; Wei, H.; Zhang, J. Effect of acid rain on soil microbial networks complexity, community assembly and ecosystem multifunctionality. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2025, 1–15. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.L.; Staehelin, C.; Dayan, F.E.; Song, Y.Y.; Su, Y.J.; Zeng, R.S. Simulated acid rain accelerates litter decomposition and enhances the allelopathic potential of the invasive plant Wedelia trilobata (Creeping Daisy). Weed Sci. 2012, 60, 462–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, T.; Ullah, S.; Zhong, L.; Xu, Y.; Wei, G.; Yang, M. Impact of simulated acid rain on soil base cations dissolution between Eucalyptus pure plantations and Eucalyptus–Castanopsis fissa mixed plantations. Forests 2023, 14, 2159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Z.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, H.; Wei, H.; Lu, T.; Chen, X.; Li, H.; Yang, J.; Liu, Z. Response and driving factors of soil enzyme activity related to acid rain: A meta-analysis. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2023, 30, 105072–105083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Guo, C. General Biochemistry Course Experiment Guidance; Chemical Industry Press: Beijing, China, 2009. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Mandels, M. Microbial sources of cellulases. Biotechnol. Bioeng. Symp. 1975, 5, 81–105. [Google Scholar]
- Agnihotri, S.; Dutt, D.; Tyagi, C.H.; Kumar, A.; Upadhyaya, J.S. Production and biochemical characterization of a novel cellulose-poor alkali-thermo-tolerant xylanase from Coprinellus disseminatus SW-1 NTCC 1165. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2010, 26, 1349–1359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camassola, M.; Dillon, A.J.P. Biological pretreatment of sugar cane bagasse for the production of cellulases and xylanases by Penicillium echinulatum. Ind. Crop. Prod. 2009, 29, 642–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernfeld, P. Enzyme of starch degradation and synthesis. Adv. Enzymol. Relat. Subj. Biochem. 1951, 12, 379–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bernfeld, P. Amylases α and β. Methods Enzymol. 1955, 1, 149–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McClaugherty, C.A.; Linkins, S.C. Temperature responses of enzymes in tow forest soils. Soil Biol. Biochem. 1990, 22, 29–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| N Fertilization Treatments | Acid Deposition Treatments | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| A0 | A0.25 | A0.5 | |
| N0 | 1.44 | 3.00 | 6.00 |
| N3 | 1.23 | 2.79 | 5.79 |
| N6 | 1.01 | 2.57 | 5.57 |
| N9 | 0.80 | 2.36 | 5.36 |
| Variables | Parameter | C. lanceolata | C. camphora | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Intercept | N | A | N × A | Intercept | N | A | N × A | ||
| Mass loss | F | 4188.2 | 4.4 | 0.4 | 25.7 | 9962.1 | 3.2 | 26.4 | 59.5 |
| p | <0.01 | <0.05 | >0.05 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.05 | <0.01 | <0.01 | |
| Water content | F | 3455.9 | 2.7 | 81.1 | 4.1 | 6818.6 | 9.6 | 46.8 | 1.8 |
| p | <0.01 | >0.05 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | >0.05 | |
| Fungal biomass | F | 7982.4 | 130.7 | 4.5 | 8.3 | 5298.6 | 79.6 | 5.8 | 2.6 |
| p | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.05 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.05 | |
| CO2 release | F | 3156.2 | 1.9 | 0.1 | 7.1 | 14,849.1 | 28.6 | 18.7 | 73.5 |
| p | <0.01 | >0.05 | >0.05 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | |
| Exo-1,4-β-glucanase | F | 27,388.5 | 20.3 | 710.1 | 157.8 | 85,751.2 | 340.5 | 414.3 | 177.3 |
| p | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | |
| Carboxymethyl cellulase | F | 12,619.2 | 99.1 | 832.0 | 71.3 | 76,322.1 | 556.4 | 10.91 | 1855.2 |
| p | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | |
| β-Glucosidase | F | 53,945.2 | 32.4 | 106.3 | 228.1 | 16,502.2 | 5.0 | 62.6 | 200.0 |
| p | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | |
| α-Amylase | F | 9584.9 | 33.8 | 7.3 | 24.8 | 43,911.6 | 73.9 | 33.7 | 150.5 |
| p | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | |
| β-Amylase | F | 45,016.8 | 107.1 | 119.9 | 7.4 | 17,462.4 | 25.4 | 83.7 | 23.2 |
| p | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | |
| Laccase | F | 23,057.5 | 193.7 | 842.9 | 493.2 | 14,434.5 | 319.7 | 285.6 | 286.8 |
| p | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | |
| Peroxidase | F | 4467.9 | 70.1 | 184.1 | 147.4 | 10,732.9 | 204.7 | 151.3 | 24.3 |
| p | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lin, Y.; Kong, X.; He, Z.; He, X. Urea Fertilization Buffered Acid-Inhibiting Effect on Litter Decomposition in Subtropical Plantation Forests of Southern China. Forests 2025, 16, 1110. https://doi.org/10.3390/f16071110
Lin Y, Kong X, He Z, He X. Urea Fertilization Buffered Acid-Inhibiting Effect on Litter Decomposition in Subtropical Plantation Forests of Southern China. Forests. 2025; 16(7):1110. https://doi.org/10.3390/f16071110
Chicago/Turabian StyleLin, Yonghui, Xiangshi Kong, Zaihua He, and Xingbing He. 2025. "Urea Fertilization Buffered Acid-Inhibiting Effect on Litter Decomposition in Subtropical Plantation Forests of Southern China" Forests 16, no. 7: 1110. https://doi.org/10.3390/f16071110
APA StyleLin, Y., Kong, X., He, Z., & He, X. (2025). Urea Fertilization Buffered Acid-Inhibiting Effect on Litter Decomposition in Subtropical Plantation Forests of Southern China. Forests, 16(7), 1110. https://doi.org/10.3390/f16071110







