Polymers Comprising Cholesterol: Synthesis, Self-Assembly, and Applications
Abstract
:1. Introduction
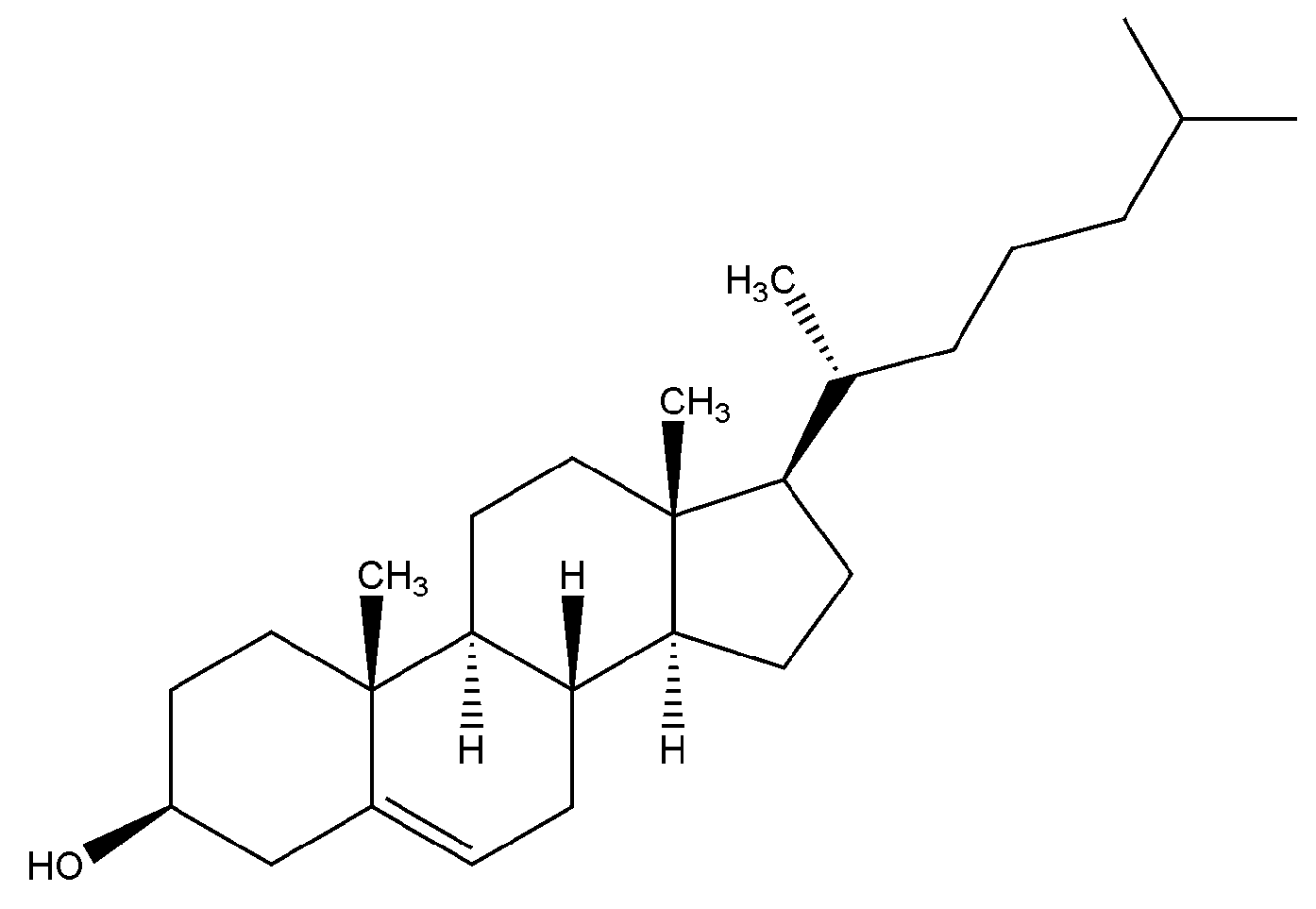
2. Synthesis of Polymers Bearing Cholesterol
2.1. Main-chain polymers

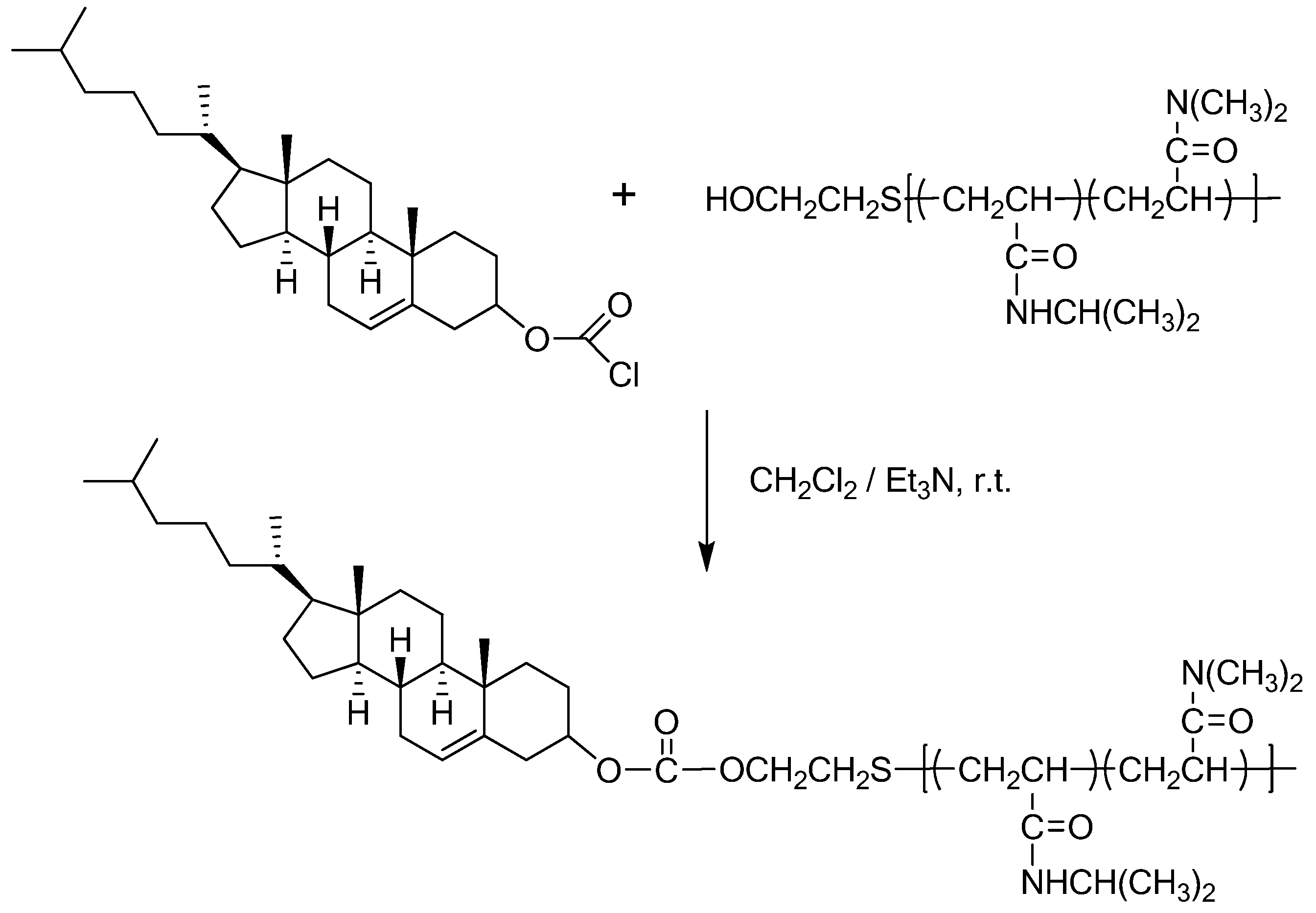
| Abbreviation | Polymer | Synthesis method | Self-assembly | Application | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chol-PAMPS | Poly(2-(acrylamido)-2-methylpropanesulfonic acid) sodium salt end-capped with cholesterol | Free radical polymerization through initiator containing cholesterol moiety | Core-shell structured micelle / intermolecularly bridged “flower-type” micelles | Not Available | [12] |
| Chol-P(NIPAAm-co-DMAAm) | Cholesteryl end-capped poly(N-isopropylacrylamide-co-N,N-dimethylacrylamide) | Esterification of hydroxyl end-group of precursor polymer and cholesteryl chloroformate | Spherical, star-like, cuboid-like micelles | Temperature-sensitive drug delivery system (DDS) | [13,26] |
| Chol-MPC | poly[2-(methacryloyl-oxy)ethyl phosphoryl-choline] with cholesterol end-group | ATRP through macroinitiator containing cholesterol moiety | Spherical micelles | DDS carriers | [15,16] |
| Chol-PEG | Cholesterol terminated poly(ethylene glycol) | Commercially available | Core-shell micelles | DDS carriers | [17] |
| MeO-PEG-Chol | Methoxy poly(ethylene glycol)-cholesterol | Ester coupling reaction of cholesterol with end-groups of precursor polymer | Spherical micelles | DDS carriers | [18] |
| Chol-(L-Lactic acid)n | Cholesteryl end-capped oligo(L-lactic acid) | ROP initiated by the aluminum alkoxide generated in situ from triethylamine and Cholesterol | Smectic LC phase in neat state | Tissue engineering scaffolds | [23,24] |
| Chol-PDTC | Cholesteryl end-capped poly( 2,2-dimethyl-trimethylene carbonate) | ROP initiated by hydroxyl group in cholesterol | LC in neat state | DDS carriers | [25] |
| Chol-PTMC | Cholesteryl end-capped poly(trimethylene carbonate) | ROP initiated by hydroxyl group in cholesterol | LC in neat state | DDS carriers | [20] |
| Chol-(CL)n | Cholesterol end-capped poly(ε-caprolactone) | ROP initiated by hydroxyl group in cholesterol | LC in neat state | DDS carriers | [21] |
| Chol-(LG)m+n | Cholesterol end-capped poly(lactide-co-glycolide) | ROP initiated by hydroxyl group in cholesterol | LC in neat state | DDS carriers | [19] |
| Chol-PI | Cholesterol end-capped polyisoprene | Coupling of amine end-group of precursor polymer and 2-cholesteryl-2-oxo-1,3,2-dioxa-phospholane | Self-associated in cyclohexane | Not available | [22] |
2.2. Polymers bearing cholesterol side-chains



| Homopolymers | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Abbreviation | Polymer | Synthesis method | LC observed | Application | Reference |
| PMHS-Chol | Poly (methylhydro-siloxane) with cholesterol side-chain | Graft polymerization | Chiral smectic | N/A | [39,41] |
| PNB-Chol-n | Polynorbornene bearing cholesterol with varying spacers | ROMP | Smectic | N/A | [45] |
| PA-Chol-n | Polyacrylate bearing cholesterol with varying spacer | Radical/photo polymerization | Cholesteric | N/A | [28,46] |
| PMA-Chol-n | Polymethacrylate bearing cholesterol with varying spacer | Radical polymerization | Smectic | N/A | [32,33] |
| Block Copolymers | |||||
| PMMA-Chol-b-PS | Poly(methylmethacrylate cholesterol-b-styrene) | ATRP | Smectic | N/A | [47] |
| PCholMA-b-PHEMA | Poly(cholesteryl methacrylate-b-2-hydroxyethyl methacrylate) | RAFT | N/A | N/A | [44] |
| Polymer (Backbone + Cholesterol) | Comonomer | Synthesis method | LC observed | Application | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Poly cholesteryl oleyl carbonate | Nonmesogenic spironaphthoxazine derivatives | Free radical - AIBN | Smectic / cholesteric | Photochromics such as data storage and display devices | [48] |
| Poly methyl-hydrosiloxane with cholesterol side-chain | Nonmesogenic chiral menthol side-chain | Graft polymerization | Cholesteric | N/A | [41] |
| Poly methyl-hydrosiloxane with cholesterol side-chain | Nematic benzoate side-chain | Graft polymerization | Cholesteric / blue phases | Optical storage, pyroelectric devices | [39] |
| Poly methylhydro-siloxane with cholesterol side-chain | Flexible cross-linking agents | Graft polymerization | Smectic / chiral smectic / cholesteric | Nonlinear optical materials, piezoelectric devices | [49,50,51] |
| Poly methylhydro-siloxane with cholesterol side-chain | Sulfonated cholesterol side-chain | Graft polymerization | N/A | Electro-optic displays | [38] |
| Poly methylhydro-siloxane with cholesterol side-chain | Cross-linking agent with sulfonic acid groups | Graft polymerization | Smectic / cholesteric | N/A | [40] |
| Polyacrylate with cholesterol side-chain | Alkoxybenzoic acid & smectic side-chain | Free radical - AIBN | Smectic A / nematic | Optical applications | [52] |
3. Neat State Self-Assembly of Polymers Comprising Cholesterol
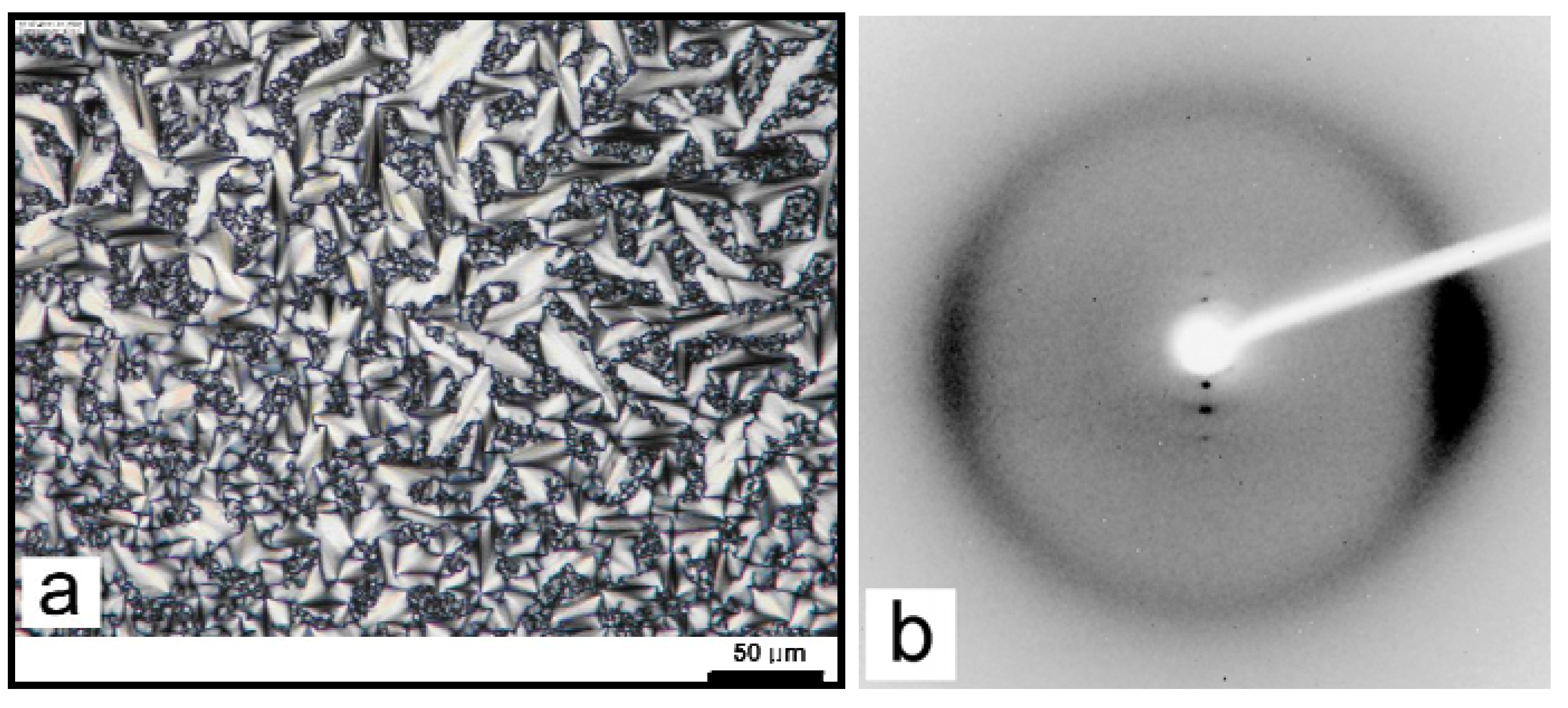
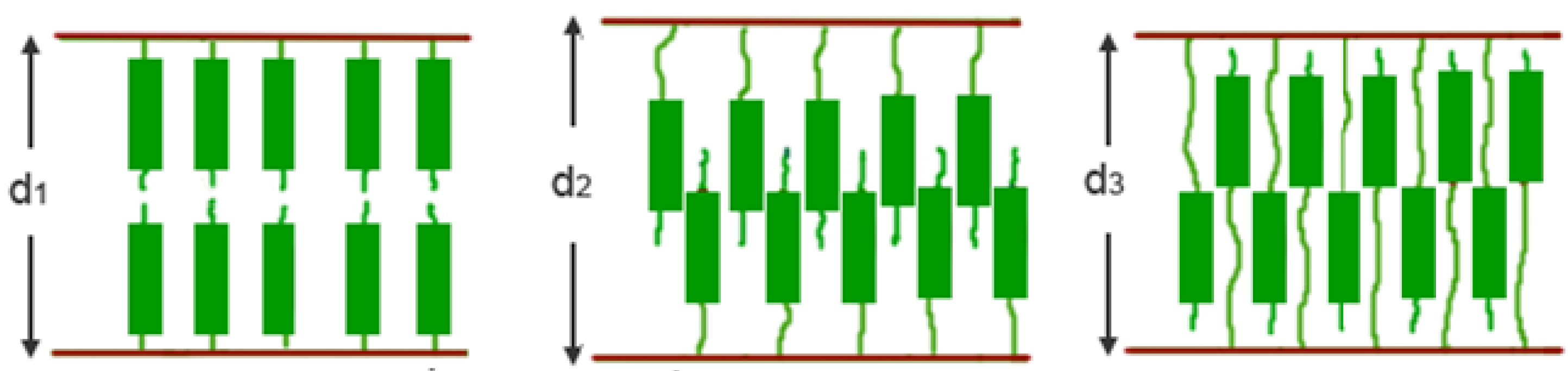
3.1. Non-mesogenic groups
3.2. Mesogenic groups
3.3. Elastomers
3.4. Dopants and ionic groups
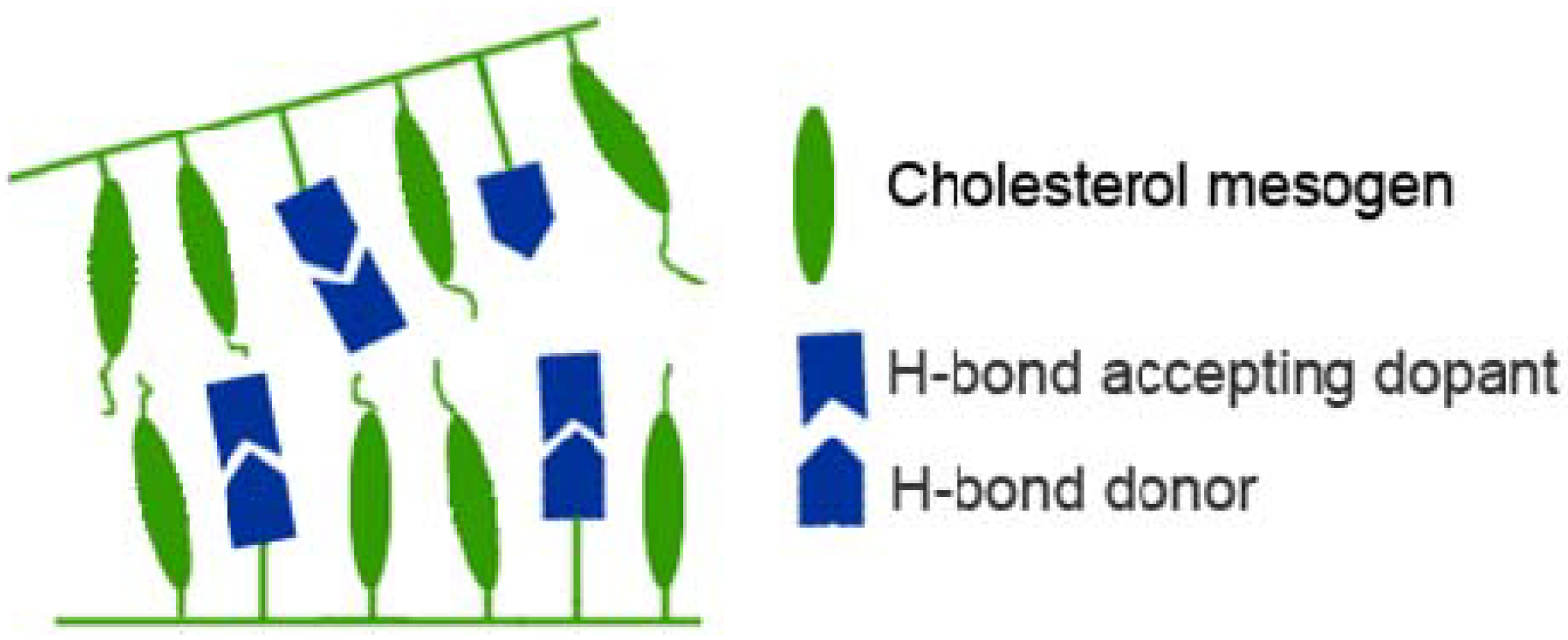
4. Solution State Self-Assembly of Polymers Comprising Cholesterol
4.1. Micelles formed by polymers comprising cholesterol
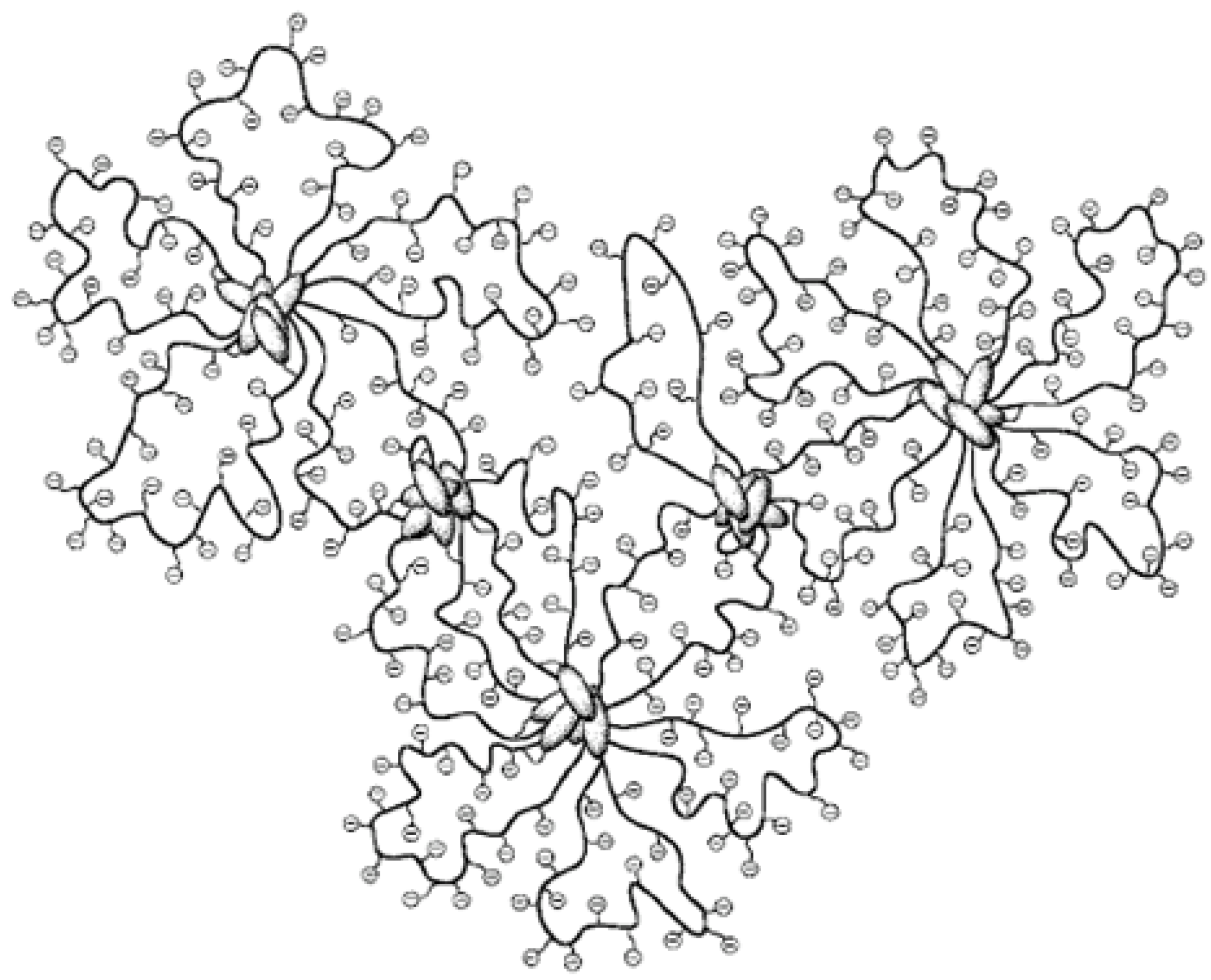
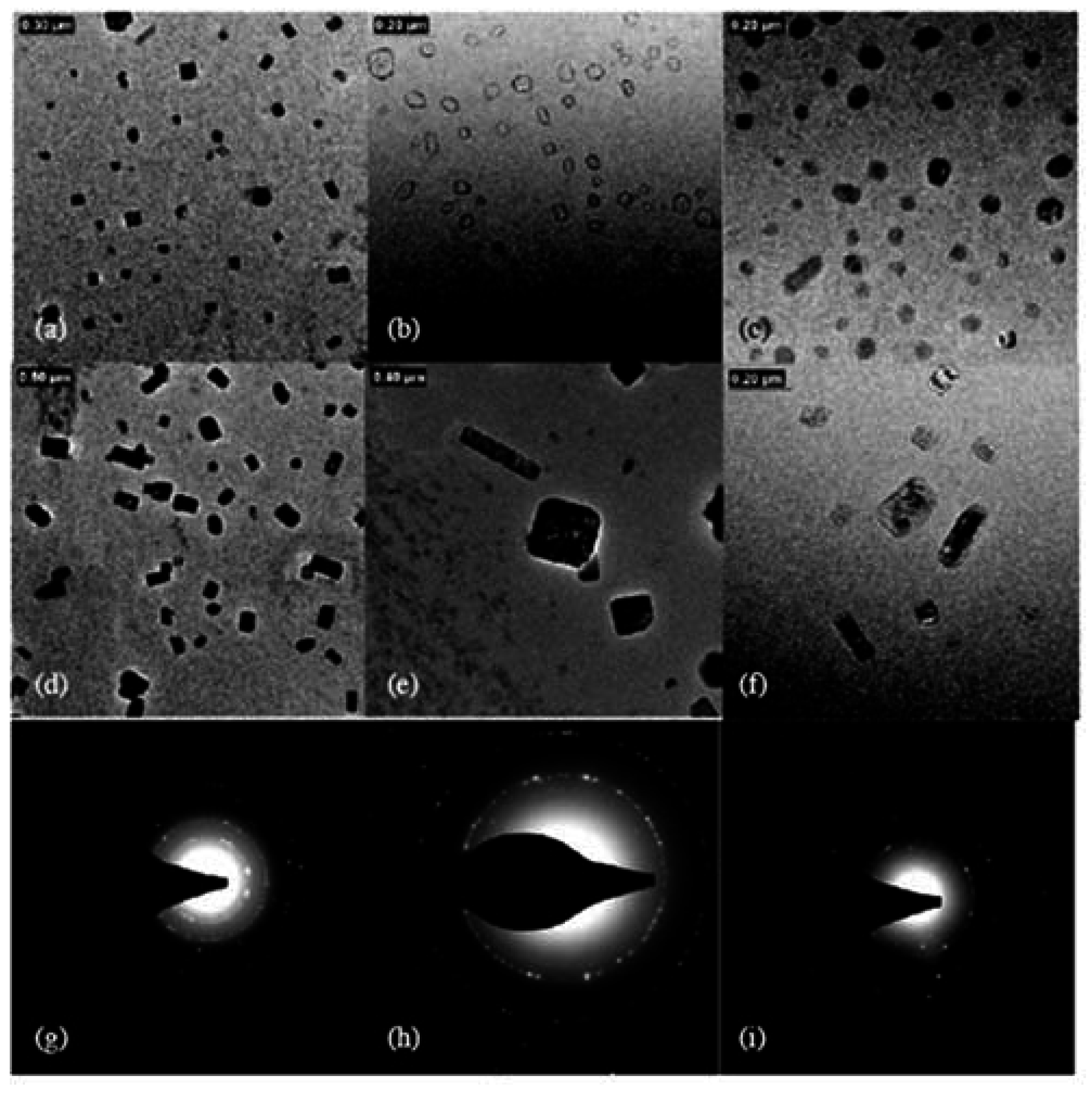
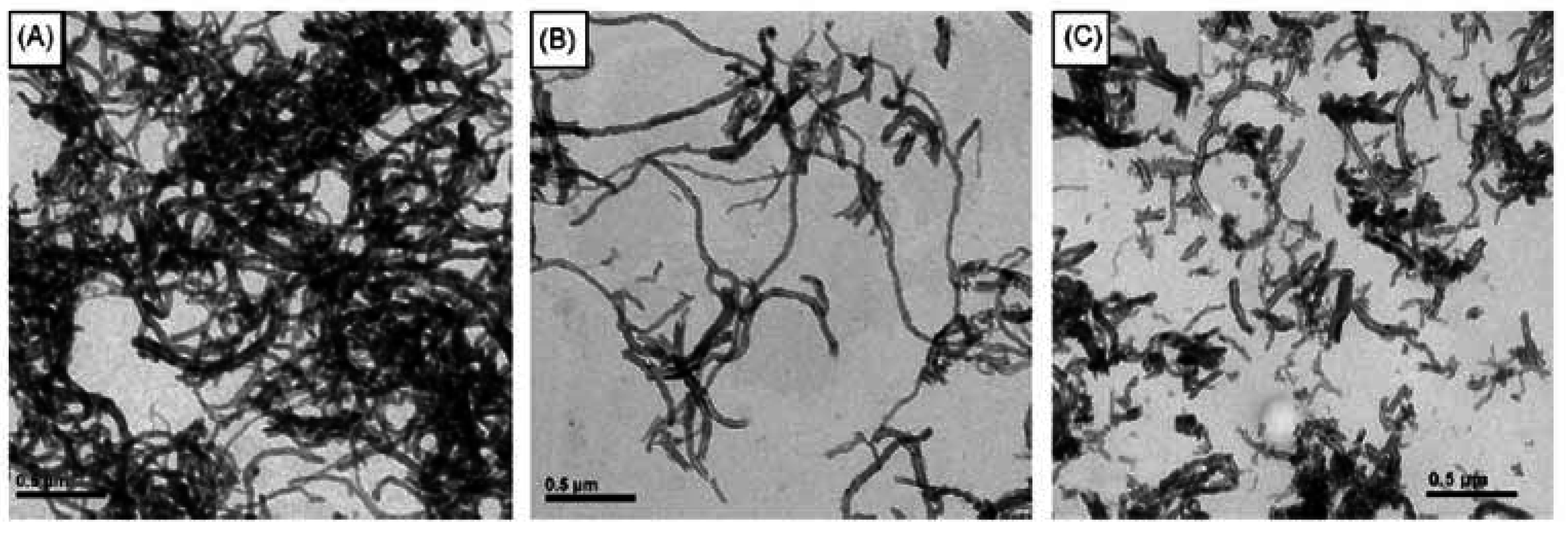
4.2. Physical gels formed by self-assembled cholesterol containing polymers

4.3. Solution properties of polymers comprising cholesterol in an organic solvent
5. Summary: Current and Future Directions
Acknowledgments
References
- Drummond, C.J.; Fong, C. Surfactant self-assembly objects as novel drug delivery vehicles. Curr. Opin. Colloid Interface S. 1999, 4, 449–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kato, T.; Mizoshita, N.; Kishimoto, K. Functional liquid-crystalline assemblies: Self-organized soft materials. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2006, 45, 38–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tschierske, C. Micro-segregation, molecular shape and molecular topology partners for the design of liquid crystalline materials with complex mesophase morphologies. J. Mater. Chem. 2001, 11, 2647–2671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodby, J.W.; Gortz, V.; Cowling, S.J.; Mackenzie, G.; Martin, P.; Plusquellec, D.; Benvegnu, T.; Boullanger, P.; Lafont, D.; Queneau, Y.; Chambert, S.; Fitremann, J. Thermotropic liquid crystalline glycolipids. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2007, 36, 1971–2032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mannock, D.A.; McElhaney, R.N. Thermotropic and lyotropic phase properties of glycolipid diastereomers: Role of headgoup and interfacial interactions in determining phase behaviour. Curr. Opin. Colloid Interface S. 2004, 8, 426–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munoz, J.; Alfaro, M.C. Rheological and phase behaviour of amphiphilic lipids. Gras. Aceit. 2000, 51, 6–25. [Google Scholar]
- Seddon, J.M.; Robins, J.; Gulik-Krzywicki, T.; Delacroix, H. Inverse micellar phases of phospholipids and glycolipids. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2000, 2, 4485–4493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thiemann, T.; Vill, V. Homologous series of liquid crystalline steroidal lipids. J. Phys. Chem. Ref. Data 1997, 26, 291–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gautrot, J.E.; Zhu, X.X. Biodegradable polymers based on bile acids and potential biomedical applications. J. Biomater. Sci. Polym. Ed. 2006, 17, 1123–1139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, J.Q.; Li, H.; Zhu, X.X. Recent advances in functional polymers based on steroid cholic acid. Chin. J. Org. Chem. 2004, 24, 1129–1132. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, X.X.; Nichifor, M. Polymeric materials containing bile acids. Acc. Chem. Res. 2002, 35, 539–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yusa, S.; Kamachi, M.; Morishima, Y. Self-association of cholesterol-end-capped poly(sodium 2-(acrylamido)-2-methylpropanesulfonate) in aqueous solution. Macromolecules 2000, 33, 1224–1231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.M.; Pramoda, K.P.; Yang, Y.Y.; Chow, S.Y.; He, C. Cholesteryl-grafted functional amphiphilic poly(N-isopropylacrylamide-co-N-hydroxylmethylacrylamide): synthesis, temperature-sensitivity, self-assembly and encapsulation of a hydrophobic agent. Biomaterials 2004, 25, 2619–2628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.M.; Yang, Y.Y.; Leong, K.W. Thermally responsive polymeric micellar nanoparticles self-assembled from cholesteryl end-capped random poly(N-isopropylacrylamide-co-N,N-dimethylacrylamide): Synthesis, temperature-sensitivity, and morphologies. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2003, 266, 295–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, J.P.; Ji, J.; Chen, W.D.; Shen, J.C. Novel biomimetic surfactant: Synthesis and micellar characteristics. Macromol. Biosci. 2005, 5, 164–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, J.P.; Ji, J.; Chen, W.D.; Shen, J.C. Novel biomimetic polymersomes as polymer therapeutics for drug delivery. J. Controlled Rel. 2005, 107, 502–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.P.; Ji, J.; Chen, W.D.; Shen, J.C. Biomimetic amphiphiles for polymeric micellar carrier system. ASBM6: Adv. Biomater. VI 2005, 288–289, 465–468. [Google Scholar]
- Qian, X.Q.; Lai, J.Y.; Zhan, S.L.; Zhang, J.; Wang, L.Q.; Tu, K.H. Novel MePEG-Chol and MepPEG-St mixed micellar systems for drug delivery: Preparation and characterization. Rare Met. Mat. Eng. 2008, 37, 655–658. [Google Scholar]
- Zou, T.; Cheng, S.X.; Zhuo, R.X. Synthesis and enzymatic degradation of end-functionalized biodegradable polyesters. Colloid Polym. Sci. 2005, 283, 1091–1099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, T.; Li, F.; Cheng, S.X.; Zhuo, R.X. Synthesis and characterization of end-capped biodegradable oligo/poly(trimethylene carbonate)s. J. Biomater. Sci., Polym. Ed. 2006, 17, 1093–1106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Wang, Q.R.; Jiang, X.S.; Cheng, S.X.; Zhuo, R.X. Studies on functionalization of poly(e-caprolactone) by a cholesteryl moiety. J. Biomater. Sci., Polym. Ed. 2005, 16, 1095–1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kostakis, K.; Mourmouris, S.; Charalabidis, D.; Pitsikalis, M. Association behavior of polyisoprenes having cholesterol and phosphatidylcholine analogous end groups. Eur. Phys. J. E 2003, 10, 55–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hwang, J.; Iyer, S.; Li, L.; Claussen, R.; Harrington, D.; Stupp, S. Self-assembling biomaterials: liquid crystal phases of cholesteryl oligo (L-lactic acid) and their interactions with cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 9662–9667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klok, H.; Hwang, J.; Iyer, S.; Stupp, S. Cholesteryl-(L-lactic acid)n building blocks for self-assembling biomaterials. Macromolecules 2002, 35, 746–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, T.; Zou, T.; Cheng, S.; Zhuo, R. Synthesis and characterization of biodegradable cholesteryl end-capped polycarbonates. Biomacromolecules 2005, 6, 524–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.M.; Yang, Y.Y.; Leong Kam, W. Thermally responsive polymeric micellar nanoparticles self-assembled from cholesteryl end-capped random poly(N-isopropylacrylamide-co-N,N-dimethylacrylamide): Synthesis, temperature-sensitivity, and morphologies. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2003, 266, 295–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Finkelmann, H.; Ringsdorf, H.; Sol, W.; Wendofl, J. Synthesis of cholesteric liquid crystalline polymers. Die Makromol. Chem. 1978, 179, 829–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freidzon, Y.S.; Kharitonov, A.V.; Shibaev, V.P.; Platé, N.A. Thermotropic liquid crystalline polymers--19. Peculiarities of the liquid crystalline structure of cholesterol-containing polymers. Eur. Polym. J. 1985, 21, 211–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leube, H.; Finkelmann, H. A “side-on” liquid crystalline polymer with the cholesterol moiety. Polym. Bull. 1988, 20, 53–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shibaev, V.; Plate, N.; Freidzon, Y. Thermotropic liquid crystalline polymers. I. Cholesterol-containing polymers and copolymers. J. Polym. Sci. Polym. Chem. Ed. 1979, 17, 1655–1670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamaguchi, T.; Asada, T. Coexistence of two different side chain packing structures in a smectic phase of liquid-crystalline side chain polymers. Liq. Cryst. 1991, 10, 215–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamaguchi, T.; Asada, T.; Hayashi, H.; Nakamura, N. Dependence of the packing structure of mesogenic groups on the flexible spacer length of liquid-crystalline side-chain polymers. Macromolecules 1989, 22, 1141–1144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Bazuin, C.; Freiberg, S.; Brisse, F.; Zhu, X. Effect of side chain structure on the liquid crystalline properties of polymers bearing cholesterol, dihydrocholesterol and bile acid pendant groups. Polymer 2005, 46, 7266–7272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Zhang, B.; He, X.; Cheng, C. Synthesis, structure and characterization of side chain cholesteric liquid crystalline polysiloxanes. Liq. Cryst. 2004, 31, 1357–1365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Zhang, B.; Jia, Y.; Wang, Y. Structures and properties of side-chain cholesteric liquid crystalline polyacrylates. Polym. J. 2003, 35, 160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Zhang, B.; Liu, L.; Meng, F. Synthesis, structures, and properties of side-chain cholesteric liquid-crystalline polysiloxanes. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2003, 89, 3944–3950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.Y.; Hu, J.S.; Yao, D.S.; Xia, Y.; Zhang, L.F. Study on mesomorphic properties of side-chain cholesteric polymers and elastomers. Acta Polym. Sinica 2003, 799–802. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, B.Y.; Meng, F.B.; Tian, M.; Xiao, W.Q. Side-chain liquid-crystalline polysiloxanes containing ionic mesogens and cholesterol ester groups. React. Funct. Polym. 2006, 66, 551–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Meng, F.; He, X.; Lin, D. Synthesis and characterization of side chain liquid crystalline polymers exhibiting cholesteric and blue phases. Liq. Cryst. 2005, 32, 1161–1167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.Y.; Meng, F.B.; Zang, B.L.; Hu, J.S. Liquid-crystalline elastomers containing sulfonic acid groups. Macromolecules 2003, 36, 3320–3326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, B.; He, X.; Wang, J. Side-chain cholesteric liquid crystalline polymers containing menthol and cholesterol — synthesis and characterization. Colloid Polym. Sci. 2007, 285, 1077–1084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Zhang, B.; Tian, M.; Ren, S.; Guo, D. Mesomorphic properties of side-chain cholesteric liquid-crystalline elastomers. Colloid Polym. Sci. 2005, 283, 1349–1355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Zhang, B.; Guan, Y.; He, X. Side-chain cholesteric liquid-crystalline elastomers derived from smectic crosslinking units: Synthesis and phase behavior. J. Polym. Sci. A: Polym. Chem. 2004, 42, 5262–5270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Kasi, R.M. Synthesis and characterization of polycholesteryl methacrylate-polyhydroxyethyl methyacrylate block copolymers. J. Polym. Sci. A: Polym. Chem. 2008, 46, 6801–6809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, S.K.; Nguyen Le, L.T.; Kasi, R.M. Synthesis and characterization of side-chain liquid crystalline polymers bearing cholesterol mesogen. J. Polym. Sci. A: Polym. Chem. 2009, 47, 2690–2701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shannon, P.J. Photopolymerization in cholesteric mesophases. Macromolecules 1984, 17, 1873–1876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamley, I.; Castelletto, V.; Parras, P.; Lu, Z.; Imrie, C.; Itoh, T. Ordering on multiple lengthscales in a series of side group liquid crystal block copolymers containing a cholesteryl-based mesogen. Soft Matter 2005, 1, 355–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hattori, H.; Uryu, T. Synthesis and properties of photochromic liquid-crystalline copolymers containing both spironaphthoxazine and cholesteryl groups. J. Polym. Sci. A: Polym. Chem. 2000, 38, 887–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.Z.; Xiao, L.J.; Zhang, B.Y.; Xiao, W.Q. Synthesis and characterization of side-chain liquid-crystalline elastomers containing cholesterol. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2005, 98, 383–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Zhang, B.; Zhou, A.; Yang, L.; Wang, B. Side-chain cholesteric liquid crystalline elastomers derived from a mesogenic crosslinking agent: I. Synthesis and mesomorphic properties. Eur. Polym. J. 2006, 42, 2849–2858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Jia, Y.; Hu, J.; Meng, F. Synthesis and properties of polysiloxane side chain cholesteric elastomers. Liq. Cryst. 2004, 31, 387–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barmatov, E.B.; Obrascov, A.A.; Pebalk, D.A.; Barmatova, M.V. Chiral nematic phase in hydrogen-bonded blends of a side-chain smectic polymer with low molar mass dopants. Colloid Polym. Sci. 2004, 282, 530–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidtke, J.; Stille, W.; Finkelmann, H.; Kim, S. Laser emission in a dye doped cholesteric polymer network. Adv. Mater. 2002, 14, 746–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finkelmann, H.; Kim, S.; Munoz, A.; Palffy-Muhoray, P.; Taheri, B. Tunable mirrorless lasing in cholesteric liquid crystalline elastomers. Adv. Mater. 2001, 13, 1069–1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsui, T.; Ozaki, R.; Funamoto, K.; Ozaki, M.; Yoshino, K. Flexible mirror-less laser based on a free-standing film of photopolymerized cholesteric liquid crystal. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2002, 81, 3741–3743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broer, D.; Lub, J.; Mol, G. Wide-band reflective polarizers from cholesteric polymer networks with a pitch gradient. Nature 1995, 378, 467–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palffy-Muhoray, P. New design in cholesteric colour. 1998, 745–746. [Google Scholar]
- Tamaoki, N. Cholesteric liquid crystals for color information technology. Adv. Mater. 2001, 13, 1135–1147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bobrovsky, A.Y.; Boiko, N.; Shibaev, V. Photosensitive cholesteric copolymers with spiropyran-containing side groups: novel materials for optical data recording. Adv. Mater. 1999, 11, 1025–1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bobrovsky, A.; Boiko, N.; Shibaev, V.; Stumpe, J. Comparative study of photoorientation phenomena in photosensitive azobenzene-containing homopolymers and copolymers. J. Photochem. Photobiol. A 2004, 163, 347–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bobrovsky, A.; Boiko, N.; Shibaev, V.; Wendorff, J. Photoinduced textural and optical changes in a cholesteric copolymer with azobenzene-containing side groups. Liq. Cryst. 2004, 31, 351–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bobrovsky, A.; Boiko, N.; Shibaev, V. Photosensitive cholesteric copolymers with spiropyran-containing side groups I. Phase behaviour and photo-optical properties. Liq. Cryst. 2000, 27, 57–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bobrovsky, A.; Shibaev, V. Thermo-, chiro- and photo-optical properties of cholesteric azobenzene-containing copolymer in thin films. J. Photochem. Photobiol. A 2005, 172, 140–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boiko, N.; Bobrovsky, A.; Shibaev, V. New type of chiral photochromic liquid crystal polymers for colour photo-optical recording. Mol. Cryst. Liq. Cryst. 1999, 332, 173–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shibaev, P.V.; Chiappetta, D.; Sanford, R.L.; Palffy-Muhoray, P.; Moreira, M.; Cao, W.; Green, M.M. Color changing cholesteric polymer films sensitive to amino acids. Macromolecules 2006, 39, 3986–3992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Do, E.D.; Kim, K.N.; Kwon, Y.W.; Jin, J.I. Dimesogenic liquid crystal consisting of cholesterol and schiff base moieties: Dependence of LC properties on the spacer length and fluorination of the alkoxy tails. Liq. Cryst. 2006, 33, 511–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Zhang, B.; Sun, K.; Li, Q. Side chain cholesteric liquid crystalline elastomers: synthesis and phase behaviour. Liq. Cryst. 2003, 30, 1267–1275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Hu, J.; Zhang, B.; Jiang, T. New thermochromic liquid-crystalline polymer: Synthesis and phase behavior. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2005, 98, 329–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zang, B.; Hu, J.; Meng, F.; Zhang, B. New side-chain liquid-crystalline ionomers. I. Synthesis and characterization of a homopolymer derived from ionic mesogenic groups. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2004, 93, 2511–2516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Li, Q.; Zhang, B.; Zhang, L. Synthesis and mesomorphic properties of side-chain cholesteric liquid-crystalline polysiloxanes. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2005, 97, 2392–23981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhi, J.; Zhang, B.; Zang, B.; Shi, G. Synthesis and properties of photochromic cholesteric liquid crystalline polysiloxane containing chiral mesogens and azobenzene photochromic groups. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2002, 85, 2155–2162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Hung, H.; Yang, P.; Tien, K. Thermal recordable novel cholesteric liquid crystalline polyacrylates containing various chiral moieties. J. Polym. Sci. A: Polym. Chem. 2008, 46, 6214–6228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akiyama, H.; Mallia, V.; Tamaoki, N. Synthesis, liquid-crystalline properties, and photo-optical studies of photoresponsive oligomeric mesogens as dopants in a chiral glassy liquid crystal. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2006, 16, 477–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, R.; Mallia, V.; Das, S.; Tamaoki, N. Butadienes as novel photochromes for color tuning of cholesteric glasses: Influence of microscopic molecular reorganization within the helical superstructure. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2004, 14, 743–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mallia, V.; Antharjanam, P.; Das, S. Chiral nematic glasses from novel hydrogen-bonded mesogens. Chem. Lett. 2001, 30, 752–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mallia, V.; Das, S. Synthesis and studies of some cholest-5-en-3-ol-(3b)[4-phenylpyridylazo] carbonate-containing supramolecular hydrogen-bonded mesogens. Liq. Cryst. 2001, 28, 259–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mallia, V.; Tamaoki, N. Photoresponsive vitrifiable chiral dimesogens: photo-thermal modulation of microscopic disordering in helical superstructure and glass-forming properties. J. Mater. Chem. 2003, 13, 219–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mallia, V.; Tamaoki, N. Design of chiral dimesogens containing cholesteryl groups; Formation of new molecular organizations and their application to molecular photonics. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2004, 33, 76–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mallia, V.; Tamaoki, N. Photochemically driven smectic-cholesteric phase transition in an inherently photoactive dimesogen. Chem. Mater. 2003, 15, 3237–3239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mallia, V.; Tamaoki, N. Study of chiral dimesogens: liquid crystalline properties, effect of smectic cybotactic domains in controlling the chiral reflections and glassy liquid crystal forming properties. Mol. Cryst. Liq. Cryst. 2006, 454, 81–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mallia, V.; Vemula, P.; John, G.; Kumar, A.; Ajayan, P. In situ synthesis and assembly of gold nanoparticles embedded in glass-forming liquid crystals. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2007, 46, 3269–3274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kato, T.; Hirota, N.; Fujishima, A.; Frechet, J.M.J. Supramolecular hydrogen-bonded liquid-crystalline polymer complexes. design of side-chain polymers and a host-guest system by noncovalent interaction. J. Polym. Sci. A: Polym. Chem. 1996, 34, 57–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, A.; Mallia, V.; Tamaoki, N. Novel supramolecular hydrogen-bonded cholesteric mesogens: liquid crystalline, thermoptical and glass-forming properties. J. Mater. Chem. 2003, 13, 1582–1587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yusa, S.; Kamachi, M.; Morishima, Y. Hydrophobic self-association of cholesterol moieties covalently linked to polyelectrolytes: Effect of spacer bond. Langmuir 1998, 14, 6059–6067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malmsten, M.; Linse, P.; Zhang, K.W. Phase behavior of aqueous poly(ethylene oxide)/poly(propylene oxide) solutions. Macromolecules 1993, 26, 2905–2910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malmsten, M.; Lindman, B. Self-assembly in aqueous block copolymer solutions. Macromolecules 1992, 25, 5440–5445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linse, P.; Malmsten, M. Temperature-dependent micellization in aqueous block copolymer solutions. Macromolecules 1992, 25, 5434–5439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linse, P. Micellization of poly(ethylene oxide)-poly(propylene oxide) block copolymers in aqueous solution. Macromolecules 1993, 26, 4437–4449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linse, P. Micellization of poly(ethylene oxide)-poly(propylene oxide) block copolymer in aqueous solution: effect of polymer impurities. Macromolecules 1994, 27, 2685–2693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linse, P. Micellization of poly(ethylene oxide)-poly(propylene oxide) block copolymers in aqueous solution: effect of polymer polydispersity. Macromolecules 1994, 27, 6404–6417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagahama, K.; Ouchi, T.; Ohya, Y. Temperature-Induced hydrogels through self-assembly of cholesterol-substituted star PEG-b-PLLA copolymers: An injectable scaffold for tissue engineering. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2008, 18, 1220–1231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akiyoshi, K.; Kang, E.C.; Kurumada, S.; Sunamoto, J.; Principi, T.; Winnik, F.M. Controlled association of amphiphilic polymers in water: thermosensitive nanoparticles formed by self-assembly of hydrophobically modified pullulans and poly(n-isopropylacrylamides). Macromolecules 2000, 33, 3244–3249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeagle, P.L. Cholesterol and the cell membrane. Biochim. Biophys. Acta, Rev. Biomembr. 1985, 822, 267–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeagle, P.L. Modulation of Membrane Function by Cholesterol. Biochimie 1991, 73, 1303–1310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heino, S.; Lusa, S.; Somerharju, P.; Ehnholm, C.; Olkkonen, V.M.; Ikonen, E. Dissecting the role of the golgi complex and lipid rafts in biosynthetic transport of cholesterol to the cell surface. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2000, 97, 8375–8380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weiss, R.G. Thermotropic liquid crystals as reaction media for mechanistic investigations. Tetrahedron 1988, 44, 3413–3475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodby, J.W. Liquid crystals and life. Liq. Cryst. 1998, 24, 25–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yusa, S; Hashidzume, A.; Morishima, Y. Interpolymer association of cholesterol pendants linked to a polyelectrolyte as studied by quasielastic light scattering and fluorescence Techniques. Langmuir 1999, 15, 8826–8831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yusa, S.; Ikeda, K.; Yamamoto, T.; Morishima, Y. Binding of bile salts to an amphiphilic polysulfonate modified with cholesterol moieties. Eur. Polym. J. 2005, 37, 571–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaw, C.S.; Chooi, K.W.; Liu, X.M.; Tan, C.W.; Wang, L.; Yang, Y.Y. Thermally responsive core-shell nanoparticles self-assembled from cholesteryl end-capped and grafted polyacrylamides: drug incorporation and in vitro release. Biomaterials 2004, 25, 4297–4308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, H.B.; Li, Y.B.; Zhang, H.Y.; Wang, X.G. Study on thermo-sensitive amphiphilic copolymers from n-isopropylacrylamide and cholesteryl acrylate. Acta Polym. Sinica 2004, 327–332. [Google Scholar]
- Soppimath, K.S.; Liu, L.H.; Seow, W.Y.; Liu, S.Q.; Powell, R.; Chan, P.; Yang, Y.Y. Multifunctional core/shell nanoparticles self-assembled from ph-induced thermosensitive polymers for targeted intracellular anticancer drug delivery. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2007, 17, 355–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, F.M.; Xu, J.P.; Ji, J.; Shen, J.C. A novel biomimetic polymer as amphiphilic surfactant for soluble and biocompatible carbon nanotubes (CNTs). Colloids Surf. B 2008, 67, 67–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranucci, E.; Suardi, M.A.; Annunziata, R.; Ferruti, P.; Chiellini, F.; Bartoli, C. Poly(amidoamine) conjugates with disulfide-linked cholesterol pendants self-assembling into redox-sensitive nanoparticles. Biomacromolecules 2008, 9, 2693–2704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, L.; Guo, K.; Lu, J.; Venkatraman, S.S.; Luo, D.; Ng, K.C.; Ling, E.A.; Moochhala, S.; Yang, Y.Y. Biologically active core/shell nanoparticles self-assembled from cholesterol-terminated PEG-TAT for drug delivery across the blood-brain barrier. Biomaterials 2008, 29, 1509–1517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chern, C.S.; Chiu, H.C.; Chuang, Y.C. Synthesis and characterization of amphiphilic graft copolymers with poly(ethylene glycol) and cholesterol side chains. Polym. Int. 2004, 53, 420–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Ke, C.Y.; Beh, C.W.; Liu, S.Q.; Goh, S.H.; Yang, Y.Y. The self-assembly of biodegradable cationic polymer micelles as vectors for gene transfection. Biomaterials 2007, 28, 5358–5368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thompson, C.J.; Ding, C.X.; Qu, X.Z.; Yang, Z.Z.; Uchegbu, I.F.; Tetley, L.; Cheng, W.P. The effect of polymer architecture on the nano self-assemblies based on novel comb-shaped amphiphilic poly(allylamine). Colloid Polym. Sci. 2008, 286, 1511–1526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.S.; Wang, Y.M.; Li, R.S.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, Q.Q. Chitosan-based self-assembled nanomicelles as a novel carrier for paclitaxel. Chem. J. Chinese Univ. 2008, 29, 1065–1069. [Google Scholar]
- Akiyoshi, K.; Nishikawa, T.; Mitsui, Y.; Miyata, T.; Kodama, M.; Sunamoto, J. Self-assembly of polymer amphiphiles: thermodynamics of complexation between bovine serum albumin and self-aggregate of cholesterol-bearing pullulan. Colloids Surf. A 1996, 112, 91–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akiyoshi, K.; Deguchi, S.; Tajima, H.; Nishikawa, T.; Sunamoto, J. Microscopic structure and thermoresponsiveness of a hydrogel nanoparticle by self-assembly of a hydrophobized polysaccharide. Macromolecules 1997, 30, 857–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akiyoshi, K.; Ueminami, A.; Kurumada, S.; Nomura, Y. Self-association of cholesteryl-bearing poly(L-lysine) in water and control of its secondary structure by host-guest interaction with cyclodextrin. Macromolecules 2000, 33, 6752–6756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morimoto, N.; Endo, T.; Ohtomi, M.; Iwasaki, Y.; Akiyoshi, K. Hybrid nanogels with physical and chemical cross-linking structures as nanocarriers. Macromol. Biosci. 2005, 5, 710–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sugawara, A.; Yamane, S.; Akiyoshi, K. Nanogel-templated mineralization: polymer-calcium phosphate hybrid nanomaterials. Macromol. Rapid Commun. 2006, 27, 441–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van de Manakker, F.; van der Pot, M.; Vermonden, T.; van Nostrum, C.F.; Hennink, W.E. Self-assembling hydrogels based on beta-cyclodextrin/cholesterol inclusion complexes. Macromolecules 2008, 41, 1766–1773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van de Manakker, F.; Vermonden, T.; el Morabit, N.; van Nostrum, C.F.; Hennink, W.E. Rheological behavior of self-assembling PEG-β-cyclodextrin/PEG-cholesterol hydrogels. Langmuir 2008, 24, 12559–12567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, F.; Gibson, H.W. Polypseudorotaxanes and polyrotaxanes. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2005, 30, 982–1018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaneko, T.; Nagasawa, H.; Gong, J.P.; Osada, Y. Liquid crystalline hydrogels: mesomorphic behavior of amphiphilic polyacrylates bearing cholesterol mesogen. Macromolecules 2004, 37, 187–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yusa, S.; Kamachi, M.; Morishima, Y. Fluorescence studies of the self-organization of a cholesterol-bearing polymethacrylate in n-hexane solution. J. Polym. Sci. A: Polym. Chem. 1999, 37, 47–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yusa, S.; Kamachi, M.; Morishima, Y. Photophysical behavior of zinc(II) tetraphenylporphyrin covalently incorporated in a cholesterol-bearing polymethacrylate. Photochem. Photobiol. 1998, 67, 519–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2009 by the authors; licensee Molecular Diversity Preservation International, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open-access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhou, Y.; Briand, V.A.; Sharma, N.; Ahn, S.-k.; Kasi, R.M. Polymers Comprising Cholesterol: Synthesis, Self-Assembly, and Applications. Materials 2009, 2, 636-660. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma2020636
Zhou Y, Briand VA, Sharma N, Ahn S-k, Kasi RM. Polymers Comprising Cholesterol: Synthesis, Self-Assembly, and Applications. Materials. 2009; 2(2):636-660. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma2020636
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhou, Yuxiang, Victoria A. Briand, Nitin Sharma, Suk-kyun Ahn, and Rajeswari M. Kasi. 2009. "Polymers Comprising Cholesterol: Synthesis, Self-Assembly, and Applications" Materials 2, no. 2: 636-660. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma2020636
APA StyleZhou, Y., Briand, V. A., Sharma, N., Ahn, S.-k., & Kasi, R. M. (2009). Polymers Comprising Cholesterol: Synthesis, Self-Assembly, and Applications. Materials, 2(2), 636-660. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma2020636




