Fabrication of Cu/SiC Surface Composite via Thermo-Mechanical Process (Friction Stir Processing) for Heat Sink Application
Abstract
1. Introduction
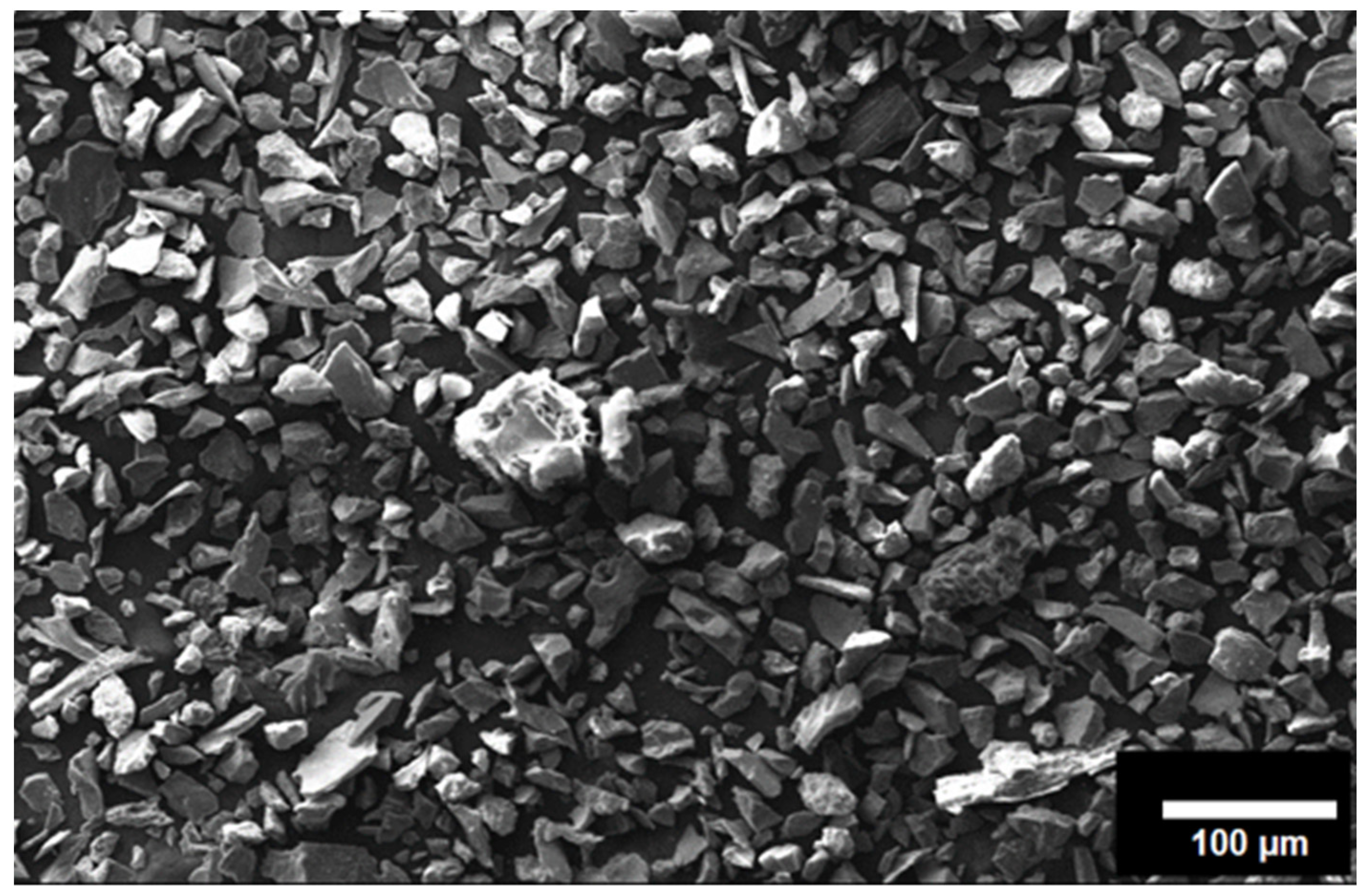
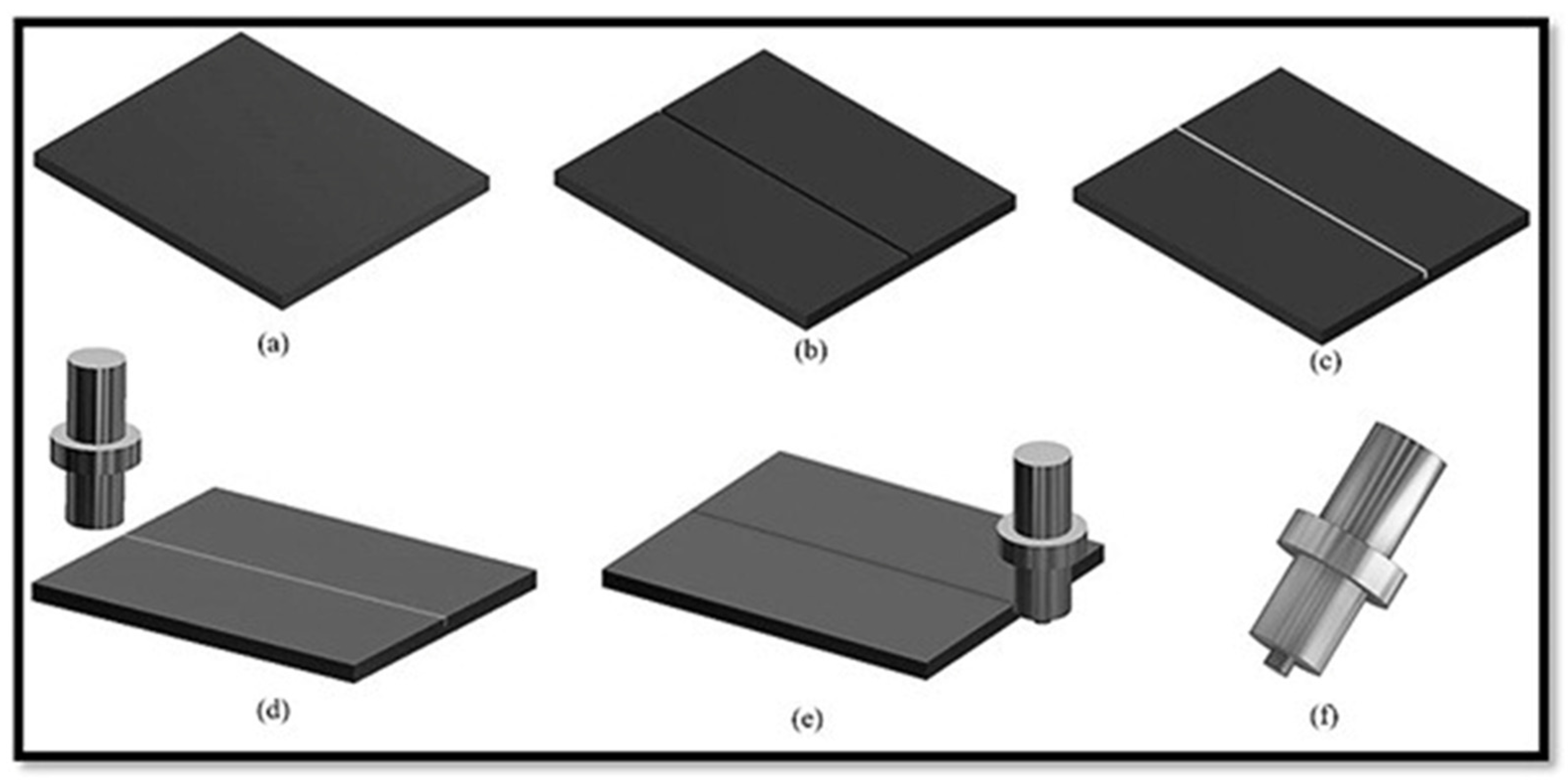
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results and Discussion
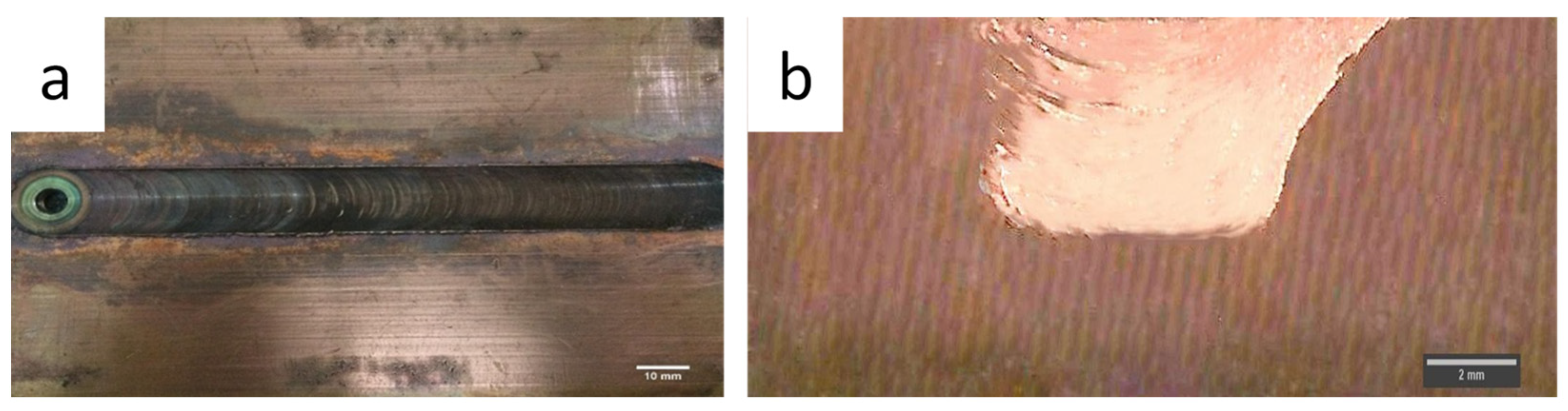
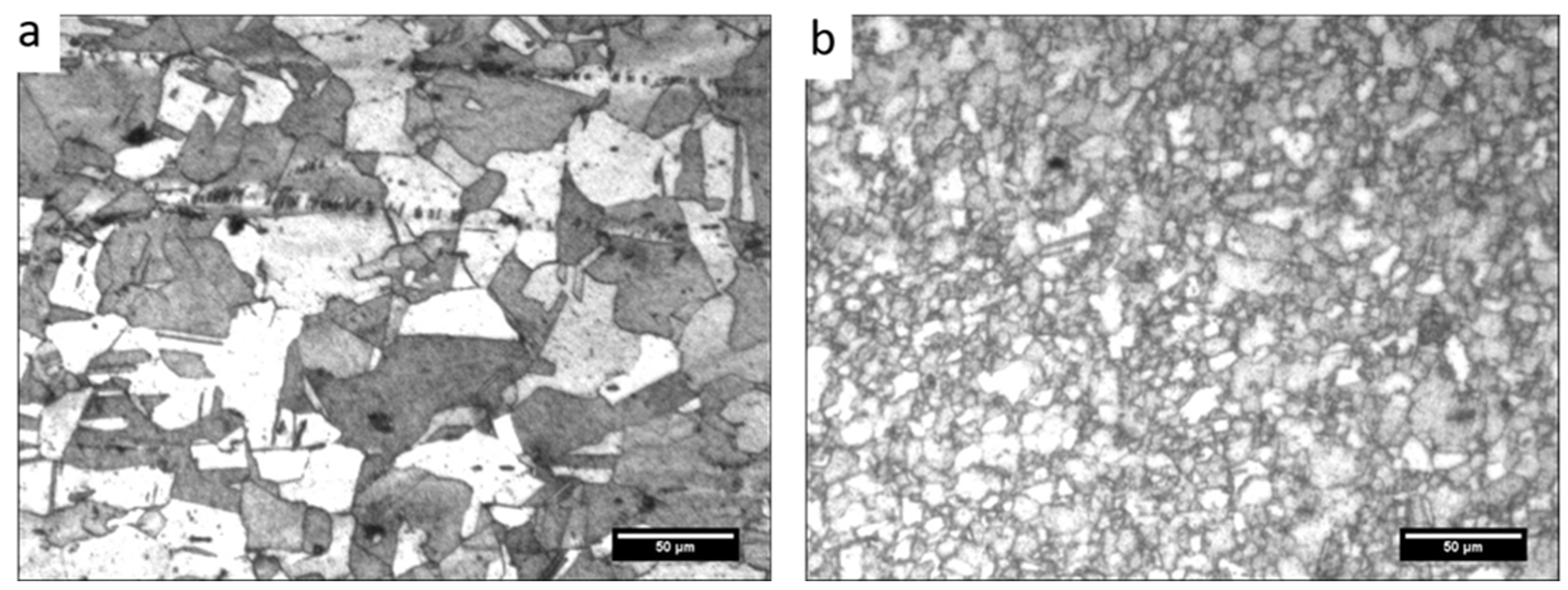
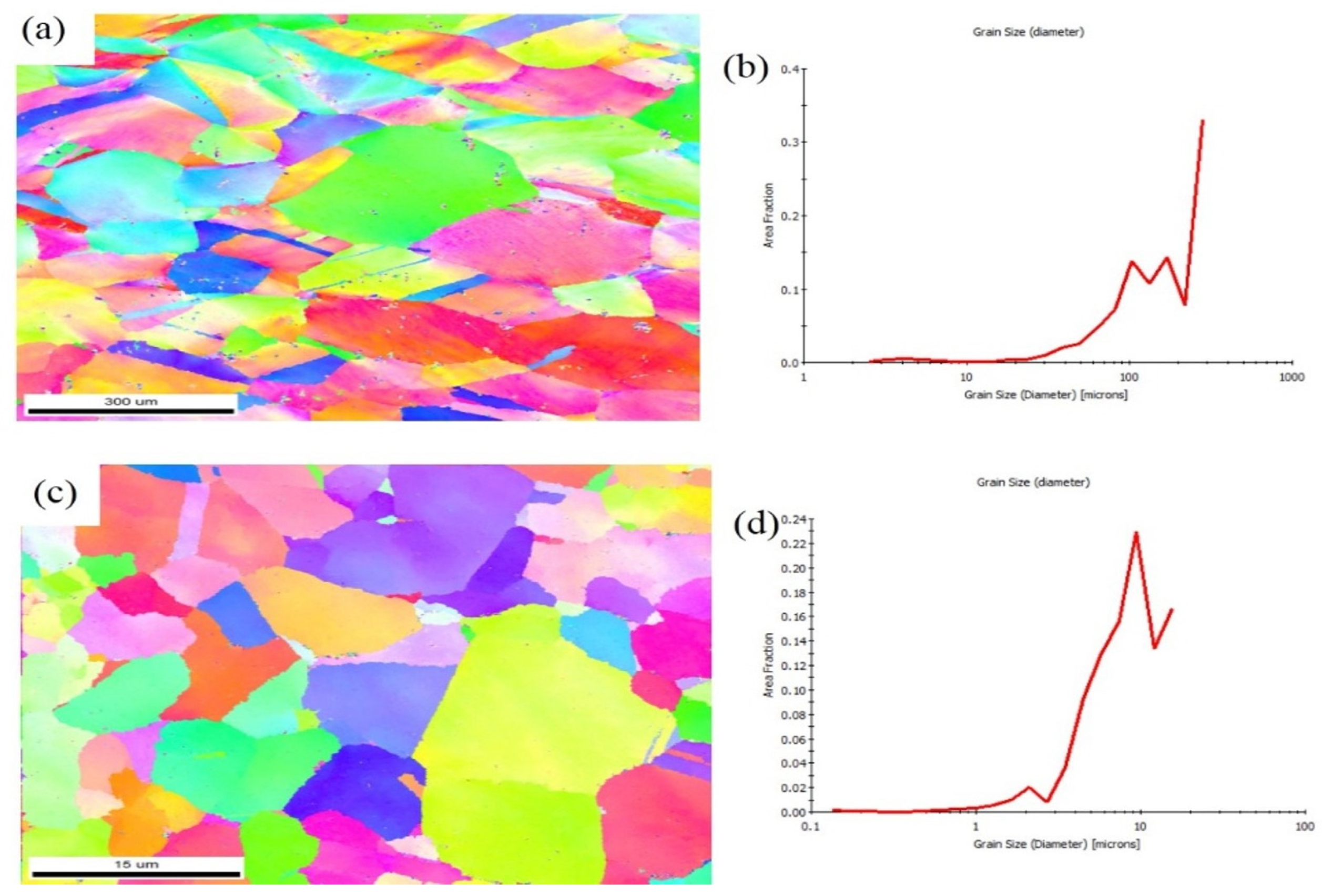
3.1. Macrostructure and Microstructure
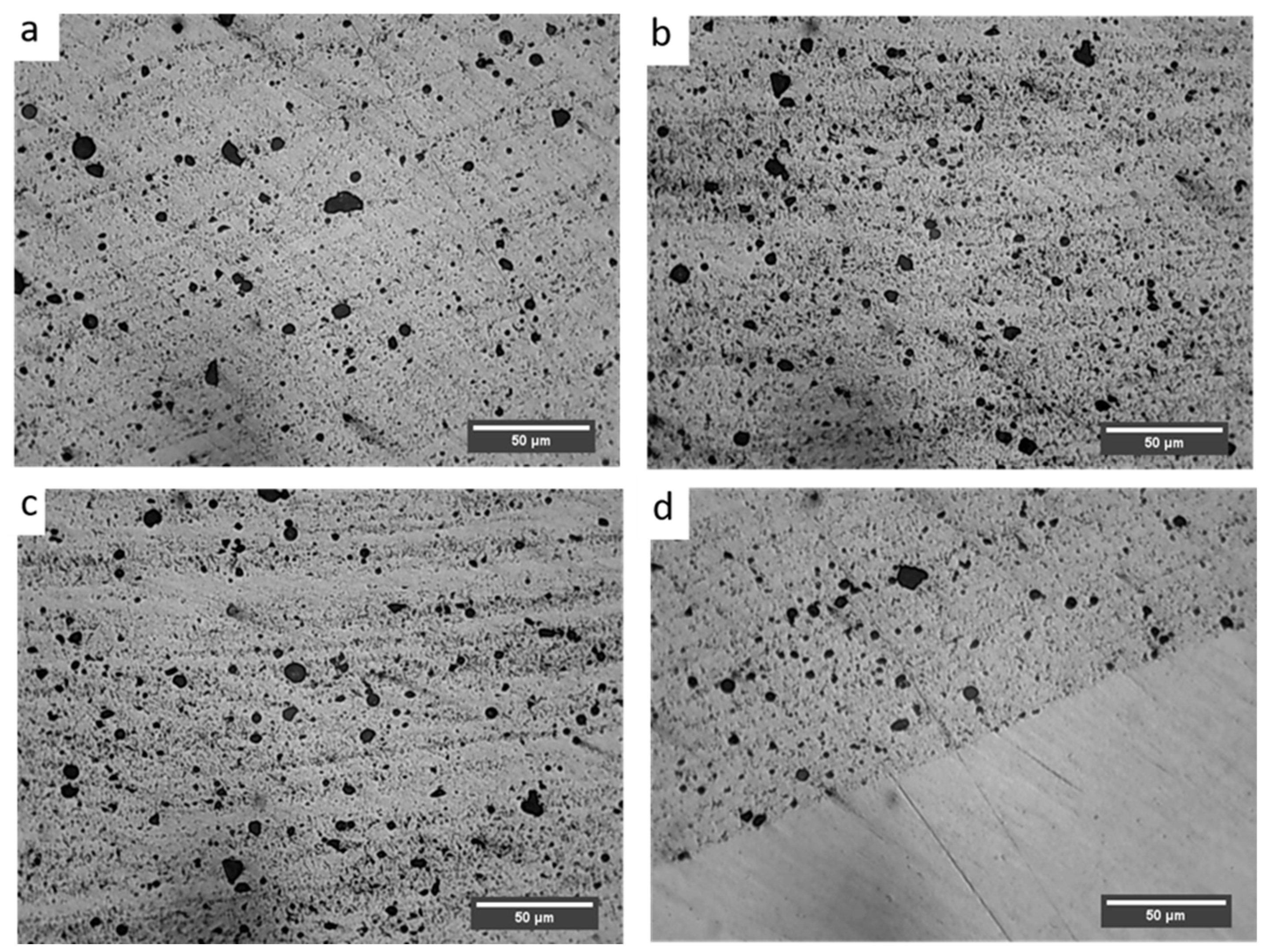
3.2. Compositinal Analysis
4. Mechanical Properties
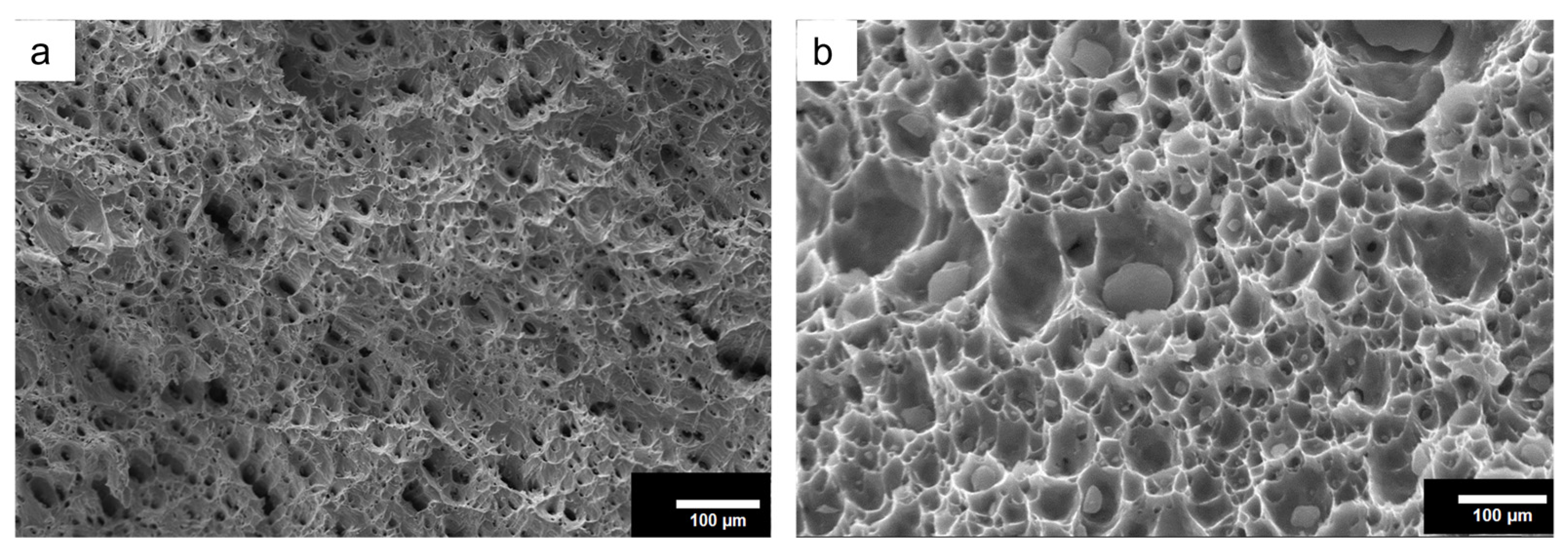
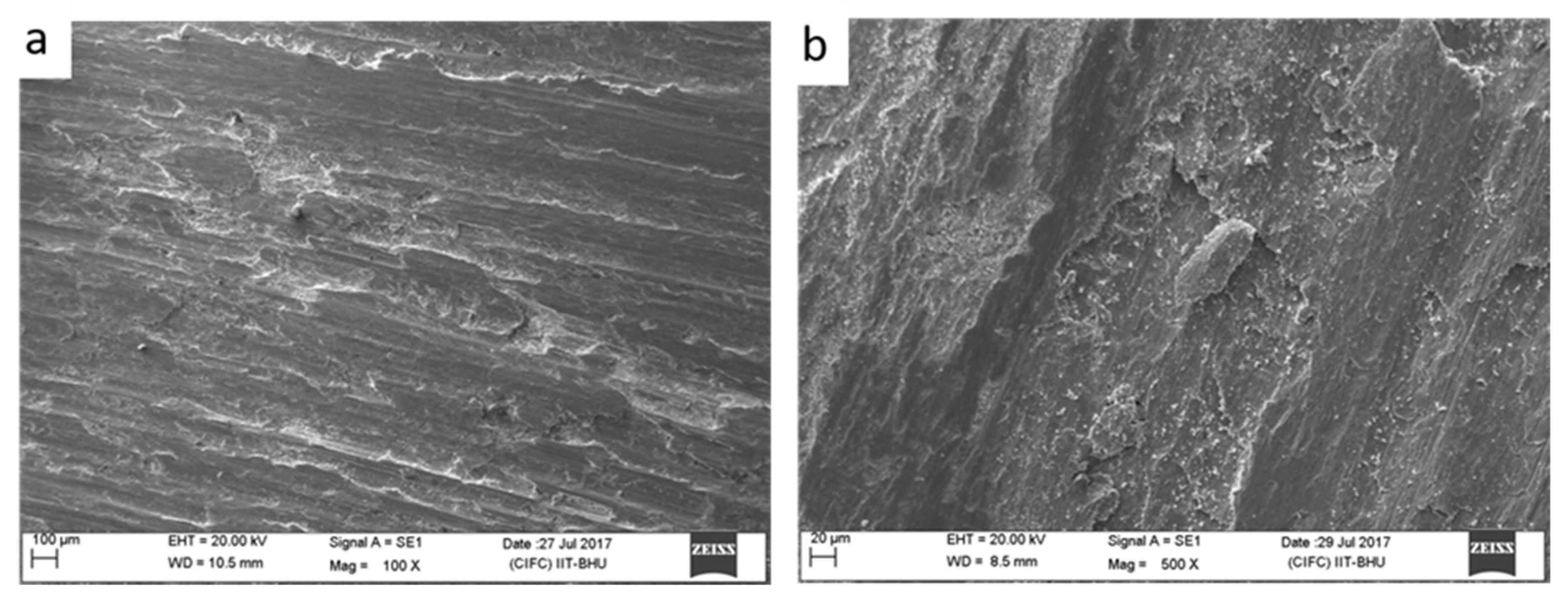
Fractography
5. Wear Properties
6. Conclusions
- The Cu/SiC composite was successfully fabricated using friction stir processing (FSP) without any defects.
- The SiC particles were uniformly and homogeneously distributed throughout the stir zone, with no signs of agglomeration or segregation along grain boundaries, which can be attributed to the solid-state nature of FSP.
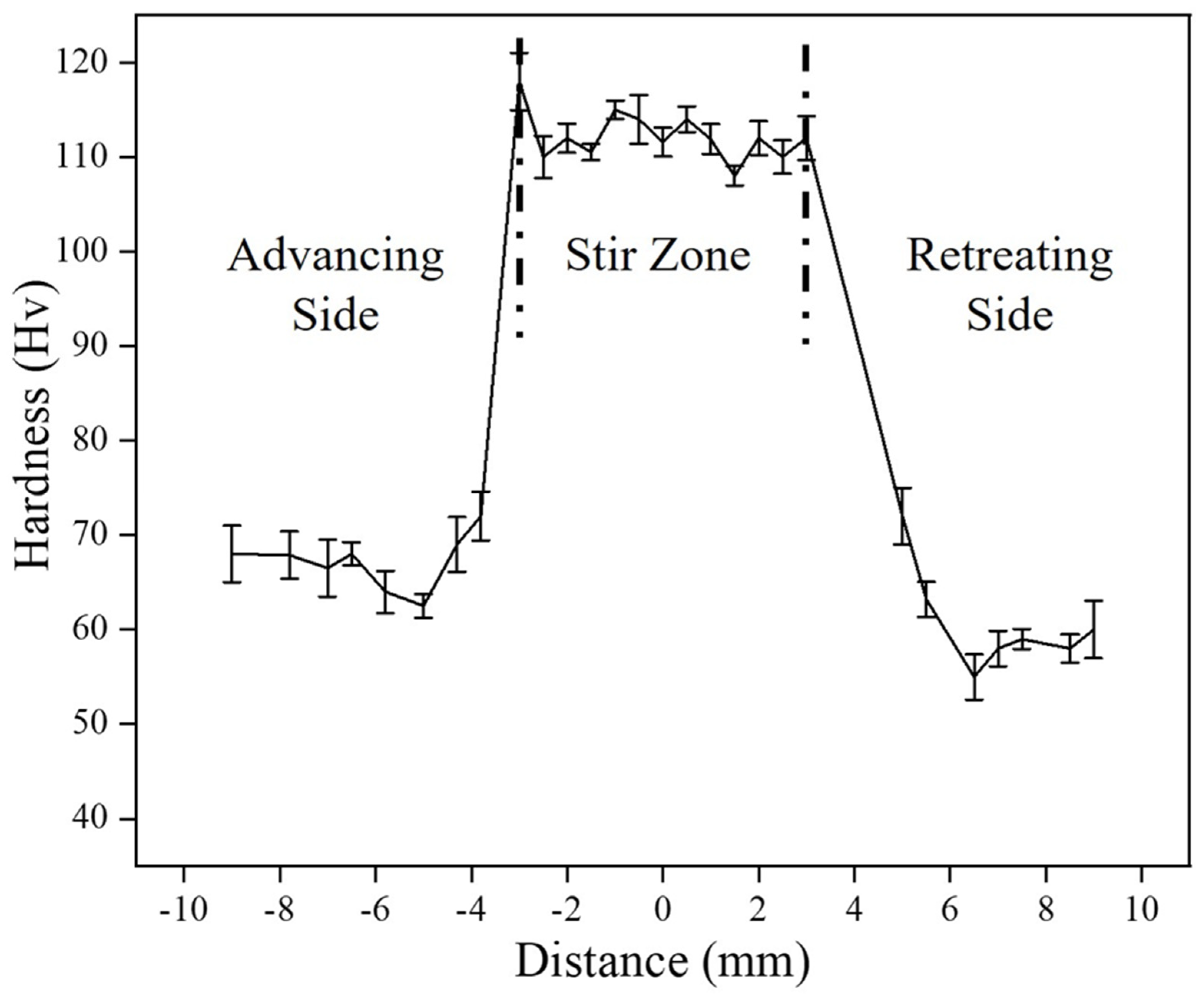
- The stir zone hardness of the composite increased by 57% compared to base copper. However, a slight decrease in hardness was observed in the heat-affected zone (HAZ), likely due to annealing effects and a reduction in dislocation density.
- The ultimate tensile strength (UTS) of the composite improved by 13%, while elongation decreased by 35%, primarily due to grain refinement, the pinning effect, and the shear lag mechanism.
- The composite exhibited enhanced wear resistance, which can be attributed to its greater hardness, the presence of hard ceramic reinforcements, and their uniform dispersion within the matrix.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mishra, R.S.; Ma, Z.Y.; Charit, I. Friction Stir Processing: A Novel Technique for Fabrication of Surface Composite. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2003, 341, 307–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arora, H.S.; Singh, H.; Dhindaw, B.K. Some Observations on Microstructural Changes in a Mg-Based AE42 Alloy Subjected to Friction Stir Processing. Metall. Mater. Trans. B 2012, 43, 92–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavaliere, P.; De Marco, P.P. Friction Stir Processing of AM60B Magnesium Alloy Sheets. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2007, 462, 393–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuller, C.B.; Mahoney, M.W. The Effect of Friction Stir Processing on 5083-H321/5356 Al Arc Welds: Microstructural and Mechanical Analysis. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 2006, 37, 3605–3615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuller, M.D.; Swaminathan, S.; Zhilyaev, A.P.; McNelley, T.R. Microstructural Transformations and Mechanical Properties of Cast NiAl Bronze: Effects of Fusion Welding and Friction Stir Processing. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2007, 463, 128–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh-Ishi, K.; McNelley, T.R. Microstructural Modification of As-Cast NiAl Bronze by Friction Stir Processing. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 2004, 35, 2951–2961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsujikawa, M.; Chung, S.W.; Tanaka, M.; Takigawa, Y.; Oki, S.; Higashi, K. High-Strengthening of Mg–5.5 Mass%Y–4.3 Mass%Zn Cast Alloy by Friction Stir Processing. Mater. Trans. 2005, 46, 3081–3084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Bauri, R.; Yadav, D.; Suhas, G. Effect of Friction Stir Processing (FSP) on Microstructure and Properties of Al–TiC in Situ Composite. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2011, 528, 4732–4739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berbon, P.B.; Bingel, W.H.; Mishra, R.S.; Bampton, C.C.; Mahoney, M.W. Friction Stir Processing: A Tool to Homogenize Nanocomposite Aluminum Alloys. Scr. Mater. 2001, 44, 61–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavaliere, P. Mechanical Properties of Friction Stir Processed 2618/Al2O3/20p Metal Matrix Composite. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2005, 36, 1657–1665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hodder, K.J.; Izadi, H.; McDonald, A.G.; Gerlich, A.P. Fabrication of Aluminum–Alumina Metal Matrix Composites via Cold Gas Dynamic Spraying at Low Pressure Followed by Friction Stir Processing. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2012, 556, 114–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morisada, Y.; Fujii, H.; Mizuno, T.; Abe, G.; Nagaoka, T.; Fukusumi, M. Modification of Thermally Sprayed Cemented Carbide Layer by Friction Stir Processing. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2010, 204, 2459–2464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morisada, Y.; Fujii, H.; Nagaoka, T.; Fukusumi, M. MWCNTs/AZ31 Surface Composites Fabricated by Friction Stir Processing. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2006, 419, 344–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.; Huang, J.; Hsieh, P. Mg Based Nano-Composites Fabricated by Friction Stir Processing. Scr. Mater. 2006, 54, 1415–1420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marode, R.V.; Lemma, T.A.; Sallih, N.; Pedapati, S.R.; Awang, M.; Hassan, A. Research Progress in Friction Stir Processing of Magnesium Alloys and Their Metal Matrix Surface Composites: Evolution in the 21st Century. J. Magnes. Alloys 2024, 12, 2091–2146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, S.; Nan, Z.; Li, Y.; Zhao, N.; Liu, Q.; Xu, G.; Cheng, X.; Yang, J. Copper Matrix Thermal Conductive Composites with Low Thermal Expansion for Electronic Packaging. Ceram. Int. 2020, 46, 18019–18025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Surekha, K.; Els-Botes, A. Development of High Strength, High Conductivity Copper by Friction Stir Processing. Mater. Des. 2011, 32, 911–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajkumar, K.; Aravindan, S. Tribological Performance of Microwave Sintered Copper–TiC–Graphite Hybrid Composites. Tribol. Int. 2011, 44, 347–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhokey, N.B.; Paretkar, R.K. Study of Wear Mechanisms in Copper-Based SiCp (20% by Volume) Reinforced Composite. Wear 2008, 265, 117–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kennedy, F.E.; Balbahadur, A.C.; Lashmore, D.S. The Friction and Wear of Cu-Based Silicon Carbide Particulate Metaal Matrix Composites for Brake Applications. Wear 1997, 203–204, 715–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fatoba, O.S.; Popoola, O.; Popoola, A.P.I. The Effects of Silicon Carbide Reinforcement on the Properties of Cu/SiCp Composites. Silicon 2015, 7, 351–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Węglewski, W.; Pitchai, P.; Chmielewski, M.; Guruprasad, P.J.; Basista, M. Thermal Conductivity of Cu-Matrix Composites Reinforced with Coated SiC Particles: Numerical Modeling and Experimental Verification. Int. J. Heat. Mass. Transf. 2022, 188, 122633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akbarpour, M.R.; Gazani, F.; Mousa Mirabad, H.; Khezri, I.; Moeini, A.; Sohrabi, N.; Kim, H.S. Recent Advances in Processing, and Mechanical, Thermal and Electrical Properties of Cu-SiC Metal Matrix Composites Prepared by Powder Metallurgy. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2023, 140, 101191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, A.; San Marchi, C.; Mortensen, A. Metal Matrix Composites in Industry; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 2003; ISBN 978-1-4020-7521-6. [Google Scholar]
- Agarwal, A.; Seretse, O.M.; Pumwa, J. Finite Element and Taguchi Response Analysis of the Application of Graphite Aluminum Mmc in Automotive Leaf Spring. J. Mech. Contin. Math. Sci. 2020, 15, 168–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agarwal, A.; Molwane, O.B.; Letsatsi, M.T. Experimental Investigation and Analysis of Heat Transfer Characteristics in Automotive Mmc Disc Brake under Steady State and Dynamic Conditions. J. Eng. Res. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinaharan, I.; Sathiskumar, R.; Murugan, N. Effect of Ceramic Particulate Type on Microstructure and Properties of Copper Matrix Composites Synthesized by Friction Stir Processing. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2016, 5, 302–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajendran, R.C.; Anto, T.; Agarwal, A.; Ilunga, M.; Jayamani, E.; Natarajan, V.D. Materials Synthesis and Characterization of Nano-Titanium Carbide-Filled Acrylonitrile Butadiene-Styrene Polymer Composites for Electromagnetic Interference Shielding. Rev. Compos. Matériaux Avancés 2024, 34, 673–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dey, A.; Kayal, N.; Molla, A.R.; Chakrabarti, O. Investigation of Thermal Oxidation of Al2O3-Coated SiC Powder. Thermochim. Acta 2014, 583, 25–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balamurugan, P.; Uthayakumar, M. Influence of Process Parameters on Cu–Fly Ash Composite by Powder Metallurgy Technique. Mater. Manuf. Process. 2015, 30, 313–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheibani, S.; Ataie, A.; Heshmati-Manesh, S. In-Situ Synthesis of Cu/Cr-Al2O3 Nanocomposite by Mechanical Alloying and Heat Treatment. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 2010, 41, 2606–2612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fathy, A.; Megahed, A.A. Prediction of Abrasive Wear Rate of in Situ Cu–Al2O3 Nanocomposite Using Artificial Neural Networks. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2012, 62, 953–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, A.S.; Mishra, N.; Biswas, K.; Basu, B. Fretting Wear Study of Cu–10wt% TiB2 and Cu–10wt% TiB2–10wt% Pb Composites. Wear 2013, 306, 138–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Kim, N.J.; Jung, J.Y.; Lee, E.-S.; Ahn, S. The Influence of Reinforced Particle Fracture on Strengthening of Spray Formed Cu-TiB2 Composite. Scr. Mater. 1998, 39, 1063–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahrami, A.; Soltani, N.; Pech-Canul, M.I.; Gutiérrez, C.A. Development of Metal-Matrix Composites from Industrial/Agricultural Waste Materials and Their Derivatives. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 46, 143–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agarwal, A.; Mthembu, L. Comparative Analysis of Boron-Al Metal Matix Composite and Aluminum Alloy in Enhancing Dynamic Performance of Vertical-Axis Wind Turbine. Processes 2024, 12, 2288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, H.; Prasad, R.; Srivastava, A.; Vashista, M.; Khan, M.Z. Utilisation of Industrial Waste (Fly Ash) in Synthesis of Copper Based Surface Composite through Friction Stir Processing Route for Wear Applications. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 196, 460–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, H.; Vashista, M.; Yusufzai, M.Z.K. Microstructure and Wear Behavior of Zircon Reinforced Copper Based Surface Composite Synthesized by Friction Stir Processing Route. Trans. Indian Inst. Met. 2018, 71, 2025–2033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, H.; Khan, M.Z.; Vashista, M. Microstructure, Mechanical and Electrical Characterization of Zirconia Reinforced Copper Based Surface Composite by Friction Stir Processing. Mater. Res. Express 2018, 5, 086505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasad, R.; Tewari, S.P.; Singh, J.K. Effect of Multi-Pass Friction Stir Processing on Microstructural, Mechanical and Tribological Behaviour of as-Cast Al–Zn–Mg–Cu Alloy. Mater. Res. Express 2019, 6, 096579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasad, R.; Tewari, S.P.; Singh, J.K. Microstructural and Wear Characterization of Friction Stir Processed ZrB2/AA7075 In-Situ Composites. Mater. Res. Express 2019, 6, 086514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pradhan, D.; Mahobia, G.S.; Chattopadhyay, K.; Singh, V. Effect of Surface Roughness on Corrosion Behavior of the Superalloy IN718 in Simulated Marine Environment. J. Alloys Compd. 2018, 740, 250–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ASTM E3-11; Standard Guide for Preparation of Metallographic Specimens. ASTM: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2017.
- ASTM E-384; Standard Test Method for Microindentation Hardness of Materials. ASTM: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2022.
- ASTM E8/E8M-16a; Standard Test Methods for Tension Testing of Metallic Materials. ASTM: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2020.
- Rajan, T.P.D.; Pillai, R.M.; Pai, B.C.; Satyanarayana, K.G.; Rohatgi, P.K. Fabrication and Characterisation of Al–7Si–0.35Mg/Fly Ash Metal Matrix Composites Processed by Different Stir Casting Routes. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2007, 67, 3369–3377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arora, H.S.; Singh, H.; Dhindaw, B.K. Composite Fabrication Using Friction Stir Processing—A Review. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2012, 61, 1043–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raja, R.; Jannet, S.; Thankachan, T. Investigation of Hybrid Copper Surface Composite Synthesized via FSP. Mater. Manuf. Process. 2021, 36, 1377–1383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, T.S.; Shalini, S.; Ramu, M.; Thankachan, T. Characterization of ZrC Reinforced AA6061 Alloy Composites Produced Using Stir Casting Process. J. Mech. Sci. Technol. 2020, 34, 143–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Jiang, W.; Li, G.; Guan, F.; Yu, Y.; Fan, Z. Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of SiCnp/Al6082 Aluminum Matrix Composites Prepared by Squeeze Casting Combined with Stir Casting. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2020, 283, 116699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



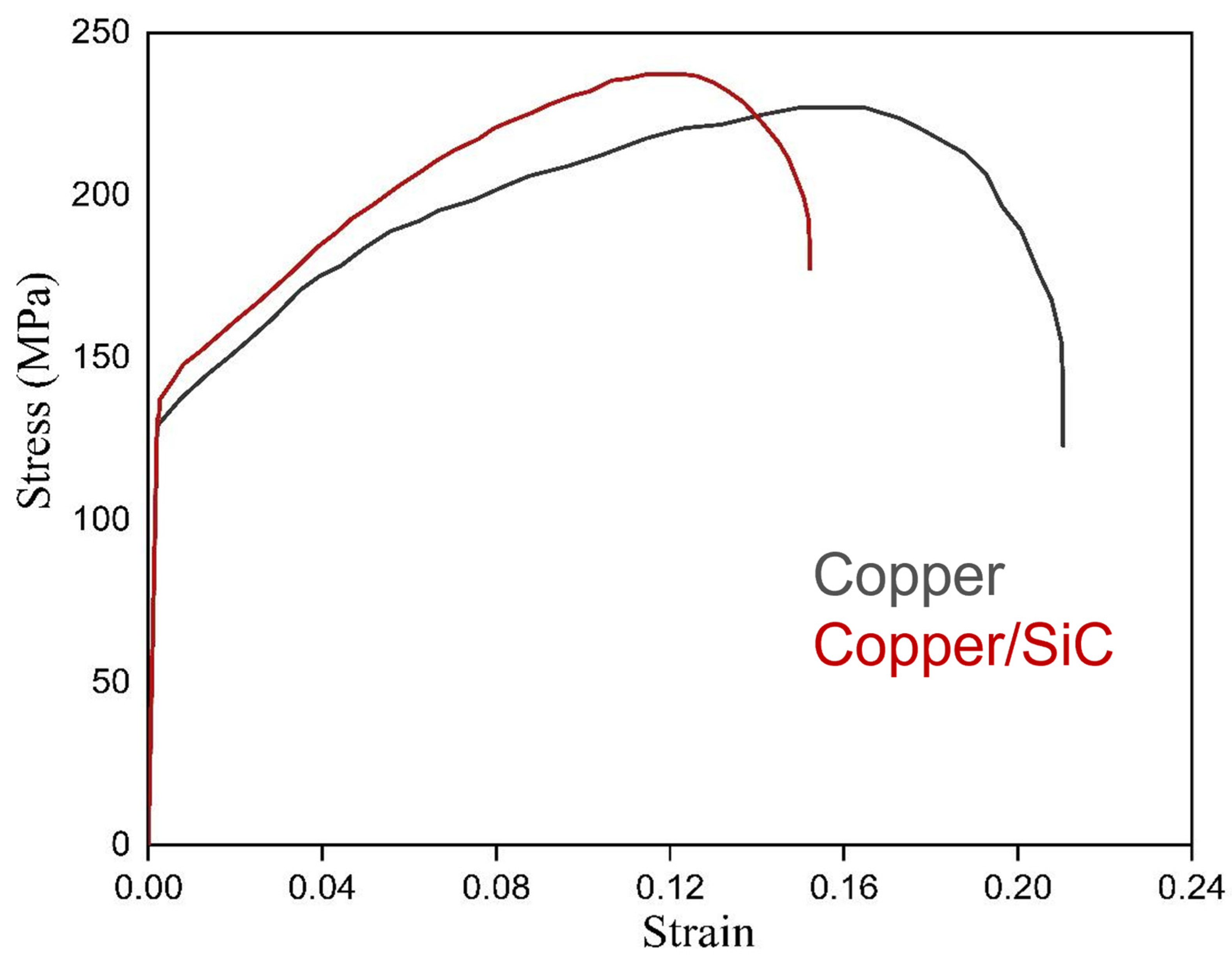

| Samples | UTS (MPa) | YS (MPa) | %EL |
|---|---|---|---|
| Base copper | 211 | 131 | 23 |
| Composite | 243 | 141 | 15 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kumar, H.; Agarwal, A.; Kalenga, M.K.W.; Prasad, R.; Kumar, P.; Chilakamarri, L.A.; Yelamasetti, B. Fabrication of Cu/SiC Surface Composite via Thermo-Mechanical Process (Friction Stir Processing) for Heat Sink Application. Materials 2025, 18, 1179. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18051179
Kumar H, Agarwal A, Kalenga MKW, Prasad R, Kumar P, Chilakamarri LA, Yelamasetti B. Fabrication of Cu/SiC Surface Composite via Thermo-Mechanical Process (Friction Stir Processing) for Heat Sink Application. Materials. 2025; 18(5):1179. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18051179
Chicago/Turabian StyleKumar, Harikishor, Abhishek Agarwal, Michel Kalenga Wa Kalenga, Rabindra Prasad, Parshant Kumar, L. Aslesha Chilakamarri, and Balram Yelamasetti. 2025. "Fabrication of Cu/SiC Surface Composite via Thermo-Mechanical Process (Friction Stir Processing) for Heat Sink Application" Materials 18, no. 5: 1179. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18051179
APA StyleKumar, H., Agarwal, A., Kalenga, M. K. W., Prasad, R., Kumar, P., Chilakamarri, L. A., & Yelamasetti, B. (2025). Fabrication of Cu/SiC Surface Composite via Thermo-Mechanical Process (Friction Stir Processing) for Heat Sink Application. Materials, 18(5), 1179. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18051179







