Regularized Contrastive Masked Autoencoder Model for Machinery Anomaly Detection Using Diffusion-Based Data Augmentation
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- (1)
- In response to the issue of not having a robust dataset for various real-world noises, we propose a novel diffusion-based data augmentation method. Our approach incorporates textual prompts from ChatGPT as input to AudioLDM. The use of diffusion-based data augmentation allows us to add noise or artifacts with limited knowledge of any target domain solely through text prompts.
- (2)
- To improve the generalization of Contrastive learning, specifically to prevent feature collapse and learn informative representation, we propose a novel learning framework that combines Contrastive learning and masked autoencoders (MAEs) with Variance—Covariance Regularization. Contrastive learning and MAEs complement each other, extracting different discriminative features from the input data. By simultaneously leveraging these two approaches, we enhance the model’s representational power and better discriminate between normal and anomalous sounds.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Data Augmentation Method
2.2. Masked Autoencoder
2.3. Contrastive Learning
2.4. Variance—Covariance Reqularization
2.5. Proposed Model
2.5.1. Implementation Detail
2.5.2. Fine-tuning Stage
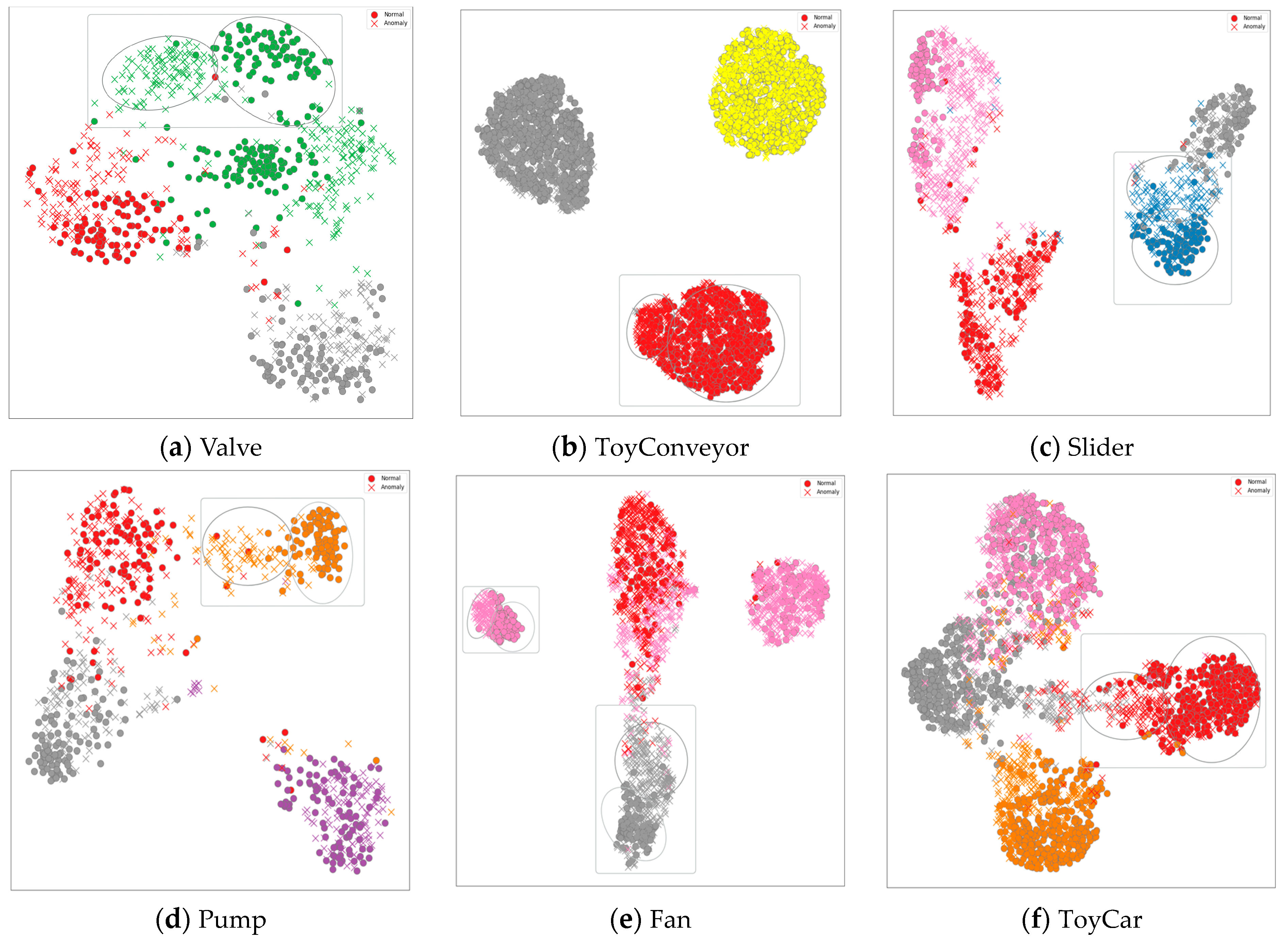
3. Results
3.1. Dataset
3.2. Performance Evaluation
3.3. Performance Comparison
4. Conclusions and Future Works
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chandola, V.; Banerjee, A.; Kumar, V. Anomaly detection: A survey. ACM Comput. Surv. 2009, 41, 1–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daniluk, P.; Gozdziewski, M.; Kapka, S.; Kosmider, M. Ensemble of Auto-Encoder Based Systems for Anomaly Detection. DCASE2020 Challenge. 2020. Available online: https://dcase.community/documents/challenge2020/technical_reports/DCASE2020_Daniluk_140_t2.pdf (accessed on 2 June 2023).
- Suefusa, K.; Nishida, T.; Purohit, H.; Tanabe, R.; Endo, T.; Kawaguchi, Y. Anomalous sound detection based on interpolation deep neural network. In Proceedings of the ICASSP 2020—2020 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Barcelona, Spain, 4–8 May 2020; pp. 271–275. [Google Scholar]
- Hojjati, H.; Armanfard, N. Self-supervised acoustic anomaly detection via contrastive learning. In Proceedings of the ICASSP 2022—2022 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Singapore, 23–27 May 2022; pp. 3253–3257. [Google Scholar]
- Xiao, F.; Liu, Y.; Wei, Y.; Guan, J.; Zhu, Q.; Zheng, T.; Han, J. The DCASE2022 Challenge Task 2 System: Anomalous Sound Detection with Self-Supervised Attribute Classification and GMM-Based Clustering. Challenge, Technical Report. Available online: https://dcase.community/documents/challenge2022/technical_reports/DCASE2022_Guan_24_t2.pdf (accessed on 2 June 2023).
- Ruff, L.; Kauffmann, J.R.; Vandermeulen, R.A.; Montavon, G.; Samek, W.; Kloft, M.; Dietterich, T.G.; Müller, K.-R. A unifying review of deep and shallow anomaly detection. Proc. IEEE 2021, 109, 756–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giri, R.; Cheng, F.; Helwani, K.; Tenneti, S.V.; Isik, U.; Krishnaswamy, A. Group masked autoencoder based density estimator for audio anomaly detection. In Proceedings of the Detection and Classification of Acoustic Scenes and Events 2020, Tokyo, Japan, 2–3 November 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Dohi, K.; Endo, T.; Purohit, H.; Tanabe, R.; Kawaguchi, Y. Flow-based self-supervised density estimation for anomalous sound detection. In Proceedings of the ICASSP 2021—2021 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Toronto, ON, Canada, 6–11 June 2021; pp. 336–340. [Google Scholar]
- Dohi, K.; Imoto, K.; Harada, N.; Niizumi, D.; Koizumi, Y.; Nishida, T.; Purohit, H.; Endo, T.; Yamamoto, M.; Kawaguchi, Y. Description and discussion on DCASE 2022 challenge task 2: Unsupervised anomalous sound detection for machine condition monitoring applying domain generalization techniques. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2206.05876. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, Y.; Guan, J.; Lan, H.; Wang, W. Anomalous Sound Detection System with Self-Challenge and Metric Evaluation for DCASE2022 Challenge Task 2. DCASE2022 Challenge, Technical Report. Available online: https://dcase.community/documents/challenge2022/technical_reports/DCASE2022_Wei_22_t2.pdf (accessed on 2 June 2023).
- Chen, B.; Bondi, L.; Das, S. Learning to adapt to domain shifts with few-shot samples in anomalous sound detection. In Proceedings of the 2022 26th International Conference on Pattern Recognition (ICPR), Montreal, QC, Canada, 21–25 August 2022; pp. 133–139. [Google Scholar]
- Gong, D.; Liu, L.; Le, V.; Saha, B.; Mansour, M.R.; Venkatesh, S.; van den Hengel, A. Memorizing normality to detect anomaly: Memory-augmented deep autoencoder for unsupervised anomaly detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Seoul, Republic of Korea, 27 October–2 November 2019; pp. 1705–1714. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, W.; Yi, M.; Zhao, X. Towards the generalization of contrastive self-supervised learning. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2111.00743. [Google Scholar]
- Dosovitskiy, A.; Beyer, L.; Kolesnikov, A.; Weissenborn, D.; Zhai, X.; Unterthiner, T.; Dehghani, M.; Minderer, M.; Heigold, G.; Gelly, S.; et al. An image is worth 16x16 words: Transformers for image recognition at scale. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2010.11929. [Google Scholar]
- Park, D.S.; Chan, W.; Zhang, Y.; Chiu, C.-C.; Zoph, B.; Cubuk, E.D.; Le, Q.V. Specaugment: A simple data augmentation method for automatic speech recognition. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1904.08779. [Google Scholar]
- Van den Oord, A.; Dieleman, S.; Schrauwen, B. Deep content-based music recommendation. In Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems 26; Neural Information Processing Systems Foundation, Inc.: La Jolla, CA, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Ko, T.; Peddinti, V.; Povey, D.; Khudanpur, S. Audio augmentation for speech recognition. In Proceedings of the Sixteenth Annual Conference of the International Speech Communication Association, Dresden, Germany, 6–10 September 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, Y.; Chen, Z.; Hershey, J.R.; Le Roux, J.; Mesgarani, N. Deep clustering and conventional networks for music separation: Stronger together. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), New Orleans, LA, USA, 5–9 March 2017; pp. 61–65. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, Y.; Mesgarani, N. Tasnet: Time-domain audio separation network for real-time, single-channel speech separation. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Calgary, AB, Canada, 15–20 April 2018; pp. 696–700. [Google Scholar]
- Jahanian, A.; Puig, X.; Tian, Y.; Isola, P. Generative models as a data source for multiview representation learning. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2106.05258. [Google Scholar]
- Antoniou, A.; Storkey, A.; Edwards, H. Data augmentation generative adversarial networks. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1711.04340. [Google Scholar]
- Tran, T.; Pham, T.; Carneiro, G.; Palmer, L.; Reid, I. A bayesian data augmentation approach for learning deep models. In Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems 30; Neural Information Processing Systems Foundation, Inc.: La Jolla, CA, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Dos Santos Tanaka, F.H.; Aranha, C. Data augmentation using GANs. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1904.09135. [Google Scholar]
- Dat, P.T.; Dutt, A.; Pellerin, D.; Quénot, G. Classifier training from a generative model. In Proceedings of the 2019 International Conference on Content-Based Multimedia Indexing (CBMI), Dublin, Ireland, 4–6 September 2019; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Yamaguchi, S.; Kanai, S.; Eda, T. Effective data augmentation with multi-domain learning gans. In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, New York, NY, USA, 7–12 February 2020; Volume 34, pp. 6566–6574. [Google Scholar]
- Besnier, V.; Jain, H.; Bursuc, A.; Cord, M.; Pérez, P. This dataset does not exist: Training models from generated images. In Proceedings of the ICASSP 2020—2020 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Barcelona, Spain, 4–8 May 2020; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Haque, A. EC-GAN: Low-sample classification using semi-supervised algorithms and GANs (Student Abstract). In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Virtual, 2–9 February 2021; Volume 35, pp. 15797–15798. [Google Scholar]
- He, R.; Sun, S.; Yu, X.; Xue, C.; Zhang, W.; Torr, P.; Bai, S.; Qi, X. Is synthetic data from generative models ready for image recognition? arXiv 2022, arXiv:2210.07574. [Google Scholar]
- Available online: https://chat.openai.com/chat (accessed on 2 June 2023).
- Liu, H.; Chen, Z.; Yuan, Y.; Mei, X.; Liu, X.; Mandic, D.; Wang, W.; Plumbley, M.D. Audioldm: Text-to-audio generation with latent diffusion models. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2301.12503. [Google Scholar]
- Purohit, H.; Tanabe, R.; Ichige, K.; Endo, T.; Nikaido, Y.; Suefusa, K.; Kawaguchi, Y. MIMII Dataset: Sound dataset for malfunctioning industrial machine investigation and inspection. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1909.09347. [Google Scholar]
- Primus, P. Reframing Unsupervised Machine Condition Monitoring as a Supervised Classification Task with Outlier-Exposed Classifiers. Techniacl Report, DCASE2020 Challenge. 2020. Available online: https://dcase.community/documents/challenge2020/technical_reports/DCASE2020_Primus_36_t2.pdf (accessed on 2 June 2023).
- Dorj, E.; Altangerel, E. Anomaly detection approach using hidden Markov model. In Proceedings of the International Forum on Strategic Technology, IFOST, Ulaanbaatar, Mongolia, 28 June–1 July 2013; Volume 2, pp. 141–144. [Google Scholar]
- Ntalampiras, S.; Potamitis, I.; Fakotakis, N. Probabilistic novelty detection for acoustic surveillance under real-world conditions. IEEE Trans. Multimed. 2011, 13, 713–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sasou, A.; Odontsengel, N. Acoustic novelty detection based on AHLAC and NMF. In Proceedings of the 2012 International Symposium on Intelligent Signal Processing and Communications Systems, Tamsui, Taiwan, 4–7 November 2012; pp. 872–875. [Google Scholar]
- Rumelhart, D.E.; Hinton, G.E.; Williams, R.J. Learning representations by back-propagating errors. Nature 1986, 323, 533–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, J.; Xiao, F.; Liu, Y.; Zhu, Q.; Wang, W. Anomalous Sound Detection Using Audio Representation with Machine ID Based Contrastive Learning Pretraining. In Proceedings of the ICASSP 2023—2023 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Rhodes Island, Greece, 4–10 June 2023; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Koizumi, Y.; Kawaguchi, Y.; Imoto, K.; Nakamura, T.; Nikaido, Y.; Tanabe, R.; Purohit, H.; Suefusa, K.; Endo, T.; Yasuda, M.; et al. Description and discussion on DCASE2020 challenge task2: Unsupervised anomalous sound detection for machine condition monitoring. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2006.05822. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Guan, J.; Zhu, Q.; Wang, W. Anomalous sound detection using spectral-temporal information fusion. In Proceedings of the ICASSP 2022—2022 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Singapore, 23–27 May 2022; pp. 816–820. [Google Scholar]
- Gong, Y.; Rouditchenko, A.; Liu, A.H.; Harwath, D.; Karlinsky, L.; Kuehne, H.; Glass, J.R. Contrastive audio-visual masked autoencoder. In Proceedings of the Eleventh International Conference on Learning Representations, Virtual, 25–29 April 2022. [Google Scholar]
- He, K.; Chen, X.; Xie, S.; Li, Y.; Dollár, P.; Girshick, R. Masked autoencoders are scalable vision learners. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, New Orleans, LA, USA, 21–24 June 2022; pp. 16000–16009. [Google Scholar]
- Mishra, S.; Robinson, J.; Chang, H.; Jacobs, D.; Sarna, A.; Maschinot, A.; Krishnan, D. A simple, efficient and scalable contrastive masked autoencoder for learning visual representations. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2210.16870. [Google Scholar]
- Bardes, A.; Ponce, J.; LeCun, Y. Vicreg: Variance-invariance-covariance regularization for self-supervised learning. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2105.04906. [Google Scholar]
- Koizumi, Y.; Saito, S.; Uematsu, H.; Harada, N.; Imoto, K. ToyADMOS: A dataset of miniature-machine operating sounds for anomalous sound detection. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE Workshop on Applications of Signal Processing to Audio and Acoustics (WASPAA), New Paltz, NY, USA, 20–23 October 2019; pp. 313–317. [Google Scholar]
- Rombach, R.; Blattmann, A.; Lorenz, D.; Esser, P.; Ommer, B. High-resolution image synthesis with latent diffusion models. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, New Orleans, LA, USA, 21–24 June 2022; pp. 10684–10695. [Google Scholar]
- Burg, M.F.; Wenzel, F.; Zietlow, D.; Horn, M.; Makansi, O.; Locatello, F.; Russell, C. A data augmentation perspective on diffusion models and retrieval. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2304.10253. [Google Scholar]
- Trabucco, B.; Doherty, K.; Gurinas, M.; Salakhutdinov, R. Effective data augmentation with diffusion models. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2302.07944. [Google Scholar]
- Mao, J.; Yin, X.; Chang, Y.; Zhou, H. Improvements to Self-Supervised Representation Learning for Masked Image Modeling. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2205.10546. [Google Scholar]
- Zbontar, J.; Jing, L.; Misra, I.; LeCun, Y.; Deny, S. Barlow twins: Self-supervised learning via redundancy reduction. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Machine Learning, Baltimore, MD, USA, 7–23 July 2022; pp. 12310–12320. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Cao, Y.; Lin, Y.; Bao, J.; Yao, Z.; Dai, Q.; Hu, H. Simmim: A simple framework for masked image modeling. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, New Orleans, LA, USA, 21–24 June 2022; pp. 9653–9663. [Google Scholar]
- Khosla, P.; Teterwak, P.; Wang, C.; Sarna, A.; Tian, Y.; Isola, P.; Maschinot, A.; Liu, C.; Krishnan, D. Supervised contrastive learning. In Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems 33; Neural Information Processing Systems Foundation, Inc.: La Jolla, CA, USA, 2020; pp. 18661–18673. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.; Song, Y.; Cheng, T. Anomalous Sounds Detection Using a New Type of Autoencoder Based on Residual Connection. DCASE2020 Challenge. 2020. Available online: https://dcase.community/documents/challenge2020/technical_reports/DCASE2020_Chen_25_t2.pdf (accessed on 2 June 2023).
- Giri, R.; Tenneti, S.V.; Cheng, F.; Helwani, K.; Isik, U.; Krishnaswamy, A. Self-supervised classification for detecting anomalous sounds. In Proceedings of the Detection and Classification of Acoustic Scenes and Events Workshop 2020, Tokyo, Japan, 2–4 November 2020. [Google Scholar]



| ChatGPT Prompts: Different Factory Noises |
|---|
| “add sharp and metallic screeching sound created by metal-cutting saws in a fabrication workshop as they cut through various metal materials” |
| “add rhythmic and pulsating buzzing sound produced by printing presses in a publishing house as they rapidly print and collate pages of books and magazines” |
| “add continuous and powerful rumbling noise accompanied by the grinding and crushing of rocks in a mining quarry as large crushers pulverize rocks into smaller fragments” |
| “add continuous and rhythmic clicking noise produced by injection molding machines in a plastic manufacturing facility as they shape molten plastic into various products” |
| “add rhythmic and repetitive whirring noise accompanied by the sound of cutting tools in a woodworking shop as they shape and carve wood materials” |
| “add continuous and powerful whirring noise accompanied by the sound of pneumatic tools in an automobile assembly line as vehicle parts are fastened” |
| Hyperparameter Name | Value |
|---|---|
| The sampling step for DDIM (DDIM_STEPS) | Random (10, 50) |
| The duration of the samples (DURATION) | 10 s |
| Random seed (SEED) | Random for each sample |
| Text prompt for audio generation (TEXT) | add (noises) exist in (factory) |
| Guidance scale (GUIDANCE_SCALE) | 2.5 |
| Methods | RC-MAE without DDA (pAUC) | RC-MAE with DDA (pAUC) |
|---|---|---|
| Valve | 98.01 | 98.37 |
| Fan | 87.44 | 88.10 |
| Pump | 83.89 | 83.25 |
| Slider | 97.16 | 97.84 |
| ToyCar | 90.10 | 91.35 |
| ToyConveyor | 65.38 | 68.70 |
| Average | 86.99 | 87.93 |
| Methods | Valve | Fan | Pump | Slider | ToyCar | ToyConveyor | Average | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AUC | pAUC | AUC | pAUC | AUC | pAUC | AUC | pAUC | AUC | pAUC | AUC | pAUC | AUC | pAUC | |
| AE Baseline [52] | 66.28 | 50.98 | 65.83 | 52.45 | 72.89 | 59.99 | 84.76 | 66.53 | 78.77 | 67.58 | 72.53 | 67.58 | 73.51 | 65.85 |
| GMADE [7] | 99.07 | 96.20 | 83.06 | 79.55 | 87.87 | 82.38 | 97.62 | 89.70 | 95.57 | 91.54 | 81.46 | 66.62 | 90.77 | 84.33 |
| MobileNetV2 [53] | 88.65 | 87.98 | 80.19 | 74.40 | 82.53 | 76.50 | 95.27 | 85.22 | 87.66 | 85.92 | 69.71 | 56.43 | 84.34 | 77.74 |
| Glow_AFF [8] | 91.40 | 75.00 | 74.90 | 65.30 | 83.40 | 73.80 | 94.60 | 82.80 | 92.20 | 84.10 | 71.50 | 59.00 | 85.20 | 73.90 |
| STgram-MFN [39] | 99.64 | 98.44 | 94.04 | 88.97 | 91.94 | 81.75 | 99.55 | 97.61 | 94.44 | 87.68 | 74.57 | 63.30 | 92.36 | 86.34 |
| AADCL [2] | 68.62 | 55.03 | 85.27 | 68.93 | 86.75 | 70.85 | 77.74 | 61.62 | 88.79 | 75.95 | 71.26 | 57.40 | 79.74 | 64.96 |
| Our Method | 99.52 | 98.37 | 95.12 | 88.10 | 92.82 | 83.25 | 99.10 | 97.84 | 95.02 | 91.35 | 84.80 | 68.70 | 94.39 | 87.93 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zahedi, E.; Saraee, M.; Masoumi, F.S.; Yazdinejad, M. Regularized Contrastive Masked Autoencoder Model for Machinery Anomaly Detection Using Diffusion-Based Data Augmentation. Algorithms 2023, 16, 431. https://doi.org/10.3390/a16090431
Zahedi E, Saraee M, Masoumi FS, Yazdinejad M. Regularized Contrastive Masked Autoencoder Model for Machinery Anomaly Detection Using Diffusion-Based Data Augmentation. Algorithms. 2023; 16(9):431. https://doi.org/10.3390/a16090431
Chicago/Turabian StyleZahedi, Esmaeil, Mohamad Saraee, Fatemeh Sadat Masoumi, and Mohsen Yazdinejad. 2023. "Regularized Contrastive Masked Autoencoder Model for Machinery Anomaly Detection Using Diffusion-Based Data Augmentation" Algorithms 16, no. 9: 431. https://doi.org/10.3390/a16090431
APA StyleZahedi, E., Saraee, M., Masoumi, F. S., & Yazdinejad, M. (2023). Regularized Contrastive Masked Autoencoder Model for Machinery Anomaly Detection Using Diffusion-Based Data Augmentation. Algorithms, 16(9), 431. https://doi.org/10.3390/a16090431





__Saraee.png)

