Abstract
As the responsive soil properties, soil microbial fractions and enzymatic activities are often recommended for assessing soil environment. Different flora, silvicultural practices, and anthropogenic activities regulate essential ecosystem processes. They could substantially affect biological properties, nutrient budgets, and biogeochemical cycles at local and regional scales. This study examined how different forest compositions influenced by various anthropogenic activities (land use change, over-exploitation, species translocation) affect soil microbial properties and enzymatic activities, as well as the effects of soil chemical properties on these patterns in important sub-tropical forest ecosystems in Southern China. The research was conducted at Lutou forest research station, located in Yueyang, Hunan Province, China. Soil samples were collected at 0–10, 10–20, and 20–40 cm depths from natural broadleaved forest (NBF), coniferous monoculture plantations (CPF), and mixed forest stand. CPF stands are directly affected by human interference and frequent harvesting practices, whereas mixed forest and NBF stands are naturally grown forests with minimal human interference. Enzymes continually play a positive role in preserving soil health. The results showed that the interaction effect of forest type and soil depth significantly influenced urease, sucrase, and protease activity (all p < 0.001); however, no clear patterns were observed. Soil microbial carbon (MBC) and soil microbial nitrogen (MBN) were remarkably higher in 0–10 cm in mixed forest and NBF stand compared to CPF stand. For the upper soil layer, soil organic carbon (SOC) was higher in mixed forest, whereas, for the remaining two layers, it was observed to be highest in NBF. Moreover, the microbial quotient (MBC/SOC) was considerably higher in NBF forest in all soil layers than in mixed forest and CPF stand. Soil organic carbon (SOC) and soil total nitrogen (TN) had a strong positive relationship with MBC compared to MBN. Our study contributes toward an enhanced understanding of soil enzymatic responses and microbial soil dynamics’ biological patterns, controls, and activities in different rural forest ecosystems.
1. Introduction
Soil biological attributes are crucial for ecosystem functioning since they involve soil organic matter (SOM) decomposition and nutrient cycling [1,2]. SOM maintenance is desirable for enduring land use because of its beneficial effects on soil fertility. As an active element of SOM, soil microbial biomass is greatly involved in nutrient storage and transformations. Nutrients released during the turnover of soil microbial biomass are often plant-available. Soil microbial fractions have a turnover time of less than two years; therefore, they can respond rapidly to conditions that eventually alter SOM levels [3]. Due to its rapid turnover rate, soil microbial biomass is a delicate indicator of any climate changes [4], crop rotations [4,5], soil enzymatic activity [6,7], soil respiration [8], and pollutant toxicity [9].
As imperative and responsive soil biological properties, soil microbial fractions and enzymatic activities are often recommended for assessing the soil environment [10]). The living fractions, such as soil microbial biomass carbon (MBC) and soil microbial biomass nitrogen (MBN), have been advocated as valuable and sensitive measures of changes in several functions in soil [11]. The soil MBC usually comprises only 1%–5% of the total soil organic carbon (SOC). Still, this little percentage (microbial quotient) has been reported to change invariably and provide a valuable indicator of soil biological processes [12].
At the same time, soil enzymes are critical indicators of the catabolic activity of soil microorganisms. Soil enzymes play a crucial role in soil quality maintenance and provide us with fundamental and early detection signals for soil metabolic activity and nutrient status [13]. These enzymes play a vital role in the overall biochemical functioning of the soil ecosystem [14]. They respond to any changes far faster than many other soil indicators. They are often closely linked with microbial activities. Although soil enzymes are present in a very minimal quantity, their role in soil health maintenance can never be ignored [15].
Soil pH and nutrient availability regulate soil’s biological properties [2]. Earlier forestry-related studies in different urban and rural ecosystems have revealed that soil C and N enrichment affects the soil respiration rates [15,16] and soil microbial biomass either by increasing or decreasing them [17,18]. These changes in microbial properties could substantially affect the nutrient budgets and biogeochemical cycles at local and regional scales [18,19]. Soil depth is also a potential factor influencing the soil microbial status in terrestrial ecosystems. Some studies demonstrate high variability in the soil MBC and MBN alongside the soil depth gradient [20,21]. Generally, these studies have shown that activities of soil microbial biomass and the responses to soil C and N enrichment along depth increase in soil are challenging to predict, possibly due to the intricate interactions between soil microorganisms, soil nutrients, and soil depths.
Since the 1980s, different large-scale afforestation programs have been introduced in China, which has led to an upsurge in plantation forests, resulting in the conversion of many natural and mixed forests into coniferous monoculture plantations [22,23]. The management practices of all these forest types are entirely different, whereas plantations are exposed to extensively managed techniques [24]. Coniferous plantations are generally fast-growing timber species with shorter rotation periods than mixed and natural broadleaved forests [25]. Natural forests typically have stable vegetation with less human interference and natural rotation cycles than plantations. Natural forest conversion to coniferous monoculture plantations is usually found to lessen SOC stocks and decrease SOM quality [25,26]. Therefore, there is a general perception that monoculture plantations are usually substandard compared to naturally grown forests regarding nutrient cycling and soil quality [27,28]. Hence, further studies are needed to comprehend these responses’ underlying mechanisms broadly.
Because soil microbial biomass and enzymatic activities integrate soil physiochemical attributes and respond to silvicultural practices, they could be considered apposite biological forms of soil quality indicators. Therefore, the objectives of this research were to assess: (1) how the different forest compositions will influence the patterns of soil microbial biomass dynamics and soil enzymatic activity and the relationship between them, and (2) to investigate the effect of soil properties (i.e., soil pH, nutrient availability) on soil microbial and enzymatic patterns. We hypothesized that the naturally regenerated forest and mixed forest stands would have prominently better soil microbial activity (MBC, MBN, MBN/TN and microbial quotient (MBC/SOC), and enzymatic activity (urease, sucrose, protease, and catalase) than the coniferous monoculture plantations because of the inferior litter quality, slower litter decomposition rate, and nutrient cycling in coniferous monoculture plantations.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Sites and Forest Composition
Sampling sites were located in the Lutou forest research station in Yueyang city (E 113°51′52′′~113°58′24′′, N 28°31′17′′~28°38′00′′), Hunan province, central China (Figure 1). The research station covers an area of about 4762 ha. The climate is a humid subtropical monsoon with abundant rainfall and four distinct seasons [29]. Yueyang experiences an average annual temperature, precipitation, and humidity of 17.07 °C, 1312 mm, and 82%, respectively. The soil type is lateritic red soil. Soil structure is clay-loam. This soil tends to be acidic and low in calcium, which is why growers often add lime to raise the pH and add some of the missing minerals. It is soft and easily broken into smaller pieces. The red soils in China have been deteriorating recently and facing various threats, such as soil erosion, acidification, and pollution, etc.
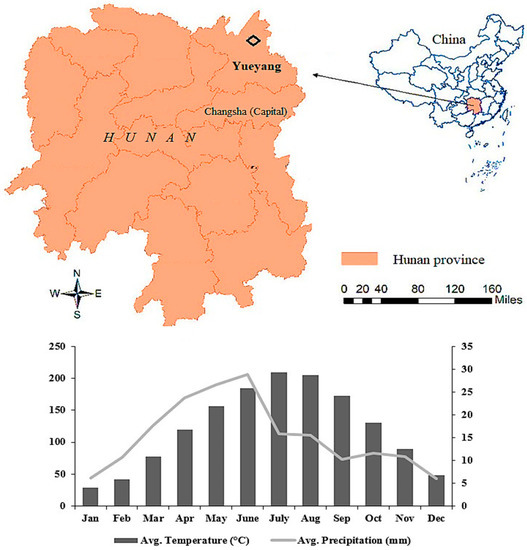
Figure 1.
Location and climatic conditions of the study area.
Three forest stands were selected in rural forest ecosystems: naturally regenerated broadleaved forest (NBF), coniferous monoculture plantation forest (CPF), and mixed forest stands. Castanopsis eyeri specie was present in NBF stand, whereas CPF was established by planting fast-growing Cunninghamia lanceolata timber tree species. Mixed forest stands comprised broadleaved and coniferous species, including Castanopsis eyeri and Pinus massoniana.
The C. eyeri (NBF) stand in the research station is the largest and most complete community of Castonpsis, with an average age of 60. The forest is neat, and the forest canopy is undulating. It is mainly distributed on mountain slopes. The average slope gradient is 20–25°. The average age of CPF stand is 30 years, and it is present on both flat soil and mountain slopes at the research station. The P. massoniana + C. eyeri mixed forest is a vital forest type at Lutou forest station. It is distributed on the ridges, hillsides, and mountain slopes. The average slope gradient is 20–25°. The elevation range is 800 m, 427 m, and 777 m for NBF, CPF, and mixed forest stands, respectively.
Mixed forest and NBF stands were almost adjacent, whereas CPF stand was 300–400 m from other forest stands. There was no artificial irrigation channel present in any forest type. The watering was purely natural due to abundant rainfall. Littering and understory vegetation is a natural phenomenon; however, to minimize the direct influence of littering and understory vegetation, such as shrub and herb layer, we selected those trees where the presence of understory vegetation around the tree canopy projection area was considerably less. Still, these are open field conditions; therefore, indirect influence might be possible. CPF stands are directly affected by human interference and frequent harvesting practices, whereas mixed forest and NBF stands are naturally grown forests with minimal human interference. Therefore, the occurrence and long-term settling of littering was less in CPF due to monoculture species and regular silvicultural practices compared to natural and mixed forest stands [30].
2.2. Soil Sampling and Treatment
Nine spots were selected for soil sampling (three from each forest type). Three 20 × 20 m plots were established per forest stand, and the sampling was conducted in October 2020 across nine selected plots. We tried to select the plots with almost uniform topography to minimize the local terrain impact on trees/vegetation. Soil samples were collected using a steel soil auger (3.5 cm diameter) from 0–10 cm, 10–20 cm, and 20–40 cm. Three replicates per forest type and soil depth were collected. After collection, all the samples were properly cleaned, and any roots or stones were sorted out. The soils were placed in plastic bags and immediately stored with ice bags before bringing to the National Engineering Laboratory for Applied Technology in Forestry and Ecology in South China, Central South University of Forestry and Technology, Changsha.
Soil samples were sieved through a 2 mm mesh to remove stones and plant residues in the laboratory. All the sieved soil samples were adequately mixed and divided into three sub-samples. One sub-sample from each forest type per soil depth was air-dried (room temperature) for the soil chemical analysis (soil pH, soil organic carbon (SOC), and dissolved organic carbon (DOC). The second subsample was placed at 4 °C for soil microbial properties analysis (MBC, MBN, MBC/MBN, MBN/TN, and MBC/SOC) to use within one week. For enzymatic activity analysis, the third subsample was stored at −80 °C until further use. Three composite samples per forest type per soil depth were used. The soil characteristics, such as total N (TN), C/N ratio, and available nutrients (nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium), are shown in our already published article [30].
2.3. Chemical Analysis of Soil Samples
2.3.1. Soil pH and Enzymes Activity Determination
Soil pH was determined using a potentiometric method (1:2.5 soil:water). Urease activity was determined using the method described in Ref. [31]. Sucrase activity was measured by following the method of Ref. [32]. Protease activity was measured using ninhydrin colorimetry methods [33]. Catalase activity was determined with KMnO4 (0.1 mol L−1 KMnO4 ug g–1, 30 °C, 20 h). Here, we briefly mentioned the activity of the enzyme determination methods; however, complete details are mentioned in our recently published article [15].
2.3.2. Soil Microbial Activity Analysis
Soil microbial biomass fractions (MBC and MBN) were determined using the chloroform fumigation-extraction method [34]. For each plot, half of the prepared samples were fumigated with ethanol-free chloroform in an evacuated extractor at 25 °C for 24 h. The remaining soil samples were treated as control (CK). Briefly, ∼10 g per moist soil (dry weight equivalent) of fumigated and non-fumigated samples were extracted with 50 mL (0.5 mol L–1) K2SO4 (soil:extractant = 1:4) after shaking for approximately 60 min on a reciprocal shaker. The extracts were filtered through a 7 cm diameter Whatman #42 filter paper and stored at −15 °C for further analysis. Total organic carbon (TOC) and total N (TN) in the extracts were determined with a Shimadzu TOC/TN analyzer (TOC-L CPH, Shimadzu, Japan).
The MBC and MBN were calculated as:
EC = (Fumigated soil TOC) − (Non-fumigated soil TOC) and EN = (Fumigated soil TN) − (Non-fumigated soil TN). The extraction factors are KEC (0.45) and KEN (0.54). Soil TOC extracted from the non-fumigated samples was used as the soil dissolved organic C (DOC).
2.4. Statistical Analysis
Two-way nested analysis of variance (ANOVA) was conducted with SPSS (17.0, Chicago, IL, USA) to evaluate the effects of forest composition, vertical soil depths profiles, and their interactions on microbial and chemical properties. A correlation analysis (Pearson) was performed to explore the associations between different pairs of soil variables. Before conducting the statistical analyses, soil microbial and chemical variables data were inspected for normality check (Shapiro–Wilk test), outliers check (box plot method), and homogeneity of variances check (Levene’s test), and no transformations were found necessary. The Origin 2018 package was used to create all the figures. The statistical significance level was set at p < 0.05, and the mean that shows a significant difference was compared using Tukey’s test.
3. Results
3.1. Soil pH, DOC, and Enzymatic Responses
The soil pH was higher in CPF and lower in NBF, and it was significantly different among forest types (p < 0.001) and soil depths (p < 0.001). In CPF and mixed forest, it was highest in the 0–10 cm soil layer, whereas, in NBF, it was higher in the 10–20 cm soil layer (Table 1). The DOC concentrations varied from 92.29 mg.kg−1 to 445.12 mg.kg−1 among all the forest types and soil depths. The DOC was higher in mixed forest in the 0–10 and 10–20 cm soil layers, whereas, in the 20–40 cm soil layer, it was higher in CPF (Table 1 and Table 2).

Table 1.
Soil pH, soil organic carbon (SOC), and dissolved organic carbon (DOC) at three soil depths along NBF, mixed forest, and CPF stands. Values are the mean (SE in parentheses) of three replicates.

Table 2.
Two-way ANOVA results for the effects of forest type, soil depth, and forest type × soil depth at p < 0.05, p < 0.01, and p < 0.001 significant level.
Regarding soil enzymes, the interaction effect of forest type and soil depth was significant for urease, sucrase, and protease activity (all p < 0.001). In contrast, it was not significant for catalase activity (p = 0.06). Overall, no clear patterns were observed for the mean enzymatic activity among forest types and soil depths (Table 2 and Table 3). In addition, apart from catalase, the interaction effect of forest types × soil depth was observed to be significant for the other three enzymes (p < 0.001) (Table 2).

Table 3.
Soil enzymatic activity at three soil depths along NBF, mixed forest, and CPF stands.
3.2. Soil Microbial Properties and Microbial Quotient
The soil microbial biomass fractions (MBC and MBN) in mixed forest and NBF stands were remarkably higher in the 0–10 cm soil layer than CPF stands. However, in the remaining two layers, they were also significantly different, but the pattern was not clear (all p < 0.001) (Figure 2a,b and Table 2). The MBC/SOC ratio (microbial quotient) was considerably higher in NBF forest in all the soil layers than in mixed forest and CPF (all p < 0.01) (Figure 2c). No specific patterns were observed in MBN/TN (Figure 2d). The interaction effect of forest types × soil depth was not significant for MBC/MBN (p = 0.08) and MBN/TN (0.06) (Table 2).
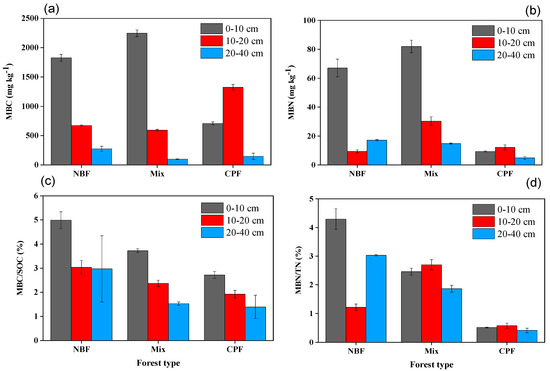
Figure 2.
(a) Soil microbial biomass carbon (MBC), (b) soil microbial biomass nitrogen (MBN), (c) soil microbial quotient (MBC/SOC), and (d) soil MBN ratio to soil total N (MBN/TN) at three soil depths along NBF, mixed forest, and CPF stands. Values are means of three replicates.
Based on a combined dataset for three forest types and three soil depths, strong positive linear relationships were observed for SOC and soil TN with MBC and MBN. The association values were: between SOC and MBC (R = 0.73, p = 0.01), and MBN (R = 0.46, p = 0.02), (Figure 3a,b), and soil TN and MBC (R = 0.65, p = 0.01), and MBN (R = 0.38, p = 0.02), (Figure 4a,b).
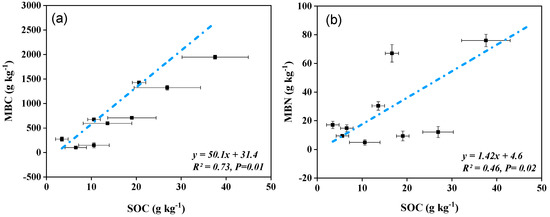
Figure 3.
A linear relationship between soil organic carbon (SOC) and (a) soil microbial biomass carbon (MBC), and (b) soil microbial biomass nitrogen (MBN) across the soil depths and sub-tropical forest types in northeastern Hunan province, south central China.
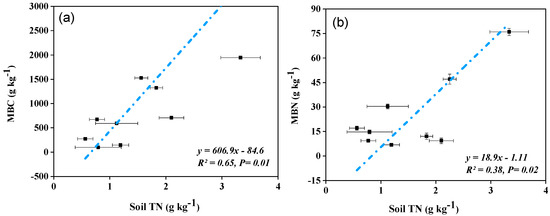
Figure 4.
A linear relationship between soil total nitrogen (TN) and (a) soil microbial biomass carbon (MBC), and (b) soil microbial biomass nitrogen (MBN) across the soil depths and sub-tropical forest types in northeastern Hunan province, south central China.
3.3. Correlations between Soil Enzymatic Responses, Chemical, and Microbial Properties
Soil pH was negatively correlated to microbial quotient and MBN/TN. MBC and MBN were positively related to C/N, DOC, and AK. Apart from the only positive correlation between MBN and urease, the other enzymes were not associated with MBC and MBN.
Soil microbial quotient revealed no correlation between any of the soil variables except pH and AK. MBN/TN was positively correlated to MBN. Urease was positively correlated with DOC, AP, MBN, and MBN/TN. Sucrase revealed no correlation with any of the soil microbial and chemical parameters. Protease was positively correlated to AP and negatively to sucrase. Catalase showed a positive correlation with sucrase and a negative correlation with soil C/N ratio and protease (Table 4).

Table 4.
Pearson’s correlation of the soil pH, soil nutrients, soil enzymatic activity, and soil microbial biomass dynamics at three soil depths along the forest stands in northeastern Hunan province, central south China.
4. Discussion and Conclusions
The soil pH was significantly different among forest types and soil depths (p < 0.001), while it was highest in the top layer of CPF. In mixed forest stands, the soil pH showed variable increasing/decreasing trends concerning the soil depth, indicating that soil depth played a minor role concerning soil pH. The highest pH in the upper layer of CPF stand could be due to the liming application. As CPF is an artificial stand, these stands are directly affected by human interference and frequent harvesting practices, and liming is one of them. Because cation exchange capacity (CEC) is generally low in the red soils of southern China, liming and application of organic matter as effective approaches are primarily used to increase these soils’ CEC and base saturation. SOC carried the basic cations and acted as the decomposers’ energy source; this led to the supply of nutrients in the soil, such as N, P, and K [35,36]. Usually, the plant litterfall affects the accumulation of SOC and nutrient turnover [37]. Almost all leaf litter of the plants falls totally on the top layer of the soil, and this leaf litter contains the majority of the organic carbon. Compared to NBF and CPF, the SOC was higher on the topmost layer in mixed forest, probably due to higher inputs and the decomposition of mixed litter biomass. Among the three forest types, a higher C/N value was observed in mixed stands than in NBF and CPF; moreover, the C/N values decreased as soil depth increased. This can be attributed to the competition between the plants and soil microbes due to more C-rich rhizodeposits [38,39]. The higher amount of DOC also explains this in mixed stands. Overall, the C/N ratio was low compared to the usual standards. The possible reason could be higher rainfall and temperature in this area. As rain falls, the C/N ratio also declines. It has also been found that, the higher the temperature, the lower the C/N ratio. When organic matter decays, C is dissipated more rapidly than N, thus bringing down the C/N ratio. When an organic substrate has a C/N ratio between 1 and 15, rapid mineralization and release of N occur, which is available for plant uptake. The lower the C/N ratio, the more rapidly N will be released into the soil for immediate plant use. Friedel et al. [40] mentioned that a higher C/N ratio represents the effect of competition between the soil microbes and plants. A higher C/N ratio also represents the activation of soil microbes by carbon-rich deposits in the soil with increased demand of N. Consequently, N becomes immobilized in the microbial biomass. Similarly, when the C/N ratio lowers, there is a great chance and the potential to remove N from microbial biomass.
In this study, protease and sucrase activity were highly linked with forest type and soil depth change. Higher amounts of SOC and N in the topsoil could explain the significant difference in protease activity compared to the other two layers [41]. Soil sucrase enzyme is linked to the biomass of soil microbiota [42]; thus, variations in SOC and SOM can also alter the contents of sucrase enzymes. These findings were also supported by Zhang et al. [43], who observed that soil sucrase activity was significantly correlated with changes in vegetation type and soil quality parameters. Urease indicates the availability of N in various land use systems and habitats [44]. It is evident from the results that urease activity was highest in mixed stands except for a slight difference in NBF and mixed forest stands. Total N content was also highest in mixed forest stand, probably due to the increased activity of the urease enzyme; these results are per Ref. [45]. For cell formation, plants require a great deal of N; therefore, soil urease hydrolysis N activity increased to satisfy the absorption of soil-accessible N. Simultaneously, soil urease is active in urea hydrolysis, with extracellular enzymes accounting for the majority of the enzyme activity. These acts also increased the surface area of microbes in contact with active organic compounds and the energy sources needed for microbial metabolism. Catalase’s primary job is to degrade organic matter into a form that plants can use. In this study, catalase enzyme activity was highest in 10–20 cm soil depth of NBF forest type and lowest in 10–20 cm soil depth of CBF forest type among all the forest types and soil profiles. Due to the restricted supply of oxygen in the soil during cold weather, soil catalase activity was enhanced to a certain extent in other forest types and soil profiles to minimize the influence of soil oxygen deprivation on aerobic microorganisms [46].
Many factors have been suggested to explain the effects of vegetation type on microbial biomass in soils. For example, soil processes, stand conditions, differences in the quantity and quality of substrate inputs via varying litter and root types and associated nutrient specificity, and different management regimes and depositions can be crucial drivers to influence soil microbial biomass. The study showed that all stand types differ significantly regarding soil microbial biomass fractions. MBC and MBN were substantially lower in CPF stands than in NBF and mixed stands. This indicates that NBF and mixed stands would be more important in sustaining soil fertility. Many factors have an active contribution to microbial biomass in forest ecosystems. For instance, the quality and quantity of substrate via leaf and root litter and specific nutrients can be the most important drivers of soil microbial biomass [47]. Besides this, SOC also has a significant influence on soil microbial biomass. SOC and soil microbial mass have a directly proportional relationship [48]. Thus, a higher amount of MBC and MBN in NBF and mixed stands compared to CPF can mainly be due to more readily available SOC in these stands. This is also supported by the significant correlation of SOC with MBC and MBN [27]. A reduction in the SOC in CPF may be due to poor litter quality and recalcitrant compounds. These factors led to a decreased decomposition rate due to slow transformation of organic matter into mineral soil particles. MBC and SOC are well-established and widely accepted microbial quotients in soil science. Monitoring changes in microbial quotient influenced by various factors allows to select favorable systems, contributing to sustainable agricultural practices. It is commonly observed that a higher microbial quotient in an acidic soil medium represents stress in the forest microbial community [49]. As a consequence, the production of biomass is also decreased because a majority of the C is used in the process of respiration by the microbial communities.
MBC and MBN were positively correlated with C/N, DOC, and AK. The highest C/N ratio, DOC, and AN in the topsoil in each forest type further indicate the close relationship of microbial biomass with C and N. Moreover, a positive and significant correlation of MBN with urease was as per expectations. Urease is vital in indicating the available N in the natural forest ecosystem. Similar results have been shown in previous studies in Refs. [50,51]. Soil enzymatic activity often has a negative relationship with soil nutrients produced by enzymes and a positive relationship with the accessibility of substrates catalyzed by enzymes [52,53]. The most appropriate explanation can be the decomposition rate of SOM. At the same time litterfall can play a huge part in all this mechanism [54,55].
The soil’s biological properties continually play a positive role in preserving soil health. However, we did not observe significant changes in most enzymes in any of the treatments, probably due to the decrease in soil microbial biomass as the soil depth increased. The soil C/N ratio is a significant indicator because microorganisms require a good balance of C/N ratio to remain active. The C/N ratio can be regulated by choosing suitable combinations of organic materials and adding bulking agents to ensure a final ratio within the optimum range. Although our research provided some interesting results, this study was only conducted in rural forest ecosystems. In contrast, suburban and urban forest ecosystems’ soils are more exposed to anthropogenic activities, which leaves a research gap. Therefore, we advise that future research should include different research methods (both lab-based and field-based experiments) and examine soil microbial patterns, diversity, and community composition; moreover, it should consider the influence of various biotic and abiotic factors on the microbial patterns and their responsive functions in diverse rural, suburban, and urban forest ecosystems. Different research methods will validate each other and provide a strong basis for comparisons.
Author Contributions
T.H.F., X.C., A.S., M.H.U.R., U.K., and W.Y.: Conceptualization, Methodology, Data curation, Formal analysis, Writing—original draft, review & editing, Project administration, Supervision, Resources, Funding acquisition. T.H.F., X.C., U.K., M.A., A.S.A., W.Y., and B.R.: Methodology, Software, Validation, Data curation, Writing—review & editing. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was financially supported by research funding from the Central South University of Forestry and Technology and the Hunan province educational finance department (No.70702-45200003). The authors would like to acknowledge Taif University Researchers Supporting project number (TURSP 2020/257), Taif University, Saudi Arabia.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank Xiang Zhang and Arfien Sayman for their help in conducting fieldwork.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Pertile, M.; Antunes, J.E.L.; Araujo, F.F.; Mendes, L.W.; Van den Brink, P.J.; Araujo, A.S.F. Responses of soil microbial biomass and enzyme activity to herbicides imazethapyr and flumioxazin. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 7694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farooq, T.H.; Ma, X.; Rashid, M.H.U.; Wu, W.; Xu, J.; Tarin, M.W.K.; He, Z.; Wu, P. Impact of stand density on soil quality in Chinese Fir (Cunninghamia Lanceolata) monoculture. Appl. Ecol. Environ. Res. 2019, 17, 3553–3566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Y.; Li, B.; Huang, Z.; Zhang, H.; Wu, X.; Farooq, T.H.; Wu, P.; Li, M.; Ma, X. Characteristics and driving factors of rhizosphere bacterial communities of Chinese Fir Provenances. Forests 2021, 12, 1362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durán, J.; Morse, J.L.; Groffman, P.M.; Campbell, J.L.; Christenson, L.M.; Driscoll, C.T.; Fahey, T.J.; Fisk, M.C.; Mitchell, M.J.; Templer, P.H. Winter climate change affects growing-season soil microbial biomass and activity in northern hardwood forests. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2014, 20, 3568–3577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaschuk, G.; Alberton, O.; Hungria, M. Three decades of soil microbial biomass studies in Brazilian ecosystems: Lessons learned about soil quality and indications for improving sustainability. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2010, 42, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDaniel, M.D.; Grandy, A.S. Soil microbial biomass and function are altered by 12 years of crop rotation. Soil 2016, 2, 583–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moorhead, D.L.; Rinkes, Z.L.; Sinsabaugh, R.L.; Weintraub, M.N. Dynamic relationships between microbial biomass, respiration, inorganic nutrients and enzyme activities: Informing enzyme-based decomposition models. Front. Microbiol. 2013, 4, 223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mgelwa, A.S.; Hu, Y.-L.; Xu, W.-B.; Ge, Z.-Q.; Yu, T.-W. Soil carbon and nitrogen availability are key determinants of soil microbial biomass and respiration in forests along urbanized rivers of southern China. Urban For. Urban Green. 2019, 43, 126351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antisari, L.V.; Carbone, S.; Gatti, A.; Vianello, G.; Nannipieri, P. Toxicity of metal oxide (CeO2, Fe3O4, SnO2) engineered nanoparticles on soil microbial biomass and their distribution in soil. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2013, 60, 87–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pose-Juan, E.; Igual, J.M.; Sánchez-Martín, M.J.; Rodríguez-Cruz, M.S. Influence of herbicide triasulfuron on soil microbial community in an unamended soil and a soil amended with organic residues. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, J.S.; Gupta, V.K. Soil microbial biomass: A key soil driver in management of ecosystem functioning. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 634, 497–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, T.; Wang, Y.; Hui, D.; Jing, X.; Feng, W. Soil properties rather than climate and ecosystem type control the vertical variations of soil organic carbon, microbial carbon, and microbial quotient. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2020, 148, 107905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahu, N.; Vasu, D.; Sahu, A.; Lal, N.; Singh, S.K. Strength of microbes in nutrient cycling: A key to soil health. In Agriculturally Important Microbes for Sustainable Agriculture; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2017; pp. 69–86. [Google Scholar]
- Sherene, T. Role of soil enzymes in nutrient transformation: A review. Bio Bull. 2017, 3, 109–131. [Google Scholar]
- Farooq, T.H.; Kumar, U.; Mo, J.; Shakoor, A.; Wang, J.; Rashid, M.H.U.; Tufail, M.A.; Chen, X.; Yan, W. Intercropping of peanut–tea enhances soil enzymatic activity and soil nutrient status at different soil profiles in subtropical southern China. Plants 2021, 10, 881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Decina, S.M.; Hutyra, L.R.; Gately, C.K.; Getson, J.M.; Reinmann, A.B.; Gianotti, A.G.S.; Templer, P.H. Soil respiration contributes substantially to urban carbon fluxes in the greater Boston area. Environ. Pollut. 2016, 212, 433–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarzhanov, D.A.; Vasenev, V.I.; Vasenev, I.I.; Sotnikova, Y.L.; Ryzhkov, O.V.; Morin, T. Carbon stocks and CO2 emissions of urban and natural soils in Central Chernozemic region of Russia. Catena 2017, 158, 131–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Treseder, K.K. Nitrogen additions and microbial biomass: A meta-analysis of ecosystem studies. Ecol. Lett. 2008, 11, 1111–1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DeForest, J.L.; Zak, D.R.; Pregitzer, K.S.; Burton, A.J. Atmospheric nitrate deposition and the microbial degradation of cellobiose and vanillin in a northern hardwood forest. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2004, 36, 965–971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koerner, B.A.; Klopatek, J.M. Carbon fluxes and nitrogen availability along an urban–rural gradient in a desert landscape. Urban Ecosyst. 2010, 13, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorenz, K.; Kandeler, E. Microbial biomass activities in urban soils in two consecutive years. J. Plant Nutr. Soil Sci. 2006, 169, 799–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sushko, S.; Ananyeva, N.; Ivashchenko, K.; Vasenev, V.; Kudeyarov, V. Soil CO2 emission, microbial biomass, and microbial respiration of woody and grassy areas in Moscow (Russia). J. Soils Sediments 2019, 19, 3217–3225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farooq, T.H.; Yan, W.; Rashid, M.H.U.; Tigabu, M.; Gilani, M.M.; Zou, X.H.; Wu, P.F. Chinese fir (Cunninghamia Lanceolata) a green gold of China with continues decline in its productivity over the successive rotations: A review. Appl. Ecol. Environ. Res. 2019, 17, 11055–11067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farooq, T.H.; Shakoor, A.; Wu, X.; Li, Y.; Rashid, M.H.U.; Zhang, X.; Gilani, M.M.; Kumar, U.; Chen, X.; Yan, W. Perspectives of plantation forests in the sustainable forest development of China. iFor.-Biogeosci. For. 2021, 14, 166–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farooq, T.H.; Wu, W.; Tigabu, M.; Ma, X.; He, Z.; Rashid, M.H.U.; Gilani, M.M.; Wu, P. Growth, biomass production and root development of Chinese fir in relation to initial planting density. Forests 2019, 10, 236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Wang, Q.; Wang, S.; Yu, X. Characteristics of soil microbial biomass carbon and nitrogen and their relationships with soil nutrients in Cunninghamia lanceolata plantations. Ying Yong Sheng Tai Xue Bao J. Appl. Ecol. 2006, 17, 2292–2296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, K.; Zhu, J.J.; Yan, Q.L.; Sun, O.J. Changes in soil P chemistry as affected by conversion of natural secondary forests to larch plantations. For. Ecol. Manag. 2010, 260, 422–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burton, J.; Chen, C.; Xu, Z.; Ghadiri, H. Gross nitrogen transformations in adjacent native and plantation forests of subtropical Australia. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2007, 39, 426–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farooq, T.H.; Xincheng, X.; Shakoor, A.; Rashid, M.H.U.; Bashir, M.F.; Nawaz, M.F.; Kumar, U.; Shahzad, S.M.; Yan, W. Spatial distribution of carbon dynamics and nutrient enrichment capacity in different layers and tree tissues of Castanopsis eyeri natural forest ecosystem. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 10250–10262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farooq, T.H.; Chen, X.; Shakoor, A.; Li, Y.; Wang, J.; Rashid, M.H.U.; Kumar, U.; Yan, W. Unraveling the influence of land-use change on δ13C, δ15N, and soil nutritional status in coniferous, broadleaved, and mixed forests in southern china: A field investigation. Plants 2021, 10, 1499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paudel, B.R.; Udawatta, R.P.; Anderson, S.H. Agroforestry and grass buffer effects on soil quality parameters for grazed pasture and row-crop systems. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2011, 48, 125–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Z.; He, Z.; Huang, Z.; Fan, S.; Yu, Z.; Wang, M.; Zhou, X.; Fang, C. Effects of harvest residue management on soil carbon and nitrogen processes in a Chinese fir plantation. For. Ecol. Manag. 2014, 326, 163–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Li, T.; Li, F.; Lemcoff, J.H.; Cohen, S. Fertilization regulates soil enzymatic activity and fertility dynamics in a cucumber field. Sci. Hortic. 2008, 116, 21–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vance, E.D.; Brookes, P.C.; Jenkinson, D.S. An extraction method for measuring microbial biomass C. Soil Biol. Biochem. 1987, 19, 703–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swift, M.J.; Heal, O.W.; Anderson, J.M.; Anderson, J.M. Decomposition in Terrestrial Ecosystems; University of California Press: Berkeley, CA, USA, 1979; Volume 5, ISBN 0520040015. [Google Scholar]
- Haynes, R.J. Labile organic matter fractions as centralcomponents of the quality of agricultural soils: Anoverview. Adv. Agron. 2005, 5, 221–268. [Google Scholar]
- Xiong, Y.; D’Atri, J.J.; Fu, S.; Xia, H.; Seastedt, T.R. Rapid soil organic matter loss from forest dieback in a subalpine coniferous ecosystem. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2011, 43, 2450–2456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuzyakov, Y.; Friedel, J.K.; Stahr, K. Review of mechanisms and quantification of priming effects. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2000, 32, 1485–1498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allard, V.; Robin, C.; Newton, P.C.D.; Lieffering, M.; Soussana, J.F. Short and long-term effects of elevated CO2 on Lolium perenne rhizodeposition and its consequences on soil organic matter turnover and plant N yield. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2006, 38, 1178–1187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedel, J.K.; Langer, T.; Siebe, C.; Stahr, K. Effects of long-term waste water irrigation on soil organic matter, soil microbial biomass and its activities in central Mexico. Biol. Fertil. Soils 2000, 31, 414–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sardans, J.; Peñuelas, J. Drought decreases soil enzyme activity in a Mediterranean Quercus ilex L. forest. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2005, 37, 455–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou-Long, J.; Zheng, L.; Shu-Duan, L.; An-Ding, X.; Chao, Y.; Yan, Z.; Guo-Shun, L.; Xie-Feng, Y. Effects of consecutive turnover of green manure and N fertilizer on soil microbial biomass and enzyme activity in tobacco-planted field. Indian J. Agric. Res. 2013, 47, 185–191. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Cui, D.; Yang, H.; Kasim, N. Differences of soil enzyme activities and its influencing factors under different flooding conditions in Ili Valley, Xinjiang. PeerJ 2020, 8, e8531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verhoef, H.A.; Brussaard, L. Decomposition and nitrogen mineralization in natural and agroecosystems: The contribution of soil animals. Biogeochemistry 1990, 11, 175–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Wu, J.; Li, G.; Yan, L. Changes in soil carbon fractions and enzyme activities under different vegetation types of the northern Loess Plateau. Ecol. Evol. 2020, 10, 12211–12223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, F.; Peng, X.; Zhao, P.; Yuan, J.; Zhong, C.; Cheng, Y.; Cui, C.; Zhang, S. Soil microbial biomass, basal respiration and enzyme activity of main forest types in the Qinling Mountains. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e67353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fanin, N.; Moorhead, D.; Bertrand, I. Eco-enzymatic stoichiometry and enzymatic vectors reveal differential C, N, P dynamics in decaying litter along a land-use gradient. Biogeochemistry 2016, 129, 21–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradford, M.A.; Davies, C.A.; Frey, S.D.; Maddox, T.R.; Melillo, J.M.; Mohan, J.E.; Reynolds, J.F.; Treseder, K.K.; Wallenstein, M.D. Thermal adaptation of soil microbial respiration to elevated temperature. Ecol. Lett. 2008, 11, 1316–1327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, H.; He, Z.L.; Wilson, M.; Campbell, C.D. Microbial biomass and community structure in a sequence of soils with increasing fertility and changing land use. Microb. Ecol. 2000, 40, 223–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Liu, G.; Xue, S.; Song, Z. Geoderma Rhizosphere soil microbial activity under different vegetation types on the Loess. Geoderma 2011, 161, 115–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.; Xiao, Q.; Cheng, H.; Shi, B.; Shen, Y.; Li, S. Seasonal dynamics of soil microbial activity after biochar addition in a dryland maize field in North-Western China. Ecol. Eng. 2017, 104, 141–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, W. Agricultural and ecological significance of soil enzymes: Soil carbon sequestration and nutrient cycling. In Soil Enzymology; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2010; pp. 43–60. [Google Scholar]
- Amin, B.A.Z.; Chabbert, B.; Moorhead, D.; Bertrand, I. Impact of fine litter chemistry on lignocellulolytic enzyme efficiency during decomposition of maize leaf and root in soil. Biogeochemistry 2014, 117, 169–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, W.; Farooq, T.H.; Chen, Y.; Wang, W.; Shabbir, R.; Kumar, U.; Riaz, M.U.; Alotaibi, S.S.; Peng, Y.; Chen, X. Soil Nitrogen Transformation Process Influenced by Litterfall Manipulation in Two Subtropical Forest Types. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 923410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farooq, T.H.; Li, Z.; Yan, W.; Shakoor, A.; Kumar, U.; Shabbir, R.; Peng, Y.; Alotaibi, S.; Wróbel, J.; Kalaji, H.M. Variations in litterfall dynamics, C: N: P stoichiometry and associated nutrient return in pure and mixed stands of Camphor tree and Masson pine forests in Subtropical China. Front. Environ. Sci. 2022, 10, 903039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).