Designing the Uniform Stochastic Photomatrix Therapeutic Systems
Abstract
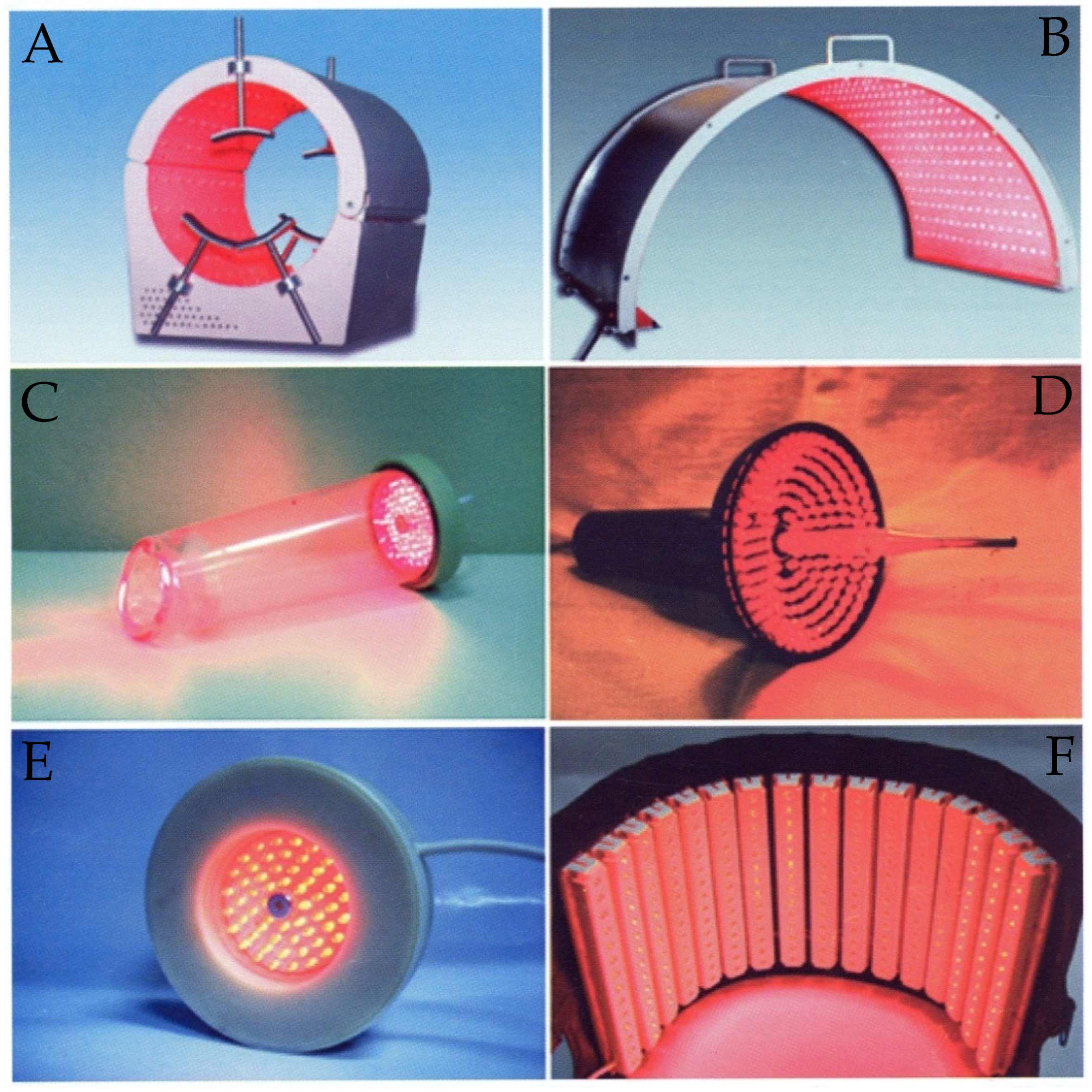
1. Introduction
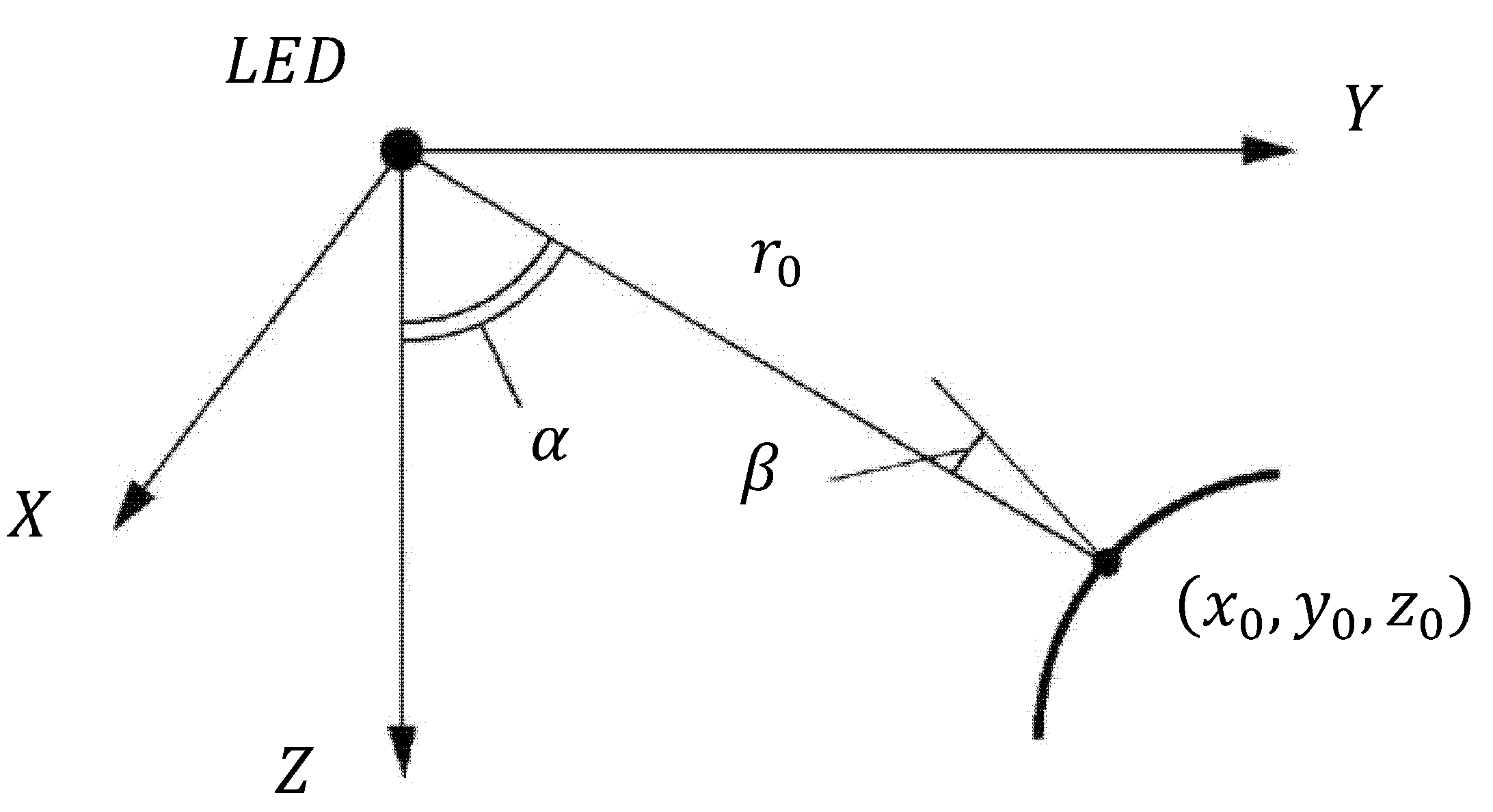
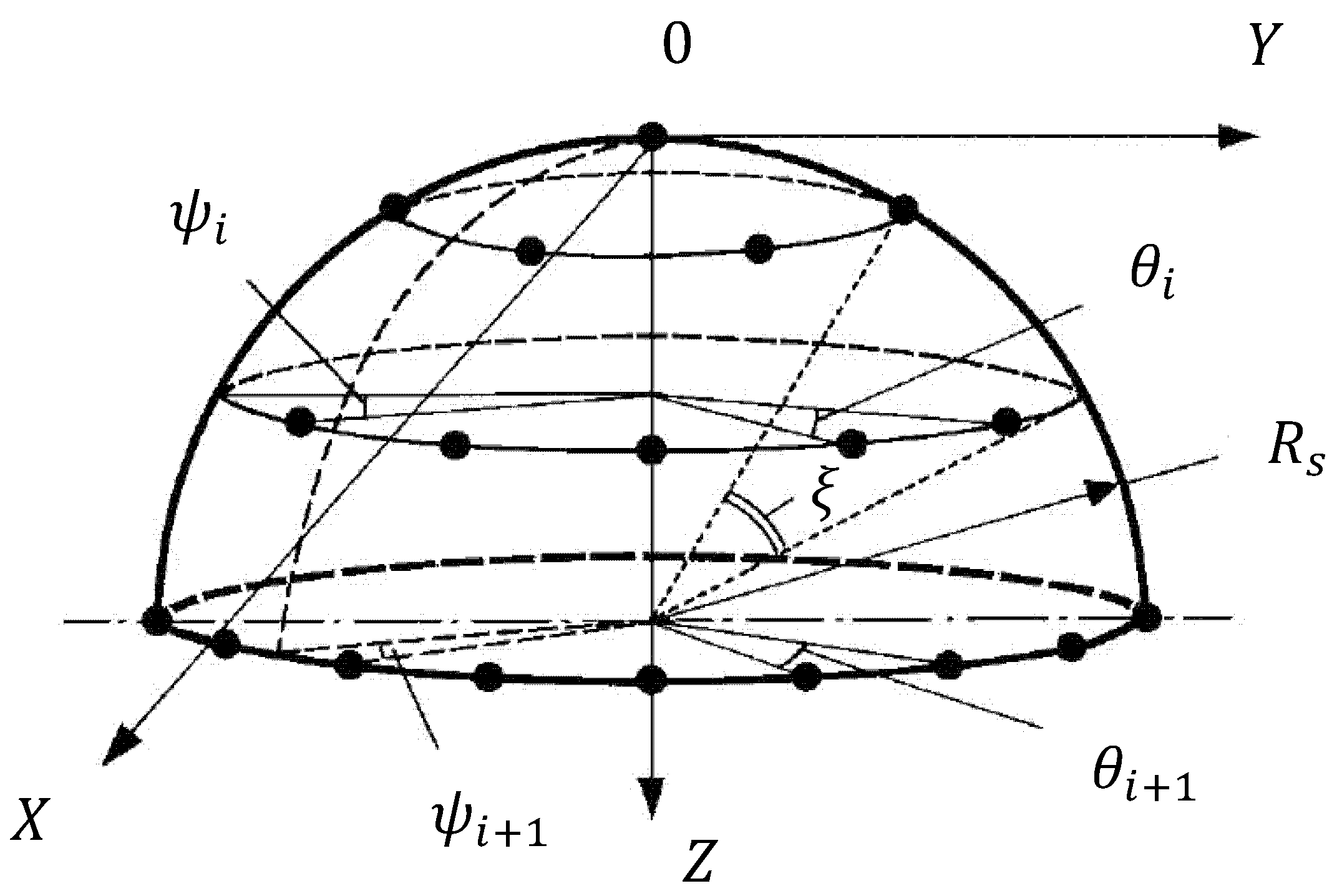
2. Theory
- -
- wavelength of LED irradiation at maximum , nm;
- -
- half-width of irradiation spectrum , nm;
- -
- luminous intensity at given current through LED, mcd;
- -
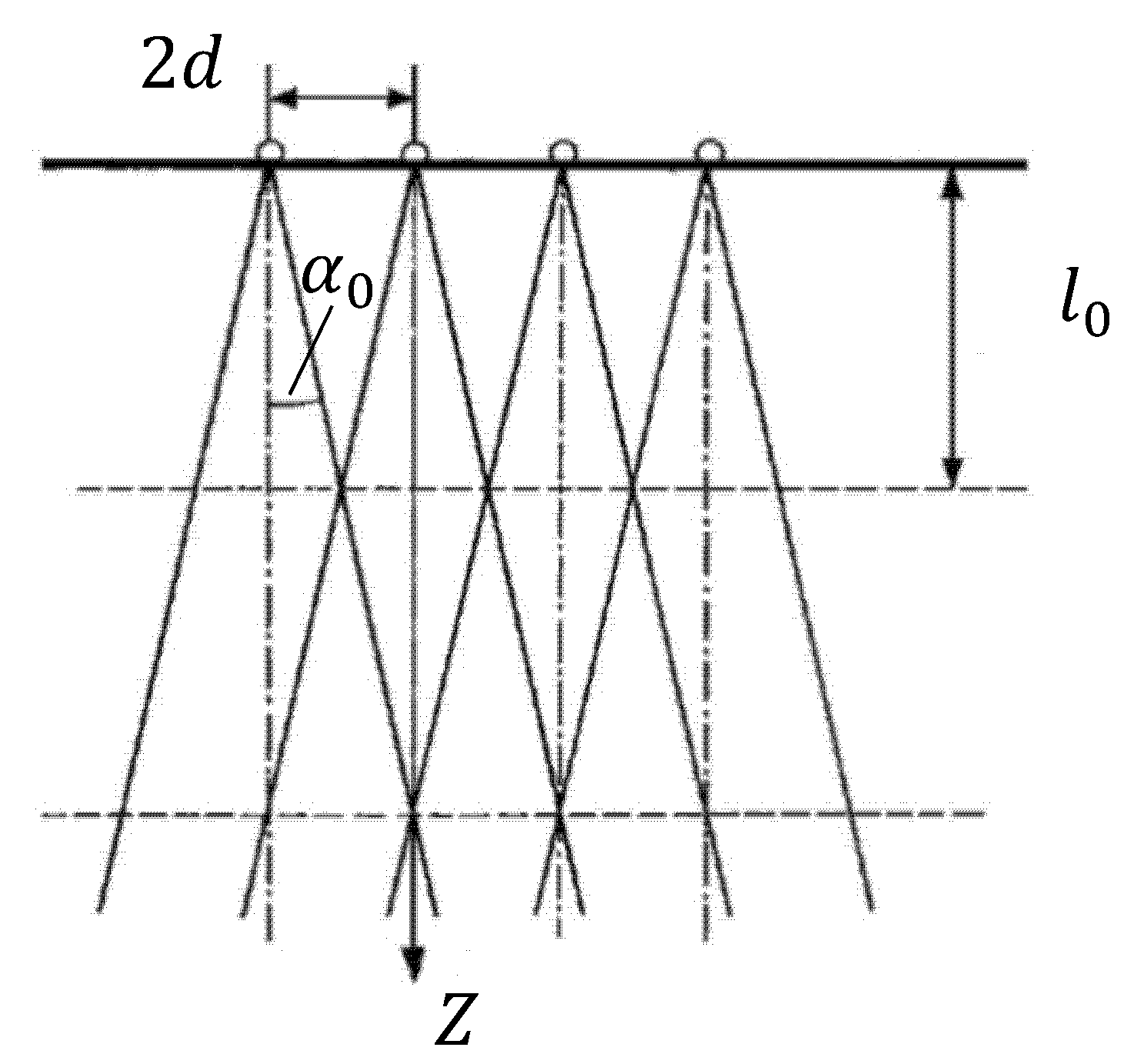
- double aperture angle , deg;
- -
- general voltage and current characteristics;
- -
- dependence of the luminous intensity on the direct current through LED;
- -
- maximum permissible electrical features of LED;
- -
- physical dimensions for particular LED and total amount of them;
- -
- general geometrical sizes of PMTS and shape of matrix surface.
- -
- LED irradiation is quasi-monochromatic;
- -
- each LED is considered to be a point source radiating within the dimensional aperture angle;
- -
- the wavelength of the LED irradiation belongs to visible and near-infrared ranges;
- -
- the optical axis of LED is normal to the inner surface of PMTS and to irradiated biotissue.
- (1)
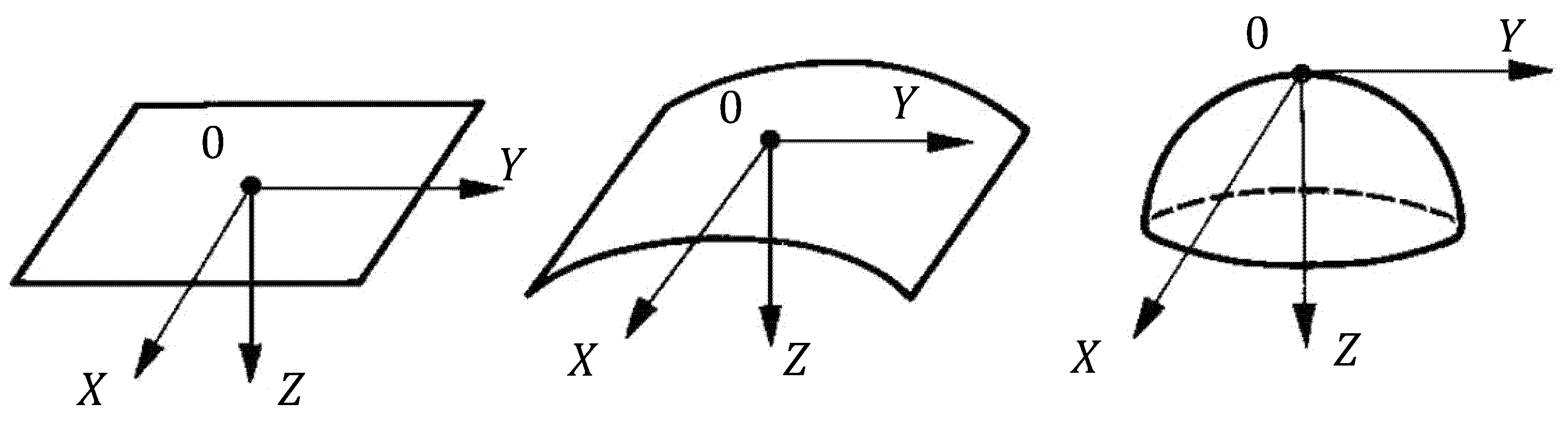
- flat PMTS irradiates a flat surface;
- (2)
- flat PMTS irradiates a cylindrical surface;
- (3)
- flat PMTS irradiates a spherical surface;
- (4)
- cylindrical PMTS irradiates a flat surface;
- (5)
- cylindrical PMTS irradiates a cylindrical surface;
- (6)
- cylindrical PMTS irradiates a spherical surface;
- (7)
- spherical PMTS irradiates a flat surface;
- (8)
- spherical PMTS irradiates a spherical surface.
3. Construction and Results
3.1. Features of Standard Programmable Tools
namespace DMP0101
{ class cDMP0101
{ static void Main(string[[] args)
{ Random GU = new Random();
Random GV = new Random();
int N = 8; // length of sequences U и V
Console.WriteLine("N = {0}", N);
int[[] U = new int[N]; // U sequence
int[[] V = new int[N]; // V sequence
int[[,] A = new int[N, N]; // result matrix
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++)
for (int j = 0; j < N; j++) A[i, j] = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) // one of the axes
{ Console.Write("i = {0,3} | ", i);
for (int j = 0; j < N; j++) // another axis
{ int u = GU.Next(N); // random value u
U[j] = u; // random sequence U
int v = GV.Next(4*N) % N; // random value v
V[j] = v; // random sequence V
A[u, v]++; // <u,v> point generation counter
}
Console.Write("U = ");
for (int m = 0; m < N; m++)
Console.Write("{0,4}", U[m]);
Console.WriteLine();
Console.Write(" | V = ");
for (int m = 0; m < N; m++)
Console.Write("{0,4}", V[m]);
Console.WriteLine();
}
Console.WriteLine("Matrix A");
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++)
{ for (int j = 0; j < N; j++)
Console.Write("{0,4}", A[i, j]);
Console.WriteLine();
}
Console.ReadKey(); // result viewing
}
}
}
N = 8
i = 0 | U = 5 0 2 3 2 1 6 4
| V = 6 0 5 5 3 5 3 3
i = 1 | U = 1 3 6 0 1 2 3 3
| V = 2 6 6 7 2 1 6 1
i = 2 | U = 2 0 4 0 5 1 3 5
| V = 2 1 5 1 5 0 4 1
i = 3 | U = 2 6 0 3 2 1 6 0
| V = 0 1 1 1 3 6 4 5
i = 4 | U = 2 7 0 1 0 1 7 1
| V = 0 0 7 1 7 3 7 7
i = 5 | U = 5 0 4 2 3 6 1 3
| V = 6 1 1 5 0 6 7 6
i = 6 | U = 3 3 2 1 5 0 3 3
| V = 6 3 6 5 5 3 6 5
i = 7 | U = 5 5 0 4 0 3 1 7
| V = 4 4 5 2 4 2 7 3
Matrix A
1 4 0 1 1 2 0 3
1 1 2 1 0 2 1 3
2 1 1 2 0 2 1 0
1 2 1 1 1 2 5 0
0 1 1 1 0 1 0 0
0 1 0 0 2 2 2 0
0 1 0 1 1 0 2 0
1 0 0 1 0 0 0 1
using nsDeonYuliTwist32D; // twister uniform generator
namespace DMP0102
{ class cDMP0102
{ static void Main(string[[] args)
{ uint w = 3; // number bit length
cDeonYuliTwist32D GU = new cDeonYuliTwist32D();
GU.x0 = 1; // U sequence beginning
GU.w = w; // number bit length
GU.Start(); // GU generator start
cDeonYuliTwist32D GV = new cDeonYuliTwist32D();
GV.x0 = 4; // V sequence beginning
GV.w = w; // number bit length
GV.Start(); // GV generator start
int N = 1 << (int)w; // U and V sequences length
Console.WriteLine("w = {0} N = {1}", w, N);
uint[[] U = new uint[N]; // U sequence
uint[[] V = new uint[N]; // V sequence
int[[,] A = new int[N, N]; // result matrix
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++)
for (int j = 0; j < N; j++) A[i, j] = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) // one of the axis
{ Console.Write("i = {0,3} | ", i);
for (int j = 0; j < N; j++) // another axis
{ uint u = GU.Next(); // random value u
U[j] = u; // random sequence U
uint v = GV.Next(); // random value v
V[j] = v; // random sequence V
A[u, v]++; // <u,v> point generation counter
}
Console.Write("U = ");
or (int m = 0; m < N; m++)
Console.Write("{0,4}", U[m]);
Console.WriteLine();
Console.Write(" | V = ");
for (int m = 0; m < N; m++)
Console.Write("{0,4}", V[m]);
Console.WriteLine();
}
Console.WriteLine("Matrix A");
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++)
{ for (int j = 0; j < N; j++)
Console.Write("{0,4}", A[i, j]);
Console.WriteLine();
}
Console.ReadKey(); // result viewing
}
}
}
w = 3 N = 8
i = 0 | U = 1 6 7 4 5 2 3 0
| V = 4 5 2 3 0 1 6 7
i = 1 | U = 3 5 7 1 2 4 6 0
| V = 1 2 4 6 0 3 5 7
i = 2 | U = 7 3 6 2 5 1 4 0
| V = 2 5 1 4 0 7 3 6
i = 3 | U = 6 7 4 5 2 3 0 1
| V = 5 2 3 0 1 6 7 4
i = 4 | U = 5 7 1 2 4 6 0 3
| V = 2 4 6 0 3 5 7 1
i = 5 | U = 3 6 2 5 1 4 0 7
| V = 5 1 4 0 7 3 6 2
i = 6 | U = 7 4 5 2 3 0 1 6
| V = 2 3 0 1 6 7 4 5
i = 7 | U = 7 1 2 4 6 0 3 5
| V = 4 6 0 3 5 7 1 2
Matrix A
0 0 0 0 0 0 2 6
0 0 0 0 3 0 3 2
3 3 0 0 2 0 0 0
0 3 0 0 0 2 3 0
0 0 0 8 0 0 0 0
5 0 3 0 0 0 0 0
0 2 0 0 0 6 0 0
0 0 5 0 3 0 0 0
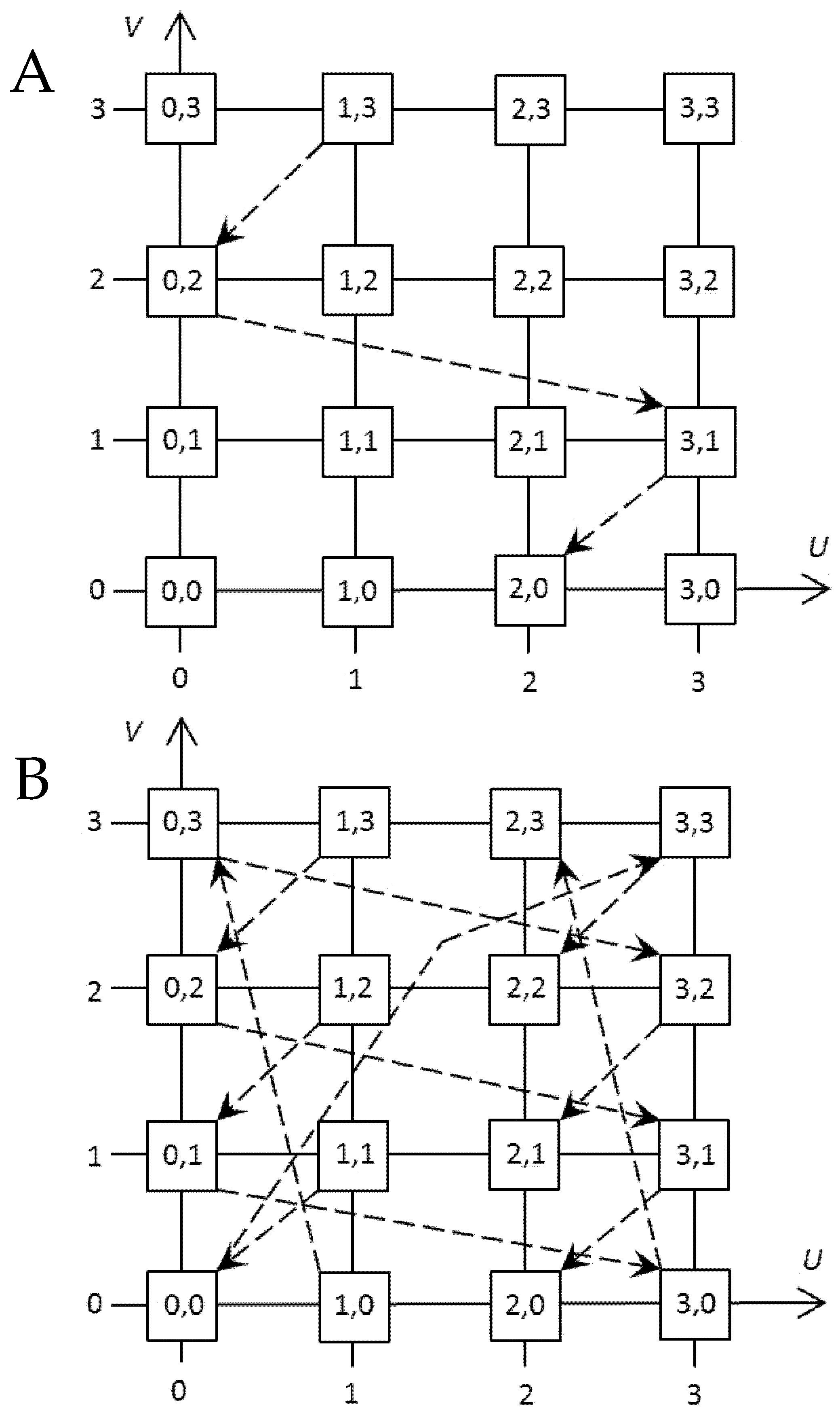
3.2. Features of Designing the Stochastic Programmable Tools
- -
- the discrete grid of the Descartes plane must contain all points in its nodes;
- -
- each point is unique and represented once only.
using nsDeonYuliPlaneTwist32D; //plane twist generator
namespace DMP0103
{ class cDMP0103
{ static void Main(string[[] args)
{ cDeonYuliPlaneTwist32D TP =
new cDeonYuliPlaneTwist32D();
int w = 3; // random number bit length
int N = 1 << w; // track length
TP.SetW(w);
TP.Start(); // generator start
Console.WriteLine("w = {0} N = {1}", w, N);
int[[,] A = new int[N, N]; // result matrix
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++)
for (int j = 0; j < N; j++) A[i, j] = 0;
uint u = 0; // point job coordinates on plane
uint v = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++)
for (int j = 0; j < N; j++)
{ TP.Next(ref u, ref v); // point on grid
A[u, v]++; // generation counter for <u,v>
}
Console.WriteLine("Matrix A");
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++)
{ for (int j = 0; j < N; j++)
Console.Write("{0,4}", A[i, j]);
Console.WriteLine();
}
Console.ReadKey(); // result viewing
}
}
}
w = 3 N = 8
Matrix A
1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1
1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1
1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1
1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1
1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1
1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1
1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1
1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Menyaev, Y.A.; Zharov, V.P. Experience in development of therapeutic photomatrix equipment. Biomed. Eng. 2006, 40, 57–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menyaev, Y.A.; Zharov, V.P. Experience in the use of therapeutic photomatrix equipment. Biomed. Eng. 2006, 40, 144–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menyaev, Y.A.; Zharov, V.P. Phototherapeutic technologies for oncology. Proc. SPIE 2005, 5973, 271–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zharov, V.P.; Zmievskoi, G.N.; Meniaev, I.; Salishchev, D.N.; Kalinin, K.I.; Stepanchuk, N. Development of an algorithm for calculating the spatial distribution of the radiation intensity of photomatrix therapeutic apparatuses. Biomed. Eng. 2002, 36, 188–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zharov, V.P.; Menyaev, Y.A.; Gorchak, Y.Y.; Utkina, K.V.; Menyaev, Y.A. Methods for photoultrasonic treatment of festering wounds in oncological patients. Crit. Rev. Biomed. Eng. 2001, 29, 111–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zharov, V.P.; Menyaev, Y.A.; Kabisov, R.K.; Al’kov, S.V.; Nesterov, A.V.; Savrasov, G.V. Design and application of low-frequency ultrasound and its combination with laser radiation in surgery and therapy. Crit. Rev. Biomed. Eng. 2001, 29, 502–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menyaev, Y.A.; Zharova, I.Z. A technique for surgical treatment of infected wounds based on photodynamic and ultrasound therapy. Biomed. Eng. 2006, 40, 284–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menyaev, Y.A.; Zharov, V.P.; Mishanin, E.A.; Kuzmich, A.P.; Bessonov, S.E. Combined photovacuum therapy of copulative dysfunction. Proc. SPIE 2006, 6078, 241–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menyaev, Y.A.; Zharov, V.P. Combination of photodynamic and ultrasonic therapy for treatment of infected wounds in animal model. Proc. SPIE 2006, 6087, 30–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vel’sher, L.Z.; Podkolzin, A.A.; Stakhanov, M.L.; Gorchak, Y.Y.; Zharov, V.P.; Menyaev, Y.A.; Zmievskoi, G.N.; Rozhdestvin, V.N. A combined method for wound treatment based on exposure to low-intensity radiation and ultrasound. Biomed. Eng. 2003, 37, 262–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zharov, V.P.; Kalinin, K.I.; Menyaev, Y.A.; Zmievskoy, G.N.; Savin, A.A.; Stulin, I.D.; Shihkerimov, R.K.; Shapkina, A.V.; Velsher, L.Z.; Stakhanov, M.L. Phototherapeutic treatment of patients with peripheral nervous system diseases by means of LED arrays. Proc. SPIE 2001, 4244, 143–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zharov, V.P.; Menyaev, Y.A.; Kalinin, K.L.; Zmievskoy, G.N.; Velsher, L.Z.; Podkolzin, A.A.; Stakhanov, M.L.; Gorchak, Y.Y.; Sarantsev, V.P. Combined photoultrasonic treatment of infected wounds. Proc. SPIE 2001, 4244, 133–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zharov, V.P.; Menyaev, Y.A.; Gorchak, Y.V.; Zmievskoi, G.N.; Bagdasarov, V.V.; Ambrozevich, E.G.; Shchepilov, D.V.; Kazarova, E.A. Photoultrasonic treatment of septic wounds. Biomed. Eng. 2001, 35, 6–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, Y.; Qiu, H.; Wang, Y.; Huang, N.; Liu, T.C.Y. Light-Emitting Diodes for Healthcare and Well-being: Materials, Processes, Devices and Applications. In Light-Emitting Diodes; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2019; pp. 485–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadis, M.A.; Cooper, P.R.; Milward, M.R.; Gorecki, P.C.; Tarte, E.; Churm, J.; Palin, W.M. Development and application of LED arrays for use in phototherapy research. J. Biophotonics 2017, 10, 1514–1525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, J.; Guo, L.; Xiong, D. Design of a multi-band LED phototherapy system with therapeutic evaluation. Proc. SPIE 2019, 11334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akşahin, M. Multifunctional phototherapy device design. Electrica 2019, 19, 65–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohli, H.; Srivastava, S.; Sharma, S.K.; Chouhan, S.; Oza, M. Design of Programmable LED Based Phototherapy System. Int. J. Opt. 2019, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ugarte, M.F.; Chávarri, L.; Briz, S. Note: Design of a dose-controlled phototherapy system based on hyperspectral studies. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 2013, 84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ugarte, M.F.; Chávarri, L.; Briz, S.; Padrón, V.M.; García-Cuesta, E. Active multispectral imaging system for photodiagnosis and personalized phototherapies. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 2014, 85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sorbellini, E.; Rucco, M.; Rinaldi, F. Photodynamic and photobiological effects of light-emitting diode (LED) therapy in dermatological disease: An update. Lasers Med. Sci. 2018, 33, 1431–1439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sauder, D.N. Light-emitting diodes: Their role in skin rejuvenation. Int. J. Dermatol. 2010, 49, 12–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutta, S.; Shenoy, J.; Kamath, S.P.; Mithra, M.; Baliga, S.; Sarpangala, M.; Mukund, P.S. Light Emitting Diode (LED) Phototherapy versus Conventional Phototherapy in Neonatal Hyperbilirubinemia: A Single Blinded Randomized Control Trial from Coastal India. BioMed. Res. Int. 2019, 2019, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foley, J.S.; David, B.; Bradle, V.J.; Rudio, C.; Calderhead, R.G. 830 nm light-emitting diode (led) phototherapy significantly reduced return-to-play in injured university athletes: A pilot study. Laser Ther. 2016, 25, 35–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karaduta, O.; Zaman, L. Shk-9: A new tool in approach of glycoprotein annotation. Software 2018, 7, 302–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menyaev, Y.A.; Nedosekin, D.A.; Sarimollaoglu, M.; Juratli, M.A.; Galanzha, E.I.; Tuchin, V.V.; Zharov, V.P. Optical Clearing in Photoacoustic Flow Cytometry. Biomed. Opt. Express 2013, 4, 3030–3041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menyaev, Y.A.; Carey, K.A.; Nedosekin, D.A.; Sarimollaoglu, M.; Galanzha, E.I.; Stumhofer, J.S.; Zharov, V.P. Preclinical Photoacoustic Models: Application for Ultrasensitive Single Cell Malaria Diagnosis in Large Vein and Artery. Biomed. Opt. Express 2016, 7, 3643–3658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreno, I. Image-like illumination with LED arrays: Design. Opt. Lett. 2012, 37, 839–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Wu, D.; Qin, Z.; Chen, F.; Luo, X.; Liu, S. New reversing design method for LED uniform illumination. Opt. Express 2011, 19, A830–A840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Z.; Xue, D.; Ji, Z. Designing LED array for uniform illumination distribution by simulated annealing algorithm. Opt. Express 2012, 20, A843–A855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abeysekera, S.K.; Kalavally, V.; Ooi, M.; Kuang, Y.C. Impact of circadian tuning on the illuminance and color uniformity of a multichannel luminaire with spatially optimized LED placement. Opt. Express 2020, 28, 130–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, R.; Zheng, Z.; Li, H.; Liu, X. Optimization design of irradiance array for LED uniform rectangular illumination. Appl. Opt. 2012, 51, 2257–2263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pal, S. Optimization of LED array for uniform illumination over a target plane by evolutionary programming. Appl. Opt. 2015, 54, 8221–8227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.; Wang, H.; Wu, R.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zheng, Z.; Li, H.; Liu, X. Uniform illumination design by configuration of LEDs and optimization of LED lens for large-scale color-mixing applications. Appl. Opt. 2013, 52, 3998–4005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Wang, K.; Chen, F.; Liu, S. New freeform lenses for white LEDs with high color spatial uniformity. Opt. Express 2012, 20, 24418–24428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teng, T.C.; Sun, W.S.; Lin, J.L. Designing an LED luminaire with balance between uniformity of luminance and illuminance for non-Lambertian road surfaces. Appl. Opt. 2017, 56, 2604–2613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Zhang, H.; Liu, S.; Wang, X. Effective freeform TIR lens designed for LEDs with high angular color uniformity. Appl. Opt. 2018, 57, 4216–4221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feller, W. An Introduction to Probability Theory and Its Applications, 3rd ed.; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2008; p. 528. [Google Scholar]
- Gnedenko, B. Theory of Probability, 6th ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1998; p. 520. [Google Scholar]
- Kolmogorov, A.N.; Fomin, S.V. Elements of the Theory of Functions and Functional Analysis, 1st ed.; Dover Publications: Mineola, NY, USA, 1999; p. 128. [Google Scholar]
- Cramer, H. Mathematical Methods of Statistics, 1st ed.; Princeton University Press: Princeton, NJ, USA, 1999; p. 575. [Google Scholar]
- Knuth, D.E. Art of Computer Programming, Volume 2: Seminumerical Algorithms, 3rd ed.; Addison-Wesle: Boston, MA, USA, 2014; p. 784. [Google Scholar]
- Knuth, D.E. Art of Computer Programming, Volume 4A: Combinatorial Algorithms, Part 1, 1st ed.; Addison-Wesley: Boston, MA, USA, 2011; p. 912. [Google Scholar]
- van der Waerden, B.L. Algebra: Volume, I; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 1991; p. 265. ISBN 978-0-387-40624-4. [Google Scholar]
- van der Waerden, B.L. Algebra: Volume II; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 1991; p. 284. ISBN 978-0-387-40625-1. [Google Scholar]
- Deon, A.F.; Menyaev, Y.A. The Complete Set Simulation of Stochastic Sequences without Repeated and Skipped Elements. J. Univers. Comput. Sci. 2016, 22, 1023–1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deon, A.F.; Menyaev, Y.A. Parametrical Tuning of Twisting Generators. J. Comput. Sci. 2016, 12, 363–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Deon, A.F.; Menyaev, Y.A. Twister Generator of Arbitrary Uniform Sequences. J. Univers. Comput. Sci. 2017, 23, 353–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deon, A.F.; Menyaev, Y.A. The Uniform Twister Plane Generator. J. Comput. Sci. 2018, 14, 260–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Deon, A.; Menyaev, Y. Poisson Twister Generator by Cumulative Frequency Technology. Algorithms 2019, 114, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deon, A.F.; Menyaev, Y.A. Twister Generator of Random Normal Numbers by Box-Muller Model. J. Comput. Sci. 2020, 16, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Matsumoto, M.; Nishimura, T. Mersenne twister: A 623-dimensionnally Equidistributed Uniform Pseudorandom Number Generator. ACM Trans. Modeling Comput. Simul. 1998, 8, 3–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sutton, C.; McCallum, A. An Introduction to Conditional Random Fields. Found. Trends Mach. Learn. 2012, 4, 267–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quattoni, A.; Collins, M.; Darrell, T. Conditional Random Fields for Object Recognition. In Proceedings of the 17th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Denver, CO, USA, 3–10 December 2004; pp. 1097–1104. [Google Scholar]
- Bekkerman, R.; Sahami, M.; Learned-Miller, E. Combinatorial Markov Random Fields. In Proceedings of the 17th European Conference on Machine Learning, Berlin, Germany, 18 September 2006; pp. 30–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarawagi, S.; Cohen, W.W. Semi-Markov Conditional Random Fields for Information Extraction. In Proceedings of the 17th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Barcelona, Spain, 4–11 December 2005; pp. 1185–1192. [Google Scholar]
- Rimstad, K.; Omre, H. Skew-Gaussian Random Fields. Spat. Stat. 2014, 10, 43–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Y. Uniform Modulus of Continuity of Random Fields. Monatshefte für Mathematik 2010, 159, 163–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, Y.; Szummer, M.; Minka, T.P. Bayesian Conditional Random Fields. In Proceedings of the AISTATS’05: 10th International Workshop on Artificial Intelligence and Statistics, Savannah, Barbados, 6–8 January 2005; pp. 269–276. [Google Scholar]
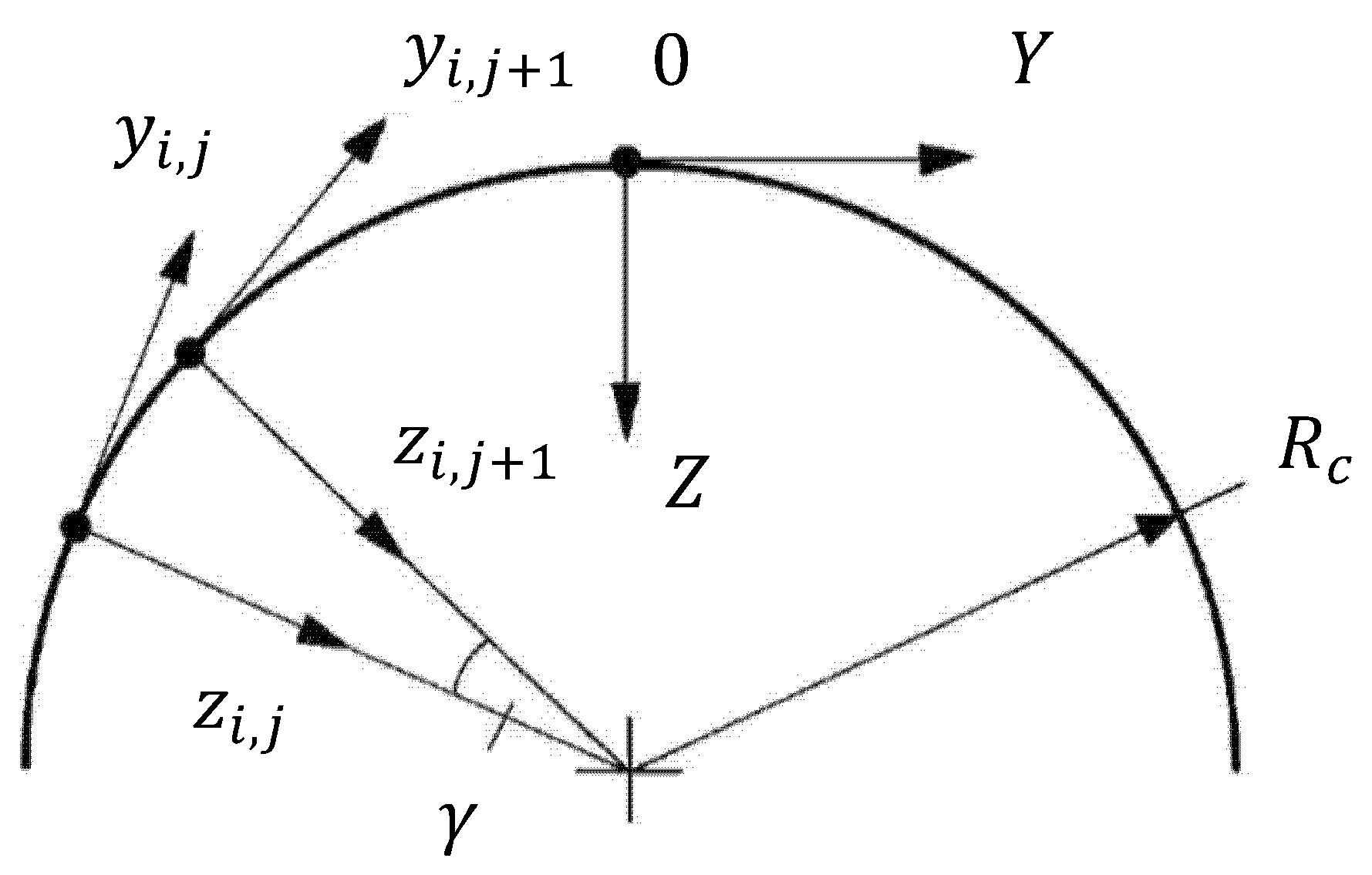
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Karaduta, O.K.; Deon, A.F.; Menyaev, Y.A. Designing the Uniform Stochastic Photomatrix Therapeutic Systems. Algorithms 2020, 13, 41. https://doi.org/10.3390/a13020041
Karaduta OK, Deon AF, Menyaev YA. Designing the Uniform Stochastic Photomatrix Therapeutic Systems. Algorithms. 2020; 13(2):41. https://doi.org/10.3390/a13020041
Chicago/Turabian StyleKaraduta, Oleg K., Aleksei F. Deon, and Yulian A. Menyaev. 2020. "Designing the Uniform Stochastic Photomatrix Therapeutic Systems" Algorithms 13, no. 2: 41. https://doi.org/10.3390/a13020041
APA StyleKaraduta, O. K., Deon, A. F., & Menyaev, Y. A. (2020). Designing the Uniform Stochastic Photomatrix Therapeutic Systems. Algorithms, 13(2), 41. https://doi.org/10.3390/a13020041





