Study on Acoustic Properties of Helmholtz-Type Honeycomb Sandwich Acoustic Metamaterials
Highlights
- With the rapid development of the economy and society, noise pollution seriously affects people's work, life, and health, and has become one of the most important factors of environmental pollution. This paper proposes a Helmholtz honeycomb sandwich structure to solve the problem of poor acoustic performance in traditional honeycomb sandwich panels.
- Combining Helmholtz resonators with different resonance frequencies into a honeycomb structure ensures the lightweight characteristics of the structure while improving its acoustic performance.
- Theoretical analysis, numerical simulation, and laboratory experiments have confirmed that under both vertical and irregular incidence conditions, the Helmholtz honeycomb sandwich structure has significantly improved acoustic performance compared to traditional honeycomb panel structures within a certain frequency range.
Abstract
1. Introduction
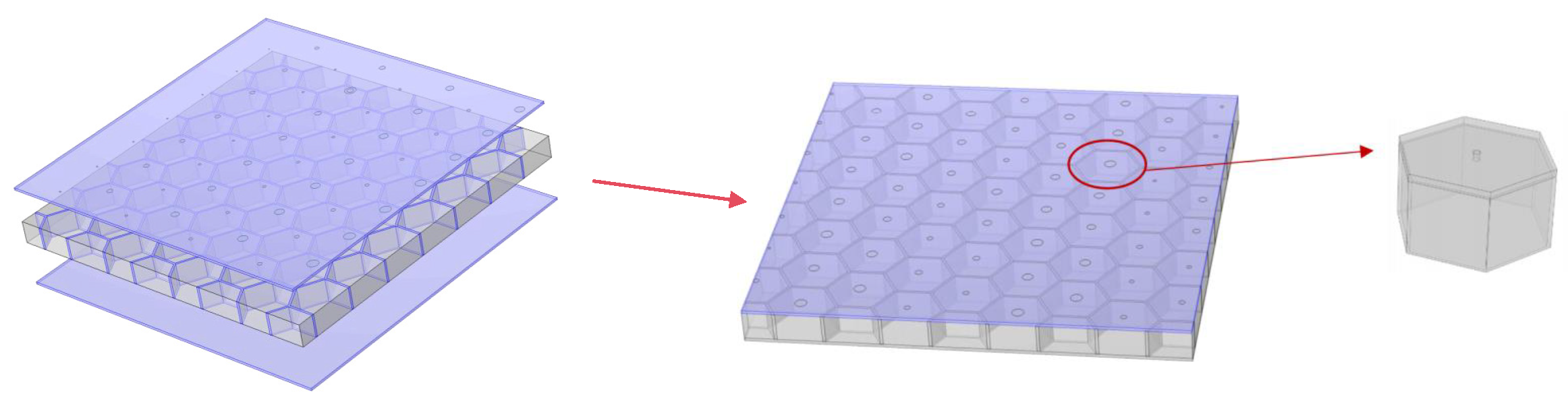
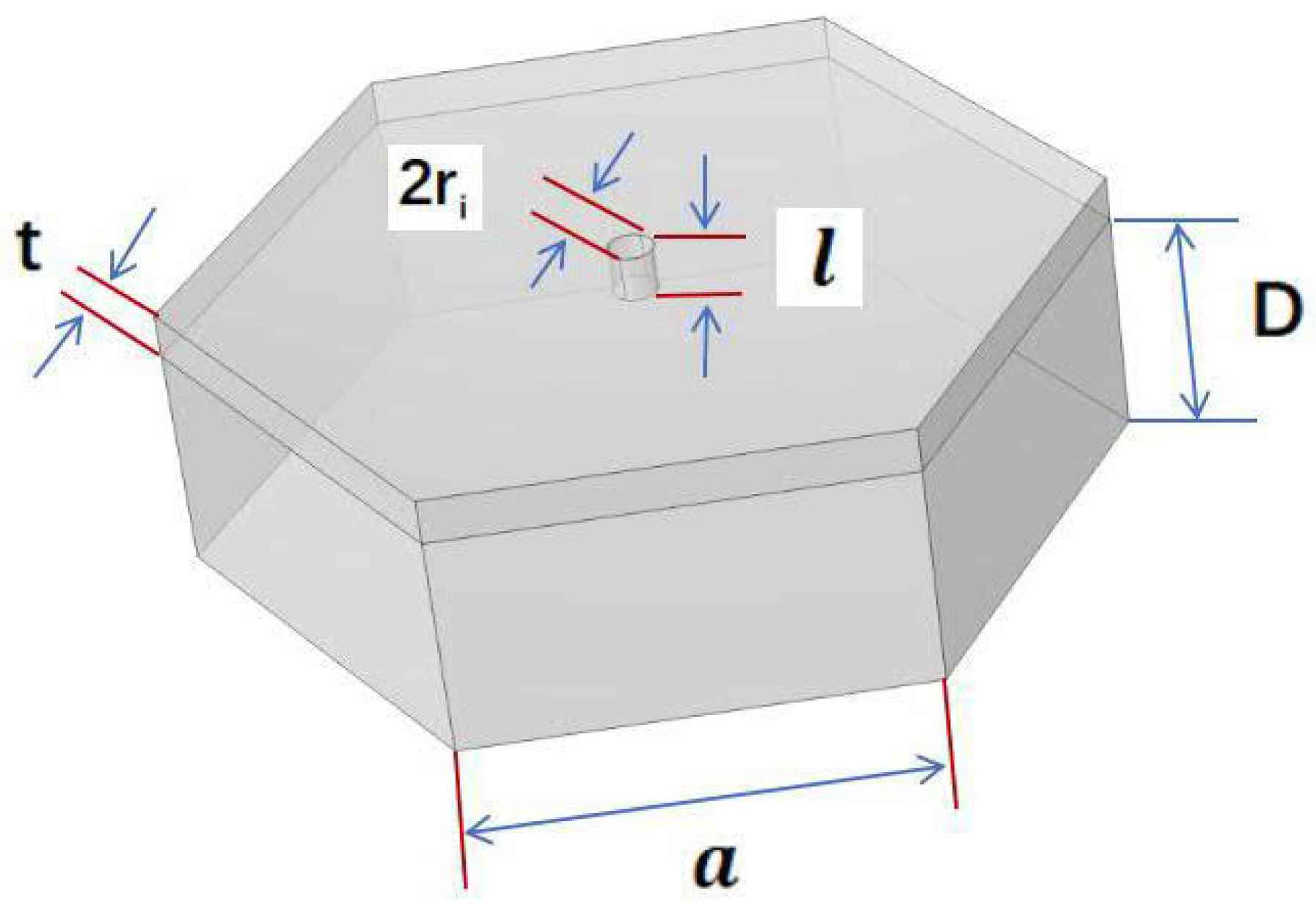
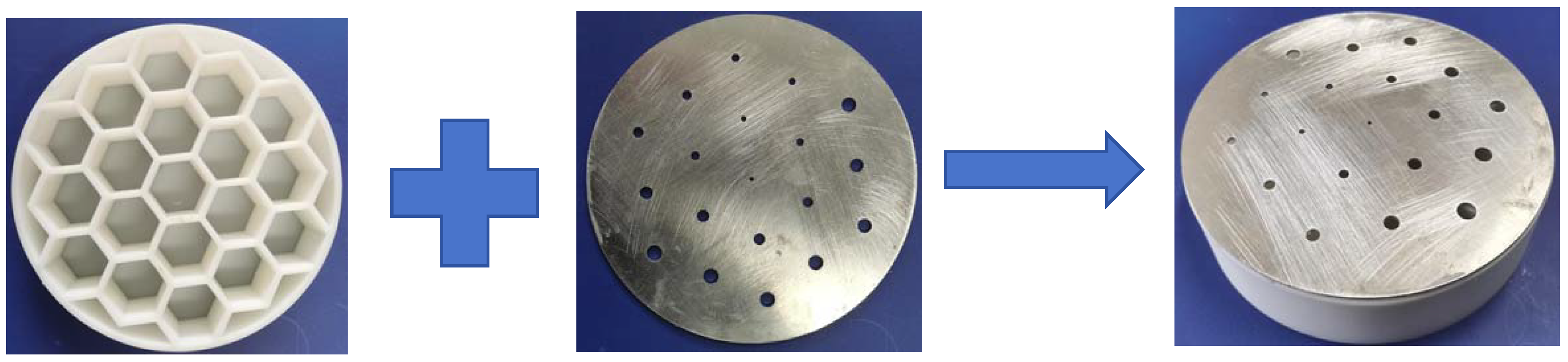
2. Structure of the HHSAM
3. Sound Absorption of Multiple Helmholtz Units
3.1. Sound Absorption Theory
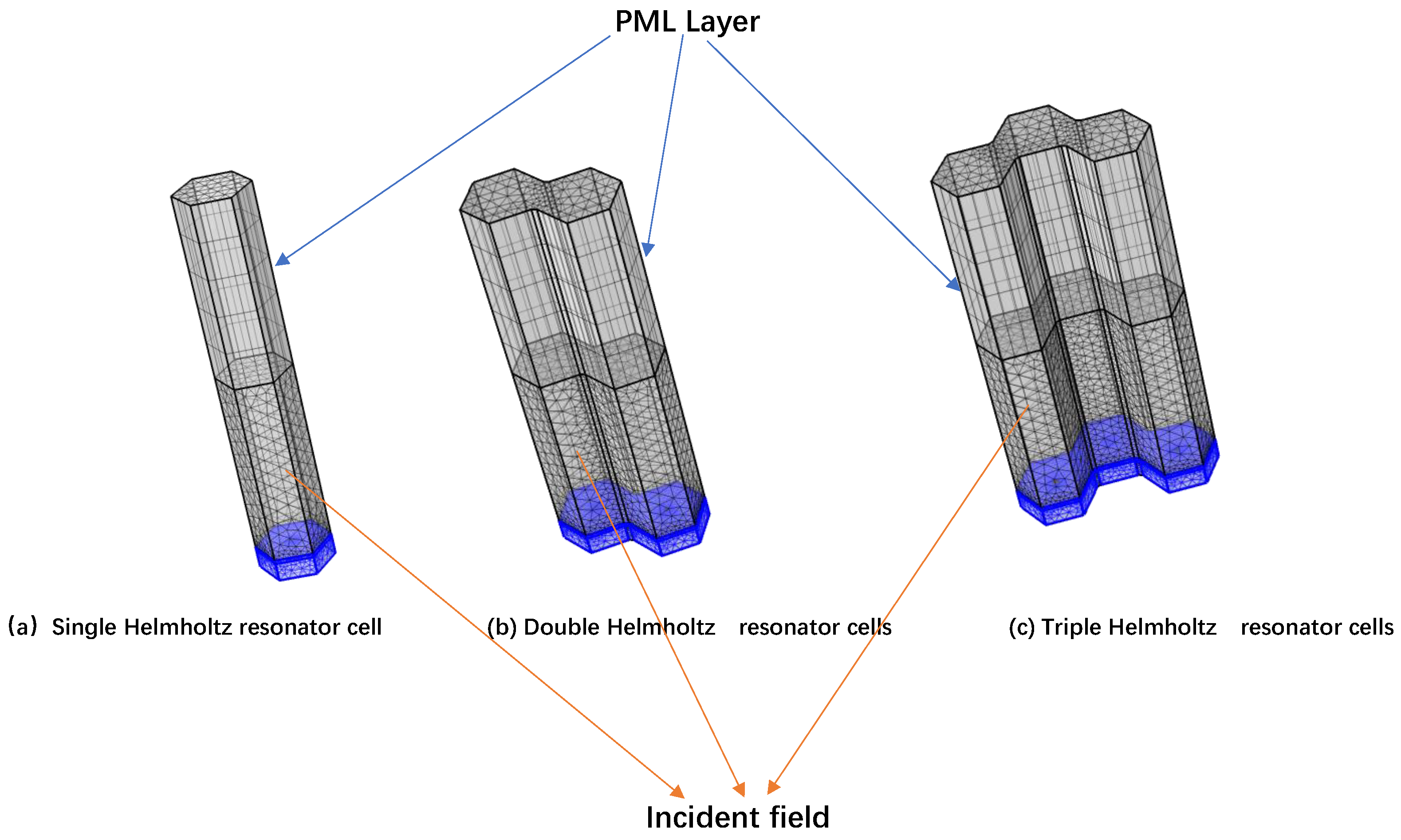
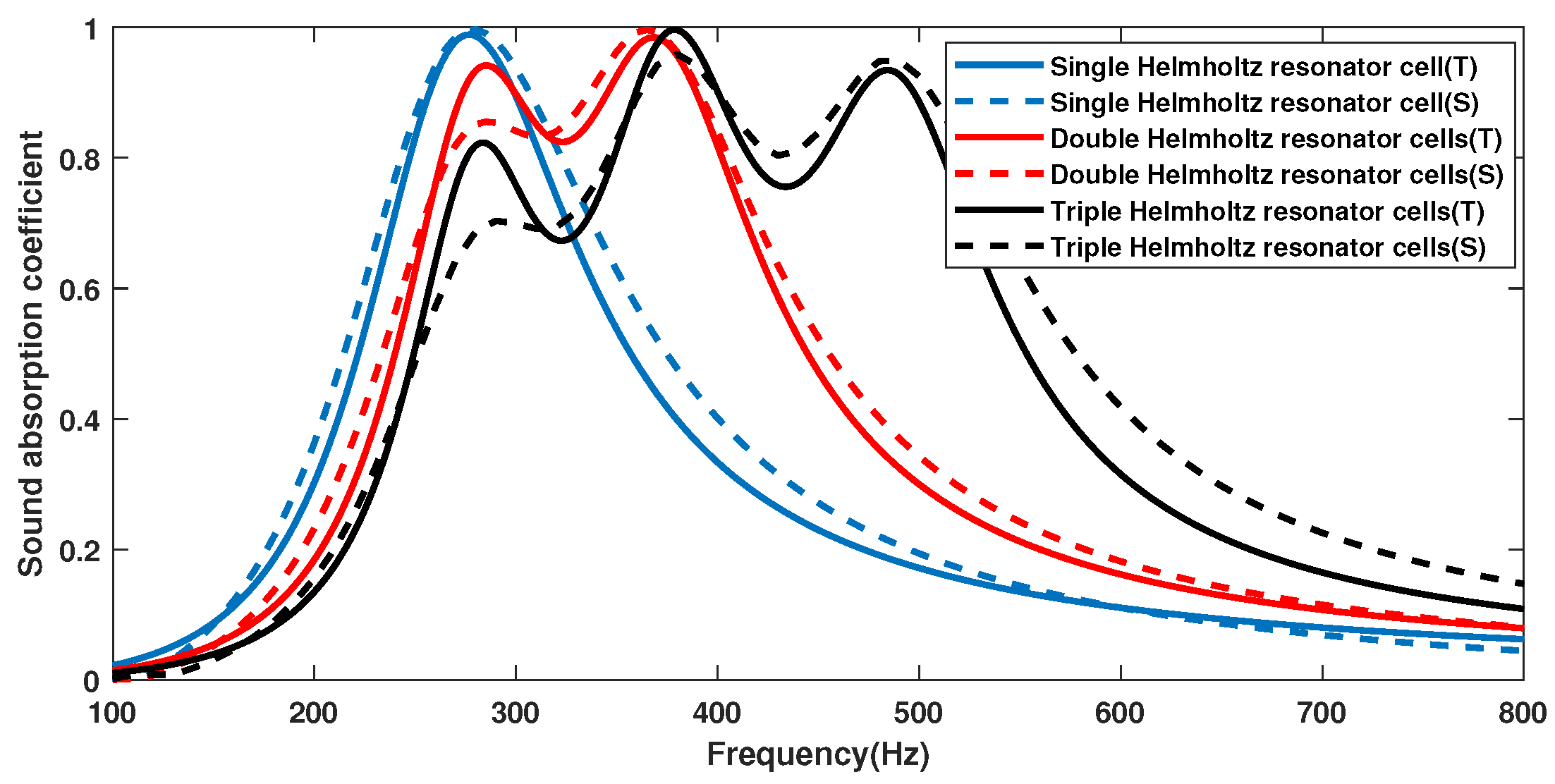
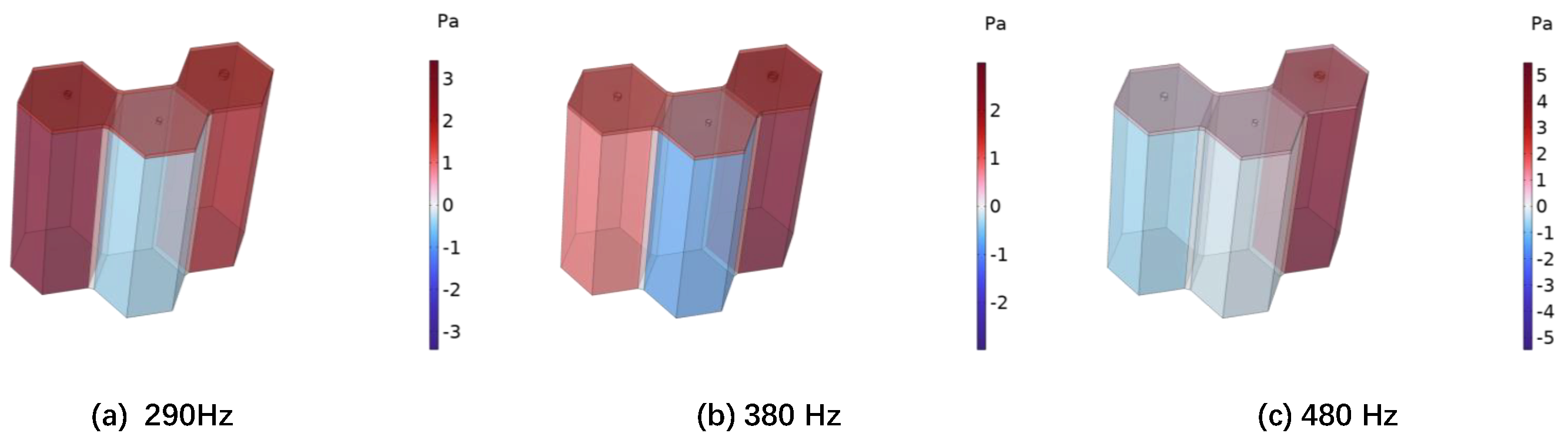
3.2. Numerical Simulation
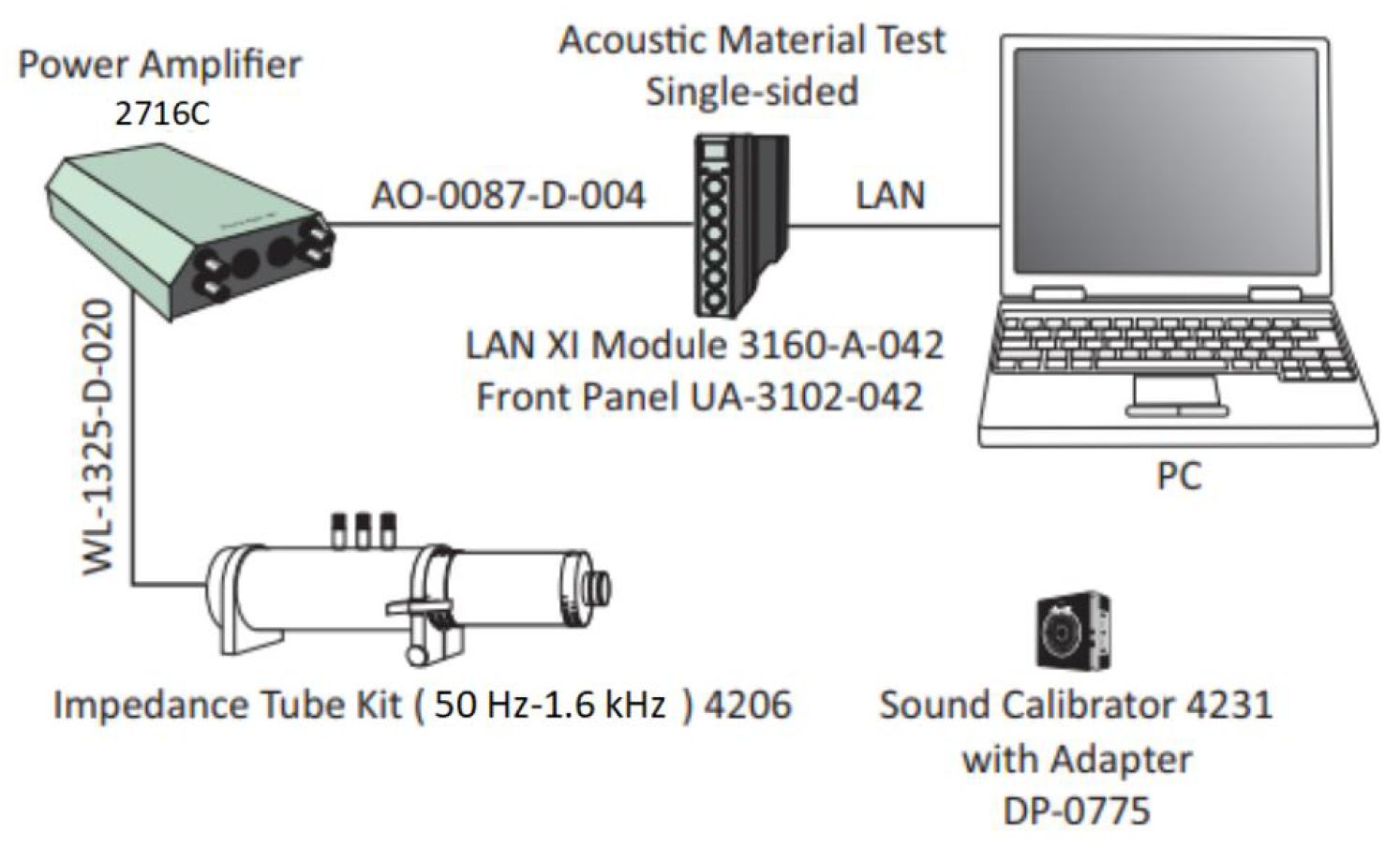
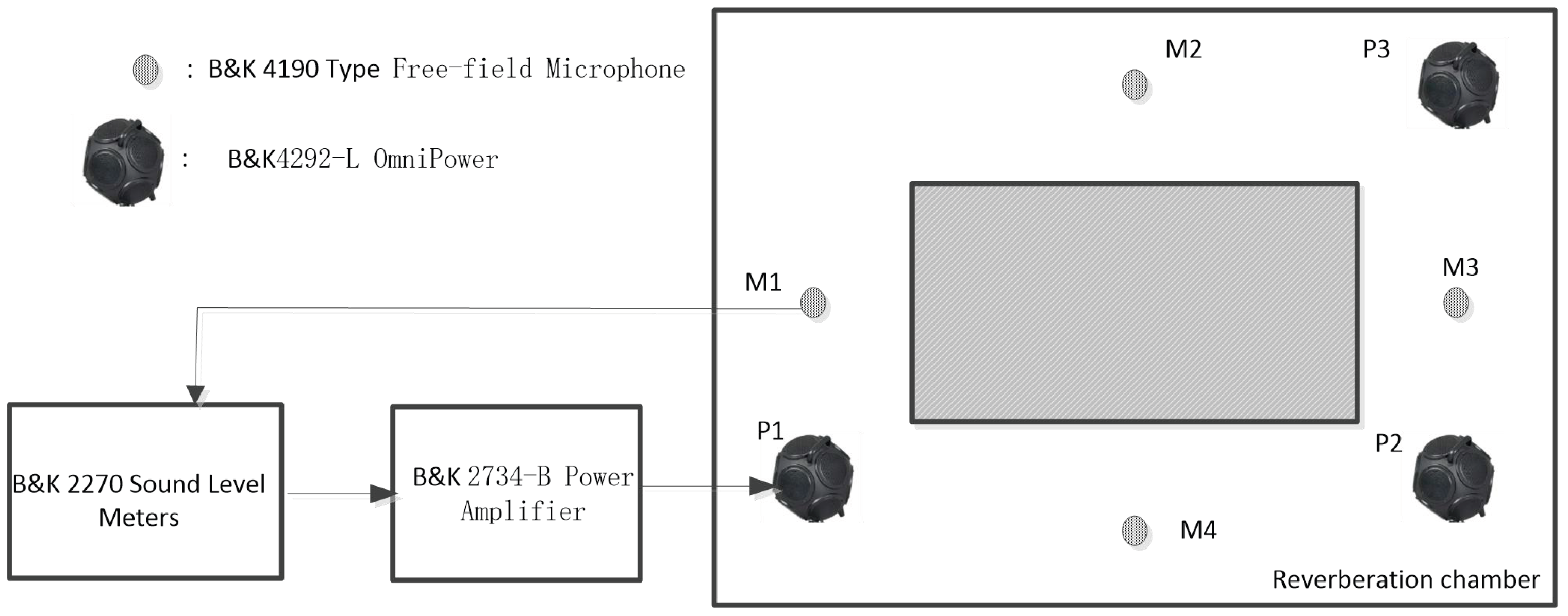
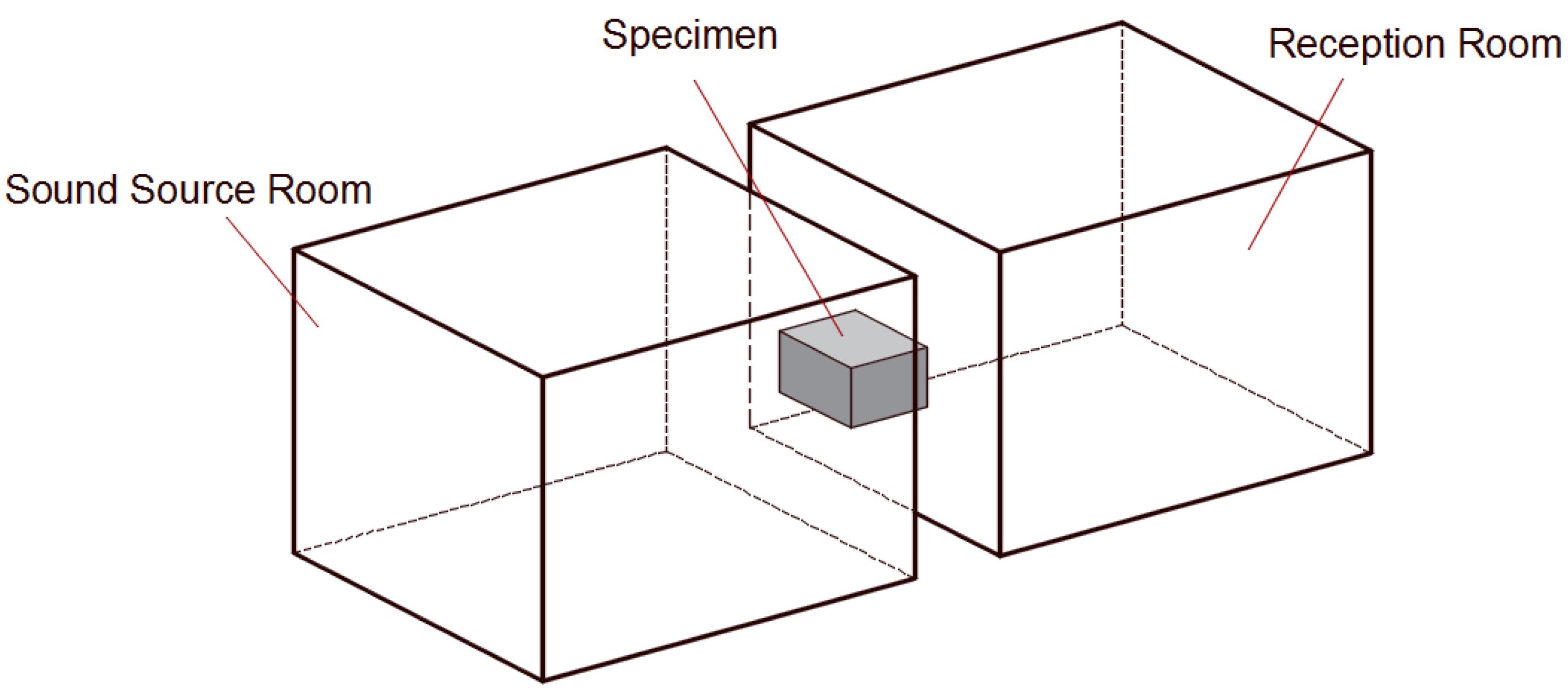
4. Experimental Study on the HHSAM Structure’s Acoustic Performance
4.1. Acoustic Performance Under Vertical Incidence
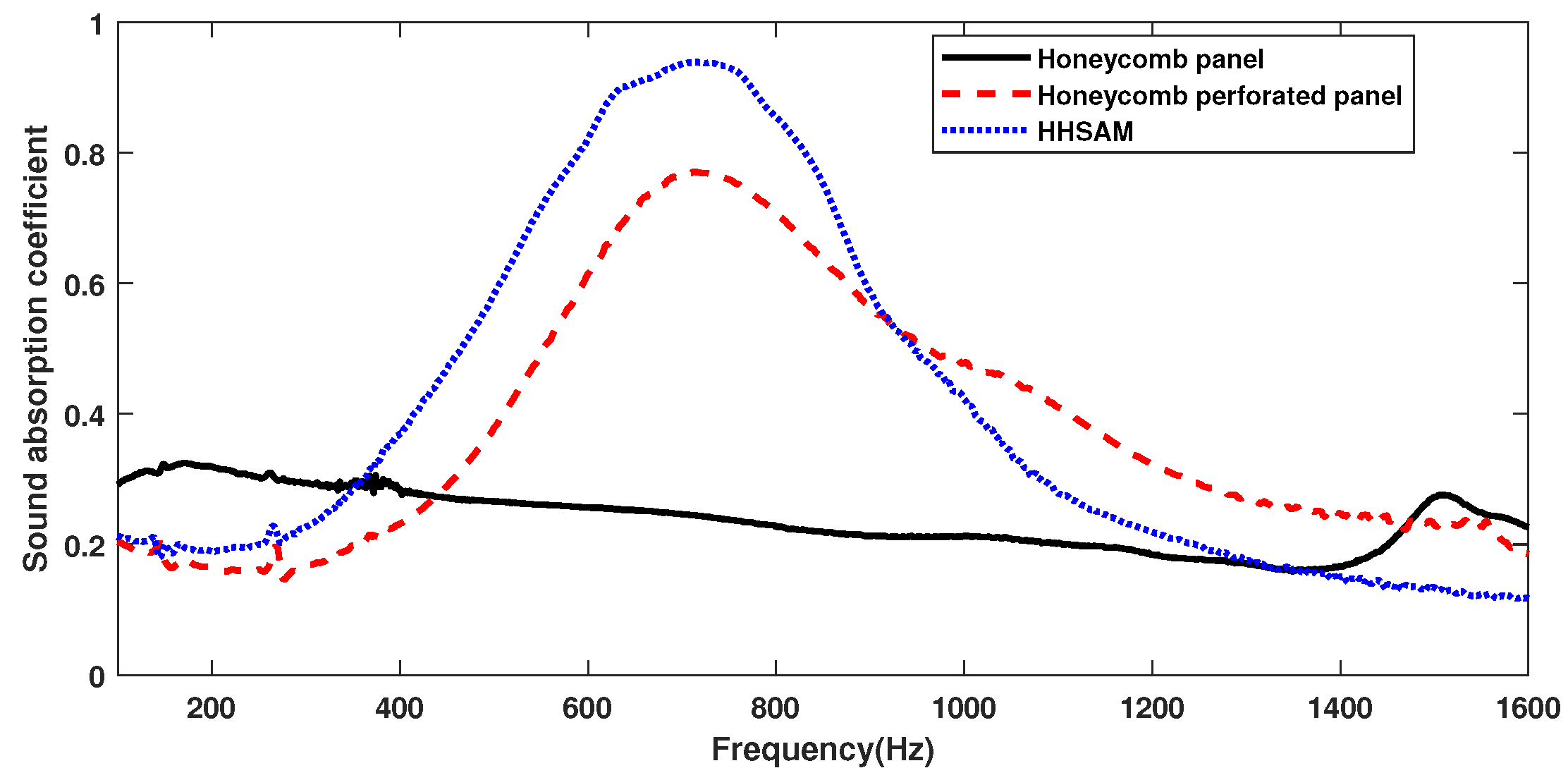
4.1.1. Sound Absorption
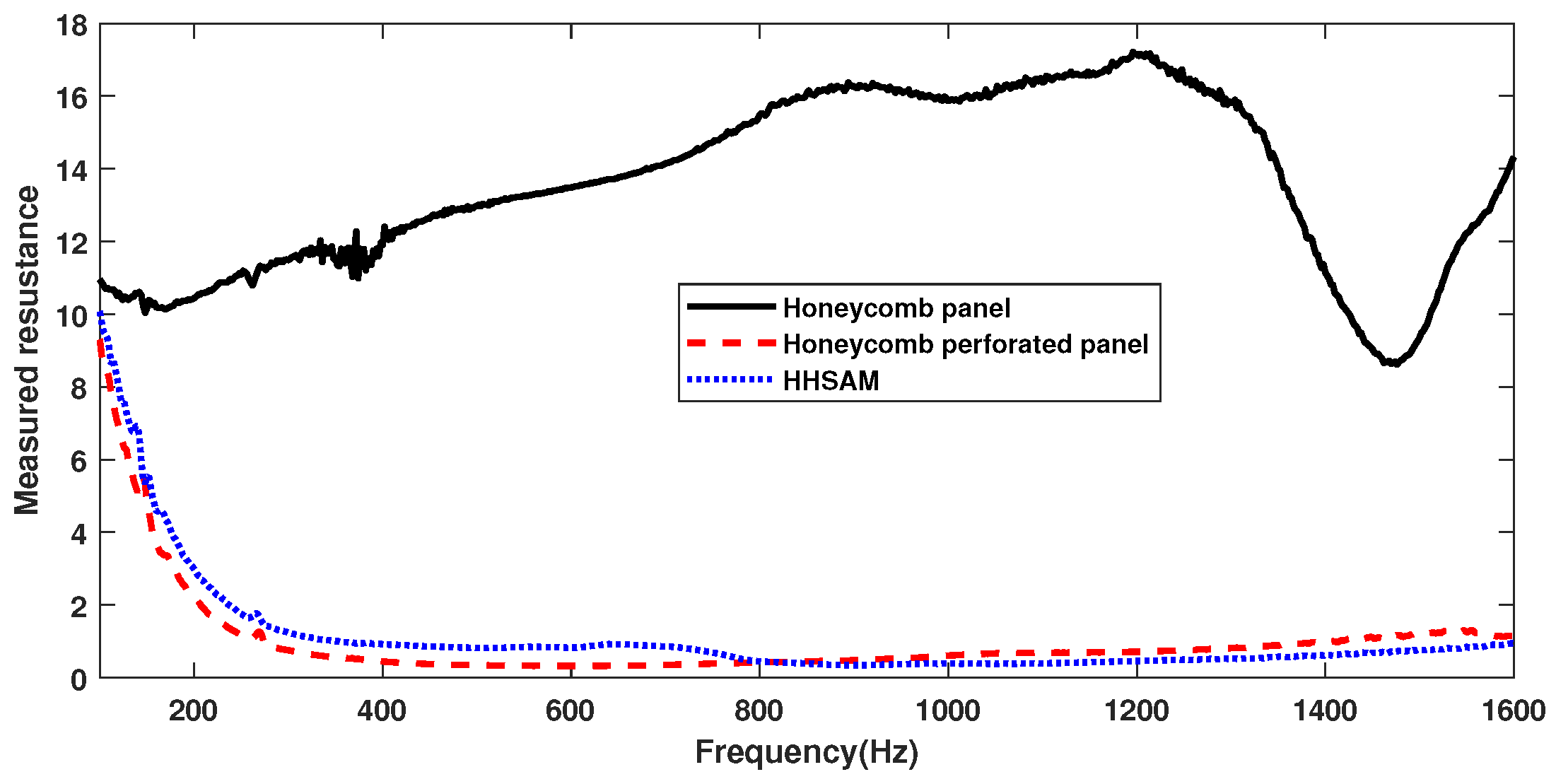
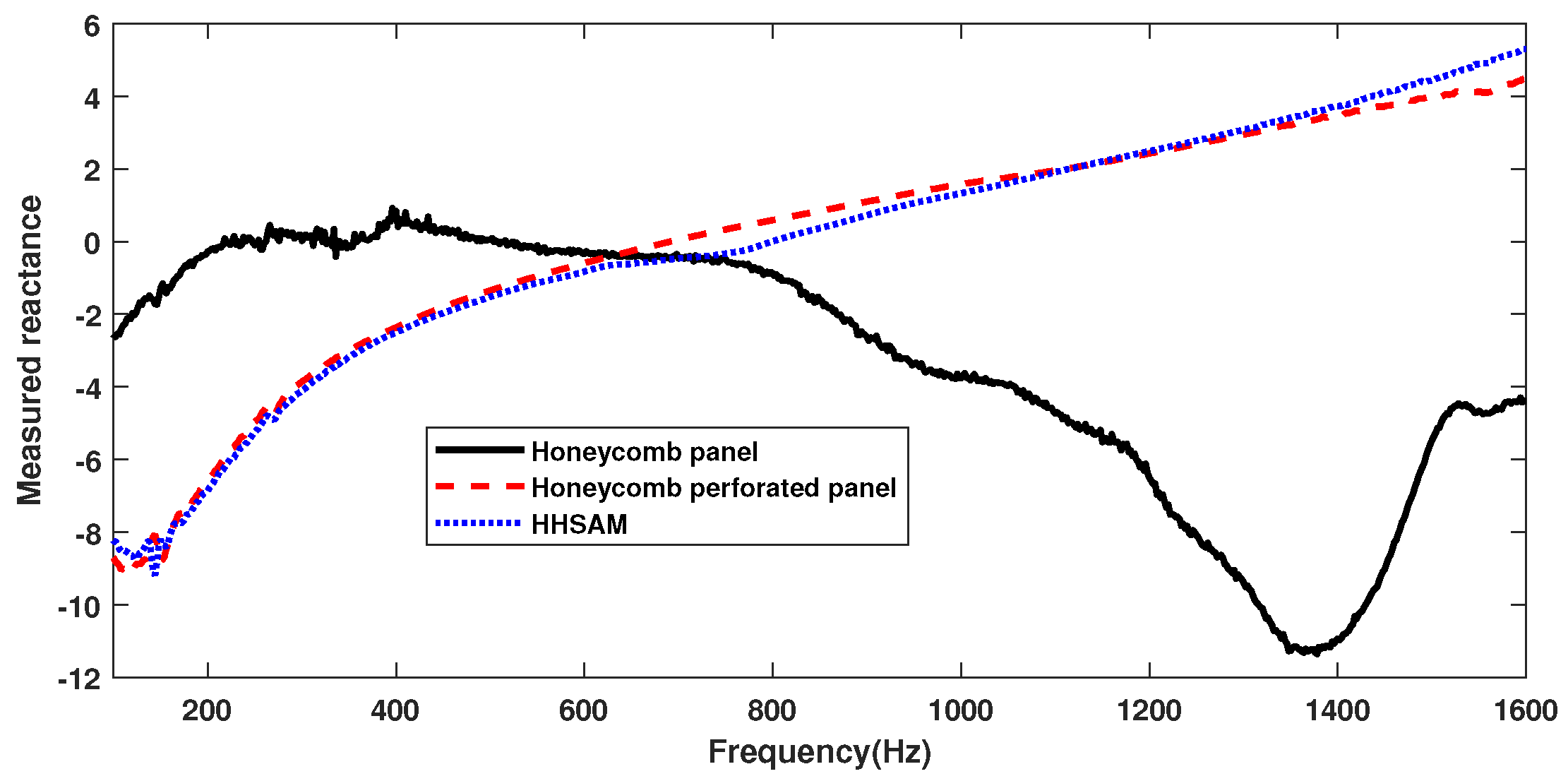
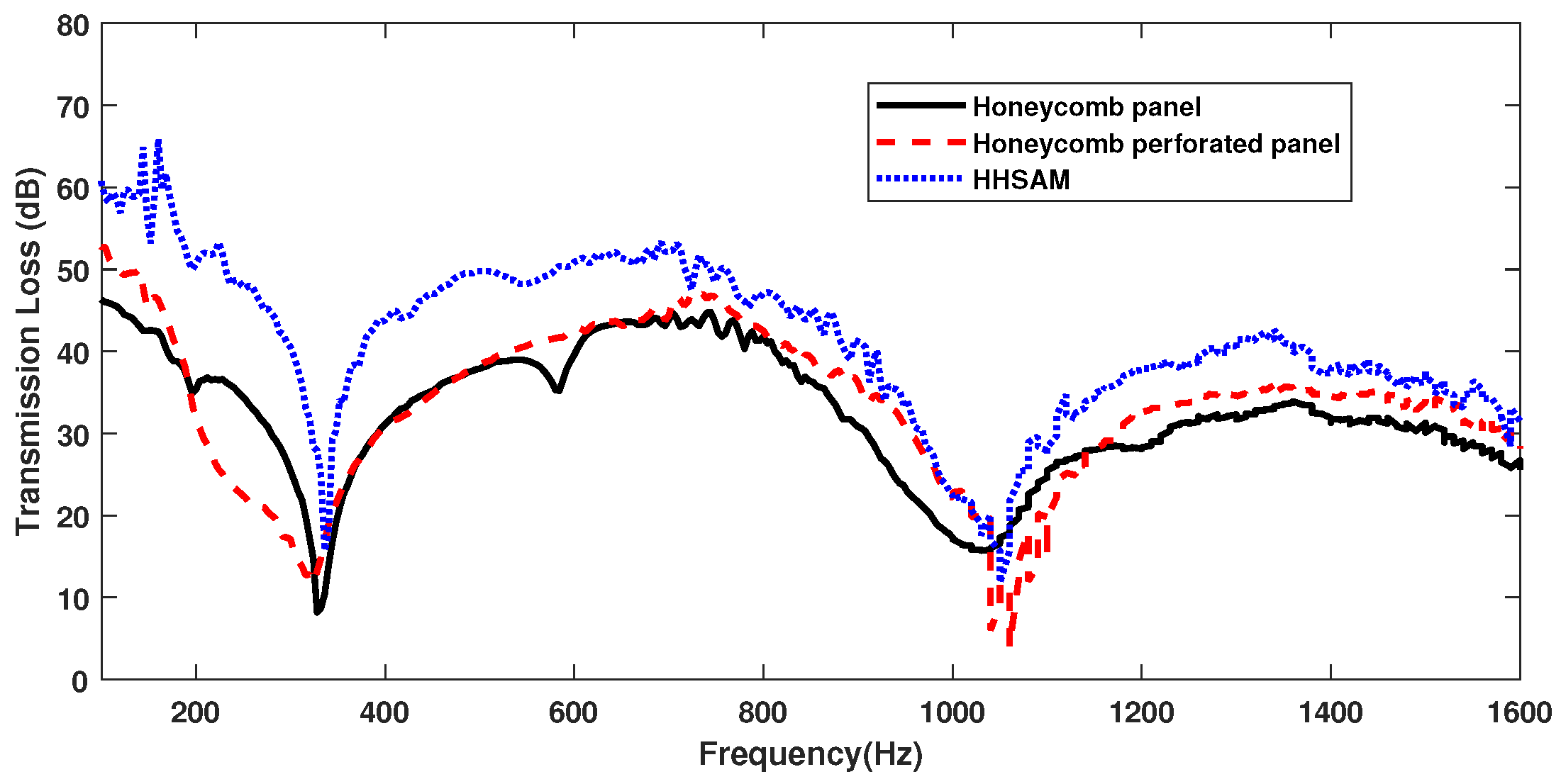
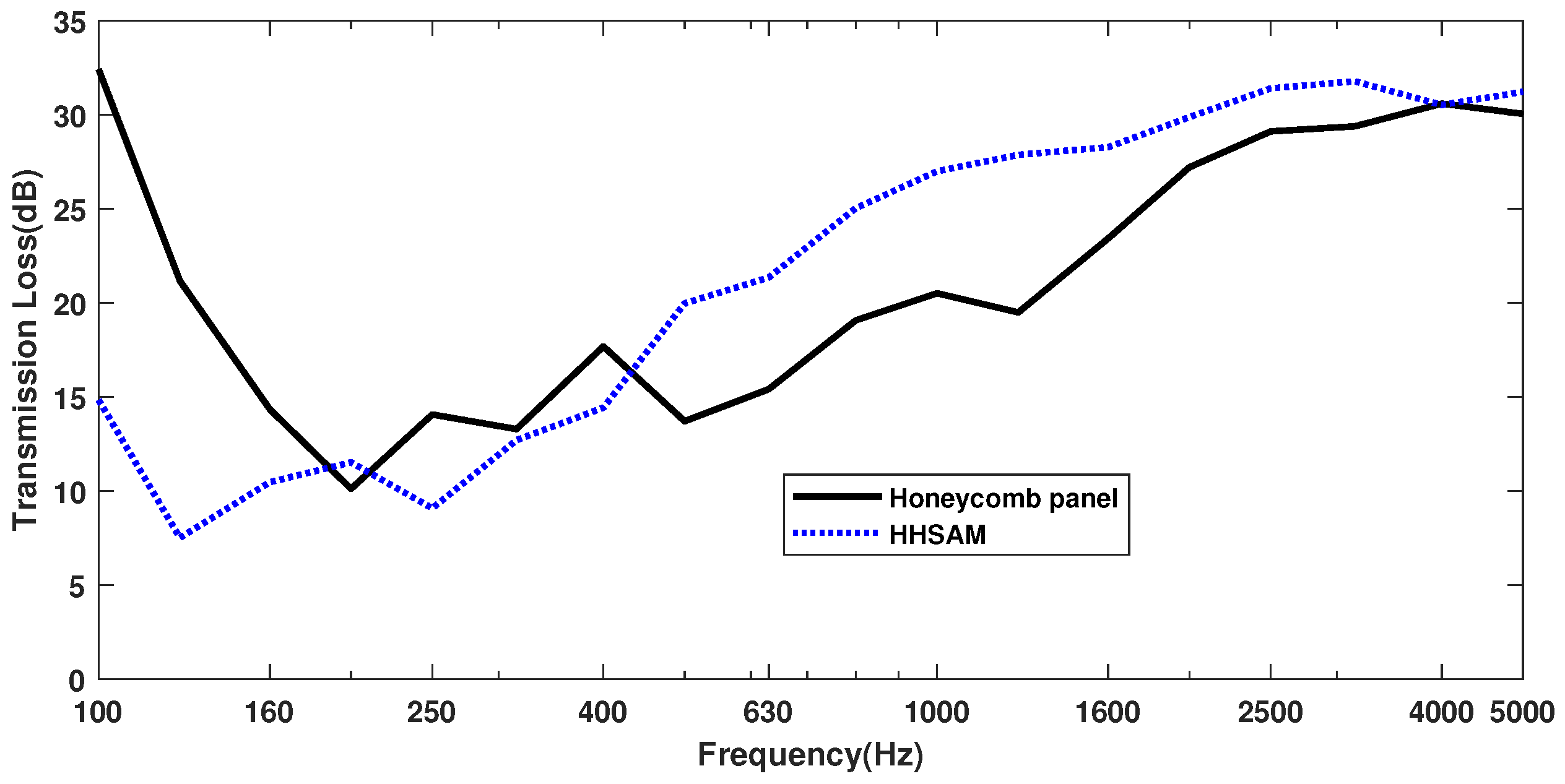
4.1.2. Sound Insulation Property
4.2. Acoustic Performance Under Scattered Sound Field Conditions
4.2.1. Sound Absorption
4.2.2. Sound Insulation Property
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, Y.B.; Xie, J.L.; Lee, H.M.; Lee, H.P. Industrial noise reduction measures based on the Italian prioritisation index. J. Build. Eng. 2025, 99, 111642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danilevicius, A.; Karpenko, M.; Krivanek, V. Research on the noise pollution from different vehicle categories in the urban area. Transport 2023, 38, 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Z.F.; Zhao, X.Q. Reducing construction noise: Sound masking effect on soundscape dominated by construction noise. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2025, 22, 797–832. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, D.L.; Liu, X.H.; Ren, Z.C.; Li, M.N. Relation between noise pollution and life satisfaction based on the 2019 China social survey. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 7015. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, S.; Xiang, T.B.; Lee, H.P. Ventilated acoustic metamaterial window panels for simultaneous noise shielding and air circulation. Appl. Acoust. 2020, 159, 107088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quader, M.A.; Rahman, M.M.; Chisty, M.A.; Hattawi, K.S.A.; Islam, E.A.M.K. Evaluation of noise pollution impact on health in Dhaka city, Bangladesh. Front. Public Health 2024, 12, 2296–2565. [Google Scholar]
- Monazzam, M.; Karimi, E.; Abbaspour, M.; Nassiri, P.; Taghavi, L. Spatial traffic noise pollution assessment—A case study. Int. J. Occup. Med. Environ. Health 2015, 28, 625–634. [Google Scholar]
- Stanovsk, M.; Tomskov, H.; Slachtov, H.; Potuznkov, D.; Argalsov, L. Health impact of environmental and industrial noise—A narrative review. Med. Pr. 2024, 75, 425–431. [Google Scholar]
- Stosiak, M.; Yatskiv, I.; Prentkovskis, O.; Karpenko, M. Reduction of pressure pulsations over a wide frequency range in hydrostatic system. Machines 2025, 13, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.M.; Hua, Y.T.; Wang, Z.M.; Lim, K.M.; Lee, H.P. A review of the application of active noise control technologies on windoes: Challenges and limitations. Appl. Acoust. 2021, 174, 107753. [Google Scholar]
- He, M.F.; Hu, W.B. A study on composite honeycomb sandwich panel structure. Mater. Des. 2008, 29, 709–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, X.; Lee, H.; Weisgraber, T.H.; Shusteff, M.; DeOtte, J.; Duoss, E.B. Ultralight, ultrastiff mechanical metamaterials. Science 2014, 344, 1373–1377. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.L.; Zhang, Y.L.; Xie, S. A lightweight multilayer honeycomb membrane-type acoustic metamaterial. Appl. Acoust. 2020, 168, 107427. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, W.C.; Ng, C.F. Sound insulation improvement using honeycomb sandwich panels. Appl. Acoust. 1998, 53, 163–177. [Google Scholar]
- Ng, C.F.; Hui, C.K. Low frequency sound insulation using stiffness control with honeycomb panels. Appl. Acoust. 2008, 69, 293–301. [Google Scholar]
- Kang, L.D.; Liu, B.L.; An, F.Y.; Wei, D.P. Mechanical and vibro-acoustic performance of sandwich panel with perforated honeycomb cores. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2022, 152, 1539–1546. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Y.; Li, B.B.; Chen, Z.F.; Sui, N.; Chen, Z.; Saeed, M.U.; Li, Y.F.; Fu, R.; Wu, C.; Jing, Y. Acoustic properties of glass fiber assembly-filled honeycomb sandwich panels. Compos. Part B 2016, 96, 281–286. [Google Scholar]
- Boztoprak, Y.; Ünal, M.; Özada, Ç.; Kuzu, E.; Özer, H.; Ergin, F.; Yazıcı, M. Sound insulation performance of honeycomb core aluminum sandwich panels with flexible epoxy-based foam infill. Compos. Struct. 2023, 319, 117149. [Google Scholar]
- Rajaram, S.; Nutt, S. Measurement of sound transmission losses of honeycomb partitions with added gas layers. Noise Control Eng. J. 2006, 54, 101–105. [Google Scholar]
- Naify, C.J.; Huang, C.Z.; Sneddon, M.; Nutt, S. Transmission loss of honeycomb sandwich structures with attached gas layers. Appl. Acoust. 2011, 72, 71–77. [Google Scholar]
- Meng, H.; Galland, M.A.; Ichchou, M.; Xin, F.X.; Lu, T.J. On the low frequency acoustic properties of novel multifunctional honeycomb sandwich panels with micro-perforated faceplates. Appl. Acoust. 2019, 152, 31–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, X.Y.; Ji, J.; Jing, Y. Composite honeycomb metasurface panel for broadband sound absorption. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2018, 144, 255–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sui, N.; Yan, X.; Huang, T.Y.; Xu, J.; Yuan, F.G.; Jing, Y.A. Lightweight yet sound-proof honeycomb acoustic metamaterial. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2015, 106, 171905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, K.; Wu, J.H.; Guan, D.; Gao, N.S.; Jing, L. A lightweight low-frequency sound insulation membrane-type acoustic metamaterial. AIP Adv. 2016, 6, 025116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peiffer, A.; Grunewald, M.; Lempereur, P.; Ni, S.; Xiang, Y.; Huang, T.Y.; Xu, J.; Yuan, F.G. Comment on “A lightweight yet sound-proof honeycomb acoustic metamaterial”. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2015, 107, 216101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, H.; Huang, X.C.; Chen, Y.Y.; Theodossiades, S.; Chronopoulos, D. Structural vibration absorption in multilayered sandwich structures using negative stiffness nonlinear oscillators. Appl. Acoust. 2021, 182, 108240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasser, D.; Mohamed, A.E. Numerical and experimental investigation of negative stiffness beams and honeycomb structures. Eng. Struct. 2024, 301, 117163. [Google Scholar]









Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gai, X.-L.; Li, X.-H.; Guan, X.-W.; Xing, T.; Cai, Z.-N.; Hu, W.-C. Study on Acoustic Properties of Helmholtz-Type Honeycomb Sandwich Acoustic Metamaterials. Materials 2025, 18, 1600. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18071600
Gai X-L, Li X-H, Guan X-W, Xing T, Cai Z-N, Hu W-C. Study on Acoustic Properties of Helmholtz-Type Honeycomb Sandwich Acoustic Metamaterials. Materials. 2025; 18(7):1600. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18071600
Chicago/Turabian StyleGai, Xiao-Ling, Xian-Hui Li, Xi-Wen Guan, Tuo Xing, Ze-Nong Cai, and Wen-Cheng Hu. 2025. "Study on Acoustic Properties of Helmholtz-Type Honeycomb Sandwich Acoustic Metamaterials" Materials 18, no. 7: 1600. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18071600
APA StyleGai, X.-L., Li, X.-H., Guan, X.-W., Xing, T., Cai, Z.-N., & Hu, W.-C. (2025). Study on Acoustic Properties of Helmholtz-Type Honeycomb Sandwich Acoustic Metamaterials. Materials, 18(7), 1600. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18071600





