Abstract
Creating machines that behave and work in a way similar to humans is the objective of artificial intelligence (AI). In addition to pattern recognition, planning, and problem-solving, computer activities with artificial intelligence include other activities. A group of algorithms called “deep learning” is used in machine learning. With the aid of magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), deep learning is utilized to create models for the detection and categorization of brain tumors. This allows for the quick and simple identification of brain tumors. Brain disorders are mostly the result of aberrant brain cell proliferation, which can harm the structure of the brain and ultimately result in malignant brain cancer. The early identification of brain tumors and the subsequent appropriate treatment may lower the death rate. In this study, we suggest a convolutional neural network (CNN) architecture for the efficient identification of brain tumors using MR images. This paper also discusses various models such as ResNet-50, VGG16, and Inception V3 and conducts a comparison between the proposed architecture and these models. To analyze the performance of the models, we considered different metrics such as the accuracy, recall, loss, and area under the curve (AUC). As a result of analyzing different models with our proposed model using these metrics, we concluded that the proposed model performed better than the others. Using a dataset of 3264 MR images, we found that the CNN model had an accuracy of 93.3%, an AUC of 98.43%, a recall of 91.19%, and a loss of 0.25. We may infer that the proposed model is reliable for the early detection of a variety of brain tumors after comparing it to the other models.
1. Introduction
The brain, which is the primary component of the human nervous system, and the spinal cord make up the human central nervous system (CNS) [1]. The majority of bodily functions are managed by the brain, including analyzing, integrating, organizing, deciding, and giving the rest of the body commands. The human brain has an extremely complicated anatomical structure [2]. There are some CNC disorders, including stroke, infection, brain tumors, and headaches, that are exceedingly challenging to recognize, analyze, and develop a suitable treatment for [3].
A brain tumor is a collection of abnormal cells that develops in the inflexible skull enclosing the brain [4,5,6]. Any expansion within such a constrained area can lead to issues. Any type of tumor developing inside the skull results in brain injury, which poses a serious risk to the brain [7,8]. In both adults and children, brain tumors rank as the tenth most-prevalent cause of death [9]. There are many different types of tumors, and each one has extremely low survival rates based on the texture, location, and shape [10,11,12].
Around 250,000 people are affected by brain tumors every year, with 2% of those cases being confirmed as malignancies [13]. The predicted number of adults in the United States with a brain tumor in 2020 was 23,890, with 13,590 men and 10,300 women. In 2020, 1879 reported cases of brain cancer were anticipated to be diagnosed in Australia. Every year, 14.1% of Americans are affected by primary brain tumors, of which 70% are children. Although there is no early therapy for primary brain tumors, they do have long-term negative effects [14,15]. Brain tumor cases increased significantly globally between 2004 and 2020 from nearly 10% to 15% [16].
There are about 130 different forms of tumors that can affect the brain and CNS, all of which can range from benign to malignant, from exceedingly rare to common [5]. The 130 brain cancers are divided into primary and secondary tumors [17]:
- Primary brain tumors: Primary brain tumors are those that develop in the brain. A primary brain tumor may develop from the brain cells and may be encased in nerve cells that surround the brain. This type of brain tumor can be benign or malignant [18].
- Secondary brain tumors: The majority of brain malignancies are secondary brain tumors, which are cancerous and fatal. Breast cancer, kidney cancer, or skin cancer are examples of conditions that begin in one area of the body and progress to the brain. Although benign tumors do not migrate from one section of the body to the other, secondary brain tumors are invariably cancerous [19].
A study stated that brain tumors are responsible for about 85–90 percent of all significant CNS tumors [20]. To drastically lower the fatality rate from brain tumors, early identification is important [21]. Medical experts have significantly utilized medical imaging for tumor identification [22]. One of the most-popular methods for the early diagnosis of brain tumors is magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) [23]. Radiologists routinely manually detect brain tumors [24].
The amount of time it takes to grade a tumor depends on the radiologist’s skill and experience. However, the process of identifying a tumor is imprecise and expensive. A patient’s odds of survival can be significantly lowered by misdiagnosing a brain tumor, which can result in serious problems. The MRI technique is becoming more and more popular as a solution to address the limitations of human diagnosis.
In the healthcare industry, deep learning is frequently utilized for analysis, classification, and detection [25,26,27]. The first time the CNN was utilized was in 1980 [28,29,30]. The CNN’s computing capacity is based on a model of the human brain. Humans notice and recognize objects based on their outward appearance. Similar in operation, the CNN is renowned for processing images. Some of the most well-known CNN models include ResNet (152 layers), GoogLeNet (22 layers), AlexNet (8 layers), and VGG (16–19) [31,32,33].
Figure 1 depicts an outline of the primary concepts in this work. The first section introduces brain tumors, MRI for brain tumor detection, and the CNN. In the second section, we review earlier studies on brain tumors using various machine learning models. The proposed architecture is presented in Section 3. The methodology is described in Section 4, where we give a step-by-step breakdown of this research. We also discuss the machine learning models and performance metrics that we used in this study. The performance analysis of the machine learning models is covered in Section 5. The final summary of this research and some future prospects in this field of study are offered in Section 6.
Figure 1.
Outline of this paper.
2. Related Works
In this section we are studied previous researches works about brain tumor detection using ML models. In Table 1 we have summarized some previous works.

Table 1.
Literature Review.
Almadhoun et al. [17] proposed a deep educational model using an MRI dataset for brain tumor detection. In addition to the deep educational model, they applied four other transfer learning models: VGG16, MobileNet, ResNet-50, and Inception V3. They used a dataset of 10,000 MR images with a 200 × 200 pixel resolution to evaluate their models. The dataset was divided into two categories with 5000 images each: brain tumors and non-brain tumors. Their proposed model, the deep educational model, performed better; the training accuracy was 100%, and the test accuracy was 98%.
Musallam et al. [34] introduced a DCNN model using an MRI dataset for detecting brain tumors. In their proposal, a lightweight model with a few convolutions, max-pooling, and iterations was used. The researchers also analyzed VGG16, VGG19, and CNN-SVM. Glioma (934), meningioma (945), no tumor (606), and pituitary(909) were the four subcategories of the 3394 MR images. The suggested model achieved an overall accuracy of 97.72%, a detection rate of 99% for glioma, a detection rate of 98.26% for meningioma, a detection rate of 95.95% for pituitary, and a detection rate of 97.14% for normal images.
Wozniak et al. [35] developed a cutting-edge correlation learning method (CLM) for deep neural network structures that integrates the CNN with a conventional architecture. Meningioma (708 images), glioma (1426 images), and pituitary (930 images) tumors were among the 3064 brain cancers they investigated. Their designed CLM model had an accuracy of around 96%, a precision of about 95%, and a recall of about 95%.
Garg et al. [36] suggested the naive Bayes, random forest, neural network, KNN, and decision tree machine learning models for detecting brain tumors, as well as a hybrid ensemble classifier (KNN-RF-DT). They evaluated the machine learning models using 2556 brain tumor images, with 85% of the data used for training and 15% for testing. For the classification, thirteen features were identified as a result of feature extraction by SWT, PCA, and GLCM. The proposed approach for identifying and categorizing brain tumors was evaluated, and the results showed that the method had an accuracy of 97.305%, a precision of 97.73%, a specificity of 97.60%, a sensitivity of 97.04%, and a reliability of 97.41%.
Nayak et al. [37] proposed dense EfficientNet, which is a CNN-based network, to detect brain tumor images using MRI. The researchers also analyzed ResNet-50, MobileNet, and MobileNetV2, with their dense EfficientNet performing better. They obtained a 98.78% accuracy and a 98.0% F1-score after training the dense EfficientNet model. Four different types of MRI were employed in their research to identify brain tumors. The total dataset comprised 3260 MR images.
Obeidavi et al. [38] introduced a CNN-based residual network for the early detection of brain tumors using a dataset of 2000 MR images. They employed the BRATS 2015 MRI dataset, and the findings for the residual networks were promising. The accuracy of their proposed model was 97.05%. Additionally, they considered other metrics, achieving a mean accuracy of 97.05%, a global accuracy of 94.43%, a mean IoU of 54.21%, a weighted IoU of 93.64%, and a mean BF score of 57.027%. One-hundred epochs were utilized during training to improve the performance.
Khalil et al. [39] proposed a modified two-step dragonfly algorithm for brain tumor segmentation using 3D MR images. The greatest difficulties in identifying and segmenting the early stages of brain tumors are variations in the tumor size and structure. To overcome these challenges, the researchers employed a two-step dragonfly algorithm to precisely extract the original contour point. To obtain the results using the proposed model, they used BRATS 2017 3D MR brain tumor dataset. They achieved an accuracy that was about 5% higher than that of the previous researchers, who performed a nearly identical study. To validate their findings, they also applied a variety of techniques, including fuzzy C-means, SVM, and random forests. To evaluate their results, they considered the metrics of the accuracy, precision, and recall. After evaluating their proposed model, they obtained an accuracy of 98.20%, a recall of 95.13%, and a precision of 93.21%, which were better than the other models. The main weakness in this study was that the researchers only focused on the entire tumor segment, and they did not takeinto account many tumors per slice.
Sajid et al. [40] introduced a hybrid CNN model to detect brain tumors using BRATS MR images. The analysis and validation were performed on the effectiveness of a unique two-phase training method and sophisticated regularization approaches, such as dropout. Their suggested hybrid model combined two- and three-path networks, which enhanced the model’s performance. The model may be effective for a variety of segmentation tasks, according to the capacity analysis of the CNNs, and better performance may be obtained with more training instances. After examining their model, they discovered that their Dice score was 86%, their sensitivity was 86%, and their specificity was 91%.
Lotlikar et al. [15] proposed a KNN classifier for the early detection of abnormalities of the fetal brain. They also considered other classifiers such as RF, NB, and RBF for their research. After evaluating their selected models, they obtained an accuracy of 95.6% and an AUC of 99% for their KNN classifier. To obtain better results, they would need to collect a large number of fetal brain images for their ongoing research. Attallah et al. [41] proposed a deep-learning-based machine learning architecture for the early diagnosis of embryonic neurodevelopmental abnormalities (ENDs). After evaluating various models, they found that their proposed framework showed promising results for detecting ENDs.
Stadlbauer et al. [42] used a physiological MRI approach in combination with nine different common machine learning models for the early detection of brain tumors. Many performance indicators, including the accuracy, precision, F-score, AUROC, and classification error, were taken into account when evaluating the model. In their research, they mentioned that ML-based radiophysiomics might be helpful in detecting brain tumors in the clinical setting. Aamir et al. [43] proposed an automated method for brain tumor detection using MR images. They discovered after evaluating the proposed ML model that it demonstrated superior classification performance compared to existing approaches, showing a 98.95% accuracy.
In our research work, we collected different types of brain tumor MR images. To assess how well our proposed CNN model worked, we also took into account various machine learning models. In our research, the CNN achieved better results compared to the transfer learning models. However, other authors have shown good results when working on transfer learning models and achieved results better than 90% [44]. In our future research, we took this into account and tried to deeply understand this issue. In contrast to the majority of other researchers, we utilized a large dataset of 3264 MRI scans, which is considerably more than what is typically used in many studies. Initially, our system took a long time to process because of the low GPU resources, but we improved the system and lowered the training time. Though other research works had some limitations, we worked to enhance our method, shorten the training period, and increase the performance.
3. Methodology
3.1. Proposed Architecture
In our study, an input image with a size of 32 × 32 pixels was sent to an initial convolutional layer with 16 filters, a 32 × 32 × 16 feature map, and a kernel size of 3 × 3 in order to search for the most-generic features. The convolutional layer’s output was then forwarded to a max-pooling layer feature map of 15 × 15 × 16 to decrease the size of the spatial data for the subsequent layer by half. The max-pooling procedure selected the greatest number of elements or pixels from the feature map area that the filter has covered. This result was then fed to a further convolutional layer with filter values of 32 and a 13 × 13 × 32 feature map with a 3 × 3 kernel size. After that, the output was then forwarded to the max-pooling layer feature map of 6 × 6 × 32 to cut the amount of spatial data for the next layer in half. Another convolutional layer and another pooling layer came next. The feature map of 4 × 4 × 64 in size was made up of 64 filter values and a kernel size of 3 × 3 in the final convolutional layer, while the final pooling layer had a feature map of 2 × 2 × 64. The newly created 4160-dimensional fully connected dense layer received the flattened final output of the previous convolutional layer. This output was sent to the final output layer, which included a softmax activation function. While the last layer employed a softmax activation with no dropout for the output, all the other layers utilized a dropout of 0.5 with a ReLU activation function. The above-proposed CNN architecture’s configuration is depicted in Figure 2. The model was trained, validated, and tested using 80 epochs, a batch size of 18, and a learning rate of 0.01. Along with the Adam optimizer, a categorical cross-entropy-based loss function was calculated to find the loss value.
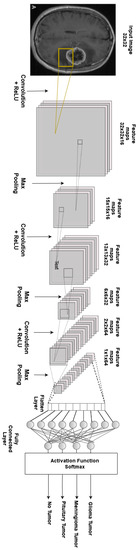
Figure 2.
Proposed CNN Architecture.
The methodology is divided into a few important stages. First, we collected our data from an available online source (kaggle.com (accessed on 10 November 2022)), then we pre-processed our datasets. We used the holdout validation system in the validation stage. We applied various machine learning models to train our images. Our dataset was split into three groups: 80% for training, 10% for testing, and 10% for validation. We tried to validate four different types of brain images: glioma tumors, meningioma tumors, no tumor, and pituitary tumors. Then, in order to validate our findings, we considered several types of metrics including the accuracy, recall, AUC, and loss. Figure 3 shows the step-by-step breakdown of this research.
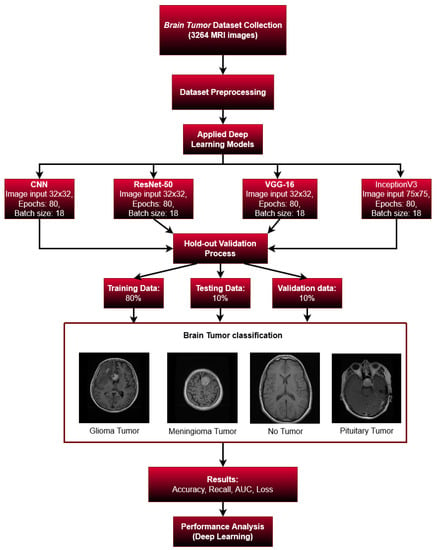
Figure 3.
Overall Study.
3.2. Environment Setup
We set up our environment using a fully cloud-based Google Colab Pro+ platform. The Google Colab Pro+ platform was developed using an NVIDIA Tesla K80, T4, and P100 GPUs. This platform also used a 52 Gb high-RAM runtime. It is quicker and more efficient to train machine learning models using a highly customized platform.
3.3. Dataset Collection
We obtained the dataset from publicly accessible online data on kaggle.com to detect brain tumors [45]. Images from magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) were used to construct the dataset. We selected MR images for our research since MRI is the best technique for detecting brain tumors. Meningioma (937 photos), no tumor (500 images), pituitary tumor (900 images), and glioma tumor (926 images) were the four different types of brain tumor data that we used in our study. In total, we used 3264 MRI data in our dataset. Table 2 displays the breakdown of the dataset, and Figure 4 shows the MR images according to the various forms of brain tumor.

Table 2.
Dataset.
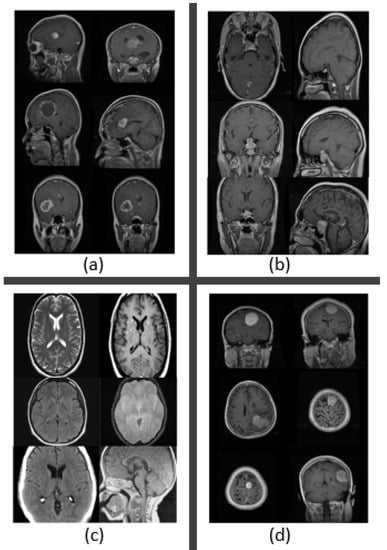
Figure 4.
MR images of brain tumors. (a) Glioma tumor. (b) Pituitary tumor. (c) No tumor. (d) Meningioma tumor.
3.4. Pre-Processing of the Dataset
Pre-processing is an essential stage, where the data are processed to make them usable for training purposes. Since the MR images were obtained from a patient database, they were not clear and low-quality. In order to prepare our images for further processing, we normalized them at this stage. In order to smooth the images and remove the blurred images from the original images, the authors also used Gaussian and Laplacian filters.
3.5. Data Division and Augmentation
Our dataset was small and only included MR images, but deep neural networks require a large dataset to produce promising results. Our dataset included a total of 3264 MR images, with 80% of the data used for training and the remaining images used for testing and validation at a rate of 10% and 10%, respectively. The amount of the original data can be increased by augmentation, and then, the training can be improved. Additionally, this enhances the model’s capacity for learning. Therefore, we performed data augmentation by mirroring the MR images and applied rotation, width and height shifting, and zooming. The datasets were then validated using the holdout validation method.
3.6. Validation Process
For the dataset of the 3264 scan images, it was critical to choose the best validation procedure. We used a holdout validation process, keeping 80% of the data for training and 20% for testing. The holdout validation technique is the most-commonly used method and produces effective results [46]. The holdout method typically involves splitting the dataset into two parts: a training set and a testing set, which helps the model train faster. The training set was used to train the deep learning model, while the testing set was used to evaluate the model’s performance. In the holdout method, 80% of the dataset was randomly selected to be used as the training set, and the remaining 20% was used as the testing set. The model was trained on the training set and then evaluated on the testing set to estimate its performance. The advantage of using 80% of the data for training is that the model has more data to learn from, which can help it generalize better to new, unseen data. However, the testing set is not representative of the overall data, so the performance estimate may be biased.
3.7. Performance Metrics
To evaluate the machine learning models and analyze their performances, we considered some metrics such as the accuracy, recall, and area under the curve (AUC).
3.7.1. Accuracy
Accuracy measures the number of correct predictions divided by the total number of samples. Applying Equation (1), we can calculate the accuracy.
where:
- TP = True positive;
- TN = True negative;
- FN = False negative;
- FP = False positive.
3.7.2. Recall
Recall is one of the another most important metrics to evaluate machine learning model. The recall can be calculated as:
3.7.3. Area under the Curve
AUC stands for the area under the curve. The AUC evaluates how effectively the model distinguishes between both positive and negative categories. Higher AUC values indicate a better performance of the model.
4. Machine Learning Models
4.1. Transfer Learning Models
Transfer learning is a type of machine learning that is frequently employed with previously trained neural networks [47,48,49]. For image categorization and detection, some transfer learning models, including VGG16, ResNet-50, and Inception V3, are frequently utilized [50,51]. Transfer learning methods have the greatest advantages in terms of cost and time efficiency [52]. Instead of beginning from scratch, which takes more time and requires the utilization of GPU resources and big image databases, the pre-trained models are leveraged to transfer information and complete the task [53,54].
4.1.1. ResNet-50
The short form of the residual network is ResNet-50. ResNet-50 is an adaptation of the ResNet architecture that has 50 deep layers and has been trained using at least one million examples from the ImageNet database [55]. The ResNet-50 architecture comprises a series of average pooling convolutional units [56].
Although the residual network layer is connected to the layers further ahead, in typical neural networks, each layer’s output is connected to the next input layer [57]. Figure 5 shows the residual block of the transfer learning model [58]. If there is a large amount of data accessible and there are more layers and parameters, the accuracy will increase. However, when the number of parameters or layers increases, issues such as vanishing gradients start to occur. At this moment, residual networks operate more effectively and provide good solutions. They might skip superfluous or unnecessary layers to achieve greater accuracy. Using residual connections, some layers can be skipped. Skip-connections can be placed between two or more layers [59,60,61].
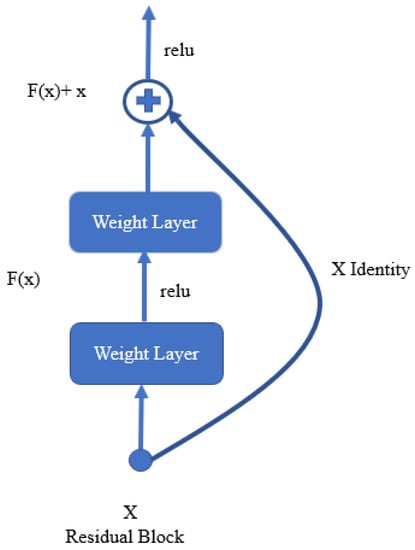
Figure 5.
Residual block.
4.1.2. VGG16
The VGG16 network structure was proposed by Zisserman and Simonyan in 2014, which is one of the VGG-NET-based networks [62]. VGG16 is a deeper network for detecting and classifying images, similar to AlexNet [62,63,64]. The ImageNet database can be used to train VGG16 [65]. When recognizing and categorizing the images, the dataset can be expressed with greater accuracy using VGG16 [66]. One benefit of VGG16 is that it performs better when dealing with vast amounts of data and in complex context recognition tasks [67,68,69]. The VGG16 network includes 16 convolutional layers and a 3 by 3 receptive field. There are a total of 5 such layers, each with a size of 2 × 2 (max-pooling layers). The final max-pooling layer is followed by 3 completely linked layers. The ReLU activation function is utilized to activate the hidden layer in VGG16, and the final layers use the softmax classifier [58]. Figure 6 shows the VGG16 architecture.
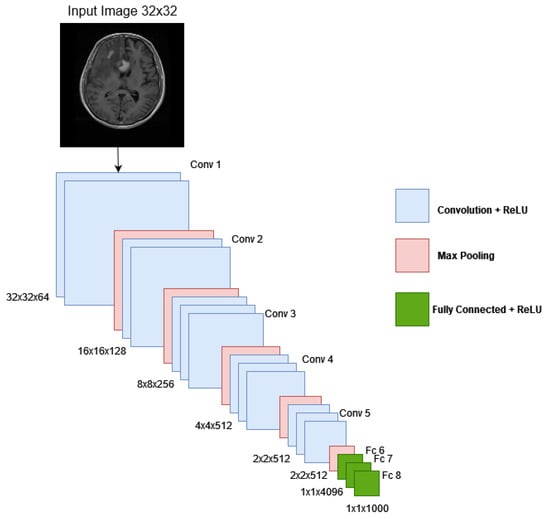
Figure 6.
Architecture of VGG16.
4.1.3. Inception V3
The Inception v3 model is a deep learning network model that is mostly used for image categorization and detection [70,71,72,73]. The training of Inception V3 is difficult with a low computer configuration; sometimes, it takes few days to train the model [71,74]. Compared to Inception V1, which GoogLeNet released in2014, Inception V3 is an upgrade [75]. In 2015, Inception V3 was released with 42 layers and minimal error rates compared to its predecessors. The steps of the Inception process are convolution, pooling, dropout, fully connected, and softmax [76,77]. Figure 7 shows the architecture of Inception V3 [78].
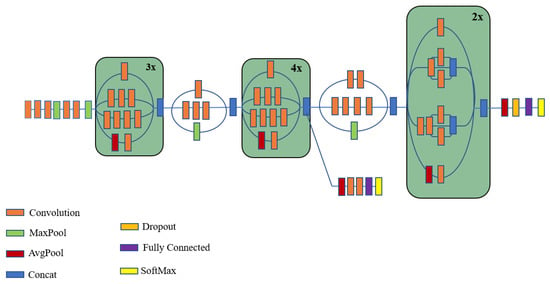
Figure 7.
Architecture of Inception V3.
5. Results’ Analysis and Discussion
The results of various types of developed deep learning models—i.e., the VGG16, CNN, ResNet-50, and Inception V3 classification algorithms—on the brain tumor MR image dataset are analyzed in Table 3, and comparisons are shown in Figure 8. In Table 3, we present the performance of the models with respect to the accuracy, area under the curve (AUC), recall, and loss function results. After analyzing the methods of the CNN, VGG16, ResNet-50, and Inception V3, it was observed that the CNN outperformed the other deep learning models based on the findings in Table 1. The CNN achieved a validation accuracy of 93.3%, a validation AUC of 98.43%, a validation recall of 91.1%, and a validation loss of 0.260.

Table 3.
Deep learning models’ performance on brain tumor detection.
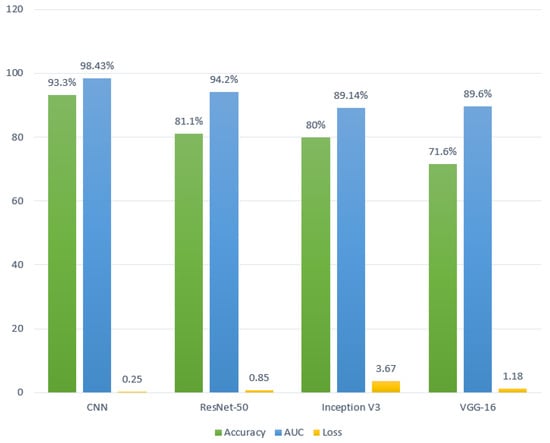
Figure 8.
Performance analysis of the proposed model in terms of the accuracy, AUC, and loss.
In Figure 9, the validation accuracy with respect to the training accuracy graphs for the CNN, ResNet-50, Inception V3, and VGG16 are presented accordingly. The blue lines present the training accuracy, and the orange lines present the validation accuracy. Here, the CNN achieved the highest validation accuracy of 93.30% with a training accuracy value of 90.50%. ResNet-50 achieved a validation accuracy of 81.10% with the highest training accuracy value of 98.43%. Inception V3 achieved a validation accuracy of 80% and a training accuracy of 91.79%. However, VGG16 achieved the least validation accuracy of 71.60% and the least training accuracy of 79.20%. While implementing the models, the epochs were selected to be 80, and the batch size was selected to be 18 with the Adam optimizer. According to the accuracy graph analysis, the CNN performed better than the other models, because the validation accuracy had a great output curve with respect to the training accuracy, and no over-fitting or under-fitting problems occurred.
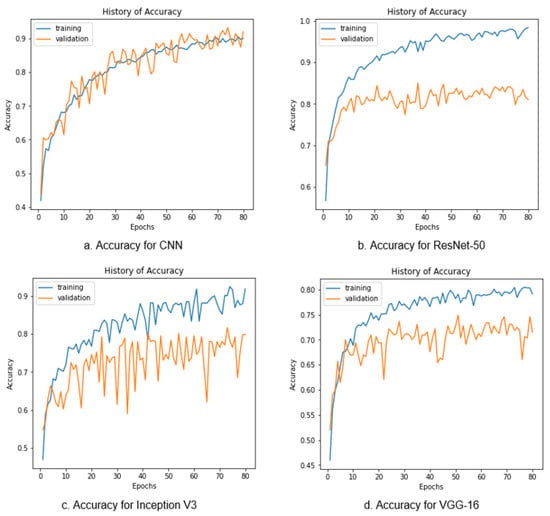
Figure 9.
Accuracy Graphs for the CNN, ResNet-50, Inception V3, and VGG16.
In Figure 10, the validation AUC with respect to the training AUC graphs for the CNN, ResNet-50, VGG16, and Inception V3 are presented accordingly. The blue lines present the training AUC, and the orange lines present the validation AUC. Here, the CNN achieved the highest validation accuracy of 93.30% with a training accuracy value of 90.50%. The AUC determines the model’s performance and assesses the model’s ability to differentiate between classes. The higher the AUC value, the better the model’s performance is. Here, the CNN achieved the highest validation AUC of 98.43% with a training AUC value of 98.40%. ResNet-50 achieved a validation AUC of 94.20% with the highest training AUC value of 99.95%. Inception V3 achieved the least validation AUC of 89.14% and a training accuracy of 96.97%. However, VGG16 achieved a validation AUC of 89.60% and the least training accuracy of 95.32%.
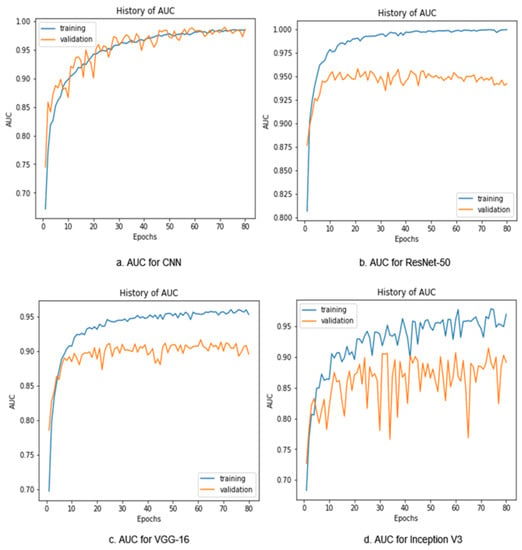
Figure 10.
AUC graph for the CNN, ResNet-50, Inception V3, and VGG16.
In Figure 11, the validation loss with respect to the training loss graphs for the CNN, ResNet-50, VGG16, and Inception V3 are presented accordingly. The blue lines present the training loss, and the orange lines present the validation loss. The loss is a penalty for making an incorrect prediction. However, the loss is a number that indicates how inaccurate the model’s prediction is at each epoch. If the loss is zero, the model’s prediction is perfect; otherwise, the loss is greater. To calculate the loss in the detection process, we used the categorical cross-entropy loss function. The categorical cross-entropy is a loss function that is mostly used in multi-class classification tasks. Here, the CNN achieved the lowest validation loss of 0.250 with a training loss value of 0.289. ResNet-50 achieved a validation loss of 0.853 with a very low training loss value of 0.063. Inception V3 achieved the highest validation loss of 3.67 and a training loss of 0.535. However, VGG16 achieved a validation loss of 1.18 and a training loss of 0.533.
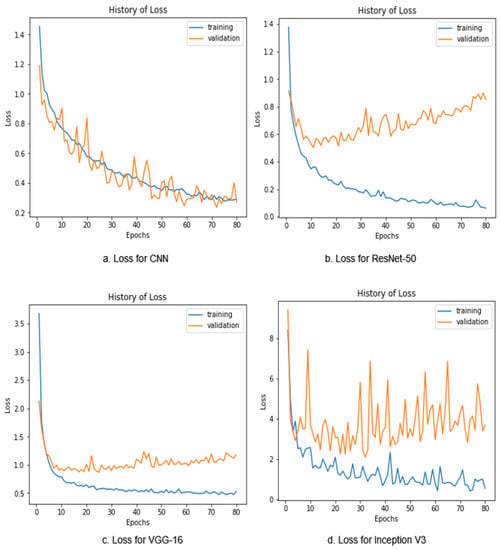
Figure 11.
Loss graph for the CNN, ResNet-50, Inception V3, and VGG16.
In Figure 8, a comparison is made in terms of the accuracy, AUC, and loss of the models. The performance of the models was considered in terms of the accuracy, AUC, and loss. From Figure 5, we can observe that the CNN achieved the highest validation accuracy and validation AUC compared to the other models, which were 93.30% and 98.43%, respectively. Apart from that, the CNN achieved the lowest validation loss of 0.25. However, Inception V3 achieved the highest loss of 3.67 and the least AUC score of 89.14%. Besides, VGG16 achieved the least accuracy score of 71.60% with a high loss value of 1.18. In addition, ResNet-50 achieved the second-highest accuracy and AUC score with a lower loss value. After analyzing the overall scores and performance, the proposed CNN was considered the bestmodel for detecting multiple brain tumors using MR images.
In this research, we tried to analyze various transfer learning models; however, we did not conduct experiments to evaluate how these models work. Considering the fine-tuning of the pre-trained models, we will explore this in future research and strive to gain a deeper understanding of them. In addition, another limitation of this study is that we did not visualize the important areas of the brain tumors due to the lack of any post hoc explanation tools.
6. Conclusions and Future Works
Early detection of brain tumors can play a significant role in preventing higher mortality rates globally. Due to the tumor’s form, changing size, and structure, the correct detection of brain tumors is still highly challenging. Clinical diagnosis and therapy decision-making for brain tumor patients are greatly influenced by the classification of MR images. Early brain tumor identification using MR images and the tumor segmentation method appear promising. Nevertheless, there is still a long way to go before the tumor location can be precisely recognized and categorized. For the purposes of early brain tumor detection in our study, we used a variety of MRI brain tumor images. Deep learning models also have a significant impact on classification and detection. We proposed a CNN model for the early detection of brain tumors, where we obtained promising result using a large amount of MR images. We employed a variety of indicators to ensure the efficiency of the ML models during the evaluation process. In addition to the proposed model, we also took into account a few other ML models to assess our outcomes. Regarding the limitations of our research, as the CNN had several layers and the computer did not have a good GPU, the training process took a long time. If the dataset is large, such as having a thousand images, it would take more time to train. After improving our GPU system, we minimized the training time. Future work can be performed to better correctly identify brain cancers by using individual patient information gathered from any source.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, M.I.M. and M.M.; methodology, M.I.M. and M.M.; software, M.I.M. and M.M.; validation, M.I.M. and M.M.; formal analysis, M.I.M.; investigation, M.M.; resources, A.A.; data curation, M.I.M.; writing—original draft preparation, M.I.M.; writing—review and editing, M.I.M. and M.M.; visualization, M.I.M. and M.M.; supervision, A.A.; project administration, A.A.; funding acquisition, A.A. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Qureshi, S.A.; Raza, S.E.A.; Hussain, L.; Malibari, A.A.; Nour, M.K.; Rehman, A.U.; Al-Wesabi, F.N.; Hilal, A.M. Intelligent Ultra-Light Deep Learning Model for Multi-Class Brain Tumor Detection. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 3715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zahoor, M.M.; Qureshi, S.A.; Bibi, S.; Khan, S.H.; Khan, A.; Ghafoor, U.; Bhutta, M.R. A New Deep Hybrid Boosted and Ensemble Learning-Based Brain Tumor Analysis Using MRI. Sensors 2022, 22, 2726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arabahmadi, M.; Farahbakhsh, R.; Rezazadeh, J. Deep Learning for Smart Healthcare—A Survey on Brain Tumor Detection from Medical Imaging. Sensors 2022, 22, 1960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tandel, G.S.; Biswas, M.; Kakde, O.G.; Tiwari, A.; Suri, H.S.; Turk, M.; Laird, J.R.; Asare, C.K.; Ankrah, A.A.; Khanna, N.; et al. A review on a deep learning perspective in brain cancer classification. Cancers 2019, 11, 111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gore, D.V.; Deshpande, V. Comparative study of various techniques using deep Learning for brain tumor detection. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE International Conference for Emerging Technology (INCET), Belgaum, India, 5–7 June 2020; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- DeAngelis, L.M. Brain tumors. N. Engl. J. Med. 2001, 344, 114–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borole, V.Y.; Nimbhore, S.S.; Kawthekar, D.S.S. Image processing techniques for brain tumor detection: A review. Int. J. Emerg. Trends Technol. Comput. Sci. (IJETTCS) 2015, 4, 2. [Google Scholar]
- Amin, J.; Sharif, M.; Yasmin, M.; Fernandes, S.L. Big data analysis for brain tumor detection: Deep convolutional neural networks. Future Gener. Comput. Syst. 2018, 87, 290–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iorgulescu, J.B.; Sun, C.; Neff, C.; Cioffi, G.; Gutierrez, C.; Kruchko, C.; Ruhl, J.; Waite, K.A.; Negoita, S.; Hofferkamp, J.; et al. Molecular biomarker-defined brain tumors: Epidemiology, validity, and completeness in the United States. Neuro-Oncology 2022, 24, 1989–2000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mabray, M.C.; Barajas, R.F.; Cha, S. Modern brain tumor imaging. Brain Tumor Res. Treat. 2015, 3, 8–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cha, S. Update on brain tumor imaging: From anatomy to physiology. Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2006, 27, 475–487. [Google Scholar]
- Ranjbarzadeh, R.; Bagherian Kasgari, A.; Jafarzadeh Ghoushchi, S.; Anari, S.; Naseri, M.; Bendechache, M. Brain tumor segmentation based on deep learning and an attention mechanism using MRI multi-modalities brain images. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 10930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tiwari, P.; Pant, B.; Elarabawy, M.M.; Abd-Elnaby, M.; Mohd, N.; Dhiman, G.; Sharma, S. CNN Based Multiclass Brain Tumor Detection Using Medical Imaging. Comput. Intell. Neurosci. 2022, 2022, 1830010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anaya-Isaza, A.; Mera-Jiménez, L. Data Augmentation and Transfer Learning for Brain Tumor Detection in Magnetic Resonance Imaging. IEEE Access 2022, 10, 23217–23233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lotlikar, V.S.; Satpute, N.; Gupta, A. Brain Tumor Detection Using Machine Learning and Deep Learning: A Review. Curr. Med. Imaging 2022, 18, 604–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.; Zaccagna, F.; Rundo, L.; Testa, C.; Agati, R.; Lodi, R.; Manners, D.N.; Tonon, C. Convolutional neural network techniques for brain tumor classification (from 2015 to 2022): Review, challenges, and future perspectives. Diagnostics 2022, 12, 1850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almadhoun, H.R.; Abu-Naser, S.S. Detection of Brain Tumor Using Deep Learning. Int. J. Acad. Eng. Res. (IJAER) 2022, 6, 29–47. [Google Scholar]
- Sapra, P.; Singh, R.; Khurana, S. Brain tumor detection using neural network. Int. J. Sci. Mod. Eng. (IJISME) ISSN 2013, 1, 2319–6386. [Google Scholar]
- Soomro, T.A.; Zheng, L.; Afifi, A.J.; Ali, A.; Soomro, S.; Yin, M.; Gao, J. Image Segmentation for MR Brain Tumor Detection Using Machine Learning: A Review. IEEE Rev. Biomed. Eng. 2022, 16, 70–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cancer-Types. Brain Tumor: Statistics. 2022. Available online: https://www.cancer.net/cancer-types/brain-tumor/statistics (accessed on 15 November 2022).
- Zhang, Y.; Li, A.; Peng, C.; Wang, M. Improve glioblastoma multiforme prognosis prediction by using feature selection and multiple kernel learning. IEEE/ACM Trans. Comput. Biol. Bioinform. 2016, 13, 825–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaishnav, P.K.; Sharma, S.; Sharma, P. Analytical review analysis for screening COVID-19 disease. Int. J. Mod. Res. 2021, 1, 22–29. [Google Scholar]
- Mamun, M.; Bin Shawkat, S.; Ahammed, M.S.; Uddin, M.M.; Mahmud, M.I.; Islam, A.M. Deep Learning Based Model for Alzheimer’s Disease Detection Using Brain MRI Images. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE 13th Annual Ubiquitous Computing, Electronics, and Mobile Communication Conference (UEMCON), New York, NY, USA, 26–29 October 2022; pp. 510–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatterjee, I. Artificial intelligence and patentability: Review and discussions. Int. J. Mod. Res. 2021, 1, 15–21. [Google Scholar]
- Mamun, M.; Mahmud, M.I.; Hossain, M.I.; Islam, A.M.; Ahammed, M.S.; Uddin, M.M. Vocal Feature Guided Detection of Parkinson’s Disease Using Machine Learning Algorithms. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE 13th Annual Ubiquitous Computing, Electronics, and Mobile Communication Conference (UEMCON), New York, NY, USA, 26–29 October 2022; pp. 566–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mamun, M.; Uddin, M.M.; Kumar Tiwari, V.; Islam, A.M.; Ferdous, A.U. MLHeartDis:Can Machine Learning Techniques Enable to Predict Heart Diseases? In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE 13th Annual Ubiquitous Computing, Electronics, and Mobile Communication Conference (UEMCON), New York, NY, USA, 26–29 October 2022; pp. 561–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmud, M.I.; Mamun, M.; Abdelgawad, A. A Deep Analysis of Textual Features Based Cyberbullying Detection Using Machine Learning. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE Global Conference on Artificial Intelligence and Internet of Things (GCAIoT), Maidu, Egypt, 18–21 December 2022; pp. 166–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Usman, K.; Rajpoot, K. Brain tumor classification from multi-modality MRI using wavelets and machine learning. Pattern Anal. Appl. 2017, 20, 871–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, C.; Yang, Y.; Juneja, S.; GSeetharam, T. IoT data visualization for business intelligence in corporate finance. Inf. Process. Manag. 2022, 59, 102736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhankhar, A.; Juneja, S.; Juneja, A.; Bali, V. Kernel parameter tuning to tweak the performance of classifiers for identification of heart diseases. Int. J. E-Health Med. Commun. (IJEHMC) 2021, 12, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, T.Y.; RoyChowdhury, A.; Maji, S. Bilinear CNN models for fine-grained visual recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Santiago, Chile, 7–13 December 2015; pp. 1449–1457. [Google Scholar]
- Acharya, U.R.; Oh, S.L.; Hagiwara, Y.; Tan, J.H.; Adam, M.; Gertych, A.; San Tan, R. A deep convolutional neural network model to classify heartbeats. Comput. Biol. Med. 2017, 89, 389–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Demir, F.; Abdullah, D.A.; Sengur, A. A new deep CNN model for environmental sound classification. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 66529–66537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musallam, A.S.; Sherif, A.S.; Hussein, M.K. A New Convolutional Neural Network Architecture for Automatic Detection of Brain Tumors in Magnetic Resonance Imaging Images. IEEE Access 2022, 10, 2775–2782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woźniak, M.; Siłka, J.; Wieczorek, M. Deep Neural Network Correlation Learning Mechanism for CT Brain Tumor Detection. Neural Comput. Appl. 2021, 1–16. Available online: https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s00521-021-05841-x (accessed on 15 November 2022).
- Amin, J.; Sharif, M.; Haldorai, A.; Yasmin, M.; Nayak, R.S. Brain tumor detection and classification using machine learning: A comprehensive survey. Complex Intell. Syst. 2022, 8, 3161–3183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nayak, D.R.; Padhy, N.; Mallick, P.K.; Zymbler, M.; Kumar, S. Brain Tumor Classification Using Dense Efficient-Net. Axioms 2022, 11, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obeidavi, M.R.; Maghooli, K. Tumor Detection in Brain MRI using Residual Convolutional Neural Networks. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE International Conference on Machine Vision and Image Processing (MVIP), Ahvaz, Iran, 23–24 February 2022; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Khalil, H.A.; Darwish, S.; Ibrahim, Y.M.; Hassan, O.F. 3D-MRI brain tumor detection model using modified version of level set segmentation based on dragonfly algorithm. Symmetry 2020, 12, 1256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sajid, S.; Hussain, S.; Sarwar, A. Brain tumor detection and segmentation in MR images using deep learning. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 2019, 44, 9249–9261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Attallah, O.; Sharkas, M.A.; Gadelkarim, H. Deep learning techniques for automatic detection of embryonic neurodevelopmental disorders. Diagnostics 2020, 10, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stadlbauer, A.; Marhold, F.; Oberndorfer, S.; Heinz, G.; Buchfelder, M.; Kinfe, T.M.; Meyer-Bäse, A. Radiophysiomics: Brain Tumors Classification by Machine Learning and Physiological MRI Data. Cancers 2022, 14, 2363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aamir, M.; Rahman, Z.; Dayo, Z.A.; Abro, W.A.; Uddin, M.I.; Khan, I.; Imran, A.S.; Ali, Z.; Ishfaq, M.; Guan, Y.; et al. A deep learning approach for brain tumor classification using MRI images. Comput. Electr. Eng. 2022, 101, 108105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haq, A.u.; Li, J.P.; Khan, S.; Alshara, M.A.; Alotaibi, R.M.; Mawuli, C. DACBT: Deep learning approach for classification of brain tumors using MRI data in IoT healthcare environment. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 15331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sayedgomaa. Brain Tumor Kaggle. Available online: https://www.kaggle.com/code/sayedgomaa/brain-tumor/notebook (accessed on 21 December 2022).
- Dwork, C.; Feldman, V.; Hardt, M.; Pitassi, T.; Reingold, O.; Roth, A. The reusable holdout: Preserving validity in adaptive data analysis. Science 2015, 349, 636–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, B.; Pan, S.J.; Zhang, Y.; Yeung, D.Y.; Yang, Q. Adaptive transfer learning. In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Atlanta, GA, USA, 11–15 July 2010; Volume 24, pp. 407–412. [Google Scholar]
- Zhuang, F.; Qi, Z.; Duan, K.; Xi, D.; Zhu, Y.; Zhu, H.; Xiong, H.; He, Q. A comprehensive survey on transfer learning. Proc. IEEE 2020, 109, 43–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loey, M.; Manogaran, G.; Taha, M.H.N.; Khalifa, N.E.M. A hybrid deep transfer learning model with machine learning methods for face mask detection in the era of the COVID-19 pandemic. Measurement 2021, 167, 108288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peirelinck, T.; Kazmi, H.; Mbuwir, B.V.; Hermans, C.; Spiessens, F.; Suykens, J.; Deconinck, G. Transfer learning in demand response: A review of algorithms for data-efficient modelling and control. Energy 2022, 7, 100126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahsan, M.; Gomes, R.; Denton, A. Application of a convolutional neural network using transfer learning for tuberculosis detection. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE International Conference on Electro Information Technology (EIT), Brookings, SD, USA, 20–22 May 2019; pp. 427–433. [Google Scholar]
- Thenmozhi, K.; Reddy, U.S. Crop pest classification based on deep convolutional neural network and transfer learning. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2019, 164, 104906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heidari, M.; Rafatirad, S. Using transfer learning approach to implement convolutional neural network model to recommend airline tickets by using online reviews. In Proceedings of the 2020 15th IEEE International Workshop on Semantic and Social Media Adaptation and Personalization (SMA), Zakynthos, Greece, 29–30 October 2020; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Rahman, T.; Chowdhury, M.E.; Khandakar, A.; Islam, K.R.; Islam, K.F.; Mahbub, Z.B.; Kadir, M.A.; Kashem, S. Transfer learning with deep convolutional neural network (CNN) for pneumonia detection using chest X-ray. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 3233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akiba, T.; Suzuki, S.; Fukuda, K. Extremely large minibatch sgd: Training resnet-50 on imagenet in 15 minutes. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1711.04325. [Google Scholar]
- Almourish, M.H.; Saif, A.A.; Radman, B.M.; Saeed, A.Y. COVID-19 diagnosis based on CT images using pre-trained models. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE International Conference of Technology, Science and Administration (ICTSA), Taiz, Yemen, 22–24 March 2021; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, P.; Tan, Y. Estimation of economic indicators using residual neural network ResNet-50. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE International Conference on Data Mining Workshops (ICDMW), Beijing, China, 8–11 November 2019; pp. 206–209. [Google Scholar]
- Theckedath, D.; Sedamkar, R. Detecting affect states using VGG16, ResNet-50 and SE-ResNet-50 networks. Comput. Sci. 2020, 1, 79. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Haija, Q.A.; Manasra, G.F. Development of Breast Cancer Detection Model Using Transfer Learning of Residual Neural Network (ResNet-50). Am. J. Sci. Eng. 2020, 1, 30–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Setiawan, A.W. The Effect of Image Dimension and Exposure Fusion Framework Enhancement in Pneumonia Detection Using Residual Neural Network. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE International Seminar on Application for Technology of Information and Communication (iSemantic), Wuhan, China, 4–6 Feburary 2022; pp. 41–45. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, T.; Zhang, Q.; Yuan, J.; Wang, C.; Li, C. Multi-Type Object Tracking Based on Residual Neural Network Model. Symmetry 2022, 14, 1689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simonyan, K.; Zisserman, A. Very deep convolutional networks for large-scale image recognition. arXiv 2014, arXiv:1409.1556. [Google Scholar]
- da Rocha, D.A.; Ferreira, F.M.F.; Peixoto, Z.M.A. Diabetic retinopathy classification using VGG16 neural network. Res. Biomed. Eng. 2022, 38, 761–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pravitasari, A.A.; Iriawan, N.; Almuhayar, M.; Azmi, T.; Irhamah, I.; Fithriasari, K.; Purnami, S.W.; Ferriastuti, W. UNet-VGG16 with transfer learning for MRI-based brain tumor segmentation. TELKOMNIKA (Telecommun. Comput. Electron. Control.) 2020, 18, 1310–1318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, J.; Dong, W.; Socher, R.; Li, L.J.; Li, K.; Fei-Fei, L. ImageNet: A large-scale hierarchical image database. In Proceedings of the 2009 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Miami, FL, USA, 20–25 June 2009; pp. 248–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H. Garbage recognition and classification system based on convolutional neural network VGG16. In Proceedings of the 2020 3rd IEEE International Conference on Advanced Electronic Materials, Computers and Software Engineering (AEMCSE), Shenzhen, China, 24–26 April 2020; pp. 252–255. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, J.; Wang, Z. YOLO V3+ VGG16-based automatic operations monitoring and analysis in a manufacturing workshop under Industry 4.0. J. Manuf. Syst. 2022, 63, 134–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Yi, M.; Wu, M.; Wang, J.; He, Y. Breast Pathological Image Classification Based on VGG16 Feature Concatenation. J. Shanghai Jiaotong Univ. (Sci.) 2022, 27, 473–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, H. Face Expression Classification Using Squeeze-Excitation Based VGG16 Network. In Proceedings of the 2022 2nd IEEE International Conference on Consumer Electronics and Computer Engineering (ICCECE), Guangzhou, China, 14–16 January 2022; pp. 482–485. [Google Scholar]
- Jignesh Chowdary, G.; Punn, N.S.; Sonbhadra, S.K.; Agarwal, S. Face mask detection using transfer learning of inceptionv3. In Big Data Analytics, Proceedings of the 8th International Conference, BDA 2020, Sonepat, India, 15–18 December 2020; Proceedings 8; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2020; pp. 81–90. [Google Scholar]
- Xia, X.; Xu, C.; Nan, B. Inception-v3 for flower classification. In Proceedings of the 2017 2nd IEEE International Conference on Image, Vision and Computing (ICIVC), Chengdu, China, 2–4 June 2017; pp. 783–787. [Google Scholar]
- Tio, A.E. Face shape classification using inception v3. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1911.07916. [Google Scholar]
- Mujahid, M.; Rustam, F.; Álvarez, R.; Luis Vidal Mazón, J.; Díez, I.d.l.T.; Ashraf, I. Pneumonia Classification from X-ray Images with Inception-V3 and Convolutional Neural Network. Diagnostics 2022, 12, 1280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.; Chen, D.; Hao, L.; Liu, X.; Zeng, Y.; Chen, J.; Zhang, G. Pulmonary image classification based on inception-v3 transfer learning model. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 146533–146541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Yang, C.; Huang, J.; Liu, S.; Zhuo, Y.; Lu, X. Deep learning framework based on integration of S-Mask R-CNN and Inception-v3 for ultrasound image-aided diagnosis of prostate cancer. Future Gener. Comput. Syst. 2021, 114, 358–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrew, A.; Santoso, H. Compare VGG19, ResNet-50, Inception-V3 for review food rating. Sink. J. Dan Penelit. Tek. Inform. 2022, 7, 845–494. [Google Scholar]
- Al Husaini, M.A.S.; Habaebi, M.H.; Gunawan, T.S.; Islam, M.R.; Elsheikh, E.A.; Suliman, F. Thermal-based early breast cancer detection using inception V3, inception V4 and modified inception MV4. Neural Comput. Appl. 2022, 34, 333–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, W.J.; Chen, L.B.; Hsu, C.H.; Lin, C.P.; Yang, T.C. A Deep Learning-Based Intelligent Medicine Recognition System for Chronic Patients. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 44441–44458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).