Identification of the Nut Rot Pathogen Affecting Castanopsis carlesii Based on Morphological and Phylogenetic Analyses
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Collection and Isolation
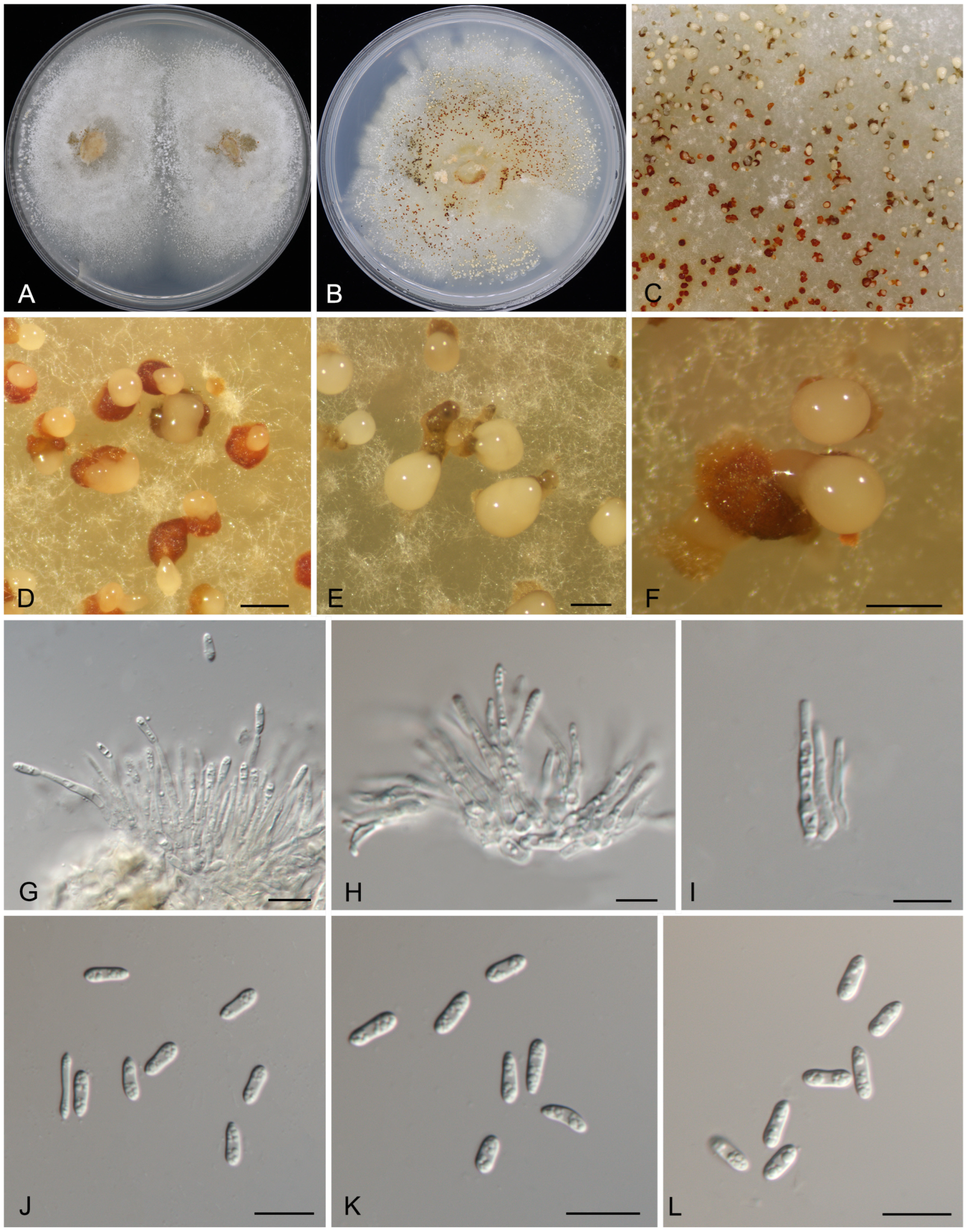
2.2. Morphological Identification and Characterization
2.3. Sequence Data
2.4. Phylogenetic Analyses
2.5. Pathogenicity Trials
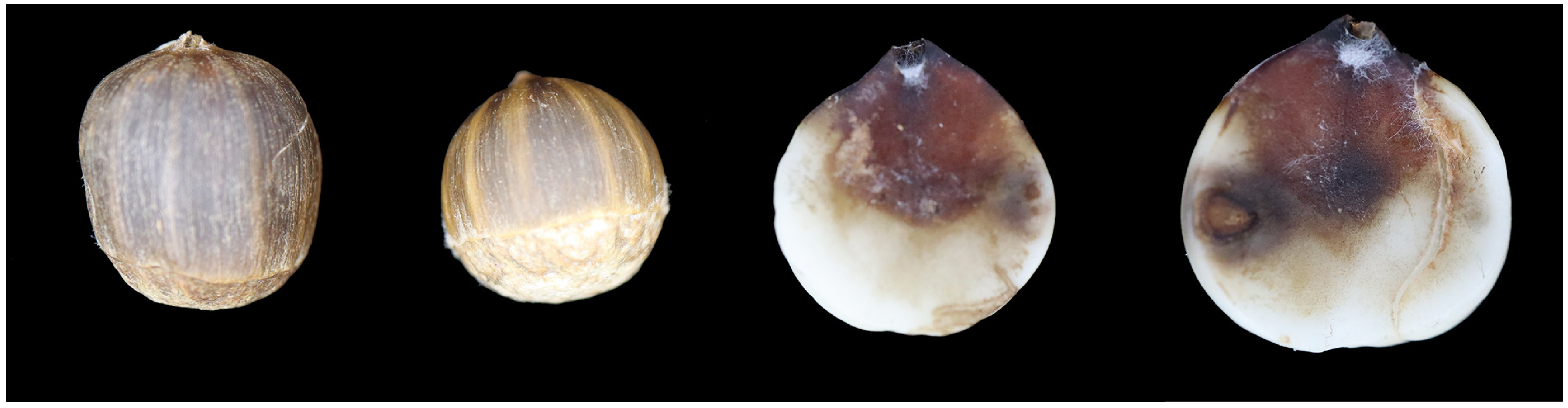
3. Results
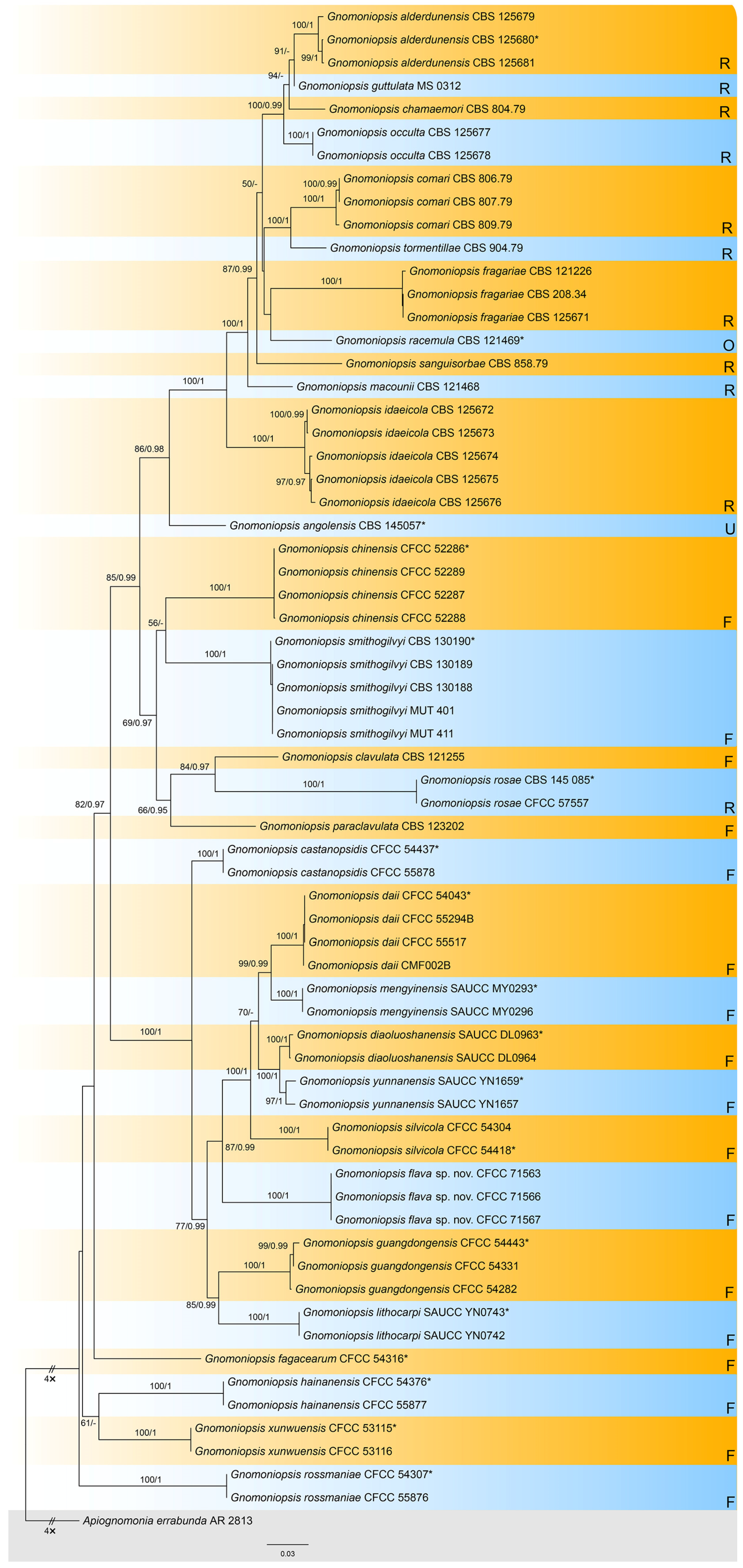
3.1. Phylogenetic Analysis
3.2. Taxonomy
3.3. Pathogenicity Test
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cheng, Y.P.; Hwang, S.Y.; Lin, T.P. Potential refugia in Taiwan revealed by the phylogeographical study of Castanopsis carlesii Hayata (Fagaceae). Mol. Ecol. 2005, 14, 2075–2085. [Google Scholar]
- Zhong, X.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, J.; He, L.; Sun, R. Maxent modeling for predicting the potential geographical distribution of Castanopsis carlesii under various climate change scenarios in China. Forests 2023, 14, 1397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Liu, X.; Xie, J.; Zhang, Q.; Yang, Z.; Schindlbacher, A.; Yang, Y. Contribution of above ground litterfall and roots to the soil CO2 efflux of two sub-tropical Cunninghamia lanceolata and Castanopsis carlesii forests. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2021, 311, 108671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, B.Y.; Wang, Y.F.; Li, G.Q.; He, R.J.; Huang, Y.L. Genus Castanopsis: A review on phytochemistry and biological activities. Fitoterapia 2024, 179, 106216. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Visentin, I.; Gentile, S.; Valentino, D.; Gonthier, P.; Tamietti, G.; Cardinale, F. Gnomoniopsis castanea sp. nov. (Gnomoniaceae, Diaporthales) as the causal agent of nut rot in sweet chestnut. J. Plant Pathol. 2012, 94, 411–419. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, N.; Tian, C.M. An emerging pathogen from rotted chestnut in China: Gnomoniopsis daii sp. nov. Forests 2019, 10, 1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shuttleworth, L.A.; Liew, E.C.Y.; Guest, D.I. Survey of the incidence of chestnut rot in south-eastern Australia. Australas. Plant Pathol. 2013, 42, 63–72. [Google Scholar]
- Shuttleworth, L.A.; Guest, D.I. The infection process of chestnut rot, an important disease caused by Gnomoniopsis smithogilvyi (Gnomoniaceae, Diaporthales) in Oceania and Europe. Australas. Plant Pathol. 2017, 46, 397–405. [Google Scholar]
- Crous, P.W.; Summerell, B.A.; Shivas, R.G.; Burgess, T.I.; Decock, C.A.; Dreyer, L.L.; Granke, L.L.; Guest, D.I.; Hardy, G.E.S.J.; Hausbeck, M.K.; et al. Fungal Planet Description Sheets: 107–127. Persoonia 2012, 28, 138–182. [Google Scholar]
- Shuttleworth, L.A.; Walker, D.M.; Guest, D.I. The chestnut pathogen Gnomoniopsis smithogilvyi (Gnomoniaceae, Diaporthales) and its synonyms. Mycotaxon 2016, 130, 929–940. [Google Scholar]
- Sakalidis, M.L.; Medina-Mora, C.M.; Kolp, M.; Fulbright, D.W. First report of Gnomoniopsis smithogilvyi causing chestnut brown rot on chestnut fruit in Michigan. Plant Dis. 2019, 103, 2134. [Google Scholar]
- Dennert, F.G.; Broggini, G.A.; Gessler, C.; Storari, M. Gnomoniopsis castanea is the main agent of chestnut nut rot in Switzerland. Phytopathol. Mediterr. 2015, 54, 199–211. [Google Scholar]
- Pasche, S.; Calmin, G.; Auderset, G.; Crovadore, J.; Pelleteret, P.; Mauch-Mani, B.; Barja, F.; Paul, B.; Jermini, M.; Lefort, F. Gnomoniopsis smithogilvyi causes chestnut canker symptoms in Castanea sativa shoots in Switzerland. Fungal Genet. Biol. 2016, 87, 9–21. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Jiang, N.; Fan, X.L.; Tian, C.M. Identification and characterization of leaf-inhabiting Fungi from Castanea plantations in China. J. Fungi 2021, 7, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, N.; Liang, L.Y.; Tian, C.M. Gnomoniopsis chinensis (Gnomoniaceae, Diaporthales), a new fungus causing canker of Chinese chestnut in Hebei Province, China. MycoKeys 2020, 67, 19–32. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Linaldeddu, B.T.; Deidda, A.; Scanu, B.; Franceschini, A.; Alves, A.; Abdollahzadeh, J.; Phillips, A.J.L. Phylogeny, morphology and pathogenicity of Botryosphaeriaceae, Diatrypaceae and Gnomoniaceae associated with branch diseases of hazelnut in Sardinia (Italy). Eur. J. Plant Pathol. 2016, 146, 259–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sogonov, M.V.; Castlebury, L.A.; Rossman, A.Y.; Mejía, L.C.; White, J.F. Leaf-inhabiting genera of the Gnomoniaceae, Diaporthales. Stud. Mycol. 2008, 62, 1–77. [Google Scholar]
- Barr, M.E. The Diaporthales in North America with emphasis on Gnomonia and its segregates. Mycologia 1978, 7, 43–184. [Google Scholar]
- Walker, D.M.; Castlebury, L.A.; Rossman, A.Y.; Sogonov, M.V.; White, J.F. Systematics of genus Gnomoniopsis (Gnomoniaceae, Diaporthales) based on a three-gene phylogeny, host associations and morphology. Mycologia 2010, 102, 1479–1496. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, S.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, R.; Liu, S.; Liu, X.; Zhang, X. Morphological and phylogenetic analyses reveal four new species of Gnomoniopsis (Gnomoniaceae, diaporthales) from China. J. Fungi 2022, 8, 770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, N.; Voglmayr, H.; Bian, D.R.; Piao, C.G.; Wang, S.K.; Li, Y. Morphology and phylogeny of Gnomoniopsis (Gnomoniaceae, Diporthales) from Fagaceae leaves in China. J. Fungi 2021, 7, 792. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Q.; Jiang, N.; Tian, C.M. Tree inhabiting gnomoniaceous species from China, with Cryphogonomonia gen. nov. proposed. MycoKeys 2020, 69, 71–89. [Google Scholar]
- Udayanga, D.; Miriyagalla, S.D.; Manamgoda, D.S.; Lewers, K.S.; Gardiennet, A.; Castlebury, L.A. Molecular reassessment of diaporthalean fungi associated with strawberry, including the leaf blight fungus, Paraphomopsis obscurans gen. et comb. nov. (Melanconiellaceae). IMA Fungus 2021, 12, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaklitsch, W.M.; Voglmayr, H. European species of Dendrostoma (Diaporthales). MycoKeys 2019, 59, 1–26. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Mejía, L.C.; Castlebury, L.A.; Rossman, A.Y.; Sogonov, M.V.; White, J.F. Phylogenetic placement and taxonomic review of the genus Cryptosporella and its synonyms Ophiovalsa and Winterella (Gnomoniaceae, Diaporthales). Mycol. Res. 2008, 112, 23–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mejía, L.C.; Castlebury, L.A.; Rossman, A.Y.; Sogonov, M.V.; White, J.F. A systematic account of the genus Plagiostoma (Gnomoniaceae, Diaporthales) based on morphology, host associations, and a four-gene phylogeny. Stud. Mycol. 2011, 68, 211–235. [Google Scholar]
- Walker, D.M.; Castlebury, L.A.; Rossman, A.Y.; Struwe, L. Host conservatism or host specialization? Patterns of fungal diversification are influenced by host plant specificity in Ophiognomonia (Gnomoniaceae, Diaporthales). Biol. J. Linnean Soc. 2013, 111, 1–16. [Google Scholar]
- Doyle, J.J. Isolation of plant DNA from fresh tissue. Focus 1990, 12, 13–15. [Google Scholar]
- White, T.J.; Bruns, T.; Lee, S.; Taylor, J. Amplification and direct sequencing of fungal ribosomal RNA genes for phylogenetics. PCR Protoc. Guide Methods Appl. 1990, 18, 315–322. [Google Scholar]
- Carbone, I.; Kohn, L.M. A method for designing primer sets for speciation studies in filamentous ascomycetes. Mycologia 1999, 91, 553–556. [Google Scholar]
- Glass, N.L.; Donaldson, G.C. Development of primer sets designed for use with the PCR to amplify conserved genes from filamentous ascomycetes. Appl. Environ. Microb. 1995, 61, 1323–1330. [Google Scholar]
- O’Donnell, K.; Cigelnik, E. Two divergent intragenomic rDNA ITS2 types within a monophyletic lineage of the fungus Fusarium are nonorthologous. Mol. Phylogenet Evol. 1997, 7, 103–116. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Katoh, K.; Toh, H. Parallelization of the MAFFT multiple sequence alignment program. Bioinformatics 2010, 26, 1899–1900. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Miller, M.A.; Pfeiffer, W.; Schwartz, T. Creating the CIPRES Science Gateway for inference of large phylogenetic trees. In Proceedings of the Gateway Computing Environments Workshop, GCE, New Orleans, LA, USA, 14 November 2010; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Stamatakis, A. RAxML version 8: A tool for phylogenetic analysis and post-analysis of large phylogenies. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 1312–1313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ronquist, F.; Huelsenbeck, J.P. MrBayes 3: Bayesian phylogenetic inference under mixed models. Bioinformatics 2003, 19, 1572–1574. [Google Scholar]
- Benigno, A.; Aglietti, C.; Cacciola, S.O.; Moricca, S. Trunk injection delivery of biocontrol strains of Trichoderma spp. effectively suppresses nut rot by Gnomoniopsis castaneae in Chestnut (Castanea sativa Mill.). Biology 2024, 13, 143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galdames, R.E. First report of Gnomoniopsis castaneae associated with branch dieback on chestnut tree (Castanea sativa) in Southern Chile. Plant Dis. 2024, 108, 3186. [Google Scholar]
- Çakar, D. Significance of Gnomoniopsis smithogilvyi as kernel rot of sweet chestnut in Turkey. J. Phytopathol. 2024, 172, e13293. [Google Scholar]
- Crous, P.W.; Luangsa-Ard, J.J.; Wingfield, M.J.; Carnegie, A.J.; Hernández-Restrepo, M.; Lombard, L.; Roux, J.; Barreto, R.W.; Baseia, I.G.; Cano-Lira, J.F.; et al. Fungal Planet description sheets: 785–867. Persoonia 2018, 41, 238–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, N.; Xue, H.; Piao, C.; Li, Y. Characterization and identification of Gnomoniopsis species. Terr. Ecosyst. Conserv. 2022, 2, 44–52. [Google Scholar]


| Species | Country | Host | Host Family | Strain | GenBank Accession Number | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ITS | tef1 | tub2 | |||||
| Apiognomonia errabunda | Switzerland | Fagus sylvatica | Fagaceae | AR 2813 | DQ313525 | DQ313565 | DQ862014 |
| Gnomoniopsis alderdunensis | USA | Rubus pedatus | Rosaeace | CBS 125679 | GU320826 | GU320813 | GU320788 |
| Gnomoniopsis alderdunensis | USA | Rubus parviflorus | Rosaeace | CBS 125680 * | GU320825 | GU320801 | GU320787 |
| Gnomoniopsis alderdunensis | USA | Rubus parviflorus | Rosaeace | CBS 125681 | GU320827 | GU320802 | GU320789 |
| Gnomoniopsis angolensis | Angola | Unknown | Unknown | CBS 145057 * | MK047428 | NA | NA |
| Gnomoniopsis chamaemori | Finland | Rubus chamaemorus | Rosaeace | CBS 804.79 | GU320817 | GU320809 | GU320777 |
| Gnomoniopsis chinensis | China | Castanea mollissima | Fagaceae | CFCC 52286 * | MG866032 | MH545370 | MH545366 |
| Gnomoniopsis chinensis | China | Castanea mollissima | Fagaceae | CFCC 52287 | MG866033 | MH545371 | MH545367 |
| Gnomoniopsis chinensis | China | Castanea mollissima | Fagaceae | CFCC 52288 | MG866034 | MH545372 | MH545368 |
| Gnomoniopsis chinensis | China | Castanea mollissima | Fagaceae | CFCC 52289 | MG866035 | MH545373 | MH545369 |
| Gnomoniopsis clavulata | USA | Quercus falcata | Fagaceae | CBS 121255 | EU254818 | GU320807 | EU219211 |
| Gnomoniopsis castanopsidis | China | Castanopsis hystrix | Fagaceae | CFCC 54437 * | MZ902909 | MZ936385 | NA |
| Gnomoniopsis castanopsidis | China | Castanopsis hystrix | Fagaceae | CFCC 55878 | MZ902910 | MZ936386 | NA |
| Gnomoniopsis comari | Finland | Comarum palustre | Rosaeace | CBS 806.79 | EU254821 | GU320810 | EU219156 |
| Gnomoniopsis comari | Finland | Comarum palustre | Rosaeace | CBS 807.79 | EU254822 | GU320814 | GU320779 |
| Gnomoniopsis comari | Switzerland | Comarum palustre | Rosaeace | CBS 809.79 | EU254823 | GU320794 | GU320778 |
| Gnomoniopsis daii | China | Castanea mollissima | Fagaceae | CFCC 54043 * | MN598671 | MN605519 | MN605517 |
| Gnomoniopsis daii | China | Castanea mollissima | Fagaceae | CMF002B | MN598672 | MN605520 | MN605518 |
| Gnomoniopsis daii | China | Quercus aliena | Fagaceae | CFCC 55517 | MZ902911 | MZ936387 | MZ936403 |
| Gnomoniopsis daii | China | Quercus aliena | Fagaceae | CFCC 55294B | MZ902912 | MZ936388 | MZ936404 |
| Gnomoniopsis diaoluoshanensis | China | Castanopsis chinensis | Fagaceae | SAUCC DL0963 * | ON753744 | ON759769 | ON759777 |
| Gnomoniopsis diaoluoshanensis | China | Castanopsis chinensis | Fagaceae | SAUCC DL0964 | ON753743 | ON759768 | ON759776 |
| Gnomoniopsis flava sp. nov. | China | Castanopsis carlesii | Fagaceae | CFCC 71563 * | PV257808 | PV268106 | PV339811 |
| Gnomoniopsis flava sp. nov. | China | Castanopsis carlesii | Fagaceae | CFCC 71566 | PV257809 | PV268107 | PV339812 |
| Gnomoniopsis flava sp. nov. | China | Castanopsis carlesii | Fagaceae | CFCC 71567 | PV257810 | PV268108 | PV339813 |
| Gnomoniopsis fagacearum | China | Lithocarpus glaber | Fagaceae | CFCC 54316 * | MZ902916 | MZ936392 | MZ936408 |
| Gnomoniopsis fragariae | USA | Fragaria vesca | Rosaeace | CBS 121226 | EU254824 | GU320792 | EU219144 |
| Gnomoniopsis fragariae | France | Fragaria sp. | Rosaeace | CBS 208.34 | EU254826 | GU320808 | EU219149 |
| Gnomoniopsis fragariae | USA | Fragaria sp. | Rosaeace | CBS 125671 | GU320816 | GU320793 | GU320776 |
| Gnomoniopsis guangdongensis | China | Castanopsis fargesii | Fagaceae | CFCC 54443 * | MZ902918 | MZ936394 | MZ936410 |
| Gnomoniopsis guangdongensis | China | Castanopsis fargesii | Fagaceae | CFCC 54331 | MZ902919 | MZ936395 | MZ936411 |
| Gnomoniopsis guangdongensis | China | Castanopsis fargesii | Fagaceae | CFCC 54282 | MZ902920 | MZ936396 | MZ936412 |
| Gnomoniopsis guttulata | Bulgaria | Agrimonia eupatoria | Rosaeace | MS 0312 | EU254812 | NA | NA |
| Gnomoniopsis hainanensis | China | Castanopsis hainanensis | Fagaceae | CFCC 54376 * | MZ902921 | MZ936397 | MZ936413 |
| Gnomoniopsis hainanensis | China | Castanopsis hainanensis | Fagaceae | CFCC 55877 | MZ902922 | MZ936398 | MZ936414 |
| Gnomoniopsis idaeicola | USA | Rubus sp. | Rosaeace | CBS 125672 | GU320823 | GU320797 | GU320781 |
| Gnomoniopsis idaeicola | USA | Rubus pedatus | Rosaeace | CBS 125673 | GU320824 | GU320798 | GU320782 |
| Gnomoniopsis idaeicola | France | Rubus sp. | Rosaeace | CBS 125674 | GU320820 | GU320796 | GU320780 |
| Gnomoniopsis idaeicola | USA | Rubus procerus | Rosaeace | CBS 125675 | GU320822 | GU320799 | GU320783 |
| Gnomoniopsis idaeicola | USA | Rubus procerus | Rosaeace | CBS 125676 | GU320821 | GU320811 | GU320784 |
| Gnomoniopsis lithocarpi | China | Lithocarpus fohaiensis | Fagaceae | SAUCC YN0743 * | ON753749 | ON759765 | ON759783 |
| Gnomoniopsis lithocarpi | China | Lithocarpus fohaiensis | Fagaceae | SAUCC YN0742 | ON753750 | ON759764 | ON759782 |
| Gnomoniopsis macounii | USA | Spiraea sp. | Rosaeace | CBS 121468 | EU254762 | GU320804 | EU219126 |
| Gnomoniopsis mengyinensis | China | Castanea mollissima | Fagaceae | SAUCC MY0293 * | ON753741 | ON759766 | ON759774 |
| Gnomoniopsis mengyinensis | China | Castanea mollissima | Fagaceae | SAUCC MY0296 | ON753742 | ON759767 | ON759775 |
| Gnomoniopsis occulta | USA | Potentilla sp. | Rosaeace | CBS 125677 | GU320828 | GU320812 | GU320785 |
| Gnomoniopsis occulta | USA | Potentilla sp. | Rosaeace | CBS 125678 | GU320829 | GU320800 | GU320786 |
| Gnomoniopsis paraclavulata | USA | Quercus alba | Fagaceae | CBS 123202 | GU320830 | GU320815 | GU320775 |
| Gnomoniopsis racemula | USA | Chamerion angustifolium | Onagraceae | CBS 121469 * | EU254841 | GU320803 | EU219125 |
| Gnomoniopsis rosae | New Zealand | Rosa sp. | Rosaeace | CBS 145 085 * | MK047451 | NA | NA |
| Gnomoniopsis rosae | China | Rosa chinensis | Rosaeace | CFCC 57557 | ON564617 | NA | NA |
| Gnomoniopsis rossmaniae | China | Castanopsis hainanensis | Fagaceae | CFCC 54307 * | MZ902923 | MZ936399 | MZ936415 |
| Gnomoniopsis rossmaniae | China | Castanopsis hainanensis | Fagaceae | CFCC 55876 | MZ902924 | MZ936400 | MZ936416 |
| Gnomoniopsis sanguisorbae | Switzerland | Sanguisorba minor | Rosaeace | CBS 858.79 | GU320818 | GU320805 | GU320790 |
| Gnomoniopsis silvicola | China | Castanopsis hystrix | Fagaceae | CFCC 54304 | MZ902925 | MZ936401 | MZ936417 |
| Gnomoniopsis silvicola | China | Quercus serrata | Fagaceae | CFCC 54418 * | MZ902926 | MZ936402 | MZ936418 |
| Gnomoniopsis smithogilvyi | Australia | Castanea sp. | Fagaceae | CBS 130190 * | JQ910642 | KR072534 | JQ910639 |
| Gnomoniopsis smithogilvyi | Australia | Castanea sp. | Fagaceae | CBS 130189 | JQ910644 | KR072535 | JQ910641 |
| Gnomoniopsis smithogilvyi | Australia | Castanea sp. | Fagaceae | CBS 130188 | JQ910643 | KR072536 | JQ910640 |
| Gnomoniopsis smithogilvyi | Italy | Castanea sativa | Fagaceae | MUT 401 | HM142946 | KR072537 | KR072532 |
| Gnomoniopsis smithogilvyi | New Zealand | Castanea sativa | Fagaceae | MUT 411 | HM142948 | KR072538 | KR072533 |
| Gnomoniopsis tormentillae | Switzerland | Potentilla sp. | Rosaeace | CBS 904.79 | EU254856 | GU320795 | EU219165 |
| Gnomoniopsis xunwuensis | China | Castanopsis fissa | Fagaceae | CFCC 53115 * | MK432667 | MK578141 | MK578067 |
| Gnomoniopsis xunwuensis | China | Castanopsis fissa | Fagaceae | CFCC 53116 | MK432668 | MK578142 | MK578068 |
| Gnomoniopsis yunnanensis | China | Castanea mollissima | Fagaceae | SAUCC YN1659 * | ON753746 | ON759771 | ON759779 |
| Gnomoniopsis yunnanensis | China | Castanea mollissima | Fagaceae | SAUCC YN1657 | ON753747 | ON759772 | ON759780 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, Y.; Li, A.; Jiang, N. Identification of the Nut Rot Pathogen Affecting Castanopsis carlesii Based on Morphological and Phylogenetic Analyses. Forests 2025, 16, 627. https://doi.org/10.3390/f16040627
Li Y, Li A, Jiang N. Identification of the Nut Rot Pathogen Affecting Castanopsis carlesii Based on Morphological and Phylogenetic Analyses. Forests. 2025; 16(4):627. https://doi.org/10.3390/f16040627
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Yicheng, Aining Li, and Ning Jiang. 2025. "Identification of the Nut Rot Pathogen Affecting Castanopsis carlesii Based on Morphological and Phylogenetic Analyses" Forests 16, no. 4: 627. https://doi.org/10.3390/f16040627
APA StyleLi, Y., Li, A., & Jiang, N. (2025). Identification of the Nut Rot Pathogen Affecting Castanopsis carlesii Based on Morphological and Phylogenetic Analyses. Forests, 16(4), 627. https://doi.org/10.3390/f16040627







