Abstract
Autism spectrum disorder (ASD) is a neurodevelopmental disorder that severely impairs an individual’s cognitive, linguistic, object recognition, communication, and social abilities. This situation is not treatable, although early detection of ASD can assist to diagnose and take proper steps for mitigating its effect. Using various artificial intelligence (AI) techniques, ASD can be detected an at earlier stage than with traditional methods. The aim of this study was to propose a machine learning model that investigates ASD data of different age levels and to identify ASD more accurately. In this work, we gathered ASD datasets of toddlers, children, adolescents, and adults and used several feature selection techniques. Then, different classifiers were applied into these datasets, and we assessed their performance with evaluation metrics including predictive accuracy, kappa statistics, the f1-measure, and AUROC. In addition, we analyzed the performance of individual classifiers using a non-parametric statistical significant test. For the toddler, child, adolescent, and adult datasets, we found that Support Vector Machine (SVM) performed better than other classifiers where we gained 97.82% accuracy for the RIPPER-based toddler subset; 99.61% accuracy for the Correlation-based feature selection (CFS) and Boruta CFS intersect (BIC) method-based child subset; 95.87% accuracy for the Boruta-based adolescent subset; and 96.82% accuracy for the CFS-based adult subset. Then, we applied the Shapley Additive Explanations (SHAP) method into different feature subsets, which gained the highest accuracy and ranked their features based on the analysis.
1. Introduction
Autism spectrum disorder (ASD) is a neuro-developmental disorder where it appears in human beings during the first three years [1]. It is basically characterized by several symptoms such as impairments in social interaction, communication, restricted interests, and repetitive behavior [2]. Individuals with ASD face difficulty understanding other’s feelings and thinking. They experience many problems communicating with others. As reported by the World Health Organization (WHO), throughout the world, around 1 in 270 individuals has ASD [3]. Each individual with ASD has unique characteristics, and some have exceptional abilities in visual, academic, and music skills. In this case, the most important steps are required to detect ASD and to ensure proper treatment as early as possible. These steps are helpful to decrease the effects of this disorder and to improve their condition. The symptoms of ASD are identified by different types of observations. However, a significant amount of time and effort are needed where early detection is useful for providing better treatment for ASD patients. Recently, machine learning methods are widely used for analyzing the symptoms of various severe diseases like heart disease, diabetes, and cancer tissues, etc. Therefore, many researchers explored numerous methods [4,5] that are helpful to identify ASD patients and decrease the affects of ASD more precisely.
The objective of this work was to propose a machine learning model that explores ASD of toddlers, children, adolescents, and adults at an early stage as well as to investigate the individual characteristics of them more efficiently. In this model, we generated several feature subsets of toddlers, children, adolescents, and adults using various feature selection techniques. Different classification methods were applied into primary and its feature subsets. Then, their results were compared, and we determined the best classifier for each age group and the feature subset for which the highest results were obtained. Additionally, the performance of these classifiers were investigated using a non-parametric statistical significant test. Then, we interpreted the results of the best feature subsets and selected significant features of ASD using an explainable AI method. The following concise summary of the contribution is given as follows:
- We proposed an efficient machine learning method that has the potential to identify ASD with high accuracy at an early stage.
- We concentrated on identifying important feature subsets and explained different features to know how individual features are responsible to generate the best result to diagnose ASD or not.
- To justify the performance of the classifier, we used a non-parametric statistical method and checked the classifier’s pairwise significance.
- This method is helpful to identify ASD in a simple and flexible way.
This article is structured as follows: Section 2 contains a literature review on ASD screening approaches. Section 3 represents the working steps of detecting ASD and its characteristics. Section 4 describes the experimental results and an interpretation of these results. Section 5 describes the discussion and conclusion.
2. Literature Review
Many state-of-art works were happened to investigate, classify and explore significant factors of ASD. Thabtah et al. [6,7,8,9] developed a mobile application named ASDTests for data collection related to ASD for toddlers, children, adolescents, and adults. This app was built based on Q-CHAT and AQ-10 tools to predict ASD or not. They collected ASD data using this app and uploaded them into the University of California-Irvine (UCI) Machine Learning (ML) repository. Omar et al. [10] proposed an effective machine learning model where they analyzed AQ-10 and 250 real datasets with Random Forest (RF), Classification and Regression Trees (CART) and Random Forest-Iterative Dichotomiser 3 (ID3). Sharma et al. [11] investigated these datasets by employing CFS-greedy stepwise feature selector and further applied Naïve Bayes (NB), Stochastic Gradient Descent (SGD), K-Nearest Neighbours (KNN), Random Tree (RT), and K-Star (KS) into these datasets. Satu et al. [12] collected some samples of 16–30 years children where several tree based classifiers were used to investigate them and extracted several rules for normal and autism. Erkan et al. [13] analyzed similar datasets by implementing KNN, SVM, and RF where RF showed the best performance to identify ASD. Another study by Thabtah et al. [14] generated several feature subsets of adults and adolescents using Information Gain (IG) and Chi-Squared (CHI) where Logistic Regression (LR) was used to identify ASD from them. Akter et al. [15] gathered toddlers, children, adolescents, and adults datasets and generated some transformed sets. Then, different classifiers were used to analyze them where SVM showed the best performance for the toddler as well as Adaboost provided both children and adult. In addition, Glmboost showed the best outcomes the adolescent dataset. Hossain et al. [16] investigated similar types of datasets and generated subsets using CFS, CHI, IG, One-R and Relief-F methods. Further, they employed LR, Multilayer Perceptron (MLP), Sequential minimal optimization (SMO) into them. Then, SMO showed the best accuracy 91% for child, 99.9% for adolescent, 97.58% for adult datasets. Raj et al. [17] scrutinized these datasets (i.e., excluding toddler) using SVM, LR, NB, and Convolutional Neural Network (CNN) where CNN showed the highest accuracy 98.30% for child, 96.88% for adolescent, and 99.53%, for adult, respectively. Again, Thabtah et al. [18] developed a Rules-based Machine Learning (RML) method for extracting ASD traits where RML gave higher predictive accuracy from other machine learning approaches. Chowdhury et al. [19] provided an association classification technique with seven algorithms where this method showed 97% accuracy to detect ASD. Akter et al. [20] gathered ASD dataset of different age levels and generated some transformed subsets of it. They analyzed them with several classifiers where LR outperformed other classifiers and extracted significant traits. Akter et al. [21] also extracted several autism subtypes using k-means algorithms. Then, they identified different discriminatory factors among them.
3. Methodology
In this work, we used different feature selection methods and generated some feature subsets. Then, some classification algorithms were applied into primary toddler, child, adolescent, and adult datasets and their feature subsets. The performance of different classifiers were investigated to determine which features are more useful to detect ASD from controls. Figure 1 shows the proposed model of ASD detection at early stage.
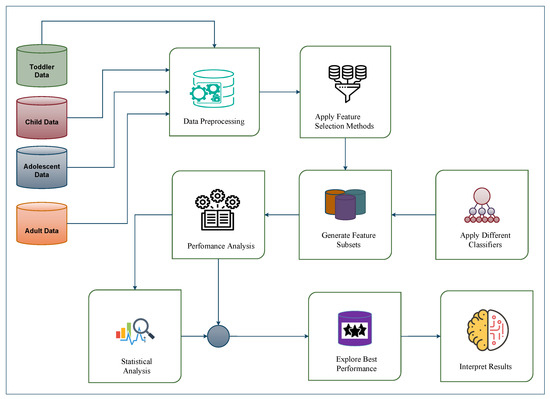
Figure 1.
The proposed framework for early ASD detection.
3.1. Data Preprocessing
Dataset Description: Thabtah et al. [6] from the Nelson Marlborough Institute of Technology developed an autism screening app called ASDTests, which was used for data collection from the target audience (toddlers, children, youths, and adults). It used Q-CHAT-10 and AQ-10 questionnaires (AQ-10 Child, AQ-10 Adolescent, and AQ-10 Adult) to determine ASD risk factors. This app automatically computed its final-score from 0 to 10. It indicates a positive prediction of ASD if the final-score is greater than 6 out of 10. In this work, we used toddler, child, adolescent, and adult ASD datasets (version 2) [22,23,24,25], where the toddler dataset consisted of 18 features; however, the child, adolescent, and adult datasets contained 23 features. These datasets contained the records of 12–36 months (toddlers), 4–11 years (child), 12–16 years (adolescent), and 18 years or greater (adult) age groups. Table 1 shows the details of these datasets, and Table 2 provides the description of individual features of these datasets that were used for analysis.

Table 1.
Data description.

Table 2.
Features description.
Data Cleaning: We cleaned these datasets to simplify this model and increased classification accuracy by deleting instances with missing values. After that, we discarded some irrelevant features (i.e., those which are not related to ASD) such as the case, whether they the used app before, the user (who completed the screening), the language, why they had taken the screening, the age description, the screening type, and the score, respectively. The score 7 to 10 was used to classify ASD prediction for the child, adolescent, and adult datasets. A value of 4 or higher was classified as ASD for the toddler dataset. In this work, we selected 16 features for the child, adolescent, and adult datasets and 15 features for the toddler dataset, respectively.
3.2. Implementing Feature Selection Methods
Feature selection is required to identify significant attributes that improve the performance of machine learning models [26]. Many state-of-the-art works were found where various significant features were identified to detect autism more efficiently [27] On the toddler, child, adolescent, and adult datasets, various feature selection techniques such as the Boruta algorithm, Correlation-based Feature Selection with Harmony Search (CFS–Harmony Search), Repeated Incremental Pruning to Produce Error Reduction (RIPPER), and Recursive Feature Elimination (RFE) were used to explore various feature subsets. A brief description about them is given as follows:
- Boruta algorithm is a wrapper algorithm based on the random forest [28] where it finds the importance of a feature by creating shadow features [29]. It is an extended system where each feature of the given data set is replicated. Then, the values of replicated variables are randomly combined, which are called shadow features. It performs its feature selection process using RF on the extended data set and evaluates the importance of each feature. Additionally, it computes the z-score of real and shadow features. It compares higher z-score values of real features than the maximum z-score value of its shadow features at every iteration. In this process, it constantly eliminates features that are deemed highly unimportant. Finally, the algorithm ends either when all features are approved or rejected or it obtains a particular limit of RF runs [30].
- Correlation-based Feature Selection (CFS–Harmony Search) is a heuristic function that evaluates the ranks of features based on their correlation [31]. For harmony search, it illustrates the point of intersection with the following parameters: the number of harmonies in memory N, the number of indicator M, the number of possible values of indicator D, the number of optimal indicator i in the harmony memory = , and the rate of harmony memory . The probability is calculated by the following equation,
- Repeated Incremental Pruning to Produce Error Reduction (RIPPER) is the rule induction algorithm that was introduced by W. Cohen in 1995 [32]. It is generated as a set of if-then-else rules that evolves several iterations of the rule learning algorithm. This model is maintained by three-steps such as grow, prune, and optimize [33] where the evaluation process is denoted as,where = the initial rule, = the rule after adding conjunct, c = the number of true instances covered by and , = the number of true instances covered by , = the number of false instances covered by , = the number of true instances covered by , and = the number of false instances covered by [34].
- Recursive Feature Elimination (RFE) is a feature selection technique that discards the least important features recursively. In this process, the initial features are trained where each important feature is acquired through any selected attributes [35]. Then, the least important features are eliminated from the initial feature set. This process is recursively repeated until the desired number of feature subsets are obtained [36]. The steps of RFE are given as follows [37]:
- Train the classifier.
- Calculate the score for all features with the ranking.
- Eliminate the feature with the lowest score.
3.3. Apply Individual Classification Methods
After generating various feature subsets, 30 widely used classifiers were implemented into all of these datasets and their subsets. Some classifiers that produced less than 70% accuracy were eliminated. Thus, the performance of NB, KS, C4.5, CART, SVM, KNN, Bagging (BG), and Random Tree (RT) were considered. Then, we compared their performance and detected the best classifier. In addition, it detects feature subsets for which the classifier shows the highest outcomes. Therefore, a brief description of them are given as follows:
- Naïve Bayes (NB) is a most constructive probabilistic classifier based on Bayes theorem [38]. It predicts target output more efficiently according to the foundation of the probability of an entity. The formula of Bayes theorem is given as,The derivation form for NB is:Here, is the subsequent probability of the target class; is the earlier probability of the class; is the prospect of the predictor specified class; and is the earlier probability of the predictor (see Equation (3)).
- K-Star (KS) is an instance-based classifier that categorizes samples or instances by differentiating it based on pre-categorized samples [39]. Some similar functions are used to determine the class of test instances. It uses an entropy-based function, which differentiates from other instance-based learners [40].
- Decision Tree (C4.5) is the extension version of the ID3 algorithm that uses the recursive divide and conquer method to produce the C4.5 decision tree [41]. When unknown data are found, this method predicts a target class by satisfying several conditions. C4.5 uses Information Gain (IG) that calculates the gain ratio by the following equation [42],
- Classification and Regression Trees (CART) use several classification and regression trees where classification trees are used to accumulate the finite number of unsorted values and determine the prediction errors. Besides, regression trees are employed for grouping sorted or ordered values and determining the prediction error by calculating the root squared difference between target and predicted values [43].
- K-Nearest Neighbour (KNN) is used for classifying instances based on their nearest neighbors [44]. It generally takes more than one neighbor and determines their distances using the Euclidean method, which is calculated with the following equation [45],where, D is distance between points.
- Support Vector Machine (SVM) generates some vectors to create a decision boundary that separates n-dimensional space into classes. This decision boundary is called a hyperplane. In the general situation, two parallel hyperplanes are generated, which concurrently minimizes the classification error and maximizes the margin of classes. It is called a maximum margin classifier [46].
- Bagging Classifier (BG) is a parallel ensemble method that generates several random subsets from substitution of the original dataset. Then, we analyzed them using the base classifier and aggregated their predictions by voting [47]. It decreases the variance and correctly predicts the target outcome.
- Random Tree (RT) is a decision tree where a set of possible trees are randomly generated with K random features. The combination of large sets of random trees is generally produced with accurate predictions more efficiently [48].
3.4. Use Evaluation Metrics for Performance Analysis of Classifiers
The performance measurement is essential for evaluating how well a classification model correctly predicts instances and achieves a desired target [17,49]. The confusion matrix provides a more detailed overview of a predictive model’s performance. It represents which classes are being predicted correctly and incorrectly and shows the measurement of type errors. In the confusion matrix, every instance in a given dataset falls into one of the four categories: True Positive (TP), True Negative (TN), False Positive (FP), and False Negative (FN) [16]. The above four category data are arranged in a matrix known as the confusion matrix. Table 3 shows the elements of the confusion matrix.

Table 3.
Confusion matrix for ASD.
In this work, we used several evaluation metrics including accuracy, kappa statistics, the F1-Score, and AUROC to assess the performance of each classifier. To calculate these metrics, the confusion matrix is required to generate and gather different types of instances from it. These metrics are described briefly as follows:
- Accuracy: It is a measure of how effective the model is used to predict outcomes [49], in terms of the total number of predictions:
- Kappa statistics (Kp): It measures observer agreement for categorical data and expected accuracy and has received considerable attention [50].
- Precision: It is a measure of true-positive predictions against all retrieved positive instances [51].
- Recall: It is a measure of correctly predicted positive observations against all relevant positive classes [51].
- F1 score: It is the harmonic average of precision and recall [52]:
- AUROC: It determines how well true-positive values are isolated from false-positive values [15]:
3.5. Determining the Performance of Classifiers Using Statistical Tests
After the classification process, we needed to justify these outcomes using various statistical methods and recheck their performance. In this work, the Wilcoxon Signed-Rank (WSR) method was used to test the statistical significance of the individual classifier. We employed this method into the outcomes of different evaluation metrics in the individual age group. A brief description of the WSR method is given as follows:
- Wilcoxon Signed-Rank Test is a non-parametric statistical test that is used to compare two independent samples. This method is considered an alternative of the t-test when the population mean is not of interest. The working formula of this method is given as follows:where W denotes test statistics; N indicates the sample size; denotes a sign function; both represent the ranked pairs of the two distributions; and indicates the rank.
3.6. Interpretation of the Results of Machine Learning Models
Explainable AI is a combination of methods that allows individual users to comprehend the results of machine learning models. In this work, we explored the best performing classifiers which generate the highest results for different feature subsets in the individual age groups. To interpret these outcomes, the SHapley Additive exPlanations (SHAP) method was used to explain which feature vectors are required to generate these predictions. The SHAP method is described in brief as follows:
- The SHAP method is a game-theoretic process to explain the output of any individual model. This model was developed by Lundberg and Lee [53]. The purpose of this method is to compute the contribution of each feature for an instance’s prediction. It associates optimal credit allocation with a local explanation using Shapley values. The simplest general SHAP values are represented as follows [54]:
- Select an objective feature function.
- Calculate the Shapley value for all features.
- Choose the highest-ranking features.
4. Experimental Results
In the primary stage, this study used the Classification and Regression Training (CARET) package in R for feature selection and classification tasks [55]. However, Boruta, CFS, RIPPER, and RFE methods were implemented to produce numerous feature subsets for different age groups (i.e., toddler, child, adolescent, and adult). Table 4 shows the details of these feature subsets, respectively. Then, different baselines (i.e., primary data) along with their feature subsets were scrutinized by eight classifiers such as NB, BG, CART, KNN, C4.5, KS, SVM, and RT, respectively. In this case, we considered the k-fold cross-validation technique for classification, where the value of k is regarded as 10. After the classification process, a non-parametric statistical WSR test was employed to evaluate the performance of individual classifiers using Knowledge Extraction based on Evolutionary Learning (KEEL) software [56]. Then, SHAP summary plots were generated using the shap package in Python for the best classifier and different subsets. Figure 2 shows the details of illustrations about how to interpret machine learning models and explore importance features for generating significant outputs.

Table 4.
The generated feature subsets of individual age groups.
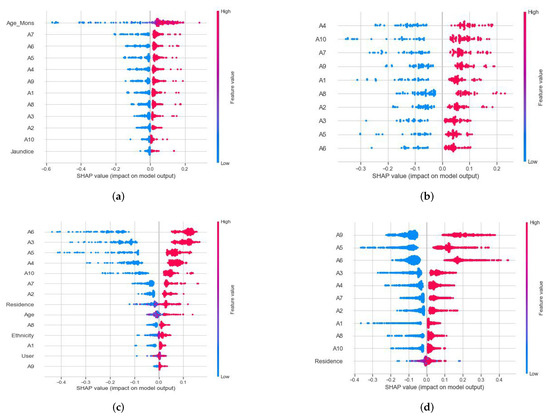
Figure 2.
Analysis of Shapley values for (a) the toddler subset of the RIPPER method, (b) the adolescent subset of the Boruta algorithm, (c) the child subset of the CFS–Harmony Search method, and (d) the adult subset of the CFS method employing the best-performing SVM.
4.1. Generating Several Feature Subsets
Different feature selection methods such as Boruta, CFS, RIPPER, and RFE were applied into four ASD baselines and generated , , , , and for intersecting with , respectively [27]. Table 4 shows several feature subsets in different age groups.
4.2. Result Analysis of Accuracy
We applied NB, BG, CART, KNN, C4.5, KS, SVM, and RT into four datasets where the highest 96.67%, 95.48%, 95.48%, and 96.06% accuracies were generated by SVM for toddler, child, adolescent, and adult datasets, respectively. After investigating the performance of these classifiers into the baseline and six feature subsets, we found greater improved accuracy to detect autism. In toddlers, SVM gave the maximum accuracy of 97.82% for (see Table 5). Then, we observed that the highest accuracy (99.61%) was calculated by SVM for and for children (see Table 6). Regarding the case of adolescents, SVM also provided the maximum accuracy of 95.87% for (see Table 7). In adults, the highest accuracy (96.82%) was found for , which was computed by SVM (see Table 8). Besides, other classifiers such as NB, KS, and KNN provided good accuracy similar to SVM. Figure 3a shows the average accuracy of individual classifiers in each age group. Here, we also observed that SVM represented the best average outcomes among all classifiers.

Table 5.
Performance analysis of classifiers for baseline and its generated feature subsets of toddlers.

Table 6.
Performance analysis of classifiers for baseline and its generated feature subsets of children.

Table 7.
Performance analysis of classifiers for baseline and its generated feature subsets of adolescents.

Table 8.
Performance analysis of classifiers for baseline and its generated feature subsets of adults.
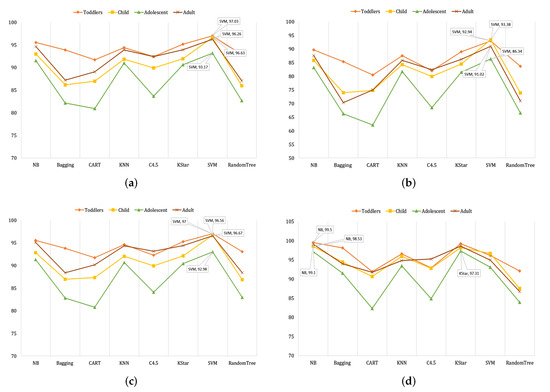
Figure 3.
The average (a) accuracy, (b) kappa statistics, (c) F1, and (d) AUROC of the toddler, child, adolescent, and adult datasets of the classifiers.
4.3. Result Analysis of Kappa Statistics
Table 5, Table 6, Table 7 and Table 8 show the outcomes of kappa statistics of NB, BG, CART, KNN, C4.5, KS, SVM, and RT for four ASD groups and their feature subsets. In toddlers, the highest kappa (94.87%) was calculated by SVM for . Regarding the case of children, SVM also provided the highest kappa of 99.21% for and . For adolescents, the maximum result (91.74%) was computed by SVM for . In the adult case, the highest kappa (99.59%) was shown by SVM for . Like the outcomes of accuracy, NB, KS, and KNN showed the closest kappa to detect autism. Besides, the average kappa statistics of the toddler, child, adolescent, and adult datasets are shown in Figure 3b. In this case, SVM again showed the best average kappa in each age group.
4.4. Result Analysis of F1-Score
The performance of F-measures in each classifier is shown in Table 5, Table 6, Table 7 and Table 8, for ASD baselines and their subsets, respectively. The maximum F1-Score (97.80%) was generated by SVM for regarding the toddler dataset. When we observed the findings of the children, SVM also gave the highest f-measure (99.90%) for and . In adolescents, the best result (95.90%) was generated by SVM for . For the adult dataset, SVM again provided the highest outcome (96.90%) for . However, NB, KS, and KNN represented good results, which were almost similar to SVM. The average F-measure of the toddler, child, adolescent, and adult datasets of different classifiers are shown in Figure 3c. Further, SVM provided the average highest results in each age group.
4.5. Result Analysis of AUROC
The results of AUROC for the baseline and their feature subsets are shown in Table 5, Table 6, Table 7 and Table 8. In toddlers, NB provided the maximum result of 99.70% for . Regarding the children, SVM and KS gave the highest result of 99.60% for and , respectively. For adolescents, the maximum result of 99.00% was produced by NB for . In adults, SVM provided a result of 99.80%, which was the best outcome for . AUROC, NB, SVM, KS, and KNN showed good outcomes, whereas the performance of NB was slightly improved over others. The average AUROC of the toddler, child, adolescent, and adult datasets of different classifiers are shown in Figure 3d. In this analysis, NB showed the highest average scores to detect autism.
4.6. Result Analysis of Non-Parametric Statistical Analysis
In this study, the performance of different classifiers were investigated using non-parametric the Wilcoxon Signed-Rank (WSR) test. We observed pairwise WSR values for toddlers (i.e., Table 9, Table 10, Table 11 and Table 12), children (i.e., Table 13, Table 14, Table 15 and Table 16), adolescents (i.e., Table 17, Table 18, Table 19 and Table 20), and adults (i.e., Table 21, Table 22, Table 23 and Table 24). At almost all age levels, SVM is a stable classifier to provide better pairwise statistical significance with other classifiers in order to improve the accuracy, kappa statistics, and f1-measure. Besides, NB sometimes shows better statistical significance for these following metrics. However, this classifier showed better pairwise WSR results with others for AUROC. Some other pairwise outcomes such as C4.5-CART, KNN-CART, KS-BG, KS-CART, KS-KNN, KS-C4.5, KS-RT, CART-RT, KNN-RT, and C4.5-RT showed almost-good outcomes in this test.

Table 9.
Pairwise WSR test for accuracy of toddlers.

Table 10.
Pairwise WSR test for kappa statistics of toddlers.

Table 11.
Pairwise WSR test for F1-measure of toddlers.

Table 12.
Pairwise WSR test for AUROC of toddlers.

Table 13.
Pairwise WSR test for accuracy of child.

Table 14.
Pairwise WSR Test for kappa statistics of children.

Table 15.
Pairwise WSR test for F1-Measure of children.

Table 16.
Pairwise WSR Test for AUROC of Child.

Table 17.
Pairwise WSR test for accuracy of adolescents.

Table 18.
Pairwise WSR test for kappa statistics of adolescents.

Table 19.
Pairwise WSR test for F1-Measure of adolescents.

Table 20.
Pairwise WSR test for AUROC of adolescents.

Table 21.
Pairwise WSR test for accuracy of adults.

Table 22.
Pairwise WSR test for kappa statistics of adults.

Table 23.
Pairwise WSR test for F1-Measure of adults.

Table 24.
Pairwise WSR test for AUROC of adults.
4.7. Exploring Significant Feature Sets and Discriminatory Factors of Individual Age Groups
For toddler datasets, SVM represented their maximum result in all metrics except AUROC for . When we considered the value of AUROC, NB showed the best result for . Then, SVM also showed their highest outcomes for all metrics for and in child datasets. In addition, KS provided the best AUROC for and . In adolescent datasets, SVM showed the best accuracy, kappa statistics, and f1-score for . However, NB represented the top AUROC for . In adult datasets, SVM also produced the highest findings in all metrics for . Therefore, it was found that the RIPPER algorithm for toddler, the Boruta algorithm for adolescent, and the CFS method for child and adult datasets were responsible to generate high results in the classification process.
Figure 2 depicts the ranks of SHAP values of toddler’s RIPPER subset, adolescent’s Boruta subset, as well as the subsets of CFS child and adult datasets. The assessment of these values was performed with the best-performing SVM for these individual subsets. For the RIPPER subset of toddlers, the most important discriminatory features were “age group identification,” “Character’s Intention (A7),” “Following relook (A6),” “Pretending Capability (A5),” and “Pointing to the interest (A4)” to detect autism at an early stage. For the CFS subset of children, “Back to the activities (A4),” “Making Friends (A10),” “Finding the character’s intention (A7),” “Understanding someone’s feeling (A9),” and “Noticing sound (A1)” were the most crucial discriminating factors. Besides, “Social activity (A6),” “Indicating toy (A3),” “Pretending Capability (A5),” “Return to work (A4),” and “Developing Relationships (A10)” were the most significant discriminating factors for the Boruta subset of adolescents. In the CFS subset of adults, “Understanding someone’s feelings (A9),” “Pretending Capability (A5),” “Social activity (A6),” “Track activities (A3),” and “Return to work (A4)” are the major discriminating factors to detect autism.
5. Discussion and Conclusions
In this study, we proposed a machine learning model that analyzed ASD datasets of individual age groups (toddlers, children, adolescents, and adults) to detect autism at an early stage. This model used different feature selection methods like Boruta, CFS, RIPPER, and RFE to generate feature subsets. Then, NB, BG, CART, KNN, C4.5, KS, SVM, and RT were employed to classify autism at an early stage. When we evaluated the performance of them, SVM was the most stable classifier to explore the best result for different age groups, respectively. Along with SVM, KS, KNN, and NB showed better results to identify autism, respectively. On the other hand, individual classifiers presented their best performance in for toddlers, for adolescents, for children and adults, and for children.
Table 25 shows the comparison of the proposed model with related previous studies. Most of the existing works were worked with version-1 ASD datasets of Thabtah et al. [6]. Besides, they did not properly focus on early detection of autism for toddlers and adolescents. Some works occurred with version-2 adolescent and adult datasets, whereas most of them did not conduct those works with more samples and machine learning approaches. Thabtah et al. [14] used CHI and IG feature ranking methods into primary adolescent and adult datasets to produce the most significant feature subsets. Then, they implemented logistic regression into primary datasets and subsets and observed the highest 99.91% accuracy for the adolescent dataset and a 97.58% accuracy for the adult dataset. In this work, we investigated all version-2 datasets of different age groups of Thabtah et al. [14] where SVM achieved a 97.82% accuracy with for the toddler dataset, a 99.61% accuracy with and for the child dataset, a 95.87% accuracy with for the adolescent dataset, and a 96.82% accuracy for the adult dataset for . Besides, we applied numerous feature selection and classification methods to justify these baselines and its feature sets more efficiently. In addition, a post hoc statistical significant test and SHAP interpretation method was used to evaluate deeply the outcomes of the proposed models. These types of evaluations did not properly occur in most of the existing works.

Table 25.
Comparison of proposed model with other previous studies.
In conclusions, the proposed machine learning framework was used to produce more-accurate and efficient results for early detection of ASD at individual age groups. Since diagnosing ASD traits is an expensive and time-consuming procedure, it is often postponed due to the difficulty of detecting autism in children and adolescents. In this process, machine learning models are efficient to detect autism at an early stage very efficiently. However, this model was not trained with various multivariate/dimensional datasets and explored significant attributes. In the future, we will integrate this framework with advanced technologies and develop a more-efficient ASD diagnosis system. This system will be applicable for the preliminary diagnosis of ASD at an early stage with low costs.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, M.B. and M.H.A.; methodology and software, M.B.; validation and formal analysis, M.H.A., M.S.S. and K.F.H.; resources, M.B. and M.S.S.; data curation, M.B.; writing—original draft preparation, M.B. and M.S.S., writing—review and editing, M.B., M.S.S., K.F.H. and M.A.M.; visualization, M.B.; supervision, M.A.M. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data used in this paper is available in the references in Section 3.1.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Landa, R.J.; Gross, A.L.; Stuart, E.A.; Faherty, A. Developmental trajectories in children with and without autism spectrum disorders: The first 3 years. Child Dev. 2013, 84, 429–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Belmonte, M.K.; Allen, G.; Beckel-Mitchener, A.; Boulanger, L.M.; Carper, R.A.; Webb, S.J. Autism and abnormal development of brain connectivity. J. Neurosci. 2004, 24, 9228–9231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- GBD 2019 Diseases and Injuries Collaborators. GBD 2019 Diseases and Injuries Collaborators Global burden of 369 diseases and injuries in 204 countries and territories, 1990–2019: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2019. Lancet 2020, 396, 1204–1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Usta, M.B.; Karabekiroglu, K.; Sahin, B.; Aydin, M.; Bozkurt, A.; Karaosman, T.; Aral, A.; Cobanoglu, C.; Kurt, A.D.; Kesim, N.; et al. Use of machine learning methods in prediction of short-term outcome in autism spectrum disorders. Psychiatry Clin. Psychopharmacol. 2019, 29, 320–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hyde, K.K.; Novack, M.N.; LaHaye, N.; Parlett-Pelleriti, C.; Anden, R.; Dixon, D.R.; Linstead, E. Applications of supervised machine learning in autism spectrum disorder research: A review. Rev. J. Autism Dev. Disord. 2019, 6, 128–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Thabtah, F.; Kamalov, F.; Rajab, K. A new computational intelligence approach to detect autistic features for autism screening. Int. J. Med. Inform. 2018, 117, 112–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Satu, M.S.; Azad, M.S.; Haque, M.F.; Imtiaz, S.K.; Akter, T.; Barua, L.; Rashid, M.; Soron, T.R.; Al Mamun, K.A. Prottoy: A smart phone based mobile application to detect autism of children in Bangladesh. In Proceedings of the 2019 4th International Conference on Electrical Information and Communication Technology (EICT), Khulna, Bangladesh, 17–19 December 2019; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Akter, T.; Ali, M.H.; Khan, M.I.; Satu, M.S.; Moni, M.A. Machine learning model to predict autism investigating eye-tracking dataset. In Proceedings of the 2021 2nd International Conference on Robotics, Electrical and Signal Processing Techniques (ICREST), Online, 5–7 January 2021; pp. 383–387. [Google Scholar]
- Akter, T.; Ali, M.H.; Khan, M.I.; Satu, M.S.; Uddin, M.; Alyami, S.A.; Ali, S.; Azad, A.; Moni, M.A. Improved transfer-learning-based facial recognition framework to detect autistic children at an early stage. Brain Sci. 2021, 11, 734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omar, K.S.; Mondal, P.; Khan, N.S.; Rizvi, M.R.K.; Islam, M.N. A machine learning approach to predict autism spectrum disorder. In Proceedings of the 2019 International Conference on Electrical, Computer and Communication Engineering (ECCE), Bazar, Bangladesh, 7–9 February 2019; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Sharma, M. Improved autistic spectrum disorder estimation using Cfs subset with greedy stepwise feature selection technique. Int. J. Inf. Technol. 2019, 14, 1251–1261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satu, M.S.; Sathi, F.F.; Arifen, M.S.; Ali, M.H.; Moni, M.A. Early detection of autism by extracting features: A case study in Bangladesh. In Proceedings of the 2019 International Conference on Robotics, Electrical and Signal Processing Techniques (ICREST), Dhaka, Bangladesh, 10–12 January 2021; pp. 400–405. [Google Scholar]
- Erkan, U.; Thanh, D.N. Autism spectrum disorder detection with machine learning methods. Curr. Psychiatry Res. Rev. Former. Curr. Psychiatry Rev. 2019, 15, 297–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thabtah, F.; Abdelhamid, N.; Peebles, D. A machine learning autism classification based on logistic regression analysis. Health Inf. Sci. Syst. 2019, 7, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akter, T.; Satu, M.S.; Khan, M.I.; Ali, M.H.; Uddin, S.; Lio, P.; Quinn, J.M.; Moni, M.A. Machine learning-based models for early stage detection of autism spectrum disorders. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 166509–166527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossain, M.D.; Kabir, M.A.; Anwar, A.; Islam, M.Z. Detecting Autism Spectrum Disorder using Machine Learning. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2009.14499. [Google Scholar]
- Raj, S.; Masood, S. Analysis and Detection of Autism Spectrum Disorder Using Machine Learning Techniques. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2020, 167, 994–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thabtah, F.; Peebles, D. A new machine learning model based on induction of rules for autism detection. Health Inform. J. 2020, 26, 264–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chowdhury, K.; Iraj, M.A. Predicting Autism Spectrum Disorder Using Machine Learning Classifiers. In Proceedings of the 2020 International Conference on Recent Trends on Electronics, Information, Communication & Technology (RTEICT), Bangalore, India, 12–13 November 2020; pp. 324–327. [Google Scholar]
- Akter, T.; Khan, M.I.; Ali, M.H.; Satu, M.S.; Uddin, M.J.; Moni, M.A. Improved machine learning based classification model for early autism detection. In Proceedings of the 2021 2nd International Conference on Robotics, Electrical and Signal Processing Techniques (ICREST), Online, 5–7 January 2021; pp. 742–747. [Google Scholar]
- Akter, T.; Ali, M.H.; Satu, M.S.; Khan, M.I.; Mahmud, M. Towards Autism Subtype Detection Through Identification of Discriminatory Factors Using Machine Learning. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Brain Informatics, Online, 17–19 September 2021; pp. 401–410. [Google Scholar]
- Thabtah, F. Autism Screening Data for Toddlers. 2019. Available online: https://fadifayez.com/ (accessed on 28 March 2022).
- Thabtah, F. Autism Screening Data for Child. 2019. Available online: https://fadifayez.com/ (accessed on 28 March 2022).
- Thabtah, F. Autism Screening Data for Adolescent. 2019. Available online: https://fadifayez.com/ (accessed on 28 March 2022).
- Thabtah, F. Autism Screening Data for Adult. 2019. Available online: https://fadifayez.com/ (accessed on 28 March 2022).
- Alzubi, R.; Ramzan, N.; Alzoubi, H. Hybrid feature selection method for autism spectrum disorder SNPs. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Conference on Computational Intelligence in Bioinformatics and Computational Biology (CIBCB), Piscataway, NJ, USA, 23–25 August 2017; pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Thabtah, F.; Zhang, L.; Abdelhamid, N. NBA game result prediction using feature analysis and machine learning. Ann. Data Sci. 2019, 6, 103–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liaw, A.; Wiener, M. Classification and regression by randomForest. R News 2002, 2, 18–22. [Google Scholar]
- Kursa, M.B.; Jankowski, A.; Rudnicki, W.R. Boruta—A system for feature selection. Fundam. Inform. 2010, 101, 271–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kursa, M.B.; Rudnicki, W.R. Feature selection with the Boruta package. J. Stat. Softw. 2010, 36, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Howlader, K.C.; Satu, M.; Awal, M.; Islam, M.; Islam, S.M.S.; Quinn, J.M.; Moni, M.A. Machine learning models for classification and identification of significant attributes to detect type 2 diabetes. Health Inf. Sci. Syst. 2022, 10, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, W.W.; Singer, Y. A simple, fast, and effective rule learner. AAAI/IAAI 1999, 99, 3. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, J.; Tiyyagura, A.; Chen, F.; Honavar, V. Feature subset selection for rule induction using RIPPER. In Proceedings of the Genetic and Evolutionary Computation Conference, Berlin, Germany, 15–19 July 1999; Volume 2, p. 1800. [Google Scholar]
- Seerat, B.; Qamar, U. Rule induction using enhanced RIPPER algorithm for clinical decision support system. In Proceedings of the 2015 Sixth International Conference on Intelligent Control and Information Processing (ICICIP), Wuhan, China, 26–28 November 2015; pp. 83–91. [Google Scholar]
- Pedregosa, F.; Varoquaux, G.; Gramfort, A.; Michel, V.; Thirion, B.; Grisel, O.; Blondel, M.; Prettenhofer, P.; Weiss, R.; Dubourg, V.; et al. Scikit-learn: Machine Learning in Python. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 2011, 12, 2825–2830. [Google Scholar]
- Ahammed, K.; Satu, M.S.; Khan, M.I.; Whaiduzzaman, M. Predicting Infectious State of Hepatitis C Virus Affected Patient’s Applying Machine Learning Methods. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE Region 10 Symposium (TENSYMP), Online, 5–7 June 2020; pp. 1371–1374. [Google Scholar]
- Guyon, I.; Weston, J.; Barnhill, S.; Vapnik, V. Gene selection for cancer classification using support vector machines. Mach. Learn. 2002, 46, 389–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- John, G.H.; Langley, P. Estimating continuous distributions in Bayesian classifiers. arXiv 2013, arXiv:1302.4964. [Google Scholar]
- Witten, I.H.; Frank, E. Data mining: Practical machine learning tools and techniques with Java implementations. Acm Sigmod Rec. 2002, 31, 76–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Painuli, S.; Elangovan, M.; Sugumaran, V. Tool condition monitoring using K-star algorithm. Expert Syst. Appl. 2014, 41, 2638–2643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alam, F.; Pachauri, S. Detection using weka. Adv. Comput. Sci. Technol. 2017, 10, 1731–1743. [Google Scholar]
- Trabelsi, M.; Meddouri, N.; Maddouri, M. A new feature selection method for nominal classifier based on formal concept analysis. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2017, 112, 186–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, B.K.; Lessler, J.; Stuart, E.A. Improving propensity score weighting using machine learning. Stat. Med. 2010, 29, 337–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sayad, S. K Nearest Neighbors—Classification. Available online: http://www.saedsayad.com/k_nearest_neighbors.htm (accessed on 28 March 2022).
- Hastie, T.; Tibshirani, R.; Friedman, J. The Elements of Statistical Learning: Data Mining, Inference, and Prediction; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Keerthi, S.S.; Shevade, S.K.; Bhattacharyya, C.; Murthy, K.R.K. Improvements to Platt’s SMO algorithm for SVM classifier design. Neural Comput. 2001, 13, 637–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.J.; Xu, Z.; Li, T.; Yang, Y. A novel bagging C4. 5 algorithm based on wrapper feature selection for supporting wise clinical decision making. J. Biomed. Inform. 2018, 78, 144–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, J.; Khan, R.; Ahmad, N.; Maqsood, I. Random forests and decision trees. Int. J. Comput. Sci. Issues (IJCSI) 2012, 9, 272. [Google Scholar]
- Hasnain, M.; Pasha, M.F.; Ghani, I.; Imran, M.; Alzahrani, M.Y.; Budiarto, R. Evaluating trust prediction and confusion matrix measures for web services ranking. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 90847–90861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalkhan, M.; Reich, R.; Czaplewski, R. Variance estimates and confidence intervals for the Kappa measure of classification accuracy. Can. J. Remote Sens. 1997, 23, 210–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, J.; Goadrich, M. The relationship between Precision-Recall and ROC curves. In Proceedings of the 23rd International Conference on Machine Learning, Pittsburgh, PA, USA, 25–29 June 2006; pp. 233–240. [Google Scholar]
- Powers, D.M. Evaluation: From precision, recall and F-measure to ROC, informedness, markedness and correlation. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2010.16061. [Google Scholar]
- Lundberg, S.M.; Lee, S.I. A unified approach to interpreting model predictions. In Proceedings of the 31st International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Long Beach, CA, USA, 4–9 December 2017; pp. 4768–4777. [Google Scholar]
- Fryer, D.; Strümke, I.; Nguyen, H. Shapley values for feature selection: The good, the bad, and the axioms. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2102.10936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuhn, M. The Caret Package. Available online: https://topepo.github.io/caret/ (accessed on 27 March 2019).
- Satu, M.; Zoynul Abedin, M.; Khanom, S.; Ouenniche, J.; Shamim Kaiser, M. Application of feature engineering with classification techniques to enhance corporate tax default detection performance. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Trends in Computational and Cognitive Engineering, Online, 21–22 October 2021; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2021; pp. 53–63. [Google Scholar]
- McNamara, B.; Lora, C.; Yang, D.; Flores, F.; Daly, P. Machine Learning Classification of Adults with Autism Spectrum Disorder. Available online: http://rstudio-pubs-static.s3.amazonaws.com/383049_1faa93345b324da6a1081506f371a8dd.html (accessed on 29 April 2018).
- Bala, M.; Prova, A.A.; Ali, M.H. Prediction of Autism Spectrum Disorder Using Feature Selection and Machine Learning Algorithms. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Computational Intelligence and Emerging Power System, Ajmer, India, 9–10 March 2021; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2022; pp. 133–148. [Google Scholar]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).