Impact of DC Electric Field Direction on Sedimentation Behavior of Colloidal Particles in Water
Abstract
1. Introduction
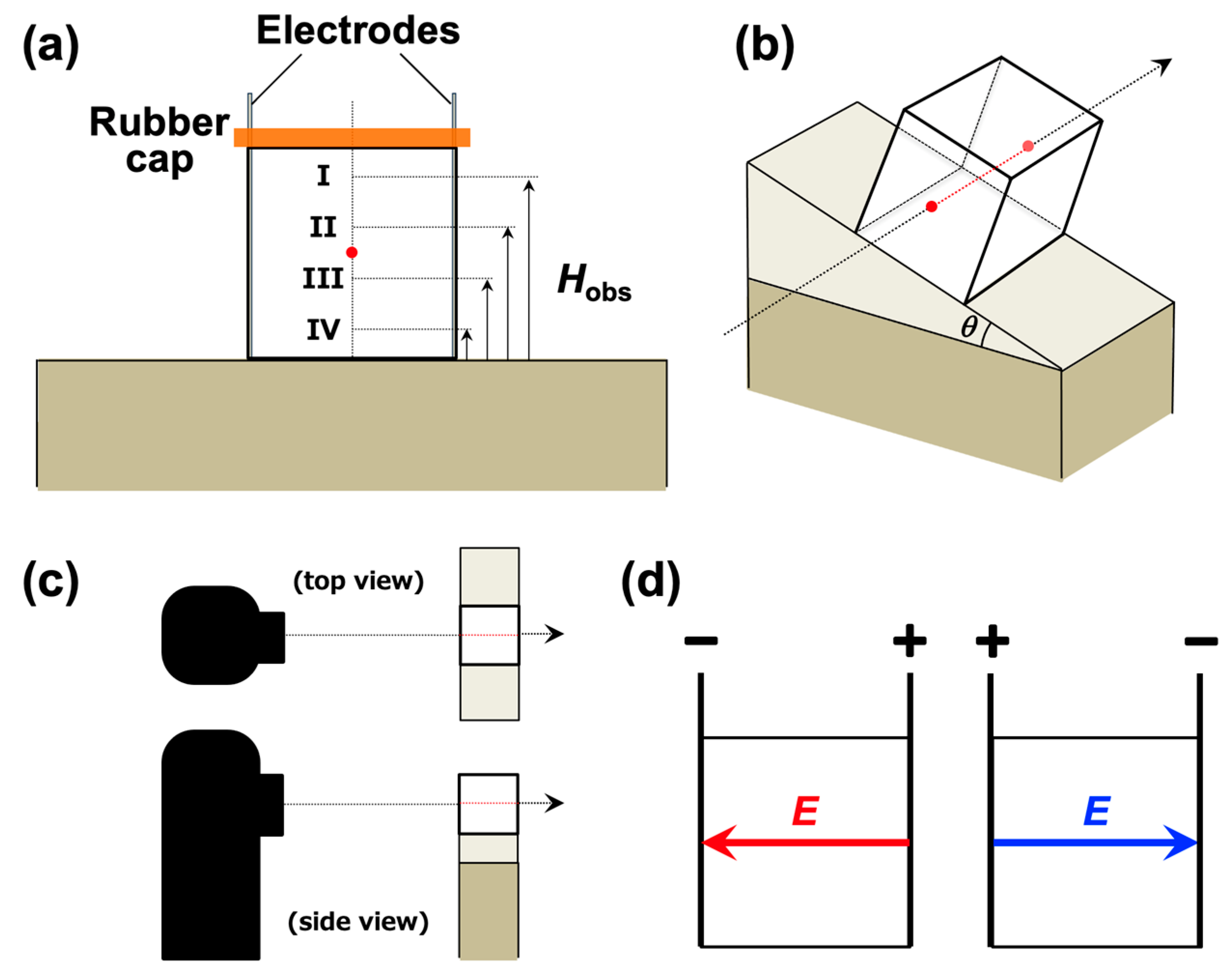
2. Experimental Methods
2.1. Sample Preparation
2.2. Observation of the Temporal Changes in the Dispersion State of PMMA Particles
3. Results and Discussion
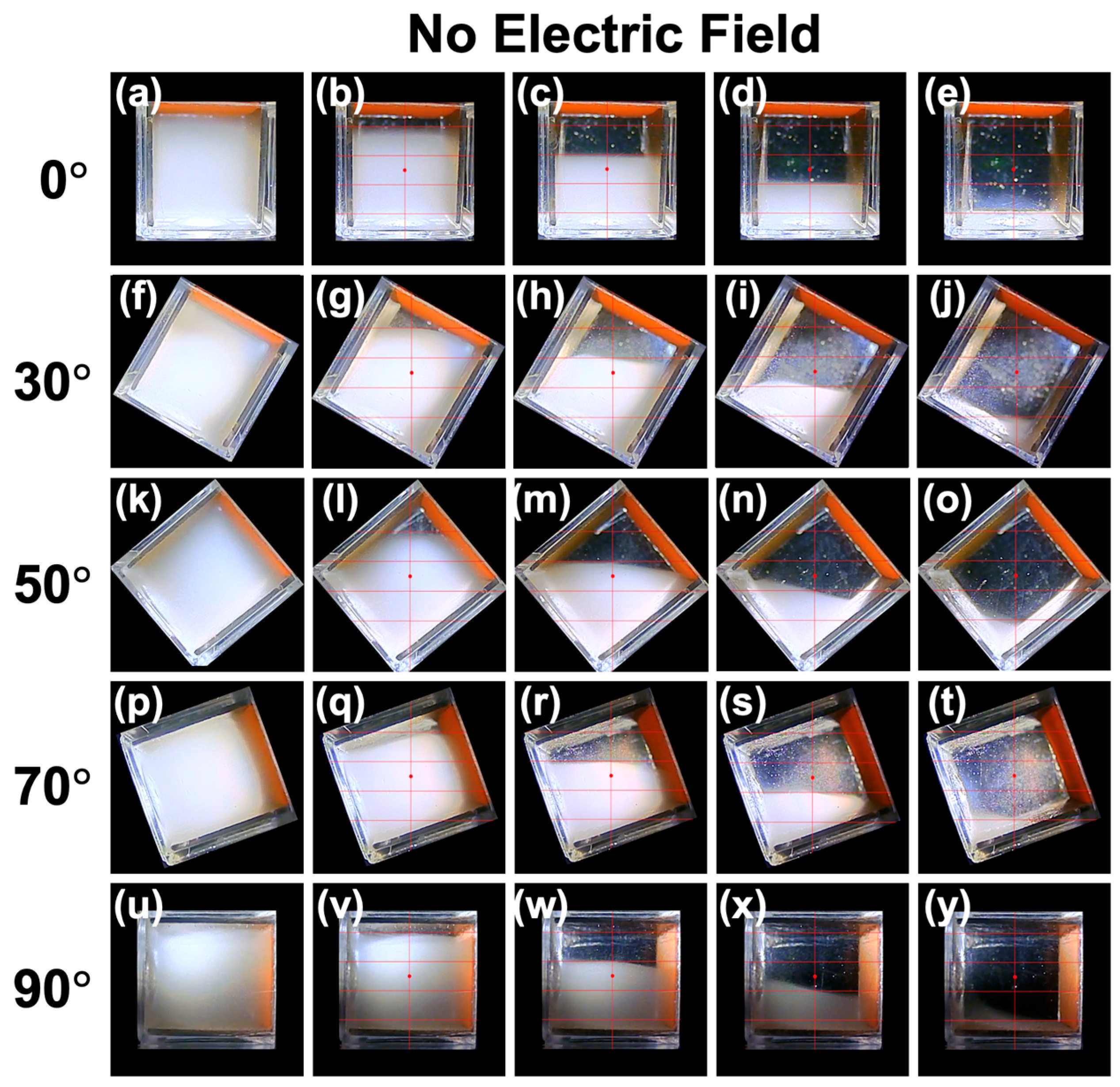
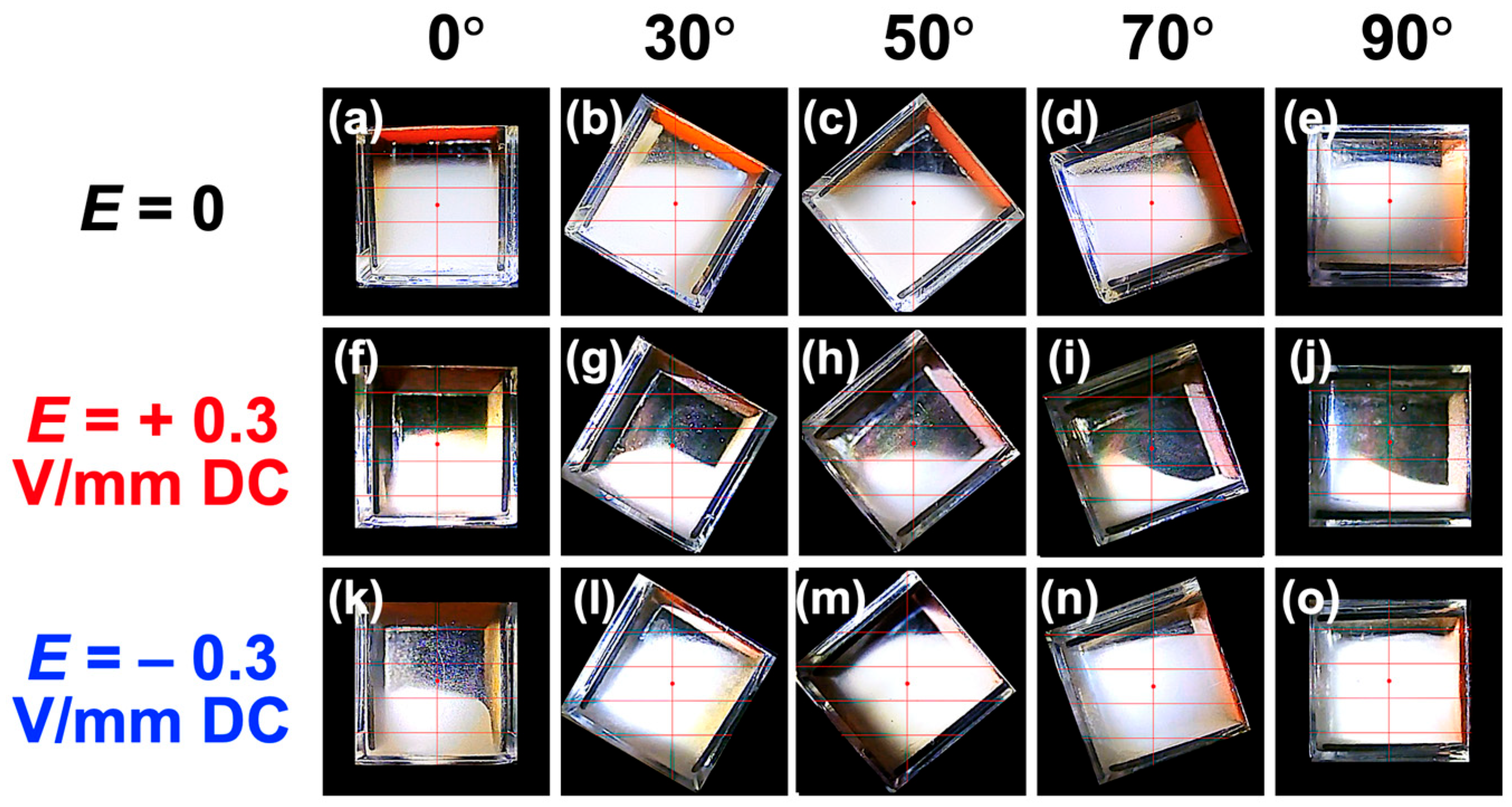
3.1. Sedimentation Behavior of PMMA Particles Under No Electric Field
- ▪ In the absence of an electric field, interference with surrounding particles can be ignored, and particles settle without forming flocs.
- ▪ The sedimentation velocity of PMMA particles follows the Stokes approximation in a stationary fluid.
- ▪ The descent velocity of the boundary can be considered equal to the sedimentation velocity of the PMMA particles.
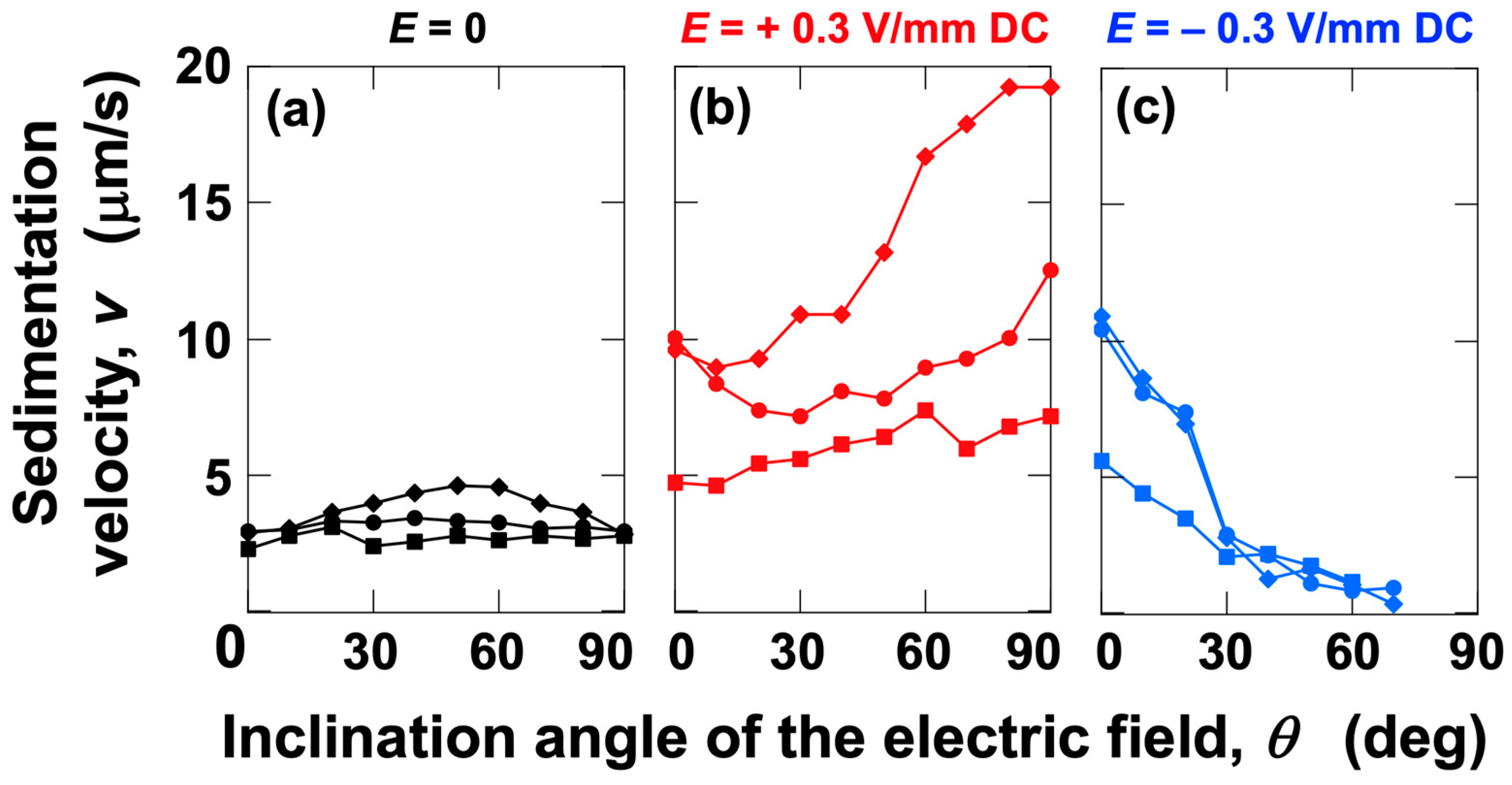
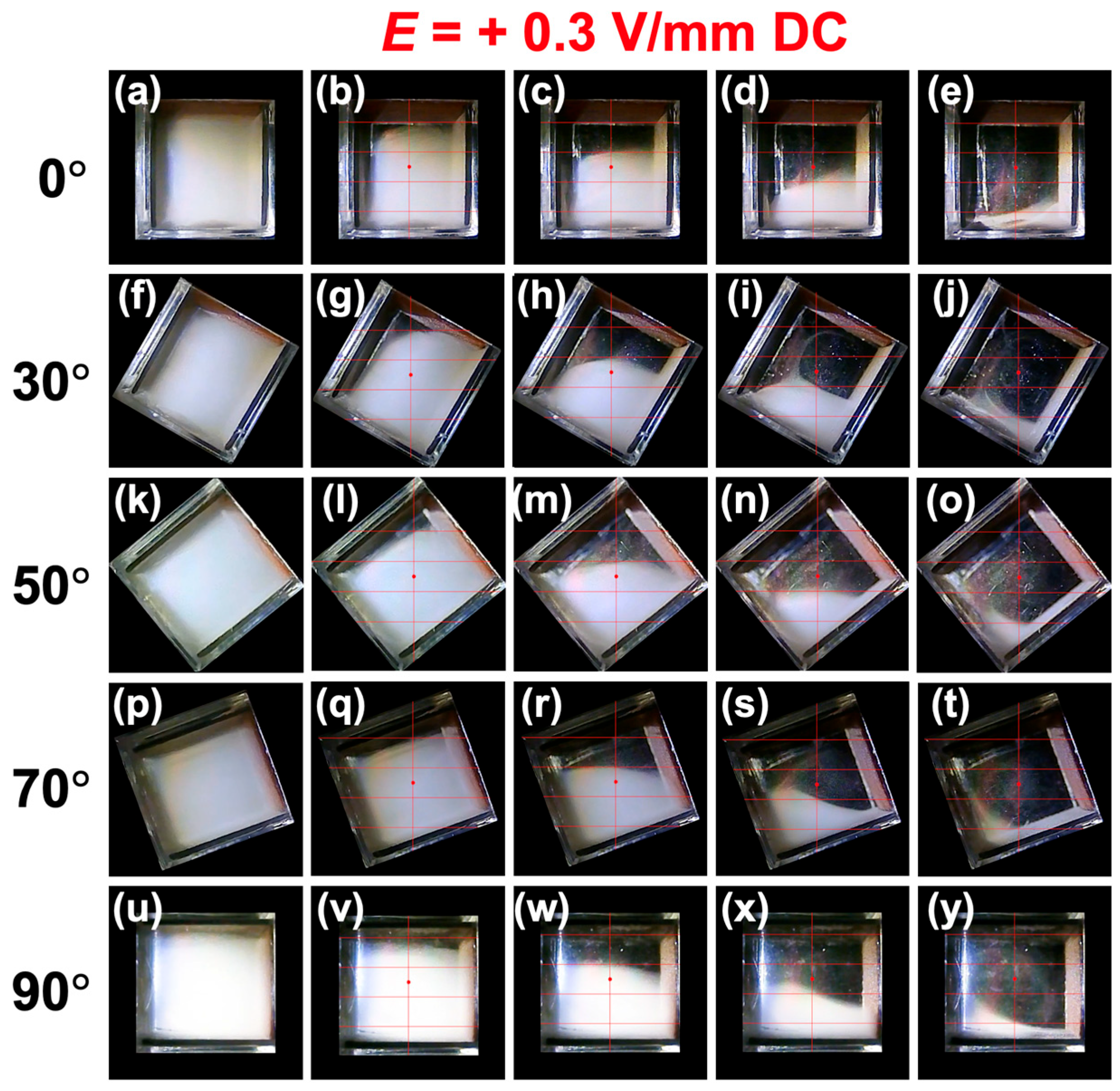
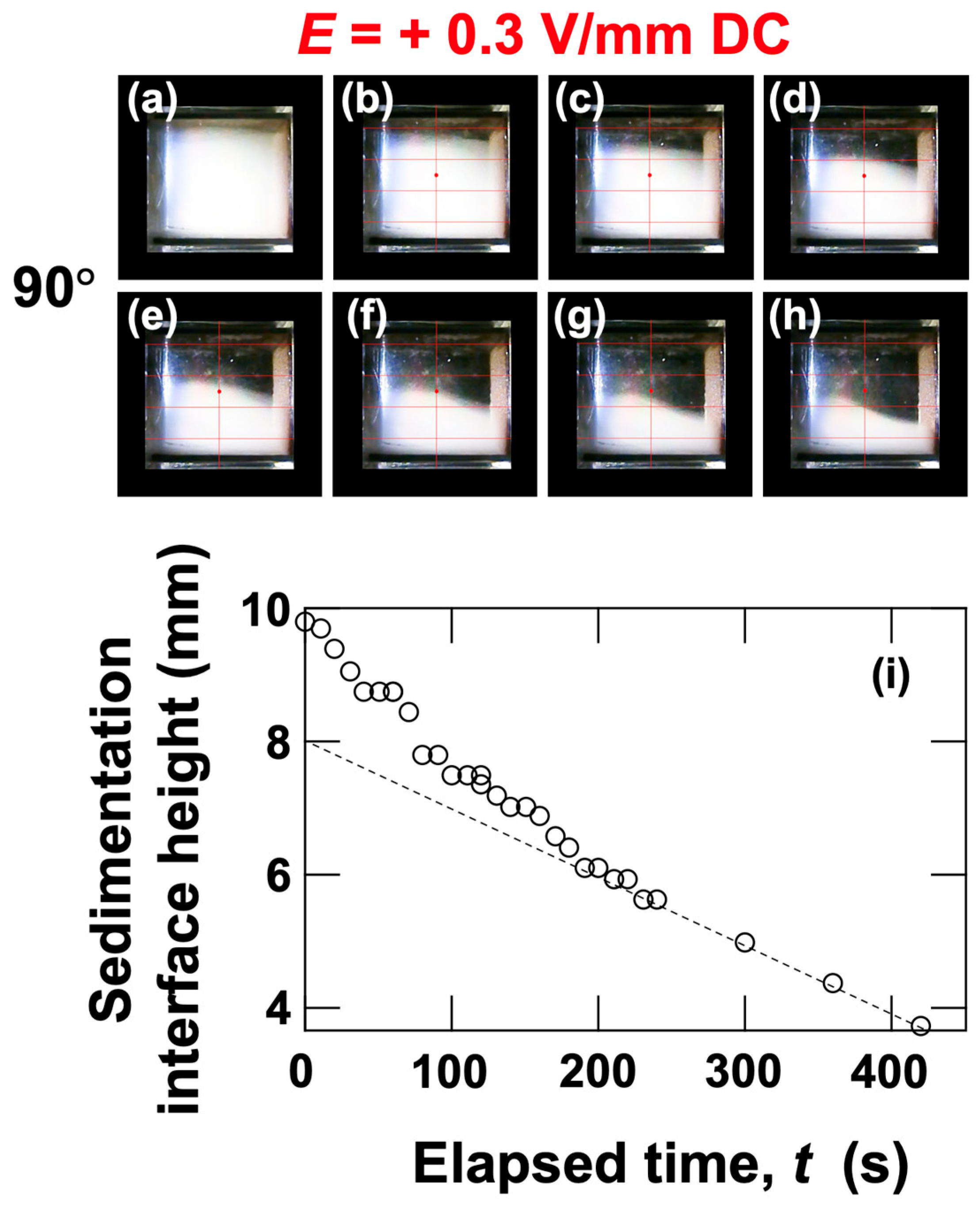
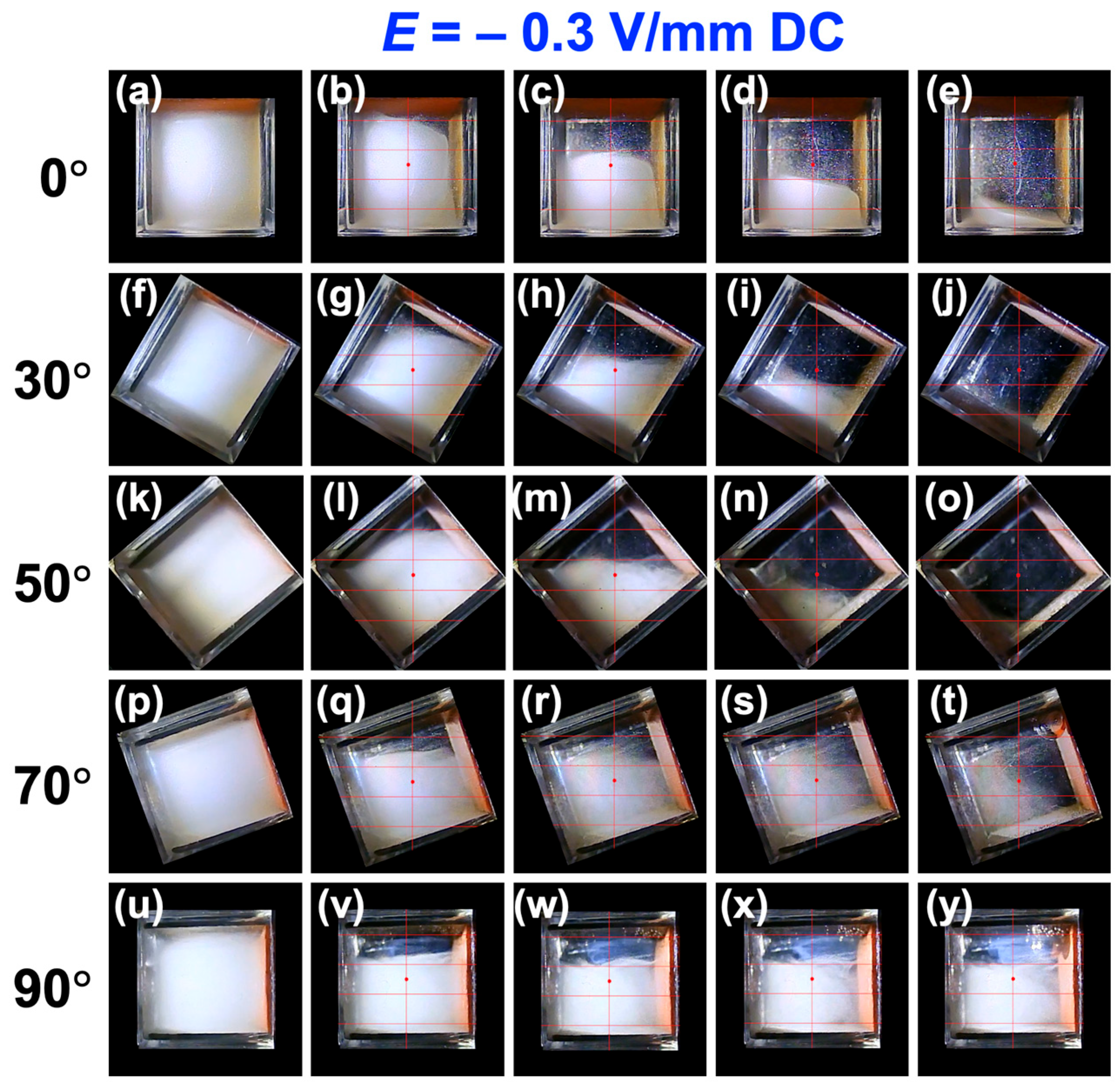
3.2. Sedimentation Velocity of PMMA Particles Under No Electric Field and Applied Electric Field
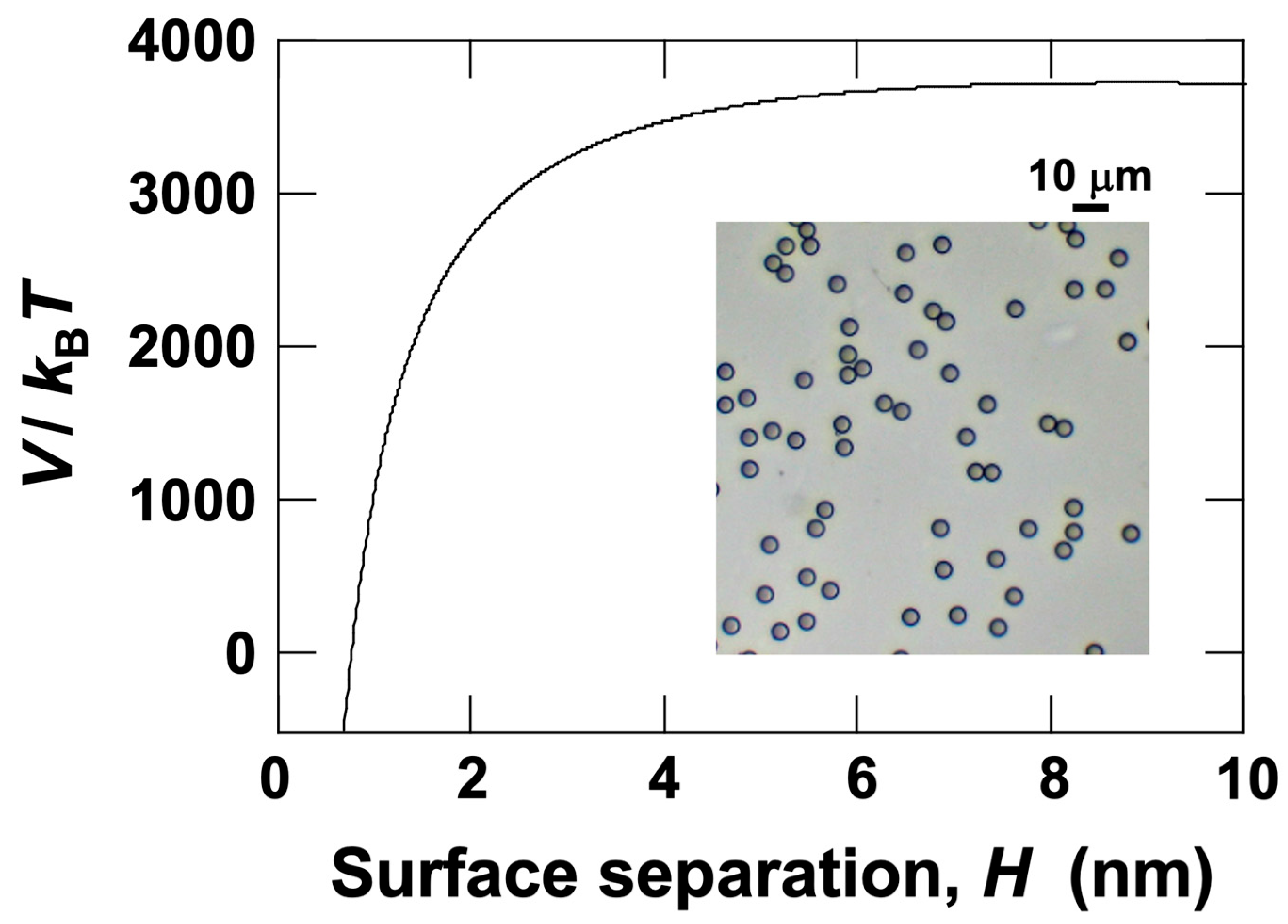
3.3. Relationship Between Electrophoretic Velocity and Sedimentation Velocity
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sun, Z.-W.; Liu, J.; Xu, S.-H. Towards an understanding of the influence of sedimentation on colloidal aggregation by Peclet number. Chin. Phys. Lett. 2005, 22, 2119–2122. [Google Scholar]
- Whitmer, J.K.; Luijten, E. Sedimentation of aggregating colloids. J. Chem. Phys. 2011, 134, 034510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pieranski, P.; Strzelecki, L.; Pansu, B. Thin colloidal crystals. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1983, 50, 900–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Derjaguin, B.; Landau, L.D. Theory of the stability of strongly charged lyophobic sols and of the adhesion of strongly charged particles in solutions of electrolytes. Acta Physicochim. URSS 1941, 14, 633–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verwey, E.J.W.; Overbeek, J.T.G. Theory of the Stability of Lyophobic Colloids; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1948. [Google Scholar]
- Kimura, H. Influence of alternating electric field on electrorheological effect of aqueous dispersions of stevensite. Appl. Clay Sci. 2024, 254, 107393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimura, H.; Takahashi, S.; Tsuchida, A. Rapid sedimentation of poly(methyl methacrylate) spheres and montmorillonite particles in water upon application of a DC electric field of the order of a few V/mm. Appl. Clay Sci. 2014, 101, 623–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimura, H.; Tsuchida, A. Sedimentation behavior of poly(methyl methacrylate) spheres in water upon application of a DC vertical electric field of the order of a few V/mm. Powder Technol. 2017, 320, 362–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimura, H. Rapid ascent of hollow particles in water induced by an electric field. Powders 2023, 2, 737–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimura, H. Co-flocculation of mixed-sized colloidal particles in aqueous dispersions under a DC electric field. Materials 2025, 18, 98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guelcher, S.A.; Solomentsev, Y.; Anderson, J.L. Aggregation of pairs of particles on electrodes during electrophoretic deposition. Powder Technol. 2000, 110, 90–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Guelcher, S.A.; Garoff, S.; Anderson, J.L. Two-particle dynamics on an electrode in AC electric fields. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2002, 96, 131–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fraden, S.; Hurd, A.J.; Meyer, R.B. Electric-field-induced association of colloidal particles. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1989, 63, 2373–2376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, Q.-h.; Liu, X.-h.; Zhou, C.-h.; Ming, N.-b. In situ studies of colloidal aggregation induced by alternating electrical fields. Phys. Rev. E 1993, 48, 2786–2791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, F.; Uchikoshi, T.; Ozawa, K.; Sakka, Y. Electrophoretic deposition of aqueous nano-γ-Al2O3 suspensions. Mater. Res. Bull. 2002, 37, 653–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohd Sharif, S.; Abu Bakar, N.F.; Naim, M.N. Deposition of fine iron oxide particles in tap water using electrophoretic deposition (EPD) technique. J. Water Process Eng. 2015, 7, 123–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trau, M.; Saville, D.A.; Aksay, I.A. Field-induced layering of colloidal crystals. Science 1996, 272, 706–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, T.; Wu, D.T.; Marr, D.W.M. Electric field-reversible three-dimensional colloidal crystals. Langmuir 2003, 19, 5967–5970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lumsdon, S.O.; Kaler, E.W.; Velev, O.D. Two-dimensional crystallization of microspheres by a coplanar AC electric field. Langmuir 2004, 20, 2108–2116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yakovlev, E.V.; Komarov, K.A.; Zaytsev, K.I.; Kryuchkov, N.P.; Koshelev, K.I.; Zotov, A.K.; Shelestov, D.A.; Tolstoguzov, V.L.; Kurlov, V.N.; Ivlev, A.V.; et al. Tunable two-dimensional assembly of colloidal particles in rotating electric fields. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 13727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harraq, A.A.; Choudhury, B.D.; Bharti, B. Field-induced assembly and propulsion of colloids. Langmuir 2022, 38, 3001–3016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimura, H.; Sakakibara, M. Electric Field-Induced Settling and Flotation of Flocs in Mixed Aqueous Suspensions of Poly(methyl methacrylate) and Aluminosilicate Hollow Particles. Materials 2025, 18, 1289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.; Nakayama, Y.; Yamamoto, R. Direct numerical simulations of electrophoresis of charged Colloids. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2006, 96, 208302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mori, T.; Nagashima, H.; Ito, Y.; Era, Y.; Tsubaki, J. Agglomeration of fine particles in water upon application of DC electric field. Miner. Eng. 2019, 133, 119–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tadros, T.F. General principles of colloid stability and the role of surface forces. In Colloid Stability: The Role of Surface Forces; Wiley-VCH: Weinheim, Germany, 2007; Volume I, pp. 1–22. [Google Scholar]
- Clift, R.; Grace, J.R.; Weber, M.E. Bubbles, Drops, and Particles. J. Fluid Mech. 1979, 94, 795–796. [Google Scholar]
- He, N.; Cui, Y.; Chin, D.W.Q.; Darnige, T.; Claudin, P.; Semin, B. Sedimentation of a single soluble particle at low Reynolds and high Péclet numbers. Phys. Rev. Fluids 2024, 9, 044502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heitkam, S.; Yoshitake, Y.; Toquet, F.; Langevin, D.; Salonen, A. Speeding up of sedimentation under confinement. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2013, 110, 178302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kimura, H. Impact of DC Electric Field Direction on Sedimentation Behavior of Colloidal Particles in Water. Materials 2025, 18, 1335. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18061335
Kimura H. Impact of DC Electric Field Direction on Sedimentation Behavior of Colloidal Particles in Water. Materials. 2025; 18(6):1335. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18061335
Chicago/Turabian StyleKimura, Hiroshi. 2025. "Impact of DC Electric Field Direction on Sedimentation Behavior of Colloidal Particles in Water" Materials 18, no. 6: 1335. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18061335
APA StyleKimura, H. (2025). Impact of DC Electric Field Direction on Sedimentation Behavior of Colloidal Particles in Water. Materials, 18(6), 1335. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18061335








