Water–HCl Sequential Leaching of Waste Barrier Material from Aluminum Electrolysis Cell
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials and Sample Preparation
2.2. Experimental Methods
2.3. Characterization
3. Results and Discussion
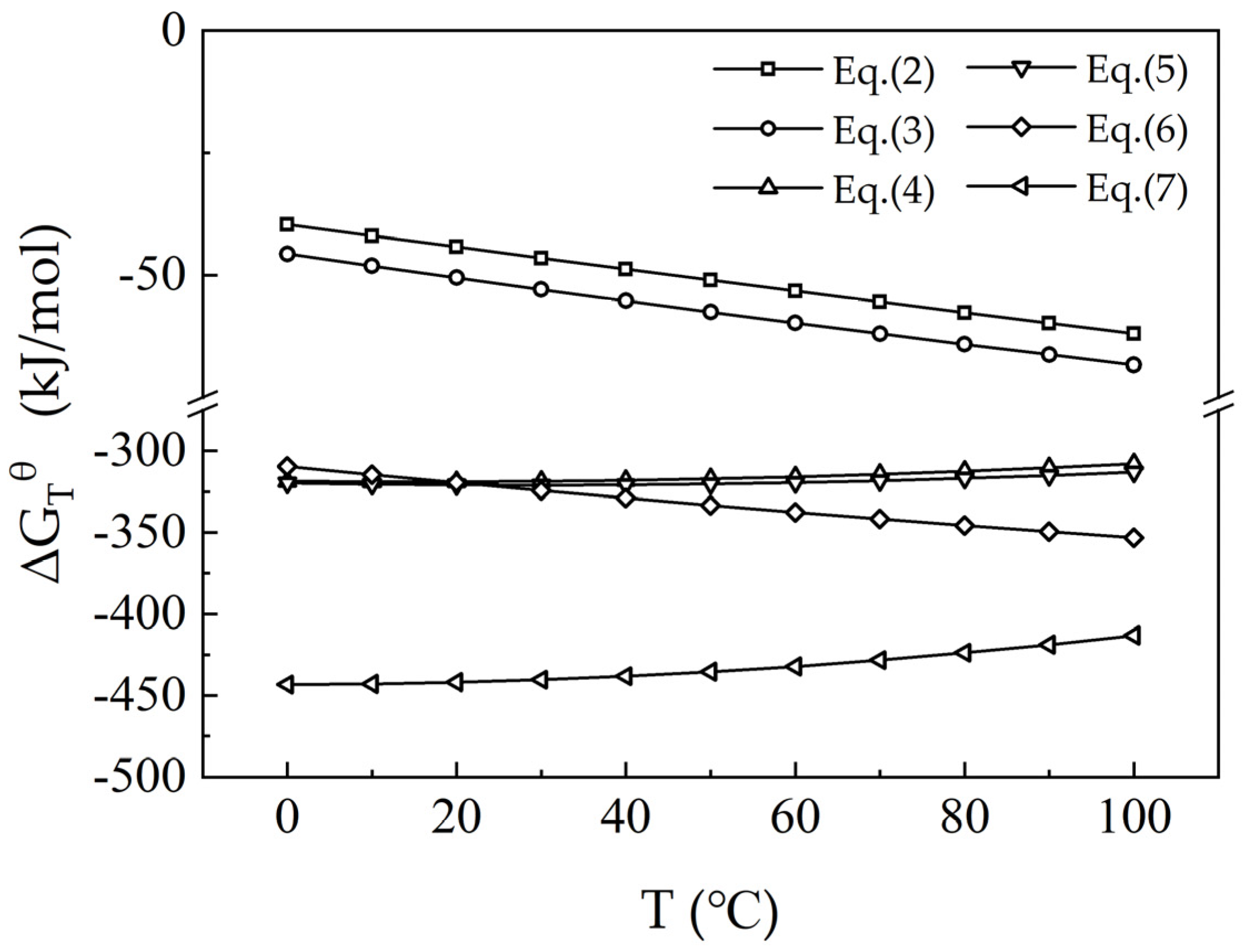
3.1. Thermodynamic Analysis of the Leaching Process
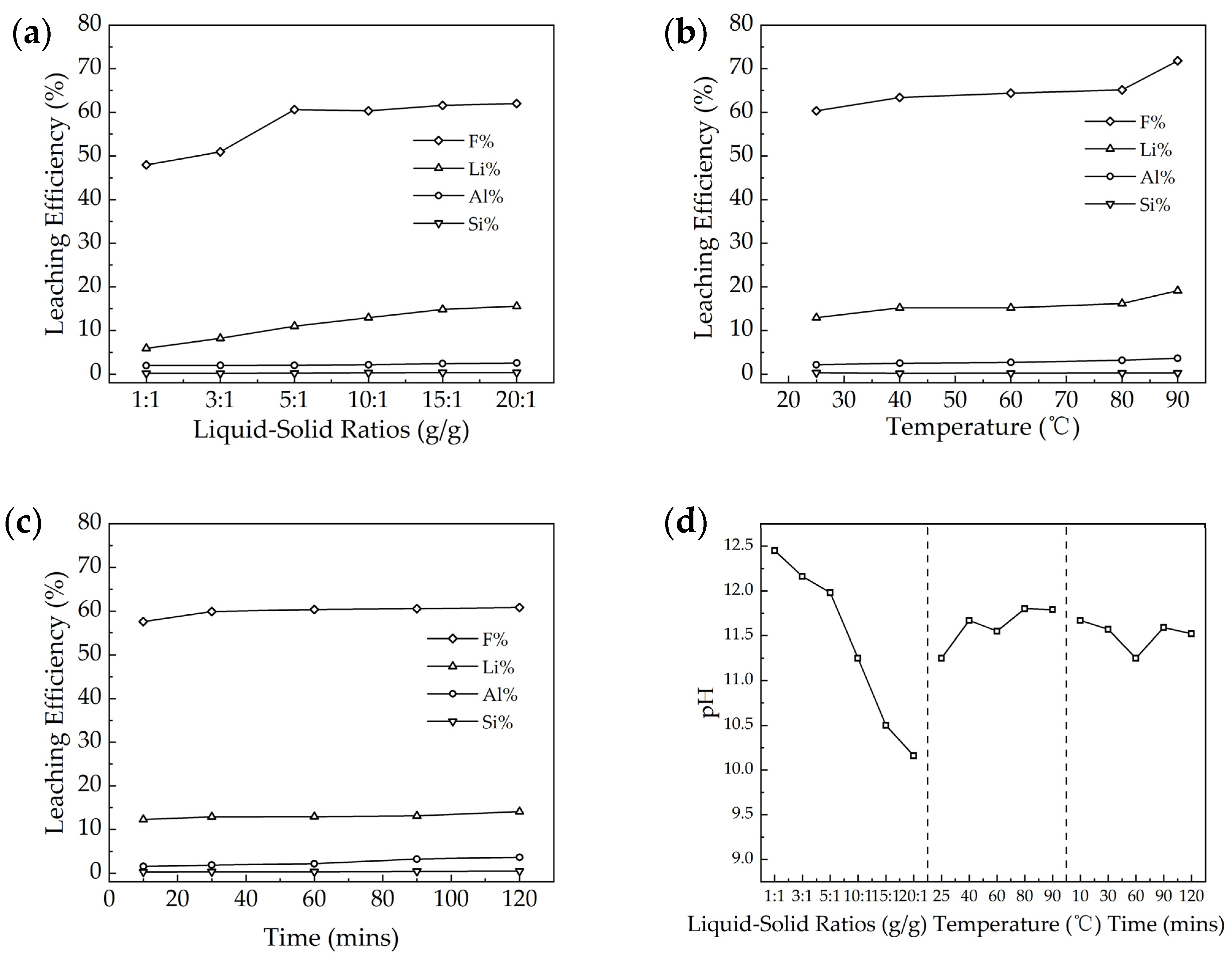
3.2. Influencing Factors in Water Leaching
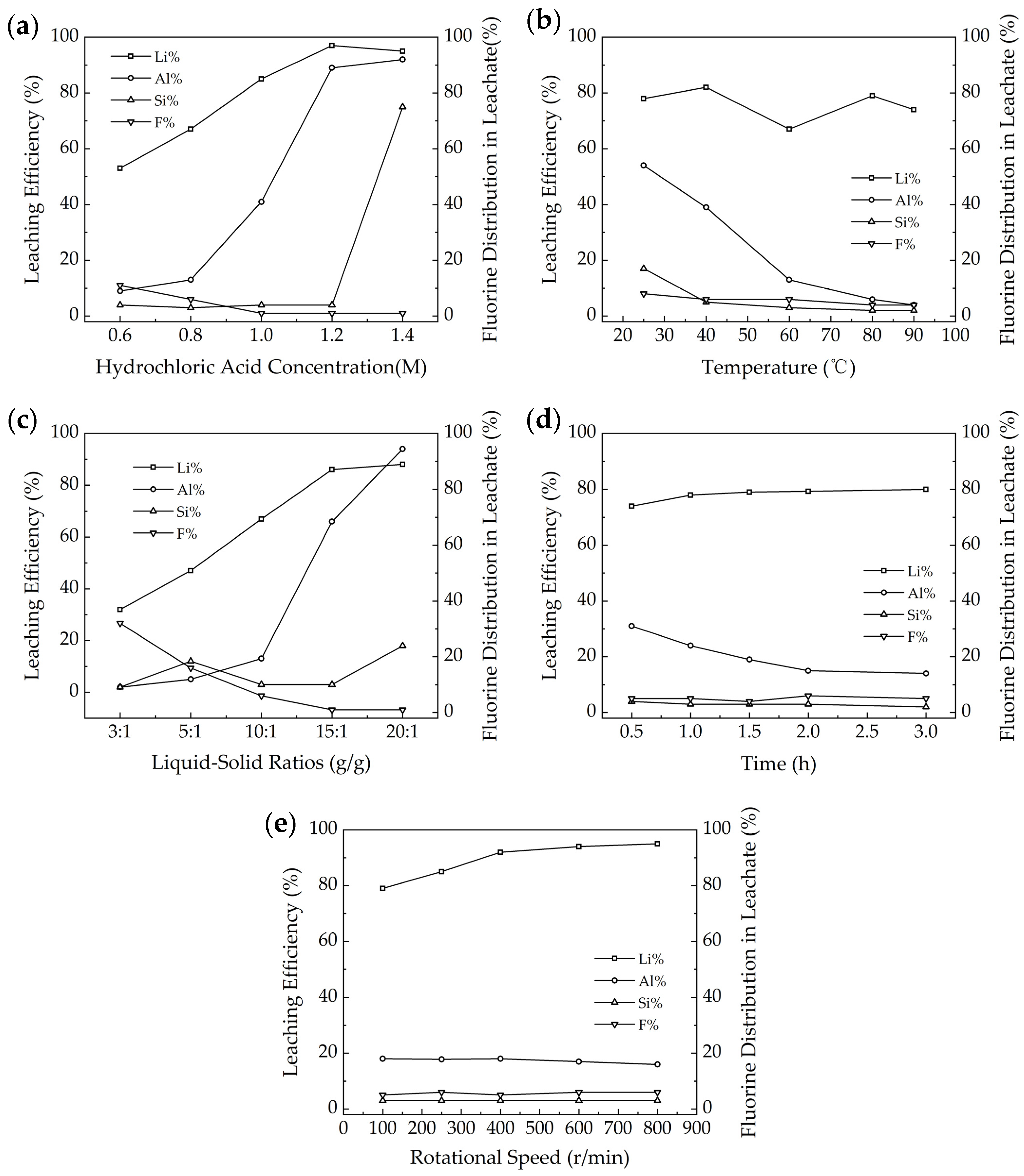
3.3. Influencing Factors in HCl Acid Leaching
3.4. Water–HCl Sequential Leaching (WHSL)
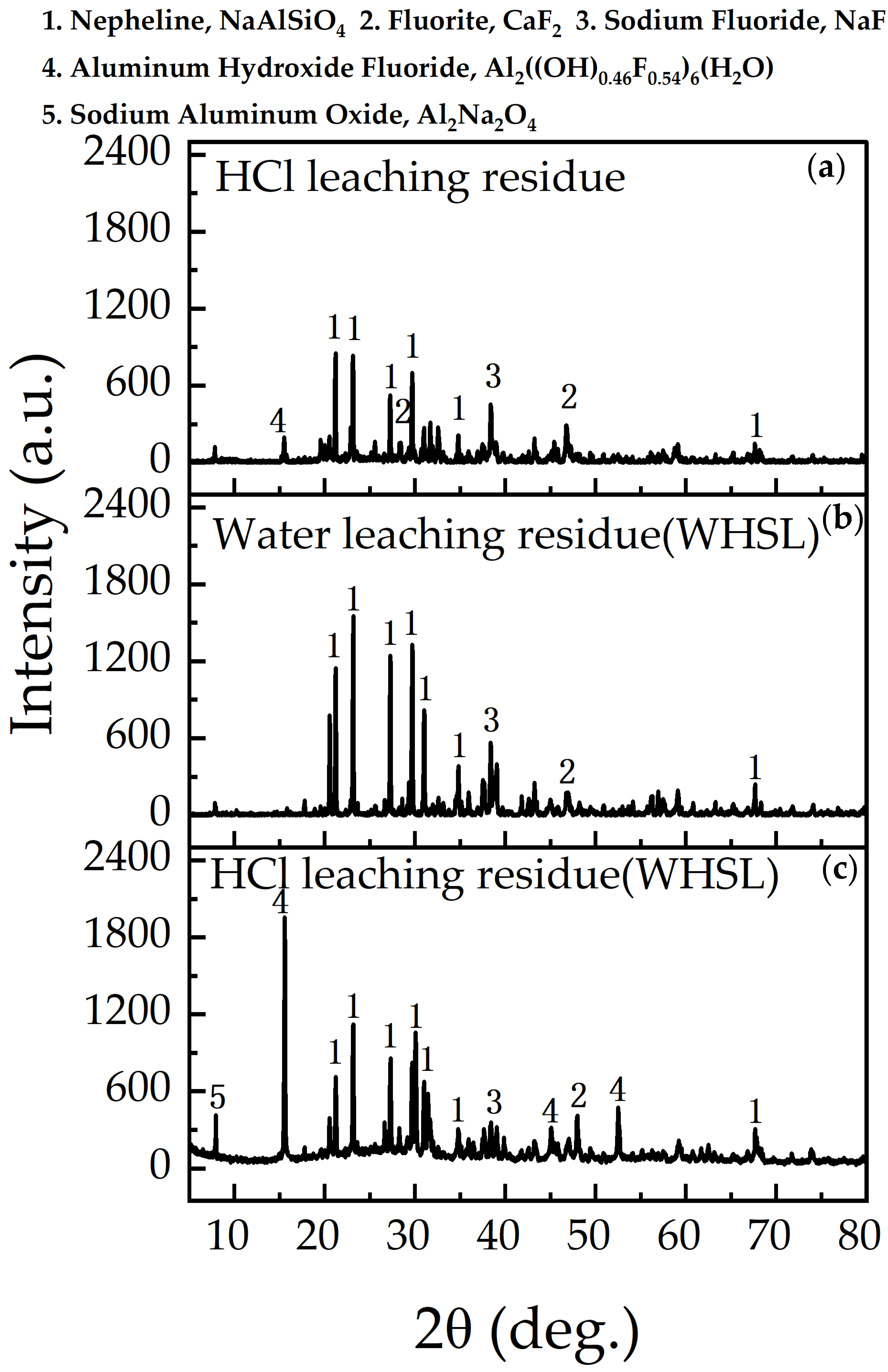
3.5. Residue Characterization and Mechanism of WHSL
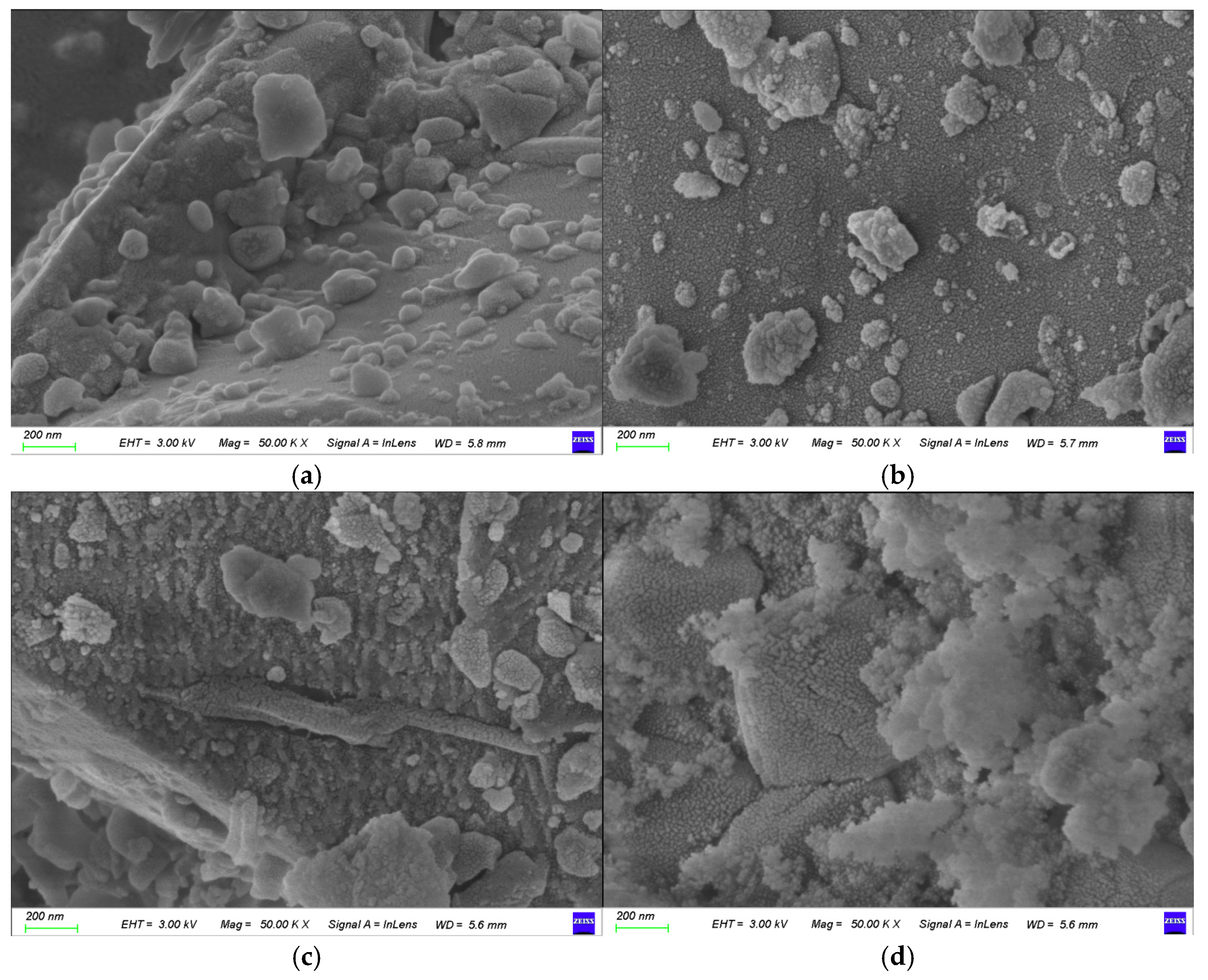
3.5.1. Surface Topography and Phase Characteristics
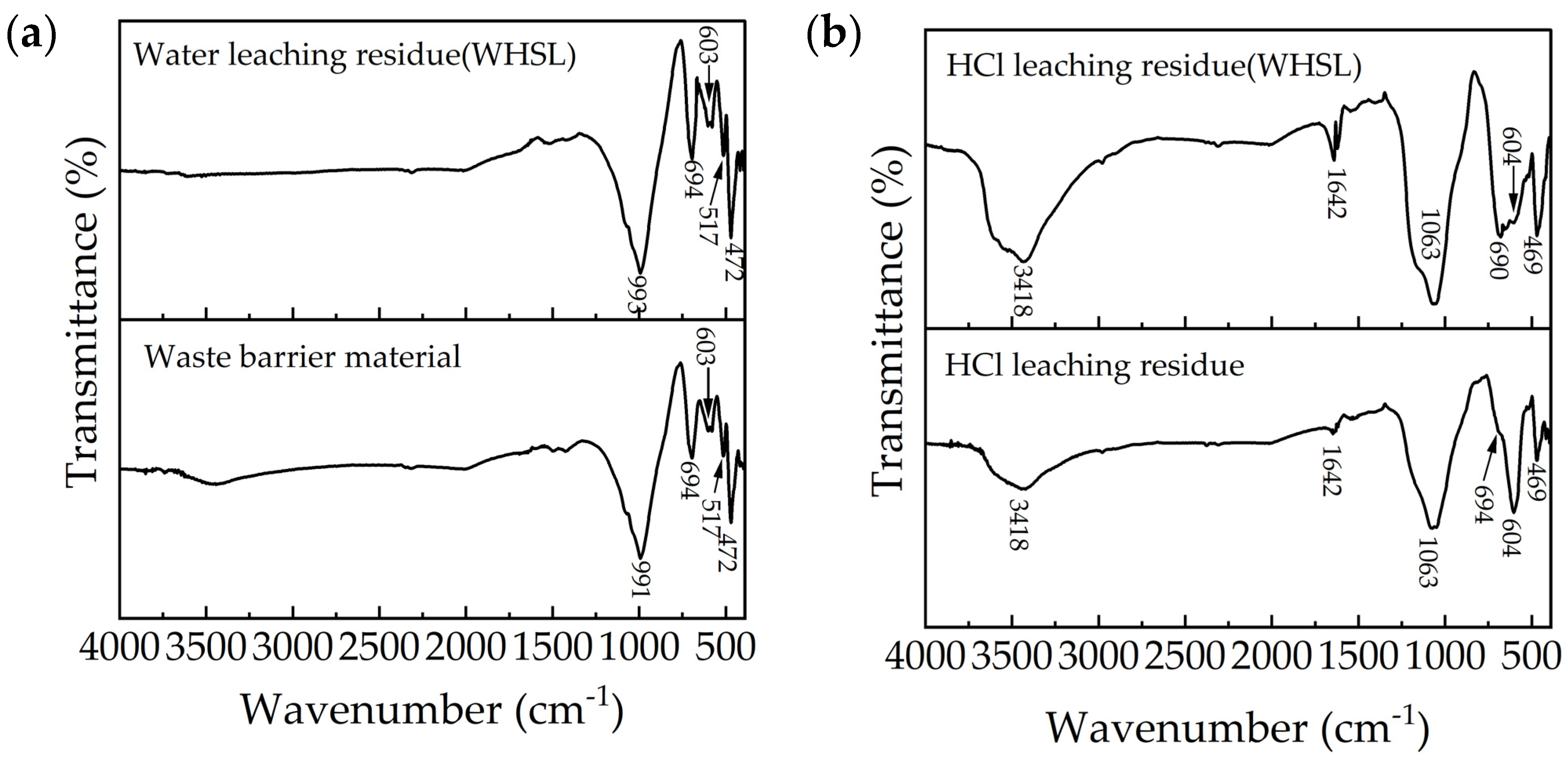
3.5.2. FTIR Analysis
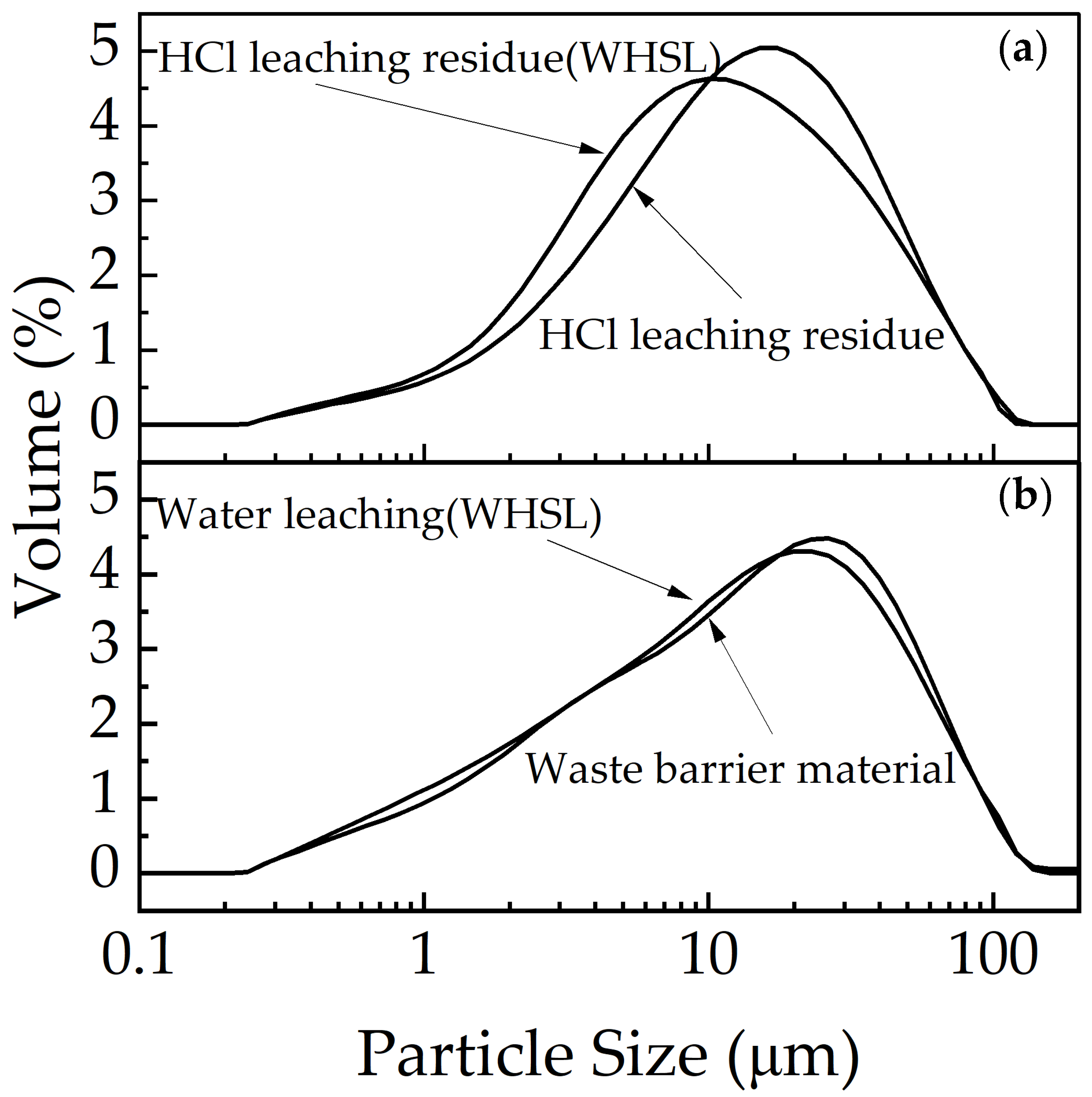
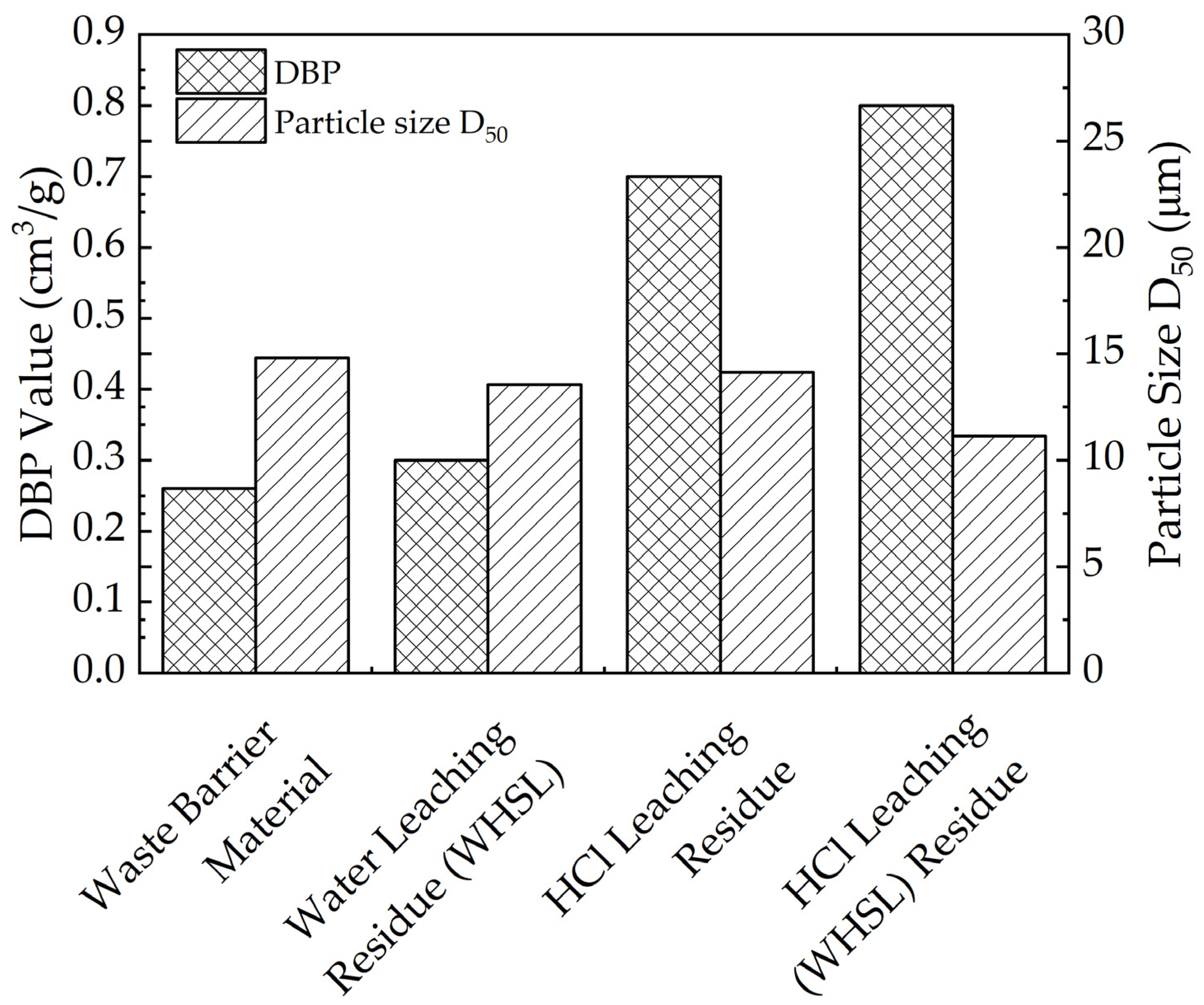
3.5.3. Particle Size and DBP Analysis
3.5.4. Proposed Mechanism
4. Summary and Conclusions
- WHSL achieved selective Li extraction without HF emission.
- In water leaching, an increased temperature and liquid-to-solid ratio accelerate Li and F extraction. Similarly, in HCl leaching, a higher HCl concentration and liquid-to-solid ratio enhance Li, Al, and Si leaching.
- SEM, particle size, and DBP analyses reveal increased surface roughness due to phase dissolution and reprecipitation, indicating enhanced porosity.
- The waste barrier material primarily consists of nepheline (NaAlSiO4), corundum (Al2O3), sodium fluoride (NaF), and silicon (Si) phases. After leaching, aluminum hydroxide fluorite ((Al2(OH)0.46F0.54)6(H2O)) and amorphous silica predominated, while unreacted nepheline persisted.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Smith, P.; Power, G. High purity alumina—Current and future production. Miner. Process. Extr. Metall. Rev. 2021, 43, 747–756. [Google Scholar]
- Fallah Fini, M.; Landry, J.-R.; Soucy, G.; Désilets, M.; Pelletier, P.; Rivoaland, L.; Lombard, D. Sludge formation in Hall–Héroult Cells: Drawbacks and significant parameters. Miner. Process. Extr. Metall. Rev. 2018, 41, 59–74. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, W.; Peng, Z.; Zhao, Y.; Cheng, J.; Ngoie, M.K.; Sun, W. A Method for Precise Separation and Enhanced Leaching of Waste Barrier Material. CN118685625A, 24 September 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, S.; Tao, W.; Zheng, Y.; Ge, H.; He, J.; Yang, Y.; Wang, Z. A novel approach for lithium recovery from waste lithium-containing aluminum electrolyte by a roasting-leaching process. Waste Manag. 2021, 134, 89–99. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Zeng, H.; Xu, R.; Wang, L. Progress in resource utilization technology of aluminum electrolysis spent pot lining. Mining Metall. 2022, 03, 50–58. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Hu, G.; Sun, W.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, L. Progress in comprehensive utilization of carbonaceous solid waste from aluminum electrolysis cells. Conserv. Util. Miner. Resour. 2021, 01, 166–171. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, Y.; Yu, X.; Shen, Q.; Zhao, Q.; Li, Y.; Wu, T. A novel approach for ultrasonic assisted organic acid leaching of waste lithium-containing aluminum electrolyte and recovery of lithium. Chem. Eng. Process. 2023, 192, 109508. [Google Scholar]
- Rui, X.; Luo, S.; Li, W.; Zhang, C.; Chen, Z.; Wang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Li, J. Clean process for selective recovery of lithium carbonate from waste lithium-bearing aluminum electrolyte Slag. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2023, 62, 14537–14547. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, S.; Tao, W.; Zheng, Y.; Yang, Y.; Yu, J.; Cui, J.; Lu, Y.; Shi, Z.; Wang, Z. Novel process for the extraction of lithium carbonate from spent lithium-containing aluminum electrolytes by leaching with aluminum nitrate and nitric acid. Hydrometallurgy 2020, 198, 105505. [Google Scholar]
- Cui, L.; Wang, W.; Chao, X.; Gao, J.; Cheng, F. Efficient lithium recovery from electrolytic aluminum slag via an environmentally friendly process: Leaching behavior and mechanism. J. Clean. Prod. 2024, 439, 140800. [Google Scholar]
- Han, Z.; Wu, Y.; Hao, P.; Tan, X.; Wei, M.; Lv, X. Efficient lithium recovery from lithium-containing spent aluminium electrolyte via NaF fluorination roasting and Al2 (SO4) 3 leaching. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2023, 5, 110948. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, C.; Wang, J.; Yang, S.; Zhang, X.; Li, S.; Lai, Y.; Tian, Z.; Jin, S.; Chen, Y. Efficient extraction and recovery of lithium from waste aluminum cryolite electrolyte. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2023, 197, 107070. [Google Scholar]
- Karimi, Z.; Rahbar-Kelishami, A. Efficient utilization of red mud waste via stepwise leaching to obtain α-hematite and mesoporous γ-alumina. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 8527. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, C.; Hou, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Huang, Y. Research progress of lithium recovery from waste aluminum electrolyte containing lithium. Metal World 2024, 5, 11–17. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.; Celestian, A.; Parise, J.B.; Xu, H.; Heaney, P.J. A new polymorph of eucryptite (LiAlSiO4), ε-eucryptite, and thermal expansion of α-and ε-eucryptite at high pressure. Am. Mineral. 2002, 87, 566–571. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, W.; Jiang, S.; Ge, W.; Zhang, Q.; Liu, T.; Zhang, X. Main geological features and genesis of lacustrine sedimentary clay−type lithium ores. Miner. Rock Geochem. Bull. 2024, 43, 64–84. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, H.; Wang, Y.; Wang, F.; Su, S.; Liu, H.; Peng, H.; Yu, Z. Chemical equilibrium in silicate systems: Part II Reaction thermodynamics. Geoscience 2006, 03, 386–398. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, C.; Zhou, S.; Wei, Y.; Li, B.; Wang, H. Recovery of fluoride from spent cathode carbon block by combustion combined with water leaching process. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 408, 137229. [Google Scholar]
- Hao, P. Study on Reaction Mechanism of Dry Barrier Material of Aluminium Reduction Cell. Ph.D. Thesis, Northeastern University, Boston, MA, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, X.; Qiu, Z.; Chen, C.; Zhang, Y. Nondestructive identification of mineral inclusions by raman mapping: Micro-magnetite inclusions in iridescent scapolite as example. Spectrosc. Spectr. Anal. 2021, 41, 2105–2109. [Google Scholar]
- Lisbona, D.F.; Steel, K.M. Recovery of fluoride values from spent pot-lining: Precipitation of an aluminium hydroxyfluoride hydrate product. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2008, 61, 182–192. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L.; Wang, D. Application of IR spectra to the study of comprehensive utilization of fly ash. Spectrosc. Spectr. Anal. 2005, 08, 1240–1242. [Google Scholar]
- Janice, L.B.; Elizabeth, B.R.; David, L.B.; Zaenal, A.; Leslie, L.B.; Naoto, M.; Teruo, H. Spectral and hydration properties of allophane and imogolite. Clays Clay Miner. 2013, 61, 57–74. [Google Scholar]
- Haleh, S.; Maryam, S.; Fouad, M. Synthesis and characterization of micro-mesoporous MCM-41 using various ionic liquids as co-templates. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2015, 217, 219–224. [Google Scholar]
- Ellerbrock, R.; Stein, M.; Schaller, J. Comparing amorphous silica, short-range-ordered silicates, and silicic acid species by FTIR. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 11708. [Google Scholar]
- Stein, M.; Georgiadis, A.; Gudat, D.; Rennert, T. Formation and properties of inorganic Si-contaminant compounds. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 265, 115032. [Google Scholar]
- Kaya, H.; Ngo, D.; Gin, S.; Kim, S.H. Spectral changes in Si–O–Si stretching band of porous glass network upon ingress of water. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 2020, 527, 119722. [Google Scholar]
- Roulia, M.; Chassapis, K.; Kapoutsis, J.; Kamitsos, E.; Savvidis, T. Influence of thermal treatment on the water release and the glassy structure of perlite. J. Mater. Sci. 2006, 41, 5870–5881. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, D.; Qiao, H.; Qin, S.; Xing, X.; Yan, K. An efficient and template-free synthesis of mesoporous silica from coal fly ash. Asia-Pac. J. Chem. Eng. 2024, 19, e3023. [Google Scholar]
- Siwińska-Stefańska, K.; Walkowiak, J.; Krysztafkiewicz, A.; Jesionowski, T. Polymer adsorption on the surface of highly dispersed silica. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2008, 254, 3591–3600. [Google Scholar]
- Nabiyouni, G.; Barati, A.; Saadat, M. Surface adsorption of polyethylene glycol and polyvinyl alcohol with variable molecular weights on zinc oxide nanoparticles. Iran. J. Chem. Chem. Eng. 2011, 8, 20–30. [Google Scholar]
- Cacua, K.; Ordoñez, F.; Zapata, C.; Herrera, B.; Pabón, E.; Buitrago-Sierra, R. Surfactant concentration and pH Effects on the zeta potential values of alumina nanofluids to inspect stability. Colloids Surf. A. 2019, 583, 123960. [Google Scholar]
- Zhong, S.; Liang, D.; Weng, W.; Chi, X.; Zhang, W.; Tan, W. Efficient extraction of Li and Rb from zinnwaldite via thermal activation and acid leaching. Miner. Eng. 2024, 216, 108898. [Google Scholar]



| Element | Al | Ca | Fe | K | Li | Na | Mg | F | Si |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Content% | 9.95 | 1.08 | 1.71 | 1.75 | 1.24 | 20.7 | 0.24 | 16.85 | 14.18 |
| pH | Zeta Potential, mv | Std, mv | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Waste barrier material | 8.96 | −42.7 | 2.11 |
| HCl leaching | 6.51 | −32.1 | 2.01 |
| Water leaching (WHSL) | 7.67 | −35.1 | 2.36 |
| HCl leaching (WHSL) | 6.08 | −29.7 | 2.25 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhao, Y.; Li, S.; Cheng, J.; Chen, Y.; Liu, W.; Sun, W.; Alam, S. Water–HCl Sequential Leaching of Waste Barrier Material from Aluminum Electrolysis Cell. Materials 2025, 18, 1748. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18081748
Zhao Y, Li S, Cheng J, Chen Y, Liu W, Sun W, Alam S. Water–HCl Sequential Leaching of Waste Barrier Material from Aluminum Electrolysis Cell. Materials. 2025; 18(8):1748. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18081748
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhao, Yujie, Saiya Li, Junfeng Cheng, Yuting Chen, Weiping Liu, Wei Sun, and Shafiq Alam. 2025. "Water–HCl Sequential Leaching of Waste Barrier Material from Aluminum Electrolysis Cell" Materials 18, no. 8: 1748. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18081748
APA StyleZhao, Y., Li, S., Cheng, J., Chen, Y., Liu, W., Sun, W., & Alam, S. (2025). Water–HCl Sequential Leaching of Waste Barrier Material from Aluminum Electrolysis Cell. Materials, 18(8), 1748. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18081748








