Investigation on High-Temperature Wear Resistance of Co-Based Superalloys Modified by Chromium–Aluminizing Coatings
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Materials
2.2. Preparation of Coatings
2.3. High-Temperature Friction Experiments
2.4. Characterization and Performance Evaluation of Coating Structures
3. Results and Analysis
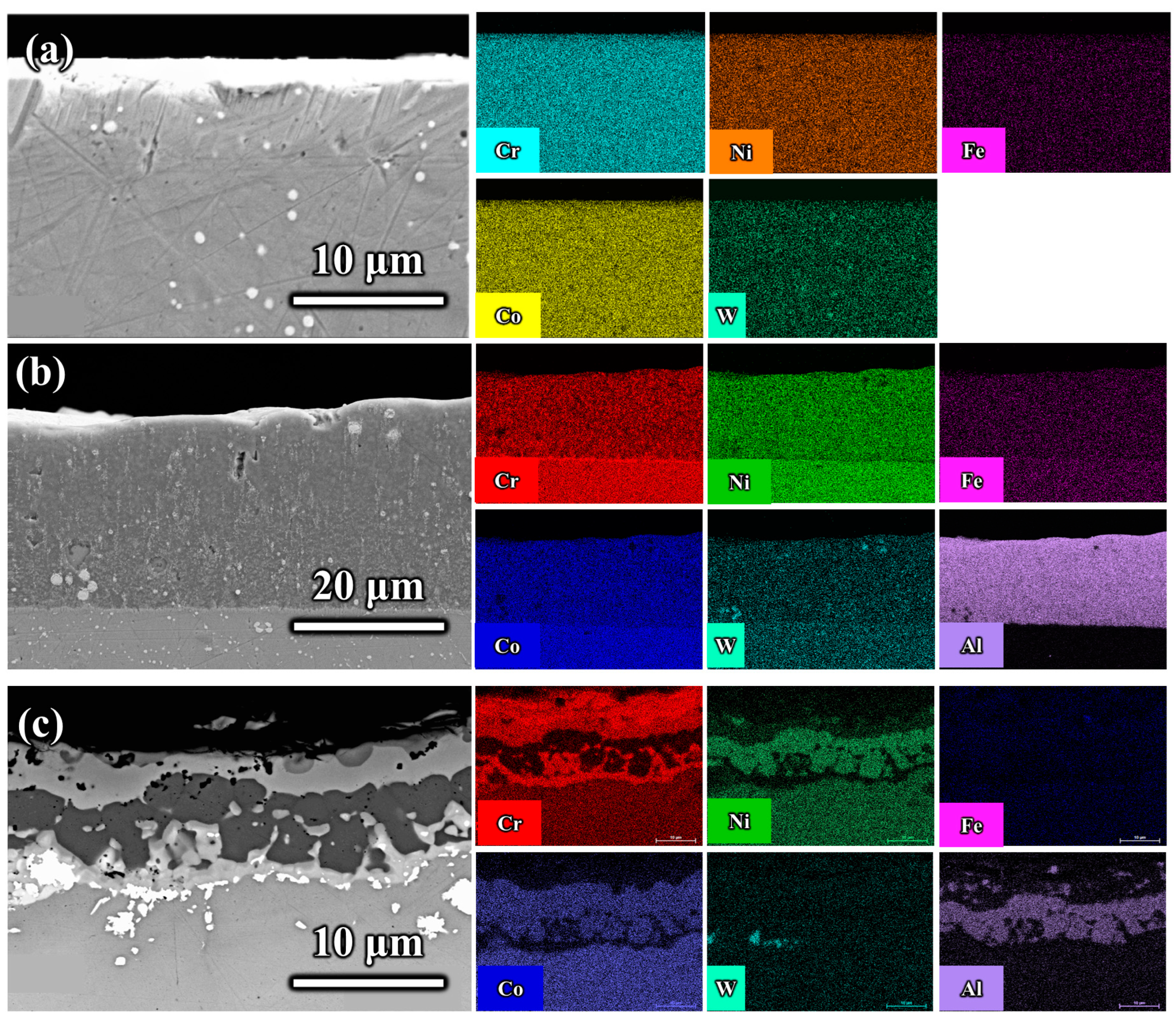
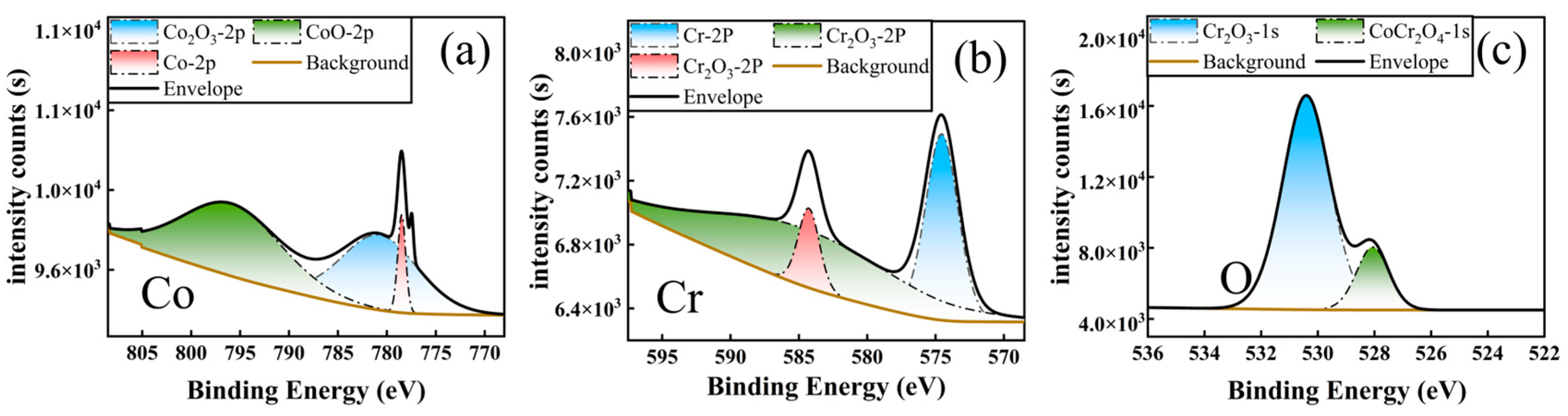
3.1. Cross-Sectional Morphology and Surface Phase Analysis of Coatings
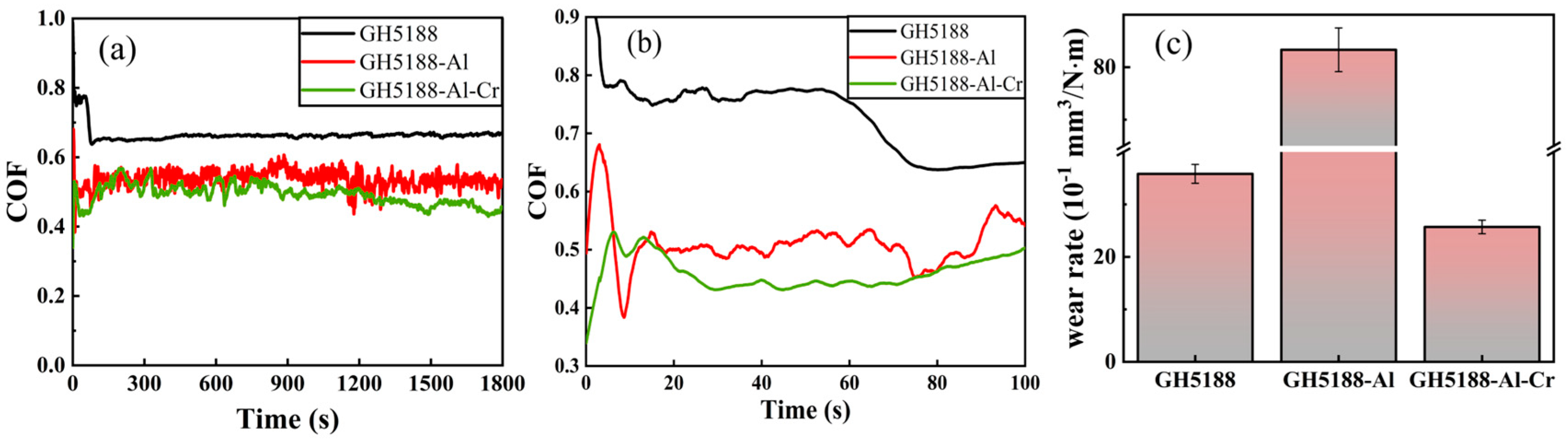
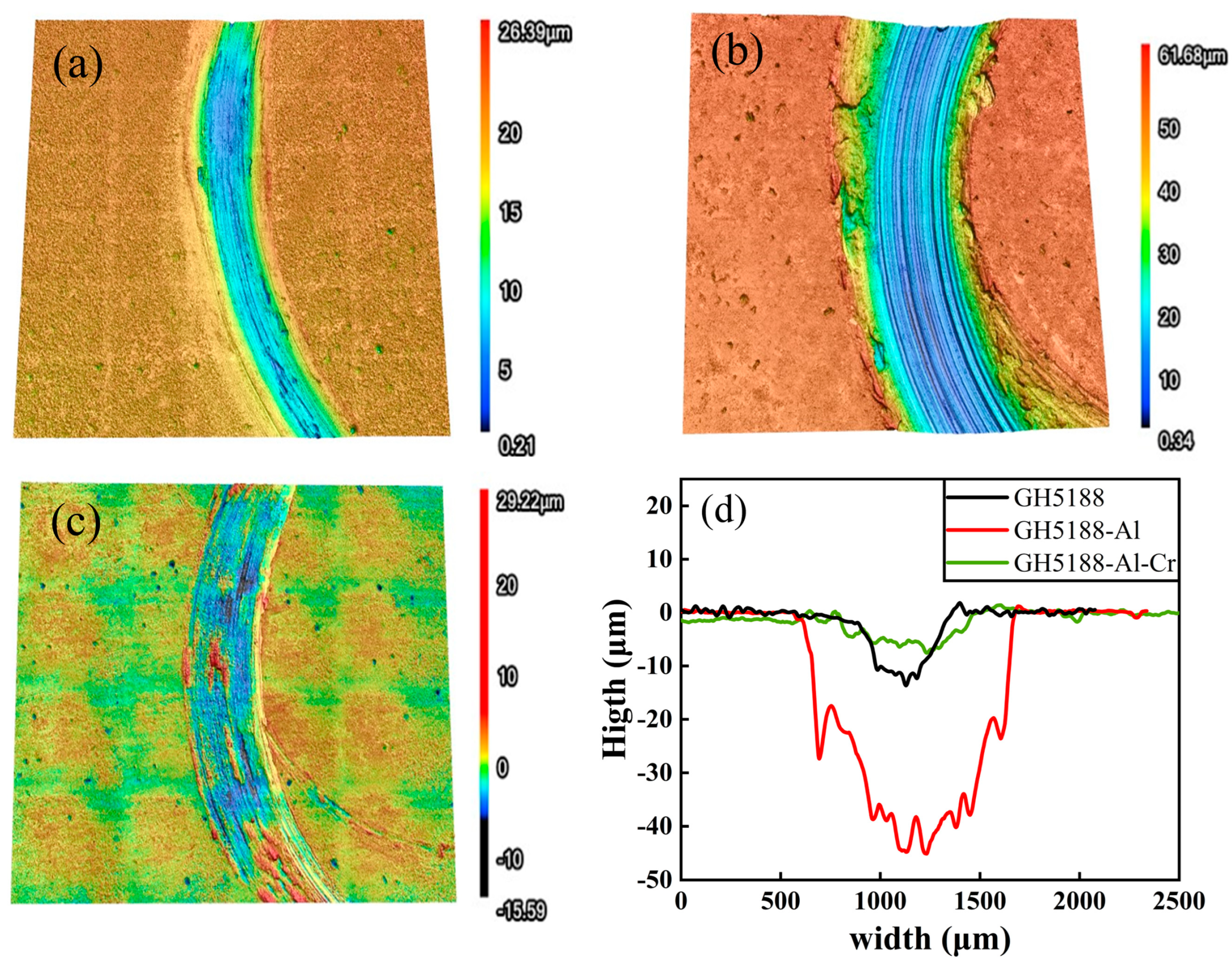
3.2. Tribological Performance
4. Discussion
4.1. Study of High-Temperature Friction Behavior of GH5188 Alloy at 700 °C
4.2. High-Temperature Friction Behavior and Oxide Debris-Shedding Mechanisms of Aluminum-Diffusion Coatings
5. Conclusions
- (1)
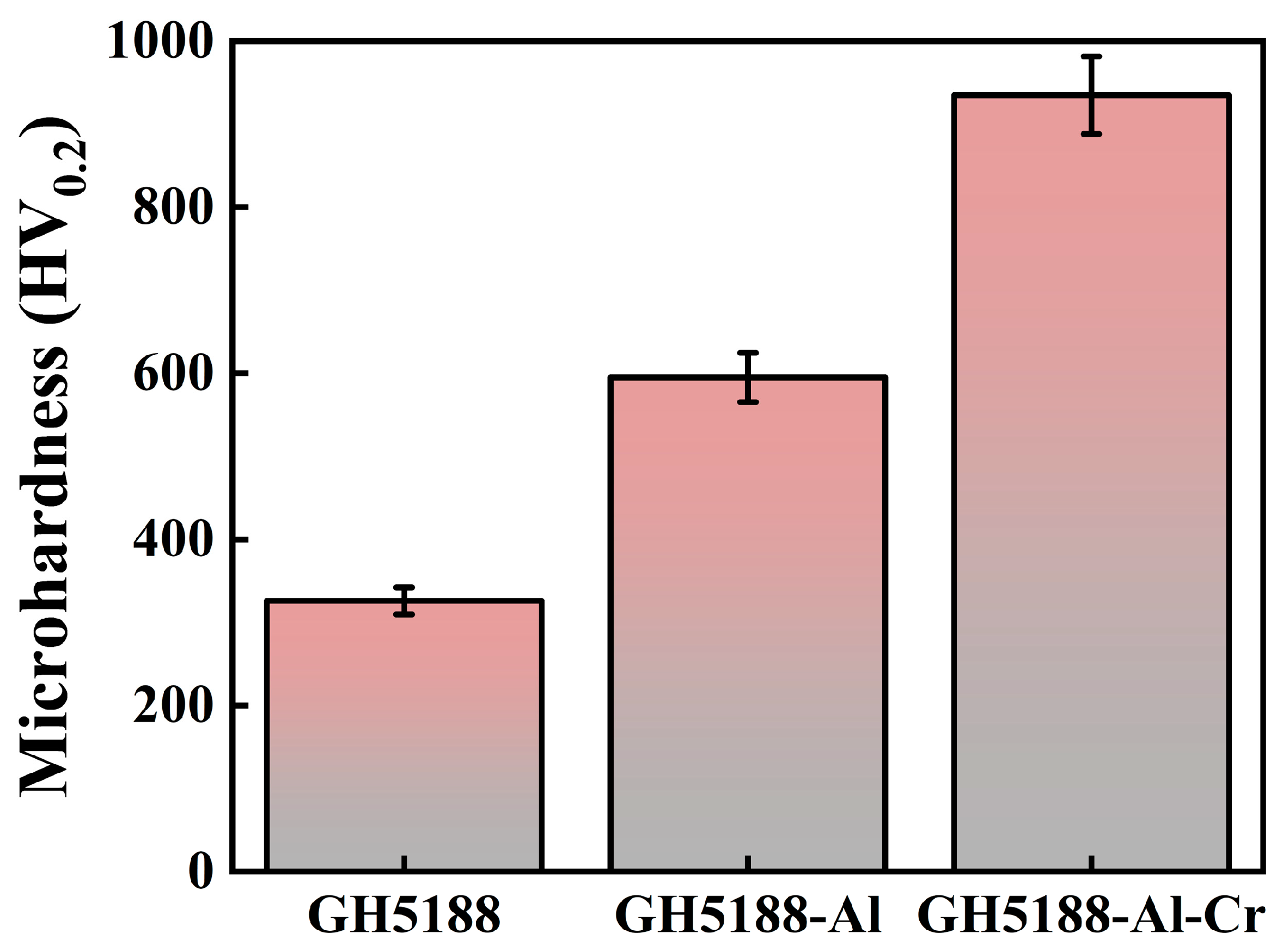
- The primary microstructure of the GH5188 alloy is austenitic, containing a small amount of Si2W. The main phases of the Al-coated layer are intermetallic compounds such as CrCo2Al and Al5Co2, while the primary phases on the surface of the Al-Cr co-diffusion layer are Cr23C6 and AlNi. The hardness of the GH5188 substrate is 326 HV0.2, the Al-coated layer reaches 595 HV0.2, and the Al-Cr co-diffusion layer achieves a hardness of 935 HV0.2. Compared with the substrate, the hardness of the Al-coated layer increased by approximately 82.5% and the hardness of the Al-Cr co-diffusion layer increased by approximately 186.8%. The high-temperature friction performance of the three samples was directly related to the structure and content of oxide debris on the wear scar surfaces. The results indicate that after high-temperature friction at 700 °C, the Al-coated layer exhibited the highest wear volume and the lowest content of oxide debris on the wear scar surface, primarily composed of CoAl2O4. The Al-Cr co-diffusion layer demonstrated the least wear, followed by the GH5188 alloy. The wear debris of both the Al-Cr co-diffusion layer and the GH5188 alloy consisted of CoCr2O4 and Cr2O3, with the Al-Cr co-diffusion layer having the highest debris content.
- (2)
- The high-temperature wear resistance of oxides on the wear scar surface is associated with the thermodynamic stability, high-temperature growth stress, and high-temperature oxidation of the wear debris. The CoAl2O4 debris of the Al-coated layer exhibits the highest growth stress, and the diffusion rate of Al3+ at high temperatures is lower than that of Cr3+, making it difficult to form stable, lubricating oxides after debris spalling. Conversely, the Cr-modified Al-coated layer increases the Cr content on the alloy surface, forming CoCr2O4 and Cr2O3 with lower growth stress. The higher diffusion rate of Cr3+ at high temperatures aids in the formation of lubricating wear debris.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li, H.; Lin, R.Q.; Fu, C.; Jiang, M.; Li, X.; Ren, Z.M.; Russell, A.M.; Cao, G.H. High-temperature oxidation behavior of Al-Cr co-deposited coatings on Co-based superalloys. Corros. Sci. 2021, 192, 109852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pillai, R.; Daghbouj, N.; Cammarata, A.; Li, B.; Bábor, P.; Polcar, T.; Ge, F. Role of Cr in enhancing the cyclic oxidation resistance of aluminide coatings on GH5188 alloy. Corros. Sci. 2022, 208, 110678. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Chen, S.; Li, Q.; Zhong, J.; Xing, F.; Zhang, L. Diffusion kinetics and interfacial stability of Al-Cr coatings on cobalt-based superalloys. Corros. Sci. 2022, 204, 110391. [Google Scholar]
- Shen, Q.; Wang, X.; Luo, G.; Sun, Y.; Wei, Q.; Xu, J.; Li, P.; Zhang, L. High-temperature tribological behavior of aluminized GH5188 under fretting conditions. Wear 2022, 204176, 488–489. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, S.Q.; Wei, M.X.; Wang, F.; Zhao, Y.T.; Zhang, K. Wear mechanisms transition of Al-Cr coatings at elevated temperatures: From oxidative to delamination wear. Wear 2022, 204379, 502–503. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Harouz, R.; Zelmatı, D.; Khelil, K. Third-body behavior and wear rate prediction of Co-based alloys with modified aluminide coatings. Wear 2023, 522, 204702. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, T.; Lin, R.Q.; Fu, C.; Jiang, H.; Ren, Z.M.; Russell, A.M.; Cao, G.H. Microstructure and wear resistance of Al-Cr gradient coatings on GH5188 alloy prepared by pack cementation. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2021, 421, 127448. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Meng, C.; Xu, X.; He, X.; Wang, C. Effect of Cr content on the tribo-oxidation behavior of Al-Cr coatings at 700 °C. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2022, 437, 128355. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, M.; Chen, Z.; Ma, Y.; Zhu, Z.; Zhang, H.; Gao, Y. Interfacial design of Al-Cr co-deposited coatings for improved thermal shock resistance. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2022, 441, 128553. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, W.; Guo, X.; Shan, Y.; Yi, G.; Wan, S.; Huang, H.; Cao, F. Friction-induced nanostructuring in Al-Cr coatings under high-temperature sliding. Tribol. Int. 2022, 167, 107395. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, H.; Liu, H.; Wang, R.; Hao, J.; Liu, X.; Chen, P.; Yang, H.; Zhang, T.; Roy, A. In-situ formation of lubricious oxides in Al-Cr coatings during high-temperature wear. Tribol. Int. 2023, 178, 108064. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, D.; Deng, W.; Li, S.; Hou, G.; Liu, X.; Zhao, X.; An, Y. Comparative study on adhesive wear resistance of aluminide and Al-Cr coatings for aero-engine applications. Tribol. Int. 2021, 155, 106785. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Z.; Chen, T.; Shi, Y.; Ren, Y.; Li, X.; Liu, Z. Synergistic effect of Al and Cr on the high-temperature tribological properties of Co-based alloys. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2021, 98, 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Yan, G.; Zheng, M.; Gu, J.; Li, C.; Wang, L.; Guo, W. Microstructural evolution and wear mechanism of Al-Cr co-deposited coatings under thermal cycling. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2022, 112, 291–302. [Google Scholar]
- Gupta, S.; Odabas, O.; Ozgurluk, Y.; Karaoglanli, A.C. Atomic-scale insights into the interfacial stability of Al-Cr coatings on Co-based superalloys. Acta Mater. 2022, 231, 117893. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, F.; Ma, G.; Zhou, Y.; Fu, Z.; Zhu, L.; She, D.; Wang, H. Deformation mechanisms of Al-Cr coatings under high-temperature contact stress. Acta Mater. 2023, 245, 118634. [Google Scholar]
- Gui, B.; Zhou, H.; Zheng, J.; Liu, X.; Feng, X.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, L. Nano-layered Al-Cr coatings deposited by hybrid HIPIMS/DC magnetron sputtering for extreme temperature applications. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2022, 606, 154876. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, R.; Li, M.; Yang, F.; Hu, Y.; Du, B.; Cao, Y.; Pei, Y.; Li, S. Thermodynamic modeling of Al-Cr interdiffusion in coated superalloys. Calphad 2022, 76, 102389. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, L.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, F.; Zang, P.; Wang, J.; Mao, S.; Zhang, X.; Lu, J. In-situ TEM observation of crack propagation in Al-Cr coatings during thermal cycling. Scr. Mater. 2022, 214, 114676. [Google Scholar]
- Góral, M.; Jung, H.G.; Jung, D.J.; Kim, K.Y. Effect of Cr on the phase composition of aluminide coatings deposited on Co-based alloys. Intermetallics 2022, 145, 107559. [Google Scholar]
- Pavlenko, I.; Kharchenko, N.; Duplák, J.; Ivanov, V.; Kostyk, K. Estimation of Wear Resistance for Multilayer Coatings Obtained by Nitrogenchroming. Metals 2021, 11, 1153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tatíčková, Z.; Tatíčková, Z.; Kudláček, J.; Zoubek, M.; Kuchař, J. Behaviour of Thermochromic Coatings under Thermal Exposure. Coatings 2023, 13, 642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dreano, A.; Sao-Joao, S.; Galipaud, J.; Guillonneau, G. The formation of a cobalt-based glaze layer at high temperature: A layered structure. Wear 2019, 23101, 440–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Zhao, W.; Yan, P.; Xia, X.; Jiao, L.; Wang, X. Effect of strain rate and high temperature on quasi-static and dynamic compressive behavior of forged GH5188 superalloy. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2023, 886, 145391. [Google Scholar]
- Su, T.; Hsu, S.-Y.; Lai, Y.-T.; Tsai, S.-Y.; Duh, J.-G. High-temperature wear resistance of Al-Cr coatings: A combinatorial study. Mater. Charact. 2022, 187, 111845. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, A.; Liu, H.; McBride, J.W. Finite element modeling of contact stresses in Al-Cr coated turbine components. Eng. Fail. Anal. 2022, 138, 106356. [Google Scholar]
- Bousser, E.; Mandrino, D.; Podgornik, B. Tribofilm formation mechanisms in Al-Cr coatings under extreme temperatures. Tribol. Lett. 2022, 70, 94. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, J.; Sun, T.; Wu, X.; Wang, R.; Li, W.; Liu, Q. First-principles study on the interfacial adhesion of Al-Cr coatings/Co-based substrates. Comput. Mater. Sci. 2023, 215, 111805. [Google Scholar]
- Bobzin, K.; Wang, F.; Zhang, F.; Zheng, L.; Zhang, H. Process-structure-property relationships in Al-Cr coatings for aerospace bearings. Adv. Eng. Mater. 2023, 25, 2201235. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, H.; Cao, Y.; Hua, K.; Sun, L.; Ding, H.; Wu, H. Fretting wear resistance of laser-cladded Al-Cr coatings on GH5188 alloy. Mater. Lett. 2023, 333, 133643. [Google Scholar]
- Watanabe, Y.; Yu, T.; Tang, H. High-temperature sliding wear behavior of Al-Cr coatings with varying Cr/Al ratios. Mater. Today Commun. 2023, 34, 105231. [Google Scholar]
- Dudova, N.; Chen, Z.; Okamoto, N.L.; Chikugo, K.; Inui, H. Creep resistance of Al-Cr coated Co-based superalloys under combined thermal-mechanical loading. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2023, 871, 144899. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.; Luo, H.; Czarske, J.; Kuschmierz, R.; Li, X.; Kosiba, K. Machine learning-assisted optimization of Al-Cr coating compositions for minimum wear rate. npj Comput. Mater. 2023, 9, 68. [Google Scholar]
- Kofstad, P.; Samal, S. High-Temperature Oxidation of Metals. Mater. Sci. Eng. 1988, 5, 209–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giggins, C.S.; Pettit, F.S. Oxidation of cobalt-base alloys. J. Electrochem. Soc. 1971, 118, 1782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Nuhfer, N.T.; Miedema, K. Oxide scales formed on directionally solidified cobalt-based alloys during exposure to air at 900 °C. Oxid. Met. 2009, 71, 219–235. [Google Scholar]
- Lobnig, R.E.; Schmidt, H.P.; Hennesen, K. Diffusion of cations in CoCr2O4 spinel. Solid State Ion. 1992, 53, 565–572. [Google Scholar]
- Stott, F.H.; Poggie, R.A.; Wert, J.J. The role of oxidation in the wear of alloys. Tribol. Int. 1998, 31, 61–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woydt, M.; Skopp, A.; Dörfel, I. Wear engineering oxides/anti-wear oxides. Wear 1998, 218, 84–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.; Sun, J.; Lu, Z. Effect of high-temperature oxidation on the wear behavior of nickel-base superalloys. Tribol. Lett. 2015, 58, 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Evans, H.E. Stress effects in high temperature oxidation of metals. Int. Mater. Rev. 1995, 40, 1–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dąbrowa, J.; Zeman, P.; Zuzjaková, Š.; Blažek, J.; Čerstvý, R.; Musil, J. Phase transformations in alumina coatings. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2018, 350, 70–79. [Google Scholar]
- Tolpygo, V.K.; Clarke, D.R.; Clarke, D.R. Surface rumpling of (Ni, Pt) Al bond coats. Acta Mater. 2000, 48, 3283–3293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarrazin, P.; Birnie, J.; Craggs, C.; Gardiner, D.J.; Graves, P.R. Stress in chromium oxide films. Oxid. Met. 1998, 50, 447–464. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, H.; Gao, Q.; Dai, J.; Chen, P.; Gao, W.; Hao, J.; Yang, H. CoCrFeNiWx HEA coatings. Tribol. Int. 2022, 172, 107574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boumaza, A.; Favaro, L.; Lédion, J.; Sattonnay, G.; Brubach, J.B.; Berthet, P.; Huntz, A.M.; Roy, P.; Tétot, R. Transition alumina phases induced by heat treatment of boehmite. J. Solid State Chem. 2009, 182, 1171–1176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biesinger, M.C.; Biesinger, M.C.; Biesinger, M.C.; Lau, L.W.M.; Gerson, A.R. Resolving surface chemical states in XPS analysis of first row transition metals. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2011, 257, 2717–2730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Erdemir, A. A crystal chemical approach to the formulation of self-lubricating nanocomposite coatings Surf. Coating. Technol. 2005, 200, 1792–1796. [Google Scholar]
- Erdemir, A.; Kofstad, P. A crystal-chemical approach to lubrication by solid oxides. Tribol. Lett. 2000, 8, 97–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kunying, D.; Tao, Z.; Zhe, W. Effect of Thermal Growth Oxide Composition and Morphology on Local Stresses in Thermal Barrier Coatings. Materials 2022, 15, 8442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benoît, P.; Abdelhamid, H.; Cécile, R. Stress determination in a thermally grown oxide on Ni38Cr alloy by use of micro/nanogauge gratings. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2021, 812, 141079. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, Y.C.; Wu, H.; Xu, T.Z.; Wang, R.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, C.H. Microstructure, tribological property and high temperature tensile property of Co-Cr-Ni-W alloy parts fabricated by laser directed energy deposition. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2024, 483, 130807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fouilland, L.; El Mansori, M.; Gerland, M. Role of welding process energy on the microstructural variations in a cobalt base superalloy hardfacing. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2007, 201, 6445–6451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Bi, J.; Meng, Z.; Li, R.; Li, Y.; Zhang, T. Tribological behaviors of high-hardness Co-based amorphous coatings fabricated by laser cladding. Tribol. Int. 2021, 162, 107142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Elements | Co | Ni | Cr | W | Fe | Mn |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| mass/% | remain | 22.00 | 22.00 | 15.00 | 3.00 | 1.25 |
| elements | Si | Cu | B | C | P | S |
| mass/% | 0.40 | 0.070 | 0.15 | 0.10 | 0.020 | 0.015 |
| Coating | Diffusion Agent Composition | Temperature | Time | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Al | Al2O3 | Cr2O3 | NH4I | |||
| Al | 30 | 65 | 5 | 900 °C | 6 h | |
| Al-Cr | 10 | 65 | 20 | 5 | 1090 °C | 6 h |
| GH5188 | GH5188-Al | GH5188-Al-Cr | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Average COF | 0.65 | 0.5 | 0.45 |
| Wear rate/×10−1 mm3/N·m | 36.824 | 83.314 | 25.706 |
| Wear scar depth/μm | 11 | 45 | 7 |
| Wear scar width/μm | 400 | 1000 | 650 |
| Types of Oxides | PBR | Eox | (GPa) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cr2O3 | 1.03 | 280 | 0.30 | 4 |
| CoCr2O4 | 1.65 | 240 | 0.28 | 72.2 |
| CoAl2O4 | 1.99 | 200 | 0.25 | 88 |
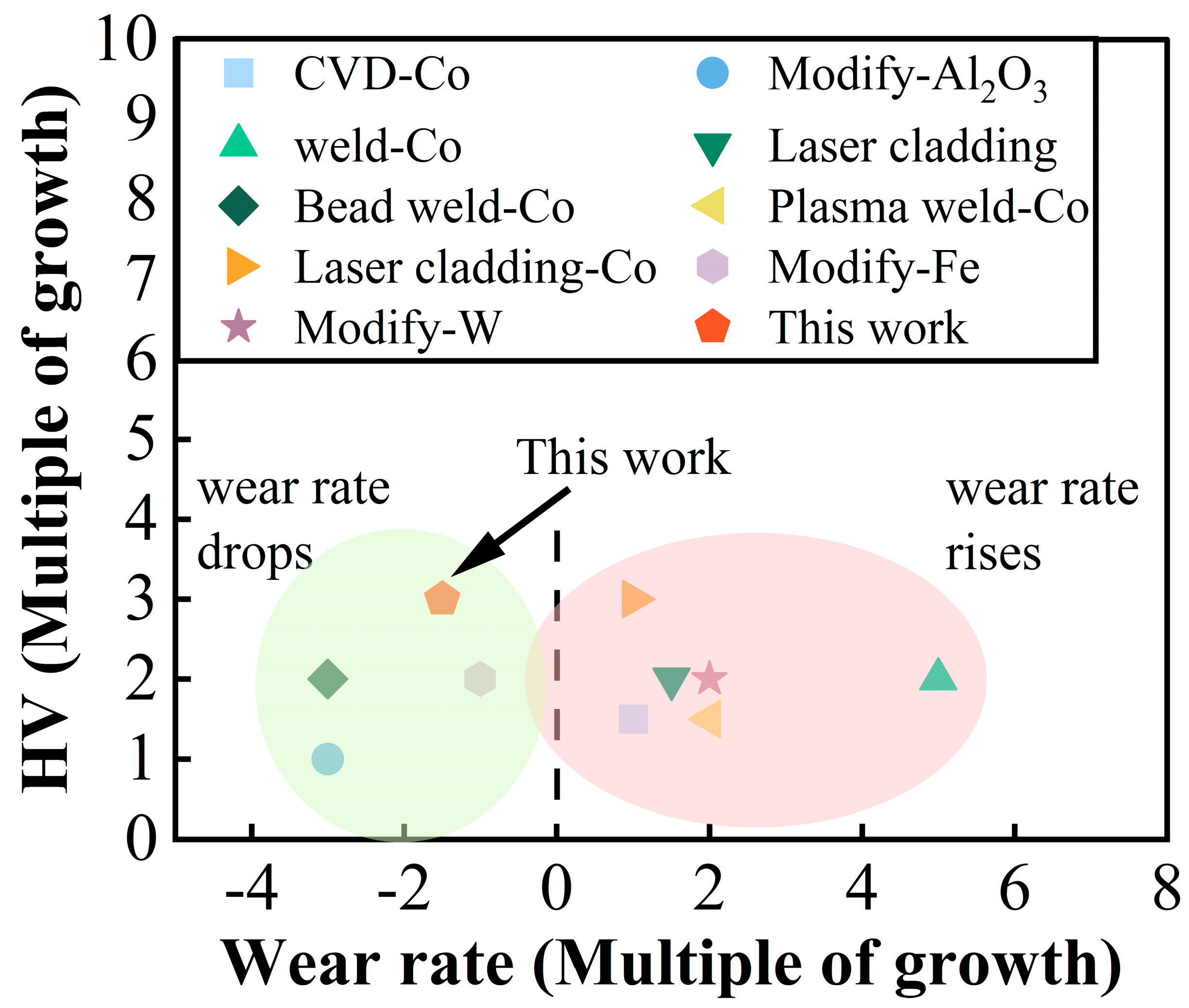
| CVD-Co | Modify-Al2O3 | Weld-Co | Laser Cladding | Weld-Co | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hardness improvement | 1.5 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 2 |
| Wear resistance improvement | −1 | 3 | −5 | −1.5 | 3 |
| Plasma Weld-Co | Laser Cladding-Co | Modify-Fe | Modify-W | This Work | |
| Hardness improvement | 1.5 | 3 | 2 | 2 | 3 |
| Wear resistance improvement | −2 | −1 | 1 | −2 | 1.5 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, Y.; Liu, J.; Zhang, X.; Pu, J. Investigation on High-Temperature Wear Resistance of Co-Based Superalloys Modified by Chromium–Aluminizing Coatings. Materials 2025, 18, 1229. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18061229
Zhang Y, Liu J, Zhang X, Pu J. Investigation on High-Temperature Wear Resistance of Co-Based Superalloys Modified by Chromium–Aluminizing Coatings. Materials. 2025; 18(6):1229. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18061229
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Yang, Ji Liu, Xuehui Zhang, and Jibin Pu. 2025. "Investigation on High-Temperature Wear Resistance of Co-Based Superalloys Modified by Chromium–Aluminizing Coatings" Materials 18, no. 6: 1229. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18061229
APA StyleZhang, Y., Liu, J., Zhang, X., & Pu, J. (2025). Investigation on High-Temperature Wear Resistance of Co-Based Superalloys Modified by Chromium–Aluminizing Coatings. Materials, 18(6), 1229. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18061229






