Microstructure Evolution and Fatigue Properties of Ti Alloy Forged by 1500 t Forging Simulator
Abstract
1. Introduction
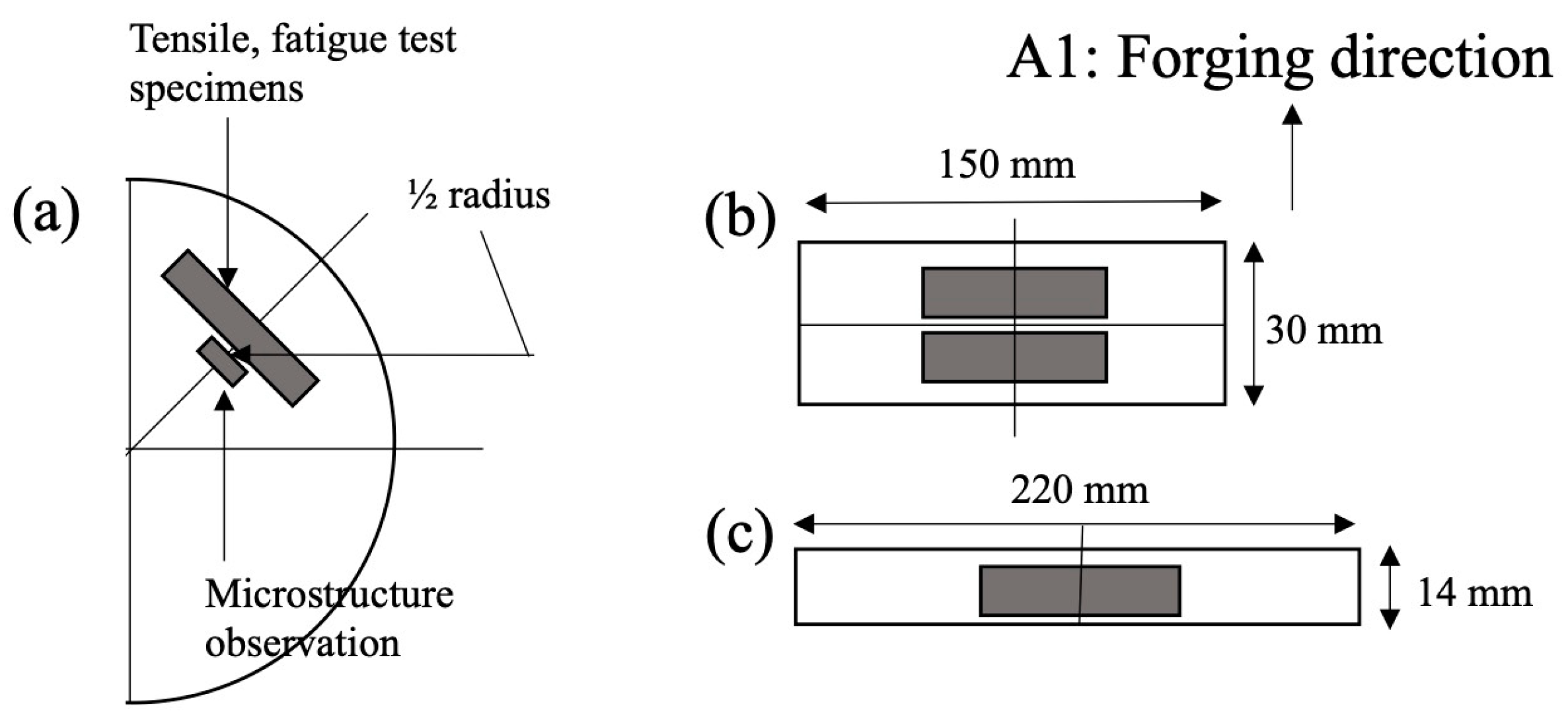
2. Materials and Methods
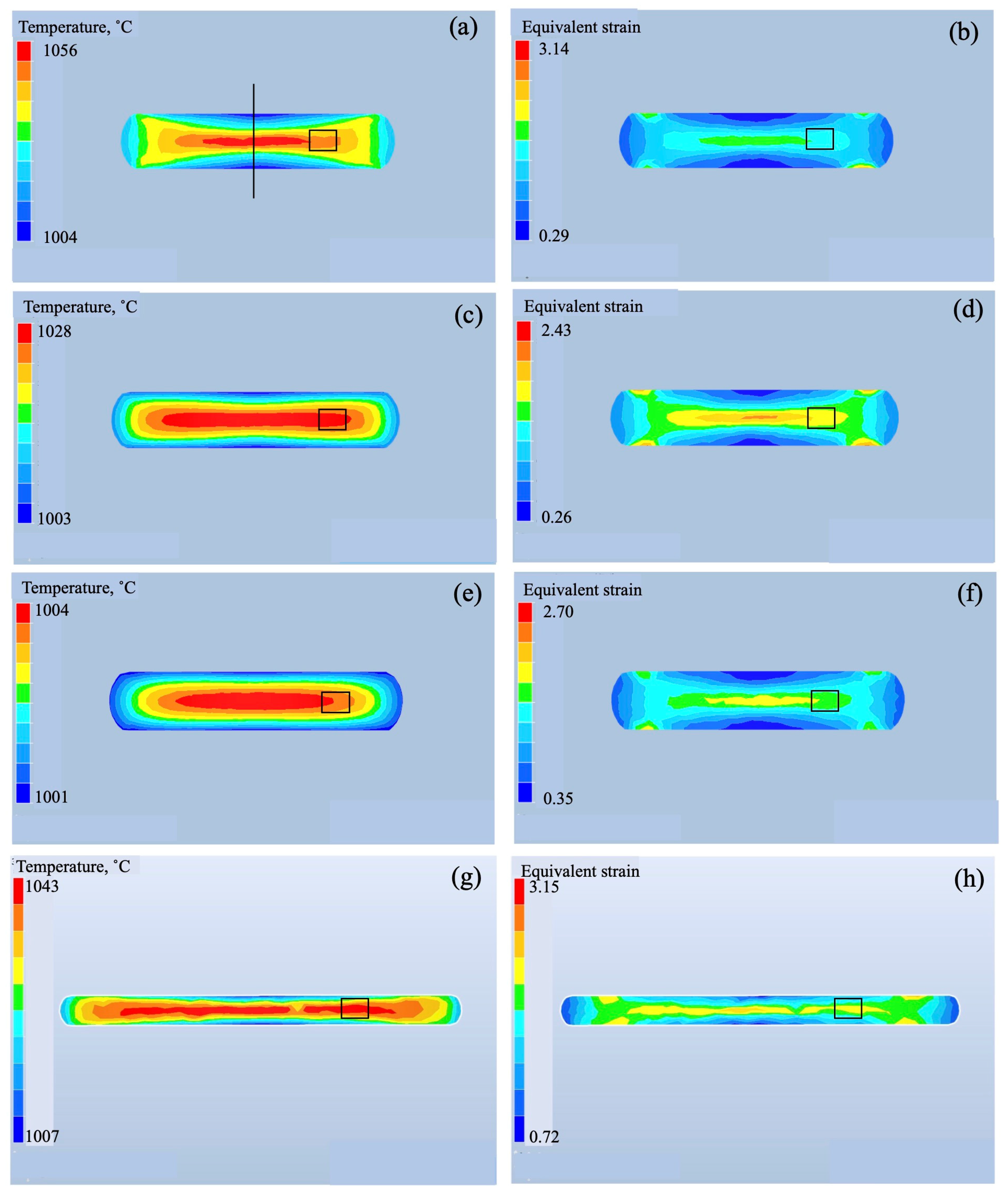
3. Results
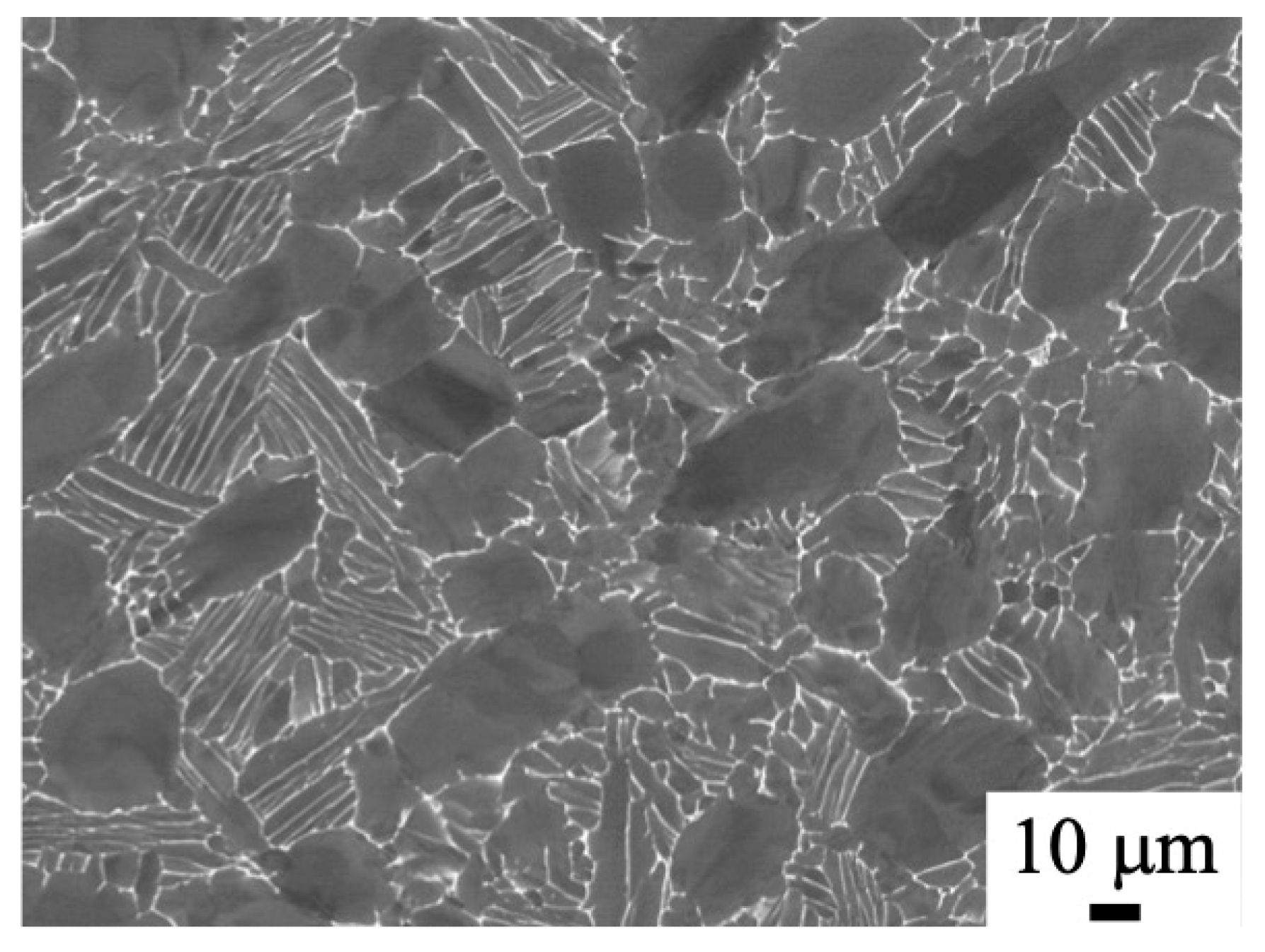
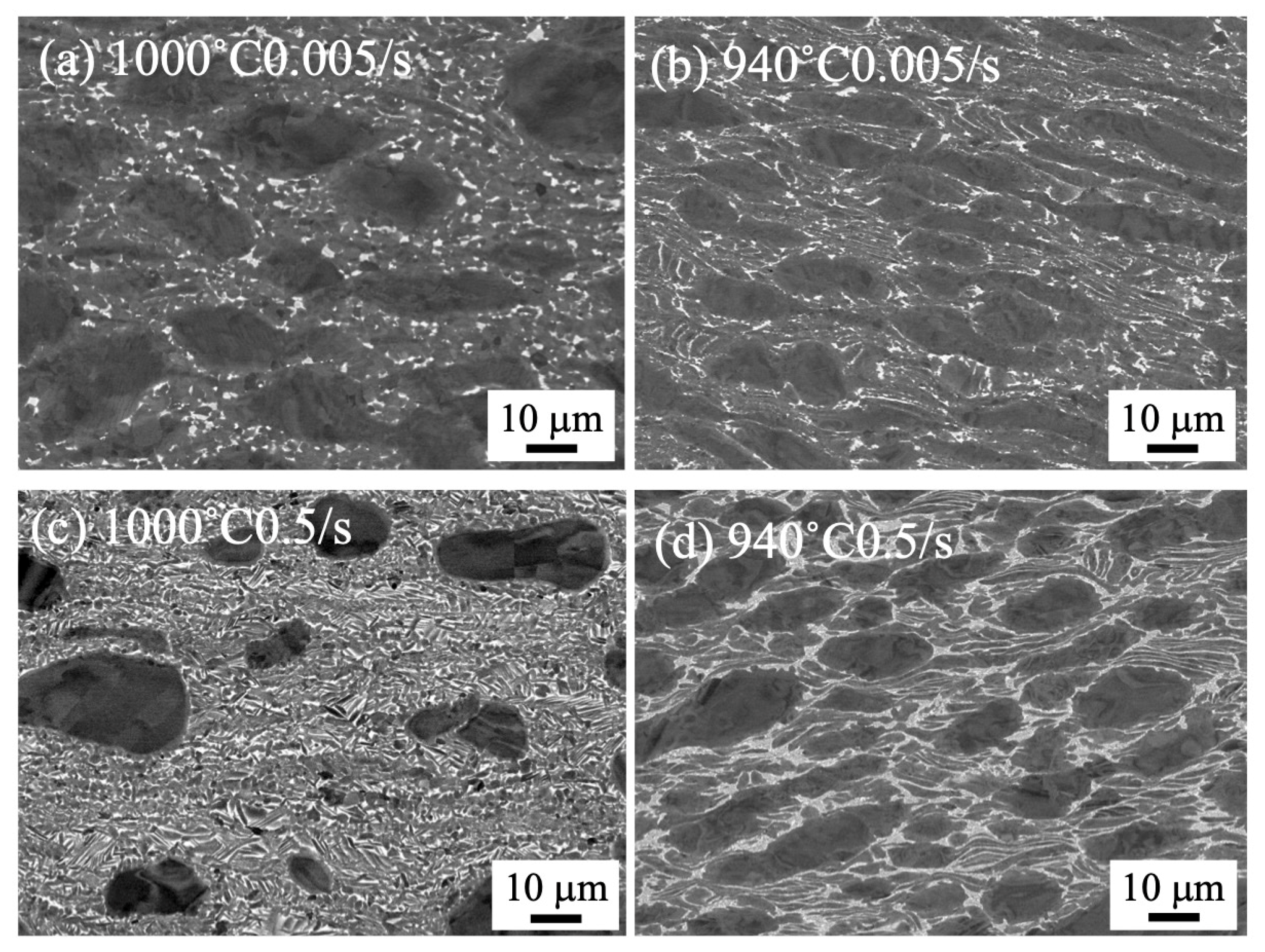
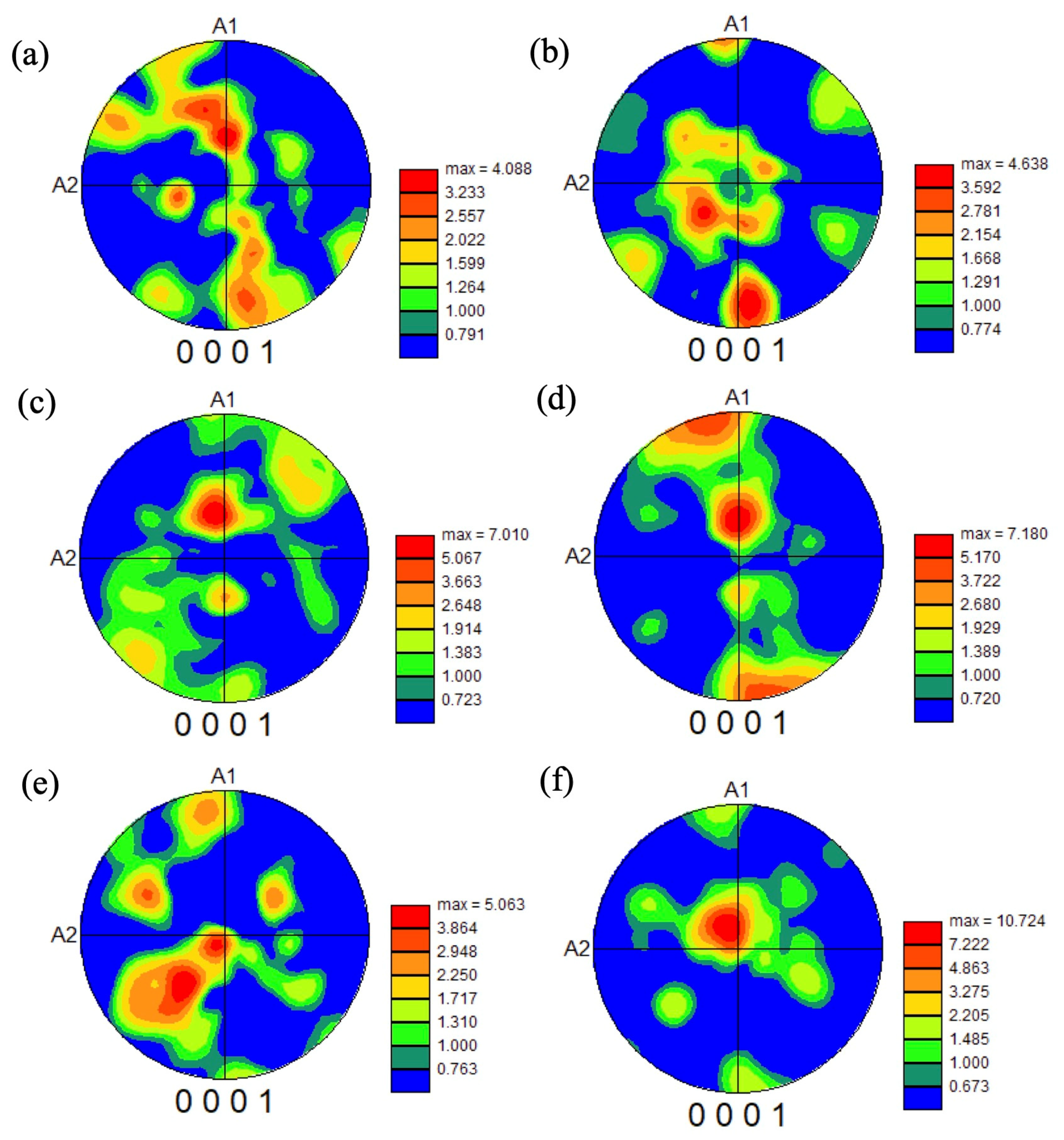
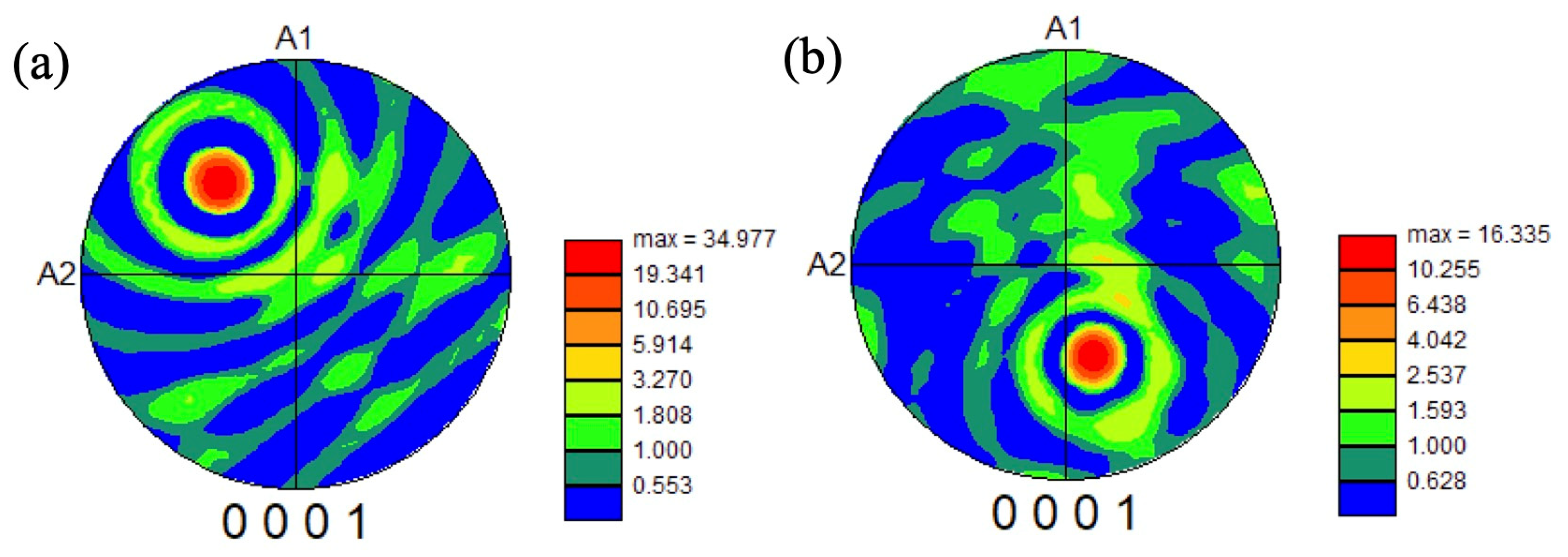
3.1. Microstructure of As-Received Billet and Forged Samples by 1500 t Forging Press
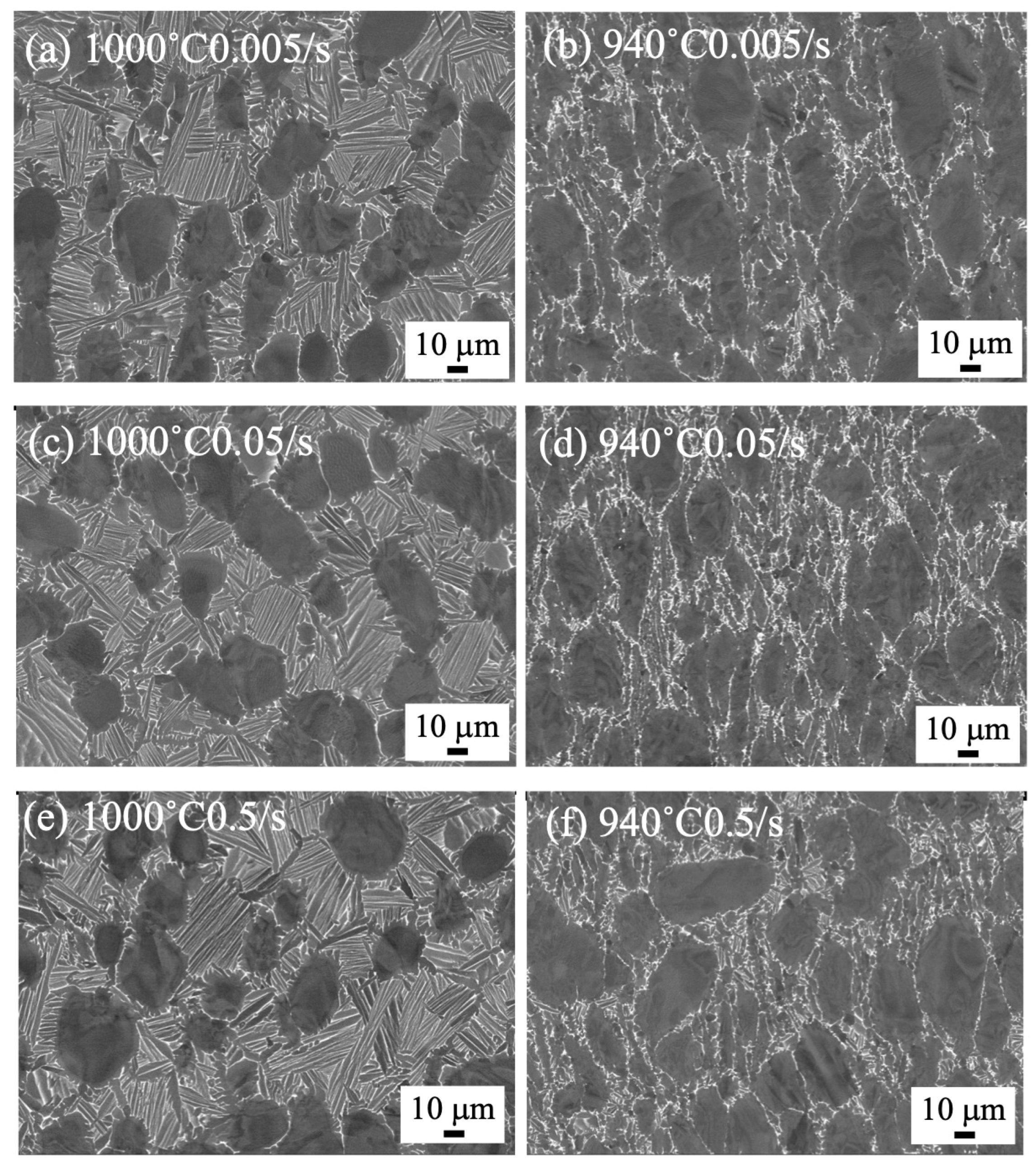
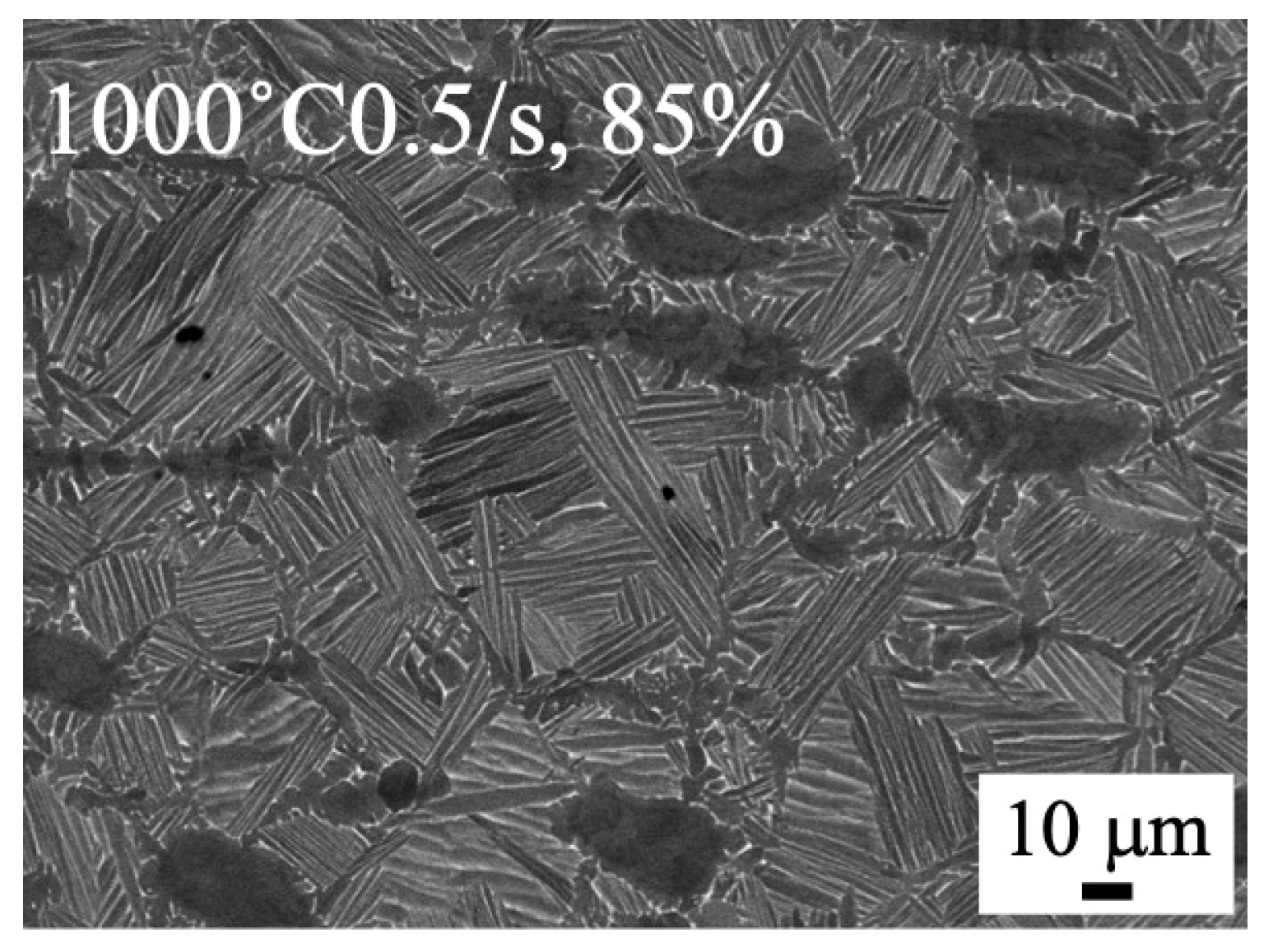
3.2. Microstructure of Forged Samples by 25 t Forging Press
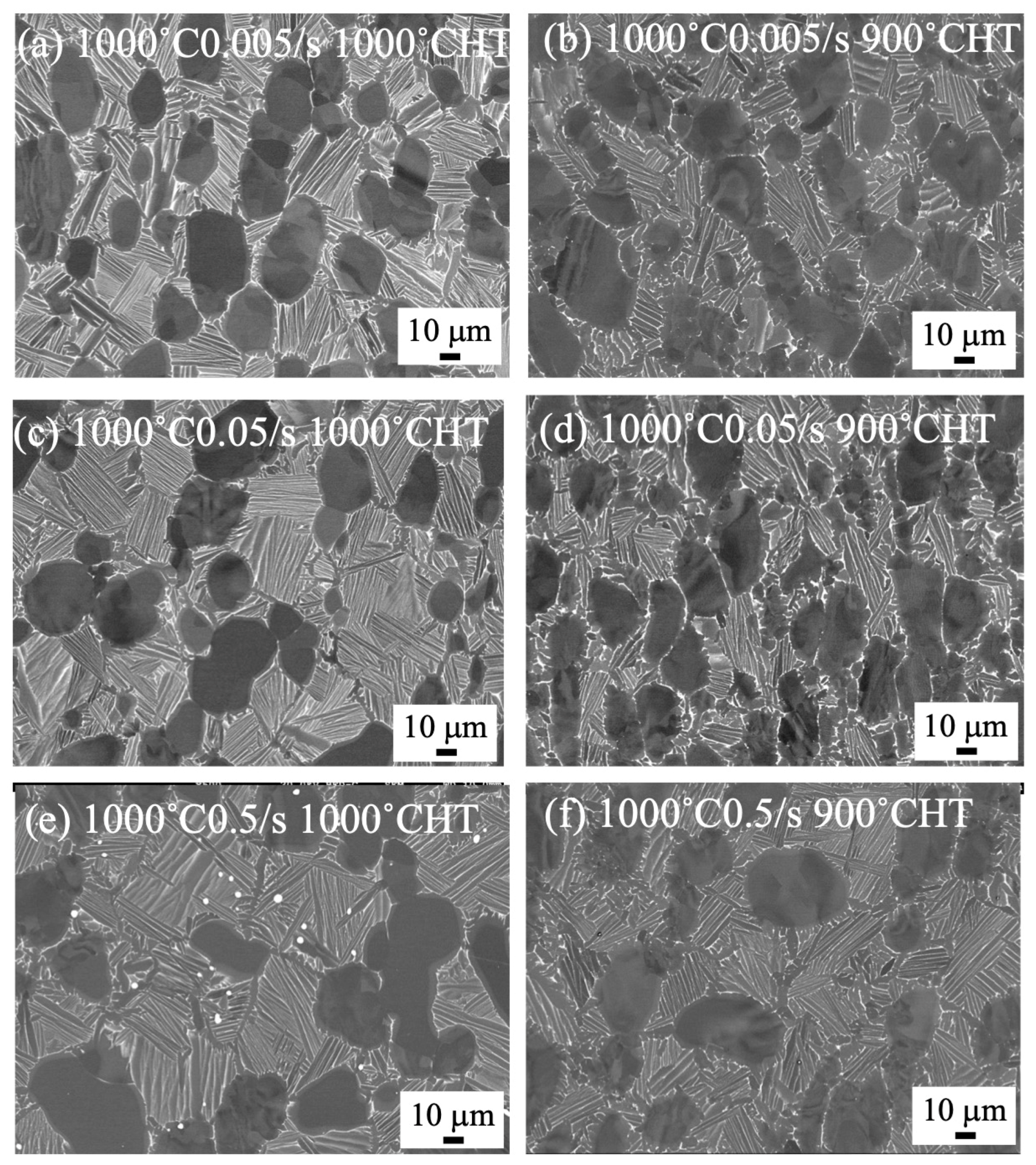
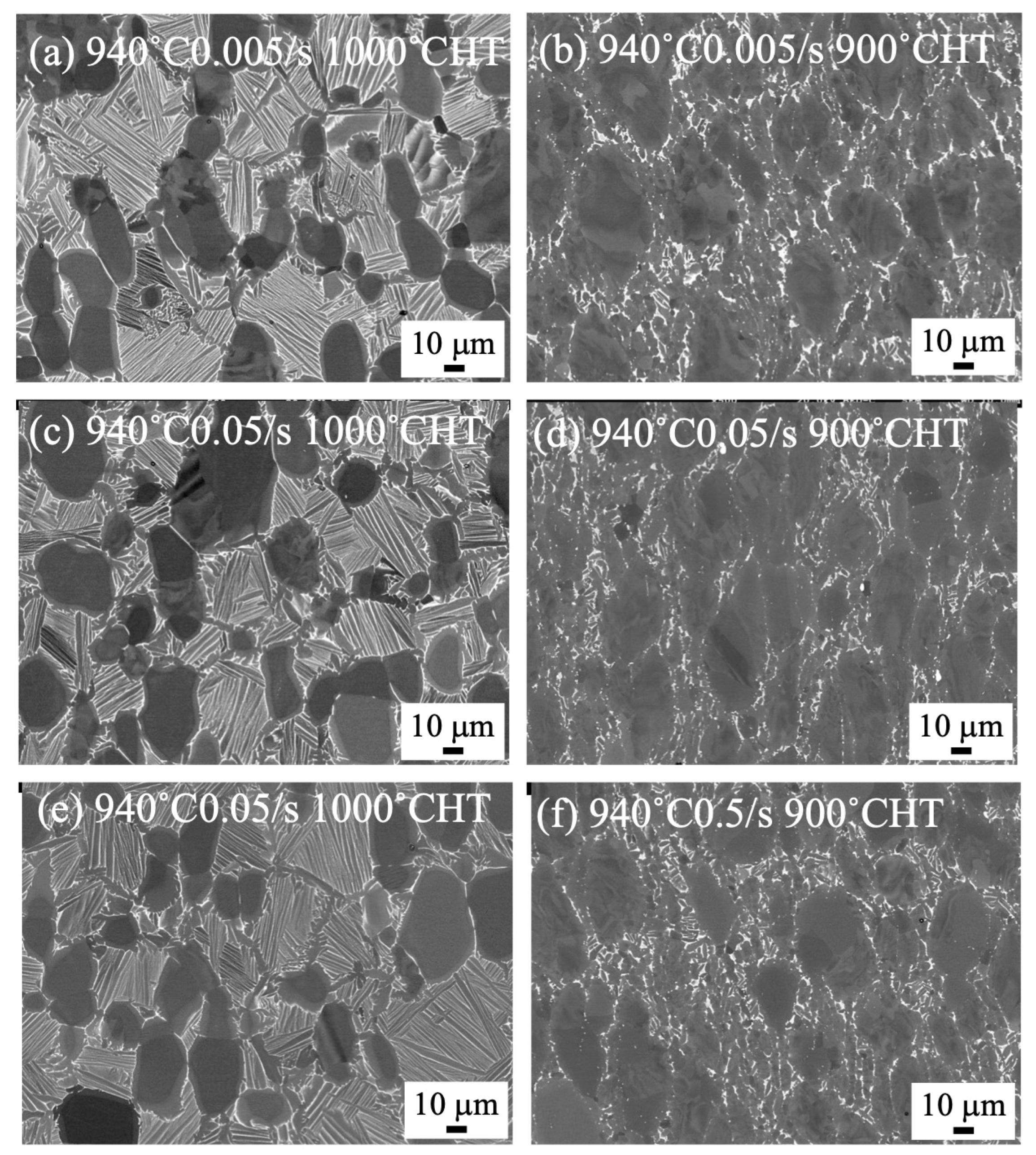
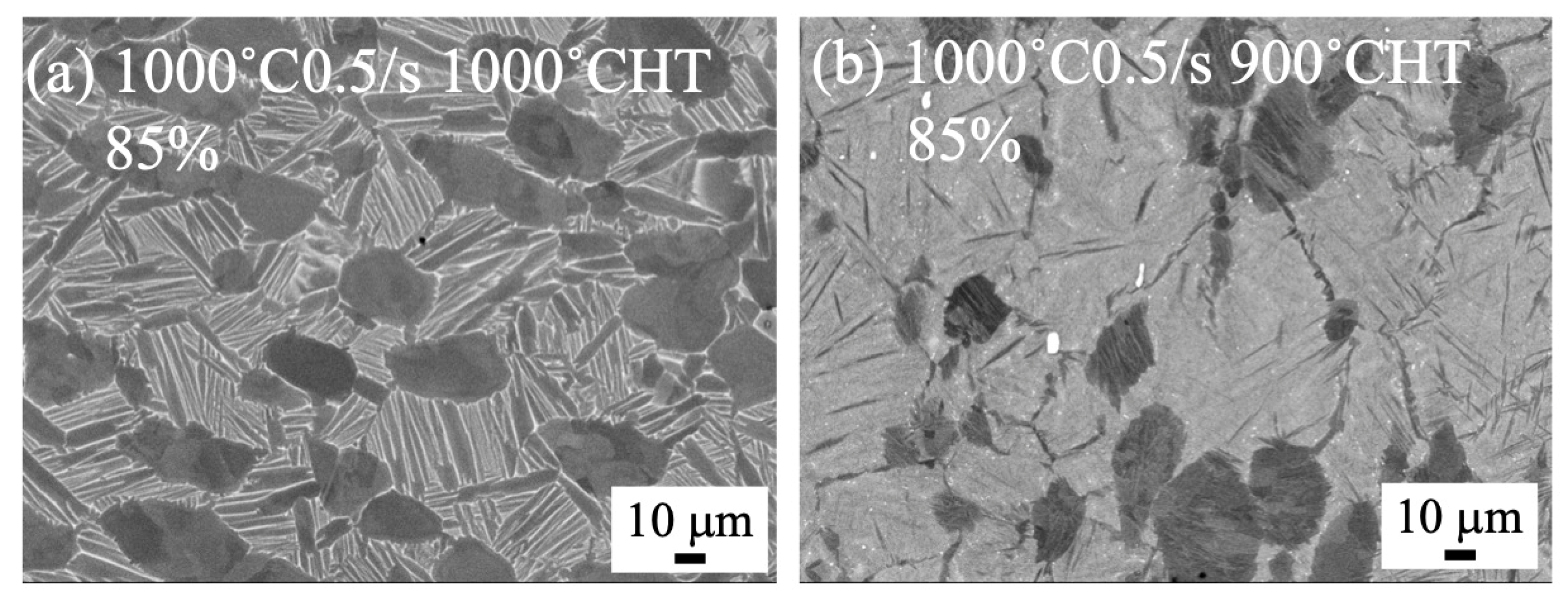
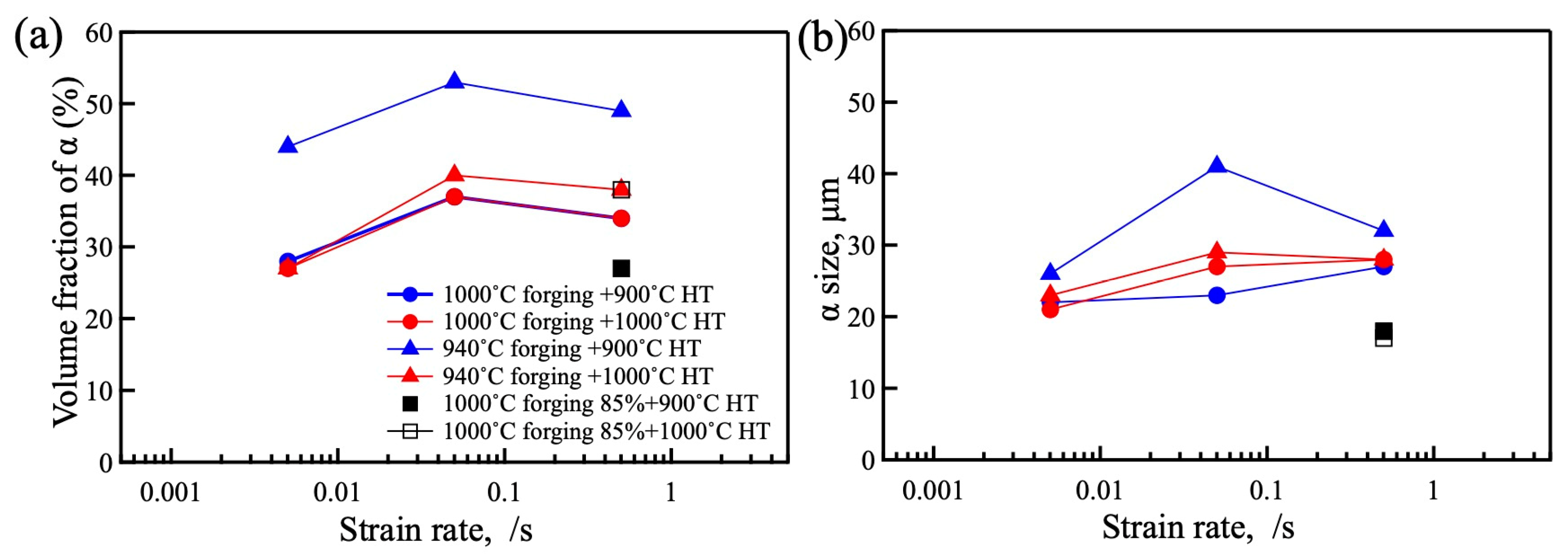
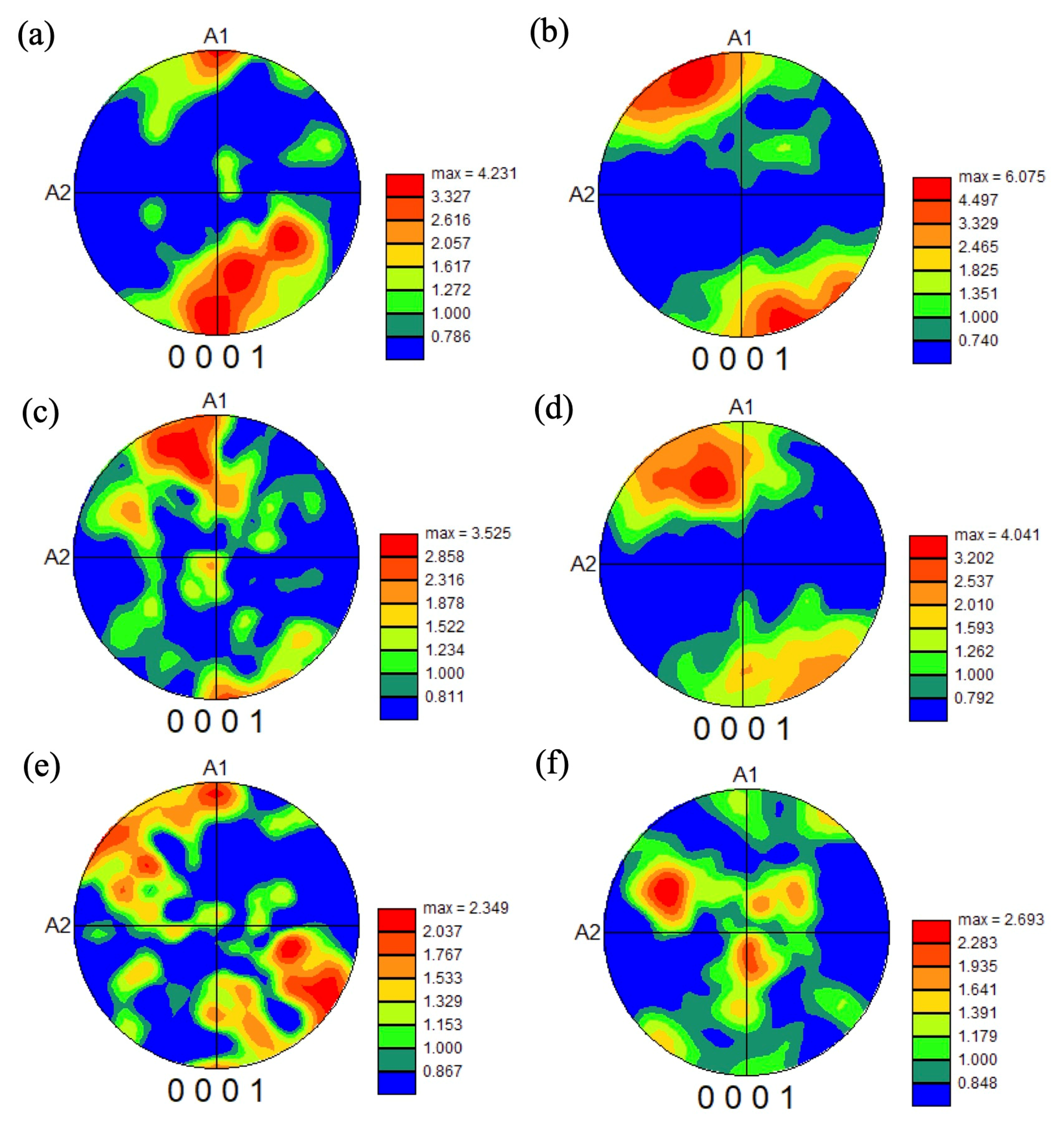
3.3. Microstructure of Heat-Treated Samples Forged by 1500 t Forging Press
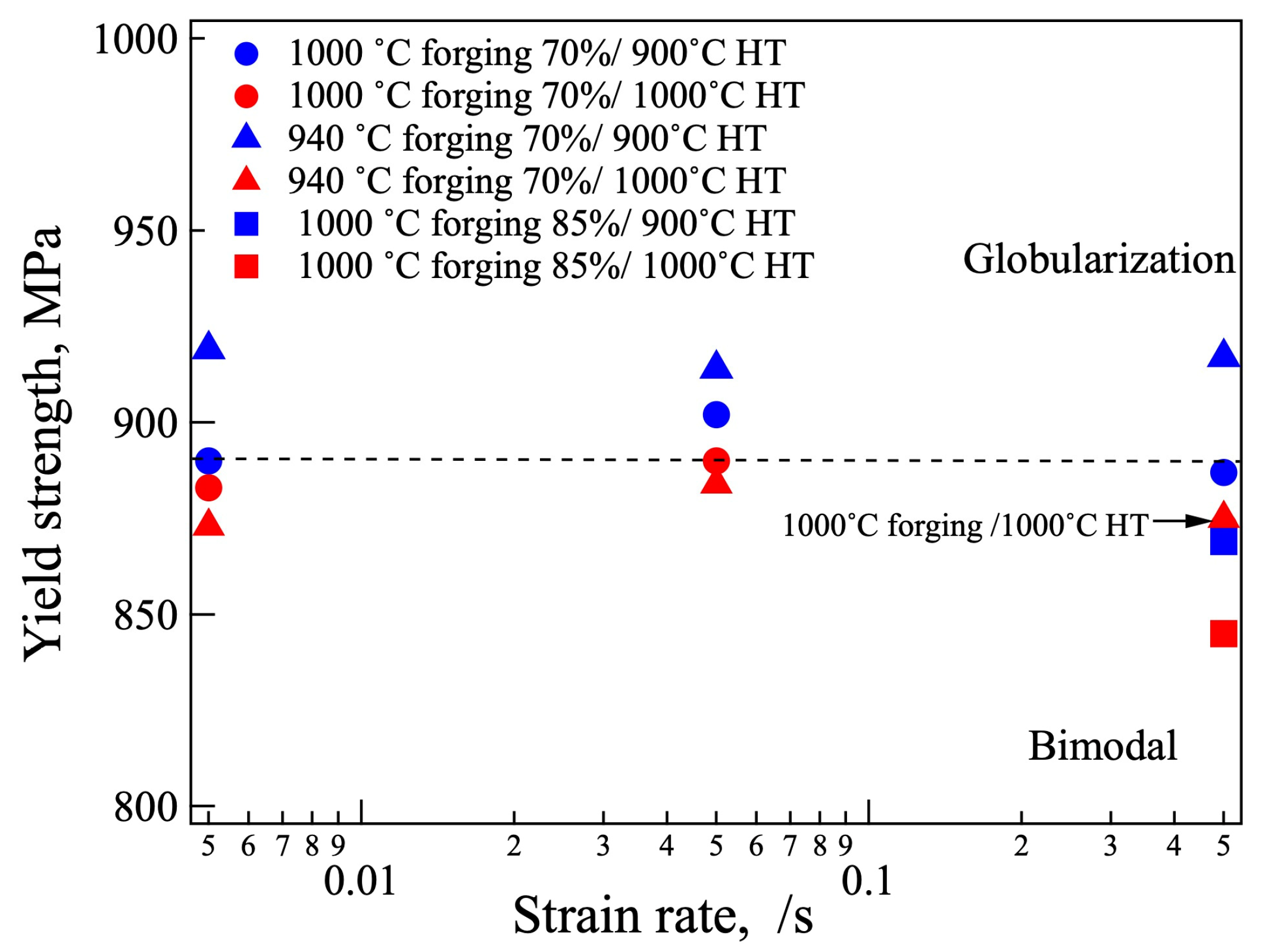
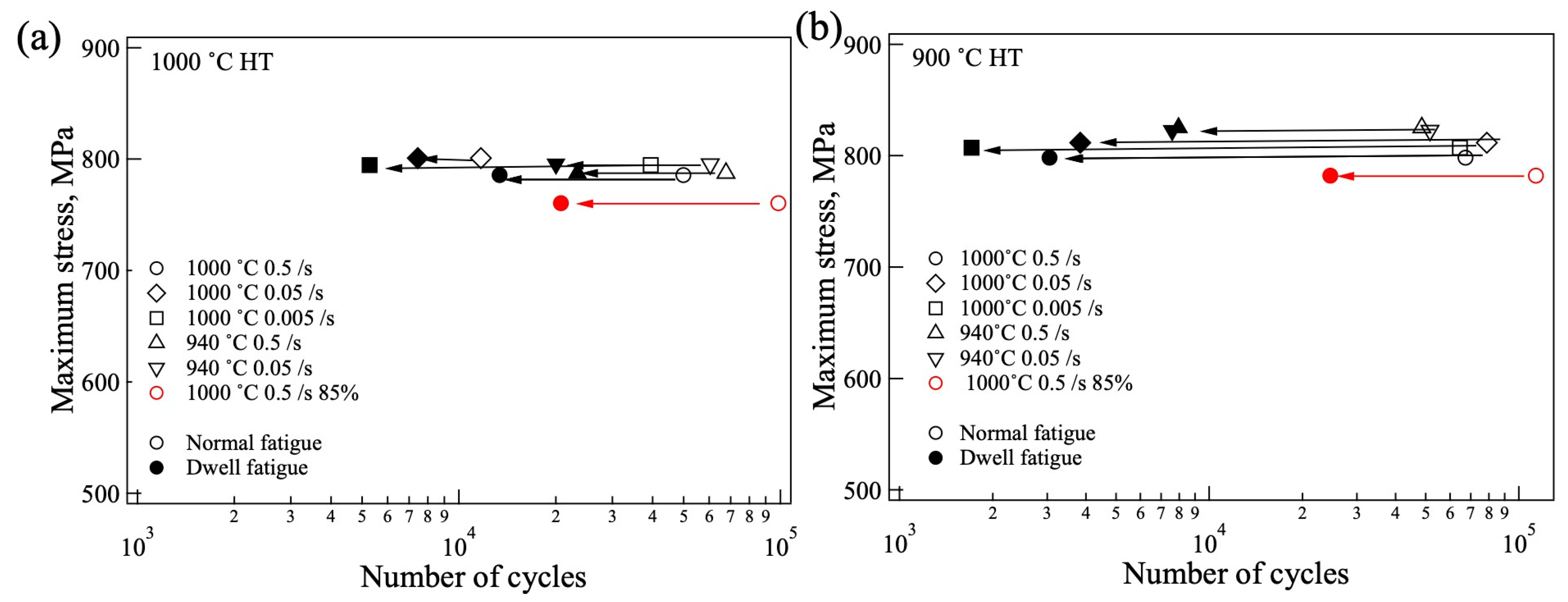
3.4. Mechanical Properties
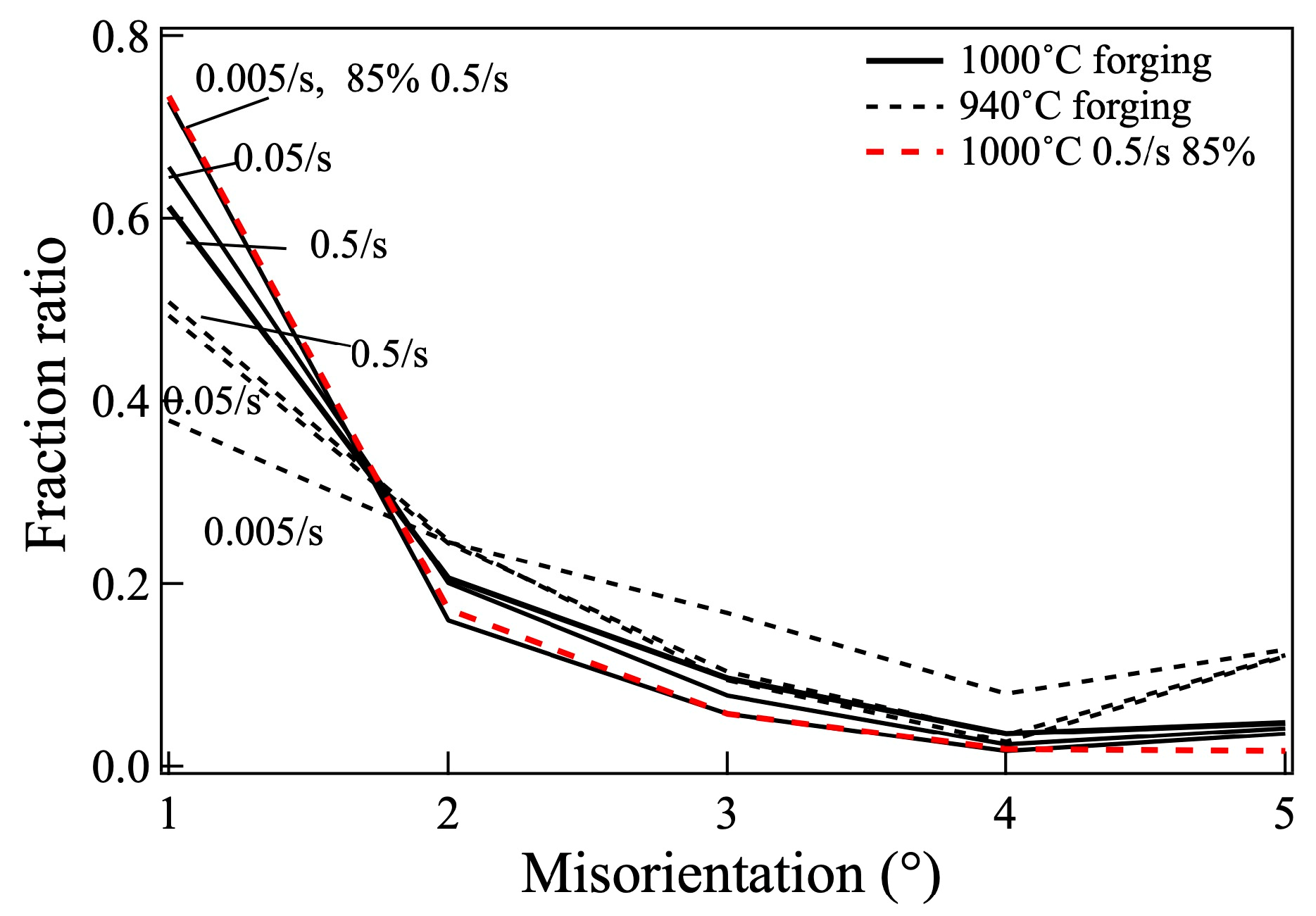
4. Discussion
4.1. Microstructure Formation of Forged Samples
4.2. Microstructure Formation of Heat-Treated Samples
4.3. Effect of Microstructure on Fatigue Life
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| TMP | Thermomechanical Processing |
| BOR | Burgers Orientation Relationship s |
| KAM | Kernel Average Misorientation |
| FEM | Finite Element Method |
References
- Williams, J.C.; Boyer, R.R. Opportunities and issues in the application of titanium alloys for aerospace components. Metals 2020, 10, 705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Semiatin, S.L. An overview of the thermomechanical processing of α/β titanium alloys: Current status and future research opportunities. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 2020, 51, 2593–2625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, J.; Ma, Y.; Lei, J.; Liu, Y.; Huang, A.; Rugg, D.; Yang, R. A comparative study on dwell fatigue of Ti-6Al-2Sn-4Zr-x Mo (x = 2 to 6) alloys on a microstructure-normalized basis. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 2014, 45, 6075–6087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bantounas, I.; Lindley, T.C.; Rugg, D.; Dye, D. Effect of microtexture on fatigue cracking in Ti–6Al–4V. Acta Mater. 2007, 55, 5655–5665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Wu, X.; Davies, C.H.J. Effect of microtexture on short crack propagation in two-phase titanium alloys. Inter. J. Fatigue 2017, 104, 206–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Briffod, F.; Shiraiwa, T.; Enoki, M.; Emura, S. Effect of macrozones on fatigue crack initiation and propagation mechanisms in a forged Ti-6Al-4V alloy under fully-reversed condition. Materialia 2022, 22, 101401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Xu, X.; Sun, T.; Thomas, R.; da Fonseca, J.Q.; Preuss, M. Microstructural effects on fatigue crack initiation mechanisms in a near-alpha titanium alloy. Acta Mater. 2023, 253, 118957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.B.; Wang, Q.J.; Liu, J.R.; Yang, R. Characterizations of microstructure and crystallographic orientation in a near-α titanium alloy billet. J. Alloys Compd. 2017, 712, 179–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, G.; Tang, B.; Zhou, Q.; Mao, X.; Dang, R. Development of a flow localization band and texture in a forged near-α titanium alloy. Metals 2020, 10, 121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Germain, L.; Gey, N.; Humbert, M.; Bocher, P.; Jahazi, M. Analysis of sharp microtexture heterogeneities in a bimodal IMI 834 billet. Acta Mater. 2005, 53, 3535–3543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gey, N.; Bocher, P.; Uta, E.; Germain, L.; Humbert, M. Texture and microtexture variations in a near-α titanium forged disk of bimodal microstructure. Acta Mater. 2012, 60, 2647–2655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kodli, B.K.; Saxena, K.K.; Dey, S.R.; Pancholi, V.; Bhattacharjee, A. Texture studies of hot compressed near alpha titanium alloy (IMI 834) at 1000 C with different strain rates. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2015, 82, 012032. [Google Scholar]
- Germain, L.; Gey, N.; Humbert, M.; Vo, P.; Jahazi, M.; Bocher, P. Texture heterogeneities induced by subtransus processing of near α titanium alloys. Acta Mater. 2008, 56, 4298–4308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, T.; Deng, Y.; Liu, W.; Teng, H.; Wang, R.; Sun, C.; Hao, D.; Zhou, J. Substructure and texture evolution of a novel near-α titanium alloy with bimodal microstructure during hot compression in α + β phase region. J. Alloys Compd. 2024, 996, 174869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, G.; Mao, X.; Tang, B.; Zhang, Y. Evolution of microstructure and texture of a near α titanium alloy during forging bar into disk. J. Alloys Compd. 2020, 831, 154750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Wang, M.; Ye, P.; Fu, W.; Cao, G.; Han, Q.; Liu, X.; Wu, H.; Fan, G. The effect of strain rate on macrozones of the α+ β phase region during thermal deformation in near-α titanium alloys. J. Mater. Res. Tech. 2025, 35, 2852–2861. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, Z.C.; Zhang, J.; Yang, H.; Wu, H. Effect of workpiece size on microstructure evolution of different regions for TA15 Ti-alloy isothermal near-β forging by local loading. J. Mater. Process Technol. 2015, 222, 234–243. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, S.; Zhang, H.; Xiao, N.; Qiu, R.; Cui, Z.; Fu, M. Mechanisms of macrozone elimination and grain refinement of near α Ti alloy via the spheroidization of the Widmannstätten structure. Acta Mater. 2023, 260, 119339. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, L.; Sun, Z.; Cao, J.; Yin, Z. The formation and evolution of macrozone in Ti-6242S alloy during thermo-mechanical processing. J. Alloys Compd. 2021, 861, 158533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Sample Name | Forging Temperature, °C | Strain Rate, s−1 | Compressed Ratio | Heat Treatment, °C |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| F940-A-H900 | 940 | 0.005 | 70 | 900 |
| F940-A-H1000 | 940 | 0.005 | 70 | 1000 |
| F940-B-H900 | 940 | 0.05 | 70 | 900 |
| F940-B-H1000 | 940 | 0.05 | 70 | 1000 |
| F940-C-H900 | 940 | 0.5 | 70 | 900 |
| F940-C-H1000 | 940 | 0.5 | 70 | 1000 |
| F1000-A-H900 | 1000 | 0.005 | 70 | 900 |
| F1000-A-H1000 | 1000 | 0.005 | 70 | 1000 |
| F1000-B-H900 | 1000 | 0.05 | 70 | 900 |
| F1000-B-H1000 | 1000 | 0.05 | 70 | 1000 |
| F1000-C-H900 | 1000 | 0.5 | 70 | 900 |
| F1000-C-H1000 | 1000 | 0.5 | 70 | 1000 |
| F1000-D-H900 | 1000 | 0.5 | 85 | 900 |
| F1000-D-H1000 | 1000 | 0.5 | 85 | 1000 |
| Sample Name | Forging Temperature, °C | Strain Rate, s−1 | Heat Treatment Temperature, °C | Maximum Stress, MPa | Maximum Stress, MPa |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| F940-B-H900 | 940 | 0.05 | 900 | 822.6 | 82.3 |
| F940-B-H1000 | 940 | 0.05 | 1000 | 795.6 | 79.6 |
| F940-C-H900 | 940 | 0.5 | 900 | 825.3 | 83.5 |
| F940-C-H1000 | 940 | 0.5 | 1000 | 787.5 | 78.8 |
| F1000-A-H900 | 1000 | 0.005 | 900 | 807.3 | 80.7 |
| F1000-A-H1000 | 1000 | 0.005 | 1000 | 794.7 | 79.5 |
| F1000-B-H900 | 1000 | 0.05 | 900 | 811.8 | 81.2 |
| F1000-B-H1000 | 1000 | 0.05 | 1000 | 801.0 | 80.1 |
| F1000-C-H900 | 1000 | 0.5 | 900 | 798.3 | 79.8 |
| F1000-C-H1000 | 1000 | 0.5 | 1000 | 785.7 | 78.6 |
| F1000-D-H900 | 1000 | 0.5 | 900 | 782.1 | 78.2 |
| F1000-D-H1000 | 1000 | 0.5 | 1000 | 760.5 | 76.1 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yamabe-Mitarai, Y.; Motohashi, N.; Kuroda, S.; Cobbinah, P.V. Microstructure Evolution and Fatigue Properties of Ti Alloy Forged by 1500 t Forging Simulator. Materials 2025, 18, 1436. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18071436
Yamabe-Mitarai Y, Motohashi N, Kuroda S, Cobbinah PV. Microstructure Evolution and Fatigue Properties of Ti Alloy Forged by 1500 t Forging Simulator. Materials. 2025; 18(7):1436. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18071436
Chicago/Turabian StyleYamabe-Mitarai, Yoko, Norie Motohashi, Shuji Kuroda, and Prince Valentine Cobbinah. 2025. "Microstructure Evolution and Fatigue Properties of Ti Alloy Forged by 1500 t Forging Simulator" Materials 18, no. 7: 1436. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18071436
APA StyleYamabe-Mitarai, Y., Motohashi, N., Kuroda, S., & Cobbinah, P. V. (2025). Microstructure Evolution and Fatigue Properties of Ti Alloy Forged by 1500 t Forging Simulator. Materials, 18(7), 1436. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18071436







