Formation of Indium-Doped Zinc Oxide Thin Films Using Ultrasonic Spray Pyrolysis: The Importance of the Water Content in the Aerosol Solution and the Substrate Temperature for Enhancing Electrical Transport
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Details
2.1. Fabrication Of Indium Doped Zinc Oxide [ZnO:In] Thin Films
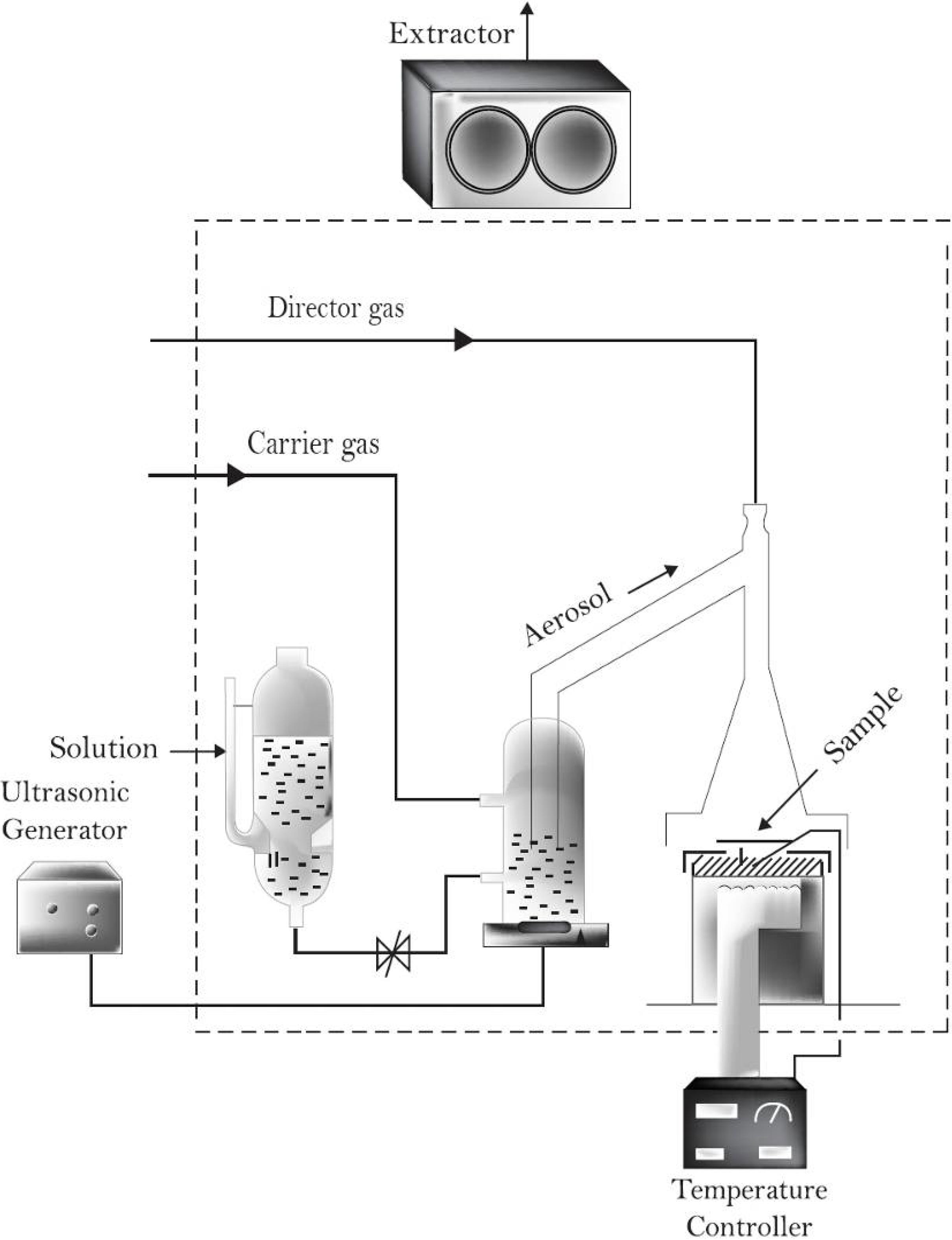
2.2. Indium-Doped Zinc Oxide Thin Solids Films Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Structural Properties

3.2. Scanning Electron Microscopy Studies

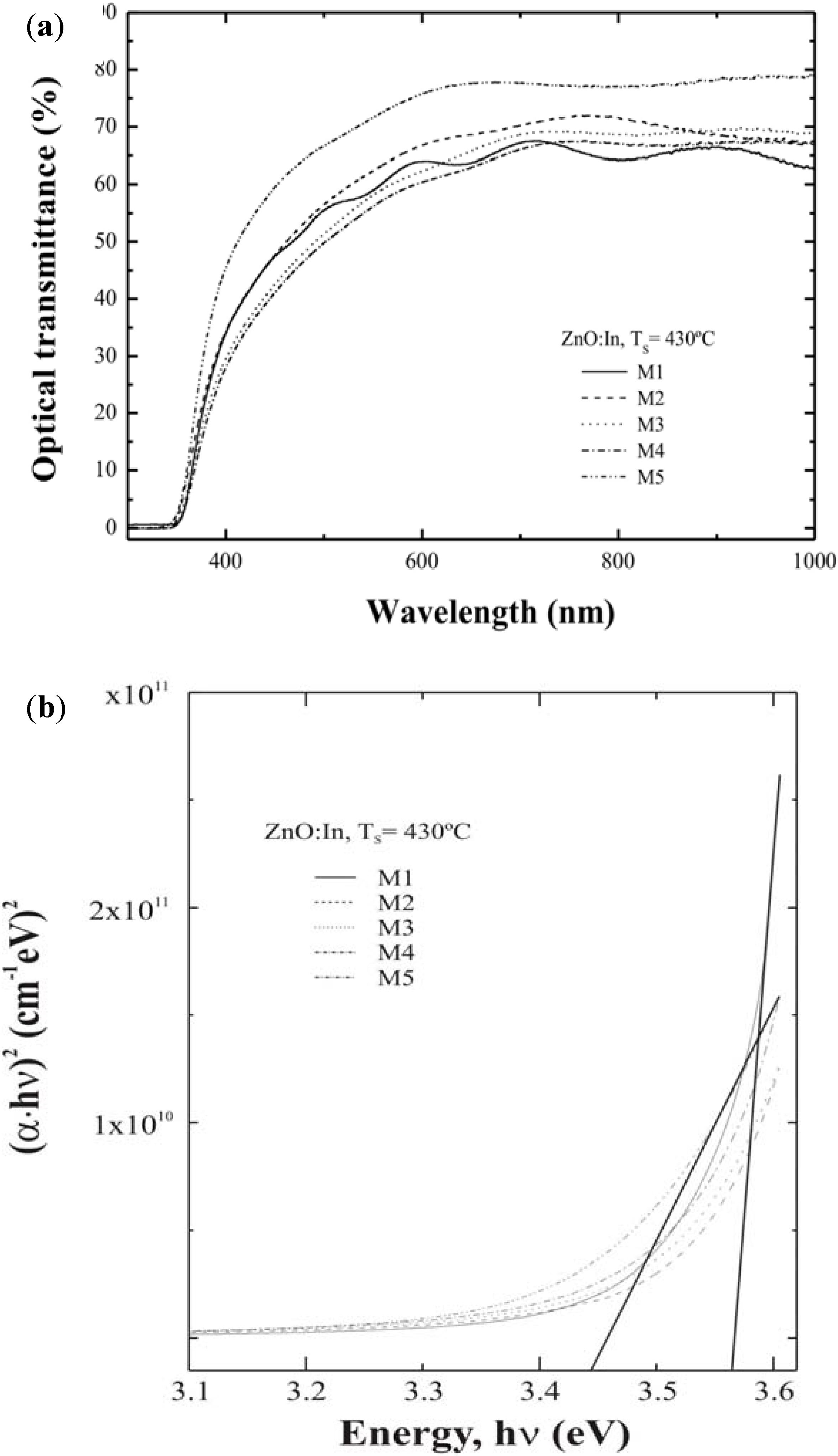
3.3. Optical Properties
3.4. Electrical Results
| ID Sample | VH2O /VTotal | Average thickness (nm) ±5.0% | Average transmittance (400–700 nm) (%) | Average transmittance (at 550 nm) (%) | Electrical Resistivity x10-3 ( Ωcm) ±5.0% | Band gap ( eV) ±5.0% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| M1 | 50/1000 | 673 | 56.87 | 58.97 | 1.54 | 3.56 |
| M2 | 100/1000 | 655 | 59.23 | 62.39 | 1.31 | 3.51 |
| M3 | 150/1000 | 680 | 55.08 | 58.19 | 1.90 | 3.49 |
| M4 | 200/1000 | 685 | 53.11 | 71.61 | 2.05 | 3.51 |
| M5 | 300/1000 | 435 | 69.05 | 79.61 | 10.17 | 3.44 |
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
References
- Granqvist, C.G. Transparent conductors as solar energy materials: A panoramic review. Mater. Sol. Cells 2007, 91, 1529–1598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beyer, W.; Hüpkes, J.; Stiebig, H. Transparent conducting oxide films for thin film silicon photovoltaics. Thin Solid Films 2007, 516, 147–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dastjerdi, R.; Montazer, M. Review: A review on the application of inorganic nano-structured materials in the modification of textiles: Focus on anti-microbial properties. Colloid. Surface. B 2010, 79, 5–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowen, A.; Li, J.; Lewis, J.; Sivaramakrishnan, K.; Alford, T.L.; Iyer, S. The properties of radio frequency sputtered transparent and conducting ZnO:F films on polyethylene naphthalate substrate. Thin Solid Films 2011, 519, 1809–1816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.J.; Lei, Q.S.; Xu, W.; Zhou, W.L. Preparation of ZnO:Al thin film on transparent TPT substrate at room temperature by RF magnetron sputtering technique. Mater. Lett. 2009, 63, 1371–1373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayakumar, O.D.; Tyagi, A.K. Effect of oxygen pressure on room-temperature ferromagnetism of Al co-doped Mn doped ZnO thin films prepared by pulsed laser deposition. Int. J. Nanotechnol. 2011, 7, 1047–1053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Xu, L.; Li, X.; Shen, X.; Wang, A. Effect of aging time of ZnO sol on the structural and optical properties of ZnO thin films prepared by sol-gel method. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2010, 256, 4543–4547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hornok, V.; Pal, E.; Oszko, A.; Dekany, I. Hydrothermal synthesis of prism-like and flower-like ZnO and indium-doped ZnO structures. Colloid. Surf. A 2009, 340, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Nolan, M.G.; Hamilton, J.A.; O’Brien, S.; Bruno, G.; Pereira, L.; Fortunato, E.; Martins, R.; Povey, I.M.; Pemble, M.E. The characterisation of aerosol assisted CVD conducting, photocatalytic indium doped zinc oxide films. J. Photochem. Photobiol. A Chem. 2011, 219, 10–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, X.J.; Jan, S.H.; Zhao, Z.L.; Suo, H.T.; Song, S.T. Fabrication of transparent conductive al-doped zno thin films by aerosol-assisted chemical vapour deposition. Inorg. Mater. 2011, 26, 607–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chamberlin, R.R.; Skarman, J.S. Chemical spray deposition process for inorganic films. J. Electrochem. Soc. 1966, 113, 86–89. [Google Scholar]
- Patil, P.S. Review versatility of chemical spray pyrolysis technique. Mater. Chem. Phys. 1999, 59, 185–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chopra, K.L.; Major, S.; Pandya, D.K. Transparent conductors, a status review. Thin solid Films 1983, 102, 1–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romero, R.; Leinen, D.; Dalchiele, E.A.; Ramos-Barrado, J.R.; Martín, F. The effects of zinc acetate and zinc chloride precursors on the preferred crystalline orientation of ZnO and Al-doped ZnO thin films obtained by spray pyrolysis. Thin Solid Films 2006, 515, 1942–1949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vimalkumar, T.V.; Poornima, N.; Sudha, K.C.; Vijayakumar, K.P. On tuning the orientation of grains of spray pyrolysed ZnO thin films. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2010, 256, 6025–6028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Josepha, B.; Gopchandrana, K.G.; Thomasa, P.V.; Koshyb, P.; Vaidyan, V.K. A study on the chemical spray deposition of zinc oxide thin films and their structural and electrical properties. Mater. Chem. Phys. 1999, 58, 71–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krunks, M.; Karber, E.; Katerski, A.; Otto, K.; Oja, A.I.; Dedova, T.; Mere, A. Solar Extremely thin absorber layer solar cells on zinc oxide nanorods by chemical spray. Sol. Energ. Mat. Sol. C. 2010, 94, 1191–1195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaier, A.; Oum, E.F.; Lakfif, F.; Kabir, A.; Boudjadar, S.; Aida, M.S. Review effects of the substrate temperature and solution molarity on the structural opto-electric properties of ZnO thin films deposited by spray pyrolysis. Mater. Sci. Semicond. Process. 2009, 12, 207–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castañeda, L.; Garcia-Valenzuela, A.; Zironi, E.P.; Cañetas-Ortega, J.; Terrones, M.; Maldonado, A. Formation of indium-doped zinc oxide thin films using chemical spray techniques: The importance of acetic acid content in the aerosol solution and the substrate temperature for enhancing electrical transport. Thin Solid Films 2006, 503, 212–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castañeda, L.; Morales-Saavedra, O.G.; Acosta, D.R.; Maldonado, A.; Olvera, M.L. Structural, morphological, optical, and nonlinear optical properties of fluorine-doped zinc oxide thin films deposited on glass substrates by the chemical spray technique. Phys. Status Solidi A 2006, 203, 1971–1981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castañeda, L.; Morales-Saavedra, O.G.; Cheang-Wong, J.C.; Acosta, D.R.; Bañuelos, J.G.; Maldonado, A.; Olvera, M.L. Influence of indium concentration and substrate temperature on the physical characteristics of chemically sprayed ZnO:In thin films deposited from zinc pentanedionate and indium sulfate. J. Phys.Condens. Matter. 2006, 18, 5105–5120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castañeda, L.; Maldonado, A.; Cheang-Wong, J.C.; Rodríguez-Baez, J.; López-Fuentes, M.; Olvera, M.L. Formation of fluorine-doped zinc oxide thin films using chemical spray techniques: Effect of acetic acid content in the aerosol solution on the physical properties. Mater. Sci. Semicond. Process. 2012, in press. [Google Scholar]
- Castañeda, L.; Maldonado, A.; Escobedo-Morales, A.; Avendaño-Alejo, M.; Gómez, H.; Vega-Pérez, J.; Olvera, M.L. Indium doped zinc oxide thin films deposited by ultrasonic spray pyrolysis technique: Effect of the substrate temperature on the physical properties. Mater. Sci. Semicond. Process. 2011, 14, 114–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castañeda, L.; Avendaño-Alejo, M.; Márquez-Beltrán, C.; Maldonado, A. Physical properties of titanium-doped zinc oxide thin solid films grown by sol-gel method. Int. J. Mater. Eng. Technol. 2010, 4, 147–159. [Google Scholar]
- Castañeda, L.; Silva-González, R.; Gracia-Jiménez, J.M.; Hernández-Torres, M.E.; Avendaño-Alejo, M.; Márquez-Beltrán, C.; Olvera, M.L.; Vega-Pérez, J.; Maldonado, A. Influence of aluminum concentration and substrate temperature on the physical characteristics of chemically sprayed ZnO:Al thin solid films deposited from zinc pentanedionate and aluminum pentanedionate. Mater. Sci. Semicond. Process. 2010, 13, 80–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castañeda, L. Influence of colloidal silver nanoparticles on the novel flower-like titanium dioxide oxygen sensor. Sensor. Mater. 2009, 21, 25–36. [Google Scholar]
- Castañeda, L.; Maldonado, A.; Olvera, M.L. Sensing properties of chemically sprayed TiO2 thin films using Ni, Ir, and Rh as catalysts. Senser. Actuator. B Chem. 2008, 133, 687–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castañeda, L. Effects of palladium coatings on oxygen sensors of titanium dioxide thin films. Mater. Sci. Eng. B 2007, 139, 149–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castañeda, L. Present status of the development and application of transparent conductors oxide thin solid films. Mater. Sci. Appl. 2011, 2, 1233–1242. [Google Scholar]
- Smith, A.; Rodriguez-Clemente, R. Morphological differences in ZnO films deposited by the pyrosol technique: Effect of HCl. Thin Solid Films 1999, 345, 192–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warren, B.E. X-ray Diffraction; Dover: New York, NY, USA, 1990; p. 253. [Google Scholar]
© 2012 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Biswal, R.; Castañeda, L.; Moctezuma, R.; Vega-Pérez, J.; Olvera, M.D.L.L.; Maldonado, A. Formation of Indium-Doped Zinc Oxide Thin Films Using Ultrasonic Spray Pyrolysis: The Importance of the Water Content in the Aerosol Solution and the Substrate Temperature for Enhancing Electrical Transport. Materials 2012, 5, 432-442. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma5030432
Biswal R, Castañeda L, Moctezuma R, Vega-Pérez J, Olvera MDLL, Maldonado A. Formation of Indium-Doped Zinc Oxide Thin Films Using Ultrasonic Spray Pyrolysis: The Importance of the Water Content in the Aerosol Solution and the Substrate Temperature for Enhancing Electrical Transport. Materials. 2012; 5(3):432-442. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma5030432
Chicago/Turabian StyleBiswal, Rajesh, Luis Castañeda, Rosario Moctezuma, Jaime Vega-Pérez, María De La Luz Olvera, and Arturo Maldonado. 2012. "Formation of Indium-Doped Zinc Oxide Thin Films Using Ultrasonic Spray Pyrolysis: The Importance of the Water Content in the Aerosol Solution and the Substrate Temperature for Enhancing Electrical Transport" Materials 5, no. 3: 432-442. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma5030432
APA StyleBiswal, R., Castañeda, L., Moctezuma, R., Vega-Pérez, J., Olvera, M. D. L. L., & Maldonado, A. (2012). Formation of Indium-Doped Zinc Oxide Thin Films Using Ultrasonic Spray Pyrolysis: The Importance of the Water Content in the Aerosol Solution and the Substrate Temperature for Enhancing Electrical Transport. Materials, 5(3), 432-442. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma5030432




