Micro-Scale Spherical and Cylindrical Surface Modeling via Metaheuristic Algorithms and Micro Laser Line Projection
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
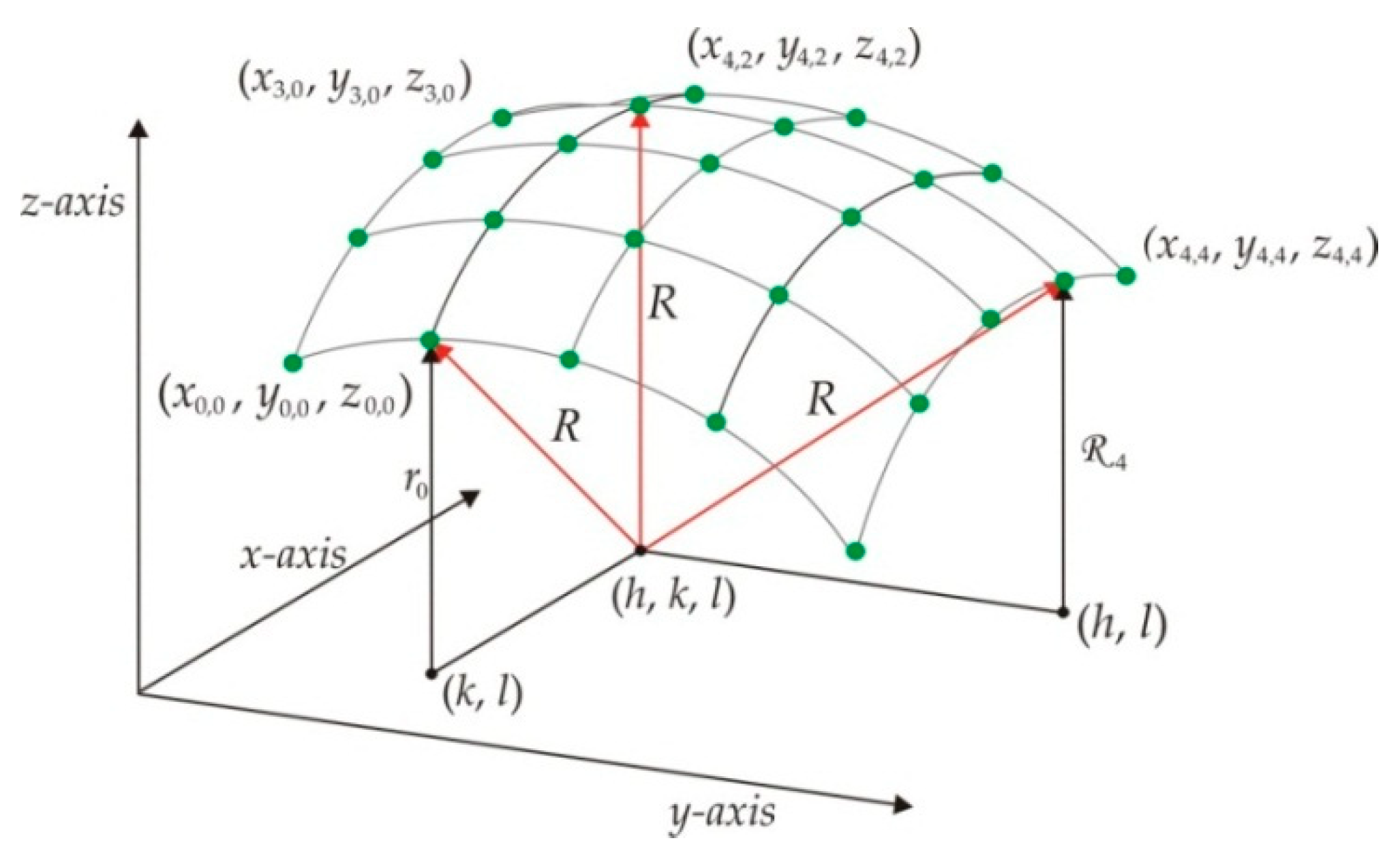
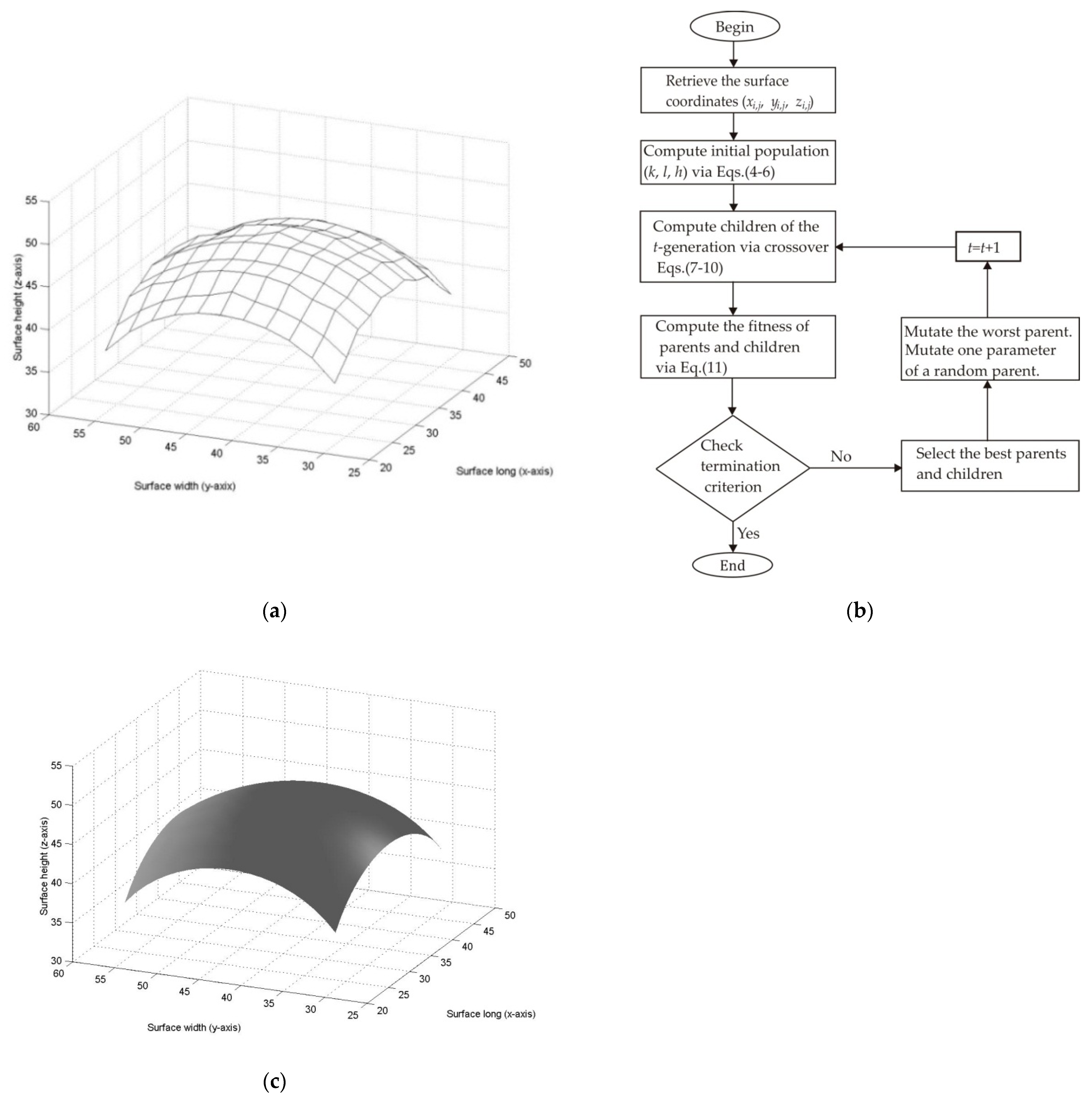
2.1. Micro-Scale Spherical Surface Modeling via Genetic Algorithm
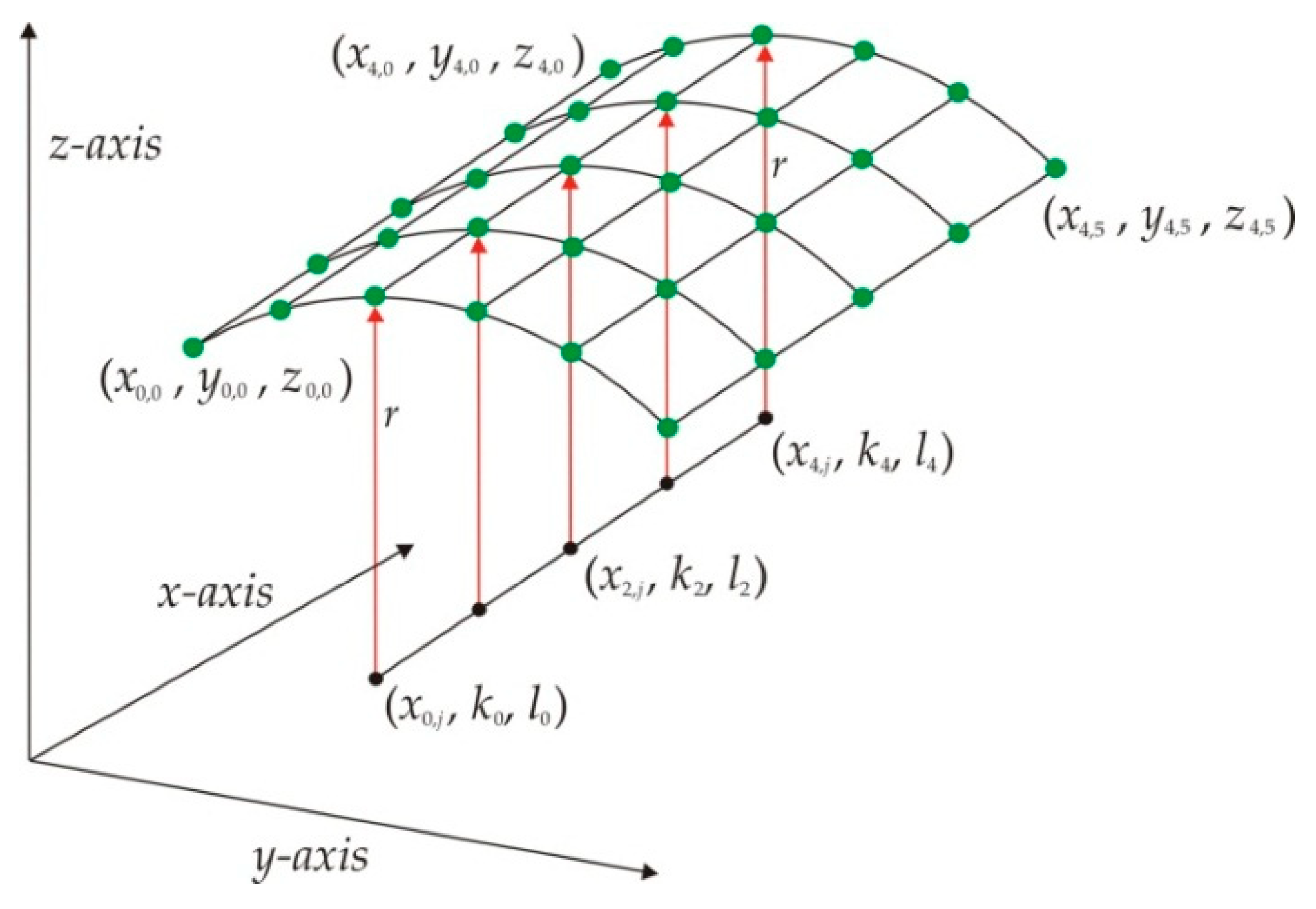
2.2. Micro-Scale Cylindrical Surface Modeling via Genetic Algorithm
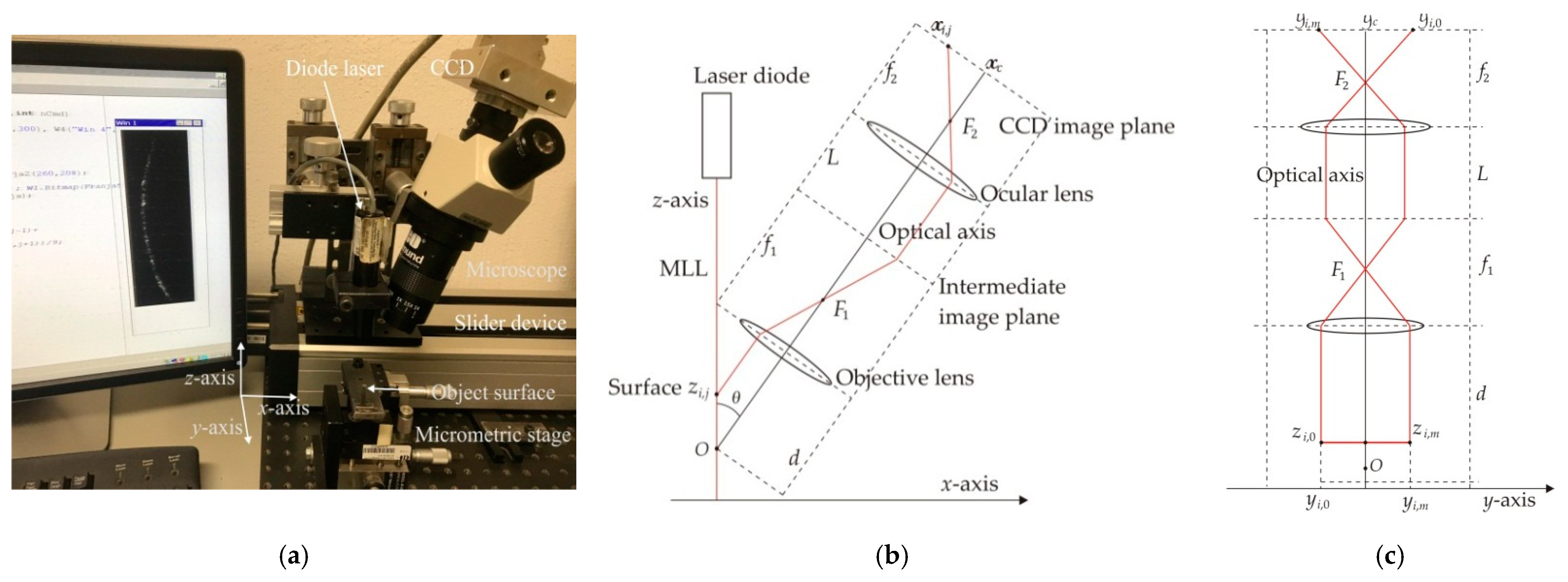
2.3. Micro-Scale Surface Contouring via Micro-Laser Line Projection
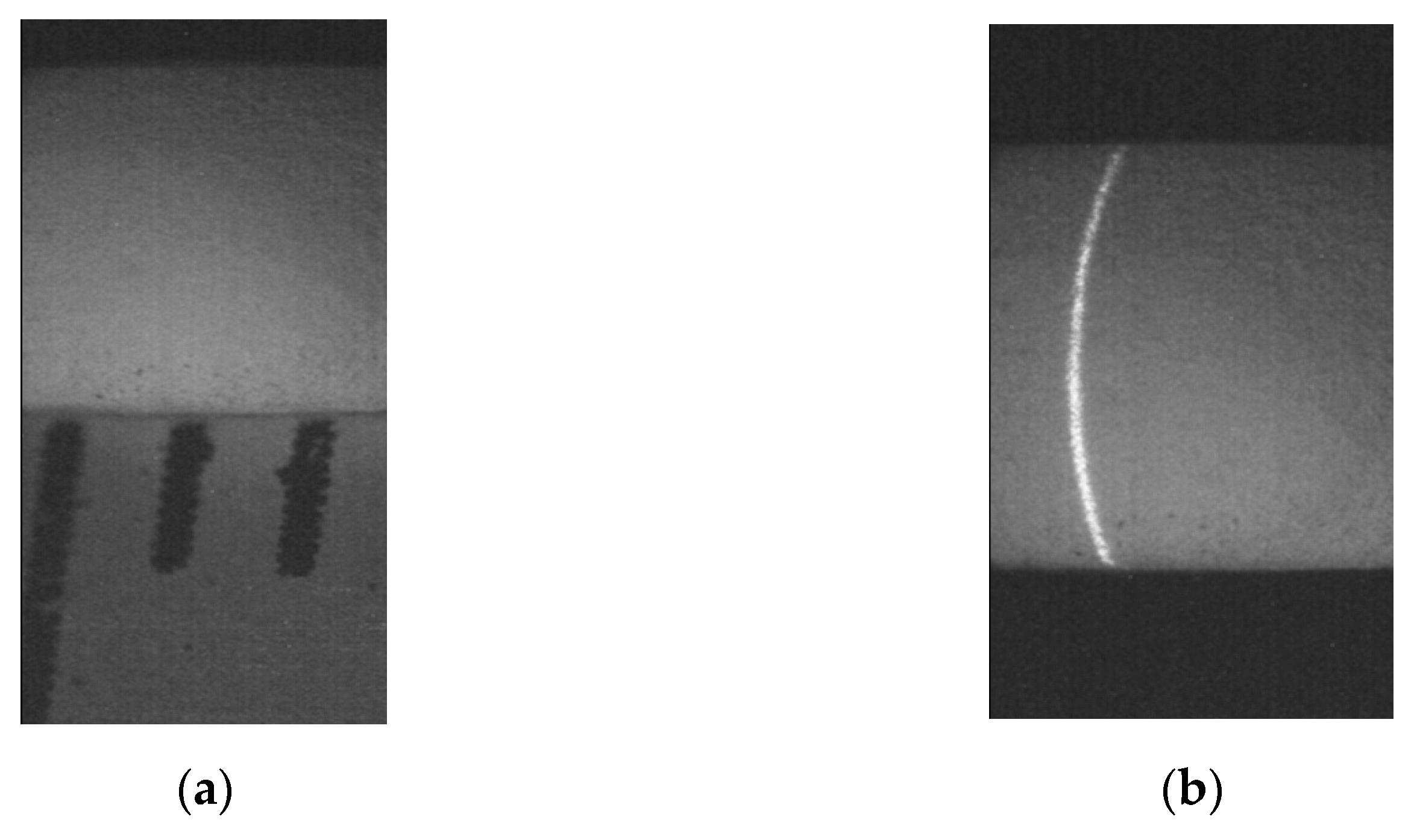
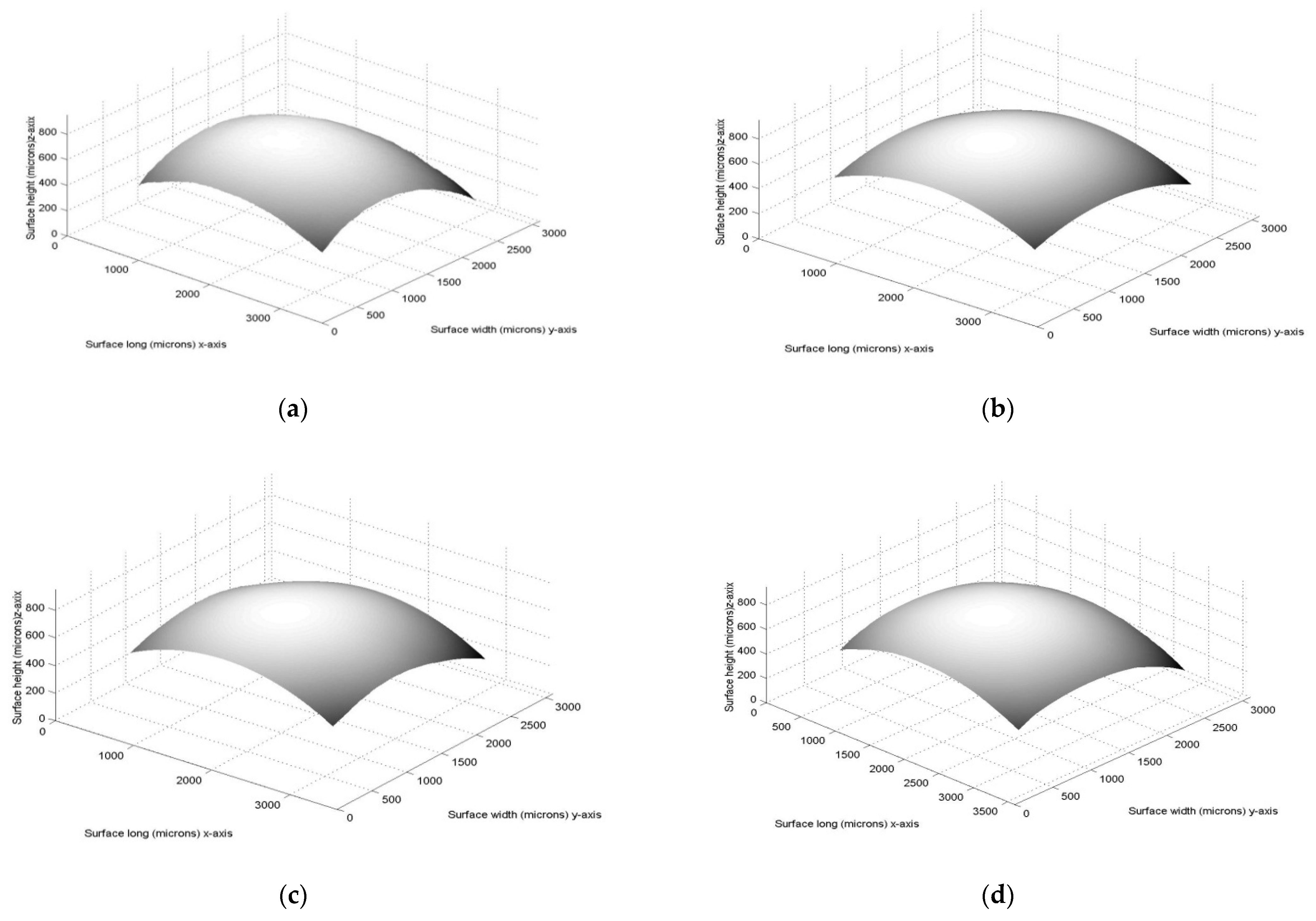
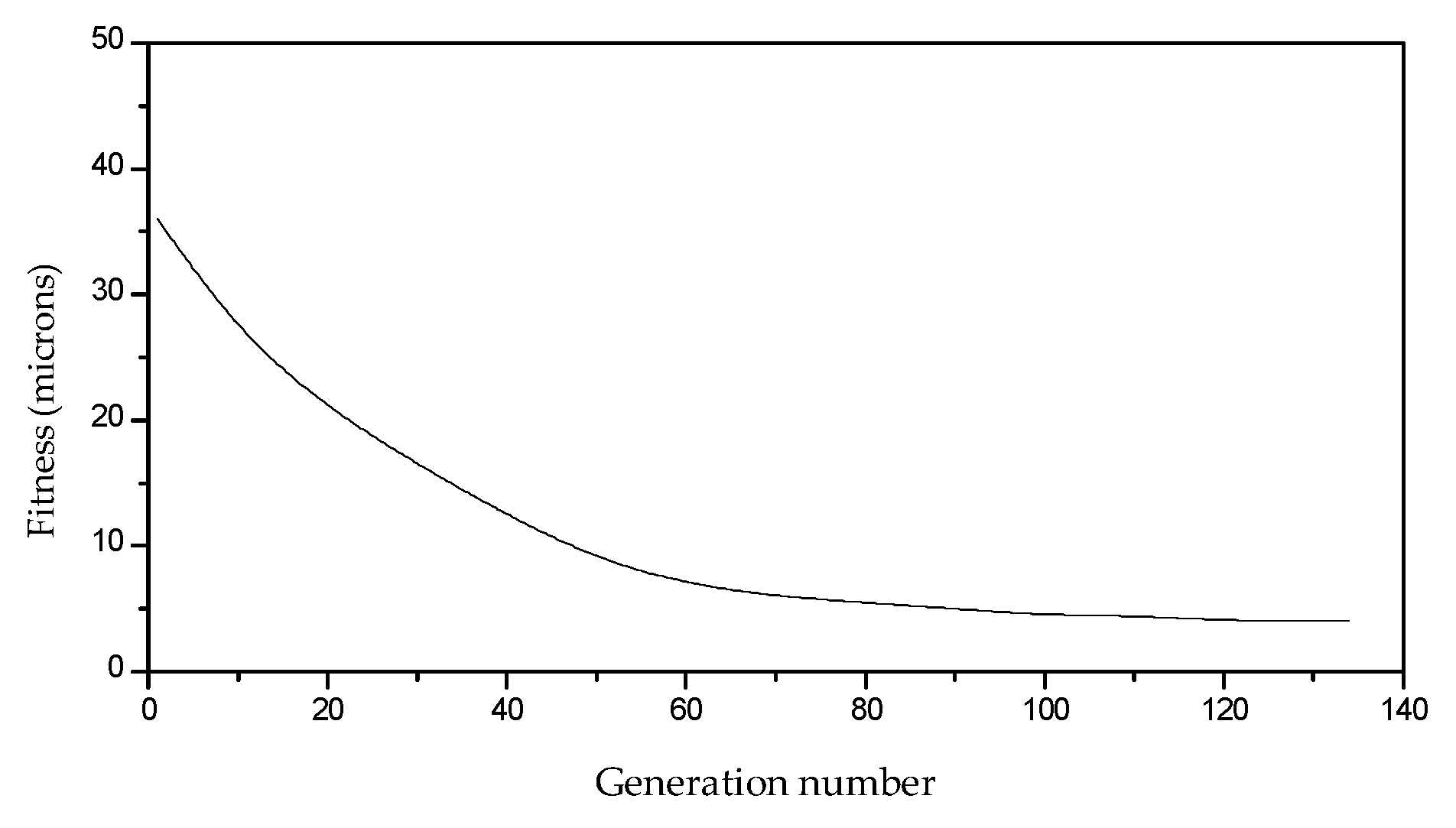
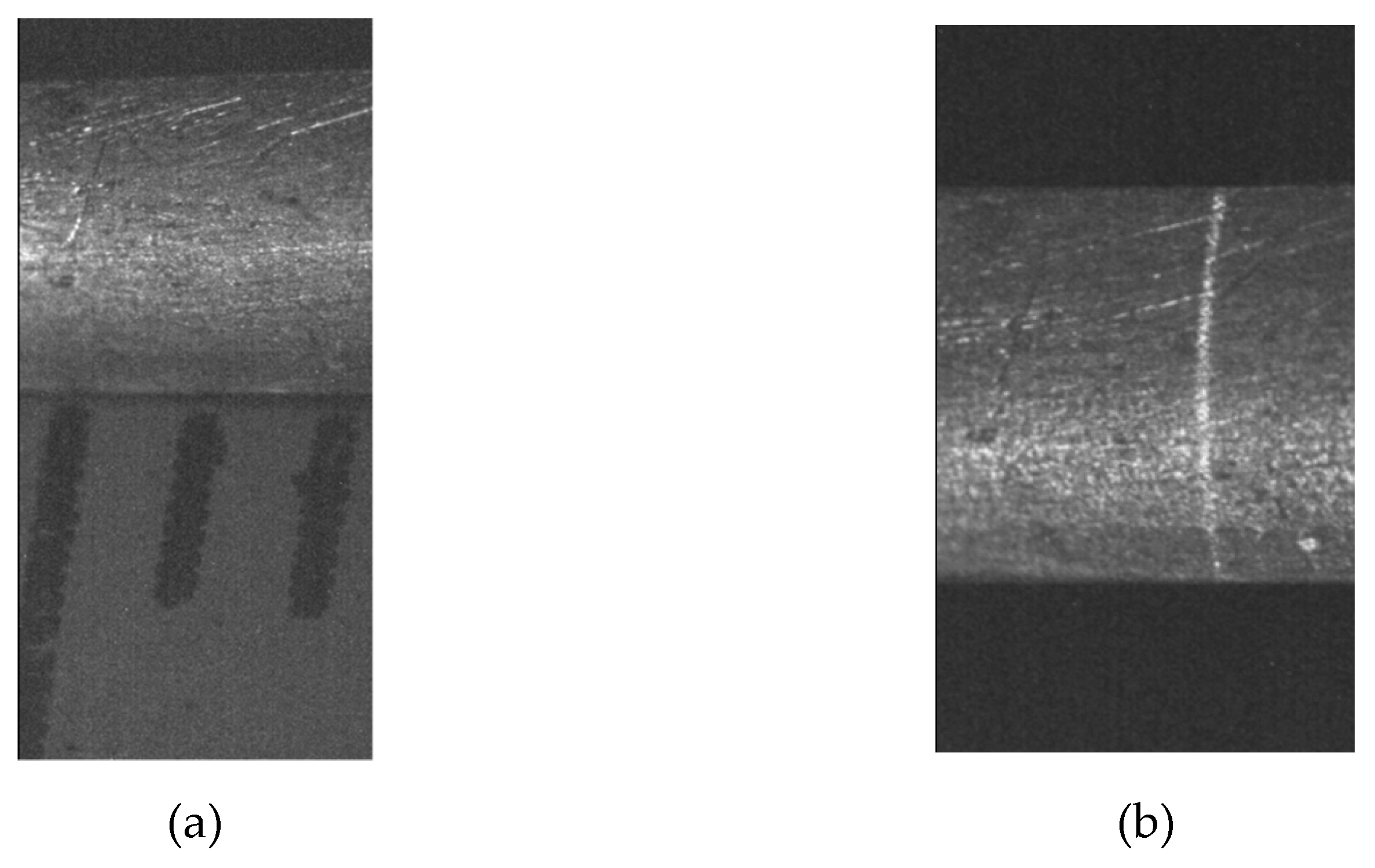
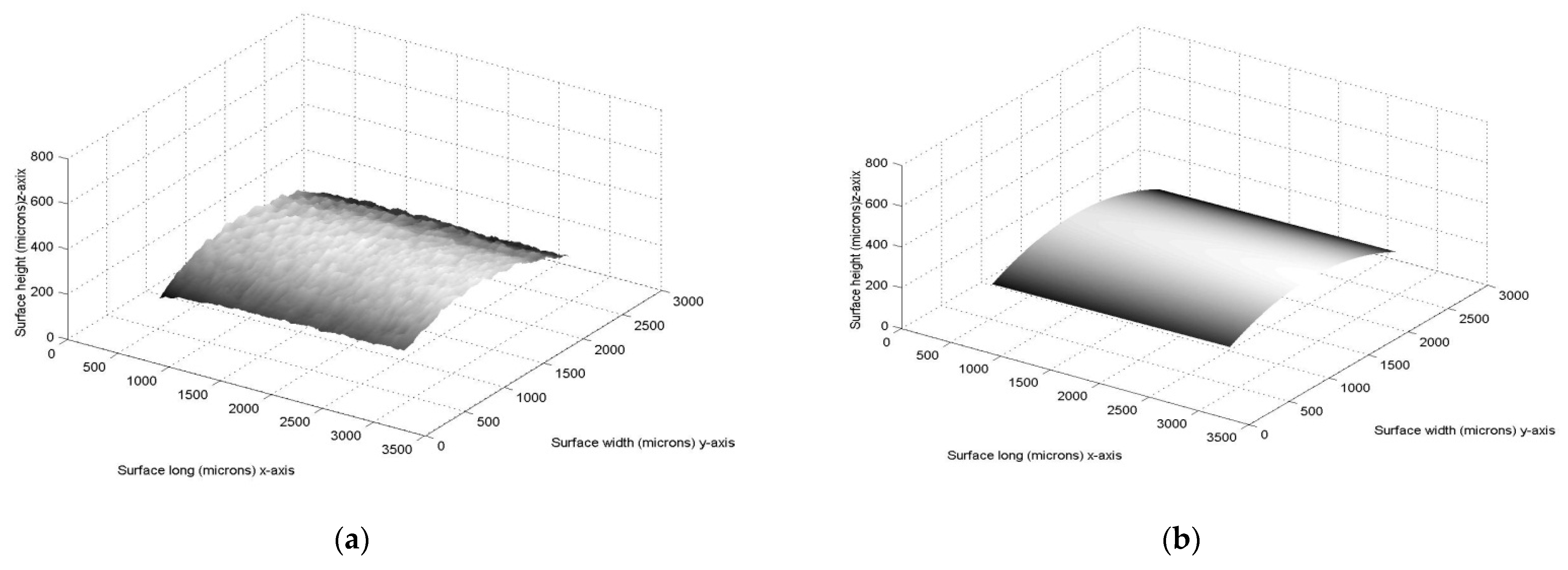
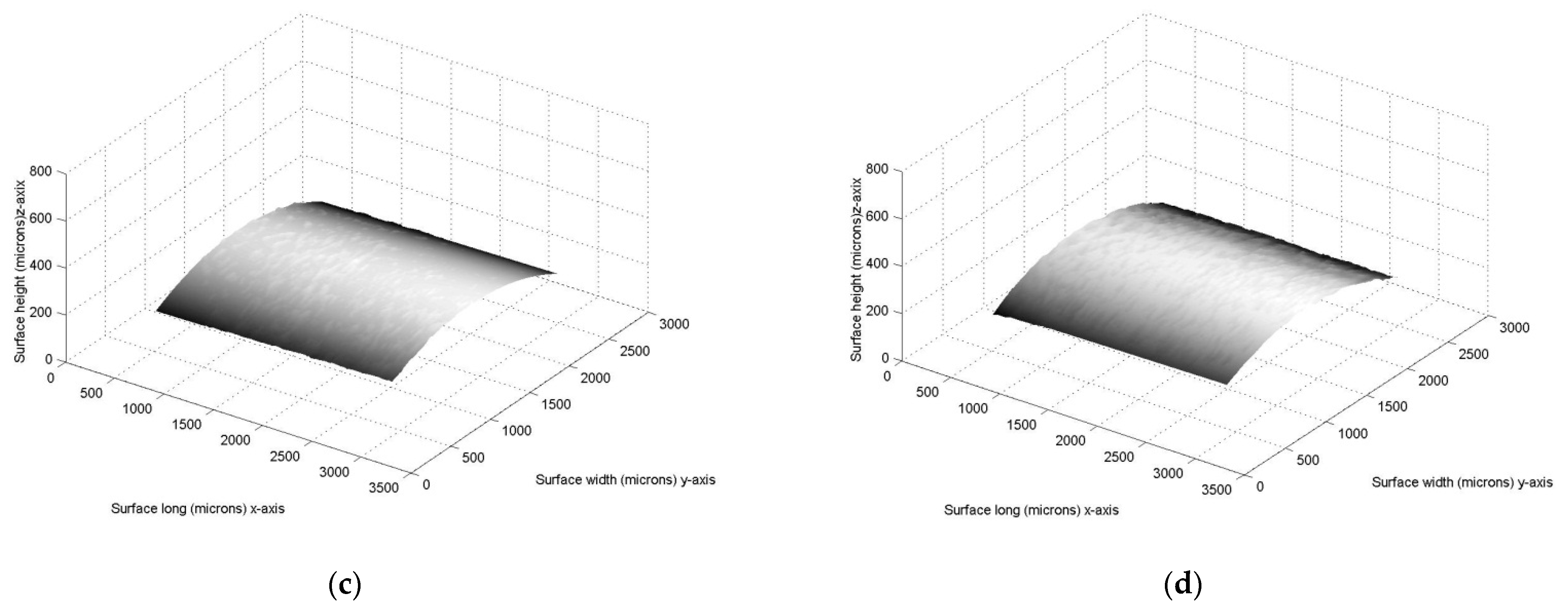
3. Results of Micro-Scale Spherical and Cylindrical Surface Modeling
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fei, W.; Narsilio, G.A.; Disfani, M.M. Impact of three–dimensional sphericity and roundness on heat transfer in granular materials. Powder Technol. 2019, 355, 770–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, P.; Liu, D.; Zhao, F.; Zhang, L. Statistical evaluation method for cylindricity deviation using local least squares cylinder. Int. J. Precis. Eng. Manuf. 2019, 20, 1347–1360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbas, A.T.; Pimenov, D.Y.; Erdakov, I.N.; Taha, M.A.; Soliman, M.S.; El Rayes, M.M. ANN surface roughness optimization of AZ61 magnesium alloy finish turning: Minimum machining times at prime machining costs. Materials 2018, 11, 808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hossein Ghasemi, A.; Mahyar Khorasani, A.; Gibson, I. Investigation on the effect of a pre–center drill hole and tool material on thrust force, surface roughness, and cylindricity in the drilling of Al7075. Materials 2018, 11, 140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foumani, M.; Razeghib, A.; Smith–Milesa, K. Stochastic optimization of two–machine flow shop robotic cells with controllable inspection times: From theory toward practice. Robot. Comput. Integr. Manuf. 2020, 61, 101822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharya, S.; Subedi, S.; Jae, L.S.; Pradhananga, N. Estimation of 3D sphericity by volume measurement—Application to coarse aggregates. Transp. Geotech. 2020, 23, 100344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, G.; Meguid, M.A. On the role of sphericity of falling rock clusters—Insights from experimental and numerical investigations. Landslides 2018, 15, 219–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Surdo, S.; Carzino, R.; Diaspro, A.; Martí, D. Single–shot laser additive manufacturing of high fill–factor microlens arrays. Adv. Optical Mater. 2018, 6, 1701190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gawedzinski, J.; Pawlowski, M.E.; Tkaczyk, T.S. Quantitative evaluation of performance of 3D printed lenses. Opt. Eng. 2017, 56, 08110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashemiboroujeni, H.; Marzdashti, S.E.; Xing, K.; Mayer, J.R.R. Five–axis machine tool coordinate metrology evaluation using the ball dome artefact before and after machine calibration. J. Manuf. Mater. Process. 2019, 3, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnold, T.; Pietag, F. Ion beam figuring machine for ultra–precision silicon spheres correction. Precis. Eng. 2015, 41, 119–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyu, X.; Li, Y.; Liu, F.; Ren, P. Fracturing proppant quality estimation based on fuzzy connectedness and shape similarity. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 79210–79224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Z.; Li, J.; Zhao, L.; Zhang, N.; Chen, X.; Miao, W.; Chen, W.; Liang, C. Preparation and characterization of a self–suspending ultra–low density proppant. RSC Adv. 2021, 11, 33083–33092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaoa, X.; Abreu, F.G.; Zhanga, W.; Wheeler, K.R. Numerical analysis of non–spherical particle effect on molten pool dynamics in laser–powder bed fusion additive manufacturing. Comput. Mater. Sci. 2020, 179, 109648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fortmeier, I.; Schulz, M.; Meeß, R. Traceability of form measurements of freeform surfaces: Metrological reference surfaces. Opt. Eng. 2019, 58, 092602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Fu, J.S.; Wanga, B.; Liu, S. Five–point cylindricity error separation technique. Measurement 2019, 145, 311–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Tao, X.; Lu, J.; Wang, X. Cylindricity error measuring and evaluating for engine cylinder bore in manufacturing procedure. Adv. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2016, 2016, 4212905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Agarwal, A.; Desai, K.A. Predictive framework for cutting force induced cylindricity error estimation in end milling of thin–walled components. Precis. Eng. 2020, 66, 209–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janecki, D.; Stępień, K.; Adamczak, S. Sphericity measurements by the radial method: II. Experimental verification. Meas. Sci. Technol. 2016, 27, 015006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Zhou, X.; Li, H.; Liu, S.; Fu, J. An algorithm for evaluating cylindricity according to the minimum condition. Measurement 2020, 158, 107698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Dong, B.; Pan, B. A flexible and easy to implement single–camera microscopic 3D digital image correlation technique. Meas. Sci. Technol. 2019, 30, 085002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, A.; Kumar, P.S.; Kumar, H.T.; Bhushan, B.B. Statistical analysis of different machining characteristics of EN–24 alloy steel during dry hard turning with multilayer coated cermet inserts. Measurement 2019, 134, 123–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyu, X.; Liu, F.; Ren, P.; Grecos, C. An Image Processing Approach to Measuring the Sphericity and Roundness of Fracturing Proppants. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 16078–16087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ameur, M.F.; Habak, M.; Kenane, M.; Aouici, H.; Cheikh, M. Machinability analysis of dry drilling of carbon/epoxy composites: Cases of exit delamination and cylindricity error. Int. J. Adv. Manufact. Technol. 2017, 88, 2557–2571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stepanova, K.; Rozlivek, J.; Puciow, F.; Krsek, P.; Pajdla, T.; Hoffmann, M. Automatic self–contained calibration of an industrial dual–arm robot with cameras using self–contact, planar constraints, and self–observation. Robot. Comput. Integr. Manuf. 2022, 73, 10225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y. A simple unified branch–and–bound algorithm for minimum zone circularity and sphericity errors. Meas. Sci. Technol. 2020, 31, 045005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Jiang, L.; Chao, X.; Tan, J. Minimum zone sphericity evaluation based on a modified cuckoo search algorithm with fuzzy logic. Meas. Sci. Technol. 2019, 30, 015008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Li, M.; Wang, C.; Wei, Q. Cylindricity error evaluation based on an improved harmony search algorithm. Sci. Program. 2018, 2018, 2483781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anantharaman, A.; Wu, X.; Hadinoto, K.; Chew, J.W. Impact of continuous particle size distribution width and particle sphericity on minimum pick up velocity in gas–solid pneumatic conveying. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2015, 130, 92–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haitjema, H. Straightness, flatness and cylindricity characterization using discrete Legendre polynomials. CIRP Ann. Manuf. Technol. 2020, 69, 457–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, K.; Mohd Salleh, M.N.; Cheng, S.; Shi, Y. Metaheuristic research a comprehensive survey. Artif. Intell. Rev. 2019, 52, 2191–2233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, X.; Kong, L.; Kong, D.; Yuan, L.; Kong, D. An improved method for NURBS surface based on particle swarm optimization BP neural network. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 184656–184663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashemian, A.; Hosseini, S.F. An integrated fitting and fairing approach for object reconstruction using smooth NURBS curves and surfaces. Comput. Math. Appl. 2018, 76, 1555–1575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, L.; Xie, Z.; Zhu, H.; Guan, Y.; Kong, M.; Zhang, B.O.; Fu, Y. Improved particle swarm optimization algorithm based on a three–dimensional convex hull for fitting a screw thread central axis. IEEE Access 2021, 76, 4902–4910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saini, D.; Kumar, S.; Singh, M.K.; Ali, M. Two view NURBS reconstruction based on GACO model. Complex Intell. Syst. 2021, 7, 2329–2346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarfraz, M.; Riyazuddin, M.; Baig, M.H. Capturing planar shapes by approximating their outlines. J. Comput. Appl. Math. 2006, 189, 494–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Zhao, H.; Zhang, C. An online–learning–based evolutionary many–objective algorithm. Inf. Sci. 2020, 509, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.Z.; Wang, Y.; Huang, P.Q. AnD: A many–objective evolutionary algorithm with angle–based selection and shift–based density estimation. Inf. Sci. 2020, 509, 400–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fathollahi–Fard, A.M.; Dulebenets, M.A.; Hajiaghaei–Keshteli, M.; Tavakkoli–Moghaddam, R.; Safaeian, M.; Mirzahosseinian, H. Two hybrid meta–heuristic algorithms for a dual–channel closed–loop supply chain network design problem in the tire industry under uncertainty. Adv. Eng. Inform. 2021, 50, 101418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasha, J.; Dulebenets, M.A.; Kavoosi, M.; Abioye, O.F.; Wang, H.; Guo, W. An Optimization model and solution algorithms for the vehicle routing problem with a factory–in–a–box. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 134743–134763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dulebenets, M.A.; Olumide, J.P.; Abioye, F.; Kavoosi, M.; Ozguven, E.E.; Moses, R.; Boot, W.R.; Sando, T. Exact and heuristic solution algorithms for efficient emergency evacuation in areas with vulnerable populations. Int. J. Disaster Risk Reduct. 2019, 39, 101114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Angelo, G.; Pilla, R.; Tascini, C.; Rompone, S. A proposal for distinguishing between bacterial and viral meningitis using genetic programming and decision trees. Soft. Comput. 2019, 23, 11775–11791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dokeroglua, T.; Sevincb, E.; Kucukyilmaza, T.; Cosarb, A. A survey on new generation metaheuristic algorithms. Comput. Ind. Eng. 2019, 137, 106040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, K.; Salleh, M.N.M.; Cheng, S.; Shi, Y. On the exploration and exploitation in popular swarm–based metaheuristic algorithms. Neural Comput. Appl. 2019, 31, 7665–7683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nallusamy, R.; Duraiswamy, K. Genetic algorithm with approximation algorithm based initial population selection for shortest path routing in mobile ad hoc networks. Wirel. Commun. 2009, 1, 346–350. [Google Scholar]
- Tan, K.C.; Chiam, S.C.; Mamun, A.A.; Goh, C.K. Balancing exploration and exploitation with adaptive variation for evolutionary multi–objective optimization. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2009, 197, 701–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muñoz–Rodríguez, J.A.; Rodríguez–Vera, R. Evaluation of the light line displacement location for object shape detection. J. Mod. Opt. 2003, 50, 137–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Huang, Q.; Zhao, J. Fabrication of an optical fiber micro–sphere with a diameter of several tens of micrometers. Materials 2014, 7, 4878–4895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassanat, A.B.; Prasath, V.B.S.; Abbadi, M.A.; Abu–Qdari, S.A.; Faris, H. An improved genetic algorithm with a new initialization mechanism based on regression techniques. Information 2018, 9, 167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belassiria, I.; Mazouzi, M.; ELfezazi, S.; Cherrafi, A.; ELMaskaoui, Z. An integrated model for assembly line re–balancing problem. Int. J. Prod. Res. 2018, 56, 5324–5344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, Y.; Rui, Z.; Yu, X.; Sang, X.; Liu, W. Estimation of distribution evolution memetic algorithm for the unrelated parallel–machine green scheduling problem. Memetic Comp. 2019, 11, 423–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, P.; Sun, Z.; Sun, Z. An improved intrusion detection algorithm based on GA and SVM. IEEE Access 2018, 6, 13624–13631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Homayouni, S.M.; Tang, S.H.; Motlagh, O. A genetic algorithm for optimization of integrated scheduling of cranes, vehicles, and storage platforms at automated container terminals. J. Comput. Appl. Math. 2014, 270, 545–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hai, D.T.; Morvan, M.; Gravey, P. Combining heuristic and exact approaches for solving the routing and spectrum assignment problem. IET Opt. 2018, 12, 65–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Jiang, L.; Chao, X.; Ding, X.; Tan, J. Improved sphericity error evaluation combining a heuristic search algorithm with the feature points model. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 2019, 90, 035105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Liang, L.; Xu, G.; Hou, C.; Liu, D. Measurement and evaluation of cylindricity deviation in cartesian coordinates. Meas. Sci. Technol. 2021, 32, 035018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Partovinia, A.; Vatankhah, E. Experimental investigation into size and sphericity of alginate micro–beads produced by electrospraying technique: Operational condition optimization. Carbohydr. Polym. 2019, 209, 389–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Talla, G.; Gangopadhyay, S.; Kona, N.B. Experimental investigation and optimization during the fabrication of arrayed structures using reverse EDM. Mater. Manufact. Process. 2017, 32, 958–969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calvo, R. Sphericity measurement through a new minimum zone algorithm with error compensation of point coordinates. Measurement 2019, 138, 291–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, P.; Liu, D.; Zhao, F.; Zhang, L. An efficient method for minimum zone cylindricity error evaluation using kinematic geometry optimization algorithm. Measurement 2019, 135, 886–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, H.; Zhu, H.; Yang, J.; Huang, X.; Hu, X. Three–dimensional angularity characterization of coarse aggregates based on experimental comparison of selected methods. Part. Sci. Technol. 2021, 1, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.C. Automatic 3D surface reconstruction and sphericity measurement of micro spherical balls of miniaturized coordinate measuring probes. Meas. Sci. Technol. 2007, 18, 1748–1755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Zhou, Y.; Tang, Z.; Luo, Q. A hybrid algorithm combining glowworm swarm optimization and complete 2–opt algorithm for spherical travelling salesman problems. Appl. Soft Comput. 2017, 58, 104–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De, T.N.; Podder, B.; Hui, N.B.; Mondal, C. Experimental estimation and numerical optimization of cylindricity error in flow forming of H30 aluminium alloy tubes. SN Appl. Sci. 2021, 3, 150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Jiang, L.; Zheng, H.; Xie, M.; Tan, J. Evaluation of minimum zone sphericity by combining single–space contraction strategy with multi–directional adaptive search algorithm. Precisi. Eng. 2019, 55, 189–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Zheng, P.; Wu, J.; Yin, H.; Zhang, L. A new method for cylindricity error evaluation based on increment–simplex algorithm. Sci. Prog. 2020, 103, 1–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Xia, Y.; Wang, R.; You, L.; Zhang, J. Optimal NURBS conversion of PDE surface–represented high–speed train heads. Optim. Eng. 2019, 20, 907–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Parameter | t | P1 | P2 | P3 | P4 | C1 | C2 | C3 | C4 | C5 | C6 | C7 | C8 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| h | 1 | 33.5896 | 29.1142 | 31.1072 | 28.2664 | 24.8035 | 30.58 | 33.3301 | 35.1367 | 27.9462 | 28.6664 | 31.0478 | 32.0006 |
| k | 1 | 44.2103 | 40.3246 | 38.2204 | 39.1703 | 37.6548 | 42.0848 | 43.1417 | 47.8128 | 36.1213 | 38.5753 | 38.8636 | 44.1221 |
| l | 1 | 21.46 | 31.1081 | 35.0979 | 25.7211 | 20.0535 | 21.7505 | 30.3015 | 34.3909 | 23.018 | 30.1367 | 32.9515 | 37.372 |
| fitness | 1.9963 | 0.5305 | 1.4442 | 0.9236 | 1.9747 | 1.1481 | 1.9987 | 4.5804 | 1.774 | 0.9567 | 0.9154 | 2.9193 | |
| h | 2 | 29.1142 | 30.58 | 28.2664 | 31.0478 | 24.1021 | 29.2203 | 30.1932 | 25.8899 | 24.7351 | 29.657 | 29.8396 | 28.2141 |
| k | 2 | 40.3246 | 42.0848 | 39.1703 | 38.8636 | 40.0788 | 41.0045 | 41.4932 | 41.898 | 35.5124 | 38.9784 | 39.0833 | 38.8631 |
| l | 2 | 31.1081 | 21.7505 | 25.7211 | 32.9515 | 20.5784 | 24.3133 | 27.9526 | 28.4532 | 21.9167 | 27.3088 | 32.5313 | 30.1781 |
| fitness | 0.5305 | 1.1481 | 0.9236 | 0.9154 | 1.872 | 0.8474 | 0.7176 | 1.7872 | 2.4692 | 0.6377 | 0.6918 | 0.9849 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rodríguez, J.A.M. Micro-Scale Spherical and Cylindrical Surface Modeling via Metaheuristic Algorithms and Micro Laser Line Projection. Algorithms 2022, 15, 145. https://doi.org/10.3390/a15050145
Rodríguez JAM. Micro-Scale Spherical and Cylindrical Surface Modeling via Metaheuristic Algorithms and Micro Laser Line Projection. Algorithms. 2022; 15(5):145. https://doi.org/10.3390/a15050145
Chicago/Turabian StyleRodríguez, J. Apolinar Muñoz. 2022. "Micro-Scale Spherical and Cylindrical Surface Modeling via Metaheuristic Algorithms and Micro Laser Line Projection" Algorithms 15, no. 5: 145. https://doi.org/10.3390/a15050145
APA StyleRodríguez, J. A. M. (2022). Micro-Scale Spherical and Cylindrical Surface Modeling via Metaheuristic Algorithms and Micro Laser Line Projection. Algorithms, 15(5), 145. https://doi.org/10.3390/a15050145





