Impact of Liquid Crystals in Active and Adaptive Optics
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Liquid Crystals in Optics
3. Spatial Light Modulators, Active and Adaptive Optics
3.1. Active and Adaptive Optics
3.2. Low Cost Active and Adaptive Optics
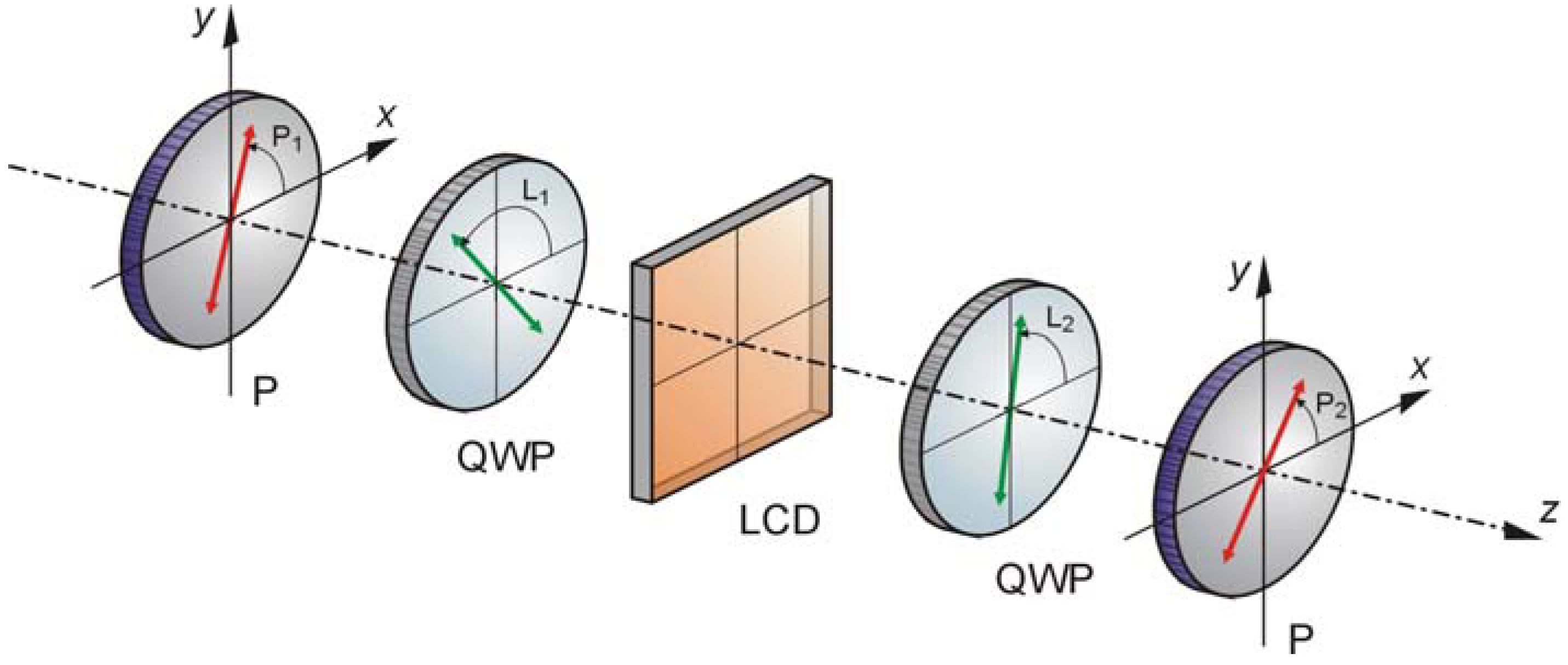
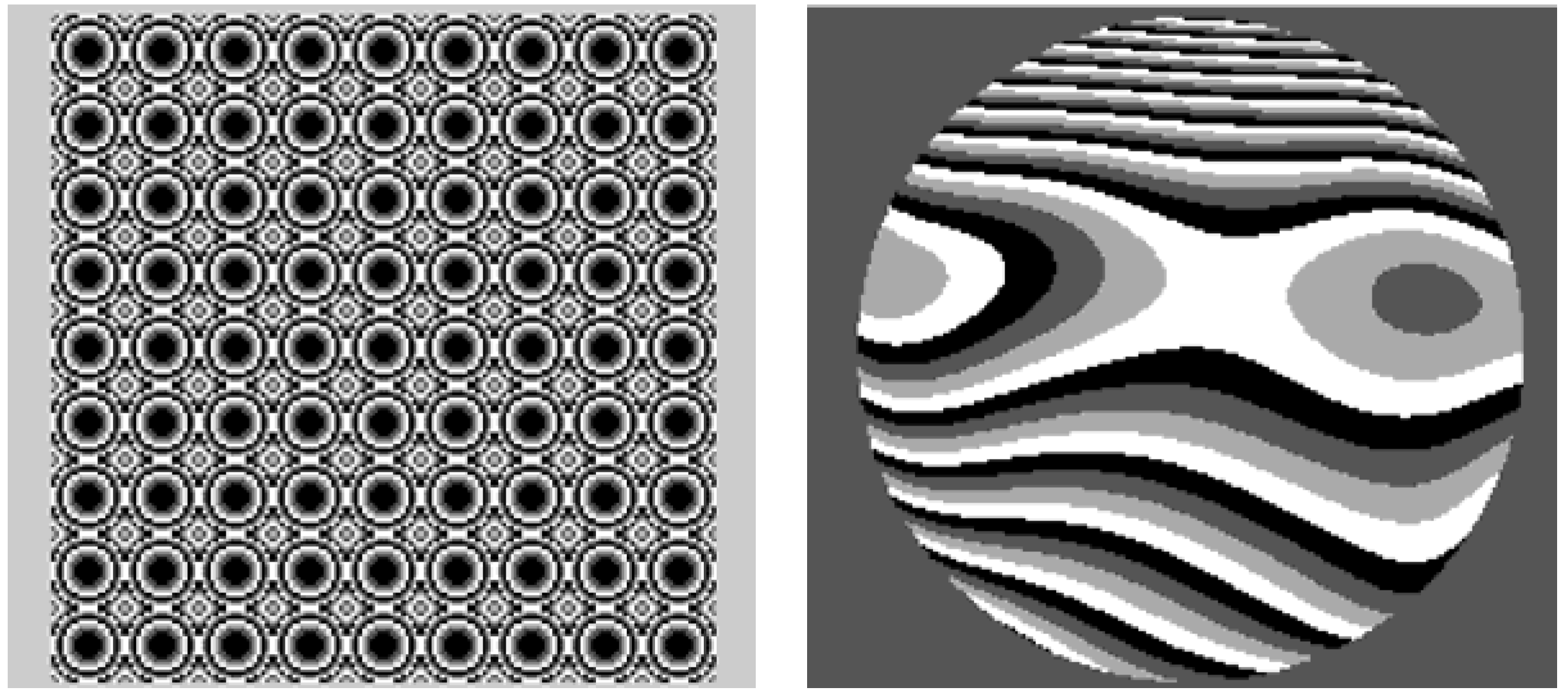

4. Final Remarks
Acknowledgements
References and Notes
- Collins, P.J.; Hird, M. Introduction to liquid crystals: Chemistry and Physics, 3rd Ed. ed; Taylor & Francis: London, UK, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Dunmur, D.; Fukuda, A.; Luckhurst, G. Physical properties of liquid crystals: nematics; INSPEC: London, UK, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Gennes, P.G.; Prost, J. The physics of liquid crystals, 2nd Ed. ed; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Chandrasekhar, S. Liquid Crystals, 2nd Ed. ed; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Khoo, I.C. Liquid Crystals: Physical properties and Nonlinear Optical Phenomena; Wiley-VCH: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1994; ISBN 0471303623. [Google Scholar]
- Figueiredo, M.; Azevedo, S.R. The physics of lyotropic liquid crystals: phase transitions and structural properties; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2005; ISBN ISBN 0198525508. [Google Scholar]
- Born, M.; Wolf, E. Principles of Optics, 6th Ed. ed; Pergamon: Oxford, UK, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Brown, G.H. Structure, properties, and some applications of liquid crystals. J. Opt. Soc. Am. 1973, 63, 1505–1514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, M.; Harrison, K.; Raynes, E. Liquid crystal materials and devices. Phys. Technol. 1980, 11, 232–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madhusudana, N. Recent advances in thermotropic liquid crystals. Curr. Sci. 2001, 80, 1018–1025. [Google Scholar]
- Love, G.; Bhandarib, R. Optical properties of a QHQ ferroelectric liquid crystal phase modulator. Opt. Commun. 1994, 110, 475–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishina, E.D.; Sherstyuk, N.E.; Stadnichuk, V.I.; Sigov, A.S.; Mukhorotov, M.; Golovko, Y.I.; van Etteger, A.; Rasing, T. Nonlinear-optical probing of nanosecond ferroelectric switching. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2003, 83, 2402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertolotti, M.; Ferrari, A.; Sibilia, C.; Alippi, A.; Nesrullajev, A.N. Optical nonlinearities in a lyotropic liquid crystal. Opt. Lett. 1987, 12, 419–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alves, S.; Cuppo, F.L.; Figueiredo, A.M. Determination of the nonlinear refractive index of lyotropic mixtures with and without ferrofluid doping: a time-resolved Z-scan experiment in millisecond time scales. J. Opt. Soc. Am. B 2006, 23, 67–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, L.J.; Saupe, A. Observation of a Biaxial Nematic Phase in Potassium Laurate-1-Decanol-Water Mixtures. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1980, 45, 1000–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartolino, R.; Chiaranza, T.; Meuti, M. Uniaxial and biaxial lyotropic nematic liquid crystals. Phys. Rev. A 1982, 26, 1116–1119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galerne, Y.; Figueiredo, A.M.; Liebert, L. Optical birefringence and temperature range of the biaxial nematic phase in a lyotropic liquid cristal. J. Chem. Phys. 1986, 84, 1732–1734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nastishin, Y.A.; Liu, H.; Schneider, T.; Nazarenko, V.; Vasyuta, R.; Shiyanovskii, S.V.; Lavrentovich, O.D. Optical characterization of the nematic lyotropic chromonic liquid crystals: Light absorption, birefringence, and scalar order parameter. Phys. Rev. E 2005, 72, 041711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boiko, O.P.; Vasyuta, R.M.; Nazarenko, V.G.; Pergamenshchik, V.M.; Nastishin, Y.A.; Lavrentovich, O.D. Polarizing properties of functional optical films based on lyotropic chromonic liquid crystals. Mol. Cryst. Liq. Cryst. 2007, 467, 181–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, H.S.; Tortora, L.; Vasyuta, R.M.; Golovin, A.B.; Augustin, E.; Finotello, D.; Lavrentovich, O.D. Lyotropic Chromonic Liquid Crystals: Effects of Additives and Optical Applications. IMID '07 Techical Digest 2007, 307–310. [Google Scholar]
- Taylor, T.R.; Fergason, J.L.; Arora, S.L. Biaxial liquid crystals. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1970, 24, 359–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luckhurst, G.R. Biaxial nematic liquid crystals: fact or fiction? Thin Solid Films 2001, 393, 40–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madsen, L.A.; Dingemans, T.J.; Nakata, M.; Samulski, E.T. Thermotropic biaxial nematic liquid crystals. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2004, 92, 145505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dingemans, T.J.; Madsen, L.A.; Zafiropoulos, N.A.; Lin, W.; Samulski, E.T. Uniaxial and biaxial nematic liquid crystals. Phil. Trans. R. Soc. A 2006, 364, 2681–2696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Severing, K.; Saalwachter, K. Biaxial nematic phase in a thermotropic liquid-crystalline side-chain polymer. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2004, 92, 125501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Acharya, B.R.; Primak, A.; Kumar, S. Biaxial nematic phase in bent-core thermotropic mesogens. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2004, 92, 145506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berardi, R.; Muccioli, L.; Zannoni, C. Field response and switching times in biaxial nematics. J. Chem. Phys. 2008, 128, 024905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, C.; Yeh, P. Extended Jones matrix method and its application in the analysis of compensators for liquid crystal displays. Displays 1999, 20, 237–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khoo, I.C. Nonlinear optics of liquid crystalline materials. Phys. Rep. 2009, 471, 221–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pishnyak, O.P.; Lavrentovich, O.D. Electrically controlled negative refraction in a nematic liquid cristal. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2006, 89, 251103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.H.; Lim, T.K.; Kim, W.T.; Jin, J.I. Dynamics of electro-optical switching processes in surface stabilized biaxial nematic phase found in bent-core liquid crystal. J. Appl. Phys. 2007, 101, 034105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobs, D.S. Selected Papers on Liquid Crystals for Optics; SPIE Press: Bellingham, WA, USA, 1992; Volume MS46. [Google Scholar]
- Zhuang, Z.; Suh, S.; Patel, J.S. Polarization controller using nematic liquid crystals. Opt. Lett. 1999, 24, 694–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bueno, J.M. Polarimetry using liquid-crystal variable retarders: theory and calibration. J. Opt. A Pure Appl. Opt. 2000, 2, 216–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calvez, L.A.; Montant, S.; Freysz, E.; Ducasse, A.; Zhuang, X.W.; Shen, Y.R. Ultrashort orientational dynamics of liquid crystals in the smectic-A phase. Chem. Phys. Lett. 1996, 258, 620–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meadowlark Optics. Swift Liquid Crystal Variable Retarders. Meadowlark Optics: Frederick, CO, USA, 2008; pp. 48–50. Available online: http://www.lamdapacific.com/Webupdate/upload/2009424182642734.pdf accessed May 8, 2009.
- Chen, X.Y.; Li, H.; Qiu, Y.S.; Wang, Y.F.; Ni, B. Tunable Photonic Crystal Mach–Zehnder Interferometer Based on Self-collimation Effect. Chinese Phys. Lett. 2008, 25, 4307–4310. [Google Scholar]
- Brzd, K.A.; Karpierz, M.A.; Fratalocchi, A.; Assanto, G.; Nowinowski-Kruszelnicki, E. Nematic liquid crystal waveguide arrays. Opto-Electron. Rev. 2005, 13, 107–112. [Google Scholar]
- Peccianti, M.; Assanto, G. Signal readressing by steering of spatial solitons in bulk nematic liquid crystals. Opt. Lett. 2001, 26, 1690–1692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sirleto, L.; Coppola, G.; Breglio, G. Optical multimode interference router based on a liquid crystal waveguide. J. Opt. A Pure Appl. Opt. 2003, 5, S298–S304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beeckman, J.; Neyts, K.; Haelterman, M. Patterned electrode steering of nematicons. J. Opt. A: Pure Appl. Opt. 2006, 8, 214–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fratalocchi, A.; Asquini, R.; Assanto, G. Integrated electro-optic switch in liquid crystals. Opt. Expr. 2005, 13, 32–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fratalocchi, A.; Assanto, G.; Brzdakiewicz, K.A.; Karpierz, M.A. Discrete propagation and spatial solitons in nematic liquid crystals. Opt.Lett. 2004, 29, 1530–1532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fratalocchi, A.; Assanto, G.; Brzdakiewicz, K.A.; Karpierz, M.A. Optical multiband vector breathers in tunable waveguide arrays. Opt. Lett. 2005, 30, 174–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fratalocchi, A.; Assanto, G. All-optical switching in a liquid crystalline waveguide. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2005, 86, 051109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fratalocchi, A.; Assanto, G.; Brzdkiewicz, K.A.; Karpierz, M.A. All-optical switching and beam steering in tunable waveguide arrays. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2005, 86, 051112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McPhail, D.; Min, G. Use of polarization sensitivity for three-dimensional optical data storage in polymer dispersed liquid crystals under two-photon illumination. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2002, 81, 1160–1162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Mukohzaka, N.; Yoshida, N.; Igasaki, Y.; Toyoda, H.; Inoue, T.; Kobayashi, Y.; Hara, T. Phase modulation characteristics analysis of optically-addressed parallel-aligned nematic liquid crystal phase-only spatial light modulator combined with a liquid crystal display. Opt. Rev. 1998, 5, 174–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayashi, T.; Shibata, T.; Kawashima, T.; Makino, E.; Mineta, T.; Masuzawa, T. Photolithography system with liquid crystal display as active gray-tone mask for 3D structuring of photoresist. Sens. Actuat. A: Phys. 2008, 144, 381–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hands, P.J.W.; Tatarkova, S.A.; Kirby, A.K.; Love, G. Modal liquid crystal devices in optical tweezing: 3D control and oscillating potential wells. Opt. Expr. 2006, 14, 4525–4537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Żmija, J.; Kłosowicz, S.J.; Kędzierski, J.; Nowinowskt-Kruszelnicki, E.; Zieliński, J.; Raszewski, Z.; Walczak, A.; Parka, J. Application of liquid crystals in optical processing of optical signals. Opto-Electron. Rev. 1997, 5, 93–106. [Google Scholar]
- Ibáñez-López, C.; Muñoz-Escrivá, L.; Saavedra, G.; Martínez-Corral, M. Manufacture of pupil filters for 3D beam shaping. Opt. Commun. 2007, 272, 197–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roggemann, M.C.; Welsh, B.M. Imaging Through Turbulence; CRC: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Hardy, J.W. Active optics: A new technology for the control of light. Proc. IEEE 1978, 66, 651–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roddier, F. Adaptive Optics in Astronomy; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Dayton, D.C.; Browne, S.L.; Sandven, S.P.; Gonglewski, J.D.; Kudryashov, A.V. Theory and laboratory demonstrations on the use of a nematic liquid-crystal phase modulator for controlled turbulence generation and adaptive optics. Appl. Opt. 1998, 37, 5579–5589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonaccini, D.; Brusa, G.; Esposito, S.; Salinari, P.; Stefanini, P.; Biliotti, V. Adaptive optics wave front corrector using addressable liquid crystal retarders II. Proc. SPIE 1991, 1543, 133–143. [Google Scholar]
- Vasiliev, A.A.; Kompanets, I.N.; Parfenov, A.V. Progress in the development and applications of optically controlled liquid crystal spatial light modulators. Sov. J. Quantum Electron. 1983, 13, 689–695. [Google Scholar]
- Amako, J.; Miura, H.; Sonehara, T. Wave-front control using liquid-crystal devices. Appl. Opt. 1993, 32, 4323–4329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bold, G.; Barnes, T.; Gourlay, J.; Sharples, R.; Haskell, T. Practical issues for the use of liquid crystal spatial light modulators in adaptive optics. Opt. Commun. 1998, 148, 323–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Hirayama, T.; Ishizuka, K.; Tonomura, A. Spherical aberration correction using a liquid-crystal spatial-light modulator in off-axis electron holography. App. Opt. 1994, 33, 6597–6602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dale, S.; Love, G.; Myers, R.; Naumov, A. Wavefront correction using a self-referencing phase conjugation system based on a Zernike cell. Opt. Commun. 2001, 191, 31–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dou, R.; Giles, M.K. Closed-loop adaptive-optics system with a liquid-crystal television as a phase retarder. Opt. Lett. 1995, 20, 1583–1585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Love, G.D.; Fender, J.S.; Restaino, S.R. Adaptive wavefront shaping with liquid crystals. Opt. Photon. News 1995, 6, 16–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Love, G.D. Wavefront control using a high quality nematic liquid crystal spatial light modulator. In Proceedings of Society of Photo-optical Instrumentation Engineers - Advanced imaging technologies and commercial applications, San Diego, CA, USA, July 10-12, 1995.
- Mu, Q.; Cao, Z.; Li, D.; Hu, L.; Xuan, L. Open-loop correction of horizontal turbulence: system design and result. Appl. Opt. 2008, 47, 4297–4301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dou, R.; Giles, M.K. Closed-loop adaptive-optics system with a liquid-crystal television as a phase retarder. Opt. Lett. 1995, 20, 1583–1585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liesener, J.; Reicherter, M.; Tiziani, H. Determination and compensation of aberrations using SLMs. Opt. Commun. 2004, 233, 161–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Love, G. Liquid-crystal phase modulator for unpolarized light. Appl. Opt. 1993, 32, 2222–2223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kelly, T.; Love, G. White-light performance of a polarization-independent liquid-crystal phase modulator. Appl. Opt. 1999, 38(10), 1986–1989. [Google Scholar]
- Kirby, A.; Love, G. Fast, large and controllable phase modulation using dual frequency liquid crystals. Opt. Expr. 2004, 12, 1470–1475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riza, N.; Jorgesen, D. Minimally invasive optical beam profiler. Opt. Expr. 2004, 12, 1892–1901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manzanera, S.; Prieto, P.M.; Ayala, D.B.; Lindacher, J.M.; Artal, P. Liquid crystal adaptive optics visual simulator: Application to testing and design of ophthalmic optical elements. Opt. Expr. 2007, 15, 16177–16188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quan, W.; Wang, Z.Q.; Mu, G.; Ning, L. Correction of the aberrations in the human eyes with SVAG1 thin-film transistor liquid-crystal display. OPTIK 2003, 114, 467–471. [Google Scholar]
- Simonov, A.N.; Vdovin, G.; Loktev, M. Liquid-crystal intraocular adaptive lens with wireless control. Opt. Expr. 2007, 15, 7468–7478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awwal, A.; Bauman, B.; Gavel, D.; Olivier, S.; Jones, S.; Silva, D.; Hardy, J.; Barnes, T.; Werner, J.; Tyson, R.; Lloyd-Hart, M. Characterization and operation of a liquid crystal adaptive optics phoropter. Proc. SPIE 2003, 5169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwasaki, T.; Kubota, T.; Tawara, A. The tolerance range of binocular disparity on a 3D display based on the physiological characteristics of ocular accommodation. Displays 2009, 30, 44–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, Q.; Cao, Z.; Li, D.; Hu, L.; Xuan, L. Liquid Crystal based adaptive optics system to compensate both low and high order aberrations in a model eye. Opt. Expr. 2007, 15, 1946–1953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naumov, A.; Yu, M.; Loktev, I.; Guralnik, R.; Vdovin, G. Liquid-crystal adaptive lenses with modal control. Opt. Lett. 1998, 23, 992–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Durán, V.; Climent, V.; Tajahuerce, E.; Jaroszewicz, Z.; Arines, J.; Bará, S. Efficient compensation of Zernike modes and eye aberration patterns using low-cost spatial light modulators. J. Biomed. Opt. 2007, 12, 014037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arines, J.; Durán, V.; Jaroszewicz, Z.; Ares, J.; Tajahuerce, E.; Prado, P.; Lancis, J.; Bará, S.; Climent, V. Measurement and compensation of optical aberrations using a single spatial light modulator. Opt. Expr. 2007, 15, 15287–15292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shirai, T. Liquid-Crystal Adaptive Optics Based on Feedback Interferometry for High-Resolution Retinal Imaging. Appl. Opt. 2002, 41, 4013–4023. [Google Scholar]
- Kitaguchi, Y.; Bessho, K.; Yamaguchi, T.; Nakazawa, N.; Mihashi, T.; Fujikado, T. In vivo measurements of cone photoreceptor spacing in myopic eyes from images obtained by an adaptive optics fundus camera. Jpn. J. Opht. 2007, 51, 456–461. [Google Scholar]
- Pal, D.; Misra, P.; Misra, A.K.; Manohar, R.; Shukla, J.P. Effect of dichroic dye on dielectric and optical properties of a nematic liquid crystal. Res. J. Phys. 2007, 1, 10–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teng, W.; Jeng, S.; Kuo, C.; Lin, Y.; Liao, C.; Chin, W. Nanoparticles-doped guest-host liquid crystal displays. Opt. Lett. 2008, 33, 1663–1665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2009 by the authors; licensee Molecular Diversity Preservation International, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open-access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Arines, J. Impact of Liquid Crystals in Active and Adaptive Optics. Materials 2009, 2, 549-561. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma2020549
Arines J. Impact of Liquid Crystals in Active and Adaptive Optics. Materials. 2009; 2(2):549-561. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma2020549
Chicago/Turabian StyleArines, Justo. 2009. "Impact of Liquid Crystals in Active and Adaptive Optics" Materials 2, no. 2: 549-561. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma2020549
APA StyleArines, J. (2009). Impact of Liquid Crystals in Active and Adaptive Optics. Materials, 2(2), 549-561. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma2020549




