Formation of Ultrafine-Grained Dual-Phase Microstructure by Warm Deformation of Austenite in High-Strength Steel
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
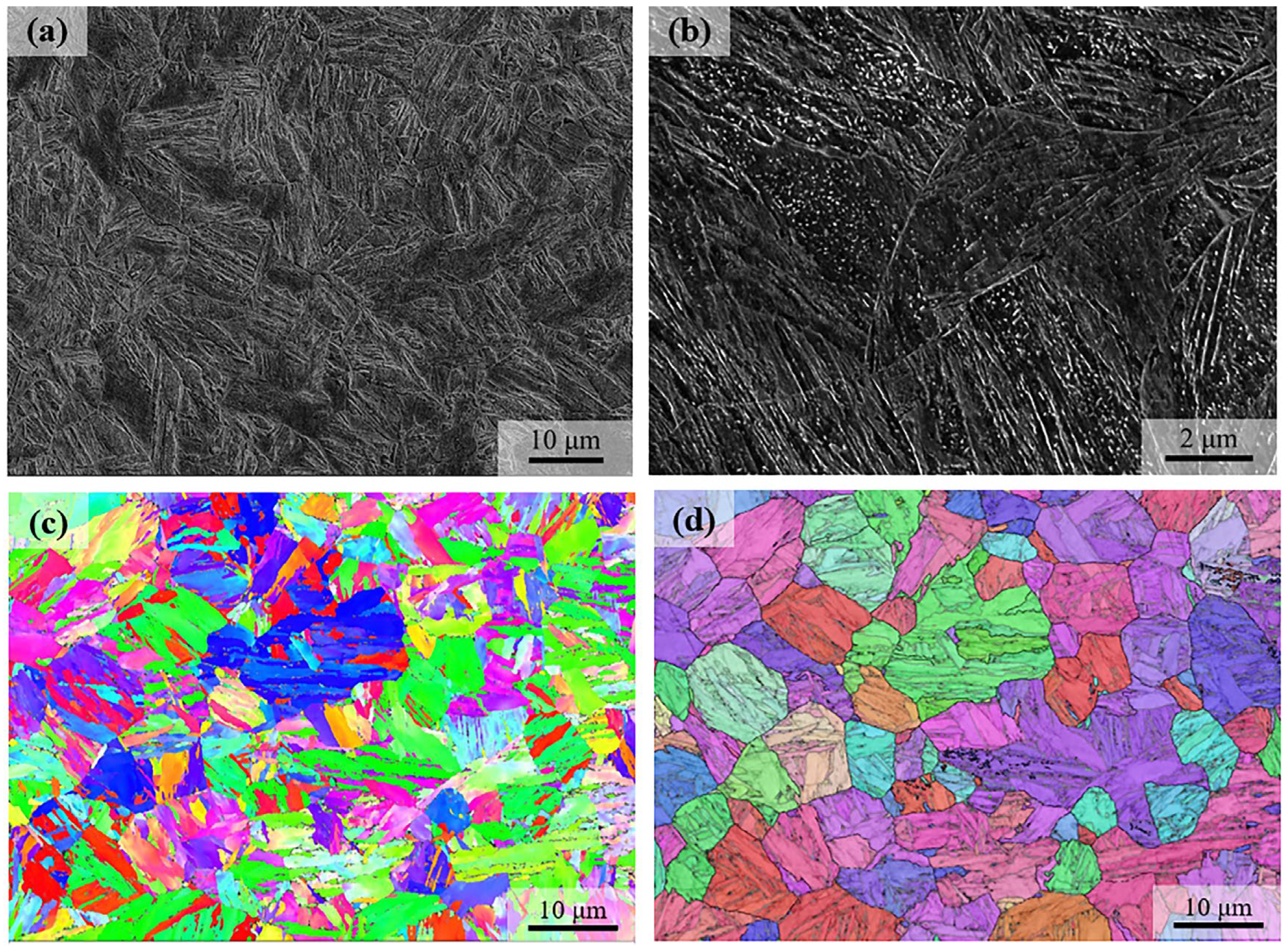
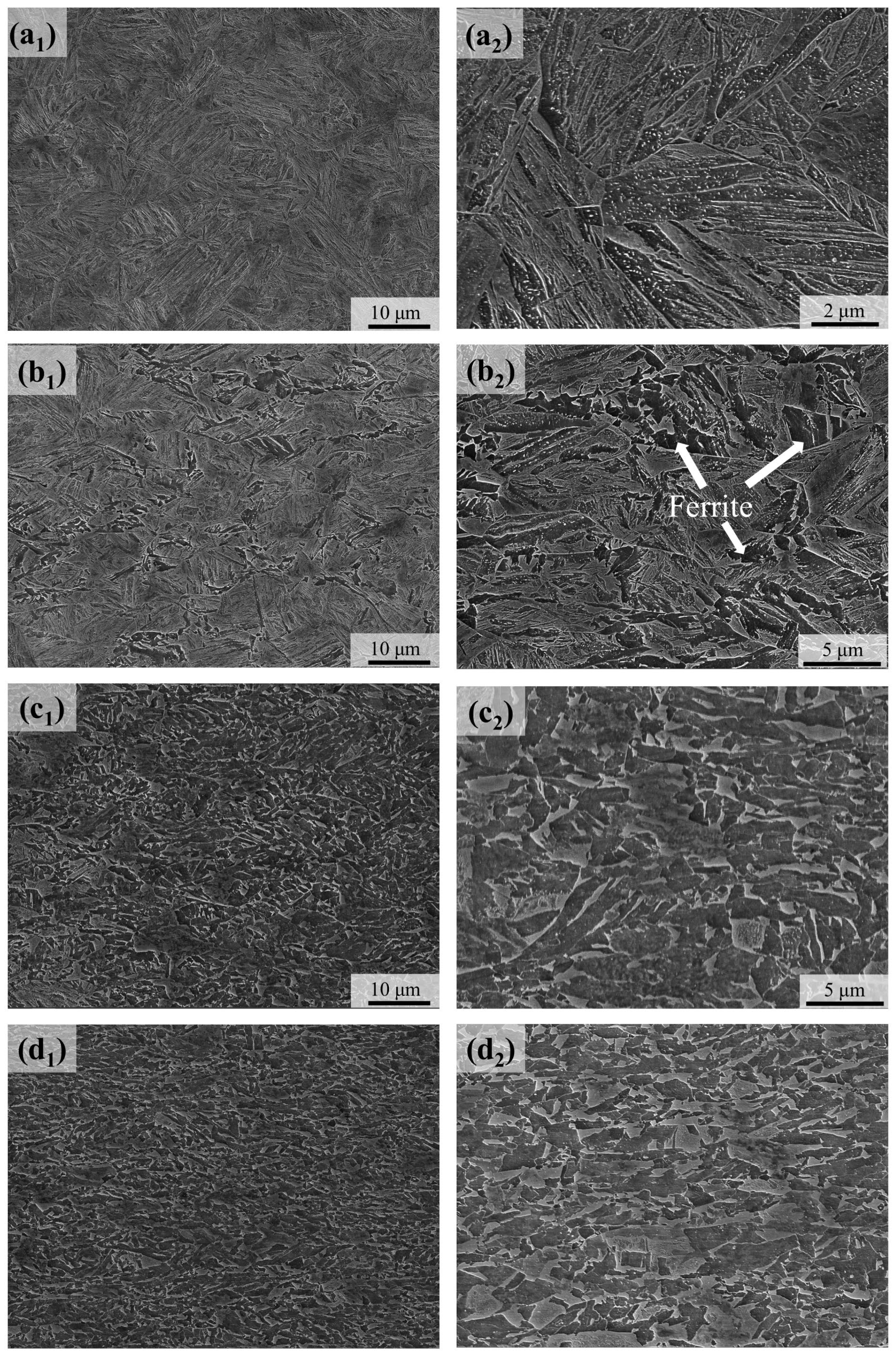
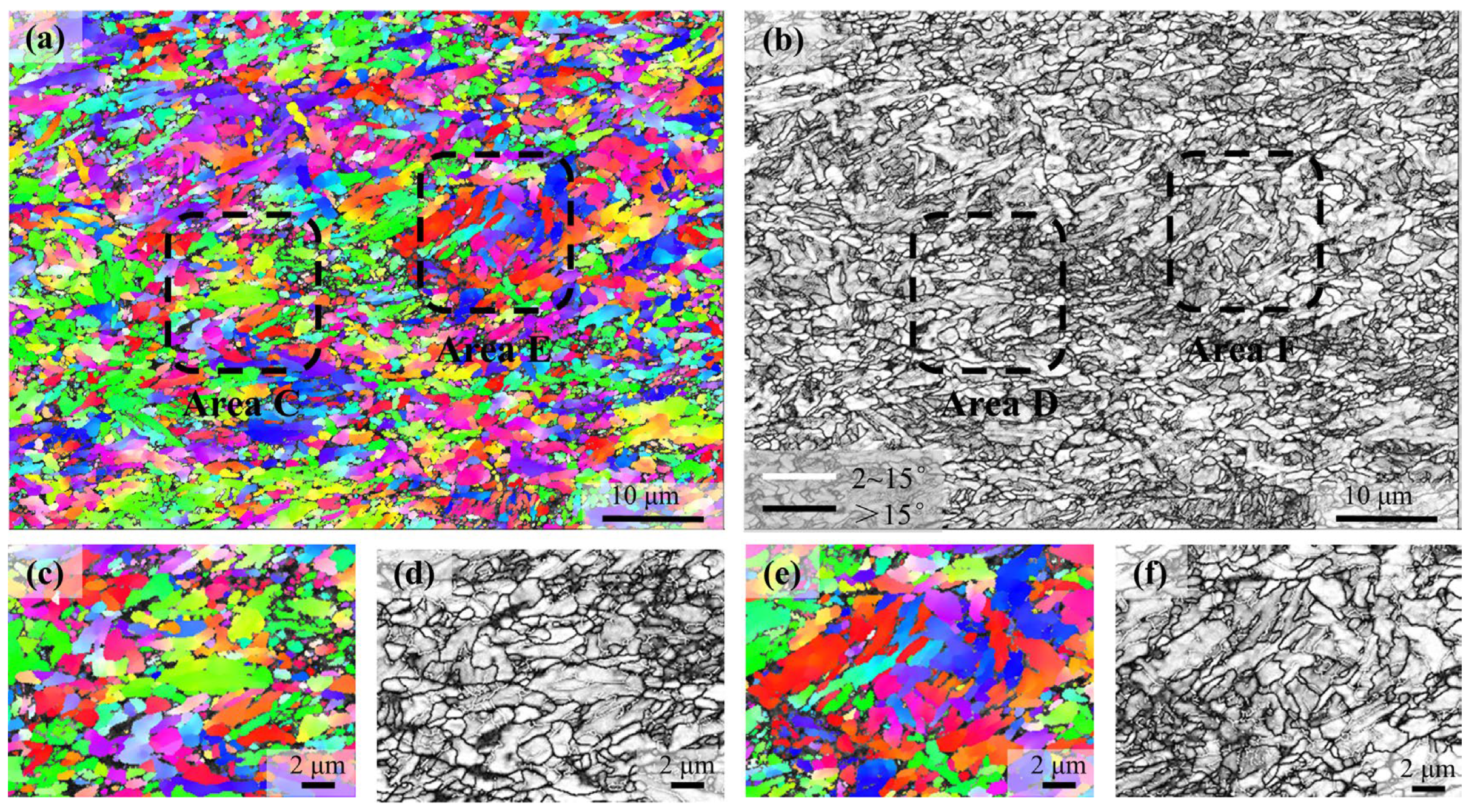
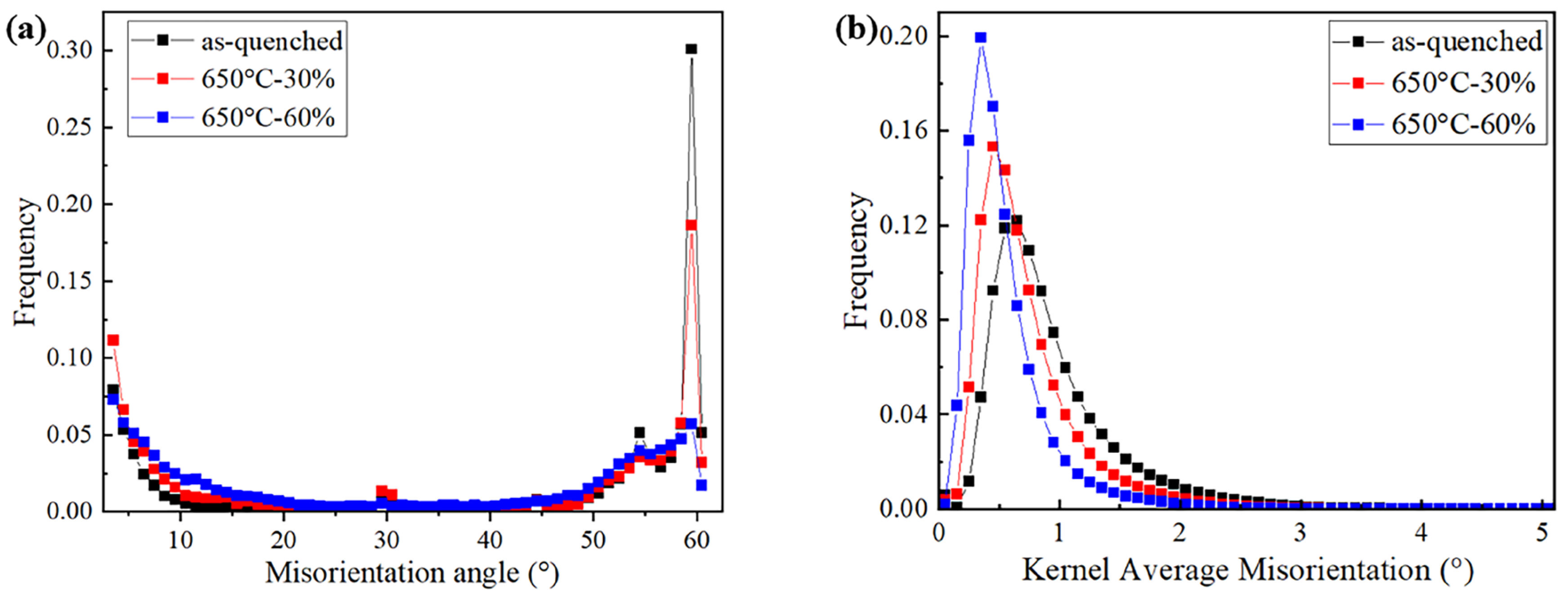
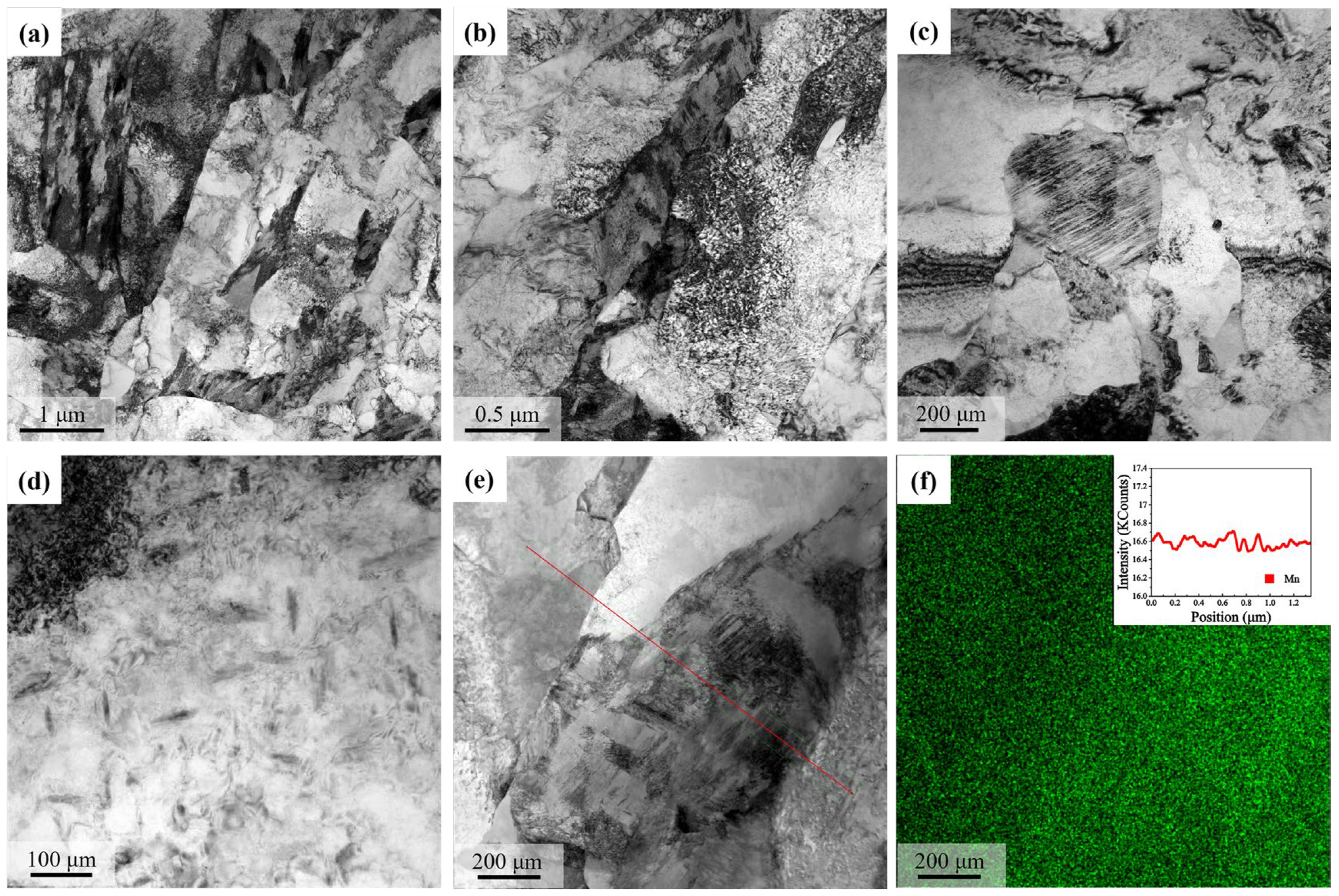
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Krauss, G. Steels: Processing, Structure, and Performance; Krauss, G., Ed.; ASM International: Materials Park, OH, USA, 2005; p. 613. [Google Scholar]
- Militzer, M. Thick Plate/Line Pipe Steel (Low-Alloyed Steels). In Encyclopedia of Materials: Metals and Alloys; Caballero, F.G., Ed.; Elsevier: Oxford, UK, 2022; pp. 115–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, P.; Maity, K.P.; Sahoo, G.; Giri, B.K. A Study on Integrating Deformation Induced Ferrite Transformation with Conventional Thermomechanical Controlled Processing at an Industrial Scale and the Associated Challenges. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Jiang, Z. Thermomechanical processing of advanced high strength steels. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2018, 94, 174–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, C.; Aranas, C.; Jonas, J.J. Dynamic transformation of deformed austenite at temperatures above the Ae3. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2016, 82, 151–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, Q.; Yang, H.; Wei, Y.; Zhou, H.; Xiao, L.; Ying, H.; Lan, S.; You, Z.; Kou, Z.; Feng, T.; et al. Transformation plasticity in high strength, ductile ultrafine-grained FeMn alloy processed by heavy ausforming. Int. J. Plast. 2022, 148, 103151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatterjee, S.; Wang, H.S.; Yang, J.R.; Bhadeshia, H.K.D.H. Mechanical stabilisation of austenite. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2006, 22, 641–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yada, H.; Li, C.-M.; Yamagata, H. Dynamic γ→α Transformation during Hot Deformation in Iron-Nickel-Carbon Alloys. ISIJ Int. 2000, 40, 200–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goncalves Rodrigues, M.V.; Siciliano, F.; Aranas, C.; da Silva Lima, M.; de Carvalho Paes Loureiro, R.; Reis, G.S.; Silva, E.S.; Paiva Leão, P.B.; Ferreira, J.C.; Gomes de Abreu, H.F.; et al. Evidence of dynamic ferrite transformation during thermomechanical simulation of an X70 microalloyed steel above Ae3 temperature. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2024, 30, 3675–3689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hodgson, P.D.; Hickson, M.R.; Gibbs, R.K. Ultrafine ferrite in low carbon steel. Scr. Mater. 1999, 40, 1179–1184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hurley, P.J.; Hodgson, P.D. Formation of ultra-fine ferrite in hot rolled strip: Potential mechanisms for grain refinement. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2001, 302, 206–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, J.-K.; Seo, D.-H.; Lee, J.-S.; Um, K.-K.; Choo, W.-Y. Formation of Ultrafine Ferrite by Strain-induced Dynamic Transformation in Plain Low Carbon Steel. ISIJ Int. 2003, 43, 746–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beladi, H.; Kelly, G.L.; Hodgson, P.D. Ultrafine grained structure formation in steels using dynamic strain induced transformation processing. International Materials Reviews 2013, 52, 14–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, R.; Ponge, D.; Raabe, D.; Speer, J.G.; Matlock, D.K. Overview of processing, microstructure and mechanical properties of ultrafine grained bcc steels. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2006, 441, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Park, N.; Tian, Y.; Shibata, A.; Tsuji, N. Dynamic Transformation Mechanism for Producing Ultrafine Grained Steels. Adv. Eng. Mater. 2018, 20, 1701016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, H.; Sun, X. Deformation induced ferrite transformation in low carbon steels. Curr. Opin. Solid State Mater. Sci. 2005, 9, 269–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Shenawy, E.; Reda, R. Optimization of TMCP strategy for microstructure refinement and flow-productivity characteristics enhancement of low carbon steel. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2019, 8, 2819–2831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Liu, Q.; Jia, S.; Ren, Y.; Wang, B. Fabricating ultrafine grain by advanced thermomechanical processing on low-carbon microalloyed steel. Scr. Mater. 2018, 152, 132–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, P.; Palmiere, E.J.; Rainforth, W.M. Thermomechanical processing route to achieve ultrafine grains in low carbon microalloyed steels. Acta Mater. 2016, 119, 43–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, Z.P.; Saleh, A.A.; Kostryzhev, A.G.; Pereloma, E.V. Strain-induced ferrite formation and its effect on mechanical properties of a dual phase steel produced using laboratory simulated strip casting. J. Alloys Compd. 2017, 721, 291–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasiri, Z.; Ghaemifar, S.; Naghizadeh, M.; Mirzadeh, H. Thermal Mechanisms of Grain Refinement in Steels: A Review. Met. Mater. Int. 2021, 27, 2078–2094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanlon, D.N.; Sietsma, J.; Zwaag, S.v.d. The Effect of Plastic Deformation of Austenite on the Kinetics of Subsequent Ferrite Formation. ISIJ Int. 2001, 41, 1028–1036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jonas, J.J.; Ghosh, C. Role of mechanical activation in the dynamic transformation of austenite. Acta Mater. 2013, 61, 6125–6131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lacroix, S.; Bréchet, Y.; Véron, M.; Quidort, D.; Kandel, M.; Iung, T. Influence of deformation on austenite to ferrite transformation in low carbon steels: Experimental approach and modelling. In Proceedings of the Materials Science and Technology Conference 2003, Chicago, IL, USA, 9 November 2003; pp. 367–379. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, Y.; Zheng, Q.; Hu, B.; Wang, P.; Zheng, C.; Li, D. Mechanism of Dynamic Strain-Induced Ferrite Transformation in a 3Mn-0.2C Medium Mn Steel. Acta Metall. Sin. 2022, 58, 649–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rios, P.R.; de, S. Bott, I.; Santos, D.B.; de Melo, T.M.F.; Ferreira, J.L. Effect of Nb on dynamic strain induced austenite to ferrite transformation. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2007, 23, 417–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hickson, M.R.; Gibbs, R.K.; Hodgson, P.D. The Effect of Chemistry on the Formation of Ultrafine Ferrite in Steel. ISIJ Int. 1999, 39, 1176–1180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, S.C.; Lim, S.H.; Hong, H.S.; Lee, K.J.; Shin, D.H.; Lee, K.S. Effects of Nb on strain induced ferrite transformation in C–Mn steel. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2003, 355, 241–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, H.; Zhu, G.; Chen, Q.; Wang, Y.; Wang, X. Mechanism of boundary induced transformation and its application in the grain refinement of large-size structural steels. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2021, 818, 141342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Park, N.; Tian, Y.; Shibata, A.; Tsuji, N. Combination of dynamic transformation and dynamic recrystallization for realizing ultrafine-grained steels with superior mechanical properties. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 39127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hodgson, P.D.; Hickson, M.R.; Gibbs, R.K. The Production and Mechanical Properties of Ultrafine Ferrite. Mater. Sci. Forum. 1998, 284–286, 63–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Wang, H.; Xu, B.; Jiang, L.; Guo, S.; Sun, X.; Yu, D.; Liu, F.; Liu, Y. Making low-alloyed steel strong and tough by designing a dual-phase layered structure. Acta Mater. 2022, 227, 117701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Son, Y.I.; Lee, Y.K.; Park, K.T.; Lee, C.S.; Shin, D.H. Ultrafine grained ferrite-marten site dual phase steels fabricated via equal channel angular pressing: Microstructure and tensile properties. Acta Mater. 2005, 53, 3125–3134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azizi-Alizamini, H.; Militzer, M.; Poole, W.J. A novel technique for developing bimodal grain size distributions in low carbon steels. Scr. Mater. 2007, 57, 1065–1068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hutchinson, B.; Hagström, J.; Karlsson, O.; Lindell, D.; Tornberg, M.; Lindberg, F.; Thuvander, M. Microstructures and hardness of as-quenched martensites (0.1–0.5%C). Acta Mater. 2011, 59, 5845–5858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adachi, Y.; Wakita, M.; Beladi, H.; Hodgson, P.D. The formation of ultrafine ferrite through static transformation in low carbon steels. Acta Mater. 2007, 55, 4925–4934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Hansen, N. Geometrically necessary boundaries and incidental dislocation boundaries formed during cold deformation. Scr. Metall. Mater. 1995, 32, 1289–1295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, S.C.; Lim, S.H.; Lee, K.J.; Shin, D.H.; Lee, K.S. Effect of Undercooling of Austenite on Strain Induced Ferrite Transformation Behavior. ISIJ Int. 2003, 43, 394–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beladi, H.; Kelly, G.L.; Shokouhi, A.; Hodgson, P.D. The evolution of ultrafine ferrite formation through dynamic strain-induced transformation. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2004, 371, 343–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishiyama, Z.; Fine, M.E.; Meshii, M.; Wayman, C.M. Martensitic transformation; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 1978. [Google Scholar]
- Ismail, K.; Perlade, A.; Jacques, P.J.; Pardoen, T.; Brassart, L. Impact of second phase morphology and orientation on the plastic behavior of dual-phase steels. Int. J. Plast. 2019, 118, 130–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, Q.; Brassart, L.; Bouaziz, O.; Gouné, M.; Verdier, M.; Parry, G.; Perlade, A.; Bréchet, Y.; Pardoen, T. Influence of martensite volume fraction and hardness on the plastic behavior of dual-phase steels: Experiments and micromechanical modeling. Int. J. Plast. 2016, 80, 187–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delince, M.; Brechet, Y.; Embury, J.D.; Geers, M.G.D.; Jacques, P.J.; Pardoen, T. Structure-property optimization of ultrafine-grained dual-phase steels using a micro structure-based strain hardening model. Acta Mater. 2007, 55, 2337–2350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, Q.; Bouaziz, O.; Goune, M.; Perlade, A.; Brechet, Y.; Pardoen, T. Microstructure refinement of dual-phase steels with 3.5 wt% Mn: Influence on plastic and fracture behavior. Mater. Sci. Eng. A Struct. Mater. Prop. Microstruct. Process. 2015, 638, 78–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godet, S.; Harlet, P.; Jacques, P.J. Grain Refinement of TRIP-Assisted Multiphase Steels through Strain-Induced Phase Transformation. Steel Res. Int. 2016, 77, 271–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beladi, H.; Timokhina, I.B.; Xiong, X.Y.; Hodgson, P.D. A novel thermomechanical approach to produce a fine ferrite and low-temperature bainitic composite microstructure. Acta Mater. 2013, 61, 7240–7250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shu, W.; Fan, Y.; Li, R.; Liu, Q.; Lai, Q. Formation of Ultrafine-Grained Dual-Phase Microstructure by Warm Deformation of Austenite in High-Strength Steel. Materials 2025, 18, 1341. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18061341
Shu W, Fan Y, Li R, Liu Q, Lai Q. Formation of Ultrafine-Grained Dual-Phase Microstructure by Warm Deformation of Austenite in High-Strength Steel. Materials. 2025; 18(6):1341. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18061341
Chicago/Turabian StyleShu, Wen, Yingqi Fan, Rengeng Li, Qing Liu, and Qingquan Lai. 2025. "Formation of Ultrafine-Grained Dual-Phase Microstructure by Warm Deformation of Austenite in High-Strength Steel" Materials 18, no. 6: 1341. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18061341
APA StyleShu, W., Fan, Y., Li, R., Liu, Q., & Lai, Q. (2025). Formation of Ultrafine-Grained Dual-Phase Microstructure by Warm Deformation of Austenite in High-Strength Steel. Materials, 18(6), 1341. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18061341





