Micro-Gap Weld Seam Contrast Enhancement via Phase Contrast Imaging
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Experimental Setup and Principle
2.2. Comparison with Existing Seam Detection Methods
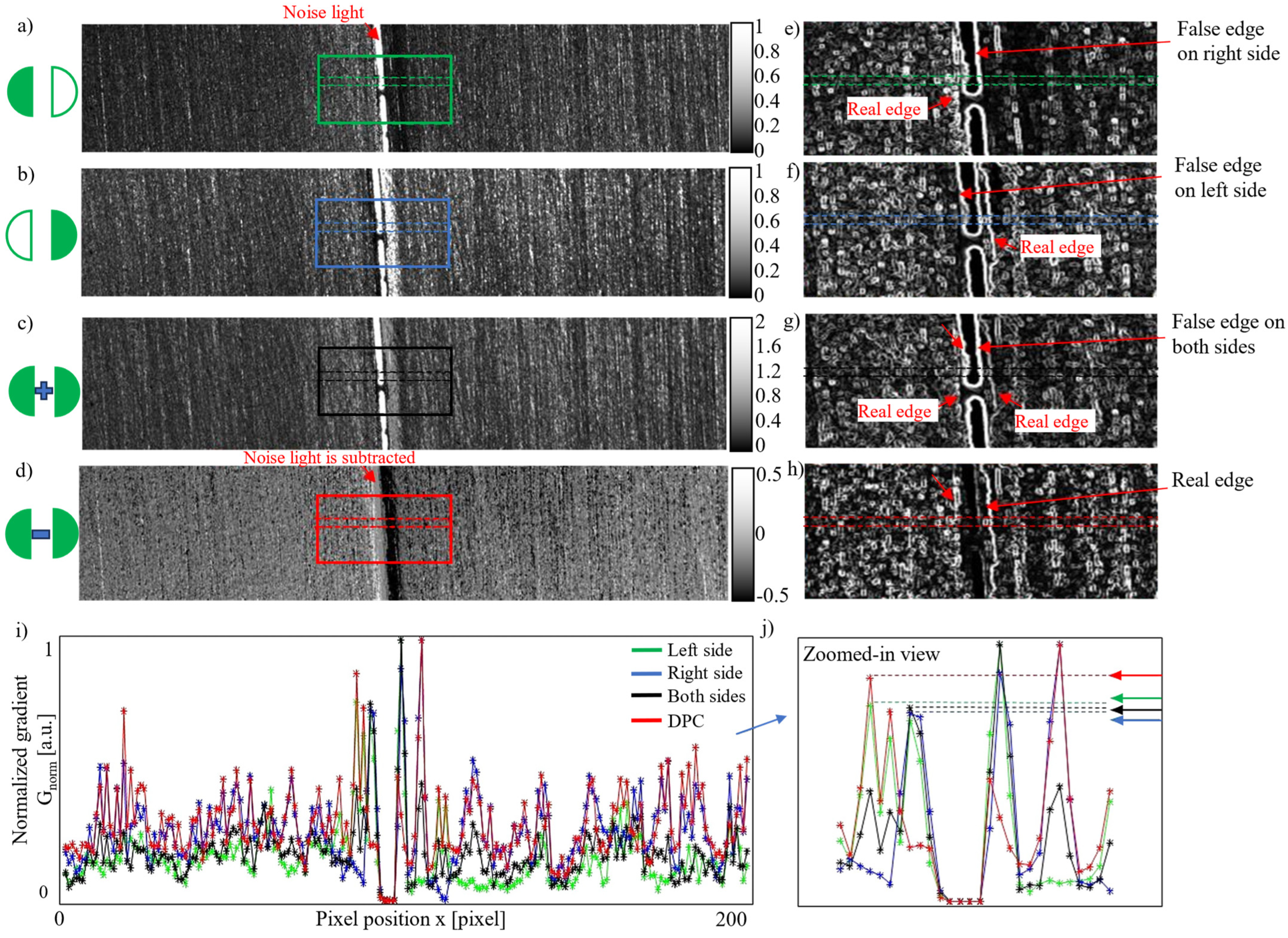
2.3. Image Processing
3. Experiment Results
3.1. Detection of Seams with Different Widths and Surface Flatness
3.2. Anti-Noise Experiment
3.3. Evaluation of Seam Detection Accuracy
4. Discussion and Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Nomenclature
| DPC | Differential phase contrast |
| OCT | Optical coherence tomography |
| LED | Light-emitting diode |
| GAN | Generative adversarial network |
| AFFNet | Attention-Enhanced Feature Fusion Network |
| PCB | Printed circuit board |
| ROI | Region of interest |
| FOV | Field of view |
References
- Gao, Y.; Xiao, J.; Xiong, G.; Zhang, H. Research on the deviation sensing of V-groove weld seam based on a novel two channel acoustic sensor. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2022, 119, 5821–5837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.; Jia, A.; Huang, W.; Wen, Z.; Hong, B.; Hong, Y. Weld seam tracking method of root pass welding with variable gap based on magnetically controlled arc sensor. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2023, 126, 5227–5243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Gao, X.; Chen, Y.; Zhou, X.; Zhang, Y.; You, D. Modeling for tracking micro gap weld based on magneto-optical sensing and Kalman filtering. IEEE Sens. J. 2020, 21, 11598–11614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Upadhyay, S.O. Robotic Tactile Sensor Probe used for Contour plotting of Weld Joint in Seam Tracking System. Int. Res. J. Eng. Technol. 2023, 10, 962–982. [Google Scholar]
- Xia, L.; Zhou, J.; Xue, R.; Li, X.; Liu, H. Real-time seam tracking during narrow gap GMAW process based on the wide dynamic vision sensing method. J. Manuf. Process. 2023, 101, 820–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Wang, H.; Huang, Y.; Rong, Y.; Meng, J.; Li, G.; Zhang, G. Welding seam recognition and tracking for a novel mobile welding robot based on multi-layer sensing strategy. Meas. Sci. Technol. 2022, 33, 055109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, A.; Chaturvedi, R.; Sharma, K.; Binhowimal, S.A.; Giri, J.; Sathish, T. Enhancing weld quality of novel robotic-arm arc welding: Vision-based monitoring, real-time control seam tracking. Ain. Shams. Eng. J. 2024, 15, 103109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, J.; Deng, Z.; Li, Z.; Liu, T.; Zhuo, R.; Chen, X. Adaptive parameter optimization approach for robotic grinding of weld seam based on laser vision sensor. Robot. Comput. Integr. Manuf. 2023, 82, 102540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Wang, Z.; Liang, Z.; Li, B.; Lin, Z. A welding seam tracking algorithm adaptive to variable groove type: An interactive segmentation passive vision method. Opt. Laser Technol. 2025, 181, 111861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boldrin, D.M.; Tosatti, L.M.; Previtali, B.; Demir, A.G. Seam tracking and gap bridging during robotic laser beam welding via grayscale imaging and wobbling. Robot. Comput. Integr. Manuf. 2024, 89, 102774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Fan, J.; Yang, H.; Yang, L.; Ji, Z.; Jing, F.; Tan, M. A fast and robust seam tracking method for spatial circular weld based on laser visual sensor. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2021, 70, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, Q.C.; Hua, H.Q.; Pham, P.T. Development of a vision system integrated with industrial robots for online weld seam tracking. J. Manuf. Process. 2024, 119, 414–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Shi, Y.; Li, C.; Gu, Y. Feature information extraction method for narrow gap U-type groove based on laser vision. J. Manuf. Process. 2023, 104, 257–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Wang, M.; Wang, S.; Zhao, H. Research and development of weld tracking system based on laser vision. Meas. Control 2022, 55, 1124–1133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cibicik, A.; Njaastad, E.B.; Tingelstad, L.; Egeland, O. Robotic weld groove scanning for large tubular T-joints using a line laser sensor. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2022, 120, 4525–4538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Cai, R.; Dai, F.; Yu, Z.; Deng, Y.; Deng, J.; Wang, Z.; Ma, G.; Zhong, W. A unified framework based on semantic segmentation for extraction of weld seam profiles with typical joints. J. Manuf. Process. 2024, 131, 2275–2287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Tian, Y.; Li, L.; Lu, Y.; Xi, F. One-shot, integrated positioning for welding initial points via co-mapping of cross and parallel stripes. Robot. Comput. Integr. Manuf. 2023, 84, 102602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Meng, K.; Cui, L.; Li, X. Weld tracking technology for all-position welding of pipes based on laser vision. Opt. Lasers Eng. 2025, 188, 108912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, F.; Hou, Z.; Xiao, R.; Xu, Y.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, H. A novel welding path generation method for robotic multi-layer multi-pass welding based on weld seam feature point. Measurement 2023, 216, 112910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johan, N.F.; Mohd Shah, H.N.; Sulaiman, M.; Naji, O.A.; Arshad, M.A. Weld seam feature point extraction using laser and vision sensor. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2023, 127, 5155–5170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Liu, J.; Chen, B.; Suo, X. Universal fillet weld joint recognition and positioning for robot welding using structured light. Robot. Comput. Integr. Manuf. 2022, 74, 102279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Zhang, X.; Liu, J.; Shi, Y.; Huang, Y. Line-structured light fillet weld positioning method to overcome weld instability due to high specular reflection. Machines 2022, 11, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Fan, J.; Yang, H.; Wang, H.; Xing, S.; Jing, F.; Tan, M. An efficient and robust complex weld seam feature point extraction method for seam tracking and posture adjustment. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2023, 19, 10704–10715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, W.; Huang, Y. A Robust Weld Seam Tracking Method by Using Intensity-Modulated Structured Light. IEEE Sens. J. 2021, 21, 5368–5376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, R.; Xu, Y.; Xu, F.; Hou, Z.; Zhang, H.; Chen, S. LSFP-tracker: An autonomous laser stripe feature point extraction algorithm based on siamese network for robotic welding seam tracking. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2023, 71, 1037–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, F.; He, L.; Hou, Z.; Xiao, R.; Zuo, T.; Li, J.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, H. An automatic feature point extraction method based on laser vision for robotic multi-layer multi-pass weld seam tracking. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2024, 131, 5941–5960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.J.; Shao, W.J.; Gong, S.H.; Jia, P.J.; Li, G. High-precision measurement of weld seam based on narrow depth of field lens in laser welding. Sci. Technol. Weld. Join. 2016, 21, 267–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nilsen, M.; Sikström, F.; Christiansson, A.-K.; Ancona, A. Robust vision-based joint tracking for laser welding of curved closed-square- butt joints. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2019, 101, 1967–1978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nilsen, M.; Sikström, F.; Christiansson, A.-K. Adaptive control of the filler wire rate during laser beam welding of squared butt joints with varying gap width. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2019, 102, 3667–3676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mattulat, T. Understanding the coaxial optical coherence tomography signal during the laser welding of hidden T-joints. J. Laser Appl. 2024, 36, 012003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Z.; Jiang, Z.; Ding, H. Optical coherence tomography for laser welding applications. Optik 2022, 257, 168784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, F.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, H.; Chen, S. Application of sensing technology in intelligent robotic arc welding: A review. J. Manuf. Process. 2022, 79, 854–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, R.; Cao, Q.; Chen, S. A novel laser stripe key point tracker based on self-supervised learning and improved KCF for robotic welding seam tracking. J. Manuf. Process. 2024, 127, 660–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, Z.; Zhao, B.; Ji, Y.; Xu, X.; Kong, Z.; Liu, T.; Luo, M. A welding seam positioning method based on polarization 3D reconstruction and linear structured light imaging. Opt. Laser Technol. 2022, 151, 108046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Huang, J.; Wu, Y.; Yang, G.; Di, S.; Yuan, H.; Cao, X.; Shin, K. A novel 3D complex welding seam tracking method in symmetrical robotic MAG welding process using a laser vision sensing. Symmetry 2023, 15, 1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.; Chen, Y.; You, D.; Xiao, Z.; Chen, X. Detection of micro gap weld joint by using magneto-optical imaging and Kalman filtering compensated with RBF neural network. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2017, 84, 570–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, W.; Rong, Y.; Huang, Y. Image contrast enhancement and denoising in micro-gap weld seam detection by periodic wide-field illumination. J. Manuf. Process. 2022, 75, 792–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Z.; Pei, Z.; Li, E.; Zhou, E.; Huang, Z.; Xing, Z.; Li, B. An image segmentation-based localization method for detecting weld seams. Adv. Eng. Softw. 2024, 194, 103662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, W.; Liu, X.; Wu, Z. A robust weld seam detection method based on particle filter for laser welding by using a passive vision sensor. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technology. 2019, 104, 2971–2980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.; Kalaichelvi, V.; Dsouza, A.; Karthikeyan, R. GAN-Based image dehazing for intelligent weld shape classification and tracing using deep learning. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 6860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mobaraki, M.; Ahani, S.; Gonzalez, R.; Yi, K.M.; Van Heusden, K.; Dumont, G.A. Vision-based seam tracking for GMAW fillet welding based on keypoint detection deep learning model. J. Manuf. Process. 2024, 117, 315–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, Y.; Jiang, Y.; Yang, M.; Chang, B.; Dong, D.U. Intelligent seam tracking in foils joining based on spatial–temporal deep learning from molten pool serial images. Robot. Comput. Integr. Manuf. 2025, 91, 102840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamilton, D.K.; Sheppard, C.J.R. Differential phase contrast in scanning optical microscopy. J. Microsc. 1984, 133, 27–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amos, W.B.; Reichelt, S.; Cattermole, D.M.; Laufer, J. Re- evaluation of differential phase contrast (DPC) in a scanning laser microscope using a split detector as an alternative to differential interference contrast (DIC) optics. J. Microsc. 2003, 210, 166–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mehta, S.B.; Sheppard, C.J.R. Quantitative phase-gradient imaging at high resolution with asymmetric illumination-based differential phase contrast. Opt. Lett. 2009, 34, 1924–1926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, L.; Waller, L. Quantitative differential phase contrast imaging in an LED array microscope. Opt. Express. 2015, 23, 11394–11403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonati, C.; Laforest, T.; Kunzi, M.; Moser, C. Phase sensitivity in differential phase contrast microscopy: Limits and strategies to improve it. Opt. Express 2020, 28, 33767–33783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, W.; Matlock, A.; Fu, S.; Qin, X.; Feng, H.; Gabel, C.V.; Tian, L.; Yi, J. LED array reflectance microscopy for scattering-based multi-contrast imaging. Opt. Lett. 2020, 45, 1647–1650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sobel, I. An Isotropic 3x3 Image Gradient Operator. In Presentation at Stanford A.I. Project 1968. 2014. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/239398674_An_Isotropic_3x3_Image_Gradient_Operator (accessed on 11 March 2025).
- Gonzalez, R.C.; Woods, R.E. Digital Image Processing, 4th ed.; Pearson Education: New York, NY, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
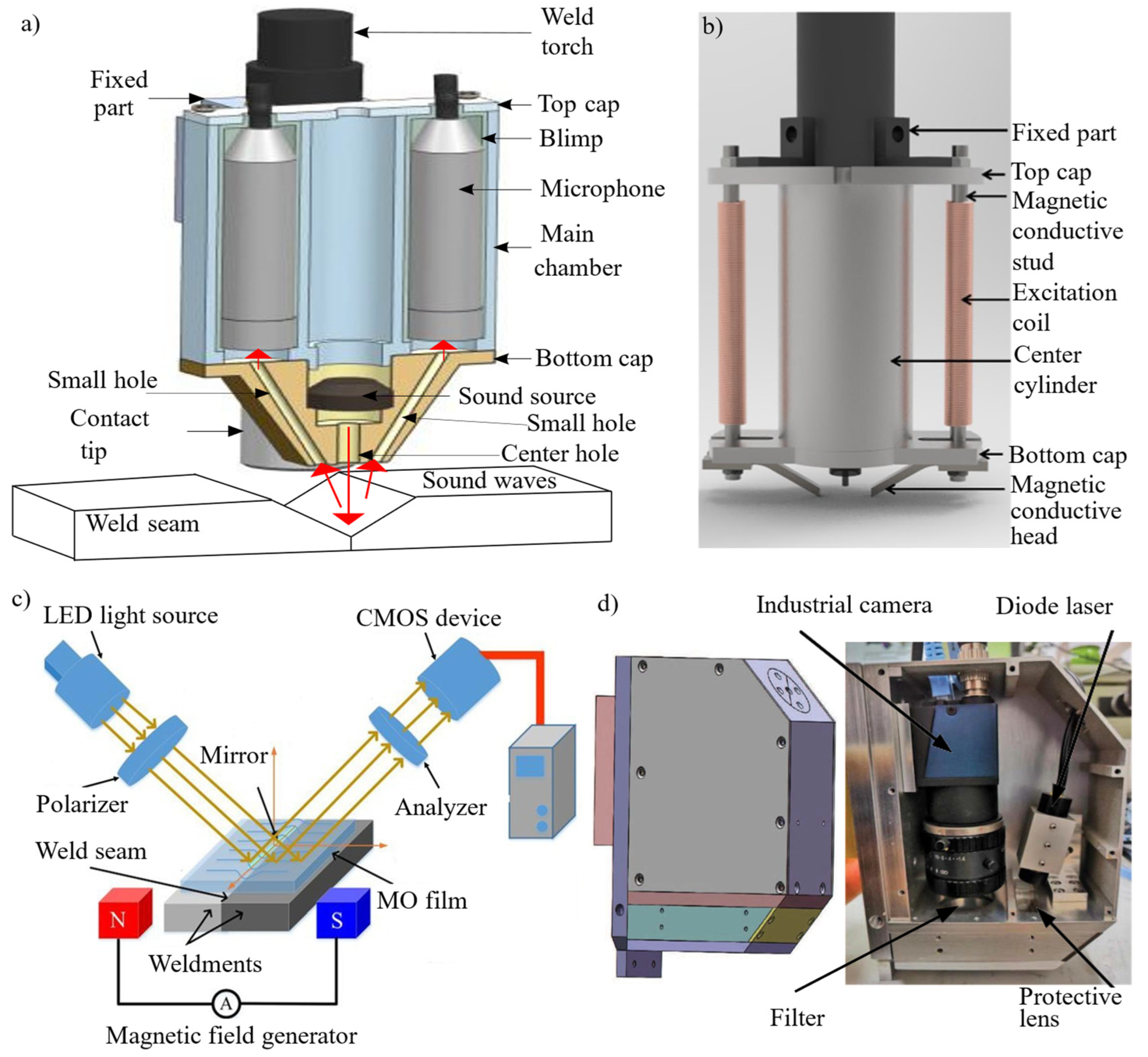


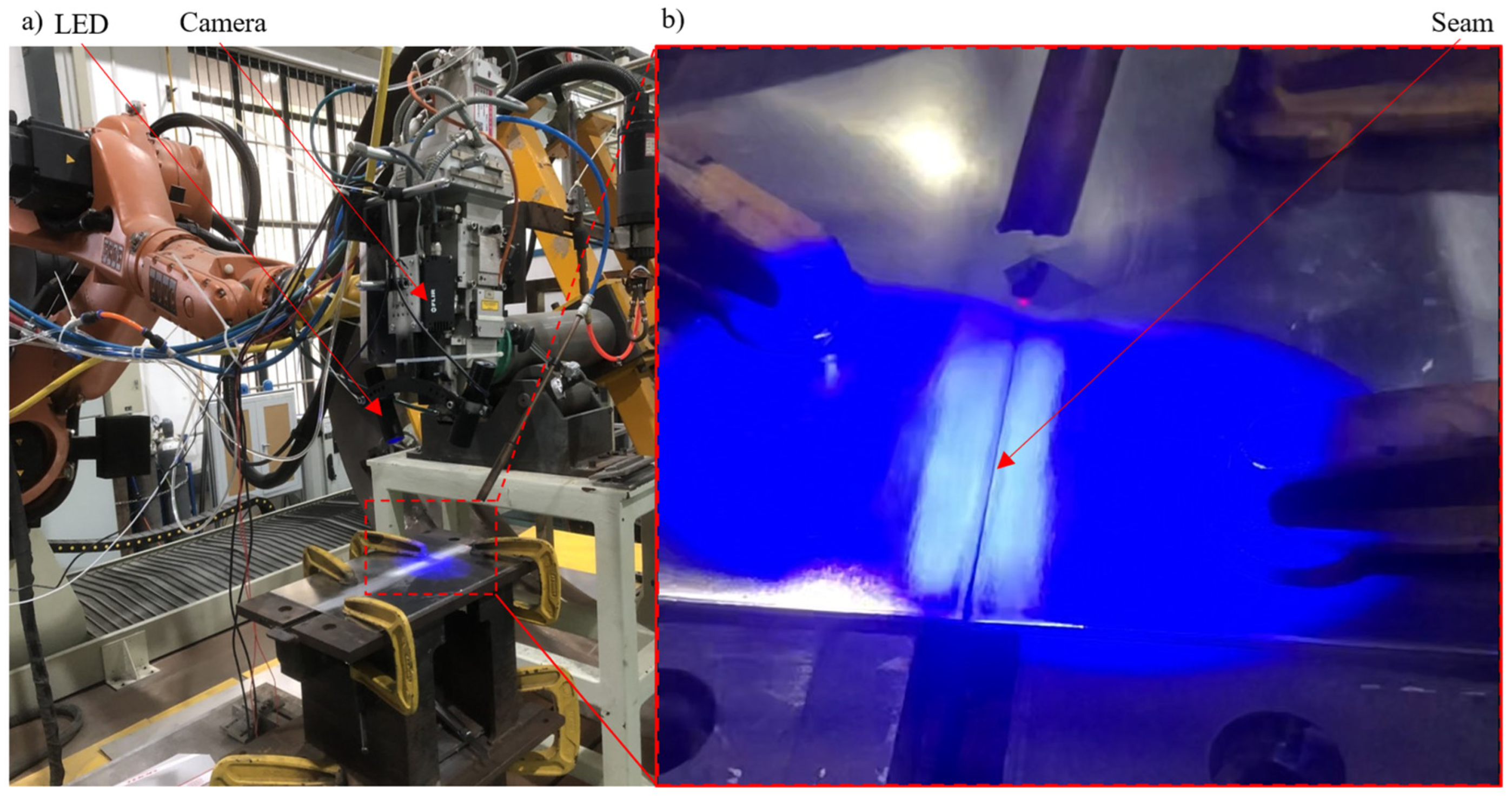
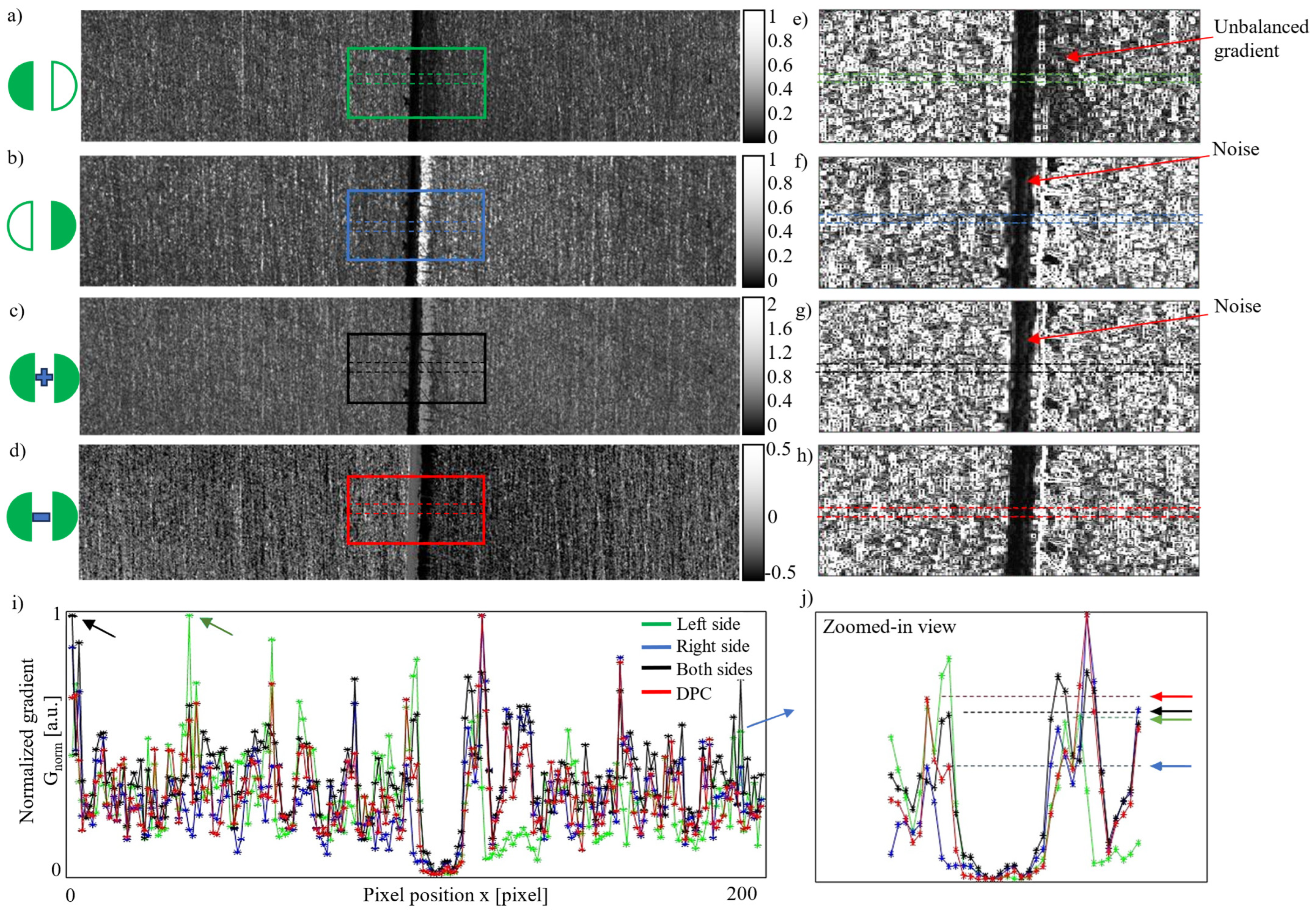
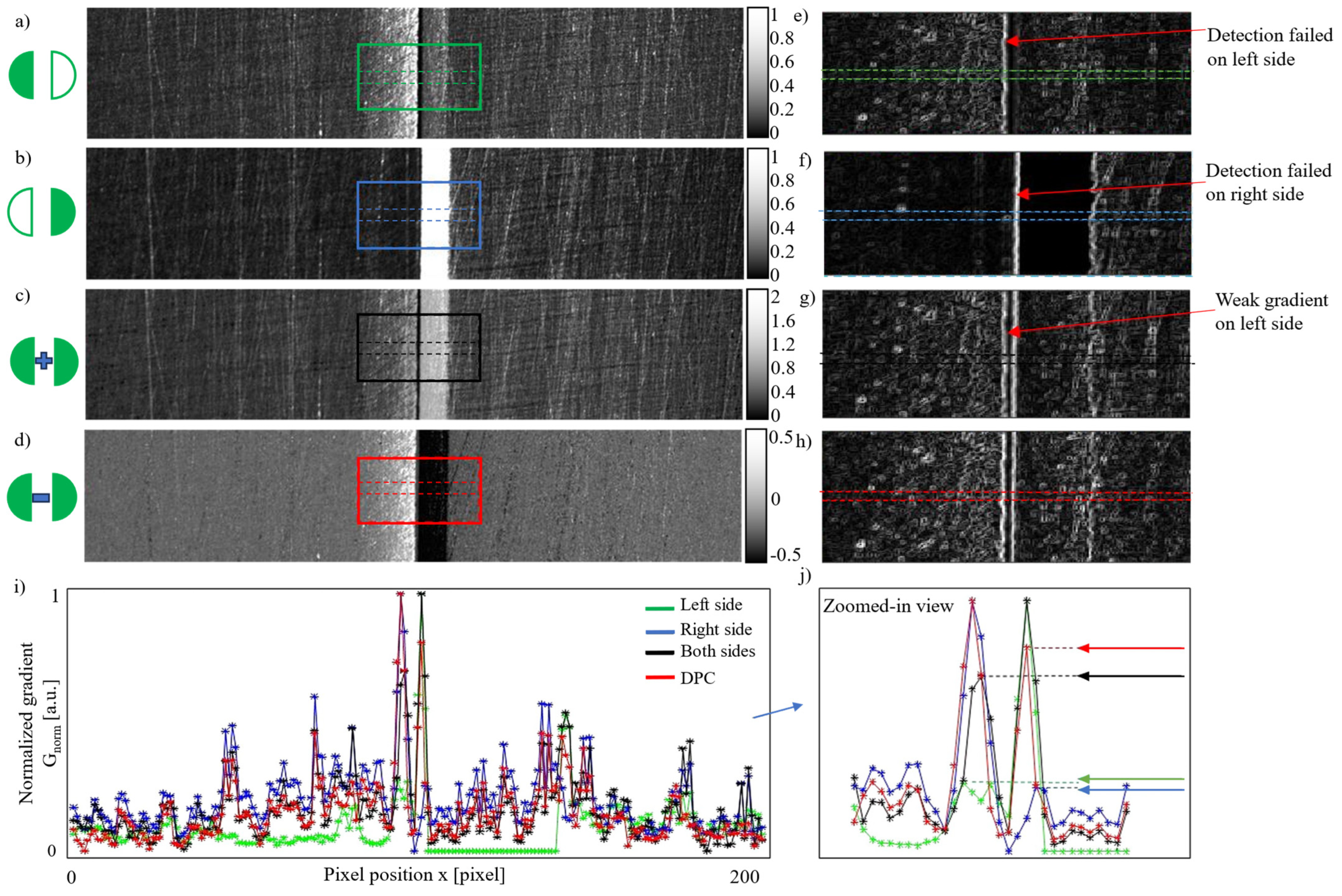
| Item | Description |
|---|---|
| Weld groove type | Tight single-square groove (seam width: ~0.06 [mm], ~0.2 [mm]; groove angle: 0°) |
| Seam type | Straight line |
| Material of the workpiece | Aluminum plate (type: 6061; 2 [mm] thickness) |
| Laser power | 1.5 [kW] |
| Welding speed | 1 [m/min] |
| Item | Mean Absolute Error [mm] | Maximum Error [mm] | Standard Deviation [mm] |
|---|---|---|---|
| Specimen with 0.2 mm seam width | 0.016 | 0.036 | 0.015 |
| Specimen with 0.06 mm seam width | 0.017 | 0.036 | 0.014 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, Y.; Yang, Y.; Shao, W. Micro-Gap Weld Seam Contrast Enhancement via Phase Contrast Imaging. Materials 2025, 18, 1281. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18061281
Yang Y, Yang Y, Shao W. Micro-Gap Weld Seam Contrast Enhancement via Phase Contrast Imaging. Materials. 2025; 18(6):1281. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18061281
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Yanfang, Yonglu Yang, and Wenjun Shao. 2025. "Micro-Gap Weld Seam Contrast Enhancement via Phase Contrast Imaging" Materials 18, no. 6: 1281. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18061281
APA StyleYang, Y., Yang, Y., & Shao, W. (2025). Micro-Gap Weld Seam Contrast Enhancement via Phase Contrast Imaging. Materials, 18(6), 1281. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18061281







