Cross-Modal Fake News Detection Method Based on Multi-Level Fusion Without Evidence
Abstract
1. Introduction
- This paper proposes a cross-modal false news detection model CM-MLF based on evidence-free multilevel fusion, and design a cross-modal alignment and secondary fusion framework to solve the problem of semantic inconsistency and information loss of multimodal features.
- This paper designs an attention mechanism and KL score-assisted weight assignment network. This network adaptively adjusts the contribution of text, image and primary fusion features in the second stage of fusion, which enhances the model’s ability to capture key features.
- Experiments on public datasets demonstrate the effectiveness of the CM-MLF model, with accuracy and other evaluation metrics outperforming other baseline models.
2. Related Work
2.1. Multimodal Complementarity
2.2. Multimodal Consistency
2.3. Multimodal Enhancement
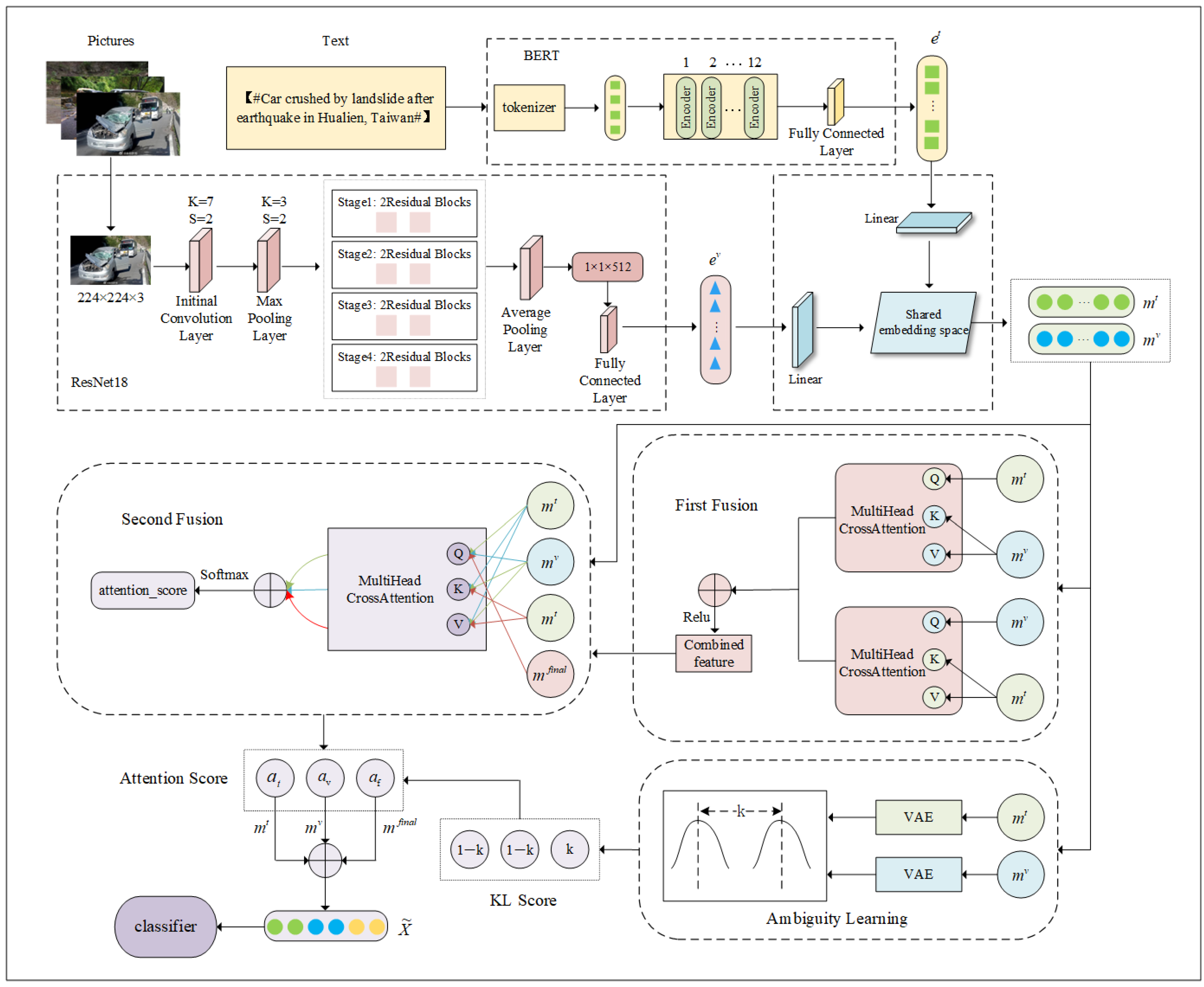
3. Methods
3.1. Model Definition
3.2. Feature Extraction
3.2.1. Text Feature Extraction
3.2.2. Image Feature Extraction
3.3. Feature Alignment
3.3.1. Similarity Matching
3.3.2. Contrast Learning
3.3.3. Soft Label
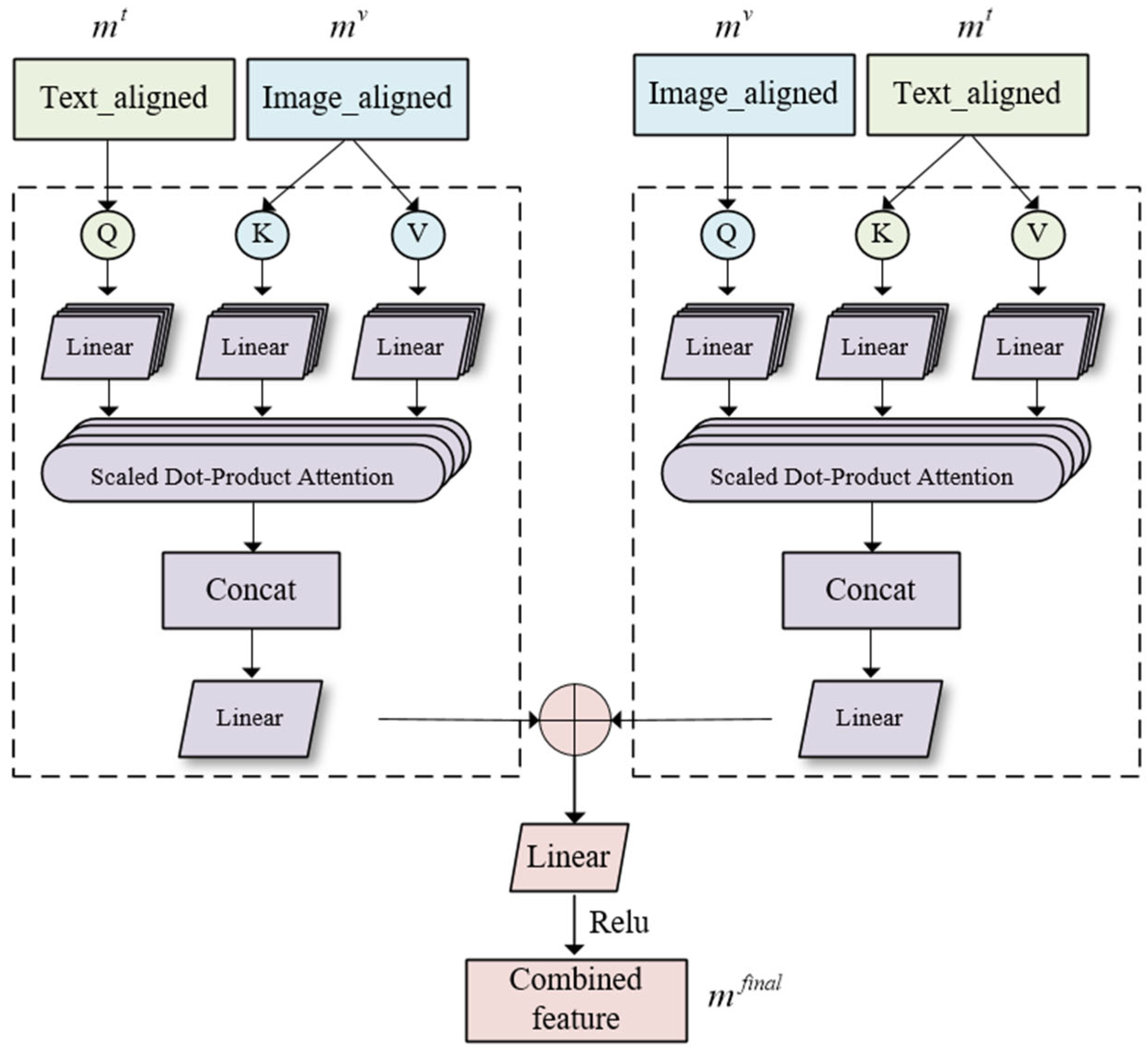
3.4. Feature Fusion
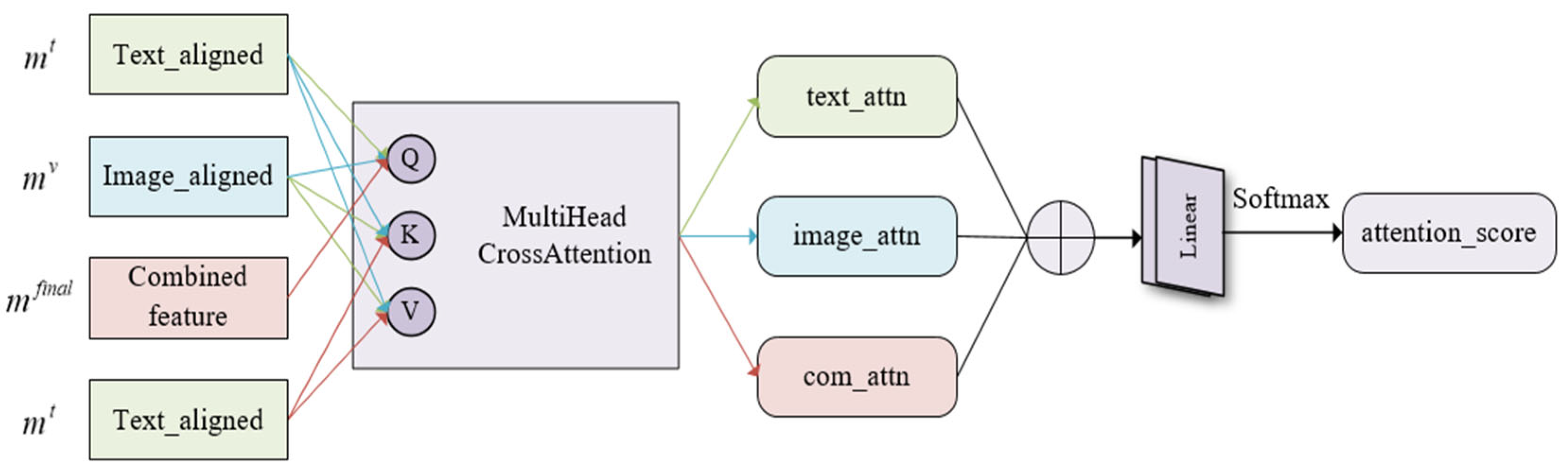
3.5. Secondary Fusion
3.5.1. Attention Weight Acquisition Network
3.5.2. Ambiguity Score Acquisition Network
3.6. Feature Detection
4. Experiment
4.1. Datasets
4.1.1. Weibo Dataset
4.1.2. Twitter Dataset
4.2. Baseline Model
4.3. Evaluation Metrics
4.4. Experimental Setup
5. Results and Discussion
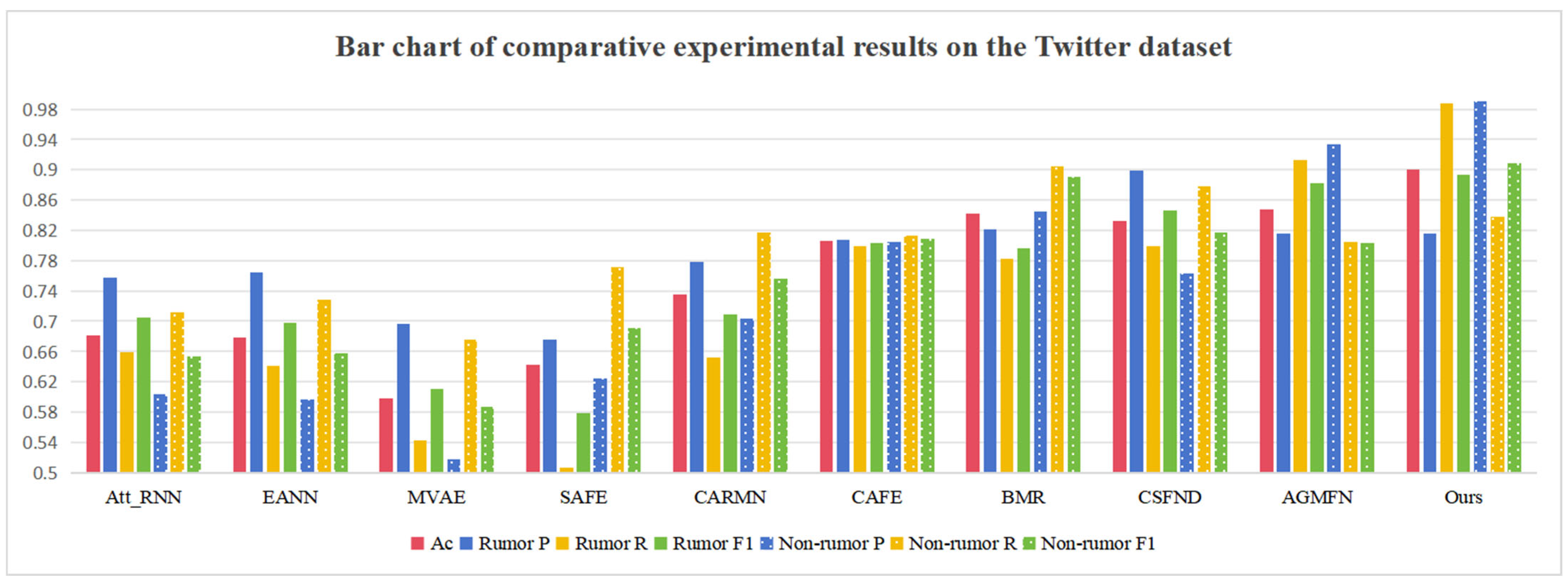
5.1. Comparative Experiment
5.2. Ablation Experiment
- (1)
- Ours-b: This variant removes the model’s multi-attention feature fusion module in favor of a simple weighted fusion to integrate aligned text and image features.
- (2)
- Ours-c: This variant removes the attention weight acquisition network and the disambiguation score acquisition network, and assigns the same weights to all three features for fusion in the secondary fusion.
- (3)
- Ours-d: This variant removes both the ablated modules and networks in Ours-b and Ours-c.
- (4)
- Ours-e: This variant removes the cross-modal feature alignment module.
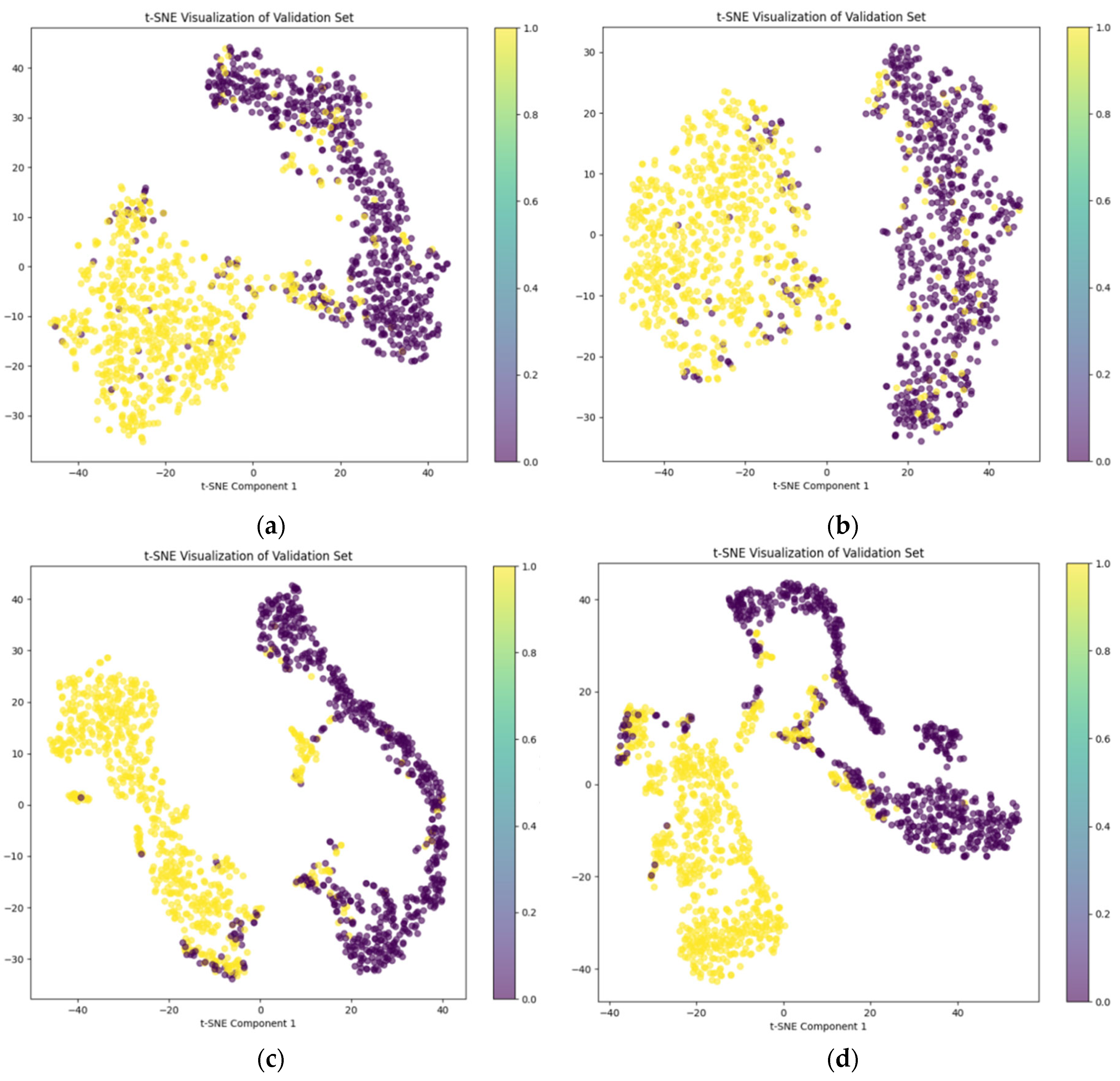
5.3. Visual Analysis
5.4. Parameter Sensitivity Experiment
5.5. Limitations
6. Conclusions
- This paper proposes a cross-modal false news detection model CM-MLF based on evidence-free multilevel fusion. The problem of semantic inconsistency of multimodal features and the problem of information loss are solved by cross-modal alignment and multilevel fusion framework. Experiments on public datasets show that the CM-MLF model outperforms the benchmark algorithm in evaluation metrics such as accuracy, verifying its effectiveness.
- A two-stage progressive fusion framework is designed to realize a multi-level feature fusion strategy and introduce an ambiguity learning module. The first stage generates primary fusion features through a cross-modal multi-head cross-attention mechanism. The second stage introduces the KL disambiguation score to assist in attention weight allocation, which further improves the model’s ability to focus on key features. Fine-grained secondary fusion is realized by adaptively adjusting the secondary fusion weights of text, image and primary fusion features.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AI | Artificial intelligence |
| NLP | Natural language processing |
| ML | Machine learning |
| KL | Kullback–Leibler divergence |
| LSTM | Long short-term memory network |
| VGG | Visual geometry group |
| CNN | Convolutional neural network |
| BN | Batch normalization |
| MLP | Multilayer perceptual machine |
References
- Shu, K.; Sliva, A.; Wang, S.; Tang, J.; Liu, H. Fake news detection on social media: A data mining perspective. ACM SIGKDD Explor. Newsl. 2017, 19, 22–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, L.; Wei, S.; Zhao, Z.; Wu, B. Deep learning for fake news detection: A comprehensive survey. AI Open 2022, 3, 133–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Ma, F.; Jin, Z.; Yuan, Y.; Xun, G.; Jha, K.; Su, L.; Gao, J. EANN: Event adversarial neural networks for multi-modal fake news detection. In Proceedings of the 24th ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery & Data Mining, London, UK, 19–23 August 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Ma, F.; Wang, H.; Jha, K.; Gao, J. Multimodal emergent fake news detection via meta neural process networks. In Proceedings of the 27th ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery & Data Mining, Virtual Event, Singapore, 14–18 August 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khattar, D.; Goud, J.S.; Gupta, M.; Varma, V. MVAE: Multimodal variational autoencoder for fake news detection. In Proceedings of the World Wide Web Conference, San Francisco, CA, USA, 13–17 May 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singhal, S.; Kabra, A.; Sharma, M.; Shah, R.R.; Chakraborty, T.; Kumaraguru, P. SpotFake+: A multimodal framework for fake news detection via transfer learning (Student abstract). In Proceedings of the 34th AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, New York, NY, USA, 7–12 February 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devlin, J.; Chang, M.-W.; Lee, K.; Toutanova, K. BERT: Pre-training of deep bidirectional transformers for language understanding. In Proceedings of the 2019 Conference of the North American Chapter of the Association for Computational Linguistics: Human Language Technologies, Minneapolis, MN, USA, 2–7 June 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sengupta, A.; Ye, Y.; Wang, R.; Liu, C.; Roy, K. Going deeper in spiking neural networks: VGG and residual architectures. Front. Neurosci. 2019, 13, 95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, X.; Wu, J.; Zafarani, R. SAFE: Similarity-aware multi-modal fake news detection. In Proceedings of the 24th Pacific-Asia Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining, Singapore, 11–14 May 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, J.; Wang, Y.; Tian, Y.; Li, Y.; Shi, L.; Wei, L. Detecting Fake News by Exploring the Consistency of Multimodal Data. Inf. Process. Manag. 2021, 58, 102610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghorbanpour, F.; Ramezani, M.; Fazli, M.A.; Rabiee, H.R. FNR: A Similarity and Transformer-Based Approach to Detect Multi-Modal Fake News in Social Media. Soc. Netw. Anal. Min. 2023, 13, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dosovitskiy, A.; Beyer, L.; Kolesnikov, A.; Weissenborn, D.; Zhai, X.; Unterthiner, T.; Dehghani, M.; Minderer, M.; Heigold, G.; Gelly, S.; et al. An Image is Worth 16x16 Words: Transformers for Image Recognition at Scale. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Learning Representations, Virtual Event, 3–7 May 2021; Available online: https://openreview.net/forum?id=YicbFdNTTy (accessed on 7 June 2025).
- Jin, Z.; Cao, J.; Guo, H.; Zhang, Y.; Luo, J. Multimodal Fusion with Recurrent Neural Networks for Rumor Detection on Microblogs. In Proceedings of the 25th ACM International Conference on Multimedia, Mountain View, CA, USA, 23–27 October 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Fang, Q.; Qian, S.; Xu, C. Multi-modal Knowledge-aware Event Memory Network for Social Media Rumor Detection. In Proceedings of the 27th ACM International Conference on Multimedia, Nice, France, 21–25 October 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, C.; Ning, N.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, B. A Multimodal Fake News Detection Model Based on Crossmodal Attention Residual and Multichannel Convolutional Neural Networks. Inf. Process. Manag. 2021, 58, 102437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Zhan, P.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, L.; Xu, Z. Multimodal Fusion with Co-attention Networks for Fake News Detection. In Proceedings of the 59th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics and the 11th International Joint Conference on Natural Language Processing (ACL-IJCNLP), Bangkok, Thailand, 1–6 August 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, P.; Cao, J.; Li, X.; Liu, H.; Sheng, Q.; Mi, X.; He, Q.; Lv, Y.; Guo, C.; Yu, Y. Improving Fake News Detection by Using an Entity-Enhanced Framework to Fuse Diverse Multimodal Clues. In Proceedings of the 29th ACM International Conference on Multimedia, Virtual Event, 20–24 October 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Li, D.; Zhang, P.; Sui, J.; Lv, Q.; Tun, L.; Shang, L. Cross-Modal Ambiguity Learning for Multimodal Fake News Detection. In Proceedings of the ACM Web Conference 2022, Lyon, France, 25–29 April 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, L.; Jian, S.; Li, D.; Shen, S. MRML: Multimodal Rumor Detection by Deep Metric Learning. In Proceedings of the 2023 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Rhodes Island, Greece, 4–10 June 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ying, Q.; Hu, X.; Zhou, Y.; Qian, Z.; Zeng, D.; Ge, S. Bootstrapping Multi-View Representations for Fake News Detection. In Proceedings of the 37th AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Washington, DC, USA, 7–14 February 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, L.; Jian, S.; Kan, Z.; Qiao, L.; Li, D. Not All Fake News Is Semantically Similar: Contextual Semantic Representation Learning for Multimodal Fake News Detection. Inf. Process. Manag. 2024, 61, 103564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Ji, K.; Gao, Y.; Chen, Z.; Ma, K.; Zhao, X. Multi-Source Heterogeneous Data Progressive Fusion for Fake News Detection. Comput. Sci. 2024, 51, 30–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, J.; Gao, J.; Huang, J.; Yang, Y. Multimodal Fake News Detection Based on Evidence Enhancement and Local Semantic Interaction. Chin. J. Comput. 2025, 48, 556–571. Available online: https://dl.ccf.org.cn/article/articleDetail.html?type=qkwz&_ack=2&id=7477135053260800 (accessed on 7 June 2025).
- Deng, X.; Wang, L.; Zeng, X.; Ye, H.; Che, X. Fake News Detection Method Based on Attention-Guided Multimodal Feature Fusion. J. Front. Comput. Sci. Technol. 2025, pp. 1–12. Available online: https://link.cnki.net/urlid/11.5602.TP.20250307.1854.002 (accessed on 7 June 2025).
- Boididou, C.; Papadopoulos, S.; Zampoglou, M.; Apostolidis, L.; Papadopoulou, O.; Kompatsiaris, Y. Detection and Visualization of Misleading Content on Twitter. Int. J. Multimed. Inf. Retr. 2018, 7, 71–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Stage | Output Size | Number of Channels | Key Operation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Conv | 112 × 112 | 64 | 7 × 7 convolutional kernel, step size is 2 |
| Maxpool | 56 × 56 | 64 | 3 × 3 maximum pooling, step size is 2 |
| Stage 1 | 56 × 56 | 64 | 2 residual blocks |
| Stage 2 | 28 × 28 | 128 | 2 residual blocks, step size is 2 |
| Stage 3 | 14 × 14 | 256 | 2 residual blocks, step size is 2 |
| Stage 4 | 7 × 7 | 512 | 2 residual blocks, step size is 2 |
| Label | Real | Fake | Total |
|---|---|---|---|
| Train | 2492 | 2877 | 5369 |
| Test | 691 | 741 | 1432 |
| Total | 3183 | 3618 | 6801 |
| Label | Real | Fake | Total |
|---|---|---|---|
| Train | 6840 | 5007 | 11,847 |
| Test | 833 | 573 | 1406 |
| Total | 7673 | 5580 | 13,253 |
| Number | Label | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | TP | Number of news stories where the truth value label is fake and the predicted label is fake |
| 2 | FP | Number of news stories where the truth value label is real and the predicted label is fake |
| 3 | TN | Number of news stories where the truth value label is real and the predicted label is real |
| 4 | FN | Number of news stories where the truth value label is fake and the predicted label is real |
| Experimental Environment | Settings |
|---|---|
| Pytorch | 1.11.0 |
| Python | 3.8 |
| Cuda | 11.3 |
| GPU | RTX 4090 (24 GB) |
| CPU | 22 vCPU AMD EPYC 7T83 64-Core Processor |
| Memory | 90 GB |
| Hard Disk | 30 GB + 50 GB |
| Experimental Parameter | Settings |
|---|---|
| Batch_size | 64 |
| Epochs | 20 |
| Optimizer | AdamW |
| Learning_rate | 2 × 10−5 |
| Weight-decay | 1× 10−4 |
| 0.4 | |
| 0.3 |
| Method | Ac | Rumor | Non-Rumor | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| P | R | F1 | P | R | F1 | ||
| Att_RNN | 0.781 | 0.802 | 0.765 | 0.783 | 0.761 | 0.801 | 0.781 |
| EANN | 0.810 | 0.831 | 0.792 | 0.812 | 0.789 | 0.829 | 0.809 |
| MVAE | 0.824 | 0.854 | 0.769 | 0.809 | 0.802 | 0.875 | 0.837 |
| SAFE | 0.763 | 0.757 | 0.799 | 0.777 | 0.772 | 0.726 | 0.749 |
| CARMN | 0.853 | 0.891 | 0.814 | 0.851 | 0.818 | 0.894 | 0.854 |
| CAFE | 0.840 | 0.855 | 0.830 | 0.842 | 0.825 | 0.851 | 0.837 |
| BMR | 0.884 | 0.875 | 0.886 | 0.880 | 0.874 | 0.881 | 0.877 |
| CSFND | 0.895 | 0.899 | 0.895 | 0.897 | 0.892 | 0.896 | 0.894 |
| AGMFN | 0.917 | 0.918 | 0.910 | 0.912 | 0.913 | 0.924 | 0.918 |
| Ours | 0.922 | 0.935 | 0.912 | 0.923 | 0.908 | 0.932 | 0.920 |
| Method | Ac | Rumor | Non-Rumor | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| P | R | F1 | P | R | F1 | ||
| Att_RNN | 0.681 | 0.758 | 0.659 | 0.705 | 0.603 | 0.712 | 0.653 |
| EANN | 0.678 | 0.765 | 0.641 | 0.698 | 0.597 | 0.729 | 0.657 |
| MVAE | 0.598 | 0.697 | 0.543 | 0.610 | 0.518 | 0.676 | 0.587 |
| SAFE | 0.643 | 0.676 | 0.506 | 0.579 | 0.625 | 0.772 | 0.691 |
| CARMN | 0.735 | 0.778 | 0.652 | 0.709 | 0.704 | 0.817 | 0.756 |
| CAFE | 0.806 | 0.807 | 0.799 | 0.803 | 0.805 | 0.813 | 0.809 |
| BMR | 0.842 | 0.821 | 0.782 | 0.796 | 0.845 | 0.904 | 0.891 |
| CSFND | 0.833 | 0.899 | 0.799 | 0.846 | 0.763 | 0.878 | 0.817 |
| AGMFN | 0.847 | 0.816 | 0.913 | 0.883 | 0.933 | 0.805 | 0.803 |
| Ours | 0.901 | 0.816 | 0.988 | 0.894 | 0.990 | 0.838 | 0.908 |
| Dataset | Method | Accuracy | F1 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rumor | Non-Rumor | |||
| Ours-b | 0.911 | 0.912 | 0.911 | |
| Ours-c | 0.906 | 0.906 | 0.906 | |
| Ours-d | 0.905 | 0.905 | 0.905 | |
| Ours-e | 0.896 | 0.895 | 0.896 | |
| Ours | 0.922 | 0.923 | 0.920 | |
| Ours-b | 0.892 | 0.891 | 0.892 | |
| Ours-c | 0.886 | 0.884 | 0.888 | |
| Ours-d | 0.883 | 0.884 | 0.885 | |
| Ours-e | 0.871 | 0.868 | 0.874 | |
| Ours | 0.901 | 0.894 | 0.908 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
He, P.; Zhang, H.; Cao, S.; Wu, Y. Cross-Modal Fake News Detection Method Based on Multi-Level Fusion Without Evidence. Algorithms 2025, 18, 426. https://doi.org/10.3390/a18070426
He P, Zhang H, Cao S, Wu Y. Cross-Modal Fake News Detection Method Based on Multi-Level Fusion Without Evidence. Algorithms. 2025; 18(7):426. https://doi.org/10.3390/a18070426
Chicago/Turabian StyleHe, Ping, Hanxue Zhang, Shufu Cao, and Yali Wu. 2025. "Cross-Modal Fake News Detection Method Based on Multi-Level Fusion Without Evidence" Algorithms 18, no. 7: 426. https://doi.org/10.3390/a18070426
APA StyleHe, P., Zhang, H., Cao, S., & Wu, Y. (2025). Cross-Modal Fake News Detection Method Based on Multi-Level Fusion Without Evidence. Algorithms, 18(7), 426. https://doi.org/10.3390/a18070426







