A New Strategy for the High-Value Utilization of Cobalt Slag: A Solid-State Reaction for the Preparation of Microwave-Absorbing Composite Materials with Excellent Properties
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Synthesis of MnCo2O4 Materials
2.3. Synthesis of MC@G Composites
2.4. Characterizations
3. Results and Discussion
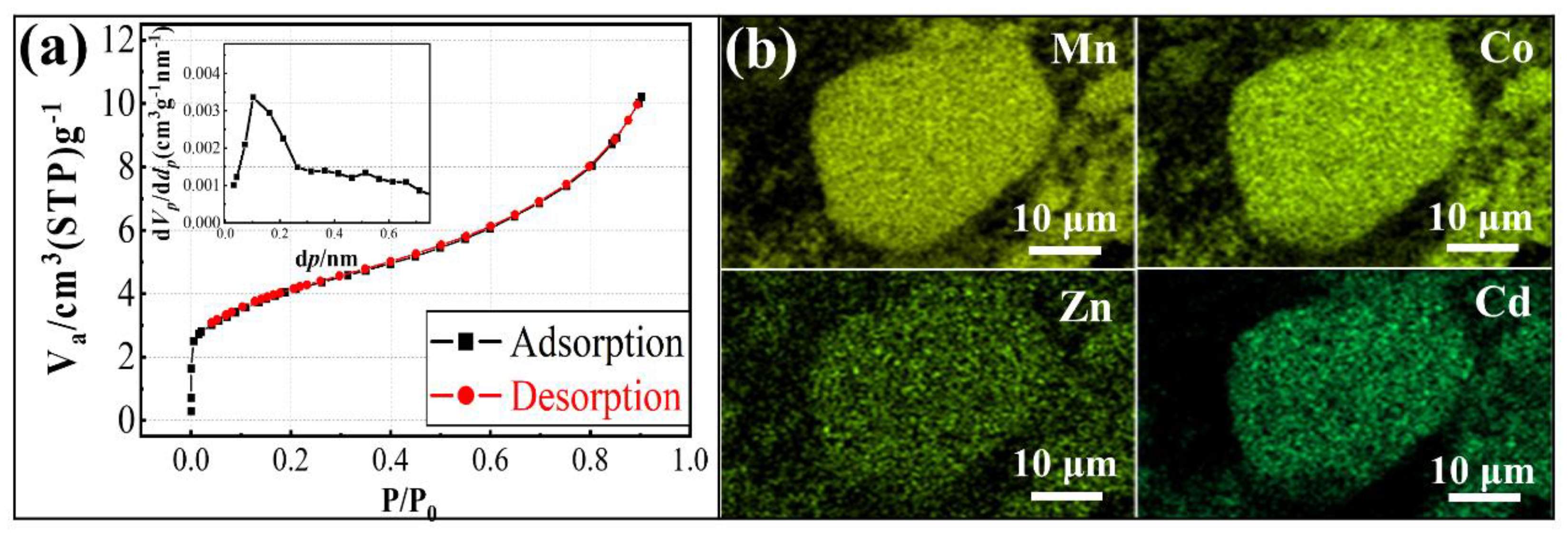
3.1. Characterization of Cobalt-Rich Slag
3.2. Preparation of MnCo2O4 and MC@G
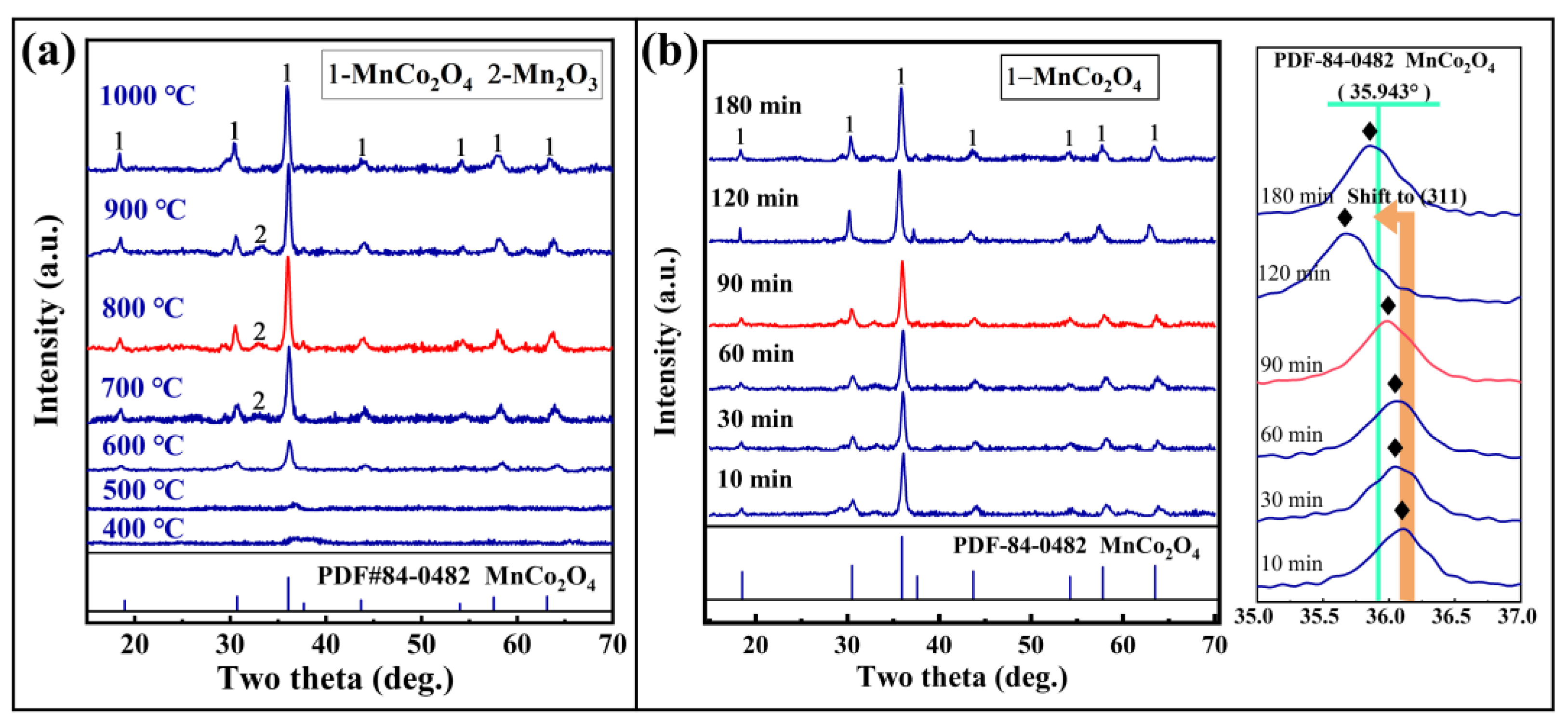
3.2.1. Analysis of the Solid-Phase Reaction in Cobalt-Rich Slag
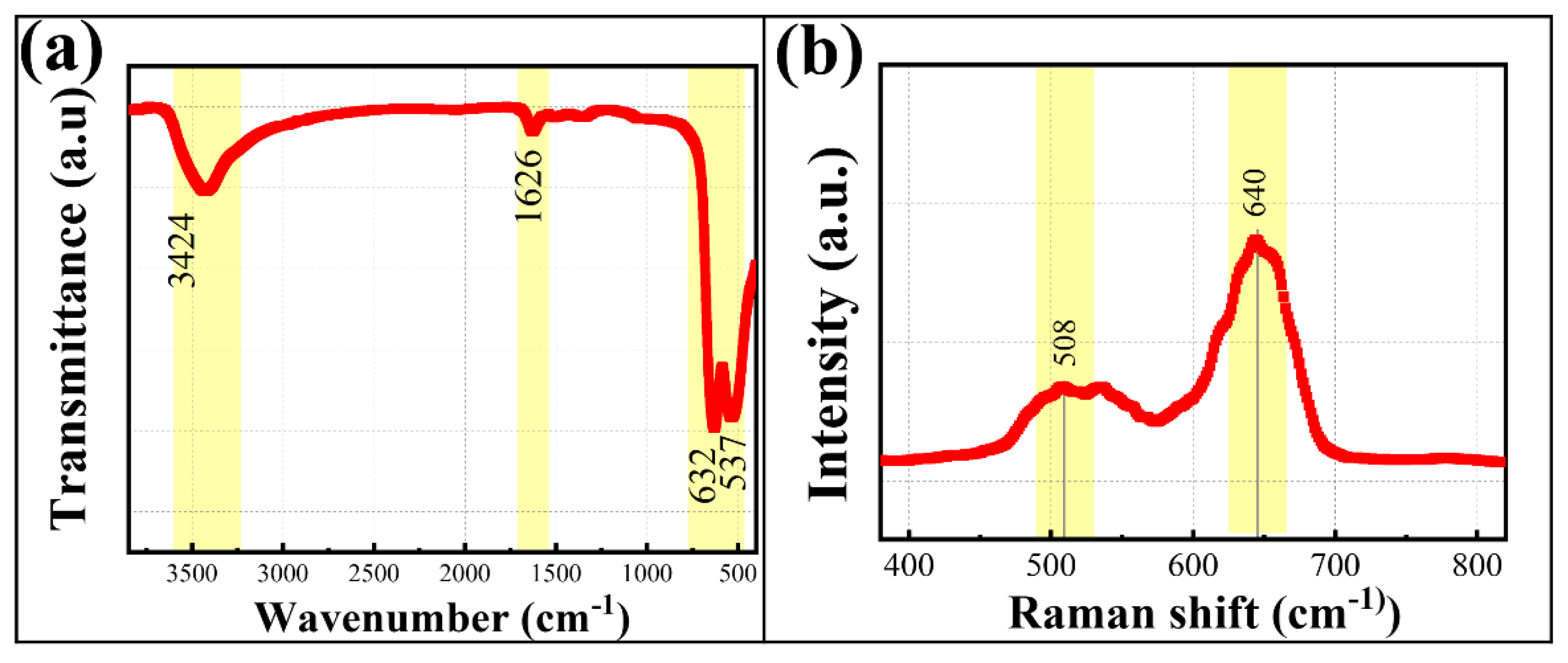
3.2.2. Physical Property Analysis of MnCo2O4
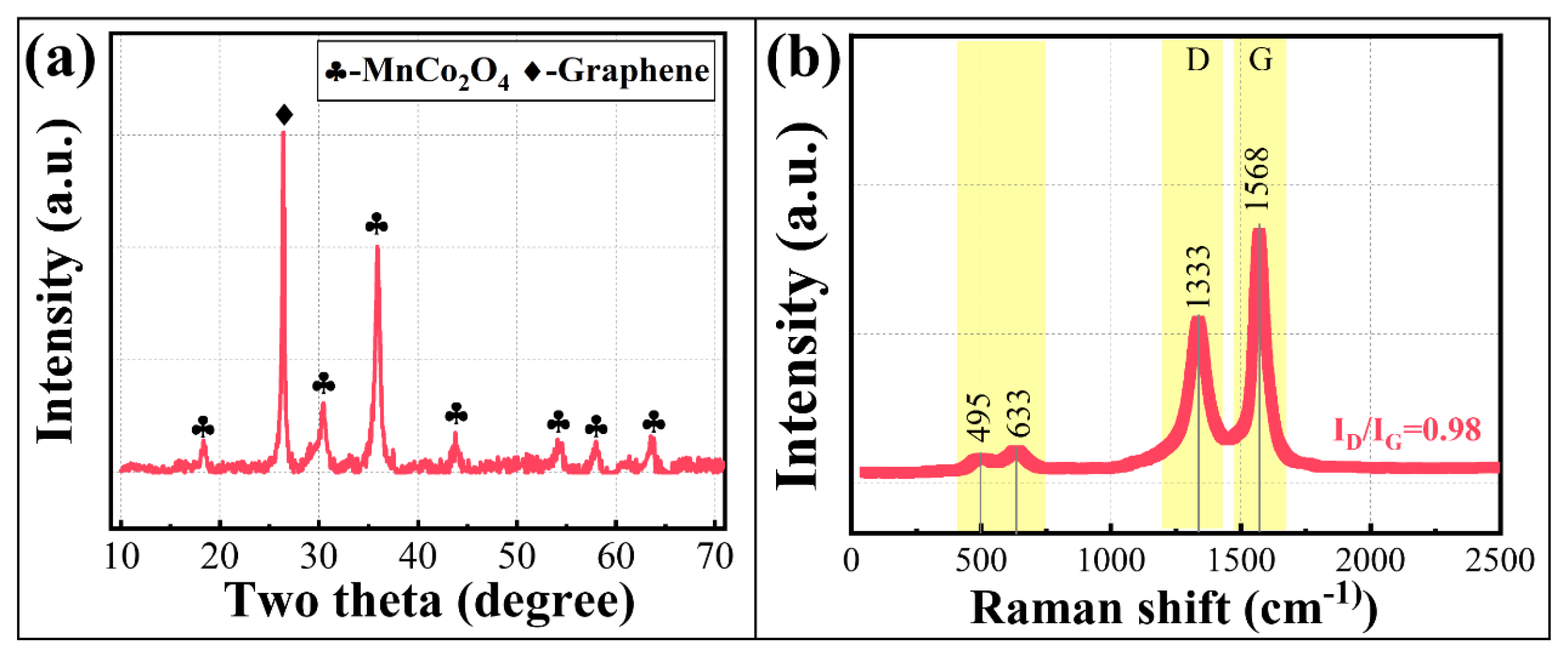
3.2.3. Physical Property Analysis of MC@G Composites
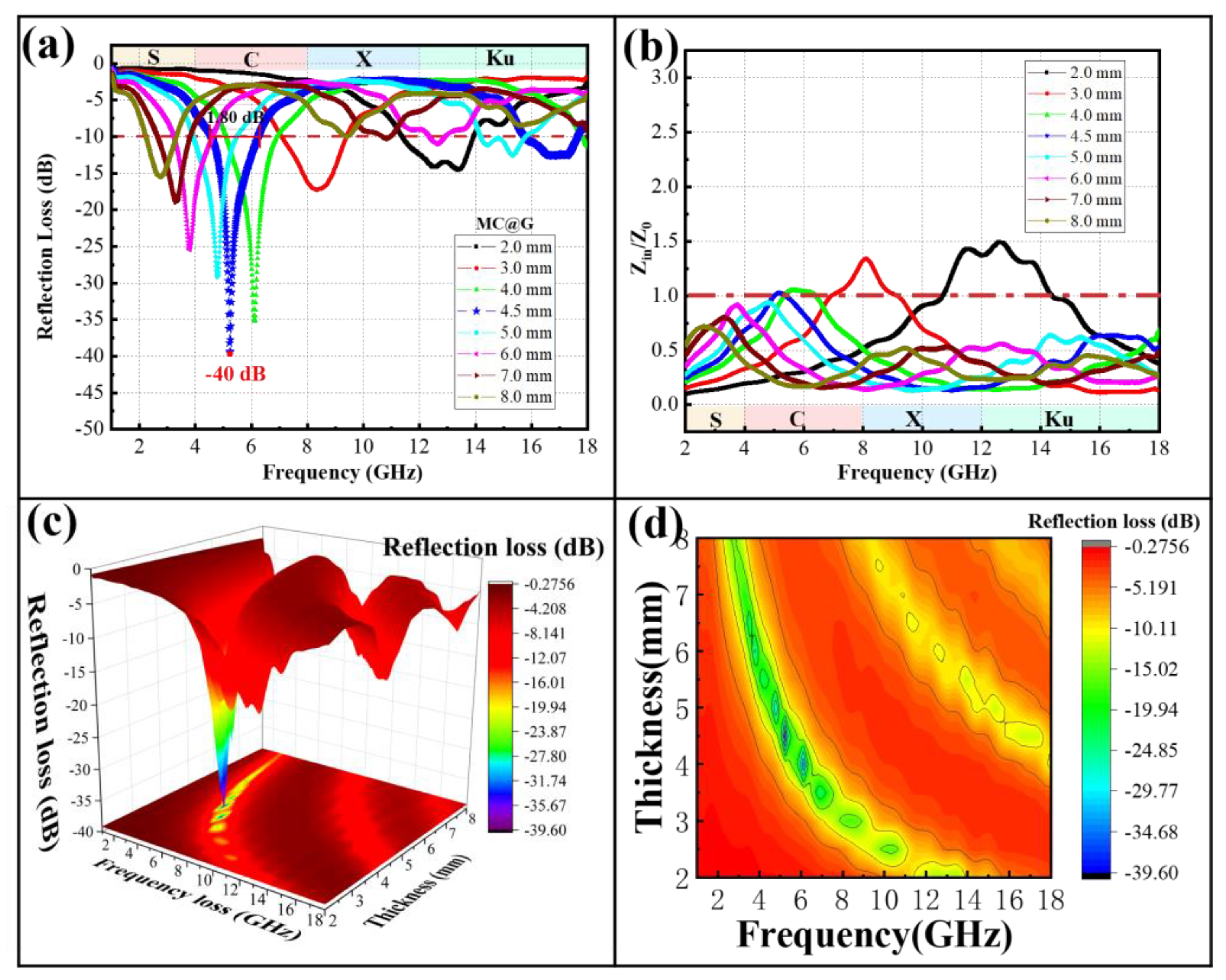
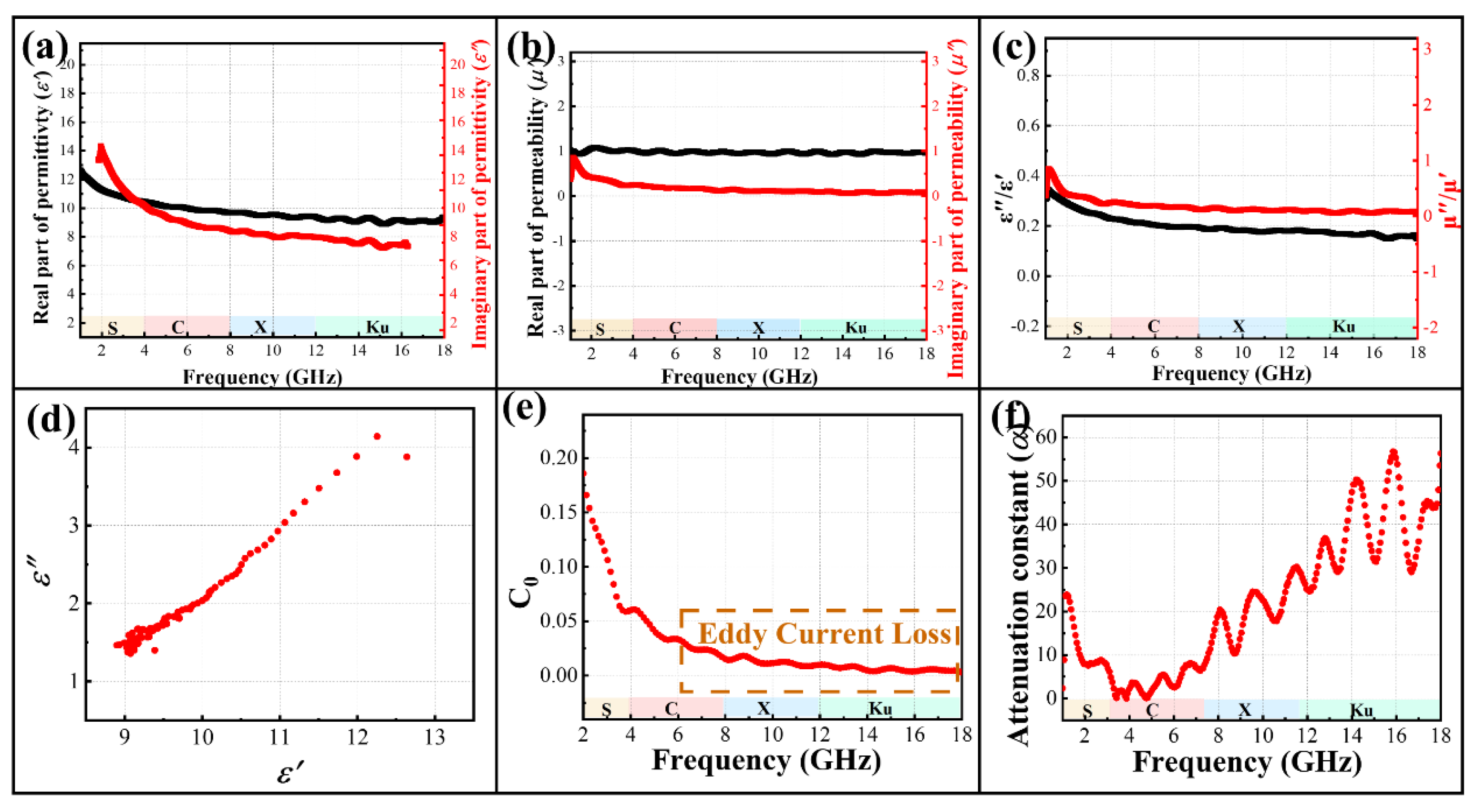
3.3. Microwave Absorption Applications
3.3.1. MnCo2O4
3.3.2. MC@G Composites
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Nomenclature
| MC@G | Graphene-encapsulated MnCo2O4 composites |
| XRD | X-ray diffraction |
| SEM | Scanning electron microscope |
| VSM | Vibrating sample magnetometer |
| FT-IR | Fourier transform infrared spectrometer |
| XPS | X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy |
| BET | Brunauer–Emmett–Teller theory |
| BJH | Barret–Joyner–Halenda theory |
| Zin/Z0 | Impedance matching performance |
| ε′ | Real parts of the dielectric constant |
| ε″ | Imaginary parts of the dielectric constant |
| μ′ | Real parts of the permeability |
| μ″ | Imaginary parts of the permeability |
| dB | Decibel |
| °C | Celsius |
| min | Minute |
| cm | Centimeter |
| mm | Millimeter |
| nm | Nanometer |
| kV | Kilovolt |
| eV | Electronvolt |
| GHz | Gigahertz |
References
- Nagashima, M.; Akasaka, M.; Morifuku, Y. Ore and Skarn Mineralogy of the Yamato Mine, Yamaguchi Prefecture, Japan, with Emphasis on Silver-, Bismuth-, Cobalt-, and Tin-bearing Sulfides. Resour. Geol. 2016, 66, 37–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Li, Q.; Xu, Y.; Nie, L.; Yang, Y.; Deng, J. Selective Recovery of Zinc and Cobalt from Purified Cobalt Residue in Zinc Hydrometallurgy. Nonferrous Met. Extr. Metall. 2019, 4, 6–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, G.; Wang, J.; Liu, B.; Sun, H.; Huang, Y. Progress and Prospect of Cobalt Recovery from Cobalt Slag Produced by Zinc Hydrometallurgy. J. Guizhou Univ. (Nat. Sci.) 2022, 2, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, S.; Sun, W.; Wang, L.; Liu, R.; Han, H.; Hu, Y.; Yang, Y. Recovery of cobalt and zinc from the leaching solution of zinc smelting slag. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2019, 7, 102777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banza, A.N.; Gock, E.; Kongolo, K. Base metals recovery from copper smelter slag by oxidising leaching and solvent extraction. Hydrometallurgy 2002, 67, 63–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Guo, H.; Zhang, C.; Liu, B.; Wang, L.; Peng, W.; Cao, Y.; Song, X.; Zhu, X. A novel method for the separation of zinc and cobalt from hazardous zinc-cobalt slag via an alkaline glycine solution. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2021, 273, 119009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q. Experimental study on cobalt enrichment of purification cobalt residue by ammonium persulfate oxidation precipitation method. China Nonferrous Metall. 2021, 50, 24–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, X.; Barbiellini, B.; Vittoria, C. Calculation of exchange constants in manganese ferrite (MnFe2O4). J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2004, 272, 306–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Geassy, A.; Nasr, M.; Omar, A.A.; Mousa, E. Reduction kinetics and catastrophic swelling of MnO2-doped Fe2O3 compacts with CO at 1073–1373 K. ISIJ Int. 2007, 47, 377–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, J.; Wang, J.; Su, Z.; Li, G.; Jiang, T. New understanding on separation of Mn and Fe from ferruginous manganese ores by the magnetic reduction roasting process. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2018, 444, 133–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shan, J.; Shi, C.; Zeng, H.; Wei, T.; Maitisaiyidi, T.; Zhu, G.; Zeng, Y.; Sun, Z. Simple solid-state synthesis of mesoporous NiCo2O4/N-doped reduced graphene oxide nanosheet composites with enhanced performance in electrochemical capacitors. J. Solid State Electrochem. 2024, 28, 2899–2909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, D.; Qin, M.; Liu, J.; Wu, G.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, H. Novel binary cobalt nickel oxide hollowed-out spheres for electromagnetic absorption applications. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 382, 122797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, F.; Brosseau, C. A review and analysis of microwave absorption in polymer composites filled with carbonaceous particles. J. Appl. Phys. 2012, 111, 061301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, H.; Zhao, Z.; Zhou, Q.; Gogotsi, Y.; Qiu, J. The role of microwave absorption on formation of graphene from graphite oxide. Carbon 2012, 50, 3267–3273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Huang, Y.; Zhang, T.; Chang, H.; Xiao, P.; Chen, H.; Huang, Z.; Chen, Y. Broadband and Tunable High-Performance Microwave Absorption of an Ultralight and Highly Compressible Graphene Foam. Adv. Mater. 2015, 27, 2049–2053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, W.Q.; Wang, X.X.; Yuan, J.; Wang, W.Z.; Cao, M.S. Temperature dependent microwave absorption of ultrathin graphene composites. J. Mater. Chem. C 2015, 3, 10017–10022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altaf, N.H.; Anjam, T.; Sajid, M.M.; Shad, N.A.; Shukrullah, S.; Naz, M.Y.; Javed, Y. Characterization of manganese/cobalt oxide composites synthesized by chemical co-precipitation method. In Proceedings of the 5th UTP-UMP-UAF Symposium on Energy Systems, Kuantan, Malaysia, 1–2 October 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhtar, M.N.; Khan, M.A. Effect of rare earth doping on the structural and magnetic features of nanocrystalline spinel ferrites prepared via sol gel route. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2018, 460, 268–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Ko, W.; Yoo, J.M.; Paidi, V.K.; Jang, H.Y.; Shepit, M.; Lee, J.; Chang, H.; Lee, H.S.; Jo, J.; et al. Structural Insights into Multi-Metal Spinel Oxide Nanoparticles for Boosting Oxygen Reduction Electrocatalysis. Adv. Mater. 2022, 34, 2107868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, H.; Liu, S.; Li, Y.; Conte, E.; Cao, Y. A Critical Review of Spinel Structured Iron Cobalt Oxides Based Materials for Electrochemical Energy Storage and Conversion. Energies 2017, 10, 1787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, L.B.; Lu, C.; Liu, M.C.; Luo, Y.C.; Kang, L.; Li, X.; Walsh, F.C. The specific capacitance of sol-gel synthesised spinel MnCo2O4 in an alkaline electrolyte. Electrochim. Acta 2014, 115, 22–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagamuthu, S.; Vijayakumar, S.; Lee, S.-H.; Ryu, K.-S. Hybrid supercapacitor devices based on MnCo2O4 as the positive electrode and FeMn2O4 as the negative electrode. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2016, 390, 202–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masoudpanah, S.M. Microwave absorption properties of ZnCo2O4 and MnCo2O4 powders synthesized by oxalate-assisted hydrothermal method. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2022, 20, 3750–3759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, A.; Luo, G.; Sun, X.; Qiao, J.; Cao, J.; Du, Z.; Li, B. Synthesis and Characterization of Co3O4/rGO Composite Magnetic Microwave Absorbing Materials. JOM 2023, 75, 407–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Z.; Du, Z.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Zhao, Z.; Hou, M.; Wang, X.; Hassan, Y.A.; Huang, X.; Yue, J.; et al. Reduced graphene oxide loaded with rich defects CoO/Co3O4 for broadband microwave absorption. Compos Part B-Eng. 2023, 249, 110403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Wang, B.; Wang, Z.; Chen, L.; Gao, C.; Xu, B.; Jia, Z.; Wu, G. Synthesis of 3D flower-like ZnO/ZnCo2O4 composites with the heterogeneous interface for excellent electromagnetic wave absorption properties. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2021, 586, 479–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanad, M.M.S.; Azab, A.A.; Taha, T.A. Introduced oxygen vacancies in cadmium ferrite anode materials via Zn2+ incorporation for high performance lithium-ion batteries. Mater. Sci. Semicond. Process. 2022, 143, 106567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Chen, P.; Shu, X.; Liu, J.; Wang, W.; Fu, B.; Cao, Y.; Peng, W.; Zhu, X.; Hu, M. Phase transition mechanism of the solid-state reaction of two variable-valence metal oxides: Cobalt and manganese oxides. J. Alloys Compd. 2023, 960, 170855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Q.; Wei, Z.; Lu, C.; Ding, M.; Ma, J. Effect of Sintering Temperature on Electrochemical Properties of MnCo2O4 Cathode Materials. J. Electron. Mater. 2023, 52, 5504–5512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Wang, Y.; Yan, Y.; He, P.; Shezad, M.; Wang, G.; Bao, L.; Liu, H. The magnetic characteristics of spinel-type MnCo2O4 at low temperatures. Ceram. Int. 2024, 50, 54482–54489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ekhlasiosgouei, O.; Bik, M.; Molin, S. Preparation of MnCo2O4 and Mn1.7CuFe0.3O4 single-layer, and novel MnCo2O4/Mn1.7CuFe0.3O4 dual-layer spinel protective coatings on complex-shaped metallic interconnects by EPD method. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2024, 83, 563–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Chen, X.; Wang, Z.; Fu, B.; Liu, J.; Peng, W.; Cao, Y.; Hu, M. Preparation of graphene-manganese cobaltate composites by solid-state roasting-ball milling and its electromagnetic wave absorption property. Mater. Res. Bull. 2025, 184, 113257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Shen, C.; Liu, J.; Zhang, W.; Yao, S. Three-dimensional MnCo2O4/graphene composites for supercapacitor with promising electrochemical properties. J. Alloys Compd. 2019, 792, 122–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Zhao, Y.; Xue, H.; Xie, J.; Feng, C.; Li, H.; Shi, D.; Muhammad, S.; Jiao, Q. Preparation of flower-like CoFe2O4@graphene composites and their microwave absorbing properties. Mater. Lett. 2018, 223, 186–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, H.; Duan, Y.; Liu, J.; Zhang, B. Low-temperature synthesis and microwave absorbing properties of Mn3O4–graphene nanocomposite. J. Mater. Res. 2018, 33, 4062–4070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, Y.; Xiao, J.; Jia, Q.; Lu, L.; Fan, H. Preparation and microwave absorption properties of ZnFe2O4/polyaniline/graphene oxide composite. Results Phys. 2019, 13, 102221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Tan, D.; Tian, K.; Hu, W.; Wang, J.; Su, M.; Li, L. Facile Preparation of Core–Shell Fe3O4@Polypyrrole Composites with Superior Electromagnetic Wave Absorption Properties. J. Phys. Chem. C 2017, 29, 15784–15792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Sun, B.; Wei, X.; Yang, L.; Wu, H. Stimulating Zn2+ permselectivity for prominent zinc anode reversibility by designing a self-assembled artificial layer. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 455, 140827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, G.; Wen, B.; Zhou, Z.; Wang, S.; Zhao, H.; Ding, S.; Yan, W. Flexible cobalt nanoparticles/carbon nanofibers with macroporous structures toward superior electromagnetic wave absorption. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2023, 636, 194–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, X.; Hong, J.; Wang, C.; Su, M.; Zhou, S. CoZnO/C@BCN nanocomposites derived from bimetallic hybrid ZIFs for enhanced electromagnetic wave absorption. J. Mater. Chem. A 2023, 11, 17737–17747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, S.; Tang, X.; Fan, W.; Lan, Q.; Li, L.; Ma, P.; Dong, W.; Wang, Z.; Liu, T. Ultralight and ordered lamellar polyimide-based graphene foams with efficient broadband electromagnetic absorption. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2022, 102, 97–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Sample | Element Contents (wt.%) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Co | Mn | Zn | Cd | Cu | |
| Cobalt-Rich Slag Before Washing | 22.01 | 19.64 | 6.19 | 3.41 | 0.03 |
| Cobalt-Rich Slag After Washing | 21.08 | 19.04 | 3.11 | 2.68 | 0.03 |
| Materials | RLmin [dB]/Thickness [mm] | EBA [GHz]/Thickness [mm] | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| MC@G | −40 dB/4.5 | 5.2 GHz/4.5 | This Study |
| Fe3O4@polypyrrole | −41.9 dB/2.0 | 6.0 GHz/2.0 | [37] |
| Fe-HPCNFs | −46.9 dB/2.0 | 3 GHz/2.0 | [38] |
| MCF/Co | −40.1 dB/3.0 | 6.24 GHz/3.0 | [39] |
| CoZnO/C@BCN | −54.9 dB/3.8 | 5.2 GHz/1.9 | [40] |
| Polyimide-based graphene foam | −61.29 dB/4.75 | 5.51 GHz/4.75 | [41] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shu, X.; Wang, Z.; Chen, R.; Fan, Y. A New Strategy for the High-Value Utilization of Cobalt Slag: A Solid-State Reaction for the Preparation of Microwave-Absorbing Composite Materials with Excellent Properties. Materials 2025, 18, 1373. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18061373
Shu X, Wang Z, Chen R, Fan Y. A New Strategy for the High-Value Utilization of Cobalt Slag: A Solid-State Reaction for the Preparation of Microwave-Absorbing Composite Materials with Excellent Properties. Materials. 2025; 18(6):1373. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18061373
Chicago/Turabian StyleShu, Xuanzhao, Zeying Wang, Rifan Chen, and Yangyang Fan. 2025. "A New Strategy for the High-Value Utilization of Cobalt Slag: A Solid-State Reaction for the Preparation of Microwave-Absorbing Composite Materials with Excellent Properties" Materials 18, no. 6: 1373. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18061373
APA StyleShu, X., Wang, Z., Chen, R., & Fan, Y. (2025). A New Strategy for the High-Value Utilization of Cobalt Slag: A Solid-State Reaction for the Preparation of Microwave-Absorbing Composite Materials with Excellent Properties. Materials, 18(6), 1373. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18061373






