Carbon Nanotubes–Gr Inspired by Geckos’ Setae Structure with Enhanced Tribological Properties
Abstract
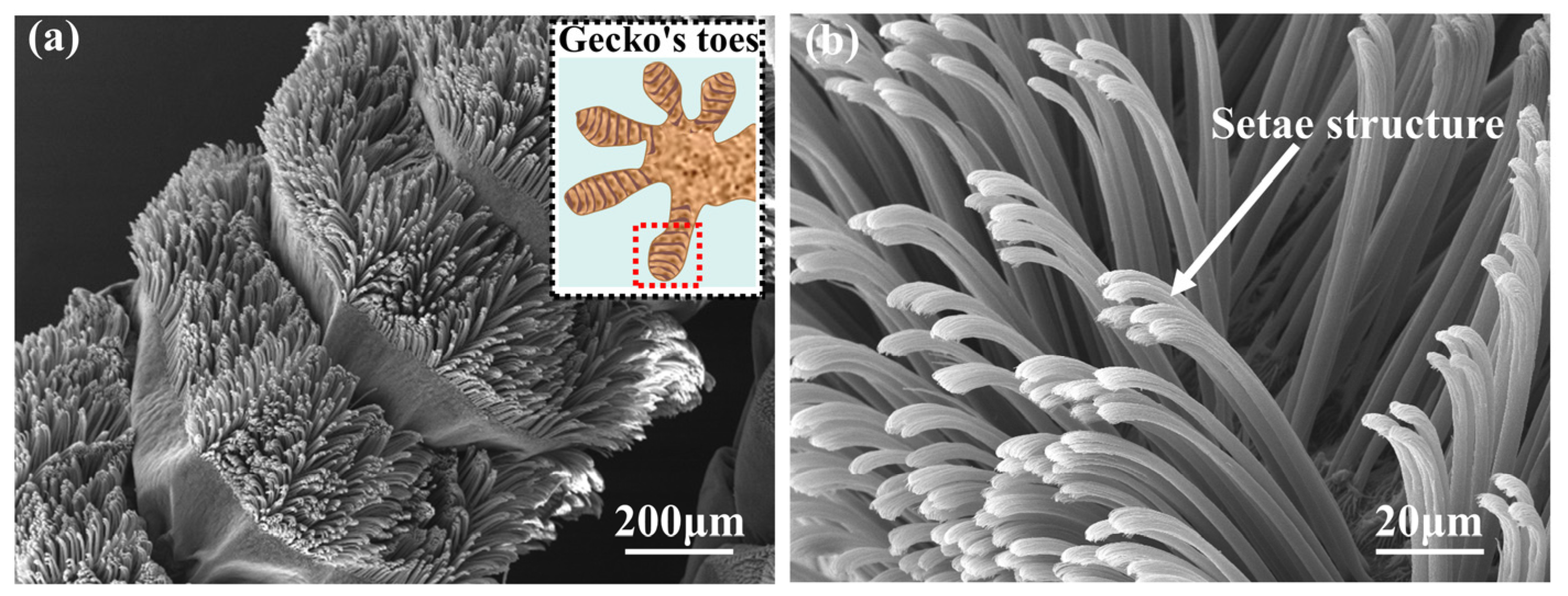
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation of CNTs-Gr
2.3. Preparation of CNTs-Gr Water-Based Lubricant
2.4. Friction Test and Characterization
3. Discussion
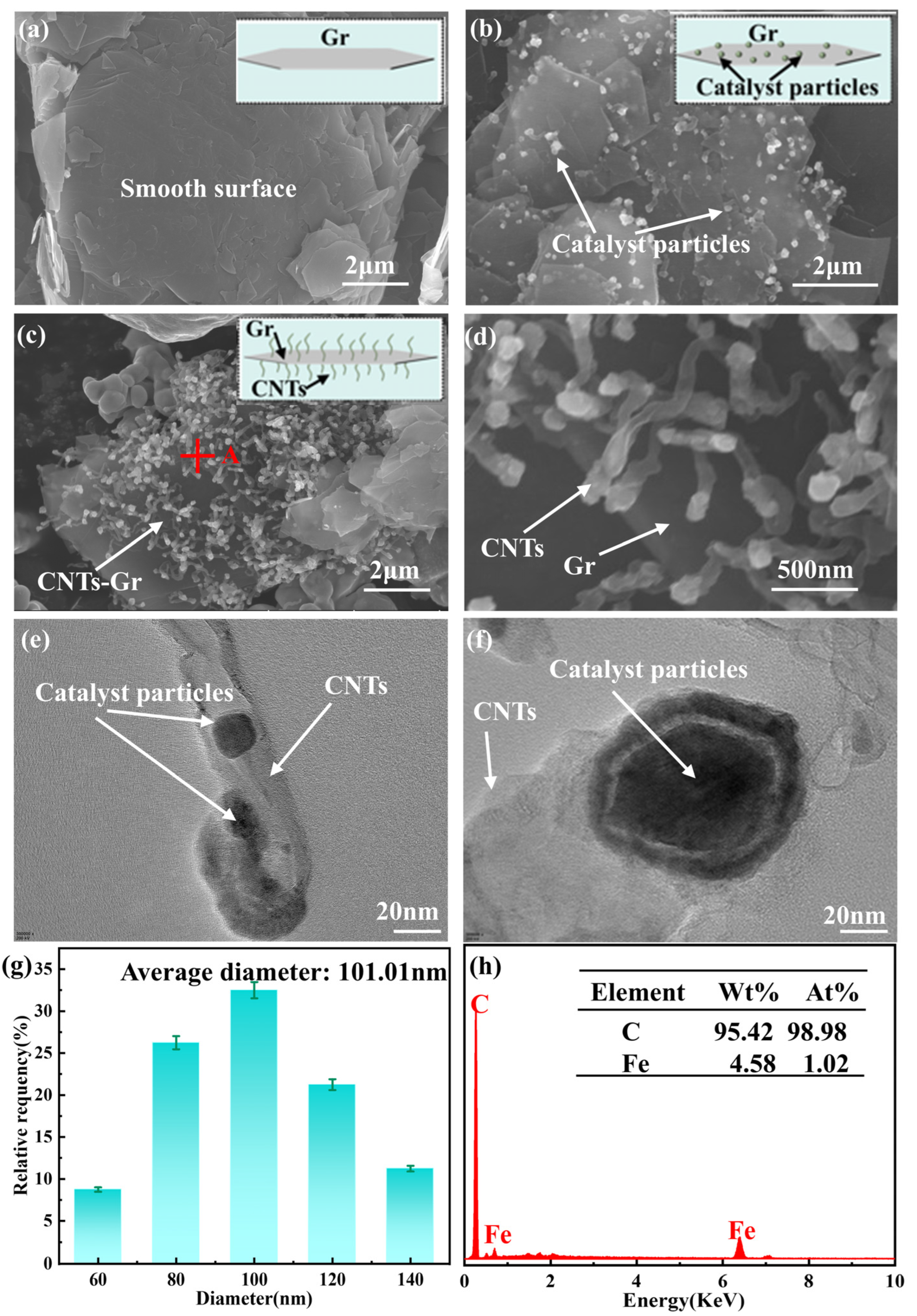
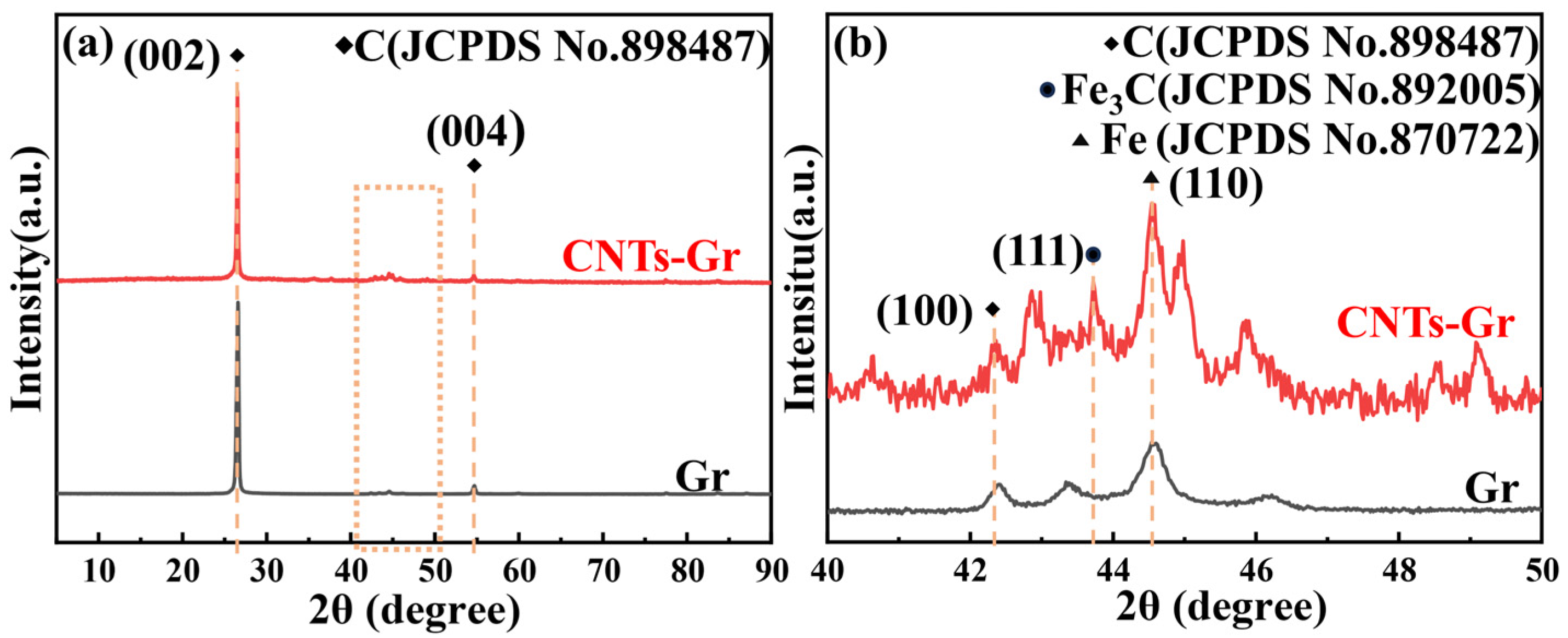
3.1. Characterization of CNTs-Gr
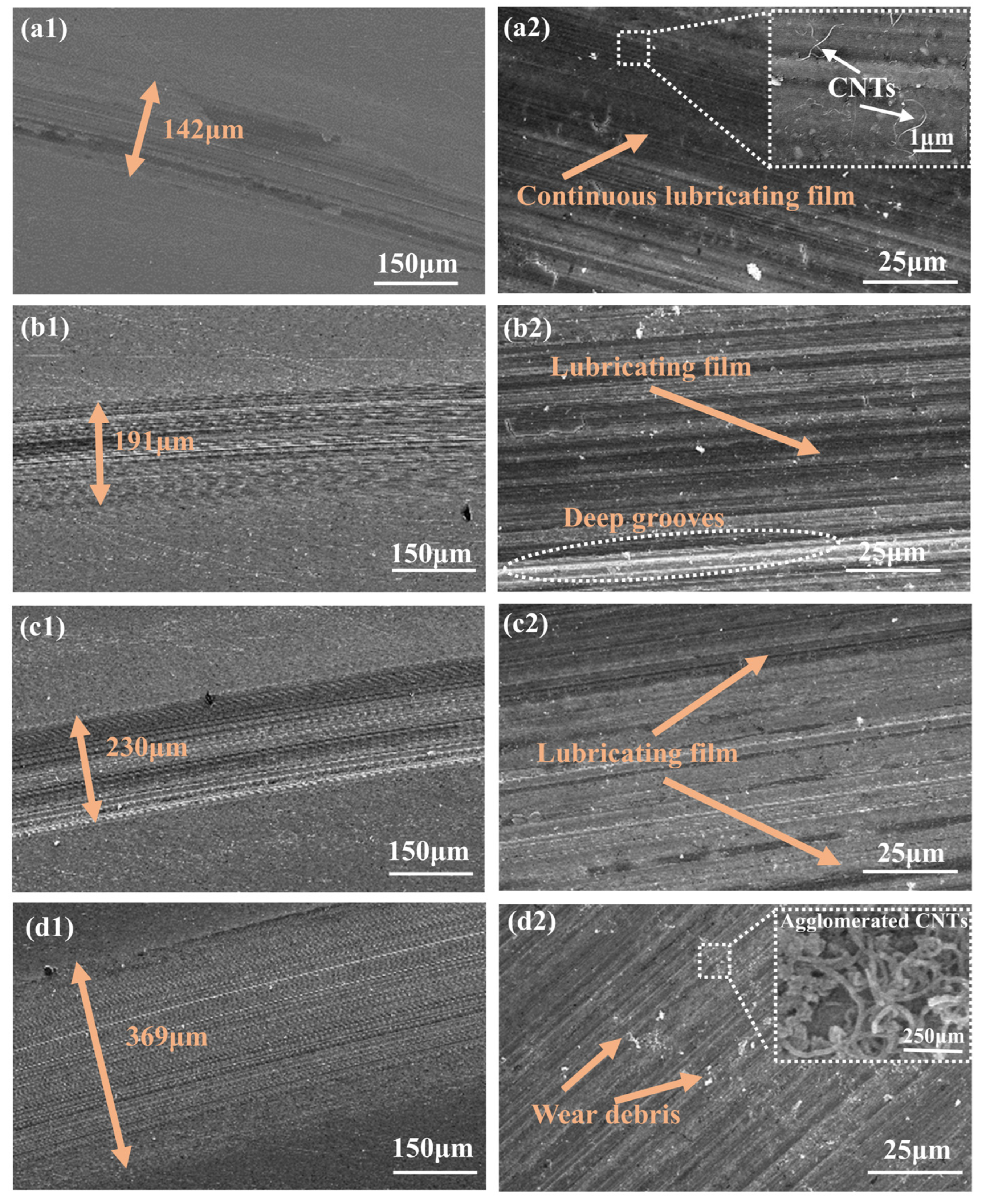
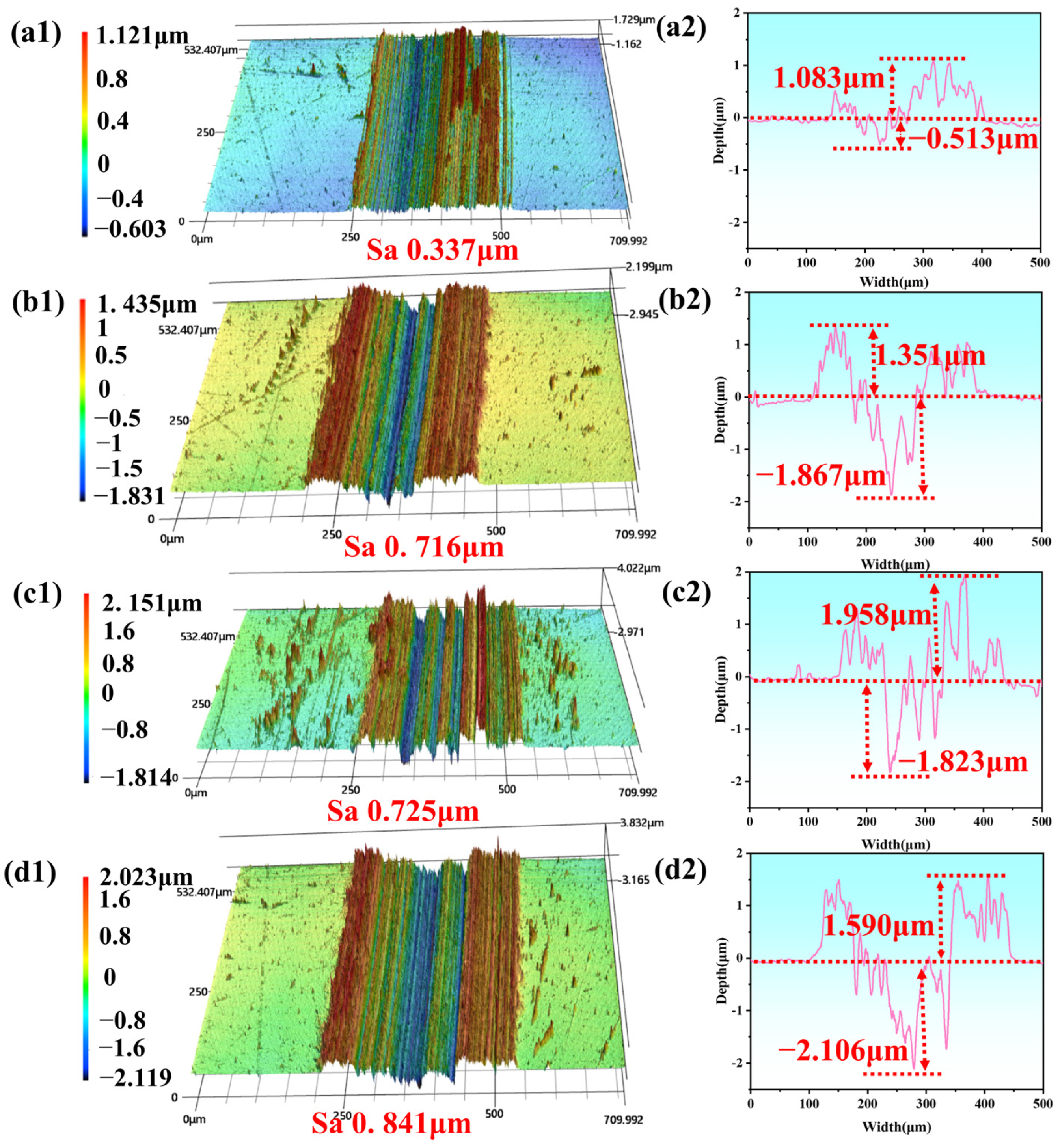
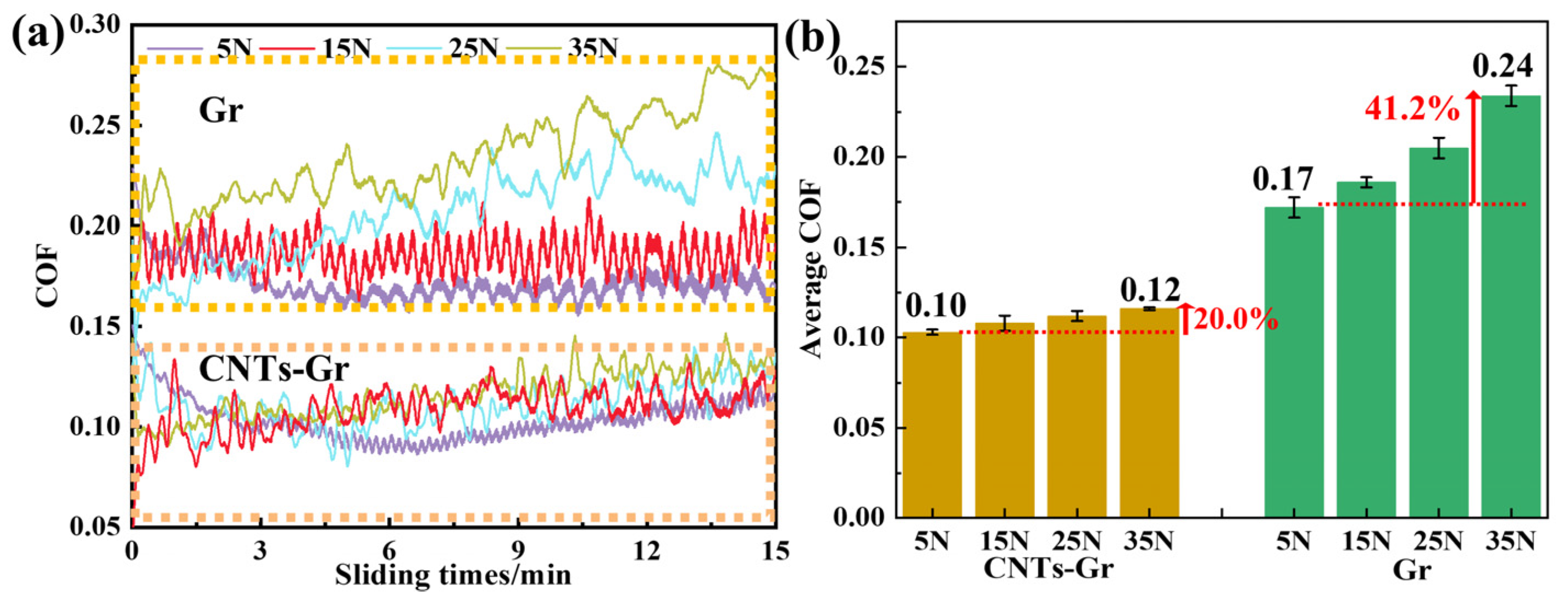
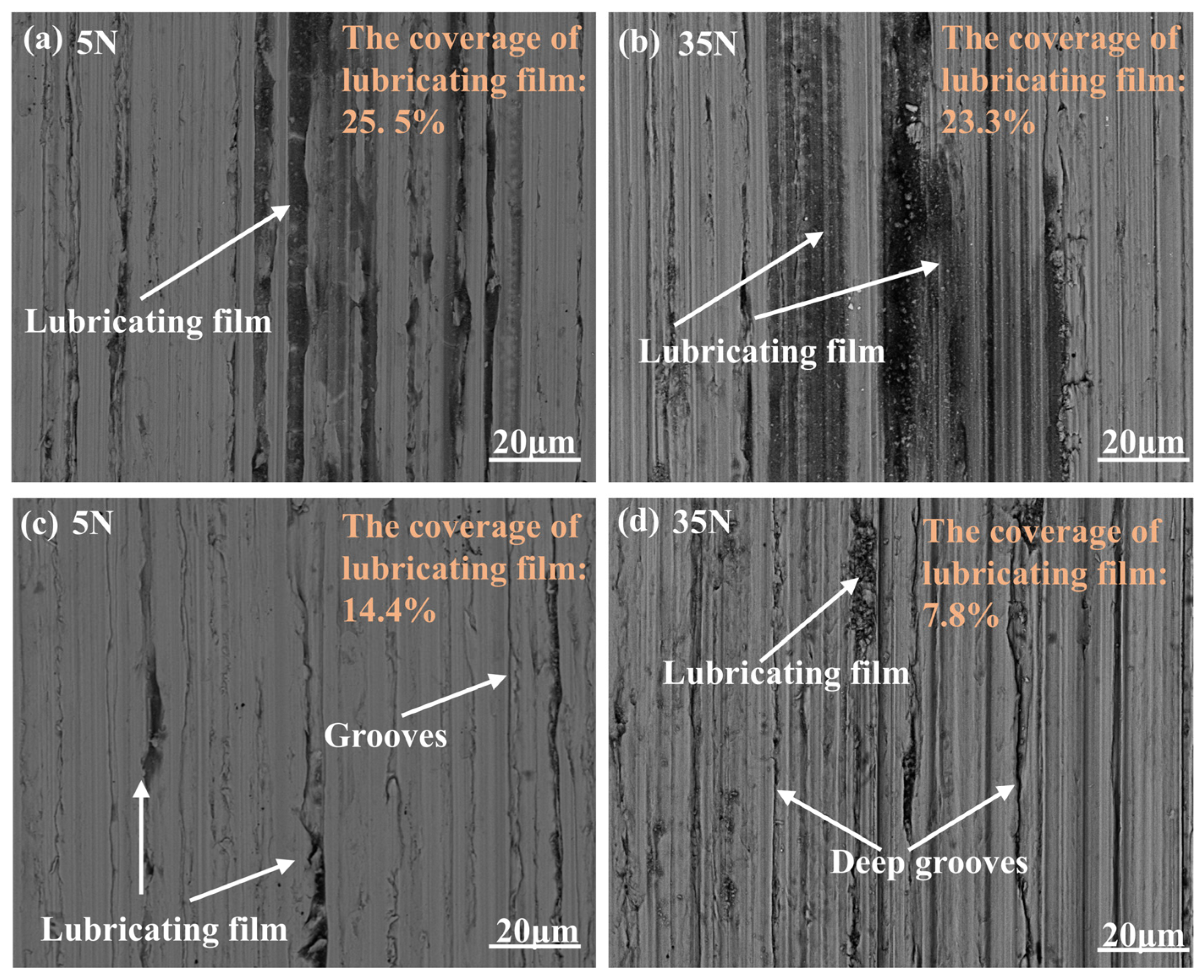
3.2. Tribological Behavior of CNTs-Gr and Characterization of the Worn Surface
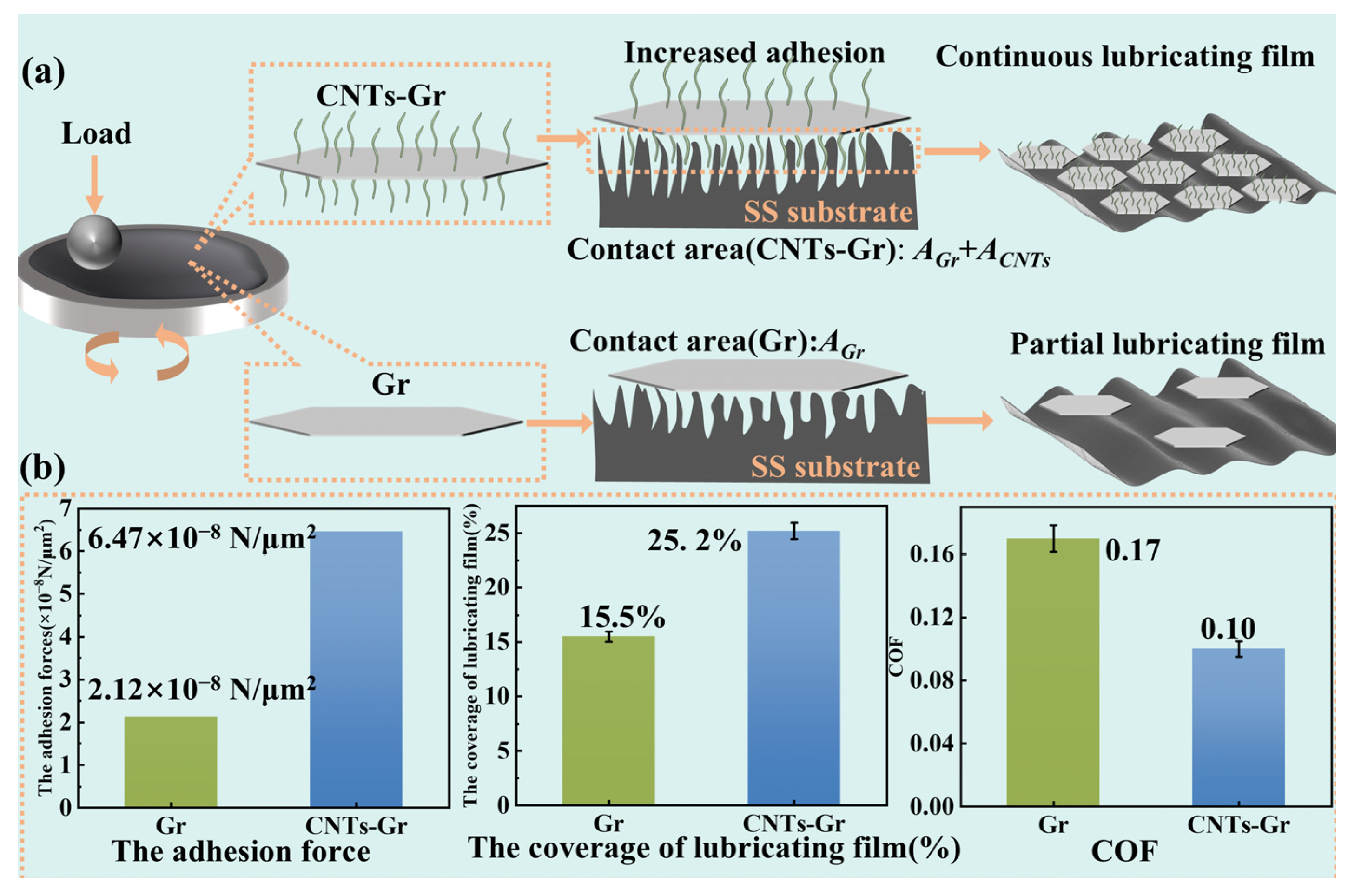
3.3. Analysis of Lubrication Mechanism
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Holmberg, K.; Erdemir, A. The impact of tribology on energy use and CO2 emission globally and in combustion engine and electric cars. Tribol. Int. 2019, 135, 389–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, F.; Xie, G.; Luo, J. Electrical bearing failures in electric vehicles. Friction 2020, 8, 4–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, J.; Zhou, X. Superlubricitive engineering—Future industry nearly getting rid of wear and frictional energy consumption. Friction 2020, 8, 643–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Wu, H.; Wang, H.; Liu, Y.; Yang, L.; Zhao, L. Tribological properties of novel palygorskite nanoplatelets used as oil-based lubricant additives. Friction 2020, 9, 332–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, L.; Ge, Y.; Zhu, L.; Chen, Y.; Yi, M. Preparation and properties of copper-plated expanded graphite/copper composites. Tribol. Int. 2021, 161, 107094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paul, G.; Shit, S.; Hirani, H.; Kuila, T.; Murmu, N.C. Tribological behavior of dodecylamine functionalized graphene nanosheets dispersed engine oil nanolubricants. Tribol. Int. 2019, 131, 605–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Zhang, H.; Gao, A.; Gong, L.; Ji, Y.; Zeng, S.; Li, S.; Wang, X. Friction and wear performance of aluminum-based self-lubricating materials derived from the 3D printed graphite skeletons with different morphologies and orientations. Tribol. Int. 2024, 195, 109614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shan, Z.; Jia, X.; Tian, R.; Yang, J.; Fan, H.; Cellulose-armored, H.S. “CNTs-soft metal” hybrid nanomaterials to improving the friction-reduction and anti-wear performance of bio-lubricants. Tribol. Int. 2024, 191, 109085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandran, A.; Unnikrishnan, N.; Jayaraj, M.; John, R.E.; George, J. Recent Advances in Graphene and Graphene-Based Technologies; IOP Publishing: Bristol, UK, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Barhoum, A.; Jeevanandam, J.; Danquah, M.K. Fundamentals of Bionanomaterials; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Xiao, J.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, W.; Chen, J.; Zhang, C. Friction of metal-matrix self-lubricating composites: Relationships among lubricant content, lubricating film coverage, and friction coefficient. Friction 2019, 8, 517–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Huang, Y.; He, Y.; Shi, Y. Nanolubricant additives: A review. Friction 2020, 9, 891–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Fang, Y.; Shang, F.; Zhang, J.; Liu, W.; Shen, H.; Guo, B. Enhancing the tribological performance of Cu-WS2 composites with Ag-shell/Cu-core structure. Powder Technol. 2023, 422, 118453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Q.; Fu, T.; Yue, Q.; Liu, H.; Ma, S.; Cai, M.; Zhou, F. Graphene oxide/brush-like polysaccharide copolymer nanohybrids as eco-friendly additives for water-based lubrication. Tribol. Int. 2021, 157, 106895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Li, X.; Deng, Y.; Chen, S.; Liang, W.; Zhang, L.; Wei, X.; Gao, S.; Wan, Y. Carbon quantum dots doped with silver as lubricating oil additive for enhancing tribological performance at various temperatures. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2022, 599, 154029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, P.; Lei, Y.; Li, W.; Fan, M. Two-dimension layered nanomaterial as lubricant additives: Covalent organic frameworks beyond oxide graphene and reduced oxide graphene. Tribol. Int. 2020, 143, 106051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Li, A.; Su, F. Excellent Lubricating Ability of Functionalization Graphene Dispersed in Perfluoropolyether for Titanium Alloy. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2019, 2, 1391–1401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Q.; Tang, T.; Zeng, Y.; Iradukunda, N.; Bethers, B.; Li, X.; Yang, Y. Review on 3D Printing of Bioinspired Structures for Surface/Interface Applications. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2023, 34, 2309323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, W.; Alkahtani, M.; Hemmer, P.R.; Liang, H. Drag-reduction of 3D printed shark-skin-like surfaces. Friction 2018, 7, 603–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Huang, J.; Guo, Z. Tomato-lotus inspired edible superhydrophobic artificial lotus leaf. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 400, 125883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Yu, B.; Sun, W.; Jiang, C.; Lu, L. Bioinspired nanostructured spiderweb for high-efficiency capturing and killing of bacteria. Sci. China Mater. 2021, 65, 518–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Wang, Z.; Li, Y.; Dai, Z. Electrostatic attraction caused by triboelectrification in climbing geckos. Friction 2020, 10, 44–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russell, A.P.; Stark, A.Y.; Higham, T.E. The Integrative Biology of Gecko Adhesion: Historical Review, Current Understanding, and Grand Challenges. Integr Comp Biol 2019, 59, 101–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Autumn, K.; Liang, Y.A.; Hsieh, S.T.; Zesch, W.; Chan, W.P.; Kenny, T.W.; Fearing, R.; Full, R.J. Full. Adhesive force of a single gecko foot-hair. Nature 2000, 405, 681–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ge, L.; Sethi, S.; Ci, L.; Ajayan, P.M.; Dhinojwala, A. Carbon nanotube-based synthetic gecko tapes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 10792–10795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benamor, A.; Hadji, Y.; Kota, S.; Chiker, N.; Liu, L.; Haddad, A.; Sahraoui, T.; Ying, G.; Hadji, M. Friction and wear characteristics of the nanolaminated ternary transition metal boride: Mn2AlB2. Wear 2022, 492–493, 204232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, K.; Yu, G.; Zhang, Z.; Wu, W.; Tian, P.; Chhattal, M.; Gong, Z.; Li, Y.; Zhang, J. Self-organized transfer film-induced ultralow friction of Graphene/MoWS4 heterostructure nanocomposite. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2022, 572, 151443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bajpai, R.; Wagner, H.D. Fast growth of carbon nanotubes using a microwave oven. Carbon 2015, 82, 327–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, H.; Cui, M.; Russell, T.P. A route to rapid carbon nanotube growth. Chem. Commun. (Camb) 2013, 49, 5159–5161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Ren, G.; Li, W.; Wang, B.; Wei, F.; Liang, Z.; Chen, D. A green modification technology of carbon nanotubes toward enhancing the tribological properties of aqueous-based lubricants. Tribol. Int. 2023, 180, 108268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Zhang, K.; Kang, X.; Zhang, L. Friction maps and wear maps of Ag/MoS2/WS2 nanocomposite with different sliding speed and normal force. Tribol. Int. 2021, 164, 107228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moghadam, A.D.; Omrani, E.; Menezes, P.L.; Rohatgi, P.K. Mechanical and tribological properties of self-lubricating metal matrix nanocomposites reinforced by carbon nanotubes (CNTs) and graphene–A review. Compos. Part B Eng. 2015, 77, 402–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bukvić, M.; Gajević, S.; Skulić, A.; Savić, S.; Ašonja, A.; Stojanović, B. Tribological Application of Nanocomposite Additives in Industrial Oils. Lubricants 2023, 12, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Z.; Xia, Y.; Liu, L.; Feng, X. Study on the conductive and tribological properties of copper sliding electrical contacts lubricated by ionic liquids. Tribol. Int. 2019, 130, 27–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grandin, M.; Wiklund, U. Wear phenomena and tribofilm formation of copper/copper-graphite sliding electrical contact materials. Wear 2018, 398–399, 227–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabaso, P.; Ville, F.; Dassenoy, F.; Diaby, M.; Afanasiev, P.; Cavoret, J.; Vacher, B.; Le Mogne, T. Boundary lubrication: Influence of the size and structure of inorganic fullerene-like MoS2 nanoparticles on friction and wear reduction. Wear 2014, 320, 161–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, H.; Liu, S. 2D nanomaterials as lubricant additive: A review. Mater. Des. 2017, 135, 319–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, K.; Wang, L.; Zou, X.; Wang, H.; Liang, C.; Zhang, D.; Wang, L.-N. Modeling bacterial adhesion on the nanopatterned surface by varying contact area. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2024, 196, 137–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Zou, M.; Wu, S.; Xu, W.; Wu, H.; Cao, A. Graphene Oxide Glue-Electrode for Fabrication of Vertical, Elastic, Conductive Columns. ACS Nano 2017, 11, 2944–2951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, J.; Sun, Y.; Shang, F.; Yan, Z.; Yao, J.; Chen, B.; Shen, H. Carbon Nanotubes–Gr Inspired by Geckos’ Setae Structure with Enhanced Tribological Properties. Materials 2025, 18, 1221. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18061221
Zhang J, Sun Y, Shang F, Yan Z, Yao J, Chen B, Shen H. Carbon Nanotubes–Gr Inspired by Geckos’ Setae Structure with Enhanced Tribological Properties. Materials. 2025; 18(6):1221. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18061221
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Jing, Yang Sun, Fengqin Shang, Zihan Yan, Jiayu Yao, Binghuan Chen, and Hangyan Shen. 2025. "Carbon Nanotubes–Gr Inspired by Geckos’ Setae Structure with Enhanced Tribological Properties" Materials 18, no. 6: 1221. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18061221
APA StyleZhang, J., Sun, Y., Shang, F., Yan, Z., Yao, J., Chen, B., & Shen, H. (2025). Carbon Nanotubes–Gr Inspired by Geckos’ Setae Structure with Enhanced Tribological Properties. Materials, 18(6), 1221. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18061221





