Effects of Solution Treatment on Microstructure Evolution and the Mechanical Properties of GH4780 Superalloy
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental
2.1. Alloy Preparation and Heat Treatment
2.2. Mechanical Tests
2.3. Microstructural Characterization
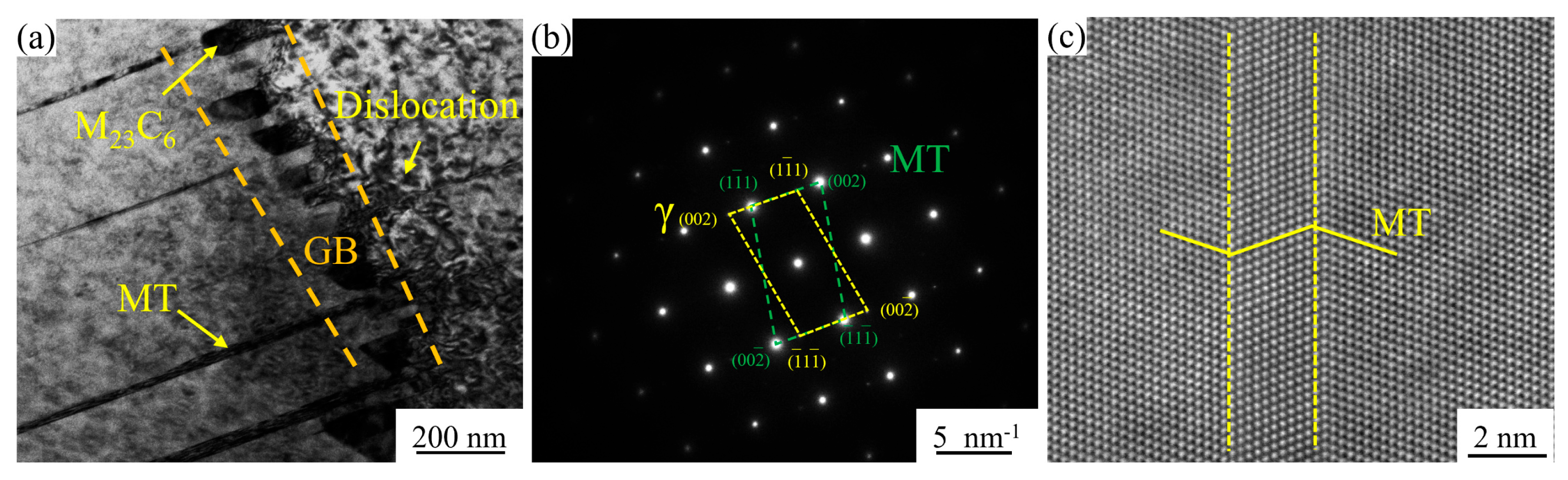
3. Results and Analysis
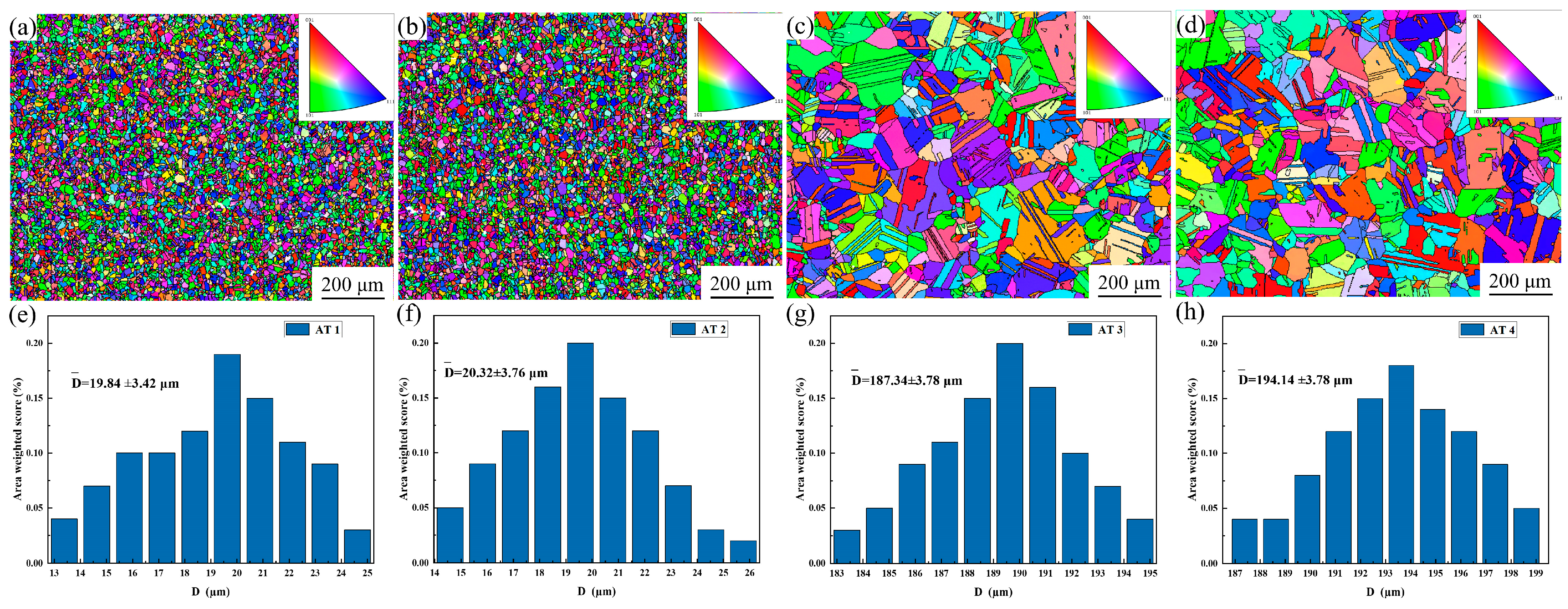
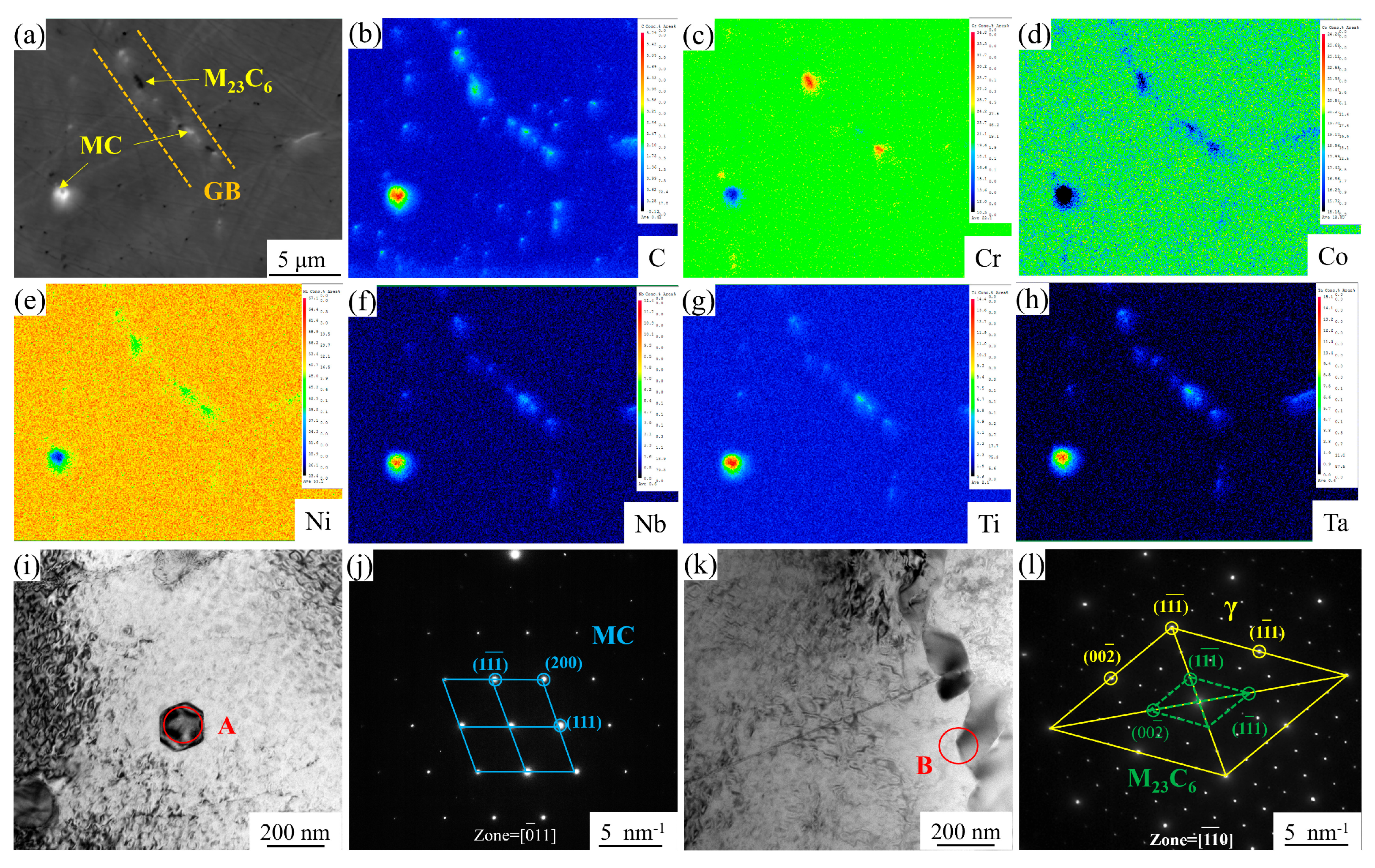
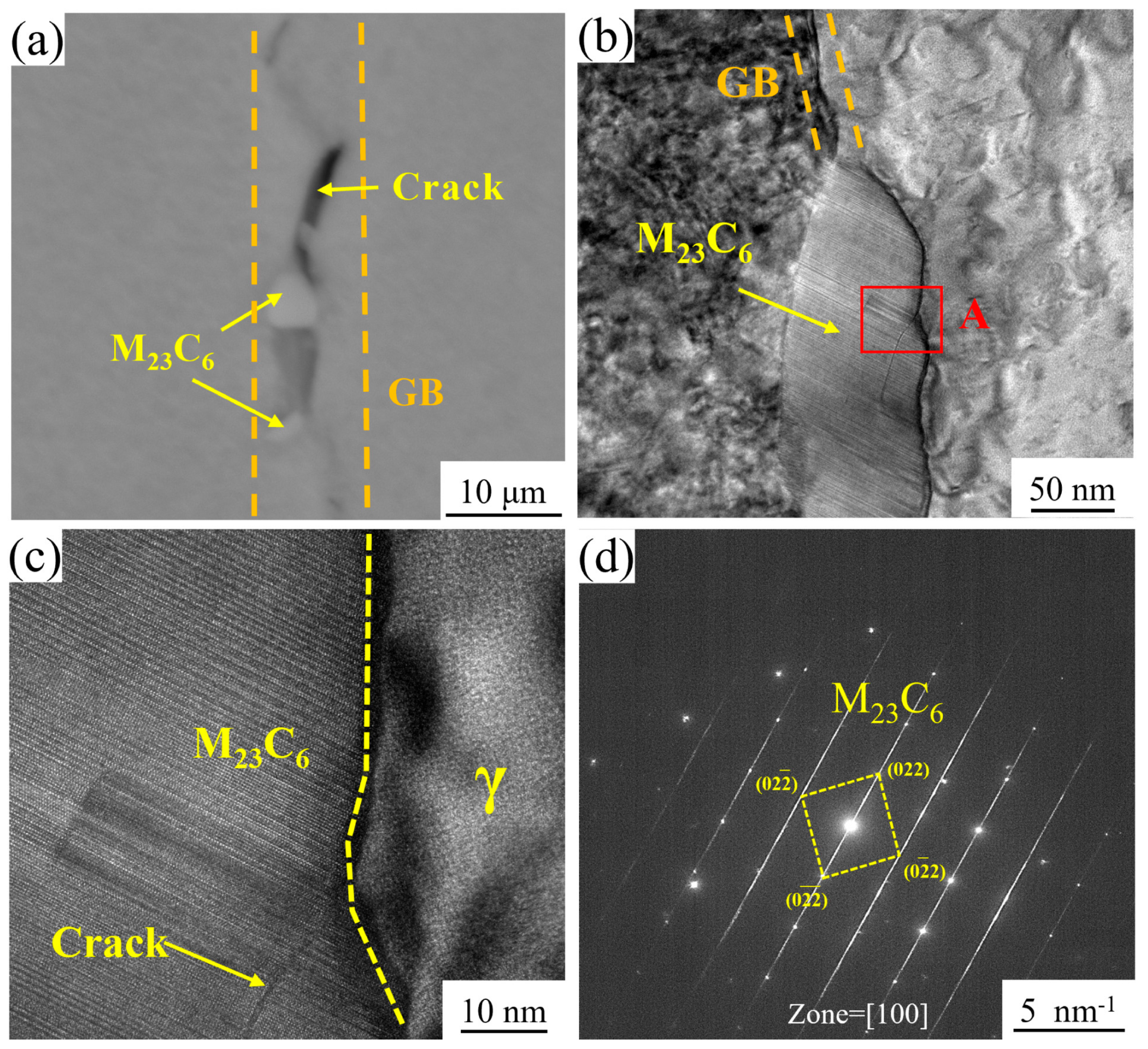
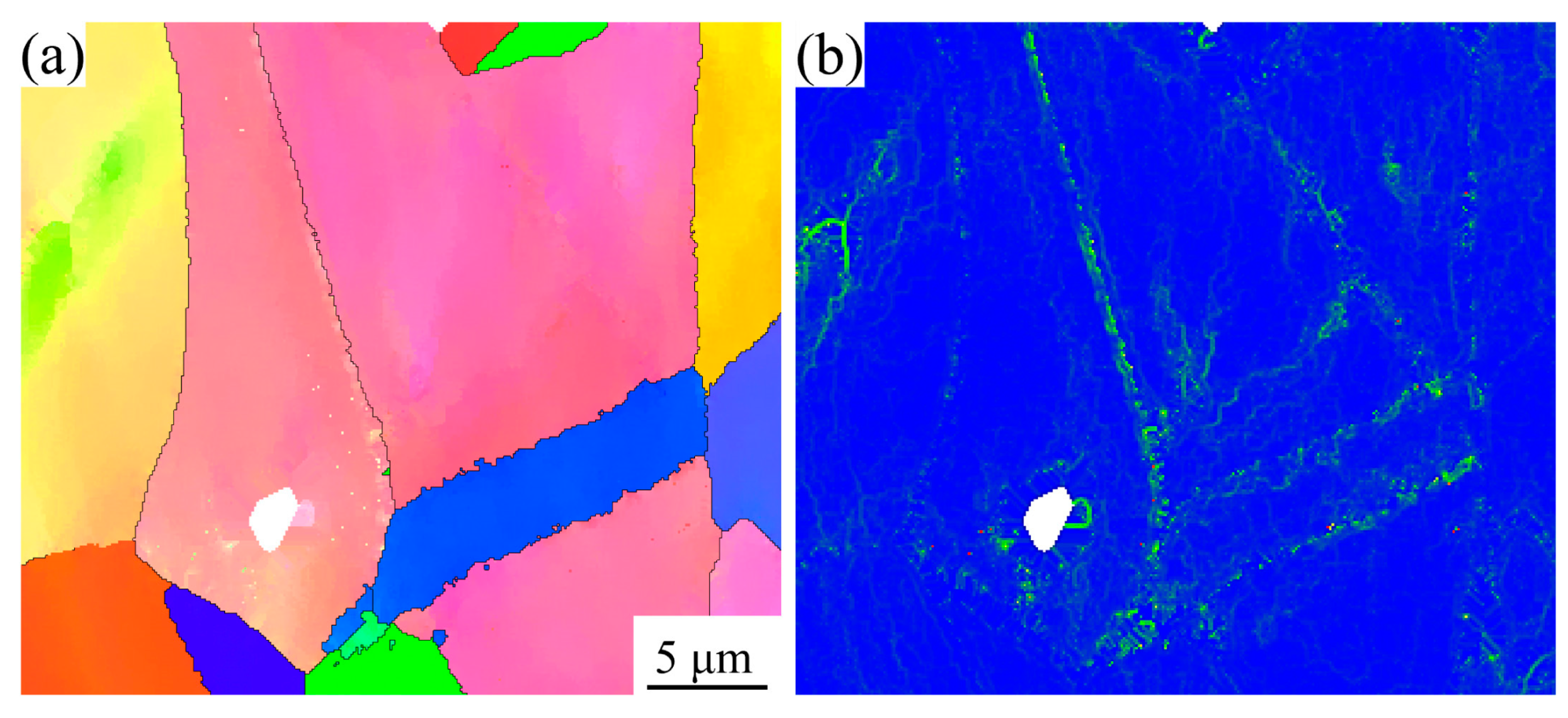
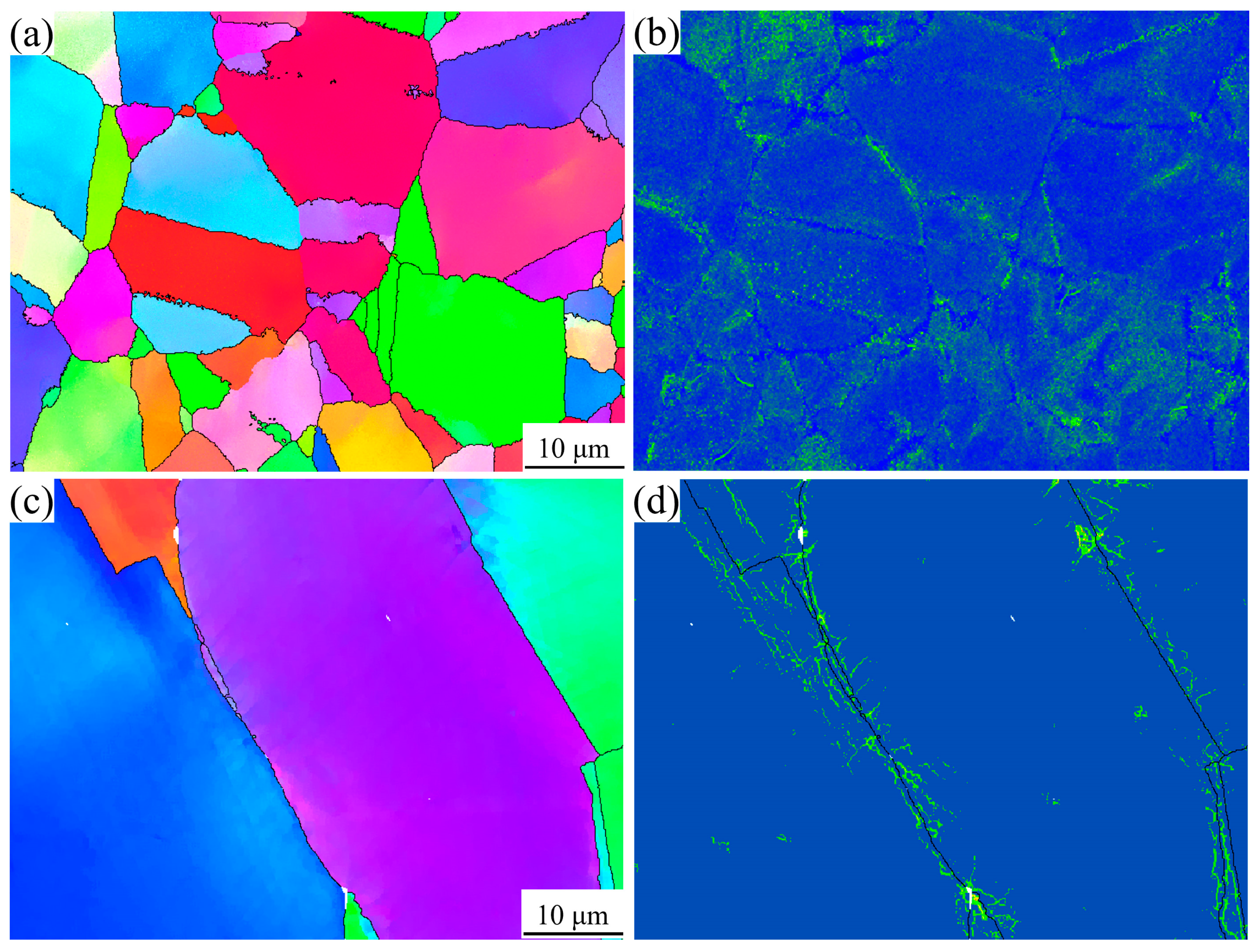
3.1. Microstructure of GH4780 Superalloy
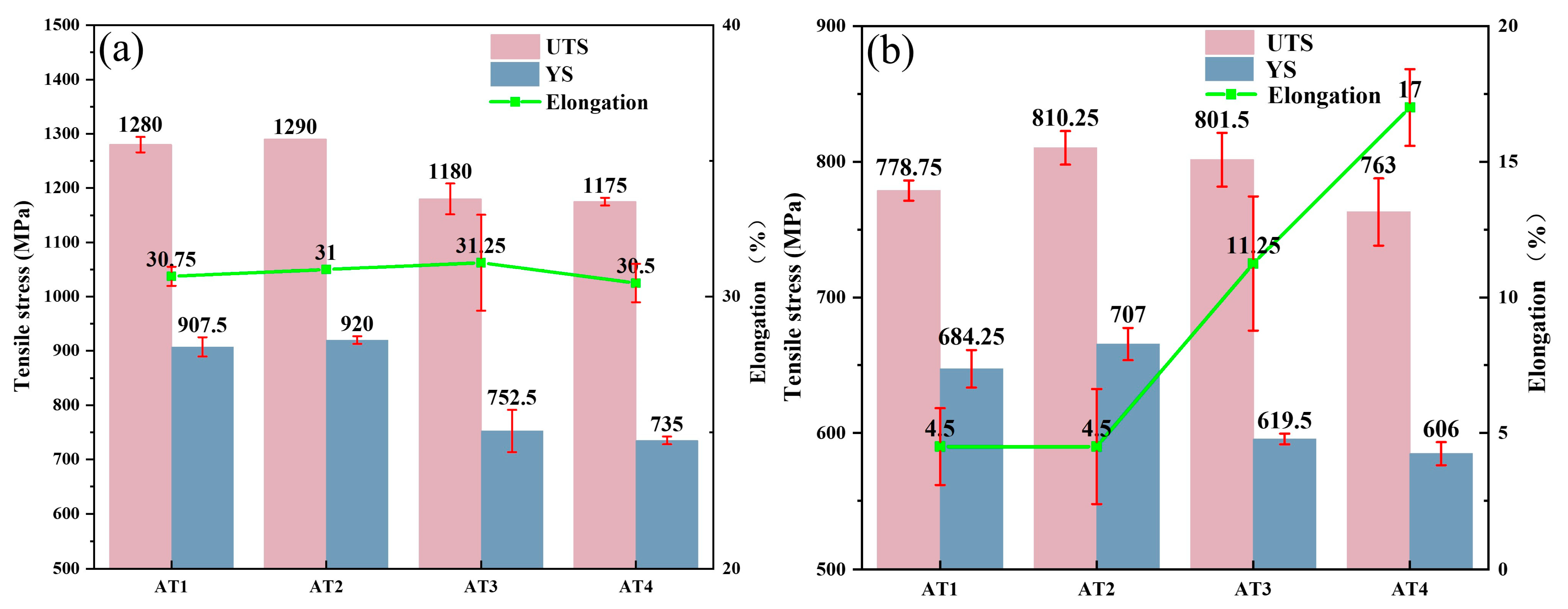
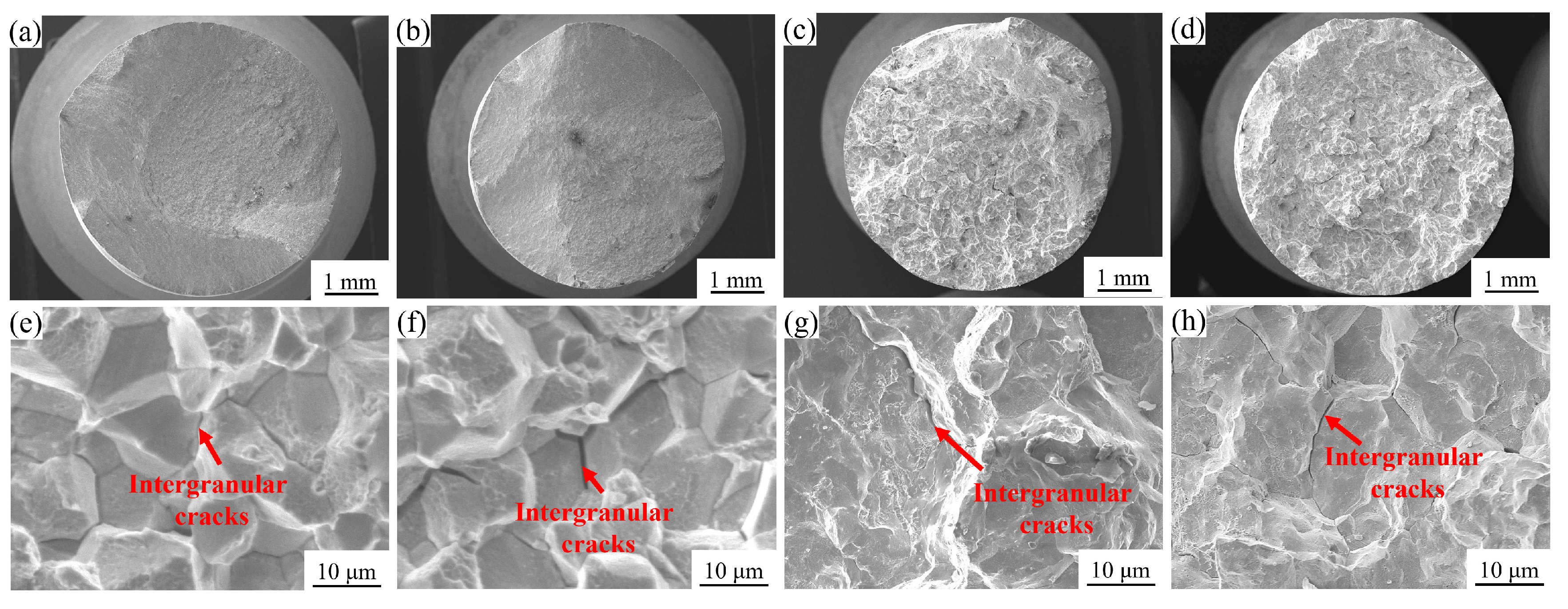
3.2. Tensile Properties of GH4780 Superalloy
4. Discussion
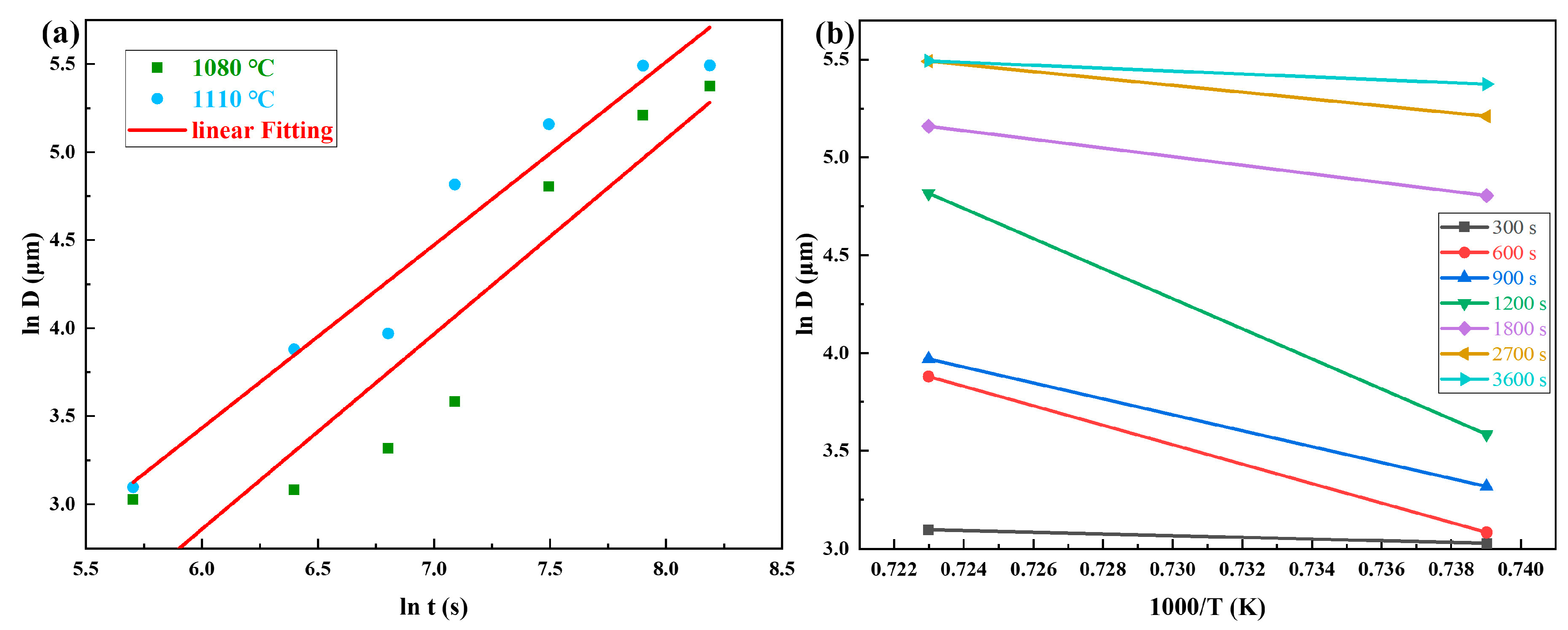
4.1. Effect of Solution Treatment on the Microstructural Evolution of GH4780 Superalloy
4.2. Effect of Grain Size on Tensile Properties of GH4780 Superalloy at Room Temperature
4.3. Effect of Microstructure on High-Temperature Tensile Properties of GH4780 Superalloy
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bryndza, G.; Tchuindjang, J.T.; Chen, F.; Habraken, A.M.; Sepúlveda, H.; Tuninetti, V.; Mertens, A.; Duchêne, L. Review of the Microstructural Impact on Creep Mechanisms and Performance for Laser Powder Bed Fusion Inconel 718. Materials 2025, 18, 276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, D.; Chen, X.; Lin, Y.C.; Yan, X.; Xie, H. Influences of stress triaxiality and forming parameters on microstructural evolution and fracture mechanisms in a Ni–Cr–Mo-based superalloy. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2024, 32, 378–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hardy, M.C.; Detrois, M.; Mcdevitt, E.T.; Argyrakis, C.; Saraf, V.; Jablonski, P.D.; Hawk, J.A.; Buckingham, R.C.; Kitaguchi, H.S.; Tin, S. Solving Recent Challenges for Wrought Ni-Base Superalloys. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 2020, 51, 2626–2650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Q.; Cheng, L.; Wang, C.; Chen, G.; Qin, H.; Zhang, P. Effect of δ phase on size effect in microtensile deformation of a nickel-based superalloy. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2019, 766, 138405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Liu, W.; Zhang, H.; Ruan, J.; Huang, H.; Zhou, X.; Meng, F.; Zhang, S.; Jiang, L. Dramatically improving thermoplasticity of FGH4096 superalloy by a novel sub-solvus temperature holding followed by extremely slow cooling. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2023, 24, 1973–1990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, Y.; Ouyang, X.; Tian, Y.; Yu, H.; Wei, G. Insight into the hot corrosion behavior of GH4251 high-temperature superalloy fabricated by selective laser melting. J. Alloys Compd. 2024, 1002, 175166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajabinezhad, M.; Bahrami, A.; Mousavinia, M.; Seyedi, S.J.; Taheri, P. Corrosion-fatigue failure of gas-turbine blades in an oil and gas production plant. Materials 2020, 13, 900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, X.; Xu, J.; Yang, Z.; Guo, Q.; Li, C.; Zhou, J.; Chen, S.-L.; Liu, S.; Ma, Z. A novel nickel-based superalloy with excellent high temperature performance designed for laser additive manufacturing. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2024, 911, 146926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xi, X.; Lin, D.; Song, X.; Luo, X.; Ma, R.; Shi, Z.; Bian, H.; Fu, W.; Dong, Z.B.; Tan, C. Strength-plasticity transition mechanism after the solution treatment of GH3230 superalloy fabricated via laser powder bed fusion. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2023, 876, 145124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Z.-L.; Jiang, S.-B.; Chen, Z.-Z.; Bao, H.-S.; Liu, Z.-D. Microstructural evolution and mechanical properties of a new Ni-based heat-resistant alloy during aging at 750 °C. J. Iron Steel Res. Int. 2017, 24, 513–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Li, N.; Jia, C.; Liu, W.; Wu, Y.; Gao, C.; Xiong, H. Effects of solution treatment on the microstructural evolution and tensile properties of GH 3230 superalloy manufactured by laser melting deposition. Mater. Charact. 2022, 194, 112339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Han, H.; Zhou, Y.; Chen, J.; Feng, S.; Tang, P.; Xiao, D.; Fu, J.; Zhang, J. Effect of solution treatment on the microstructure and elevated temperature tensile properties of forged Rene 41 superalloy. Materials 2024, 17, 6150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.; Zheng, Y.; Liu, F.; Wang, D.; Liu, F.; Huang, C.; Li, Q.; Lin, X.; Huang, W. Effect of solution temperature on the microstructure and mechanical properties of Hastelloy X superalloy fabricated by laser directed energy deposition. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2021, 820, 141537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Wang, D.; Wang, L.; Jiang, C.; Zhou, L.; Zhou, Z.; Wang, H.; Zhai, Y. The behaviour and kinematic model for γ′ evolution and grain growth during solution treatment of a powdered metallurgical Ni-based superalloy. Mater. Charact. 2023, 199, 112820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, K.; Aindow, M. Grain growth and particle pinning in a model Ni-based superalloy. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2008, 479, 365–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Zhang, R.; Cui, C.; Zhou, Y.; Sun, X. Influence of solution temperature on microstructure and creep behaviors of a Ni–Co base superalloy for turbine disc. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2022, 853, 143741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ASTM E8; Standard Test Methods for Tension Testing of Metallic Materials. ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2022.
- ASTM E21; Standard Test Methods for Elevated Temperature Tension Tests of Metallic Materials. ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2020.
- Velasco-Castro, M.; León-Cázares, F.D.; Galindo-Nava, E.I. A comprehensive review of microstructural heterogeneities in the laser powder bed fusion of nickel-base superalloys with high γ′ content. Mater. Des. 2024, 247, 113416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.; Xie, X.; Smith, G.D.; Patel, S.J. Gamma prime coarsening and age-hardening behaviors in a new nickel base superalloy. Mater. Lett. 2004, 58, 1784–1787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masoumi, F.; Jahazi, M.; Shahriari, D.; Cormier, J. Coarsening and dissolution of γ′ precipitates during solution treatment of AD730™ Ni-based superalloy: Mechanisms and kinetics models. J. Alloys Compd. 2016, 658, 981–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sellars, C.; Whiteman, J. Recrystallization and grain growth in hot rolling. Met. Sci. 1979, 13, 187–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, S.; Wang, Y.; Lv, L.; Huang, Z.; Tan, G. Normal and abnormal grain growth in a FGH96 superalloy during thermomechanical treatment. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2021, 15, 7033–7049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rohrer, G.S. “Introduction to Grains, Phases, and Interfaces—An Interpretation of Microstructure,” Trans. AIME, 1948, vol. 175, pp. 15–51, by C.S. Smith. Metall. Mater. Trans. B 2010, 41, 457–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Ning, Y.; Wang, Z.; Liu, Q. PPB structure elimination, DRX nucleation mechanisms and grain growth behavior of the 3rd-generation PM superalloy for manufacturing aviation components. Chin. J. Aeronaut. 2024, 37, 325–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, S.; Liu, S.; Li, N.; Gao, X.; Wen, X.; Wang, F.; Yuan, C. Abnormal grain growth in the Ni-based wrought superalloy GH4698 bar during heat treatment. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2024, 30, 6563–6575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, J.; Huang, H.; Mao, H.; Hua, L. Phase transformation and grain growth behaviors of superalloy IN718 during heat treatment. Mater. Today Commun. 2020, 24, 101347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reed, R. The Superalloys: Fundamentals and Applications; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2006; pp. 1–372. [Google Scholar]
- Hong, S.I.; Laird, C. Mechanisms of slip mode modification in FCC solid solutions. Acta Metall. Et Mater. 1990, 38, 1581–1594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexandre, F.; Deyber, S.; Pineau, A. Modelling the optimum grain size on the low cycle fatigue life of a Ni based superalloy in the presence of two possible crack initiation sites. Scr. Mater. 2004, 50, 25–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joseph, C.; Persson, C.; Colliander, M.H. Influence of heat treatment on the microstructure and tensile properties of Ni-base superalloy Haynes 282. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2017, 679, 520–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alabort, E.; Barba, D.; Sulzer, S.; Lißner, M.; Petrinic, N.; Reed, R.C. Grain boundary properties of a nickel-based superalloy: Characterisation and modelling. Acta Mater. 2018, 151, 377–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Lin, X.; Wang, L.; Yu, X.; Yang, H.; Lei, L.; Huang, W. Influence of grain inhomogeneity and precipitates on the stress rupture properties of Inconel 718 superalloy fabricated by selective laser melting. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2021, 803, 140702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martelli, P.A.; Sabirov, I.; Monclus, M.A.; Bassini, E.; Marchese, G.; Ugues, D. The effect of temperature and strain rate on the grain boundary sliding in a CM247 LC Ni-based superalloy processed with laser based powder bed fusion. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2024, 28, 2466–2477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, J.; Yu, H.; Cao, R.; Liu, Z.; Wang, X.; Wang, J.; Bi, Z. The effect of pre-strain on textures, nano-twins and mechanical properties of a novel Nickel-based superalloy GH4251 with low stacking fault energy. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2024, 915, 147271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Y.Q.; Tan, Y.B.; Wang, L.X.; Shi, W.; Ji, X.M.; Xiang, S. Multiple strengthening mechanisms induced by nanotwins and stacking faults in CoNiCr-superalloy MP159. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2022, 853, 143793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, T.M.; Good, B.S.; Gabb, T.P.; Esser, B.D.; Egan, A.J.; Evans, L.J.; McComb, D.W.; Mills, M.J. Effect of stacking fault segregation and local phase transformations on creep strength in Ni-base superalloys. Acta Mater. 2019, 172, 55–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Co | Cr | W | Nb | Ta | Al + Ti | C + B + Zr | Si | Ni |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 17.99 | 21.27 | 1.72 | 0.63 | 0.93 | 3.00 | 0.073 | 0.053 | Bal. |
| No. | Solution Treatment | Aging Treatment |
|---|---|---|
| AT1 | 1020 °C/1 h (AC) | 800 °C/8 h (AC) |
| AT2 | 1050 °C/1 h (AC) | 800 °C/8 h (AC) |
| AT3 | 1080 °C/1 h (AC) | 800 °C/8 h (AC) |
| AT4 | 1110 °C/1 h (AC) | 800 °C/8 h (AC) |
| ST1 | 1020 °C/1 h (WQ) | - |
| ST2 | 1050 °C/1 h (WQ) | - |
| ST3 | 1080 °C/1 h (WQ) | - |
| ST4 | 1110 °C/1 h (WQ) | - |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Feng, T.-H.; Xie, X.-F.; Liu, Y.; Qu, J.-L.; Lyu, S.-M.; Du, J.-H.; Ruan, J.-J.; Zhu, L.-L. Effects of Solution Treatment on Microstructure Evolution and the Mechanical Properties of GH4780 Superalloy. Materials 2025, 18, 1288. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18061288
Feng T-H, Xie X-F, Liu Y, Qu J-L, Lyu S-M, Du J-H, Ruan J-J, Zhu L-L. Effects of Solution Treatment on Microstructure Evolution and the Mechanical Properties of GH4780 Superalloy. Materials. 2025; 18(6):1288. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18061288
Chicago/Turabian StyleFeng, Tian-Hao, Xing-Fei Xie, Yang Liu, Jing-Long Qu, Shao-Min Lyu, Jin-Hui Du, Jing-Jing Ruan, and Li-Long Zhu. 2025. "Effects of Solution Treatment on Microstructure Evolution and the Mechanical Properties of GH4780 Superalloy" Materials 18, no. 6: 1288. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18061288
APA StyleFeng, T.-H., Xie, X.-F., Liu, Y., Qu, J.-L., Lyu, S.-M., Du, J.-H., Ruan, J.-J., & Zhu, L.-L. (2025). Effects of Solution Treatment on Microstructure Evolution and the Mechanical Properties of GH4780 Superalloy. Materials, 18(6), 1288. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18061288








