Retention of Pediatric BioFlx Crowns Versus Stainless Steel Crowns Using Different Types of Luting Cements: An In Vitro Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
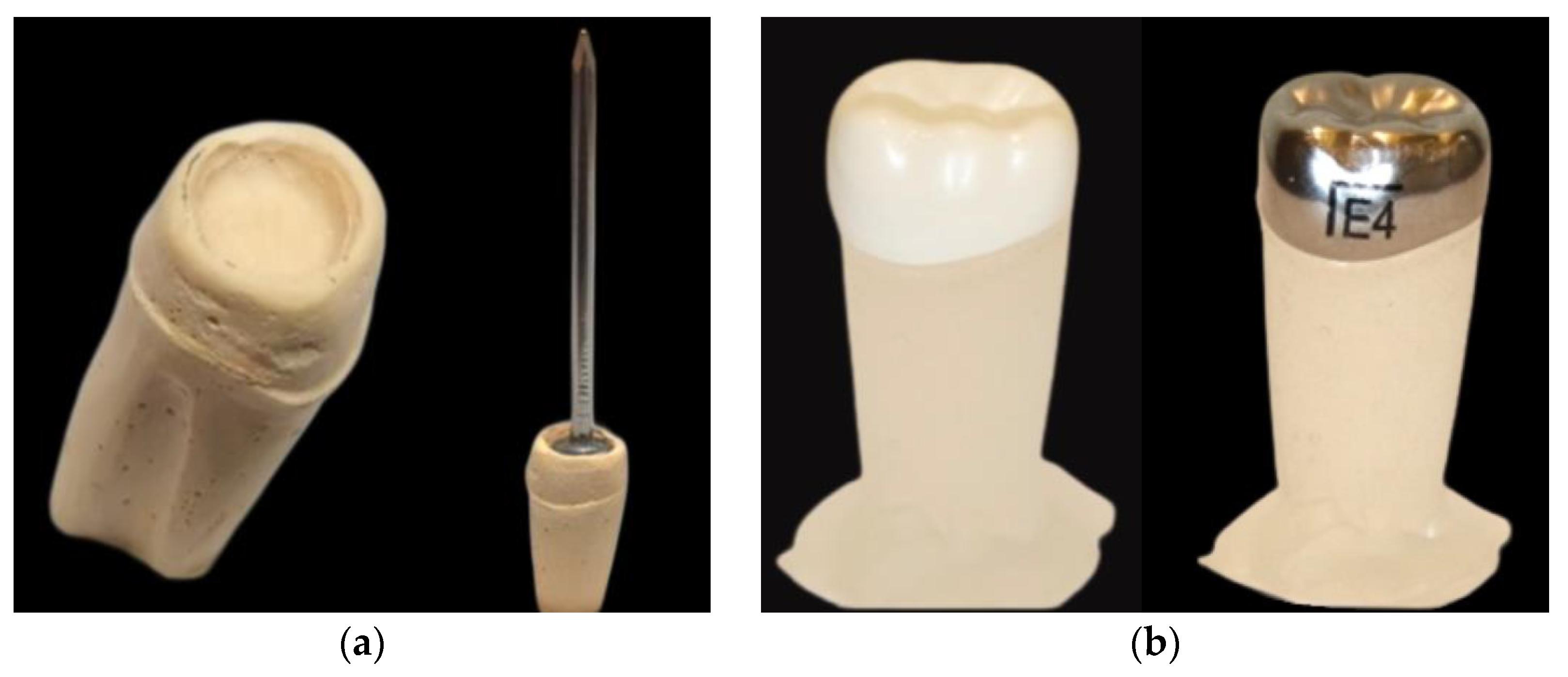
2.1. Die Preparation
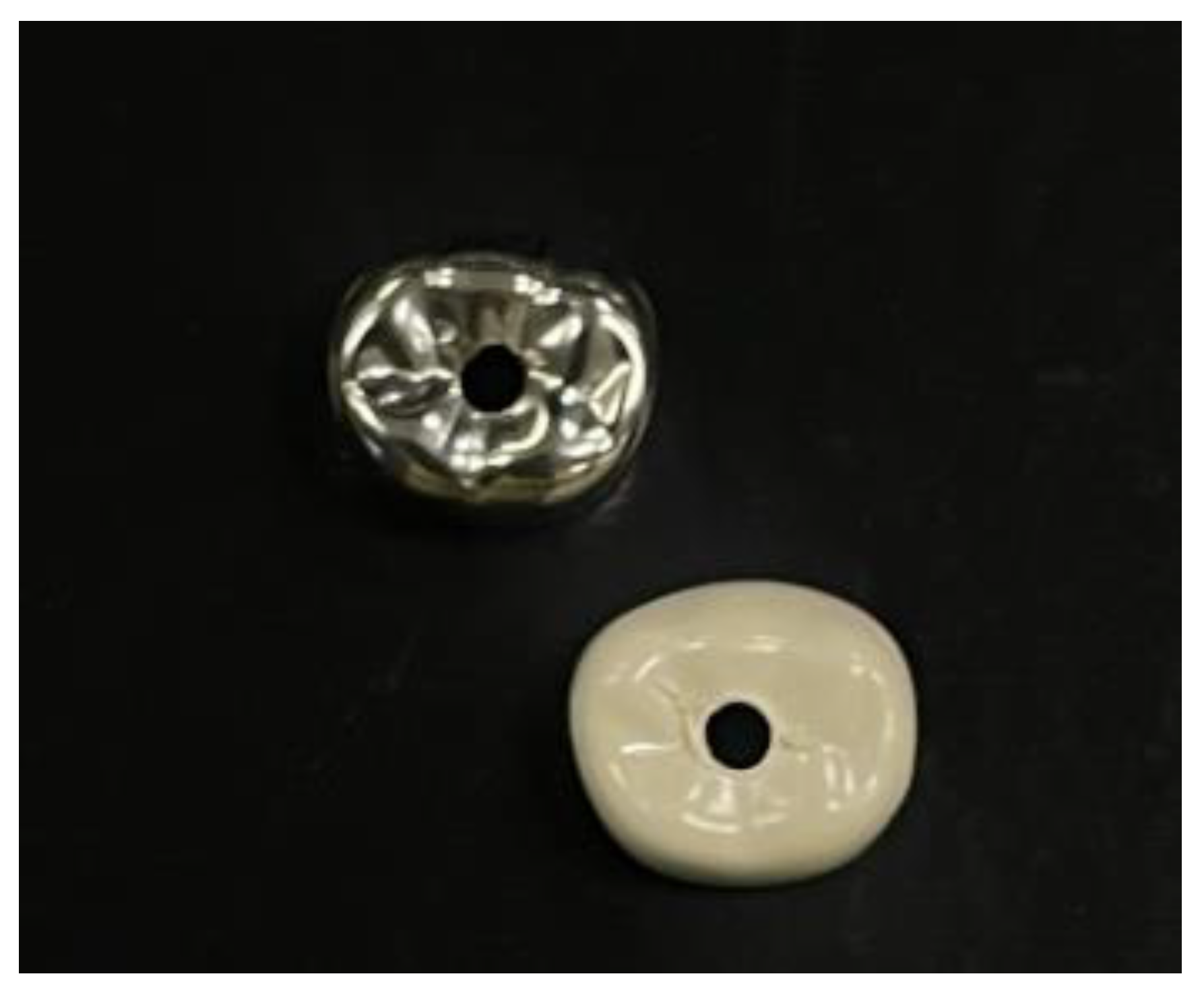
2.2. Crown Preparation
2.3. Cementation
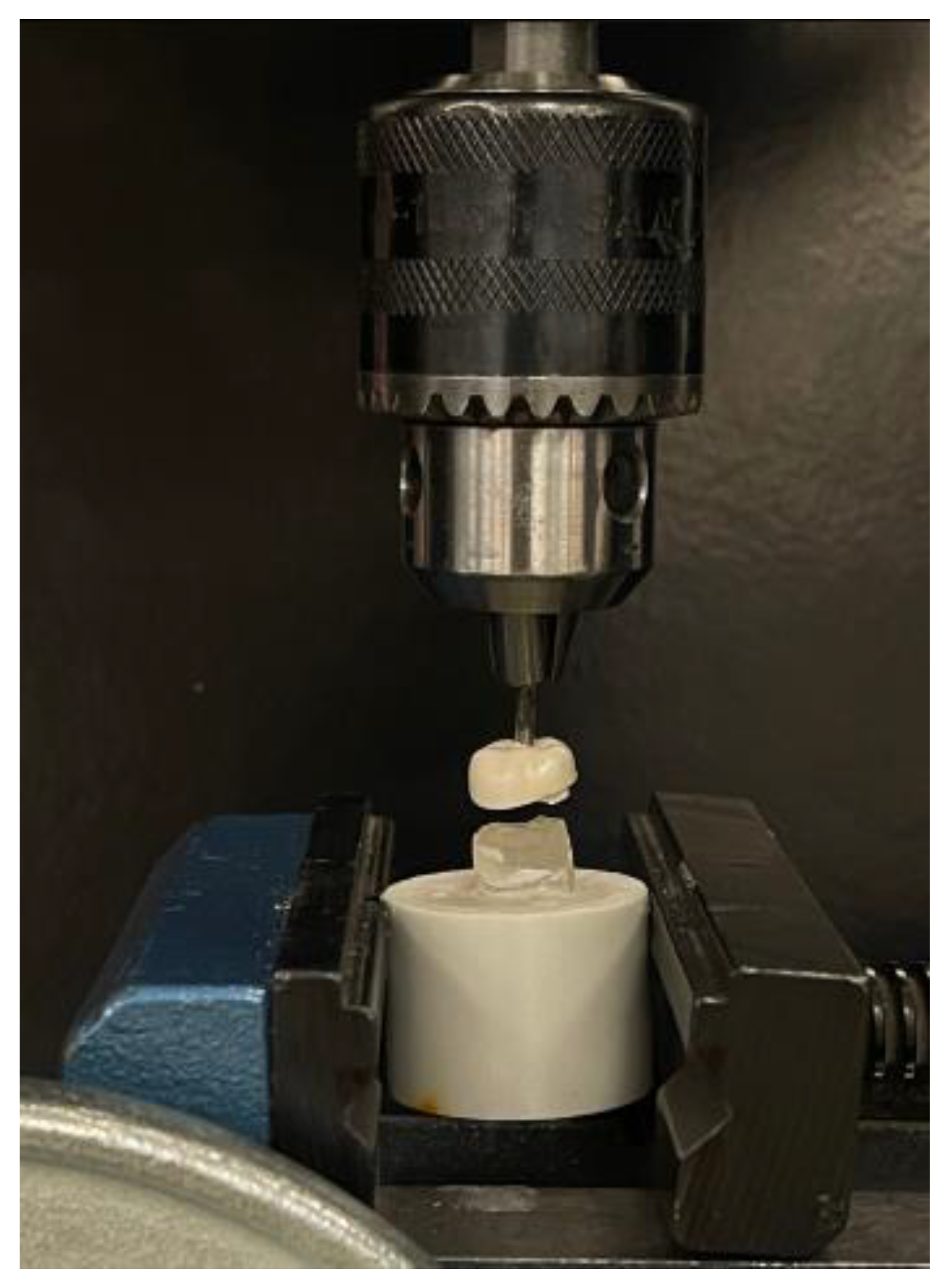
2.4. Retentive Strength Measurement
2.5. Assessment of Cement Failure Pattern
2.6. Sample Size Calculation and Statistical Analysis
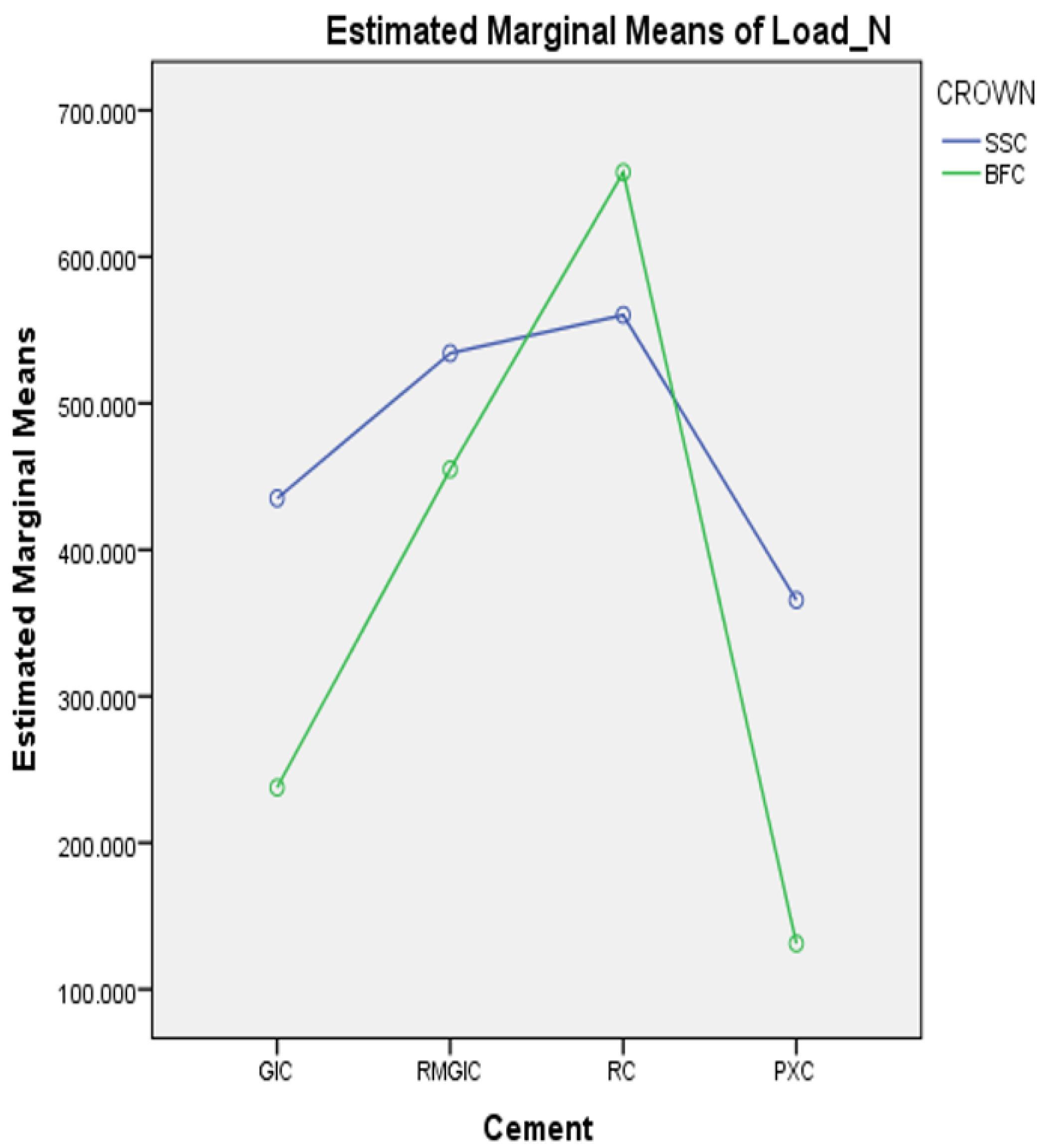
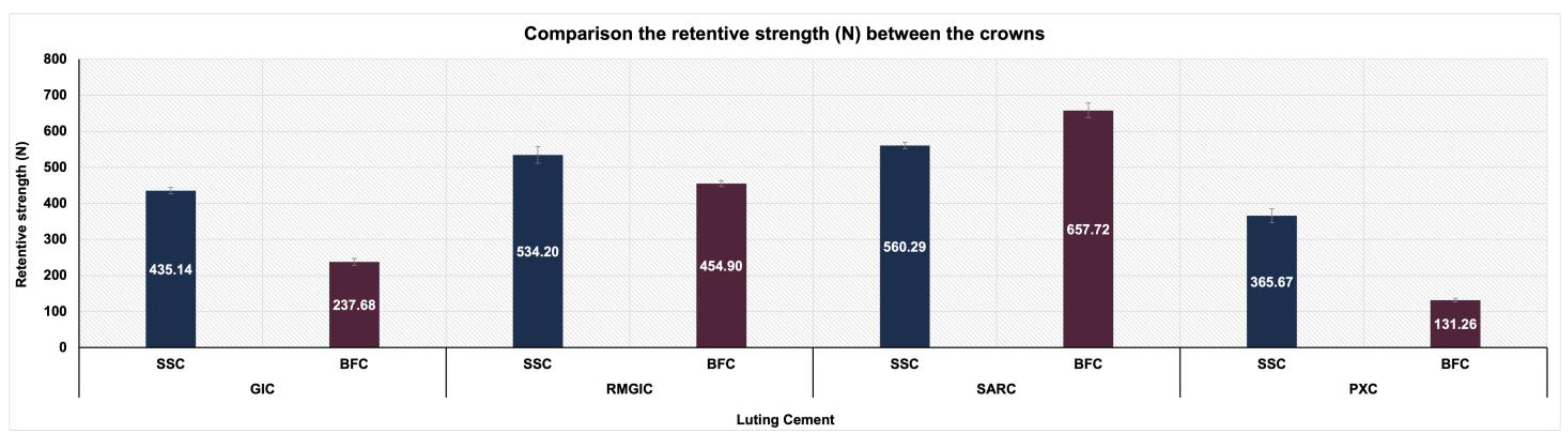
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
- Across all types of cement, SSCs exhibited significantly greater retention strengths than BFCs, except for SARC, where BFCs exhibited superiority.
- Among the four types of luting cement examined, SARC showed the highest retentive strength, whereas PXC demonstrated the lowest.
- Adhesive failure was the predominant failure pattern in SSCs; however, both adhesive and cohesive failures were observed in BFCs.
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mendes, F.M.; De Benedetto, M.S.; Zardetto, C.G.D.C.; Wanderley, M.T.; Correa, M.S.N.P. Resin Composite Restoration in Primary Anterior Teeth Using Short-Post Technique and Strip Crowns: A Case Report. Quintessence Int. 2004, 35, 689–692. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lucas-Rincón, S.E.; Robles-Bermeo, N.L.; Lara-Carrillo, E.; Scougall-Vilchis, R.J.; Pontigo-Loyola, A.P.; Rueda-Ibarra, V.; Loyola-Rodríguez, J.P.; Escoffié-Ramirez, M.; Medina-Solís, C.E. Interproximal Caries and Premature Tooth Loss in Primary Dentition as Risk Factors for Loss of Space in the Posterior Sector: A Cross-Sectional Study. Medicine 2019, 98, e14875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waggoner, W.F. Restoring Primary Anterior Teeth. Pediatr. Dent. 2002, 24, 511–516. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- American Academy of Pediatric Dentistry. Pediatric Restorative Dentistry. In The Reference Manual of Pediatric Dentistry; American Academy of Pediatric Dentistry: Chicago, IL, USA, 2024; pp. 452–465. Available online: https://www.aapd.org/globalassets/media/policies_guidelines/bp_restorativedent.pdf (accessed on 11 March 2025).
- Roberts, J.F.; Attari, N.; Sherriff, M. The Survival of Resin Modified Glass Ionomer and Stainless Steel Crown Restorations in Primary Molars, Placed in a Specialist Paediatric Dental Practice. Br. Dent. J. 2005, 198, 427–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alzanbaqi, S.D.; Alogaiel, R.M.; Alasmari, M.A.; Al Essa, A.M.; Khogeer, L.N.; Alanazi, B.S.; Hawsah, E.S.; Shaikh, A.M.; Ibrahim, M.S. Zirconia Crowns for Primary Teeth: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analyses. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public. Health 2022, 19, 2838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abushanan, A.; Sharanesha, R.B.; Aljuaid, B.; Alfaifi, T.; Aldurayhim, A. Fracture Resistance of Primary Zirconia Crowns: An In Vitro Study. Children 2022, 9, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badr, S.Y.; Rayyan, M.; Elshiekh, M. Evaluation of Fracture Resistance and Color Stability of Innovative Esthetic Crowns for Primary Posterior Molars. Egypt. Dent. J. 2021, 67, 1879–1886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Randall, R.C. Preformed Metal Crowns for Primary and Permanent Molar Teeth: Review of the Literature. Pediatr. Dent. 2002, 24, 489–500. [Google Scholar]
- Agrawal, R.; Khanduja, R.; Singhal, M.; Gupta, S.; Kaushik, M. Clinical Evaluation of Stainless Steel Crown versus Zirconia Crown in Primary Molars: An In Vivo Study. Int. J. Clin. Pediatr. Dent. 2022, 15, 15–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pani, S.C.; Saffan, A.A.; AlHobail, S.; Bin Salem, F.; AlFuraih, A.; AlTamimi, M. Esthetic Concerns and Acceptability of Treatment Modalities in Primary Teeth: A Comparison between Children and Their Parents. Int. J. Dent. 2016, 2016, 3163904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holsinger, D.M.; Wells, M.H.; Scarbecz, M.; Donaldson, M. Clinical Evaluation and Parental Satisfaction with Pediatric Zirconia Anterior Crowns. Pediatr. Dent. 2016, 38, 192–197. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Shah, P.V.; Lee, J.Y.; Wright, J.T. Clinical Success and Parental Satisfaction with Anterior Preveneered Primary Stainless Steel Crowns. Pediatr. Dent. 2004, 26, 391–395. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Champagne, C.; Waggoner, W.; Ditmyer, M.; Casamassimo, P.S.; MacLean, J. Parental Satisfaction with Preveneered Stainless Steel Crowns for Primary Anterior Teeth. Pediatr. Dent. 2007, 29, 465–469. [Google Scholar]
- Mathew, M.G.; Roopa, K.B.; Soni, A.J.; Khan, M.M.; Kauser, A. Evaluation of Clinical Success, Parental and Child Satisfaction of Stainless Steel Crowns and Zirconia Crowns in Primary Molars. J. Family Med. Prim. Care. 2020, 9, 1418–1423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, L.; Wells, M.H.; Harris, E.F.; Lou, J. Comparison of Amount of Primary Tooth Reduction Required for Anterior and Posterior Zirconia and Stainless Steel Crowns. Pediatr. Dent. 2016, 38, 42–46. [Google Scholar]
- Abo-Elsoud, A.A.E.; Mohamady, E.M.; Fathi Abdou, N.E.S. Thermomechanical Aging Effects on Vertical Marginal Gap and Fracture Resistance: A Comparative Study of Bioflx and Traditional Pediatric Crowns. BMC Oral. Health 2024, 24, 1334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subramaniam, P.; Kondae, S.; Gupta, K.K. Retentive Strength of Luting Cements for Stainless Steel Crowns: An In Vitro Study. J. Clin. Pediatr. Dent. 2010, 34, 309–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seale, N.S.; Randall, R. The Use of Stainless Steel Crowns: A Systematic Literature Review. Pediatr. Dent. 2015, 37, 145–160. [Google Scholar]
- Ram, D.; Fuks, A.B.; Eidelman, E. Long-Term Clinical Performance of Esthetic Primary Molar Crowns. Pediatr. Dent. 2003, 25, 582–584. [Google Scholar]
- Savide, N.L.; Caputo, A.A.; Luke, L.S. The Effect of Tooth Preparation on the Retention of Stainless Steel Crowns. ASDC J. Dent. Child. 1979, 46, 385–389. [Google Scholar]
- Myers, D.R.; Bell, R.A.; Barenie, J.T. The Effect of Cement Type and Tooth Preparation on the Retention of Stainless Steel Crowns. J. Pedod. 1981, 5, 275–280. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Noffsinger, D.P.; Jedrychowski, J.R.; Caputo, A.A. Effects of Polycarboxylate and Glass Ionomer Cements on Stainless Steel Crown Retention. Pediatr. Dent. 1983, 5, 68–71. [Google Scholar]
- Garcia-Godoy, F. Clinical Evaluation of the Retention of Preformed Crowns Using Two Dental Cements. J. Pedod. 1984, 8, 278–281. [Google Scholar]
- Sener, I.; Turker, B.; Valandro, L.F.; Ozcan, M. Marginal Gap, Cement Thickness, and Microleakage of 2 Zirconia Crown Systems Luted with Glass Ionomer and MDP-Based Cements. Gen. Dent. 2014, 62, 67–70. [Google Scholar]
- Erdemci, Z.Y.; Cehreli, S.B.; Tirali, R.E. Hall Versus Conventional Stainless Steel Crown Techniques: In Vitro Investigation of Marginal Fit and Microleakage Using Three Different Luting Agents. Pediatr. Dent. 2014, 36, 286–290. [Google Scholar]
- Parisay, I.; Khazaei, Y. Evaluation of Retentive Strength of Four Luting Cements with Stainless Steel Crowns in Primary Molars: An In Vitro Study. Dent. Res. J. 2018, 15, 201–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahin, I.; Karayilmaz, H.; Çiftçi, Z.Z.; Kirzioglu, Z. Fracture Resistance of Prefabricated Primary Zirconium Crowns Cemented with Different Luting Cements. Pediatr. Dent. 2018, 40, 443–448. [Google Scholar]
- Khinda, V.I.S.; Grewal, N. Retentive [Correction of Preventive] Efficacy of Glass Ionomer, Zinc Phosphate and Zinc Polycarboxylate Luting Cements in Preformed Stainless Steel Crowns: A Comparative Clinical Study. J. Indian. Soc. Pedod. Prev. Dent. 2002, 20, 41–46. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Reddy, M.; Reddy, V.; Basappa, N. A Comparative Study of Retentive Strengths of Zinc Phosphate, Polycarboxylate and Glass Ionomer Cements with Stainless Steel Crowns—An In Vitro Study. J. Indian. Soc. Pedod. Prev. Dent. 2010, 28, 245–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pathak, S.; Shashibhushan, K. In Vitro Evaluation of Stainless Steel Crowns Cemented with Resin-Modified Glass Ionomer and Two New Self-Adhesive Resin Cements. Int. J. Clin. Pediatr. Dent. 2016, 9, 197–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walia, T.; Brigi, C.; Ziadkhani, M.M.; Khayat, A.A.; Tabibzadeh, Z. Retention Force of Glass Ionomer Based Luting Cements with Posterior Primary Zirconium Crowns—A Comparative in Vitro Study. J. Clin. Pediatr. Dent. 2021, 45, 259–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ali, S.N.A.H. In Vitro Comparison of Marginal and Internal Fit Between Stainless Steel Crowns and Esthetic Crowns of Primary Molars Using Different Luting Cements. Dent. Res. J. 2019, 16, 366–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosato, L.A.; Chen, J.W.; Roggenkamp, C.L.; Su, J.M. Retentive Strengths for Prefabricated Primary Molar Zirconia Crowns Using Five Different Cements. Taiwan J. Pediatr. Dent. 2018, 18, 127–135. [Google Scholar]
- Jing, L.; Chen, J.W.; Roggenkamp, C.; Suprono, M.S. Effect of Crown Preparation Height on Retention of a Prefabricated Primary Posterior Zirconia Crown. Pediatr. Dent. 2019, 41, 229–233. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Yilmaz, Y.; Gurbuz, T.; Eyuboglu, O.; Belduz, N. The Repair of Preveneered Posterior Stainless Steel Crowns. Pediatr. Dent. 2008, 30, 429–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Innes, N.P.T.; Ricketts, D.; Chong, L.Y.; Keightley, A.J.; Lamont, T.; Santamaria, R.M. Preformed crowns for decayed primary molar teeth. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2015, 12, CD005512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waggoner, W.F. Restoring Primary Anterior Teeth: Updated for 2014. Pediatr Dent. 2015, 37, 163–170. [Google Scholar]
- Kindelan, S.A.; Day, P.; Nichol, R.; Willmott, N.; Fayle, S.A.; British Society of Paediatric Dentistry. UK National Clinical Guidelines in Paediatric Dentistry: Stainless Steel Preformed Crowns for Primary Molars. Int. J. Paediatr. Dent. 2008, 18 (Suppl. S1), 20–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lad, P.P.; Kamath, M.; Tarale, K.; Kusugal, P.B. Practical Clinical Considerations of Luting Cements: A Review. J. Int. Oral. Health 2014, 6, 116–120. [Google Scholar]
- Rector, J.A.; Mitchell, R.J.; Spedding, R.H. The Influence of Tooth Preparation and Crown Manipulation on the Mechanical Retention of Stainless Steel Crowns. ASDC J. Dent. Child. 1985, 52, 422–427. [Google Scholar]
- Yilmaz, Y.; Dalmis, A.; Gurbuz, T.; Simsek, S. Retentive Force and Microleakage of Stainless Steel Crowns Cemented with Three Different Luting Agents. Dent. Mater. J. 2004, 23, 577–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenstiel, S.F.; Land, M.F.; Crispin, B.J. Dental Luting Agents: A Review of the Current Literature. J. Prosthet. Dent. 1998, 80, 280–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hikita, K.; Van Meerbeek, B.; De Munck, J.; Ikeda, T.; Van Landuyt, K.; Maida, T.; Lambrechts, P.; Peumans, M. Bonding Effectiveness of Adhesive Luting Agents to Enamel and Dentin. Dent. Mater. 2007, 23, 71–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taran, P.K.; Kaya, M.S. A Comparison of Periodontal Health in Primary Molars Restored with Prefabricated Stainless Steel and Zirconia Crowns. Pediatr. Dent. 2018, 40, 334–339. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kayal, S.; Kang, Y.; Finkelman, M.; Swee, G.; Loo, C. Retention of Zirconia Crowns Compared to Stainless Steel Crowns: An Ex-Vivo Study. Pediatr. Dent. 2023, 45, 142–146. [Google Scholar]
- Mandyala, V.; Padakandla, P.; Kola, N.; Kedari, S.; Putta, L.; Gandhasiri, K. Comparative Evaluation of Retentive Strength of Figaro Crowns and Stainless Steel Crowns Luted with Glass Ionomer Cement and Resin-Modified Glass Ionomer Cement—An In Vitro Study. J. Dr. YSR Univ. Health Sci. 2024, 13, 36–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subramanian, E.M.G.; Kumar, A.S.; Lavanya, G. Comparative Evaluation of Marginal Leakage of SSC and Zirconia Crowns in Primary Teeth. Nveo-Nat. Volatiles Essent. Oils J. 2021, 8, 7063–7068. [Google Scholar]
- Elsayed, H.D.; Sherif, M.; Eldin, S.; Shaimaa Omer, M.M. Comparison Between Stainless-Steel, Zirconia, and Fiberglass Crowns as Full Coverage Restoration for Deciduous Molars of Children. Afr. J. Biol. Sci. 2024, 6, 51–59. [Google Scholar]
- Kameli, S.; Khani, F.; Bahraminasab, M.; Ghorbani, R.; Abbas, F.M. Bond Strength and Microleakage of Different Types of Cements in Stainless Steel Crown of Primary Molar Teeth. Dent. Res. J. 2021, 18, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radovic, I.; Monticelli, F.; Goracci, C.; Vulicevic, Z.R.; Ferrari, M. Self-Adhesive Resin Cements: A Literature Review. J. Adhes. Dent. 2008, 10, 251–258. [Google Scholar]
- Veerabadhran, M.M.; Reddy, V.; Nayak, U.A.; Rao, A.P.; Sundaram, M.A. The Effect of Retentive Groove, Sandblasting, and Cement Type on the Retentive Strength of Stainless Steel Crowns in Primary Second Molars: An In Vitro Comparative Study. J. Indian. Soc. Pedod. Prev. Dent. 2012, 30, 19–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathis, R.S.; Ferracane, J.L. Properties of a Glass-Ionomer/Resin-Composite Hybrid Material. Dent. Mater. 1989, 5, 355–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilson, A.D. Resin-Modified Glass-Ionomer Cements. Int. J. Prosthodont. 1990, 3, 425–429. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Farah, C.S.; Orton, V.G.; Collard, S.M. Shear Bond Strength of Chemical and Light-Cured Glass Ionomer Cements Bonded to Resin Composites. Aust. Dent. J. 1998, 43, 81–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Liu, Y.; Liu, Y.; Söremark, R.; Sundström, F. Flexure Strength of Resin-Modified Glass Ionomer Cements and Their Bond Strength to Dental Composites. Acta Odontol. Scand. 1996, 54, 55–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ladha, K.; Verma, M. Conventional and Contemporary Luting Cements: An Overview. J. Indian. Prosthodont. Soc. 2010, 10, 79–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srinivasan, S.R.; Mathew, M.G.; Jayaraman, J. Comparison of Three Luting Cements for Prefabricated Zirconia Crowns in Primary Molar Teeth: A 36-month Randomized Clinical Trial. Pediatr. Dent. 2023, 45, 117–124. [Google Scholar]
- Azab, M.; Moheb, D.; El Shahawy, O.; Rashed, M. Influence of Luting Cement on the Clinical Outcomes of Zirconia Pediatric Crowns. A 3-Year Split-Mouth Randomized Controlled Trial. Int. J. Paediatr. Dent. 2019, 30, 314–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yilmaz, Y.; Simsek, S.; Dalmis, A.; Gurbuz, T.; Kocogullari, M.E. Evaluation of Stainless Steel Crowns Cemented with Glass-Ionomer and Resin-Modified Glass-Ionomer Luting Cements. Am. J. Dent. 2006, 19, 106–110. [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell, C.A.; Douglas, W.H.; Cheng, Y.S. Fracture Toughness of Conventional, Resin-Modified Glass-Ionomer and Composite Luting Cements. Dent. Mater. 1999, 15, 7–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patil, A.S.; Jain, M.; Choubey, S.; Patil, M.; Chunawala, Y. Comparative evaluation of clinical success of Stainless Steel and Bioflx crowns in primary molar—A 12 month split mouth prospective randomized clinical trial. J. Indian. Soc. Pedod. Prev. Dent. 2024, 42, 37–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Score | Definition |
|---|---|
| 1 | More than 75% of cement left on the resin die. |
| 2 | Between 50 and 75% of cement left on the resin die. |
| 3 | Between 25 and 50% of cement left on the resin die. |
| 4 | More than 75% of cement left on the crown. |
| GIC | RMGIC | SARC | PXC | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SSC | 435.14 ± 8.66 | 534.20 ± 22.84 | 560.29 ± 8.74 | 365.67 ± 19.11 |
| BFC | 237.68 ± 9.37 | 454.90 ± 7.95 | 657.72 ± 20.60 | 131.26 ± 5.37 |
| p-Value * | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 |
| Crown | Cement | n | Retentive Strength (N) | 95% Confidence Interval for Mean | p-Value * | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lower | Upper | |||||
| SSC | GIC | 20 | 435.14 ± 8.66 b | 431.08 | 439.19 | <0.001 |
| RMGIC | 20 | 534.20 ± 22.84 c | 523.52 | 544.89 | ||
| SARC | 20 | 560.29 ± 8.74 d | 556.20 | 564.38 | ||
| PXC | 20 | 365.67 ± 19.11 a | 356.73 | 374.62 | ||
| BFC | GIC | 20 | 237.68 ± 9.37 b | 233.30 | 242.07 | <0.001 |
| RMGIC | 20 | 454.90 ± 7.95 c | 451.18 | 458.62 | ||
| SARC | 20 | 657.72 ± 20.60 d | 648.07 | 667.36 | ||
| PXC | 20 | 131.26 ± 5.37 a | 128.75 | 133.78 | ||
| Crown | Cement | Frequency | CFP Score | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | |||
| SSC | GIC | n | 13 | 7 | 0 | 0 |
| % | 65% | 35% | 0% | 0% | ||
| RMGIC | n | 17 | 3 | 0 | 0 | |
| % | 85% | 15% | 0% | 0% | ||
| SARC | n | 18 | 2 | 0 | 0 | |
| % | 90% | 10% | 0% | 0% | ||
| PXC | n | 0 | 0 | 5 | 15 | |
| % | 0% | 0% | 25% | 75% | ||
| BFC | GIC | n | 0 | 0 | 16 | 4 |
| % | 0% | 0% | 80% | 20% | ||
| RMGIC | n | 0 | 0 | 7 | 13 | |
| % | 0% | 0% | 35% | 65% | ||
| SARC | n | 0 | 0 | 2 | 18 | |
| % | 0% | 0% | 10% | 90% | ||
| PXC | n | 4 | 16 | 0 | 0 | |
| % | 20% | 80% | 0% | 0% | ||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
AlMawash, A.A.; Sulimany, A.M.; Alhowaish, L.A.; Alayad, A.S.; Bawazir, O.A. Retention of Pediatric BioFlx Crowns Versus Stainless Steel Crowns Using Different Types of Luting Cements: An In Vitro Study. Materials 2025, 18, 1287. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18061287
AlMawash AA, Sulimany AM, Alhowaish LA, Alayad AS, Bawazir OA. Retention of Pediatric BioFlx Crowns Versus Stainless Steel Crowns Using Different Types of Luting Cements: An In Vitro Study. Materials. 2025; 18(6):1287. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18061287
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlMawash, Amjad A., Ayman M. Sulimany, Latifa A. Alhowaish, Abdullah S. Alayad, and Omar A. Bawazir. 2025. "Retention of Pediatric BioFlx Crowns Versus Stainless Steel Crowns Using Different Types of Luting Cements: An In Vitro Study" Materials 18, no. 6: 1287. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18061287
APA StyleAlMawash, A. A., Sulimany, A. M., Alhowaish, L. A., Alayad, A. S., & Bawazir, O. A. (2025). Retention of Pediatric BioFlx Crowns Versus Stainless Steel Crowns Using Different Types of Luting Cements: An In Vitro Study. Materials, 18(6), 1287. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18061287






