Hydraulic Water Redistribution by Silver Fir (Abies alba Mill.) Occurring under Severe Soil Drought
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
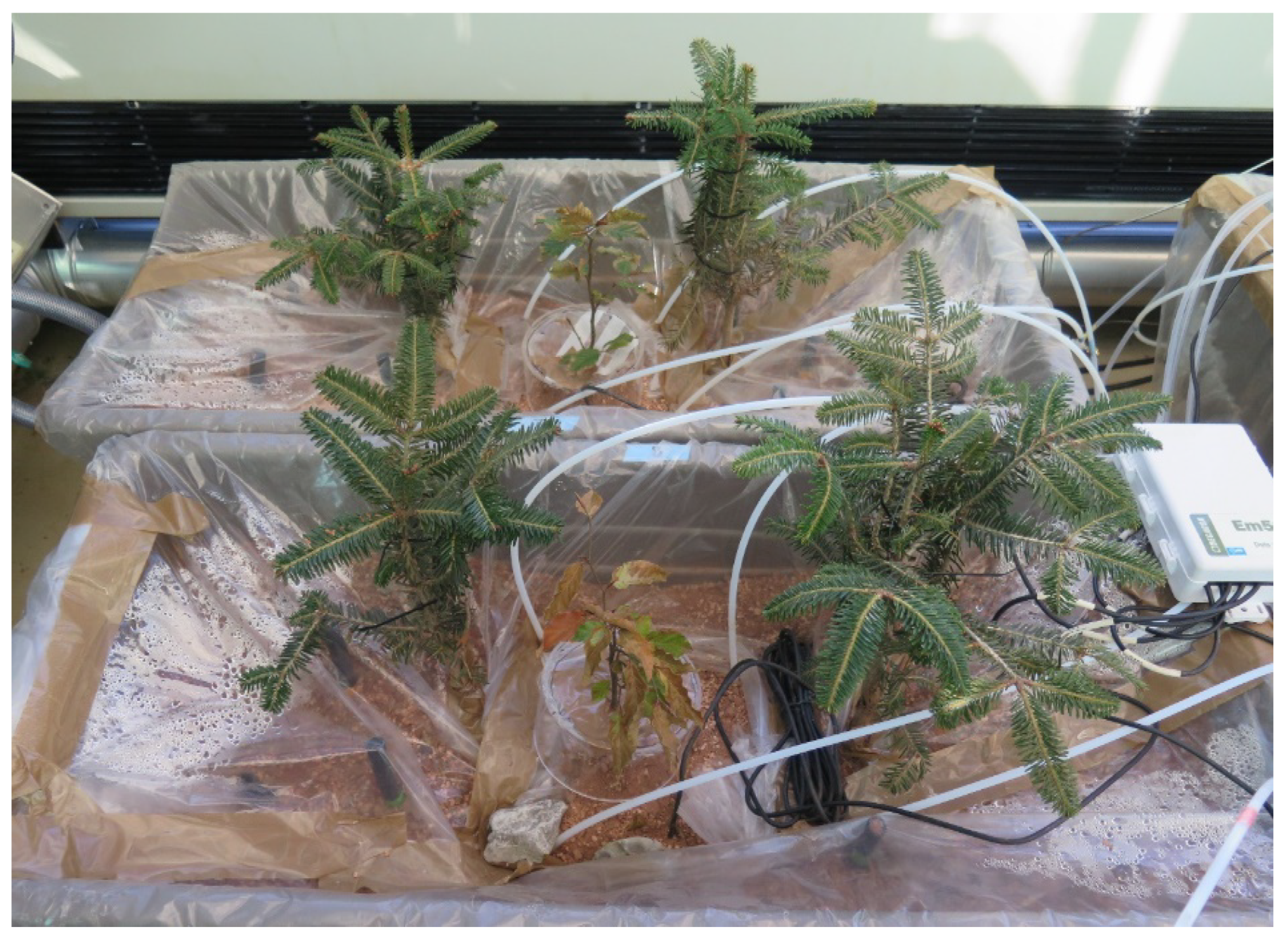
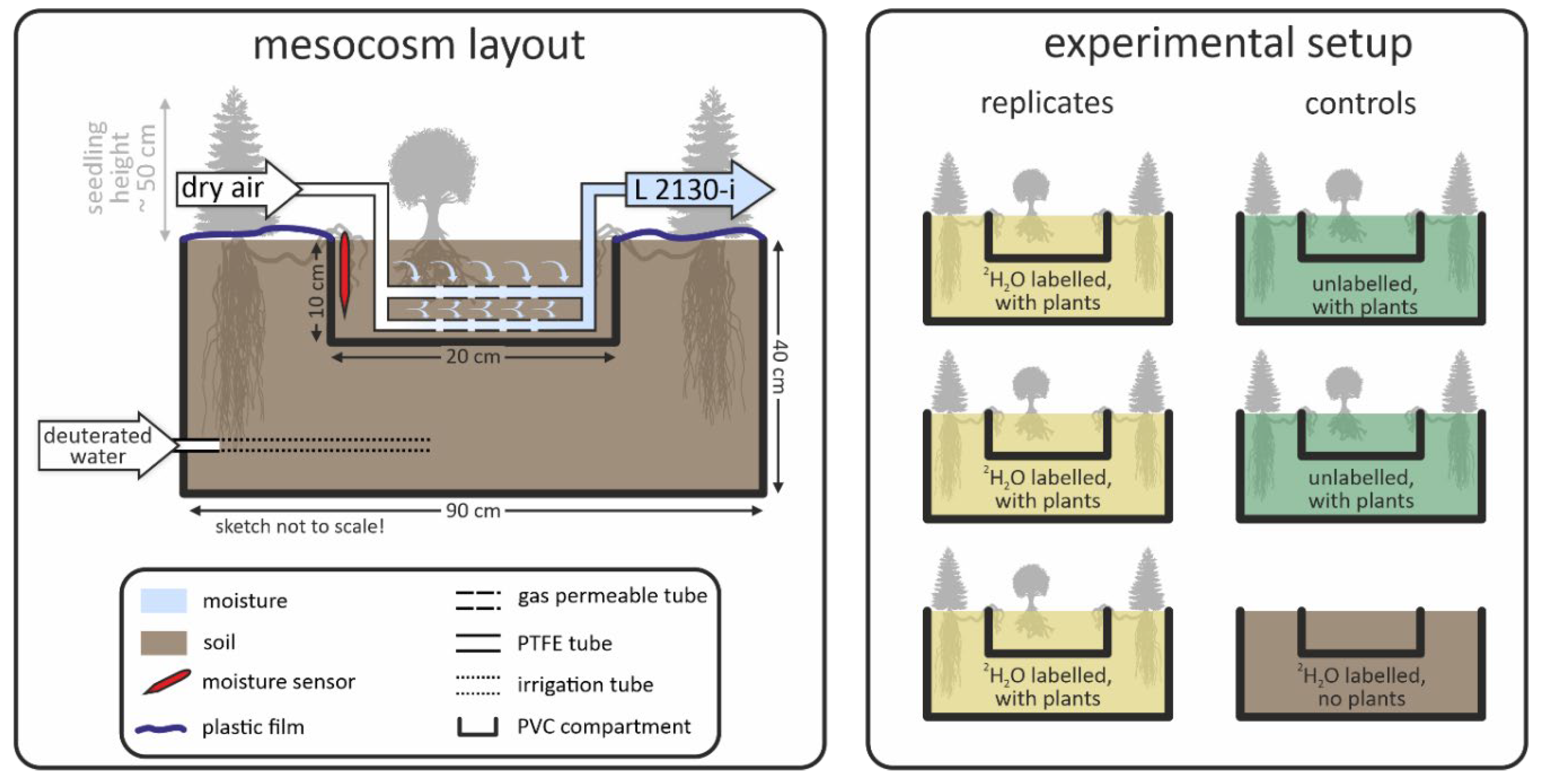
2.1. Mesocosm Setup
2.2. Environmental Parameters
2.3. Soil-Water Potential
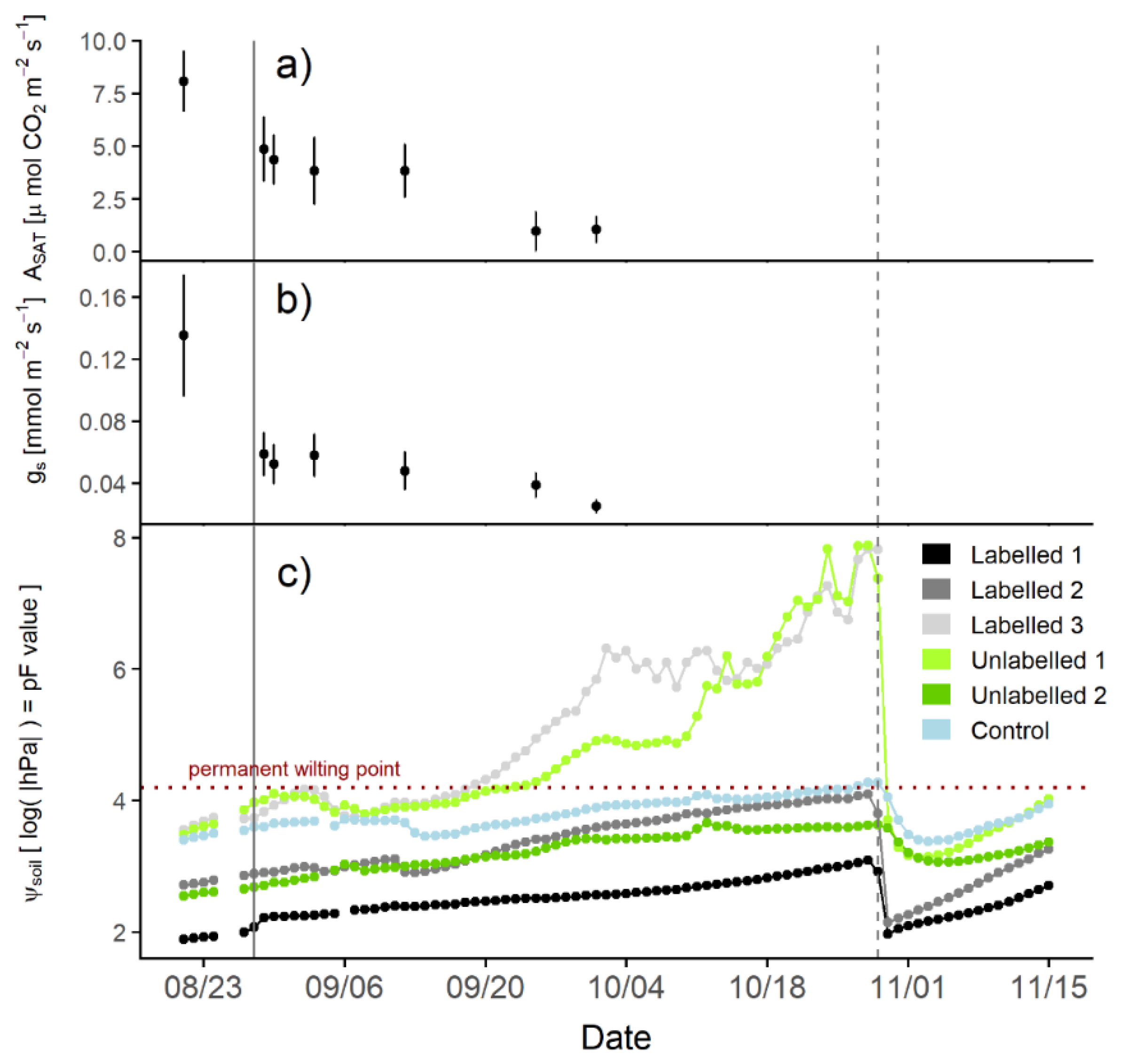
2.4. Leaf–Gas Exchange Measurements
2.5. Hydraulic-Redistribution Experiment
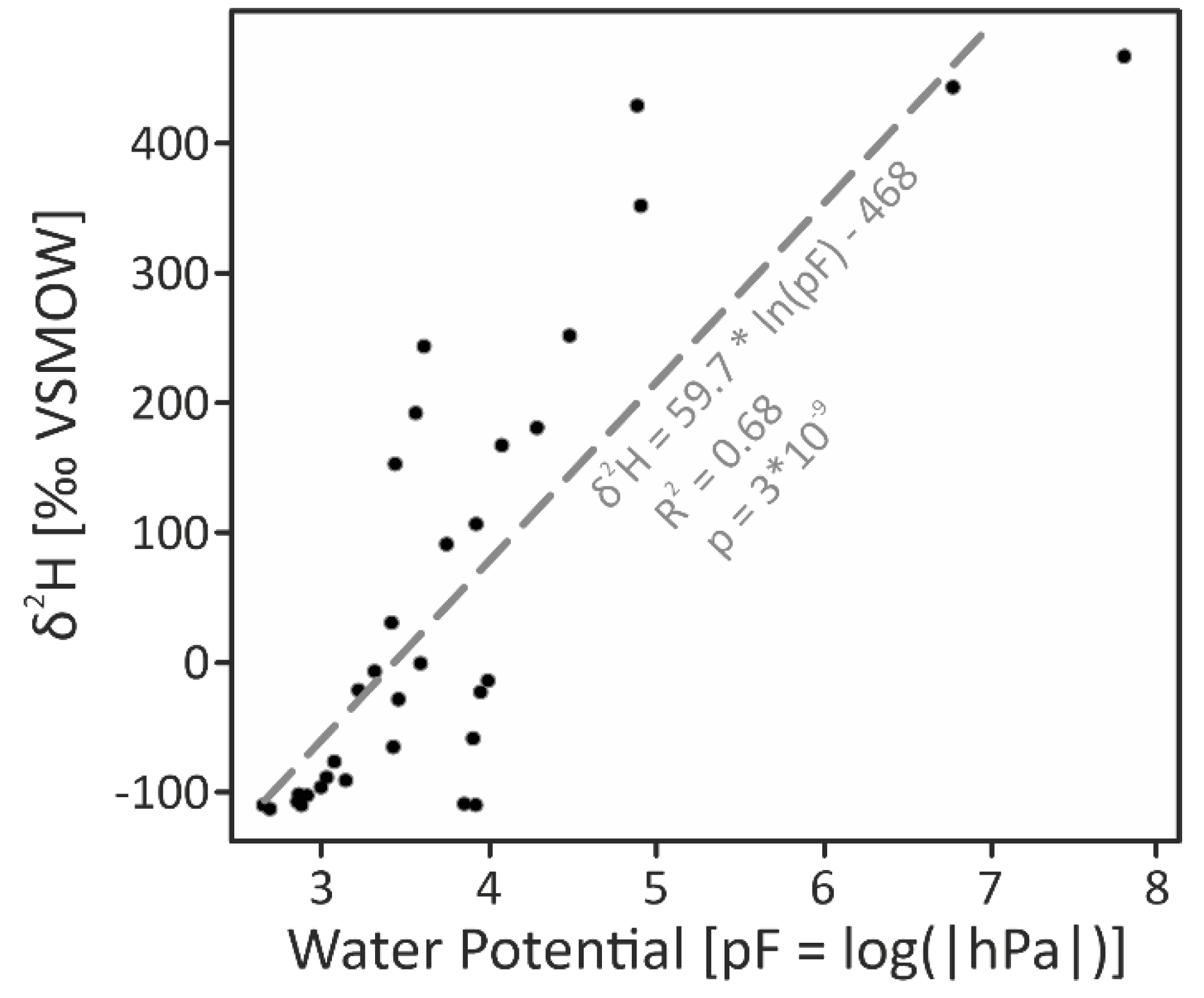
2.6. Deuterated-Water Tracing
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lee, E.; Kumar, P.; Barron-Gafford, G.A.; Hendryx, S.M.; Sanchez-Cañete, E.P.; Minor, R.L.; Colella, T.; Scott, R.L. Impact of Hydraulic Redistribution on Multispecies Vegetation Water Use in a Semiarid Savanna Ecosystem: An Experimental and Modeling Synthesis. Water Resour. Res. 2018, 54, 4009–4027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leffler, A.J.; Peek, M.S.; Ryel, R.J.; Ivans, C.Y.; Caldwell, M.M. Hydraulic Redistribution Through the Root Systems of Senesced Plants. Ecology. 2005, 86, 633–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caldwell, M.M.; Richards, J.H. Hydraulic lift: water efflux from upper roots improves effectiveness of water uptake by deep roots. Oecologia. 1989, 79, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Querejeta, J.I.; Egerton-Warburton, L.M.; Allen, M.F. Direct nocturnal water transfer from oaks to their mycorrhizal symbionts during severe soil drying. Oecologia. 2003, 134, 55–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snyder, K.A.; Richards, J.H.; Donovan, L.A. Night-time conductance in C3 and C4 species: do plants lose water at night? J. Exp. Bot. 2003, 54, 861–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakuratani, T.; Aoe, T.; Higuchi, H. Reverse flow in roots of Sesbania rostrata measured using the constant power heat balance method. Plant Cell Environ. 1999, 22, 1153–1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sekiya, N.; Araki, H.; Yano, K. Applying hydraulic lift in an agroecosystem: forage plants with shoots removed supply water to neighboring vegetable crops. Plant Soil. 2011, 341, 39–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burgess, S.S.O.; Bleby, T.M. Redistribution of soil water by lateral roots mediated by stem tissues. J. Exp. Bot. 2006, 57, 3283–3291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burgess, S.S.O.; Adams, M.A.; Turner, N.C.; Ong, C.K. The redistribution of soil water by tree root systems. Oecologia. 1998, 115, 306–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hultine, K.R.; Cable, W.L.; Burgess, S.S.O.; WILLIAMS, D.G. Hydraulic redistribution by deep roots of a Chihuahuan Desert phreatophyte. Tree Physiol. 2003, 23, 353–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nadezhdina, N.; David, T.S.; David, J.S.; Ferreira, M.I.; Dohnal, M.; Tesař, M.; Gartner, K.; Leitgeb, E.; Nadezhdin, V.; Cermak, J.; et al. Trees never rest: the multiple facets of hydraulic redistribution. Ecohydrol. 2010, 3, 431–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horton, J.L.; Hart, S.C. Hydraulic lift: A potentially important ecosystem process. Trends Ecol. Evolution. 1998, 13, 232–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neumann, R.B.; Cardon, Z.G. The magnitude of hydraulic redistribution by plant roots: a review and synthesis of empirical and modeling studies. New Phytol. 2012, 194, 337–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sardans, J.; Peñuelas, J. Hydraulic redistribution by plants and nutrient stoichiometry: Shifts under global change. Ecohydrol. 2014, 7, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, K.; D'Odorico, P. From facilitative to competitive interactions between woody plants and plants with crassulacean acid metabolism (CAM): The role of hydraulic descent. Ecohydrol. 2017, 10, e1799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scholz, F.G.; Bucci, S.J.; Hoffmann, W.A.; Meinzer, F.C.; Goldstein, G. Hydraulic lift in a Neotropical savanna: Experimental manipulation and model simulations. Agr. Forest Meteorol. 2010, 150, 629–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bleby, T.M.; McElrone, A.J.; Jackson, R.B. Water uptake and hydraulic redistribution across large woody root systems to 20 m depth. Plant Cell Environ. 2010, 33, 2132–2148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bauerle, T.L.; Richards, J.H.; Smart, D.R.; Eissenstat, D.M. Importance of internal hydraulic redistribution for prolonging the lifespan of roots in dry soil. Plant Cell Environ. 2008, 31, 177–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, R.L.; Cable, W.L.; Hultine, K.R. The ecohydrologic significance of hydraulic redistribution in a semiarid savanna. Water Resour. Res. 2008, 44, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardon, Z.G.; Stark, J.M.; Herron, P.M.; Rasmussen, J.A. Sagebrush carrying out hydraulic lift enhances surface soil nitrogen cycling and nitrogen uptake into inflorescences. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 18988–18993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCulley, R.L.; Jobbágy, E.G.; Pockman, W.T.; Jackson, R.B. Nutrient uptake as a contributing explanation for deep rooting in arid and semi-arid ecosystems. Oecologia. 2004, 141, 620–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quijano, J.C.; Kumar, P.; Drewry, D.T. Passive regulation of soil biogeochemical cycling by root water transport. Water Resour. Res. 2013, 49, 3729–3746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Jia, B.; Xie, Z. Impacts of hydraulic redistribution on eco-hydrological cycles: A case study over the Amazon basin. Sci. China Earth Sci. 2018, 61, 1330–1340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corak, S.J.; Blevins, D.G.; Pallardy, S.G. Water Transfer in an Alfalfa/Maize Association: Survival of Maize during Drought. Plant Physiol. 1987, 84, 582–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirota, I.; Sakuratani, T.; Sato, T.; Higuchi, H.; Nawata, E. A split-root apparatus for examining the effects of hydraulic lift by trees on the water status of neighbouring crops. Agroforestry Systems. 2004, 60, 181–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smart, D.R.; Carlisle, E.; Goebel, M.; Nunez, B.A. Transverse hydraulic redistribution by a grapevine. Plant Cell Environ. 2005, 28, 157–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hafner, B.D.; Tomasella, M.; Häberle, K.-H.; Goebel, M.; Matyssek, R.; Grams, T.E.E. Hydraulic redistribution under moderate drought among English oak, European beech and Norway spruce determined by deuterium isotope labeling in a split-root experiment. Tree Physiol. 2017, 37, 950–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreira, M.Z.; Scholz, F.G.; Bucci, S.J.; Sternberg, L.S.; Goldstein, G.; Meinzer, F.C.; Franco, A.C. Hydraulic lift in a neotropical savanna. Functional Ecology. 2003, 17, 573–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, D.M.; Jackson, N.A.; Roberts, J.M.; Ong, C.K. Reverse flow of sap in tree roots and downward siphoning of water by Grevillea robusta. Functional Ecology. 1999, 13, 256–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emerman, S.H.; Dawson, T.E. Hydraulic lift and its influence on the water content of the rhizosphere: an example from sugar maple, Acer saccharum. Oecologia. 1996, 108, 273–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prieto, I.; Armas, C.; Pugnaire, F.I. Hydraulic lift promotes selective root foraging in nutrient-rich soil patches. Functional Plant Biol. 2012, 39, 804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ludwig, F.; Dawson, T.E.; Kroon, H.; Berendse, F.; Prins, H.H.T. Hydraulic lift in Acacia tortilis trees on an East African savanna. Oecologia. 2003, 134, 293–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, K.; D'Odorico, P. Hydraulic lift as a determinant of tree-grass coexistence on savannas. New Phytol. 2015, 207, 1038–1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ogle, K.; Lucas, R.W.; Bentley, L.P.; Cable, J.M.; Barron-Gafford, G.A.; Griffith, A.; Ignace, D.; Jenerette, G.D.; Tyler, A.; Huxman, T.E.; et al. Differential daytime and night-time stomatal behavior in plants from North American deserts. New Phytol. 2012, 194, 464–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, T.; Feng, Q.; Si, J.; Xi, H.; Li, Z.; Chen, A. Hydraulic redistribution of soil water by roots of two desert riparian phreatophytes in northwest China’s extremely arid region. Plant Soil. 2013, 372, 297–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, T.; Feng, Q.; Si, J.; Zhang, X.; Alec, D.; Zhao, C. Evidences and magnitude of nighttime transpiration derived from Populus euphratica in the extreme arid region of China. J. Plant Biol. 2016, 59, 648–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hultine, K.R.; Scott, R.L.; Cable, W.L.; GOODRICH, D.C.; WILLIAMS, D.G. Hydraulic redistribution by a dominant, warm-desert phreatophyte: seasonal patterns and response to precipitation pulses. Functional Ecology. 2004, 18, 530–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hawkins, H.-J.; Hettasch, H.; West, A.G.; Cramer, M.D. Hydraulic redistribution by Protea ‘Sylvia’ (Proteaceae) facilitates soil water replenishment and water acquisition by an understorey grass and shrub. Functional Plant Biol. 2009, 36, 752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- David, T.S.; Pinto, C.A.; Nadezhdina, N.; Kurz-Besson, C.; Henriques, M.O.; Quilhó, T.; Cermak, J.; Chaves, M.M.; Pereira, J.S.; David, J.S. Root functioning, tree water use and hydraulic redistribution in Quercus suber trees: A modeling approach based on root sap flow. Forest Ecology and Management. 2013, 307, 136–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meinzer, F.C.; Brooks, J.R.; Bucci, S.; Goldstein, G.; Scholz, F.G.; Warren, J.M. Converging patterns of uptake and hydraulic redistribution of soil water in contrasting woody vegetation types. Tree Physiol. 2004, 24, 919–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, R.S.; Dawson, T.E.; Burgess, S.S.O.; Nepstad, D.C. Hydraulic redistribution in three Amazonian trees. Oecologia. 2005, 145, 354–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scholz, F.G.; Bucci, S.J.; Meinzer, F.C.; Goldstein, G. Maintenance of Root Function in Tropical Woody Species During Droughts: Hydraulic Redistribution, Refilling of Embolized Vessels, and Facilitation Between Plants. In Tropical Tree Physiology-Adaptations and Responses in a Changing Environment; Santiago, L.S., Ed.; Springer International Publish: Cham, Switzerland, 2016; Volume 6, ISBN 978-3-319-27420-1. [Google Scholar]
- IPCC. Climate Change 2014. The physical science basis: Working Group I contribution to the Fifth assessment report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change; Cambidge University Press: New York, NY, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Green, S.R.; Clothier, B.E. Root water uptake by kiwifruit vines following partial wetting of the root zone. Plant Soil. 1995, 173, 317–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, D.M.; Allen, S.J. Measurement of sap flow in plant stems. J. Exp. Bot. 1996, 47, 1833–1844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lott, J.E.; Khan, A.A.H.; Ong, C.K.; Black, C.R. Sap flow measurements of lateral tree roots in agroforestry systems. Tree Physiol. 1996, 16, 995–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, A.A.H.; Ong, C.K. Correction of Systematic Errors in Estimates of Transpiration Obtained Using a Constant Temperature Heat Balance Technique. Ex. Agric. 1995, 31, 461–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, T.; Feng, Q.; Si, J.; Mitchell, P.J.; Forster, M.A.; Zhang, X.; Zhao, C. Depressed hydraulic redistribution of roots more by stem refilling than by nocturnal transpiration for Populus euphratica Oliv. in situ measurement. Ecol. Evol. 2018, 8, 2607–2616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dawson, T.E. Hydraulic lift and water use by plants: implications for water balance, performance and plant-plant interactions. Oecologia. 1993, 95, 565–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dawson, T.E.; Pate, J.S. Seasonal water uptake and movement in root systems of Australian phraeatophytic plants of dimorphic root morphology: a stable isotope investigation. Oecologia. 1996, 107, 13–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zapater, M.; Hossann, C.; Bréda, N.; Bréchet, C.; Bonal, D.; Granier, A. Evidence of hydraulic lift in a young beech and oak mixed forest using 18O soil water labelling. Trees. 2011, 25, 885–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nadezhdina, N.; Cermák, J.; Gaspárek, J.; Nadezhdin, V.; Prax, A. Vertical and horizontal water redistribution in Norway spruce (Picea abies) roots in the Moravian Upland. Tree Physiol. 2006, 26, 1277–1288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Nadezhdina, N.; Steppe, K.; de Pauw, D.J.W.; Bequet, R.; Cermak, J.; Ceulemans, R. Stem-mediated hydraulic redistribution in large roots on opposing sides of a Douglas-fir tree following localized irrigation. New Phytol. 2009, 184, 932–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brooks, J.R.; Meinzer, F.C.; Warren, J.M.; Domec, J.-C.; Coulombe, R. Hydraulic redistribution in a Douglas-fir forest: lessons from system manipulations. Plant Cell Environ. 2006, 29, 138–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brooks, J.R.; Meinzer, F.C.; Coulombe, R.; Gregg, J. Hydraulic redistribution of soil water during summer drought in two contrasting Pacific Northwest coniferous forests. Tree Physiol. 2002, 22, 1107–1117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fotelli, M.N.; Nahm, M.; Radoglou, K.; Rennenberg, H.; Halyvopoulos, G.; Matzarakis, A. Seasonal and interannual ecophysiological responses of beech (Fagus sylvatica) at its south-eastern distribution limit in Europe. Forest Ecology and Management. 2009, 257, 1157–1164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simon, J.; Dannenmann, M.; Pena, R.; Gessler, A.; Rennenberg, H. Nitrogen nutrition of beech forests in a changing climate: importance of plant-soil-microbe water, carbon, and nitrogen interactions. Plant Soil. 2017, 418, 89–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knoke, T.; Hahn, A. Global Change and the Role of Forests in Future Land-Use Systems. Climate Change, Air Pollution and Global Challenges - Understanding and Perspectives from Forest Research; Elsevier: Amsterdam, Netherlands, 2013; ISBN 9780080983493. [Google Scholar]
- Zimmermann, J.; Hauck, M.; Dulamsuren, C.; Leuschner, C. Climate Warming-Related Growth Decline Affects Fagus sylvatica, But Not Other Broad-Leaved Tree Species in Central European Mixed Forests. Ecosystems. 2015, 18, 560–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rennenberg, H.; Seiler, W.; Matyssek, R.; Gessler, A.; Kreuzwieser, J. Die Buche (Fagus sylvatica L.) - ein Waldbaum ohne Zukunft im südlichen Mitteleuropa. Allg. Forst- u. J.-Ztg. 2004, 175, 210–224. [Google Scholar]
- Piovesan, G.; Biondi, F.; di Filippo, A.; Alessandrini, A.; Maugeri, M. Drought-driven growth reduction in old beech (Fagus sylvatica L.) forests of the central Apennines, Italy. Global Change Biol. 2008, 14, 1265–1281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanewinkel, M.; Cullmann, D.A.; Schelhaas, M.-J.; Nabuurs, G.-J.; Zimmermann, N.E. Climate change may cause severe loss in the economic value of European forest land. Nature Clim Change. 2013, 3, 203–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouriaud, O.; Popa, I. Comparative dendroclimatic study of Scots pine, Norway spruce, and silver fir in the Vrancea Range, Eastern Carpathian Mountains. Trees. 2009, 23, 95–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feliksik, E.; Wilczyński, S. The Effect of Climate on Tree-Ring Chronologies of Native and Nonnative Tree Species Growing Under Homogenous Site Conditions. Geochronometria. 2009, 33, 49–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magh, R.-K.; Grün, M.; Knothe, V.E.; Stubenazy, T.; Tejedor, J.; Dannenmann, M.; Rennenberg, H. Silver-fir (Abies alba MILL.) neighbors improve water relations of European beech (Fagus sylvatica L.), but do not affect N nutrition. Trees. 2018, 32, 337–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magh, R.K.; Bonn, B.; Grote, R.; Burzlaff, T.; Pfautsch, S.; Rennenberg, H. Drought Superimposes the Positive Effect of Silver Fir on Water Relations of European Beech in Mature Forest Stands. Forests. 2019, 10, 897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rehschuh, S.; Fuchs, M.; Tejedor, J.; Schäfler-Schmid, A.; Magh, R.-K.; Burzlaff, T.; Rennenberg, H.; Dannenmann, M. Admixing Fir to European Beech Forests Improves the Soil Greenhouse Gas Balance. Forests. 2019, 10, 213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Genuchten, M.T. A Closed-form Equation for Predicting the Hydraulic Conductivity of Unsaturated Soils1. Soil Science Society of America Journal. 1980, 44, 892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hodnett, M.G.; Tomasella, J. Marked differences between van Genuchten soil water-retention parameters for temperate and tropical soils: a new water-retention pedo-transfer functions developed for tropical soils. Geoderma. 2002, 108, 155–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scholander, P.F.; Hammel, H.T.; Hemmingsen, E.A.; Bradstreet, E.D. Hydrostatic Pressure and Osmotic Potential in Leaves of Mangroves and some other Plants. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 1964, 52, 119–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rothfuss, Y.; Vereecken, H.; Brüggemann, N. Monitoring water stable isotopic composition in soils using gas-permeable tubing and infrared laser absorption spectroscopy. Water Resour. Res. 2013, 49, 3747–3755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oerter, E.J.; Bowen, G. In situ monitoring of H and O stable isotopes in soil water reveals ecohydrologic dynamics in managed soil systems. Ecohydrol. 2017, 10, e1841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amelung, W.; Blume, H.-P.; Fleige, H.; Horn, R.; Kandeler, E.; Kögel-Knabner, I.; Kretzschmar, R.; Stahr, K.; Wilke, B.-M. Scheffer/Schachtschabel Lehrbuch der Bodenkunde; Springer Berlin Heidelberg: Berlin, Heidelberg, Germany, 2018; p. 243. ISBN 978-3-662-55870-6. [Google Scholar]
- Domec, J.-C.; King, J.S.; Noormets, A.; Treasure, E.; Gavazzi, M.J.; Sun, G.; McNulty, S.G. Hydraulic redistribution of soil water by roots affects whole-stand evapotranspiration and net ecosystem carbon exchange. New Phytol. 2010, 187, 171–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Töchterle, P.; Yang, F.; Rehschuh, S.; Rehschuh, R.; Ruehr, N.K.; Rennenberg, H.; Dannenmann, M. Hydraulic Water Redistribution by Silver Fir (Abies alba Mill.) Occurring under Severe Soil Drought. Forests 2020, 11, 162. https://doi.org/10.3390/f11020162
Töchterle P, Yang F, Rehschuh S, Rehschuh R, Ruehr NK, Rennenberg H, Dannenmann M. Hydraulic Water Redistribution by Silver Fir (Abies alba Mill.) Occurring under Severe Soil Drought. Forests. 2020; 11(2):162. https://doi.org/10.3390/f11020162
Chicago/Turabian StyleTöchterle, Paul, Fengli Yang, Stephanie Rehschuh, Romy Rehschuh, Nadine K. Ruehr, Heinz Rennenberg, and Michael Dannenmann. 2020. "Hydraulic Water Redistribution by Silver Fir (Abies alba Mill.) Occurring under Severe Soil Drought" Forests 11, no. 2: 162. https://doi.org/10.3390/f11020162
APA StyleTöchterle, P., Yang, F., Rehschuh, S., Rehschuh, R., Ruehr, N. K., Rennenberg, H., & Dannenmann, M. (2020). Hydraulic Water Redistribution by Silver Fir (Abies alba Mill.) Occurring under Severe Soil Drought. Forests, 11(2), 162. https://doi.org/10.3390/f11020162





