Influence of Carbon Nanotube Addition on Microstructure and Microwave Heating Performance of Polycarbosilane-Based Silicon Carbide
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
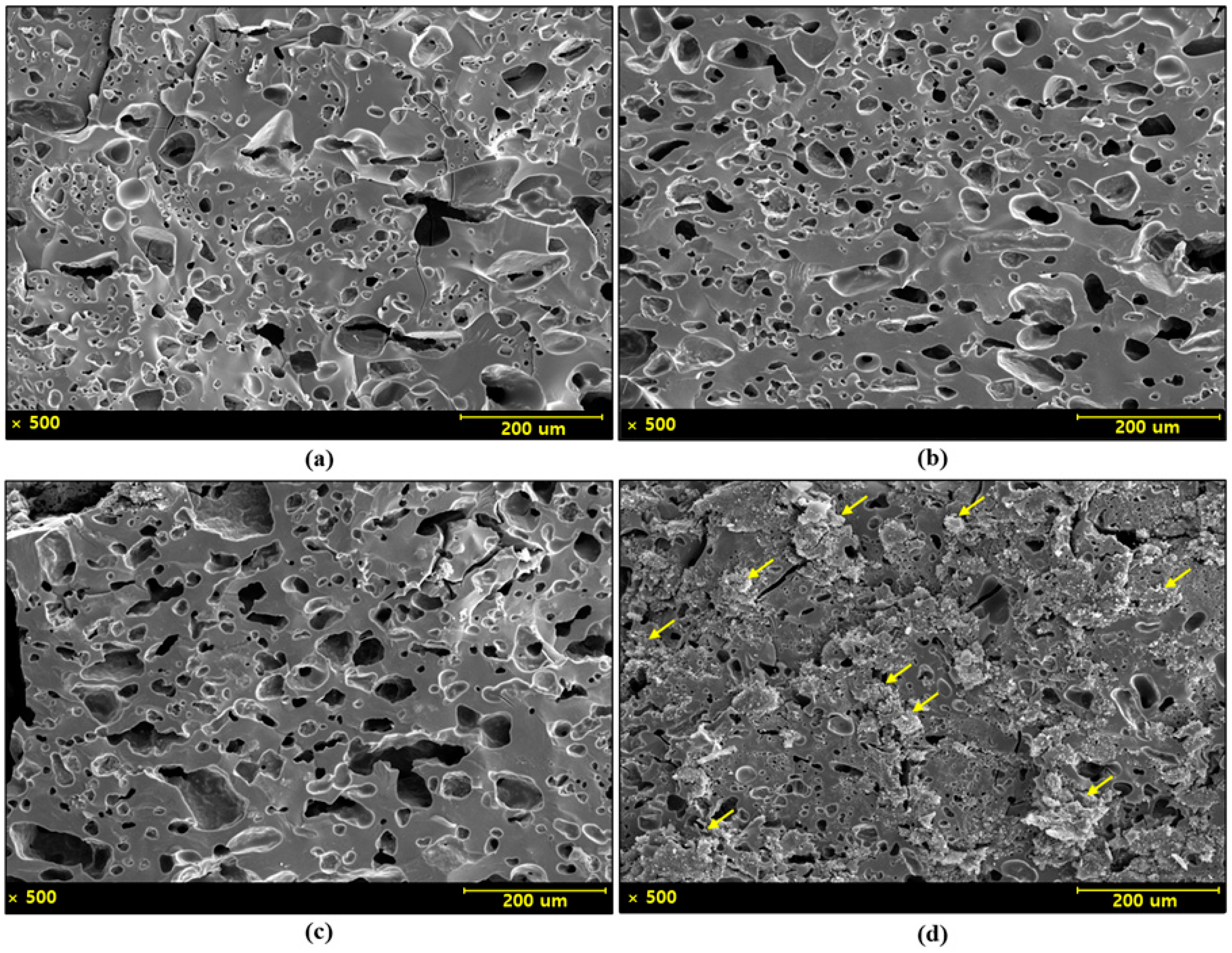
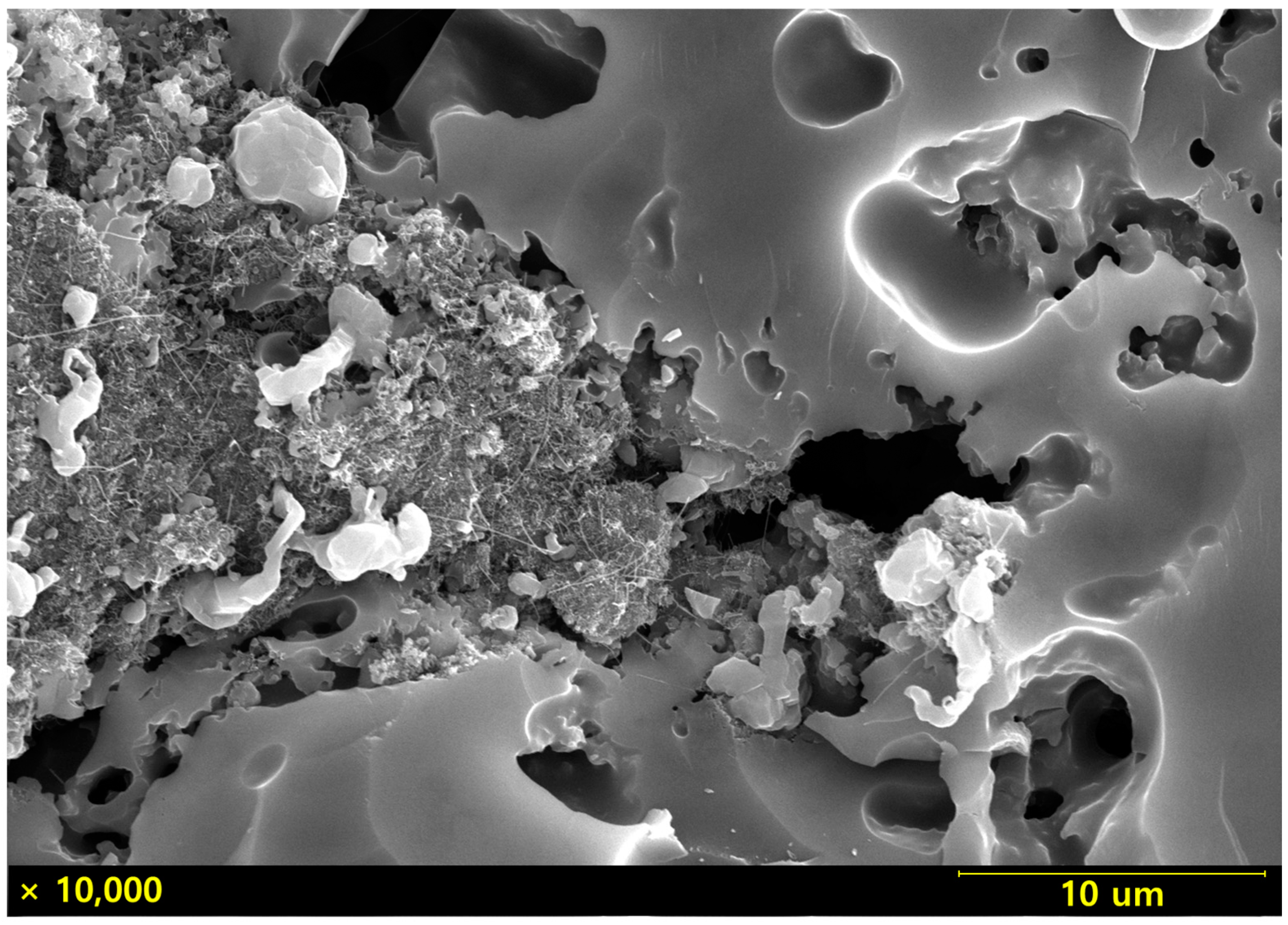
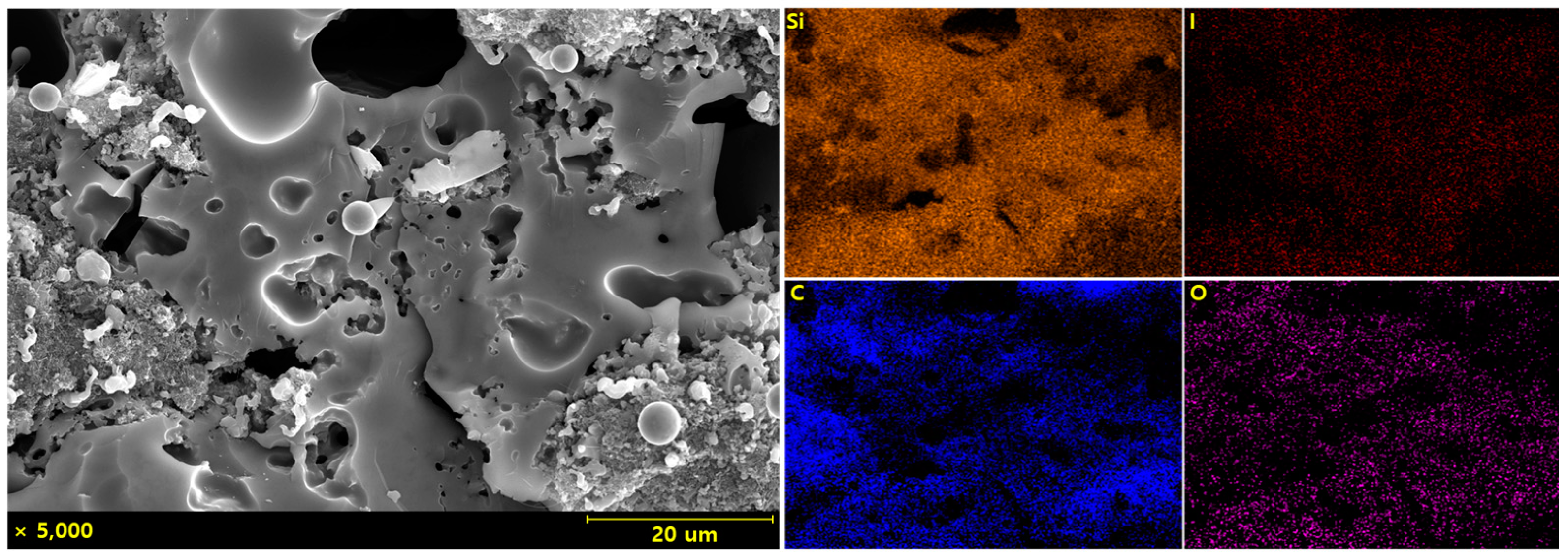
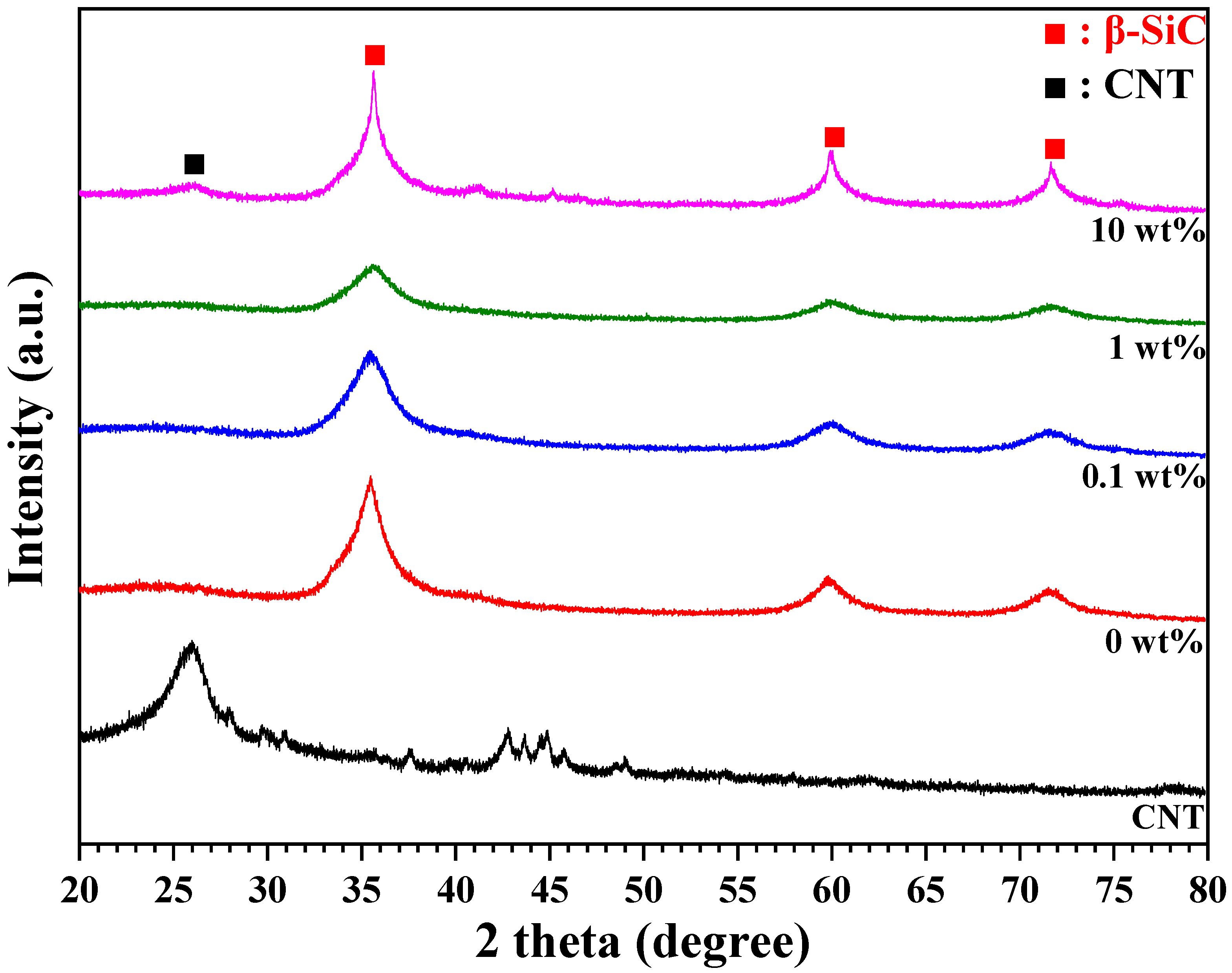
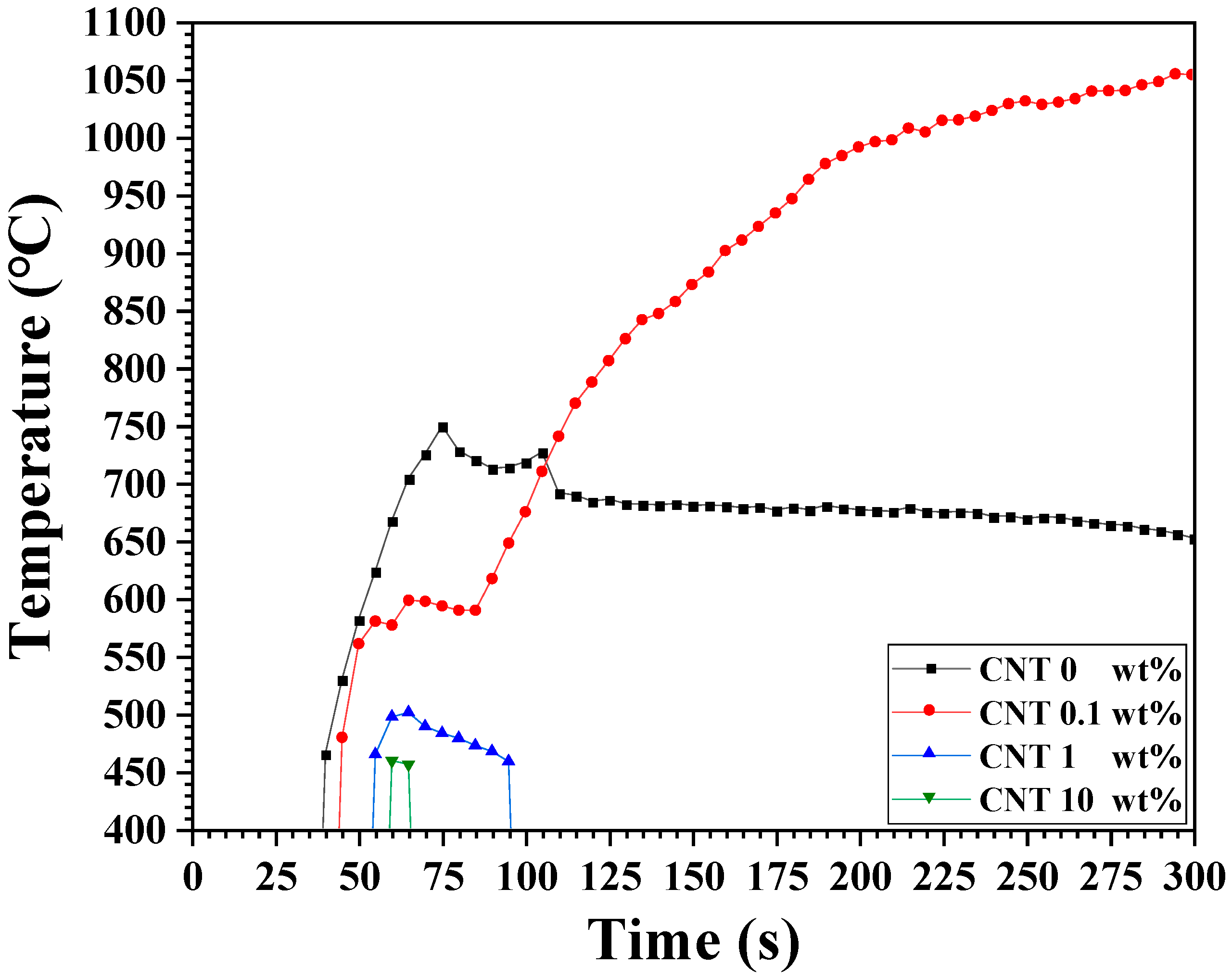
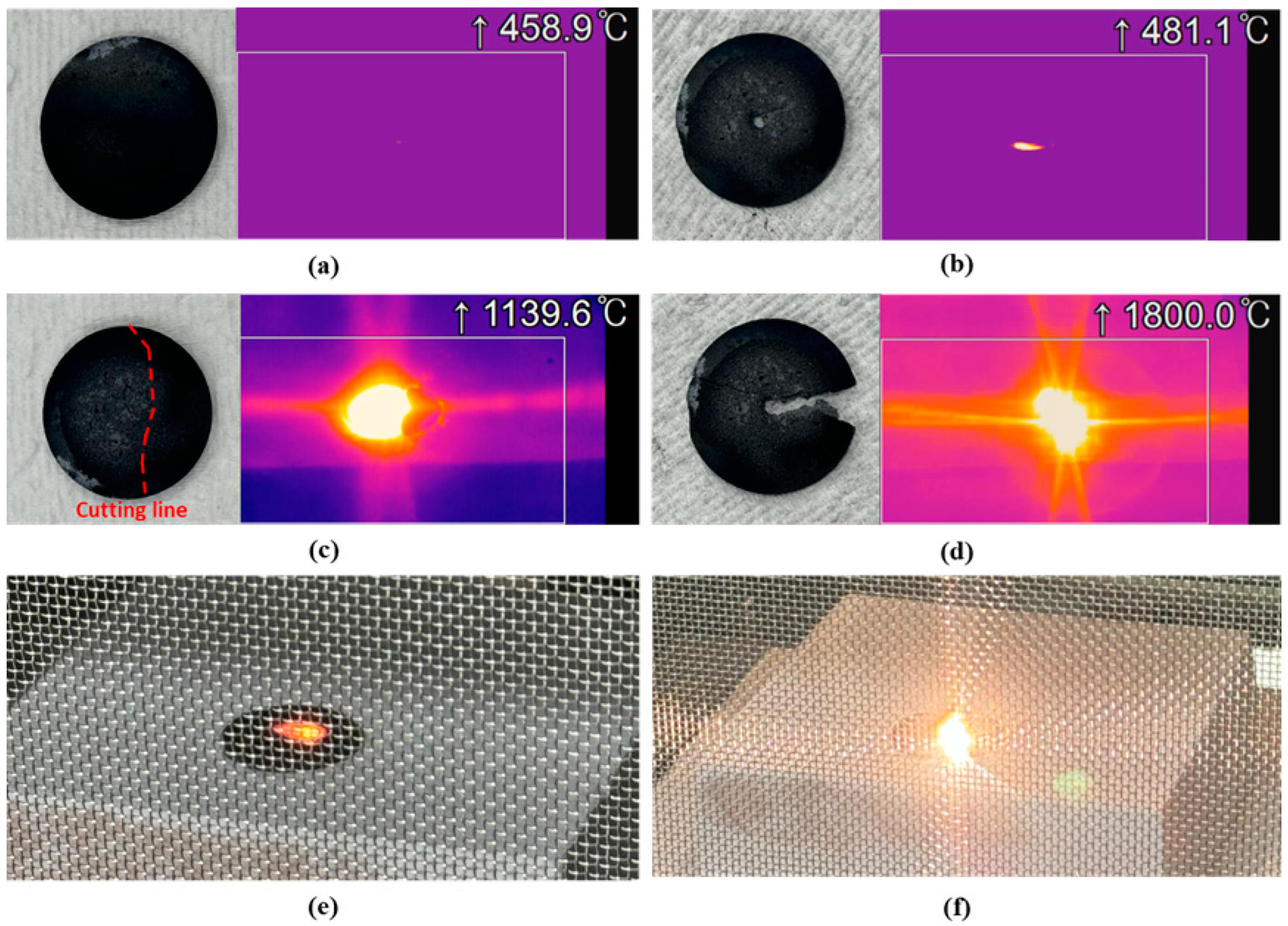
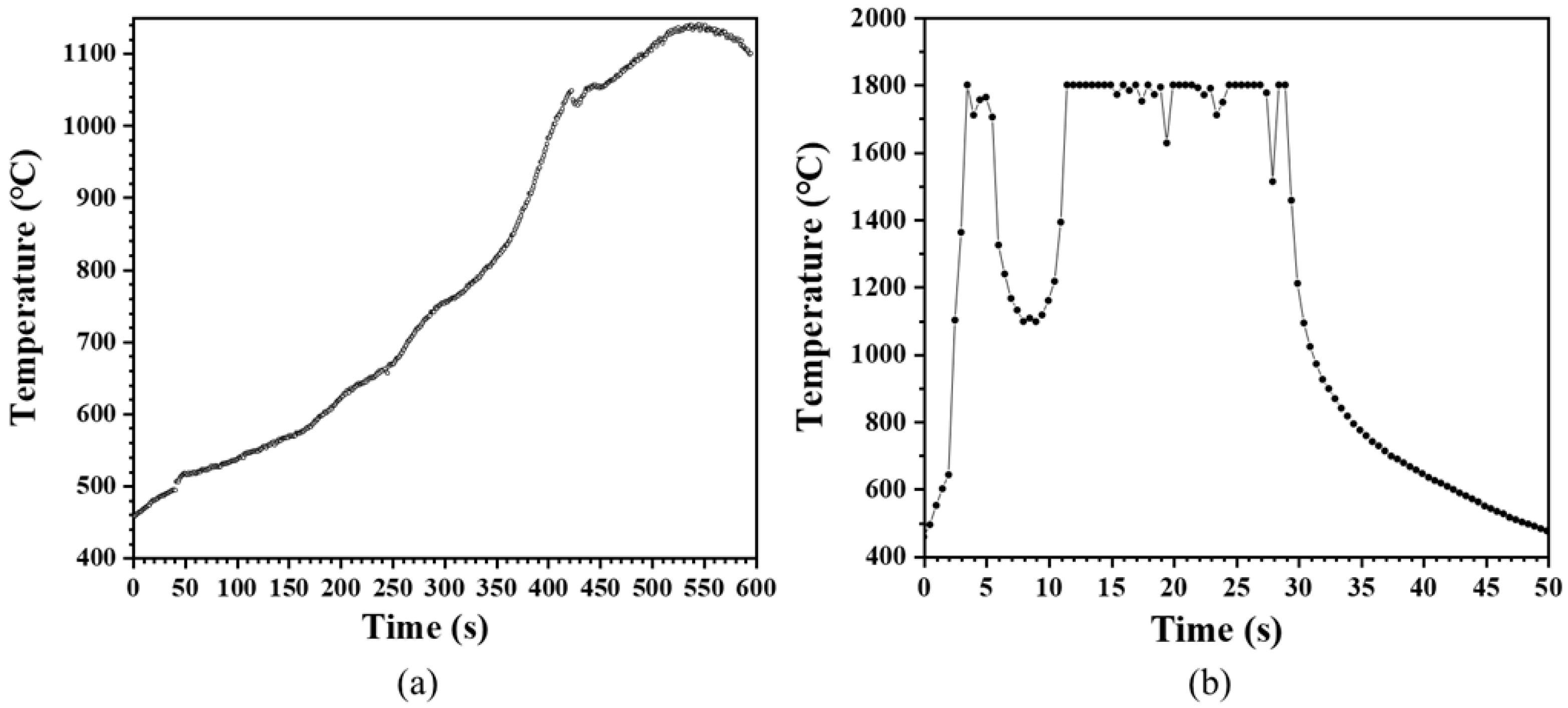
3. Results
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Eom, J.H.; Kim, Y.W.; Raju, S. Processing and properties of macroporous silicon carbide ceramics: A review. J. Asian. Ceram. Soc. 2013, 1, 220–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Dong, S.; Li, X.; Hong, C.; Zhang, X. Synthesis, properties, and multifarious applications of SiC nanoparticles: A review. Ceram. Int. 2022, 48, 8882–8913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, R.; Zhou, N.; Zhang, K.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, L.; Wang, W.; Feng, D. Progress and challenges towards additive manufacturing of SiC ceramic. J. Adv. Ceram. 2012, 10, 637–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yajima, S.; Hayashi, J.; Omori, M.M. Continuous silicon carbide fiber of high tensile strength. Chem. Lett. 1975, 4, 931–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yajima, S.; Okamura, K.; Hayashi, J. Structural analysis in continuous silicon carbide fiber of high tensile strength. Chem. Lett. 1975, 4, 1209–1212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eswara Prasad, N.; Wanhill, R.J.H. Aerospace Materials and Material Technologies: Vol. 1: Aerospace Materials; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 2017; p. 371. [Google Scholar]
- Sauder, S. Ceramic Matrix Composites: Nuclear Applications, Ceramic Matrix Composites: Materials, Modeling and Technology; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 2014; p. 609. [Google Scholar]
- Joo, Y.J.; Cho, K.Y. Microwave-assisted heating behavior of amorphous SiC fibers derived from polycarbosilane. Mater. Res. Express. 2021, 8, 035603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khishigbayar, K.E.; Joo, Y.J.; Cho, K.Y. Microwave-assisted heating of electrospun SiC fiber mats. J. Korean Ceram. Soc. 2017, 54, 499–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Zhang, L.; Cheng, L.; Wang, Y.; Yu, Z.; Huang, M.; Tu, H.; Xia, H. Effect of the polycarbosilane structure on its final ceramic yield. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2008, 28, 887–891. [Google Scholar]
- Taki, T.; Ohamura, K.; Sato, M. A study of the oxidation curing mechanism of polycarbosilane fibre by solid-state high-resolution nuclear magnetic resonance. J. Mater. Sci. 1989, 24, 1263–1267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narisawa, M.; Shimoda, M.; Okamura, K.; Sugimoto, M.; Seguchi, T. Reaction mechanism of the pyrolysis of polycarbosilane and polycarbosilazane as ceramic precursors. Bull. Chem. Soc. Jpn. 1995, 68, 1098–1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, C.H.; Beak, J.H.; Kim, S.I.; Park, S.Y.; Kim, S.Y. Investigation of the heating characteristics of microwave silicon carbide heaters under mechanochemical iodine curing process conditions. J. Korea. Cryst. Growth. Cryst. Technol. 2024, 34, 156–162. [Google Scholar]
- Hwang, C.H.; Beak, J.H.; Kim, S.I.; Kim, S.Y. Effect of Pyrolysis Temperature on Microwave Heating Properties of Oxidation-Cured Polycarbosilane Powder. Crystals 2024, 14, 1080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Volder, M.F.; Tawfick, S.H.; Baughman, R.H.; Hart, A.J. Carbon nanotubes: Present and future commercial applications. Science 2013, 339, 535–539. [Google Scholar]
- Chou, T.W.; Gao, L.; Thostenson, E.T.; Zhang, Z.; Byun, J.H. An assessment of the science and technology of carbon nanotube-based fibers and composites. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2010, 70, 1–19. [Google Scholar]
- Hong, J.S.; Cho, K.Y.; Shin, D.G.; Kim, J.I.; Rju, D.H. Iodine diffusion during iodine-vapor curing and its effects on the morphology of polycarbosilane/silicon carbide fibers. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2015, 132, 42687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasegawa, Y. New curing method for polycarbosilane with unsaturated hydrocarbons and application to thermally stable SiC fibre. Compos. Sci. Technol. 1994, 51, 161–166. [Google Scholar]
- Hong, J.S.; Cho, K.Y.; Shin, D.G.; Kim, J.I.; Oh, S.T.; Riu, D.H. Low-temperature chemical vapour curing using iodine for fabrication of continuous silicon carbide fibres from low-molecular-weight polycarbosilane. J. Mater. Chem. A 2014, 2, 2781–2793. [Google Scholar]
- Verdingovas, V.; Müller, L.; Jellesen, M.S.; Grumsen, F.B.; Ambat, R. Effect of iodine on the corrosion of Au–Al wire bonds. Corros. Sci. 2015, 97, 161–171. [Google Scholar]
- Rose, N.R.; Bonita, R.; Burek, C.L. Iodine: An environmental trigger of thyroiditis. Autoimmin. Rev. 2002, 1, 97–103. [Google Scholar]
- Boldyreva, E. Mechanochemistry of inorganic and organic systems: What is similar, what is different? Chem. Soc. Rev. 2013, 42, 7719–7738. [Google Scholar]
- Ke, C.; Liu, T.; Zhang, Y.; Xiong, Q. Energy absorption performances of silicon carbide particles during microwave heating process. Chem. Eng. Process. 2022, 172, 108796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Z.; Chen, J.; Li, B.; Li, G.; Zhang, Z.; Hou, X. Recent progress in SiC nanowires as electromagnetic microwaves absorbing materials. J. Alloy. Compd. 2020, 815, 15238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugawara, H.; Kashimura, K.; Hayashi, M.; Ishihara, S.; Mitani, T.; Shinohara, N. Behavior of microwave-heated silicon carbide particles at frequencies of 2.0–13.5 GHz. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2014, 105, 034103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arora, N.; Sharma, N.N. Arc discharge synthesis of carbon nanotubes: Comprehensive review. Diam. Relat. Mater. 2014, 50, 135–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, M.; Grasso, S.; Mckinnon, R.; Saunders, T.; Reece, M.J. Review of flash sintering: Materials, mechanisms and modelling. Adv. Appl. Ceram. 2017, 116, 24–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biesuz, M.; Sglavo, V.M. Flash sintering of ceramics. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2019, 39, 115–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cologna, M.; Rashkova, B.; Raj, R. Flash sintering of nanograin zirconia in <5 s at 850 °C. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 2010, 93, 3556–3559. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hwang, C.-H.; Beak, J.-H.; Kim, S.-Y. Influence of Carbon Nanotube Addition on Microstructure and Microwave Heating Performance of Polycarbosilane-Based Silicon Carbide. Materials 2025, 18, 1454. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18071454
Hwang C-H, Beak J-H, Kim S-Y. Influence of Carbon Nanotube Addition on Microstructure and Microwave Heating Performance of Polycarbosilane-Based Silicon Carbide. Materials. 2025; 18(7):1454. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18071454
Chicago/Turabian StyleHwang, Chang-Hun, Jong-Ha Beak, and Se-Yun Kim. 2025. "Influence of Carbon Nanotube Addition on Microstructure and Microwave Heating Performance of Polycarbosilane-Based Silicon Carbide" Materials 18, no. 7: 1454. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18071454
APA StyleHwang, C.-H., Beak, J.-H., & Kim, S.-Y. (2025). Influence of Carbon Nanotube Addition on Microstructure and Microwave Heating Performance of Polycarbosilane-Based Silicon Carbide. Materials, 18(7), 1454. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18071454





