A Lightweight and Efficient Plant Disease Detection Method Integrating Knowledge Distillation and Dual-Scale Weighted Convolutions
Abstract
1. Introduction
- DSConv Module: Dual-scale convolution for symptom variability adaptation.
- WTConcat Module: Weighted fusion for complex field condition robustness.
- Online Knowledge Distillation: Cross-species knowledge transfer.
- WD-YOLO achieves state-of-the-art performance on multiple crop datasets while maintaining real-time efficiency, advancing sustainable crop management.
2. Materials and Methods
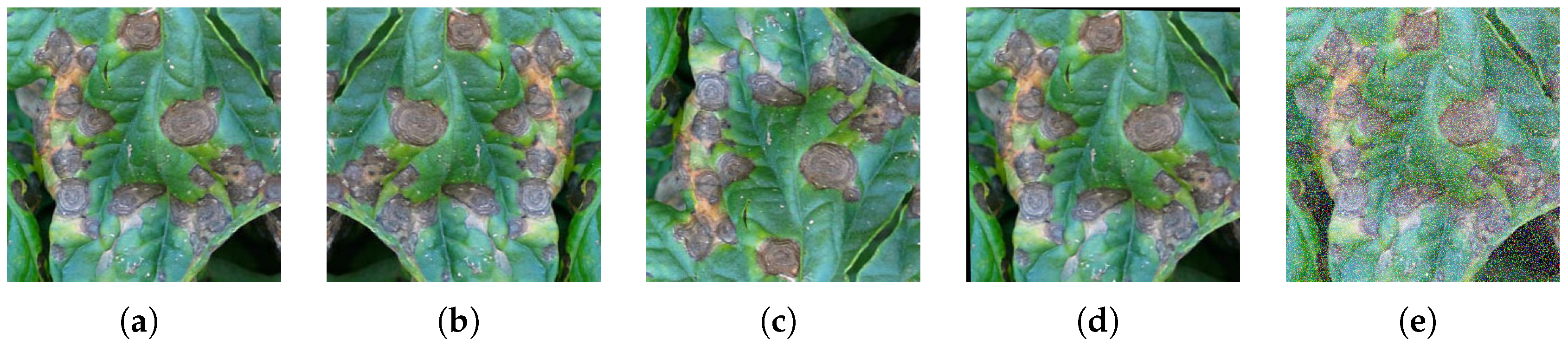
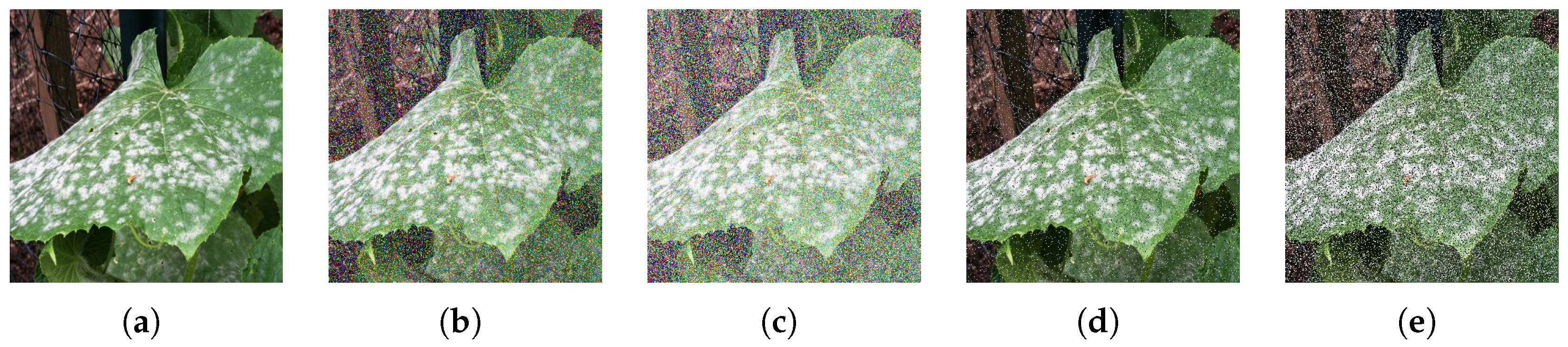
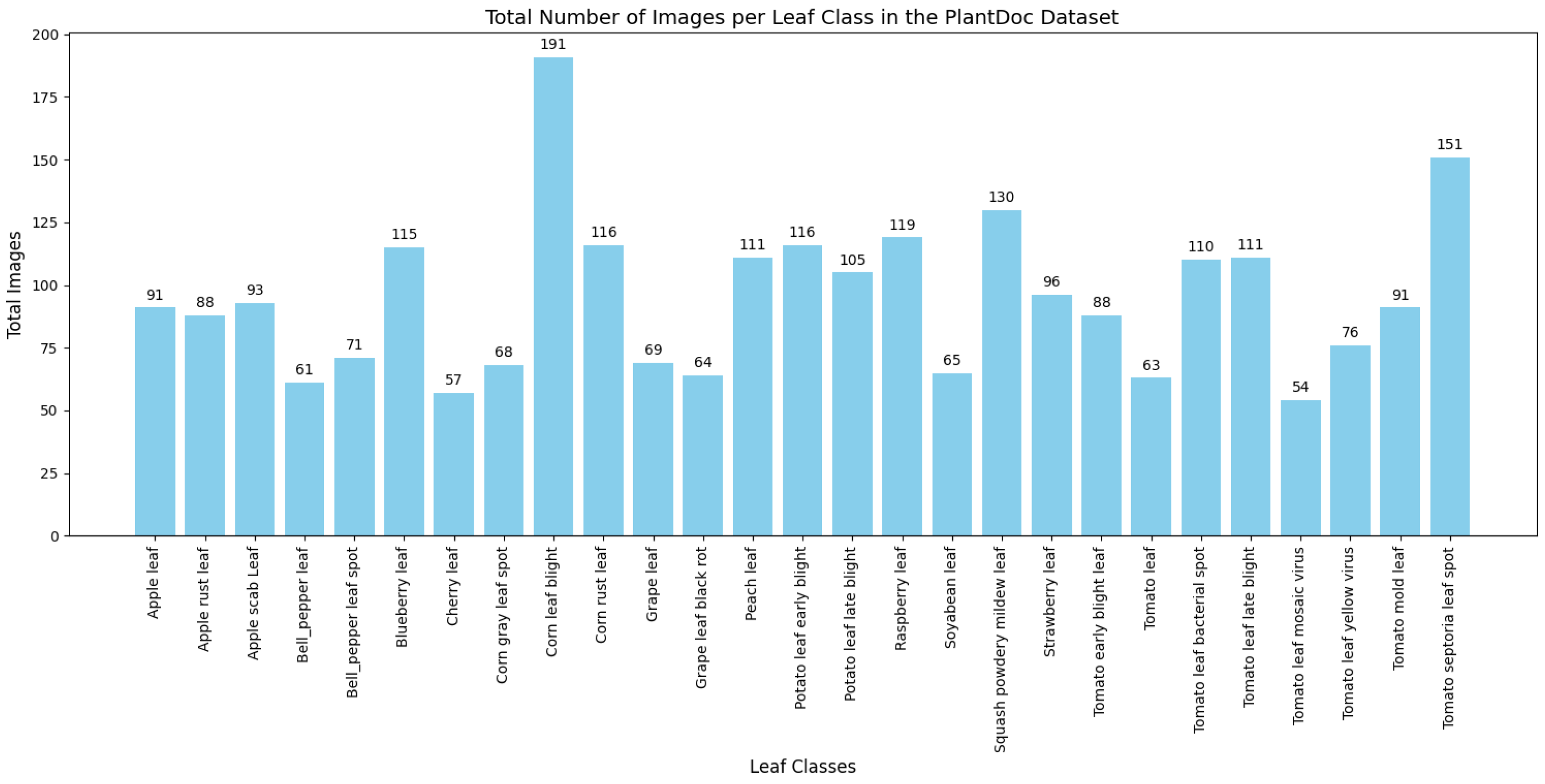
2.1. Dataset, Data Augmentation and Experimental Setup
- Horizontal/Vertical flipping: Simulates natural variations in leaf orientation.
- Affine transformations: Compensates for perspective distortions from different camera angles.
- Gaussian noise (): Enhances resilience to sensor noise and lighting variations.
2.2. Previous Work
2.2.1. YOLO and YOLOv10
2.2.2. Knowledge Distillation
2.3. DSConv
2.4. WTConcat
2.5. Experimental Design
2.5.1. Evaluation Indicators
2.5.2. Experimental Setup for Comparative Analysis
2.5.3. Ablation Study Procedure
2.5.4. Additional Experiments
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Model Training and Distillation Training Process
3.2. Comparison and Ablation Results
3.3. Visualization of Detection Results
3.4. Additional Experimental Validation of WD-YOLO
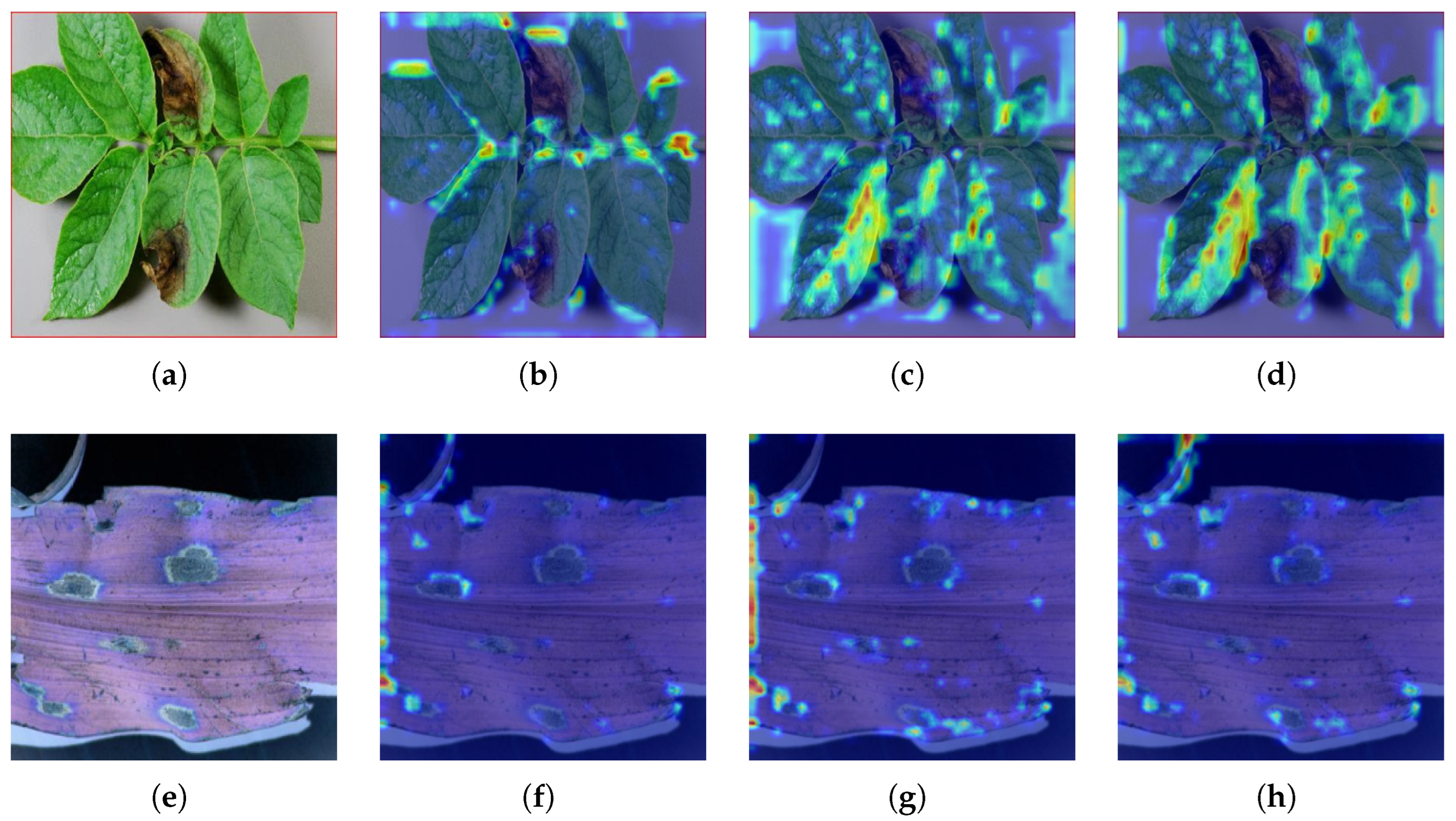
3.4.1. Visual Comparison of Heatmaps
3.4.2. Robustness to Noise
3.5. Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Redmon, J.; Divvala, S.; Girshick, R.; Farhadi, A. You only look once: Unified, real-time object detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 779–788. [Google Scholar]
- Hinton, G. Distilling the Knowledge in a Neural Network. arXiv 2015, arXiv:1503.02531. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, S.; Qiao, Y.; Li, J.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, M.; Wang, M. An improved lightweight network for real-time detection of apple leaf diseases in natural scenes. Agronomy 2022, 12, 2363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, D.; Ishak, M.K.; Maruzuki, M.I.F. EfficientNet based Convolutional Neural Network for Visual Plant Disease Detection. In Proceedings of the 2022 19th International Conference on Electrical Engineering/Electronics, Computer, Telecommunications and Information Technology (ECTI-CON), Prachuap Khiri Khan, Thailand, 24–27 May 2022; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2022; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Barbedo, J.G.A. Impact of dataset size and variety on the effectiveness of deep learning and transfer learning for plant disease classification. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2018, 153, 46–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, D.; Jain, N.; Jain, P.; Kayal, P.; Kumawat, S.; Batra, N. PlantDoc: A dataset for visual plant disease detection. In Proceedings of the 7th ACM IKDD CoDS and 25th COMAD, Hyderabad, India, 5–7 January 2020; pp. 249–253. [Google Scholar]
- Redmon, J.; Farhadi, A. YOLO9000: Better, faster, stronger. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 7263–7271. [Google Scholar]
- Redmon, J.; Farhadi, A. YOLOv3: An incremental improvement. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1804.02767. [Google Scholar]
- Bochkovskiy, A.; Wang, C.Y.; Liao, H.Y.M. YOLOv4: Optimal speed and accuracy of object detection. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2004.10934. [Google Scholar]
- Li, C.; Li, L.; Jiang, H.; Weng, K.; Geng, Y.; Li, L.; Ke, Z.; Li, Q.; Cheng, M.; Nie, W.; et al. YOLOv6: A Single-Stage Object Detection Framework for Industrial Applications. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2209.02976. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, C.Y.; Liao, H.Y.M. YOLOv7: Trainable bag-of-freebies sets new state-of-the-art for real-time object detectors. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2207.02696. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, C.Y.; Yeh, I.H.; Liao, H.Y.M. YOLOv9: Learning what you want to learn using programmable gradient information. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2402.13616. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, A.; Chen, H.; Liu, L.; Chen, K.; Lin, Z.; Han, J.; Ding, G. YOLOv10: Real-time end-to-end object detection. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2405.14458. [Google Scholar]
- Shu, C.; Liu, Y.; Gao, J.; Yan, Z.; Shen, C. Channel-wise knowledge distillation for dense prediction. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Virtual, 11–17 October 2021; pp. 5311–5320. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, B.; Cui, Q.; Song, R.; Qiu, Y.; Liang, J. Decoupled knowledge distillation. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, New Orleans, LA, USA, 18–24 June 2022; pp. 11953–11962. [Google Scholar]
- Pan, H.; Wang, C.; Qiu, M.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Y.; Huang, J. Meta-KD: A meta knowledge distillation framework for language model compression across domains. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2012.01266. [Google Scholar]
- Jia, S.; Lin, Z.; Xu, M.; Huang, Q.; Zhou, J.; Jia, X.; Li, Q. A lightweight convolutional neural network for hyperspectral image classification. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2020, 59, 4150–4163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J. YOLO-FDA: Integrating Hierarchical Attention and Detail Enhancement for Surface Defect Detection. arXiv 2025, arXiv:2506.21135. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, J.; Shen, L.; Sun, G. Squeeze-and-excitation networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–22 June 2018; pp. 7132–7141. [Google Scholar]
- Selvaraju, R.R.; Cogswell, M.; Das, A.; Vedantam, R.; Parikh, D.; Batra, D. Grad-CAM: Visual explanations from deep networks via gradient-based localization. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Venice, Italy, 22–29 October 2017; pp. 618–626. [Google Scholar]
- Shill, A.; Rahman, M.A. Plant disease detection based on YOLOv3 and YOLOv4. In Proceedings of the 2021 International Conference on Automation, Control and Mechatronics for Industry 4.0 (ACMI), Online, 8–9 July 2021; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2021; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.; Qiao, Y.; Liu, S.; Zhang, J.; Yang, Z.; Wang, M. An improved YOLOv5-based vegetable disease detection method. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2022, 202, 107345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Zhu, L.; Liu, J. PL-DINO: An Improved Transformer-Based Method for Plant Leaf Disease Detection. Agriculture 2024, 14, 691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qadri, S.A.A.; Huang, N.F.; Wani, T.M.; Bhat, S.A. Plant Disease Detection and Segmentation using End-to-End YOLOv8: A Comprehensive Approach. In Proceedings of the 2023 IEEE 13th International Conference on Control System, Computing and Engineering (ICCSCE), Penang, Malaysia, 25–26 August 2023; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2023; pp. 155–160. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, S.; Xie, L.; Huang, Q. Inception convolutional vision transformers for plant disease identification. Internet Things 2023, 21, 100650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezaei, M.; Diepeveen, D.; Laga, H.; Jones, M.G.; Sohel, F. Plant disease recognition in a low data scenario using few-shot learning. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2024, 219, 108812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]










| Model | mAP50 (%) | mAP50-95 (%) | P (%) | R (%) | Params (M) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| YOLOv10n | 56.3 | 47.9 | 56.8 | 55.4 | 2.71 |
| YOLO-DA | 58.8 | 48.0 | 59.7 | 56.9 | 2.71 |
| YOLO-DS | 61.2 | 50.3 | 59.8 | 58.7 | 2.78 |
| YOLO-WT | 60.3 | 50.0 | 58.4 | 57.9 | 2.72 |
| WD-noDis | 62.3 | 51.4 | 59.6 | 58.8 | 2.78 |
| WD-noDA | 63.8 | 52.8 | 60.0 | 59.4 | 2.78 |
| WD-YOLO | 65.4 | 53.1 | 60.4 | 60.1 | 2.78 |
| Hyperparameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Input resolution | 640 × 640 |
| Batch size | 32 |
| Maximum epochs | 500 |
| Early stopping patience | 10 epochs |
| Initial learning rate | 0.01 |
| Optimizer | SGD |
| Momentum | 0.937 |
| Weight decay | 0.0005 |
| Learning rate schedule | Cosine annealing |
| Warmup epochs | 3 |
| Warmup momentum | 0.8 |
| Warmup bias learning rate | 0.1 |
| DSConv | WTConcat | Distillation | Data Augmentation | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| YOLOv10n | ||||
| YOLO-DA | ✓ | |||
| YOLO-DS | ✓ | ✓ | ||
| YOLO-WT | ✓ | ✓ | ||
| WD-noDis | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | |
| WD-noDA | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | |
| WD-YOLO | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
| Model | mAP50 (%) | mAP50-95 (%) | P (%) | R (%) | Params (M) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| YOLOv5n | 56.6 | 48.2 | 59.3 | 55.4 | 2.84 |
| YOLOv8n | 58.0 | 49.6 | 58.2 | 56.7 | 3.34 |
| YOLOv10n | 58.8 | 48.0 | 59.7 | 56.9 | 2.71 |
| YOLOv10l | 63.1 | 52.1 | 60.5 | 60.1 | 25.76 |
| YOLOX-L | 58.8 | 44.4 | 58.7 | 55.6 | 4.06 |
| Faster-RCNN | 45.1 | 45.2 | 47.5 | 54.3 | 12.03 |
| SSD300 | 46.1 | 44.3 | 57.4 | 53.2 | 6.36 |
| RetinaNet | 52.2 | 46.6 | 54.6 | 52.3 | 9.97 |
| DETR | 48.7 | 45.7 | 53.4 | 51.2 | 12.23 |
| WD-YOLO | 65.4 | 53.1 | 60.4 | 60.1 | 2.78 |
| Noise Type | mAP50 (%) | P (%) | R (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| No noise | 65.4 | 60.4 | 60.1 |
| Gaussian noise (1) | 64.6 | 59.8 | 59.2 |
| Gaussian noise (5) | 62.9 | 58.2 | 57.4 |
| Salt-and-pepper (0.01) | 65.0 | 58.6 | 59.2 |
| Salt-and-pepper (0.05) | 63.4 | 55.9 | 55.7 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, X.; Wang, H.; Zhou, Q.; Lu, L.; Zhang, L.; Sun, C.; Wu, G. A Lightweight and Efficient Plant Disease Detection Method Integrating Knowledge Distillation and Dual-Scale Weighted Convolutions. Algorithms 2025, 18, 433. https://doi.org/10.3390/a18070433
Yang X, Wang H, Zhou Q, Lu L, Zhang L, Sun C, Wu G. A Lightweight and Efficient Plant Disease Detection Method Integrating Knowledge Distillation and Dual-Scale Weighted Convolutions. Algorithms. 2025; 18(7):433. https://doi.org/10.3390/a18070433
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Xiong, Hao Wang, Qi Zhou, Lei Lu, Lijuan Zhang, Changming Sun, and Guilu Wu. 2025. "A Lightweight and Efficient Plant Disease Detection Method Integrating Knowledge Distillation and Dual-Scale Weighted Convolutions" Algorithms 18, no. 7: 433. https://doi.org/10.3390/a18070433
APA StyleYang, X., Wang, H., Zhou, Q., Lu, L., Zhang, L., Sun, C., & Wu, G. (2025). A Lightweight and Efficient Plant Disease Detection Method Integrating Knowledge Distillation and Dual-Scale Weighted Convolutions. Algorithms, 18(7), 433. https://doi.org/10.3390/a18070433







