Transparent Conducting Oxides—An Up-To-Date Overview
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Transparent Conducting Oxides (TCOs)
2.1. TCOs in General
| Period of the PE | Compound semiconductor | Dopant | Preparation | Characterization | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2 | NiO | Li | Pulsed Laser Deposition (different Li-concentr.) | ? | [6] |
| No TCO-Layers with Be | |||||
| 3 | ZnO | Na, Al | Sol-gel, Annealing | SEM, Photoluminescence | [7,8,9] |
| Cr2O3 | Mg, N | Spray Pyrolysis | ? | [10] | |
| CuCrO2(Delafossite) | Mg | Sol-gel Technique | ? | [11] | |
| Mg1−xZnxO | In | Pulsed Laser Deposition (different substrates) | X-ray diffraction, HRTEM | [12] | |
| Mg1−xZnxO | Al | Radio Frequency Magnetron Sputtering (different substrates) | ? | [13] | |
| Mg12Al14O33 (“Mayenite”) | ? | ? | [14] | ||
| Al | |||||
2.2. Indium Tin Oxide (ITO)
2.3. Aluminum Doped Zinc Oxide (ZnO:Al)
2.4. Delafossite and Mayenite Type Transparent Conducting Oxides
3. Further Aspects to Technological Advances of Transparent Conducting Oxides
| Topic | Citation report | Av. Citations/Year | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2007 | 2008 | 2009 | 2010 | 2011 | Total | ||
| 2nd Period | |||||||
| TCO Li oxide | 4 | 0 | 3 | 7 | 5 | 19 | 3.17 |
| TCO Be oxide | x | x | x | x | x | x | x |
| 3rd Period | |||||||
| TCO Na oxide | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 3 | 3 | 3 |
| TCO Mg oxide | 8 | 7 | 8 | 8 | 9 | 40 | 8 |
| TCO Al oxide | 196 | 306 | 394 | 500 | 434 | 2122 | 192.91 |
| 4th Period | |||||||
| TCO K oxide | 1 | 2 | 5 | 3 | 1 | 12 | 2.4 |
| TCO Ca oxide | 5 | 11 | 5 | 8 | 5 | 47 | 5.88 |
| Subgroup | |||||||
| TCO Sc oxide | x | x | x | x | x | x | x |
| TCO Ti oxide | 1 | 5 | 14 | 50 | 38 | 114 | 14.25 |
| TCO V oxide | 0 | 1 | 9 | 1 | 3 | 18 | 2 |
| TCO Cr oxide | 3 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 12 | 28 | 3.5 |
| TCO Mn oxide | 0 | 0 | 3 | 1 | 1 | 5 | 1.25 |
| TCO Fe oxide | x | x | x | x | x | x | x |
| TCO Co oxide | 0 | 12 | 23 | 23 | 17 | 75 | 18.75 |
| TCO Ni oxide | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 5 | 7 | 3.5 |
| TCO Cu oxide | 18 | 40 | 44 | 73 | 76 | 268 | 33.5 |
| TCO Zn oxide | 275 | 415 | 487 | 723 | 612 | 3142 | 184.82 |
| TCO Ga oxide | 0 | 1 | 15 | 54 | 37 | 107 | 26.75 |
| 5th Period | |||||||
| TCO Rb oxide | x | x | x | x | x | x | x |
| TCO Sr oxide | 2 | 7 | 3 | 6 | 1 | 22 | 3.14 |
| Subgroup | |||||||
| TCO Y oxide | 0 | 0 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 4 | 1 |
| TCO Zr oxide | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 4 | 5 | 2.5 |
| TCO Nb oxide | 2 | 4 | 8 | 44 | 45 | 103 | 20.6 |
| TCO Mo oxide | 1 | 17 | 24 | 35 | 21 | 98 | 19.6 |
| TCO Tc oxide | radioactive! | ||||||
| TCO Ru oxide | 3 | 8 | 13 | 8 | 1 | 36 | 6 |
| TCO Rh oxide | x | x | x | x | x | x | x |
| TCO Pd oxide | x | x | x | x | x | x | x |
| TCO Ag oxide | 16 | 43 | 57 | 95 | 67 | 328 | 18.22 |
| TCO Cd oxide | 37 | 48 | 54 | 119 | 59 | 509 | 36.36 |
| TCO In oxide | 247 | 328 | 397 | 546 | 388 | 2511 | 156.94 |
| TCO Sn oxide | 346 | 406 | 493 | 641 | 519 | 3755 | 197.63 |
| 6th Period | |||||||
| TCO Cs oxide | x | x | x | x | x | x | x |
| TCO Ba oxide | x | x | x | x | x | x | x |
| Subgroup | |||||||
| TCO Hf oxide | x | x | x | x | x | x | x |
| TCO Ta oxide | 7 | 8 | 9 | 19 | 10 | 60 | 8.57 |
| TCO W oxide | 3 | 5 | 5 | 10 | 8 | 34 | 5.67 |
| TCO Re oxide | x | x | x | x | x | x | x |
| TCO Os oxide | x | x | x | x | x | x | x |
| TCO Ir oxide | x | x | x | x | x | x | x |
| TCO Pt oxide | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 0.4 |
| TCO Au oxide | x | x | x | x | x | x | x |
| TCO Hg oxide | 3 | 4 | 9 | 5 | 3 | 24 | 4.8 |
| TCO Tl oxide | x | x | x | x | x | x | x |
| TCO Pb oxide | x | x | x | x | x | x | x |
| TCO Bi oxide | x | x | x | x | x | x | x |
| Lanthanide Series | |||||||
| TCO La oxide | 0 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 1 | 3 | 1 |
| TCO Ce oxide | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 39 | 2.17 |
| TCO Pr oxide | x | x | x | x | x | x | x |
| TCO Nd oxide | x | x | x | x | x | x | x |
| TCO Pm oxide | x | x | x | x | x | x | x |
| TCO Sm oxide | 0 | 0 | 1 | 10 | 8 | 19 | 6.33 |
| TCO Eu oxide | 0 | 0 | 1 | 8 | 5 | 14 | 4.67 |
| TCO Gd oxide | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 4 | 5 | 2.5 |
| TCO Tb oxide | x | x | x | x | x | x | x |
| TCO Dy oxide | 0 | 0 | 0 | 9 | 6 | 15 | 7.5 |
| TCO Ho oxide | x | x | x | x | x | x | x |
| TCO Er oxide | x | x | x | x | x | x | x |
| TCO Tm oxide | x | x | x | x | x | x | x |
| TCO Yb oxide | x | x | x | x | x | x | x |
| TCO Lu oxide | x | x | x | x | x | x | x |
| 7th Period | |||||||
| TCO Fr oxide | x | x | x | x | x | x | x |
| TCO Ra oxide | x | x | x | x | x | x | x |
| Actinide Series | |||||||
| TCO Ac oxide | x | x | x | x | x | x | x |
| TCO Th oxide | x | x | x | x | x | x | x |
| TCO Pa oxide | x | x | x | x | x | x | x |
| TCO U oxide | radioactive! | ||||||
| … | radioactive! | ||||||

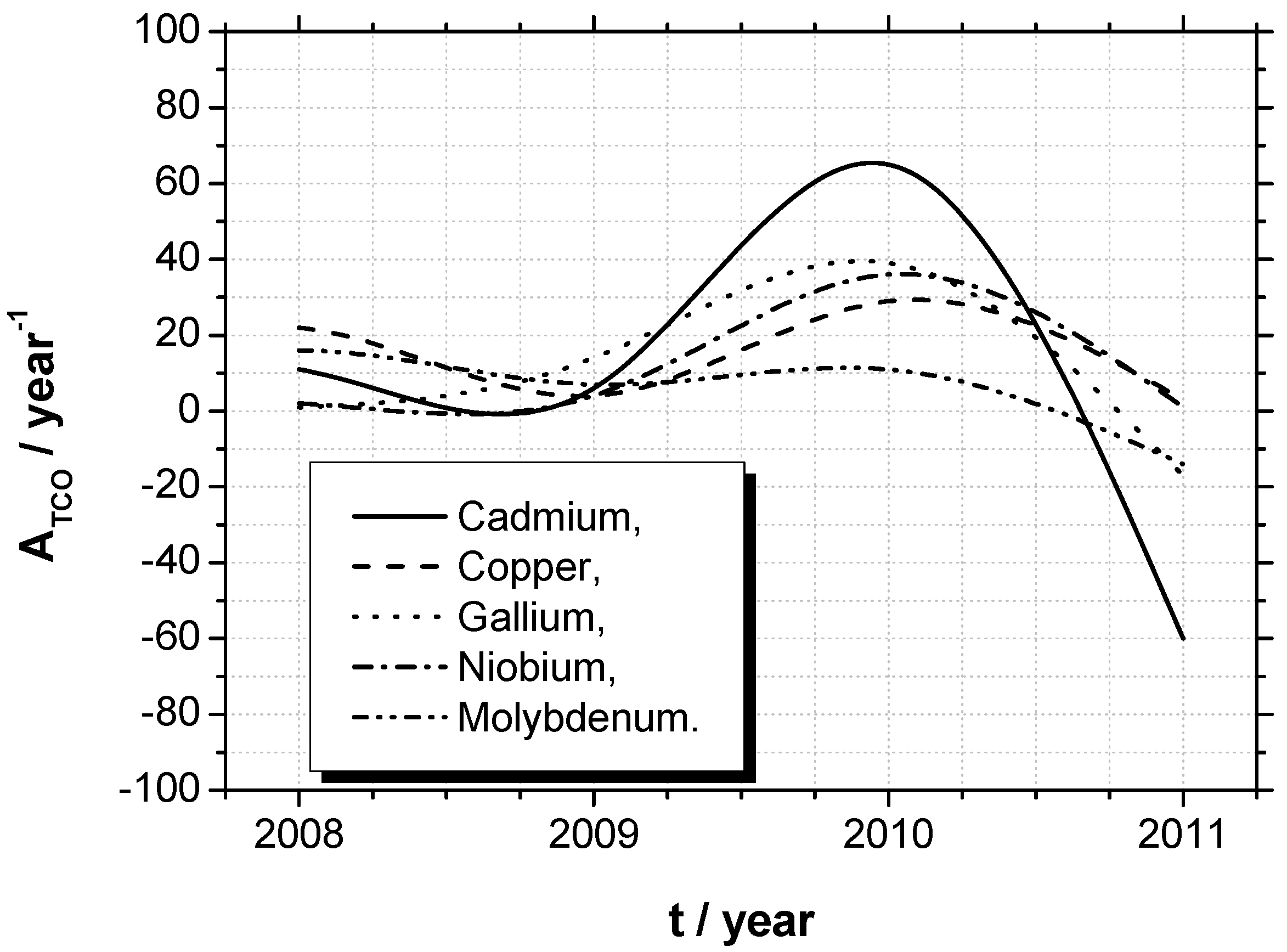
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
References
- Chopra, K.L.; Major, S.; Pandya, D.K. Transparent conductors—A status review. Thin Solid Films 1983, 102, 1–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edwards, P.P.; Porch, A.; Jones, M.O.; Morgan, D.V.; Perks, R.M. Basic materials physics of transparent conducting oxides. Dalton Trans. 2004, 19, 2995–3002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawazoe, H.; Ueda, K. Transparent conducting oxides based on the spinel structure. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 1999, 82, 3330–3336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jarzebski, Z.M. Preparation and physical properties of transparent conducting oxide films. Phys. Stat. Sol. 1982, 71, 13–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minami, T. Present status of transparent conducting oxide thin-film development for Indium-Tin-Oxide (ITO) substitutes. Thin Solid Films 2008, 516, 5822–5828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joshi, U.S.; Matsumoto, Y.; Itaka, K.; Sumiya, M.; Koinuma, H. Combinatorial synthesis of Li-doped NiO thin films and their transparent conducting properties. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2006, 252, 2524–2528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Liu, Y.; Fang, Q.; Wu, M.; Sun, X.; Lu, F. Low temperature synthesis wide optical band gap Al and (Al, Na) co-doped ZnO thin films. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2011, 257, 2341–2345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M. Comment on “low temperature synthesis wide optical band gap Al and (Al, Na) co-doped ZnO thin films”. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2011, 257, 8752–8753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Liu, Y. Response to the comment on “low temperature synthesis wide optical band gap Al and (Al, Na) co-doped ZnO thin films”. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2011, 257, 8754. [Google Scholar]
- Arca, E.; Fleischer, K.; Shvets, I.V. Magnesium, nitrogen codoped Cr2O3: A p-type transparent conducting oxide. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2011, 99, 111910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Götzendörfer, S.; Löbmann, P. Influence of single layer thickness on the performance of undoped and Mg-doped CuCrO2 thin films by sol–gel processing. J. Sol-Gel Sci. Technol. 2011, 57, 157–163. [Google Scholar]
- Lau, C.H.; Zhuang, L.; Wong, K.H. In-doped transparent and conducting cubic magnesium zinc oxide thin films grown by pulsed laser deposition. Phys. Stat. Sol. B 2007, 244, 1533–1537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellmer, K.; Vollweiler, G. Electrical transport parameters of heavily-doped zinc oxide and zinc magnesium oxide single and multilayer films heteroepitaxially grown on oxide single crystals. Thin Solid Films 2006, 496, 104–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ingram, B.J.; Bertoni, M.I.; Poeppelmeier, K.R.; Mason, K.R. Point defects and transport mechanisms in transparent conducting oxides of intermediate conductivity. Thin Solid Films 2005, 486, 86–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartnagel, H.L. Semiconducting Transparent Thin Films; Institute of Physics Publishing: Bristol, UK, 1995; ISBN 978–0750303224. [Google Scholar]
- Laux, S.; Kaiser, N.; Zöller, A.; Götzelmann, R.; Lauth, H.; Bernitzki, H. Room-temperature deposition of indium tin oxide thin films with plasma ion-assisted evaporation. Thin Solid Films 1998, 335, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paine, D.C.; Whitson, T.; Janiac, D.; Beresford, R.; Yang, C.O.; Lewis, B. A study of low temperature crystallization of amorphous thin film indium-tin-oxide. J. Appl. Phys. 1999, 85, 8445–8450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.H.; Chang, S.J.; Su, Y.K.; Chi, G.C.; Chi, J.Y.; Chang, C.A.; Sheu, J.K.; Chen, J.F. GaN metal-semiconductor-metal ultraviolet pho- todetectors with transparent indium-tin-oxide Schottky contacts. IEEE Photonics Technol. Lett. 2001, 13, 848–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheu, J.K.; Su, Y.K.; Chi, G.C.; Jou, M.J.; Chang, C.M. Effects of thermal annealing on the indium tin oxide Schottky contacts of n-GaN. Appl. Phys. Lett. 1998, 72, 3317–3319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karasawa, T.; Miyata, Y. Electrical and optical properties of indium tin oxide thin films deposited on unheated substrates by d.c. reactive sputtering. Thin Solid Films 1993, 223, 135–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.T.; Lee, J.H.; Yang, J.Y.; Ryu, S.W.; Hong, J.S.; Hong, W.P.; Kim, J.J.; Kim, H.M.; Yang, J.M.; Park, S.H. The Electronic and optical properties of IZO thin films prepared by pulsed dc magnetron sputtering. J. Korean Phys. Soc. 2007, 50, 662–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sittinger, V.; Ruske, F.; Werner, W.; Jacobs, C.; Szyszka, B.; Christie, D.J. High power pulsed magnetron sputtering of transparent conducting oxides. Thin Solid Films 2008, 516, 5847–5859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.K.; Jeong, I.H.; Kim, W.K.; Kwak, M.G. Deposition of indium-tin-oxide films on polymer substrates for application in plastic-based flat panel displays. Thin Solid Films 2001, 397, 49–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, L.-J.; dos Santos, M.P. Properties of indium tin oxide films prepared by RF reactive magnetron sputtering at different substrate temperature. Thin Solid Films 1998, 322, 56–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horng, R.-H.; Wuu, D.-S.; Lien, Y.-C.; Lan, W.-H. Low-resistance and high-transparency Ni/indium tin oxide ohmic contacts to p-type GaN. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2001, 79, 2925: 1–2925: 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.; Piqué, A.; Horwitz, J.S.; Mattoussi, H.; Murata, H.; Kafafi, Z.H.; Chrisey, D.B. Indium tin oxide thin films for organic light-emitting devices. Appl. Phys. Lett. 1999, 74, 3444: 1–3444: 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohta, H.; Orita, M.; Hirano, M.; Tanji, H.; Kawazoe, H.; Hosono, H. Highly electrically conductive indium-tin-oxide thin films epitaxially grown on yttria-stabilized zirconia (100) by pulsed-laser deposition. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2000, 76, 2740: 1–2740: 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.; Gilmore, C.M.; Piqué, A.; Horwitz, J.S.; Mattoussi, H.; Murata, H.; Kafafi, Z.H.; Chrisey, D.B. Electrical, optical, and structural properties of indium–tin–oxide thin films for organic light-emitting devices. J. Appl. Phys. 1999, 86, 6451–6461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.W.; Huang, H.C.; Kwok, H.S. On the initial growth of indium tin oxide on glass. Appl. Phys. Lett. 1996, 68, 2663: 1–2663: 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milliron, D.J.; Hill, I.G.; Shen, C.; Kahn, A.; Schwartz, J. Surface oxidation activates indium tin oxide for hole injection. J. Appl. Phys. 2000, 87, 572–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nüesch, F.; Rothberg, L.J.; Forsythe, E.W.; Le, Q.T.; Gao, Y.L. A photoelectron spectroscopy study on the indium tin oxide treatment by acids and bases. Appl. Phys. Lett. 1999, 74, 880: 1–880: 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Synowicki, R.A. Spectroscopic ellipsometry characterization of indium tin oxide film microstructure and optical constants. Thin Solid Films 1998, 313, 394–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishida, T.; Kobayashi, H.; Nakato, Y. Structures and properties of electron‐beam‐evaporated indium tin oxide films as studied by X‐ray photoelectron spectroscopy and work‐function measurements. J. Appl. Phys. 1993, 73, 4344–4350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mryasov, O.N.; Freeman, A.J. Electronic band structure of indium tin oxide and criteria for transparent conducting behavior. Phys. Rev. B 2001, 64, 233111–233113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugiyama, K.; Ishii, H.; Ouchi, Y.; Seki, K. Dependence of indium–tin–oxide work function on surface cleaning method as studied by ultraviolet and x-ray photoemission spectroscopies. J. Appl. Phys. 2000, 87, 295: 1–295: 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, Y.; Choong, V.; Gao, Y.; Hsieh, B. R.; Tang, C.W. Work function of indium tin oxide transparent conductor measured by photoelectron spectroscopy. Appl. Phys. Lett. 1996, 68, 2699–2701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jagadish, C. Zinc Oxide Bulk, Thin Films and Nanostructures, Processing, Properties and Applications; Jagadish, C., Pearton, S., Eds.; Elsevier: Oxford, UK, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Transparent Conductive Zinc Oxide: Basics and Application in Thin Film Solar Cells, 2nd ed.; Ellmer, K.; Klein, A.; Rech, B. (Eds.) Springer-Verlag: Berlin, Germany, 2008.
- Seeber, W.T.; Abou-Helal, M.O.; Barth, S.; Beil, D.; Höche, T.; Afify, H.H.; Demian, S.E. Transparent semiconducting ZnO:Al thin films prepared by spray pyrolysis. Mater. Sci. Semicond. Process. 1999, 2, 45–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nunes, P.; Malik, A.; Fernandes, B.; Fortunato, E.; Vilarinho, P.; Martins, R. Influence of the doping and annealing atmosphere on zinc oxide thin films deposited by spray pyrolysis. Vacuum 1999, 52, 45–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nunes, P.; Fernandesa, B.; Fortunatoa, E.; Vilarinhob, P.; Martinsa, R. Performances presented by zinc oxide thinfilms deposited by spray pyrolysis. Thin Solid Films 1999, 337, 176–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lokhande, B.J.; Uplane, M.D. Structural, optical and electrical studies on spray deposited highly oriented ZnO films. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2000, 167, 243–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mondragón-Suárez, H.; Reyes, A.; Castanedo-Pérez, R.; Torres-Delgado, G.; Asomoza, R. ZnO:Al thin films obtained by chemical spray: effect of the Al concentration. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2002, 193, 52–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gümü, C.; Ozkendir, O.M.; Kavak, H.; Ufuktepe, Y. Structural and optical properties of zinc oxide thin films prepared by spray pyrolysis methode. J. Optoelectron. Adv. Mater. 2006, 8, 299–303. [Google Scholar]
- Jiménez-González, A.E.; Urueta, J.A.S.; Suárez-Parra, R. Optical and electrical characteristics of aluminum-doped ZnO thin films prepared by solgel technique. J. Cryst. Growth 1998, 192, 430–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schuler, T.; Aegerter, M.A. Optical, electrical and structural properties of sol gel ZnO:Al coatings. Thin Solid Films 1999, 351, 125–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Natsume, Y.; Sakata, H. Zinc oxide films prepared by sol-gel spin-coating. Thin Solid Films 2000, 372, 30–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musat, V.; Teixeira, B.; Fortunato, E.; Monteiro, R.C.C.; Vilarinho, P. Al-doped ZnO thin films by sol–gel method. Surf. Coat. Tech. 2004, 180, 659–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valle, G.G.; Hammer, P.; Pulcinelli, S.H.; Santilli, C.V. Transparent and conductive ZnO:Al thin films prepared by sol-gel dip-coating. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2004, 24, 1009–1013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maity, R.; Kundoo, S.; Chattopadhyay, K.K. Electrical characterization and Poole-Frenkel effect in sol-gel derived ZnO:Al thin films. Sol. Energ. Mat. Sol. C 2005, 86, 217–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.J.; Deng, H.; Dai, L.P.; Chen, J.J.; Yuan, Q.L.; Li, Y. Properties of Al heavy-doped ZnO thin films by RF magnetron sputtering. Mater. Res. Bull. 2006, 41, 354–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gal, D.; Hodes, G.; Lincot, D.; Schock, H.-W. Electrochemical deposition of zinc oxide films from non-aqueous solution: A new buffer/window process for thin film solar cells. Thin Solid Films 2000, 361, 79–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, S. Polyelectrolyte Assisted Preparation and Characterization of Nanostructured ZnO Thin Films. Ph.D. Thesis, Universität Stuttgart, Stuttgart, Germany, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, J.; Ji, F.; Ma, H.-L.; Li, S.-Y. Electrical and optical properties of ZnO: Al films prepared by an evaporation method. Thin Solid Films 1996, 279, 213–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Ji, F.; Zhang, D.-H.; Ma, H.-L.; Li, S.-Y. Optical and electronic properties of transparent conducting ZnO and ZnO:Al films prepared by evaporating method. Thin Solid Films 1999, 357, 98–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Pei, Z.L.; Sun, C.; Wen, L.S.; Wang, X. Formation of Al-doped ZnO films by dc magnetron reactive sputtering. Mater. Lett. 2001, 48, 194–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ting, J.-M.; Tsai, B.S. DC reactive sputter deposition of ZnO:Al thin film on glass. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2001, 72, 273–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, G.J.; Li, D.J.; Yao, B.-L. Fabrication and characterization of transparent conductive ZnO:Al thin films prepared by direct current magnetron sputtering with highly conductive ZnO(ZnAl2O4) ceramic target. J. Cryst. Growth 2003, 247, 393–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrmann, D.; Oertel, M.; Menner, R.; Powalla, M. Analysis of relevant plasma parameters for ZnO:Al film deposition based on data from reactive and non-reactive DC magnetron sputtering. Surf. Coat. Tech. 2003, 174, 229–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.W.; Diao, X.G.; Wang, Z.; Yang, M.; Wang, T.M.; Wu, Z. Preparation and characterization of high-performance direct current magnetron sputtered ZnO:Al films. Thin Solid Films 2005, 491, 54–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimova-Malinovska, D.; Tzenov, N.; Tzolov, M.; Vassilev, L. Optical and electrical properties of R.F. magnetron sputtered ZnO:Al thin films. Mater. Sci. Eng. 1998, B52, 59–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, J.F.; Wang, H.L.; Hon, M.H. Studying of transparent conductive ZnO:Al thin films by RF reactive magnetron sputtering. J. Cryst. Growth 2000, 211, 93–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, J.F.; Shen, C.C.; Hon, M.H. Growth characteristics and residual stress of RF magnetron sputtered ZnO:Al films. Ceram. Int. 2003, 29, 245–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoo, J.S.; Lee, J.; Kim, S.; Yoon, K.; Park, I.J.; Dhungel, S.K.; Karunagaran, B.; Mangalaraj, D.; Yi, J.S. High transmittance and low resistive ZnO:Al films for thinfilm solar cells. Thin Solid Films 2005, 480, 213–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sieber, I.; Wanderka, N.; Urban, I.; Dörfel, I.; Schierhorn, E.; Fenske, F.; Fuhs, W. Electron microscopic characterization of reactively sputtered ZnO films with different Al-doping levels. Thin Solid Films 1998, 330, 108–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellmer, K.; Cebulla, R.; Wendt, R. Transparent and conducting ZnO(:Al) films deposited by simultaneous RF- and DC-excitation of a magnetron. Thin Solid Films 1998, 317, 413–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tominaga, K.; Umezu, N.; Mori, I.; Ushiro, T.; Moriga, T.; Nakabayashi, I. Transparent conductive ZnO film preparation by alternating sputtering of ZnO:Al and Zn or Al targets. Thin Solid Films 1998, 334, 35–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fenske, F.; Fuhs, W.; Nebauer, E.; Schöpke, A.; Selle, B.; Sieber, I. Transparent conductive ZnO:Al films by reactive co-sputtering from separate metallic Zn and Al targets. Thin Solid Films 1999, 343, 130–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kluth, O.; Recha, B.; Houbena, L.; Wiedera, S.; Schöpea, G.; Benekinga, C.; Wagnera, H.; Löfflb, A.; Schockb, H.W. Texture etched ZnO:Al coated glass substrates for silicon based thin film solar cells. Thin Solid Films 1999, 351, 247–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szyszka, B. Transparent and conductive aluminum doped zinc oxide films prepared by mid-frequency reactive magnetron sputtering. Thin Solid Films 1999, 351, 164–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stadler, A. Analyzing UV/Vis/NIR spectra—Part II: Correct and efficient parameter extraction. IEEE Sens. J. 2011, 11, 897–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.H.; Yang, T.L.; Wang, Q.P.; Zhang, D.J. Electrical and optical properties of Al-doped transparent conducting ZnO films deposited on organic substrate by RF sputtering. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2001, 68, 233–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, J.; Kluth, O.; Wieder, S.; Siekmann, H.; Schöpe, G.; Reetz, W.; Vetterl, O.; Lundszien, D.; Lambertz, A.; Finger, F.; et al. Development of highly efficient thin film silicon solar cells on texture-etched zinc oxide-coated glass substrates. Sol. Energ. Mat. Sol. C 2001, 66, 275–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, J.; Schöpe, G.; Kluth, O.; Rech, B.; Ruske, M.; Trube, J.; Szyszka, B.; Jiang, X.; Bräuer, G. Upscaling of texture-etched zinc oxide substrates for silicon thin film solar cells. Thin Solid Films 2001, 392, 327–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tzolov, M.; Tzenov, N.; Dimova-Malinovska, D.; Kalitzova, M.; Pizzuto, C.; Vitali, G.; Zollo, G.; Ivanov, I. Modification of the structure of ZnO:Al films by control of the plasma parameters. Thin Solid Films 2001, 396, 274–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, R.J.; Jiang, X.; Heide, G.; Szyszka, B.; Sittinger, V.; Werner, W. Growth behaviours and properties of the ZnO:Al films prepared by reactive mid-frequency magnetron sputtering. J. Cryst. Growth 2003, 249, 461–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, J.; Schöpe, G.; Kluth, O.; Rech, B.; Sittinger, V.; Szyszka, B.; Geyer, R.; Lechner, P.; Schade, H.; Ruske, M.; et al. State-of-the-art mid-frequency sputtered ZnO films for thin film silicon solar cells and modules. Thin Solid Films 2003, 442, 158–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, R.J.; Jiang, X.; Szyszka, B.; Sittinger, V.; Pflug, A. Studies on ZnO: Al thin films deposited by in-line reactive mid-frequency magnetron sputtering. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2003, 207, 341–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szyszka, B.; Sittinger, V.; Jiang, X.; Hong, R.J.; Werner, W.; Pflug, A.; Ruske, M.; Lopp, A. Transparent and conductive ZnO:Al films deposited by large area reactive magnetron sputtering. Thin Solid Films 2003, 442, 179–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, E.G.; Zhuang, D.M.; Zhang, G.; Zhao, M.; Yang, W.F. Properties of transparent conductive ZnO:Al thin films prepared by magnetron sputtering. Microelectr. J. 2004, 35, 383–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, B.-Y.; Jeong, M.-C.; Lee, W.; Myoung, J.-M. Properties of transparent conductive ZnO:Al films prepared by co-sputtering. J. Cryst. Growth 2005, 274, 453–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, S.-S.; Huang, J.-L.; Šajgalik, P. Effects of substrate temperature on the properties of heavily Al-doped ZnO films by simultaneous r.f. and d.c. magnetron sputtering. Surf. Coat. Tech. 2005, 190, 39–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Groenen, R.; Linden, J.L.; van Lierop, H.R.M.; Schram, D.C.; Kuypers, A.D.; van de Sanden, M.C.M. An expanding thermal plasma for deposition of surface textured ZnO:Al with focus on thin film solar cell applications. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2001, 173, 40–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.W.; Lau, S.P.; Wang, Y.G.; Tse, K.Y.; Hng, H.H.; Tay, B.K. Structural, electrical and optical properties of Al-doped ZnO thin films prepared by filtered cathodic vacuum arc technique. J. Cryst. Growth 2004, 268, 596–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.-J.; Kim, H.-J. Trapped oxygen in the grain boundaries of ZnO polycrystalline thin films prepared by plasma-enhanced chemical vapor deposition. Mater. Lett. 1999, 41, 159–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Groenen, R.; Löffler, J.; Sommeling, P.M.; Linden, J.L.; Hamers, E.A.G.; Schropp, R.E.I.; van de Sanden, M.C.M. Surface textured ZnO films for thin film solar cell applications by expanding thermal plasma CVD. Thin Solid Films 2001, 392, 226–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aghamalyan, N.R.; Gambaryan, I.A.; Goulanian, E.K.; Hovsepyan, R.K.; Kostanyan, R.B.; Petrosyan, S.I.; Vardanyan, E.S.; Zerrouk, A.F. Influence of thermal annealing on optical and electrical properties of ZnO films prepared by electron beam evaporation. Semicond. Sci. Technol. 2003, 18, 525–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ning, Z.Y.; Cheng, S.H.; Ge, S.B; Chao, Y.; Gang, Z.Q.; Zhang, Y.X.; Liu, Z.G. Preparation and characterization of ZnO:Al films by pulsed laser deposition. Thin Solid Films 1997, 307, 50–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.W.; Kwok, H.S. Optical properties of epitaxially grown zinc oxide films on sapphire by pulsed laser deposition. J. Appl. Phys. 1999, 86, 408–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H; Piqué, A.; Horwitz, J.S.; Murata, H.; Kafafi, Z.H.; Gilmore, C.M.; Chrisey, D.B. Effect of aluminum doping on zinc oxide thin films grown by pulsed laser deposition for organic light-emitting. Thin Solid Films 2000, 377, 798–802. [Google Scholar]
- Dolbec, R.; Khakani, M.A.E; Serventi, A.M.; Trudeau, M.; Saint-Jacques, R.G. Microstructure and physical properties of nanostructured tin oxide thin films grown by means of pulsed laser. Thin Solid Films 2002, 419, 230–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsubara, K.; Fons, P.; Iwata, K.; Yamada, A.; Sakurai, K.; Tampo, H.; Niki, S. ZnO transparent conducting films deposited by pulsed laser deposition for solar cell applications. Thin Solid Films 2003, 431, 369–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vincze, A.; Kováč, J.; Novotný, I.; Bruncko, J.; Haško, D.; Šatka, A.; Shtereva, K. Preparation and properties of ZnO layers grown by various methods. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2008, 255, 1419–1422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elam, J.W.; George, S.M. Growth of ZnO/Al2O3 alloy films using atomic layer deposition techniques. Chem. Mater. 2003, 15, 1020–1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, T.L.; Zhang, D.H.; Ma, J.; Ma, H.L.; Chen, Y. Transparent conducting ZnO:Al films deposited on organic substrates deposited by RF magnetron-sputtering. Thin Solid Films 1998, 326, 60–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshino, Y.; Inoue, K.; Takeuchi, M.; Makino, T.; Katayama, Y.; Hata, T. Effect of substrate surface morphology and interface microstructure in ZnO thin films formed on various substrates. Vacuum 2000, 59, 403–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.H.; Yang, T.L.; Ma, J.; Wang, Q.P.; Gao, R.W.; Ma, H.L. Preparation of transparent conducting ZnO:Al films on polymer substrates by RF magnetron sputtering. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2000, 158, 43–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, X.T.; Ma, J.; Zhang, D.H.; Yang, T.L.; Ma, H.L.; Yang, Y.G.; Cheng, C.F.; Huang, J. Thickness dependence of structural, optical and electrical properties of ZnO:Al films prepared on flexible substrates. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2001, 183, 137–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.H.; Yang, T.L.; Wang, Q.P.; Zhang, D.J. Electrical and optical properties of Al-doped transparent conducting ZnO films deposited on organic substrate by RF sputtering. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2001, 68, 233–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durrani, S.M.A.; Al-Shukri, A.M.; Iob, A.; Khawaja, E.E. Optical constants of zinc sulfide films determined from transmittance measurements. Thin Solid Films 2000, 379, 199–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunasekaran, M.; Ramasamy, P.; Ichimura1, M. Preparation of ternary Cd1−xZnxS alloy by photochemical deposition (PCD) and its application to photovoltaic devices. Phys. Status. Solidi C 2006, 3, 2656–2660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, S.-S.; Huang, J.-L. The effect of thickness on the properties of heavily Al-doped ZnO films by simultaneous rf and dc magnetron sputtering. Ceram. Int. 2004, 30, 497–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, J.F.; Hon, M.H. The effect of deposition temperature on the properties of Al-doped zinc oxide thin films. Thin Solid Films 2001, 386, 79–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Igasaki, Y.; Kanma, H. Argon gas pressure dependence of the properties of transparent conducting ZnO:Al films deposited on glass substrates. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2001, 169, 508–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, D.Y.; Aberle, A.G.; Xia, J. Optimisation of ZnO:Al films by change of sputter gas pressure for solar cell application. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2001, 195, 291–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brehme, S.; Fenske, F.; Fuhs, W.; Nebauer, E.; Poschenrieder, M.; Selle, B.; Sieber, I. Free-carrier plasma resonance effects and electron transport in reactively sputtered degenerate ZnO:Al films. Thin Solid Films 1999, 342, 167–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Addonizio, M.L.; Antonaia, A.; Cantele, G.; Privato, C. Transport mechanisms of RF sputtered Al-doped ZnO films by H2 process gas dilution. Thin Solid Films 1999, 349, 93–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Look, D.C. Recent advances in ZnO materials and devices. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2001, B80, 383–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feddern, K. Synthese und Optische Eigenschaften von ZnO-Nanokristallen. Ph.D. Thesis, Universität Hamburg, Hamburg, Germany, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Reuß, F. Untersuchung des Dotierverhaltens und der mag. Eigenschaften von Epitaktischen ZnO-Heterostrukturen. Ph.D. Thesis, Universität Ulm, Ulm, Germany, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Wischmeier, L. ZnO-Nanodrähte: Optische Eigenschaften und Ladungsträgerdynamik. Ph.D. Thesis, Universität Bremen, Bremen, Germany, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Waugh, K.C. Comments on “The effect of ZnO in methanol synthesis catalysts on Cu dispersion and the specific activity” [by T. Fujitani and J. Nakamura]. Catalysis Lett. 1999, 58, 163–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reitz, T.L.; Ahmed, S.; Krumpelt, M.; Kumar, R.; Kung, H.H. Characterization of CuO/ZnO under oxidizing conditions for the oxidative methanol reforming reaction. J. Mol. Catal. A Chem. 2000, 162, 275–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, Y.; Futagami, K.; Fujitani, T.; Nakamura, J. The role of ZnO in Cu/ZnO methanol synthesis catalysts—Morphology effect or active site model? Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2001, 208, 163–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, S.H.; Park, B.N.; Lee, S.B.; Boo, J.-H. Structural and optical properties of silver-doped zinc oxide sputtered films. Surf. Coat. Tech. 2005, 193, 340–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheong, K.Y.; Muti, N.; Ramanan, S.R. Electrical and optical studies of ZnO:Ga thin films fabricated via the sol–gel technique. Thin Solid Films 2002, 410, 142–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorenz, M.; Kaidashev, E.M.; von Wenckstern, H.; Riede, V.; Bundesmann, C.; Spemann, D.; Benndorf, G.; Hochmuth, H.; Rahm, A.; Semmelhack, H.-C.; et al. Optical and electrical properties of epitaxial (Mg, Cd)xZn1−xO, ZnO, and ZnO:(Ga, Al) thin films on c-plane sapphire grown by pulsed laser deposition. Solid State Electron. 2003, 47, 2205–2209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.-H.; Park, B.-O. Transparent conducting ZnO:Al, In and Sn thin films deposited by the sol–gel method. Thin Solid Films 2003, 426, 94–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsubara, K.; Fons, P.; Iwata, K.; Yamada, A.; Sakurai, K.; Tampo, H.; Niki, S. ZnO transparent conducting films deposited by pulsed laser deposition for solar cell applications. Thin Solid Films 2003, 431, 369–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tominaga, K.; Takao, T.; Fukushima, A.; Moriga, T.; Nakabayashi, I. Film properties of ZnO:Al films deposited by co-sputtering of ZnO:Al and contaminated Zn targets with Co, Mn and Cr. Vacuum 2002, 66, 511–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamoto, T. Codoping for the fabrication of p-type ZnO. Thin Solid Films 2002, 420, 100–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.G.; Zunger, A. Cluster-doping approach for wide-gap semiconductors: The case of p-type ZnO. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2003, 90, 256401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grundmann, M. Europas erste bipolare ZnO-Diode. MaterialsNews. 15th Auguest 2006. Available online: www.materialsgate.de (accessed on 19 April 2012).
- Pan, M.; Nause, J.; Rengarajan, V.; Rondon, R.; Park, E.H.; Ferguson, I.T. Epitaxial growth and characterization of p-type ZnO. J. Electron. Mater. 2007, 36, 457–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.L.; Ye, Z.Z.; Zhu, L.P.; Zeng, Y.J.; Lu, Y.F.; Zhao, B.H. Fabrication of p-type ZnO thin films via DC reactive magnetron sputtering by using Na as the Dopant source. J. Electron. Mater. 2007, 36, 498–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, S.-W.; Zu, X.-T.; Shao, L.-X.; Yuan, Z.-L.; Xiang, X.; Deng, H. Preparation of p-type ZnO:(Al, N) by a combination of sol-gel and ion-implantation techniques. Chin. Phys. 2008, B17, 2240–2244. [Google Scholar]
- Grundmann, M.; Lorenz, M. Erfolgreiche Phosphor-Dotierung von ZnO-Nanodrähten. Available online: http://www.uni-protokolle.de/nachrichten/id/146856 (accessed on 24 February 2009).
- Jin, H.-J.; Song, M.-J.; Park, C.-B. A novel phenomenon: p-Type ZnO:Al films deposited on n-Si substrate. Physica B 2009, 404, 1097–1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, Z.H.; Agashe, C.; Mergel, D. Dielectric modeling of transmittance spectra of thin ZnO:Al films. Thin Solid Films 2006, 496, 520–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, S.-S.; Huang, J.-L.; Šajgalik, P. The properties of heavily Al-doped ZnO films before and after annealing in the different atmos phere. Surf. Coat. Tech. 2004, 185, 254–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, B.-Y.; Jeong, M.-C.; Kim, D.-S.; Lee, W.; Myoung, J.-M. Post-annealing of Al-doped ZnO films in hydrogen atmosphere. J. Cryst. Growth 2005, 281, 475–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuo, S.Y.; Chen, W.C.; Lai, F.-I; Cheng, C.P.; Kuo, H.C.; Wang, S.C.; Hsieh, W.H. Effects of doping concentration and annealing temperature on properties of highly-oriented Al-doped ZnO films. J. Cryst. Growth 2006, 287, 78–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez, M.A.; Gutiérrez, M.T.; Maffiotte, C. Chemical changes of ITO/p and ZnO/p interfaces as a function of deposition parameters. Surf. Coat. Tech. 1998, 110, 68–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kluth, O.; Rech, B.; Houben, L.; Wieder, S.; Schöpe, G.; Beneking, C.; Wagner, H.; Löffl, A.; Schock, H.W. Texture etched ZnO:Al coated glass substrates for silicon based thin film solar cells. Thin Solid Films 1999, 351, 247–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klenk, R.; Linke, M.; Angermann, H.; Kelch, C.; Kirsch, M.; Klaer, J.; Köble, Ch. Die Stabilität von ZnO bei beschleunigter Alterung. In Proceedings of FVS Workshop (Session III), Berlin, Germany; 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Ibuki, S.; Yanagi, H.; Ueda, K.; Kawazoe, H.; Hosono, H. Preparation of n-type conductive transparent thin films of AgInO2:Sn with delafossite-type structure by pulsed laser deposition. J. Appl. Phys. 2000, 88, 3067: 1–3067: 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otabe, T.; Ueda, K.; Kudoh, A.; Hosono, H.; Kawazoe, H. n-Type electrical conduction in transparent thin films of delafossite-type AgInO2. Appl. Phys. Lett. 1998, 72, 1036: 1–1036: 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tate, J.; Jayaraj, M.K.; Draeseke, A.D.; Ulbrich, T.; Sleight, A.W.; Vanaja, K.A.; Nagarajan, R.; Wager, J.F.; Hoffman, R.L. p-Type oxides for use in transparent diodes. Thin Solid Films 2002, 411, 119–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doumerc, J.-P.; Wichainchai, A.; Ammar, A.; Pouchard, M.; Hagenmuller, P. On magnetic properties of some oxides with delafossite-type structure. Mater. Res. Bull. 1986, 21, 745–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagarajan, R.; Uma, S.; Jayaraj, M.K.; Tate, J.; Sleight, A.W. New CuM2/3Sb1/3O2 and AgM2/3Sb1/3O2 compounds with the delafossite structure. Solid. State Sci. 2002, 4, 787–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheets, W.C.; Stampler, E.S.; Bertoni, M.I.; Sasaki, M.; Marks, T.J.; Mason, T.O.; Poeppelmeier, K.R. Silver Delafossite Oxides. Inorg. Chem. 2008, 47, 2696–2705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marquardt, M.A.; Ashmore, N.A.; Cann, D.P. Crystal chemistry and electrical properties of the delafossite structure. Thin Solid Films 2006, 496, 146–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnabé, A.; Mugnier, E.; Presmanes, L.; Tailhades, Ph. Preparation of delafossite CuFeO2 thin films by rf-sputtering on conventional glass substrate. Mater. Lett. 2006, 60, 3468–3470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mugnier, E.; Barnabé, A.; Presmanes, L.; Tailhades, Ph. Thin films preparation by rf-sputtering of copper/iron ceramic targets with Cu/Fe = 1: From nanocomposites to delafossite compounds. Thin Solid Films 2008, 516, 1453–1456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, M.; Mehta, B.R. Effect of structural anisotropy on electronic conduction in delafossite tin doped copper indium oxide thin films. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2008, 93, 192104: 1–192104: 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Götzendörfer, S.; Löbmann, P. Influence of single layer thickness on the performance of undoped and Mg-doped CuCrO2 thin films by sol–gel processing. J. Sol-Gel Sci. Techn. 2011, 57, 157–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Götzendörfer, S.; Bywalez, R.; Löbmann, P. Preparation of p-type conducting transparent CuCrO2 and CuAl0.5Cr0.5O2 thin films by sol–gel processing. J. Sol-Gel Sci. Techn. 2009, 52, 113–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, S.H.; Desu, S.; Rastogi, A.C. Chemical spray pyrolysis deposition and characterization of p-type CuCr1−xMgxO2 transparent oxide semiconductor thin. J. Phys. Chem. Sol. 2008, 69, 2047–2056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Götzendörfer, S.; Polenzky, C.; Ulrich, S.; Löbmann, P. Preparation of CuAlO2 and CuCrO2 thin films by sol–gel processing. Thin Solid Films 2009, 518, 1153–1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahapatra, S.; Shivashankar, S.A. Low-pressure metal–organic chemical vapor deposition of transparent and p-type conducting CuCrO2 thin films with high conductivity. Chem. Vapor Depos. 2003, 9, 238–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ginley, D.; Roy, B.; Ode, A.; Warmsingh, C.; Yoshida, Y.; Parilla, P.; Teplin, C.; Kaydanova, T.; Miedaner, A.; Curtis, C.; et al. Non-vacuum and PLD growth of next generation TCO materials. Thin Solid Films 2003, 445, 193–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kudo, A.; Yanagi, H.; Hosono, H.; Kawazoe, H. SrCu2O2: A p-type conductive oxide with wide band gap. Appl. Phys. Lett. 1998, 73, 220–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, B.; Perkins, J.D.; Kaydanova, T.; Young, D.L.; Taylor, M.; Miedaner, A.; Curtis, C.; Kleebe, H.-J.; Readey, D.W.; Ginley, D.S. Preparation and characterization of sol–gel derived copper–strontium–oxide thin films. Thin Solid Films 2008, 516, 4093–4101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bobeico, E.; Varsano, F.; Minarini, C.; Roca, F. P-type strontium–copper mixed oxide deposited by e-beam evaporation. Thin Solid Films 2003, 444, 70–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.; Keszler, D.A.; Valencia, M.M.; Hoffman, R.L.; Bender, J.P.; Wager, J.F. Transparent p-type conducting BaCu2S2 films. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2002, 80, 4393: 1–4393: 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banerjee, A.N.; Chattopadhyay, K.K. Size-dependent optical properties of sputter-deposited nanocrystalline p-type transparent CuAlO2 thin films. J. Appl. Phys. 2005, 97, 084308: 1–084308: 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.Y.; Tsai, M.W. Delafossite-CuAlO2 thin films prepared by thermal annealing. J. Nano Res. 2011 2011, 13, 81–86. [Google Scholar]
- Rima, J.Y.; Songa, S.A.; Parka, S.B. Preparation of copper aluminium oxide by spray pyrolysis. Mater. Res. Soc. Symp. Proc. 2002, 703, 255–258. [Google Scholar]
- Sato, T.; Sue, K.; Tsumatori, H.; Suzuki, M.; Tanaka, S.; Kawai-Nakamura, A.; Saitoh, K.; Aida, K.; Hiaki, T. Hydrothermal synthesis of CuAlO2 with the delafossite structure in supercritical water. J. Supercrit. Fluid. 2008, 46, 173–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scanlon, D.O.; Watson, G.W. Conductivity Limits in CuAlO2 from Screened-Hybrid Density Functional Theory. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2010, 1, 3195–3199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stevens, B.L.; Hoe, C.A.; Swanborg, C.; Tang, Y.; Zhou, C.; Grayson, M.; Poeppelmeier, K.R.; Barnett, S.A. DC reactive magnetron sputtering, annealing, and characterization of CuAlO2 thin films. J. Vac. Sci. Technol. A 2011, 29, 011018: 1–011018: 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuboi, N.; Moriya, T.; Kobayashi, S.; Shimizu, H.; Kato, K.; Kaneko, F. Characterization of CuAlO2 Thin Films Prepared on Sapphire Substrates by Reactive Sputtering and Annealing. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 2008, 47, 592–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yanagi, H.; Hase, T.; Ibuki, S.; Ueda, K.; Hosono, H. Bipolarity in electrical conduction of transparent oxide semiconductor CuInO2 with delafossite structure. J. Appl. Phys. 2000, 88, 4159: 1–4159: 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.-Y.; Tsai, M.-W. Delafossite-CuAlO2 films prepared by annealing of amorphous Cu-Al-O films at high temperature under controlled atmosphere. Thin Solid Films 2011, 519, 5966–5970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.M.; He, Y.B.; Yang, B.; Polity, A.; Volbers, N.; Neumann, C.; Hasselkamp, D.; Meyer, B.K. RF reactive sputter deposition and characterization of transparent CuAlO2 thin films. Phys. Status. Solidi. C 2006, 3, 2895–2898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pellicer-Porres, J; Segura1, A.; Kim, D. Refractive index of the CuAlO2 delafossite. Semicond. Sci. Technol. 2009, 24, 015002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuboi, N.; Takahashi, Y.; Kobayashi, S.; Shimizu, H.; Kato, K.; Kaneko, F. Delafossite CuAlO2 films prepared by reactive sputtering using Cu and Al targets. J. Phys. Chem. Solids 2003, 64, 1671–1674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chavillon, B.; Cario, L.; Doussier-Brochard, C.; Srinivasan, R.; Le Pleux, L.; Pellegrin, Y.; Blart, E.; Odobel, F.; Jobic, S. Synthesis of light-coloured nanoparticles of wide band gap p-type semiconductors CuGaO2 and LaOCuS by low temperature hydro/solvothermal processes. Phys. Status Solidi. A 2010, 207, 1642–1646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ueda, K.; Hase, T.; Yanagi, H.; Kawazoe, H.; Hosono, H.; Ohta, H.; Orita, M.; Hirano, M. Epitaxial growth of transparent p-type conducting CuGaO2 thin films on sapphire (001) substrates by pulsed laser deposition. J. Appl. Phys. 2001, 89, 1790–1793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varandani, D.; Singh, B.; Mehta, B.R.; Singh, M.; Singh, V.N.; Gupta, D. Resistive switching mechanism in delafossite-transition metal oxide (CuInO2–CuO) bilayer structure. J. Appl. Phys. 2010, 107, 103703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, N.; Sleight, A.W.; Jayaraj, M.K.; Tate, J. Transparent p-type conducting CuScO2+x films. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2000, 77, 1325: 1–1325: 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yanagi, H.; Park, S.; Draeseke, A.D.; Keszler, D.A.; Tate, J. p-Type conductivity in transparent oxides and sulfide fluorides. J. Solid State Chem. 2003, 175, 34–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manoj, R.; Nisha, M.; Vanaja, K.A.; Jayaraj, M.K. Effect of oxygen intercalation on properties of sputtered CuYO2 for potential use as p-type transparent conducting films. Bull. Mater. Sci. 2008, 31, 49–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayaraj, M.K.; Draesekea, A.D.; Tatea, J.; Hoffmana, R.L. Wagera, J.F. Transparent p-n Heterojunction Thin Film Diodes. Mater. Res. Soc. Symp. P 2001, 666, F4.1.1–F4.1.9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isawa, K.; Yaegashi, Y.; Komatsu, M.; Nagano, M.; Sudo, S. Synthesis of delafossite-derived phases, RCuO2+δ with R = Y, La, Pr, Nd, Sm, and Eu, and observation of spin-gap-like behavior. Phys. Rev. B 1997, 56, 3457–3466. [Google Scholar]
- Isawa, K.; Yaegashi, Y.; Ogota, S.; Nagano, M.; Sudo, S. Thermoelectric power of delafossite-derived compounds, RCuO2+δ (R = Y, La, Pr, Nd, Sm, and Eu). Phys. Rev. B 1998, 57, 7950–7954. [Google Scholar]
- Attili, R.N.; Saxena, R.N.; Carbonari, A.W.; Filho, J.M. Delafossite oxides ABO2 (A = Ag, Cu; B = Al, Cr, Fe, In, Nd, Y) studied by perturbed-angular-correlation spectroscopy using a 111Ag(β-)111Cd probe. Phys. Rev. B 1998, 58, 2563–2569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okuda, T.; Beppu, Y.; Fujii, Y.; Onoe, T.; Terada, N.; Miyasaka, S. Specific heat of delafossite oxide CuCr1−xMgxO2 (0 ≤ x ≤ 0.03). Phys. Rev. B 2008, 77, 134423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shibasaki, S.; Kobayashi, W.; Terasaki, I. Transport properties of the delafossite Rh oxide Cu1−xAgxRh1−yMgyO2: Effect of Mg substitution on the resistivity and Hall coefficient. Phys. Rev. B 2006, 74, 235110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mugnier, E.; Barnabé, A.; Tailhades, P. Synthesis and characterization of CuFeO2+δ delafossite powders. Solid State Ionics 2006, 177, 607–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ueda, K.; Inoue, S.; Hirose, S.; Kawazoe, H.; Hosono, H. Transparent p-type semiconductor: LaCuOS layered oxysulfide. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2000, 77, 2701: 1–2701: 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wada, T.; Negami, T.; Nishitani, M. Preparation of CuInS2 films by sulfurization of CuInO films. Appl. Phys. Lett. 1993, 62, 1943: 1–1943: 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shannon, R.D.; Rogers, D.B.; Prewitt, C.T. Chemistry of noble metal oxides. I. Syntheses and properties of ABO2 delafossite compounds. Inorg. Chem. 1971, 10, 713–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheets, W.C.; Mugnier, E.; Barnabé, A.; Marks, T.J.; Poeppelmeier, K.R. Hydrothermal synthesis of delafossite-type oxides. Chem. Mater. 2006, 18, 7–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Li, D.; Z.; Zhu, X.; Dong, W.; Fang, X. Preparation of the delafossite structure p type transparent conducting oxide thin films by sol-gel process. Prog. Chem. 2009, 21, 128–133. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, M.; Mehta, B.R. Effect of structural anisotropy on electronic conduction in delafossite tin doped copper indium oxide thin films. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2008, 93, 192104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teplin, C.W.; Kaydanova, T.; Young, D.L.; Perkins, J.D.; Ginley, D.S.; Ode, A.; Readey, D.W. A simple method for the preparation of transparent p-type Ca-doped CuInO2 films: Pulsed-laser deposition from air-sintered Ca-doped Cu2In2O5 targets. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2004, 85, 3789–3791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yanagi, H.; Hase, T.; Ibuki, S.; Ueda, K.; Hosono, H. Bipolarity in electrical conduction of transparent oxide semiconductor CuInO2 with delafossite structure. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2001, 78, 1583: 1–1583: 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, X.; Wei, S.-H.; Zhang, S.B. Bipolar Doping and Band-Gap Anomalies in Delafossite Transparent Conductive Oxides. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2002, 88, 066405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yanagi, H.; Ueda, K.; Ohta, H.; Orita, M.; Hirano, M.; Hosono, H. Fabrication of all oxide transparent p–n homojunction using bipolar CuInO2 semiconducting oxide with delafossite structure. Solid State Commun. 2002, 121, 15–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benko, F.A.; Koffyberg, F.P. Opto-electronic properties of p- and n-type delafossite, CuFeO2. J. Phys. Chem. Solids 1987, 48, 431–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pellicer-Porres, J.; Segura1, A.; Gilliland, A.S.; Muñoz, A.; Rodríguez-Hernández, P.; Kim, D.; Lee, M.S.; Kim, T.Y. On the band gap of CuAlO2 delafossite. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2006, 88, 181904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buljan, A.; Alemany, P.; Ruiz, E. Electronic Structure and Bonding in CuMO2 (M = Al, Ga, Y) Delafossite-Type Oxides: An Ab Initio Study. J. Phys. Chem. B 1999, 103, 8060–8066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katayama-Yoshida, H.; Koyanagi, T.; Funashima, H.; Harima, H.; Yanase, A. Engineering of nested Fermi surface and transparent conducting p-type Delafossite CuAlO2: possible lattice instability or transparent superconductivity? Solid State Commun. 2003, 126, 135–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koyanagi, T.; Harima, H.; Yanase, A.; Katayama-yoshida, H. Materials design of p-type transparent conducting oxides of delafossite CuAlO2 by super-cell FLAPW method. J. Phys. Chem. Solids 2003, 64, 1443–1446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vidal, J.; Trani, F.; Bruneval, F.; Marques, M.A.L.; Botti, S. Effects of Electronic and Lattice Polarization on the Band Structure of Delafossite Transparent Conductive Oxides. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2010, 104, 136401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacob, A.; Parent, C.; Boutinaud, P.; Flem, G.L.; Doumerc, J.P.; Ammar, A.; Elazhari, M.; Elaatmani, M. Luminescent properties of delafossite-type oxides LaCuO2 and YCuO2. Solid State Commun. 1997, 103, 529–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagarajan, R.; Draeseke, A.D.; Sleight, A.W.; Tate, J. p-type conductivity in CuCr1−xMgxO2 films and powders. J. Appl. Phys. 2001, 89, 8022–8025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagarajan, R.; Duan, N.; Jayaraj, M.K.; Li, J.; Vanaja, K.A.; Yokochi, A.; Draeseke, A.; Tate, J.; Sleight, A.W. p-Type conductivity in the delafossite structure. Int. J. Inorg. Mater. 2001, 3, 265–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.S.; Kim, T.Y.; Kim, D. Anisotropic electrical conductivity of delafossite-type CuAlO2 laminar crystal. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2001, 79, 2028: 1–2028: 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marquardt, M.A.; Ashmore, N.A.; Cann, D.P. Crystal chemistry and electrical properties of the delafossite structure. Thin Solid Films 2006, 496, 146–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Sleight, A.W.; Jones, C.Y.; Toby, B.H. Trends in negative thermal expansion behavior for AMO2 (A = Cu or Ag; M = Al, Sc, In, or La) compounds with the delafossite structure. J. Solid State Chem. 2005, 178, 285–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dakhel, A.A. Influence of dysprosium doping on the electrical and optical properties of CdO thin films. Sol. Energy 2009, 83, 934–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coutts, T.J.; Young, D.L.; Li, X.; Mulligan, W.P.; Wu, X. Search for improved transparent conducting oxides: A fundamental investigation of CdO, Cd2SnO4, and Zn2SnO4. J. Vac. Sci. Technol. A 2000, 18, 2646–2660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dakhel, A.A. Influence of hydrogenation on the electrical and optical properties of CdO:Tl thin films. Thin Solid Films 2008, 517, 886–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Seo, J.; Jang, H.W.; Bang, J.; Lee, W.; Lee, T.; Myoung, J.-M. Effects of H2 ambient annealing in fully 0 0 2-textured ZnO: Ga thin films grown on glass substrates using RF magnetron co-sputter deposition. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2009, 255, 4616–4622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, J.; Kim, H.W.; Lee, C. Electrical resistivity and transmittance properties of Al and Ga-codoped ZnO thin films. J. Korean Phys. Soc. 2010, 56, 576–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hojo, M.; Okimura, K. Effect of Annealing with Ar Plasma Irradiation for Transparent Conductive Nb-Doped TiO2 Films on Glass Substrate. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 2009, 48, 08HK06: 1–08HK06: 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Brezesinski, T.; Antonietti, M.; Smarsly, B. Ordered mesoporous Sb-, Nb-, and Ta-doped SnO2 thin films with adjustable doping levels and high electrical conductivity. ACS Nano 2009, 3, 1373–1378. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, Y.C.; Wang, B.L.; Yen, W.T.; Ha, C.T.; Peng, C. Effect of process conditions on the optoelectronic characteristics of ZnO:Mo thin films prepared by pulsed direct current magnetron sputtering. Thin Solid Films 2010, 518, 4928–4934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prathap, P.; Devi, G.G.; Subbaiah, Y.P.V.; Ganesan, V.; Reddy, K.T.R.; Yi, J. Preparation and characterization of sprayed In2O3:Mo films. Phys. Status Solid. A 2008, 205, 1947–1951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cattin, L.; Morsli, M.; Dahou, F.; Abe, S.Y.; Khelil, A.; Bernède, J.C. Investigation of low resistance transparent MoO3/Ag/MoO3 multilayer and application as anode in organic solar cells. Thin Solid Films 2010, 518, 4560–4563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Li, H.; Ji, L.; Zhao, F.; Liu, X.; Kong, Q.; Wang, Y.; Quan, W.; Zhou, H.; Chen, J. The effect of duty cycle on the microstructure and properties of graphite-like amorphous carbon films prepared by unbalanced magnetron sputtering. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2010, 43, 505401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Fang, Q.; Wu, M.; Sun, X.; Lu, F. Low temperature synthesis wide optical band gap Al and (Al, Na) co-doped ZnO thin films. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2011, 257, 2341–2345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.R.S.; Malar, P.; Osipowicz, T.; Banerjee, S.S.; Kasiviswanathan, S. Ion beam studies on reactive DC sputtered manganese doped indium tin oxide thin films. Nucl. Instrum. Meth. Phys. Res. B 2008, 266, 1421–1424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gessert, T.; Yoshida, Y.; Fesenmaier, C.; Duenow, J.; Coutts, T. TCO thin films with permittivity control. Symposium on thin-film compound semiconductor photovoltaics. Mater. Res. Soc. 2009, 1165, 247–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Wang, X.; Shi, S.; Song, X.; Lv, J.; Cui, J.; Sun, Z. Optical and wetting properties of CuAlO2 films prepared by radio frequency magnetron sputtering. Proc. Asia Display 2007, 1799–1802. [Google Scholar]
- Giurgola, S.; Rodriguez, A.; Martinez, L.; Vergani, P.; Lucchi, F.; Benchabane, S.; Pruneri, V. Ultra thin nickel transparent electrodes. J. Mater. Sci. 2009, 20, S181–S184. [Google Scholar]
© 2012 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Stadler, A. Transparent Conducting Oxides—An Up-To-Date Overview. Materials 2012, 5, 661-683. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma5040661
Stadler A. Transparent Conducting Oxides—An Up-To-Date Overview. Materials. 2012; 5(4):661-683. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma5040661
Chicago/Turabian StyleStadler, Andreas. 2012. "Transparent Conducting Oxides—An Up-To-Date Overview" Materials 5, no. 4: 661-683. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma5040661
APA StyleStadler, A. (2012). Transparent Conducting Oxides—An Up-To-Date Overview. Materials, 5(4), 661-683. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma5040661




