Liquid Film Capillary Mechanism for Densification of Ceramic Powders during Flash Sintering
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Analysis and Discussion
2.1. Spark Plasma Sintering
2.2. Flash Sintering
2.2.1. Local Capillary Forces
2.2.2. Local Electric Conductivity
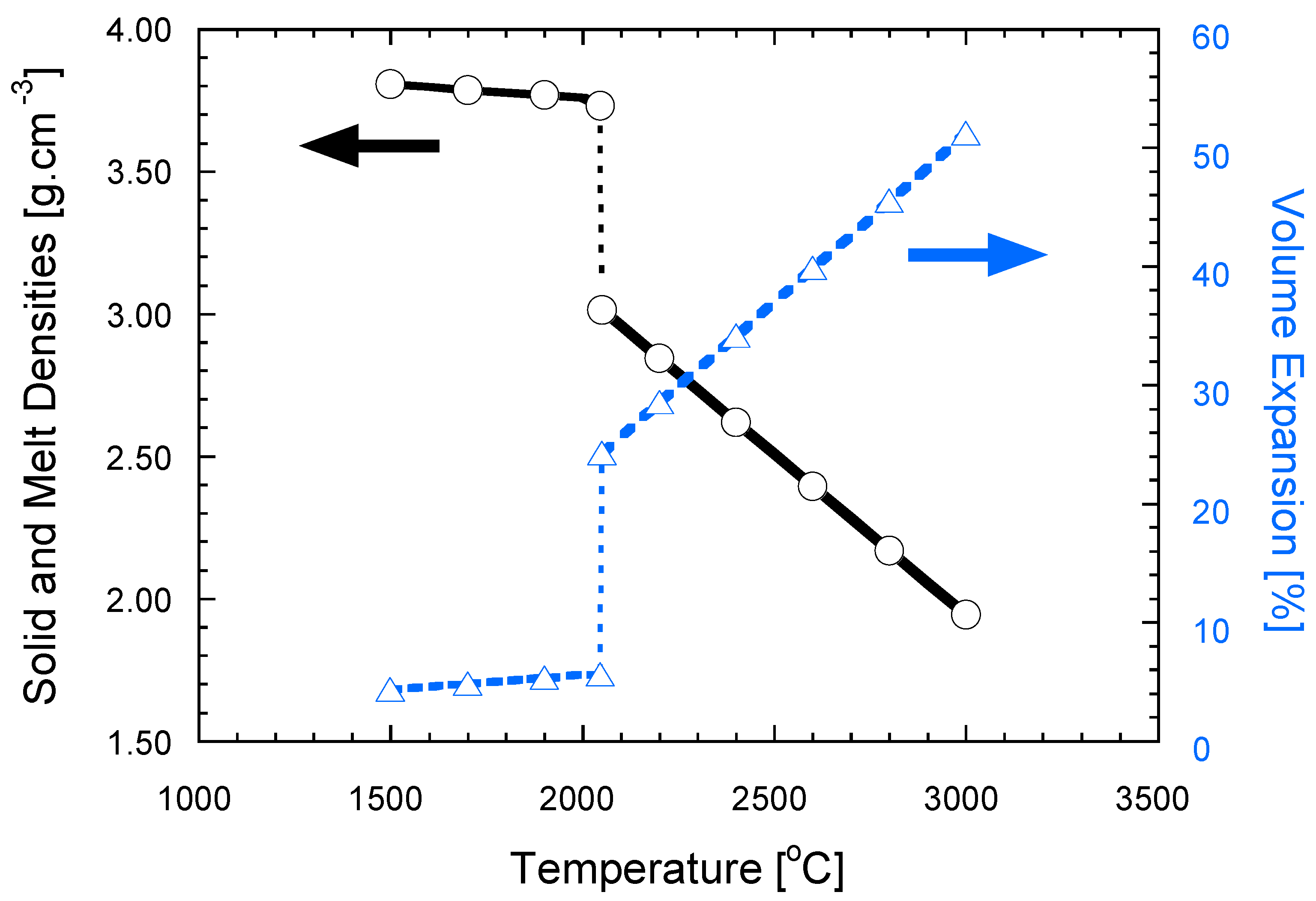
2.2.3. Local Volume Change
3. Conclusions
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| SPS | Spark Plasma Sintering |
| FS | Flash Sintering |
References
- Tokita, M. Mechanism of spark plasma sintering and its application to ceramics. Nyn Seramikkasu 1997, 10, 43–53. [Google Scholar]
- Groza, J.R.; Zavaliangos, A. Sintering activation by external electrical field. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2000, 287, 171–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munir, Z.A.; Anselmi-Tamburini, U.; Ohyanagi, M. The effect of electric field and pressure on the synthesis and consolidation of materials: A review of the spark plasma sintering method. J. Mater. Sci. 2006, 41, 763–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaim, R. Densification mechanism in spark plasma sintering of nanocrystalline ceramics. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2007, 443, 25–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olevsky, E.; Bogechev, I.; Maximenko, A. Spark-plasma sintering efficiency control by inter-particle contact area growth: A viewpoint. Scr. Mater. 2013, 69, 112–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holland, T.B.; Anselmi-Tamburini, U.; Mukherjee, A.K. Electric fields and the future of scalability in spark plasma sintering. Scr. Mater. 2013, 69, 117–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raj, R. Joule heating during flash sintering. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2012, 32, 2293–2301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Todd, R.I.; Zapata-Solvas, E.; Bonilla, R.S.; Sneddon, T.; Wilshaw, P.R. Electrical characterization of flash sintering: Thermal runaway of Joule heating. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2015, 35, 1865–1877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batista Caliman, L.; Bouchet, R.; Gouvea, D.; Soudant, P.; Steil, M.C. Flash sintering of ionic conductors: The need of a reversible electrochemical reaction. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2016, 36, 1253–1260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Y.; Stevenson, A.J.; Vernat, D.; Diaz, M.; Marinha, D. Estimating Joule heating and ionic conductivity during flash sintering of 8YSZ. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2016, 36, 749–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narayan, J. A new mechanism for field-assisted processing and flash sintering of materials. Scr. Mater. 2013, 69, 107–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naik, K.S.; Sglavo, V.M.; Raj, R. Flash sintering as a nucleation phenomenon and a model thereof. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2014, 34, 4063–4067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marder, R.; Estournès, C.; Chevallier, G.; Chaim, R. Plasma in spark plasma sintering of ceramic particle compacts. Scr. Mater. 2014, 82, 57–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marder, R.; Estournès, C.; Chevallier, G.; Chaim, R. Spark and plasma in spark plasma sintering of rigid ceramic nanoparticles: A model system of YAG. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2015, 35, 211–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Liu, Z.; Lu, J.; Shen, X.; Wang, F.; Wang, Y. The sintering mechanism in spark plasma sintering—Proof of the occurrence of spark discharge. Scr. Mater. 2014, 81, 56–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saunders, T.; Grasso, S.; Reece, M.J. Plasma formation during electric discharge (50 V) through conductive powder compact. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2015, 35, 871–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demirskyi, D.; Borodianska, H.; Grasso, S.; Sakka, Y.; Vasylkiv, O. Microstructure evolution during field-assisted sintering of zirconia spheres. Scr. Mater. 2011, 65, 683–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marder, R.; Estournès, C.; Chevallier, G.; Chaim, R. Numerical model for sparking and plasma formation during spark plasma sintering of ceramic compacts. J. Mater. Sci. 2015, 50, 4636–4645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terauds, K.; Lebrun, J.M.; Lee, H.H.; Jeon, T.Y.; Lee, S.H.; Je, J.H.; Raj, R. Electroluminescence and the measurement of temperature during stage III of flash sintering experiments. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2015, 35, 3195–3199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grasso, S.; Sakka, Y.; Rendtorff, N.; Hu, C.; Maizza, G.; Borodianska, H.; Vasylkiv, O. Modeling of the temperature distribution of flash sintered zirconia. J. Ceram. Soc. Jpn. 2011, 119, 144–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muccillo, R.; Kleitz, M.; Muccillo, E.N.S. Flash grain welding in yttria-stabilized zirconia. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2011, 31, 1517–1521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaim, R. Electric field effects during spark plasma sintering of ceramic nanoparticles. J. Mater. Sci. 2013, 48, 502–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaim, R.; Marder-Jaeckel, R.; Shen, J.Z. Transparent YAG ceramics by surface softening of nanoparticles in spark plasma sintering. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2006, 429, 74–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Jung, J.I.; Luo, J. Thermal runaway, flash sintering and asymmetrical microstructural development of ZnO and ZnO-Bi2O3 under direct currents. Acta Mater. 2015, 94, 87–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steil, M.C.; Marinha, D.; Aman, Y.; Gomes, J.R.C.; Kleitz, M. From conventional ac flash sintering of YSZ to hyper-flash and double flash. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2013, 33, 2093–2101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jha, S.K.; Lebrun, J.M.; Raj, R. Phase transformation in the alumina-titania system during flash sintering experiments. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2016, 36, 733–739. [Google Scholar]
- Jagota, A.; Dawson, P.R. Simulation of the viscous sintering of coated particles. Acta Metall. 1988, 36, 2551–2561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bichaud, E.; Chaix, J.M.; Carry, C.; Kleitz, M.; Steil, M.C. Flash sintering incubation in Al2O3/TZP composites. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2015, 35, 2587–2592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lihrmann, J.M.; Haggerty, J.S. Surface tension of alumina-containing liquids. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 1985, 68, 81–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mugele, F.; Baret, J.C. Electrowetting: From basics to applications. J. Phys. Condens. Mater. 2005, 17, R705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lakomsky, V.I. Part 3: Oxide Cathodes for the Electric Arc. In Welding and Surface Reviews; Paton, B.E., Ed.; Harwood Academic Publishers: Reading, UK, 2000; Volume 13, pp. 74–90. [Google Scholar]
- Leu, A.L.; Ma, S.M.; Eyring, H. Properties of molten magnesium oxide. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1975, 72, 1026–1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rennie, R. Oxford Dictionary of Chemistry, 6th ed.; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Biesuz, M.; Sglavo, V.M. Flash sintering of alumina: Effect of different operating conditions on densification. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, G.; Yazhenskikh, E.; Hack, K.; Wosch, E.; Müller, M. Viscosity model for oxide melts relevant to fuel slags. Part 1: Pure oxides and binary systems in the system SiO2-Al2O3-CaO-MgO-Na2O-K2O. Process. Tech. 2015, 137, 93–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirshenbaum, A.D.; Cahill, J.A. The density of liquid aluminum oxide. J. Inorg. Nucl. Chem. 1960, 14, 283–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pappis, J.; Kingery, W.D. Electrical properties of single-crystal and polycrystalline Alumina at high temperatures. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 1961, 44, 459–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pozniak, I.; Pechenkov, A.; Shatunov, A. Electrical conductivity measurement of oxide melts. In Proceedings of the International Scientific Colloquium Modelling for Material Processing, Riga, Latvia, 8–9 June 2006.
- Francis, J.S.C.; Cologna, M.; Raj, R. Particle size effects in flash sintering. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2012, 32, 3129–3136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilkinson, D.; Willemsen, J.F. Invasion percolation: A new form of percolation theory. J. Phys. A Math. Gen. 1983, 16, 3365–3374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobrovinskaya, E.R.; Lytvynov, L.A.; Pishchik, V. Sapphire: Material, Manufacturing, Applications; Springer Science + Business Media: New York, NY, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Da Silva, J.G.P.; Al-Qureshi, H.A.; Keil, F.; Janssen, R. A dynamic bifurcation criterion for thermal runaway during the flash sintering of ceramics. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2016, 36, 1261–1267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narayan, J. Grain growth model for electric field-assisted processing and flash sintering of materials. Scr. Mater. 2013, 68, 785–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gurt Santanach, J.; Weibel, A.; Estournès, C.; Yang, Q.; Laurent, C.; Peigney, A. Spark plasma sintering of alumina: Study of parameter, formal sintering analysis and hypotheses on the mechanism(s) involved in densification and grain growth. Acta Mater. 2011, 59, 1400–1408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, L.A.; Chen, I.W. Low-temperature sintering of alumina with liquid-forming additives. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 1991, 74, 2011–2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

© 2016 by the author; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons by Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chaim, R. Liquid Film Capillary Mechanism for Densification of Ceramic Powders during Flash Sintering. Materials 2016, 9, 280. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma9040280
Chaim R. Liquid Film Capillary Mechanism for Densification of Ceramic Powders during Flash Sintering. Materials. 2016; 9(4):280. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma9040280
Chicago/Turabian StyleChaim, Rachman. 2016. "Liquid Film Capillary Mechanism for Densification of Ceramic Powders during Flash Sintering" Materials 9, no. 4: 280. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma9040280
APA StyleChaim, R. (2016). Liquid Film Capillary Mechanism for Densification of Ceramic Powders during Flash Sintering. Materials, 9(4), 280. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma9040280





