Effect of Pre-Strain Induced Microstructure Evolution on Hydrogen Embrittlement Resistance of a CoCrNi Medium-Entropy Alloy
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
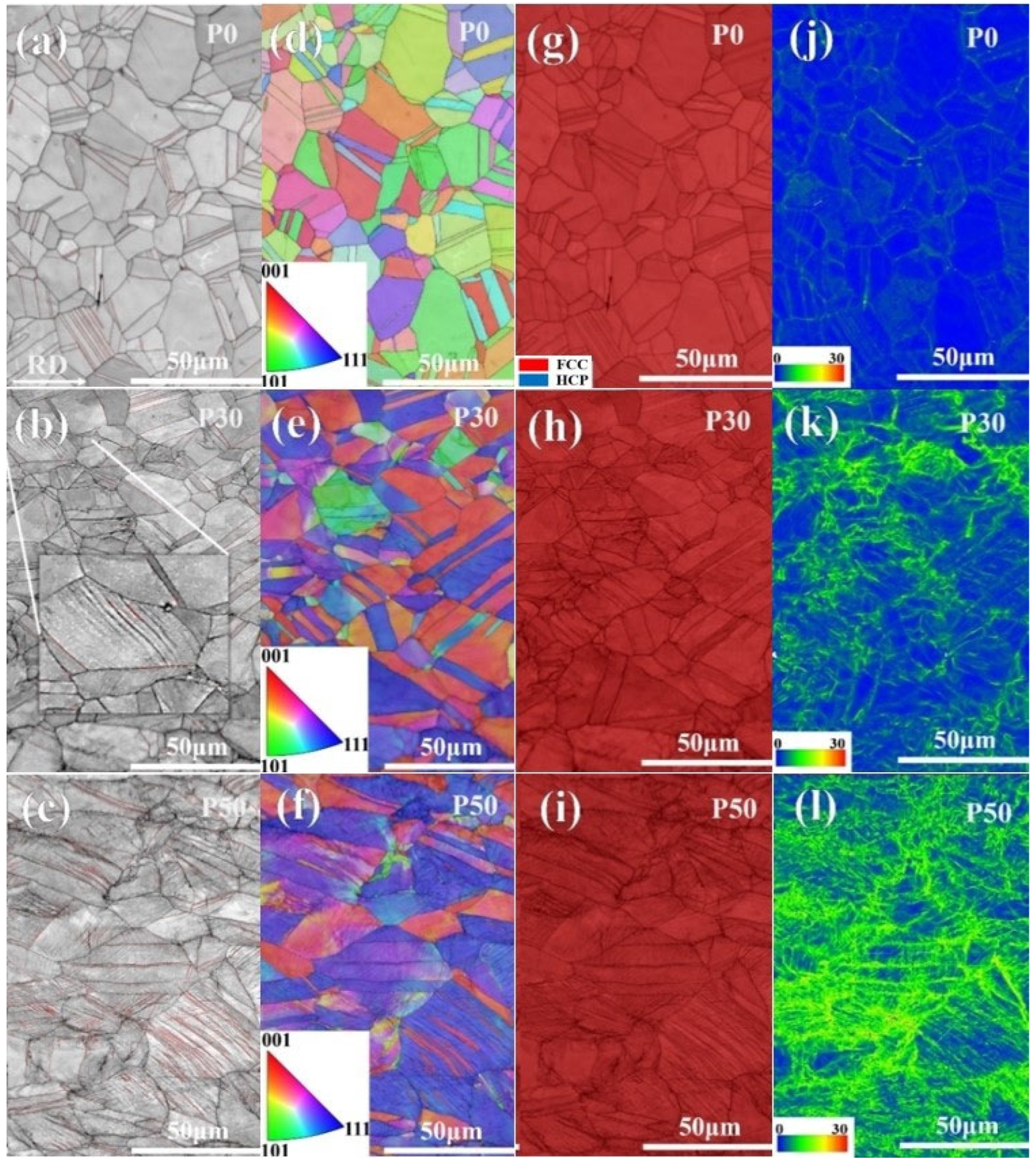
3.1. Microstructure Characterization
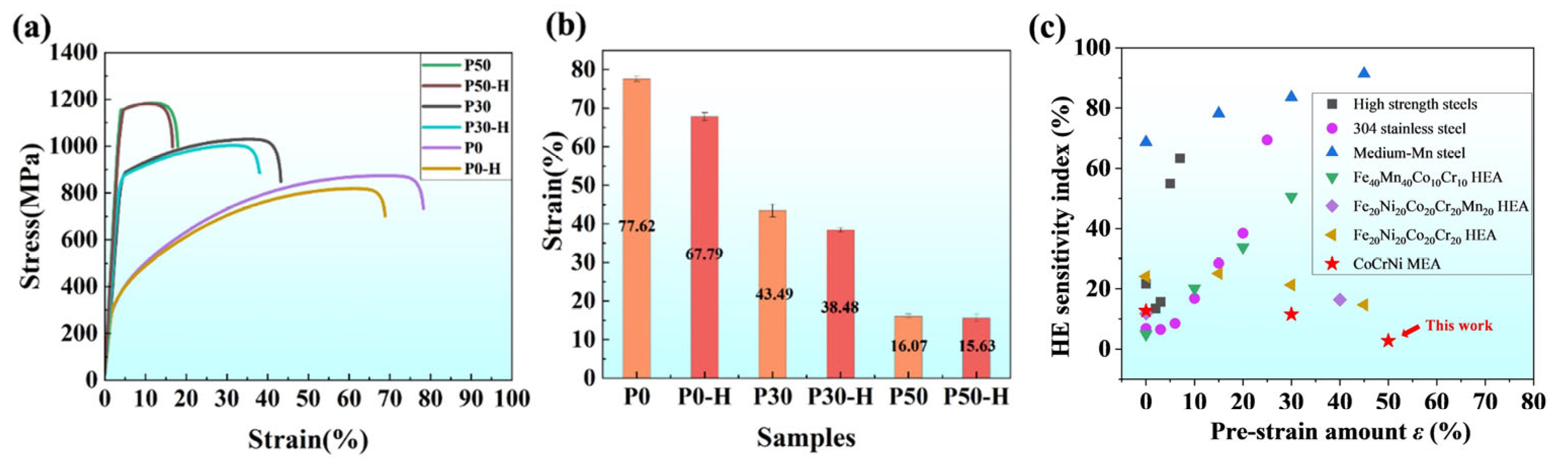
3.2. Mechanical Properties
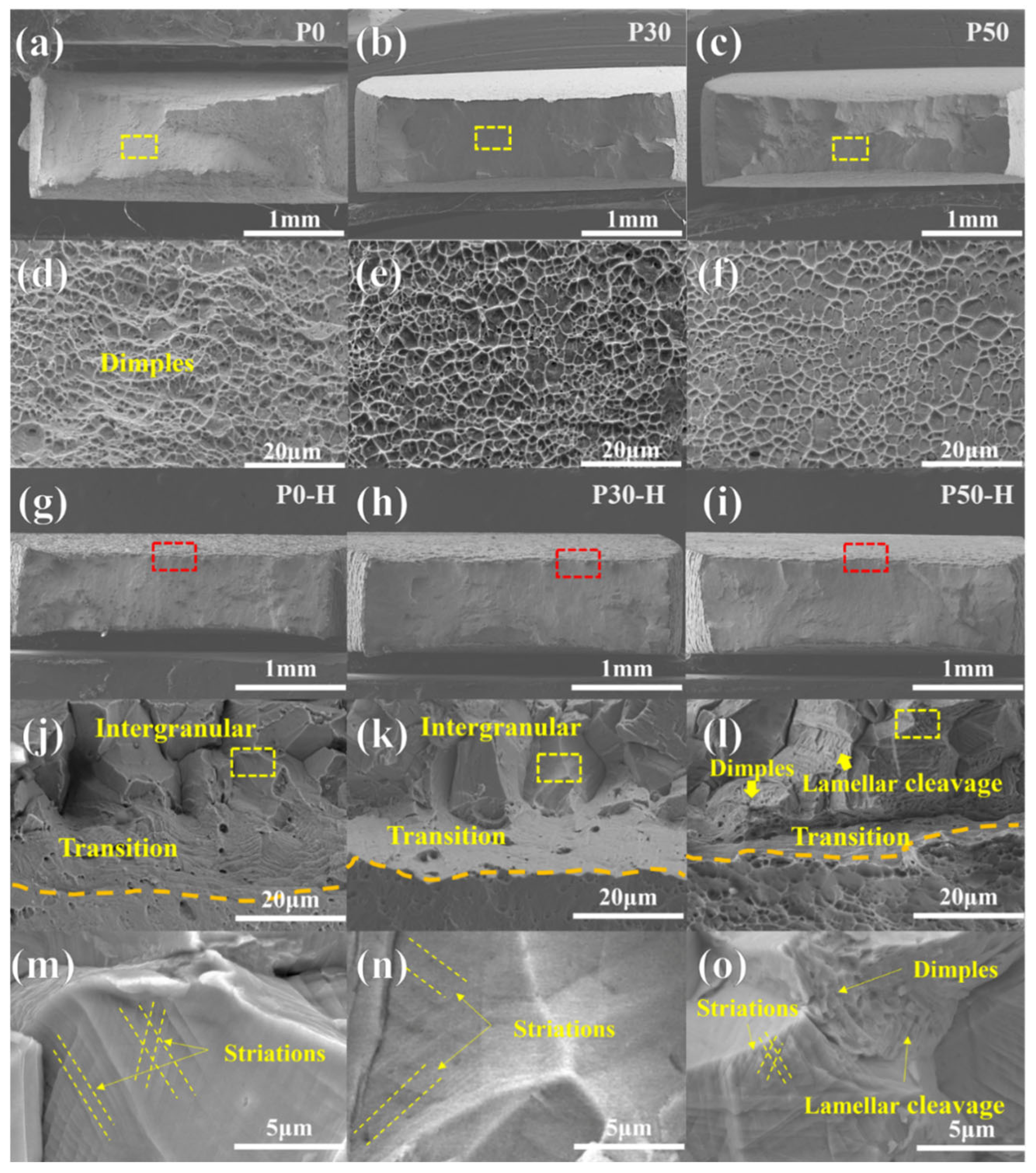
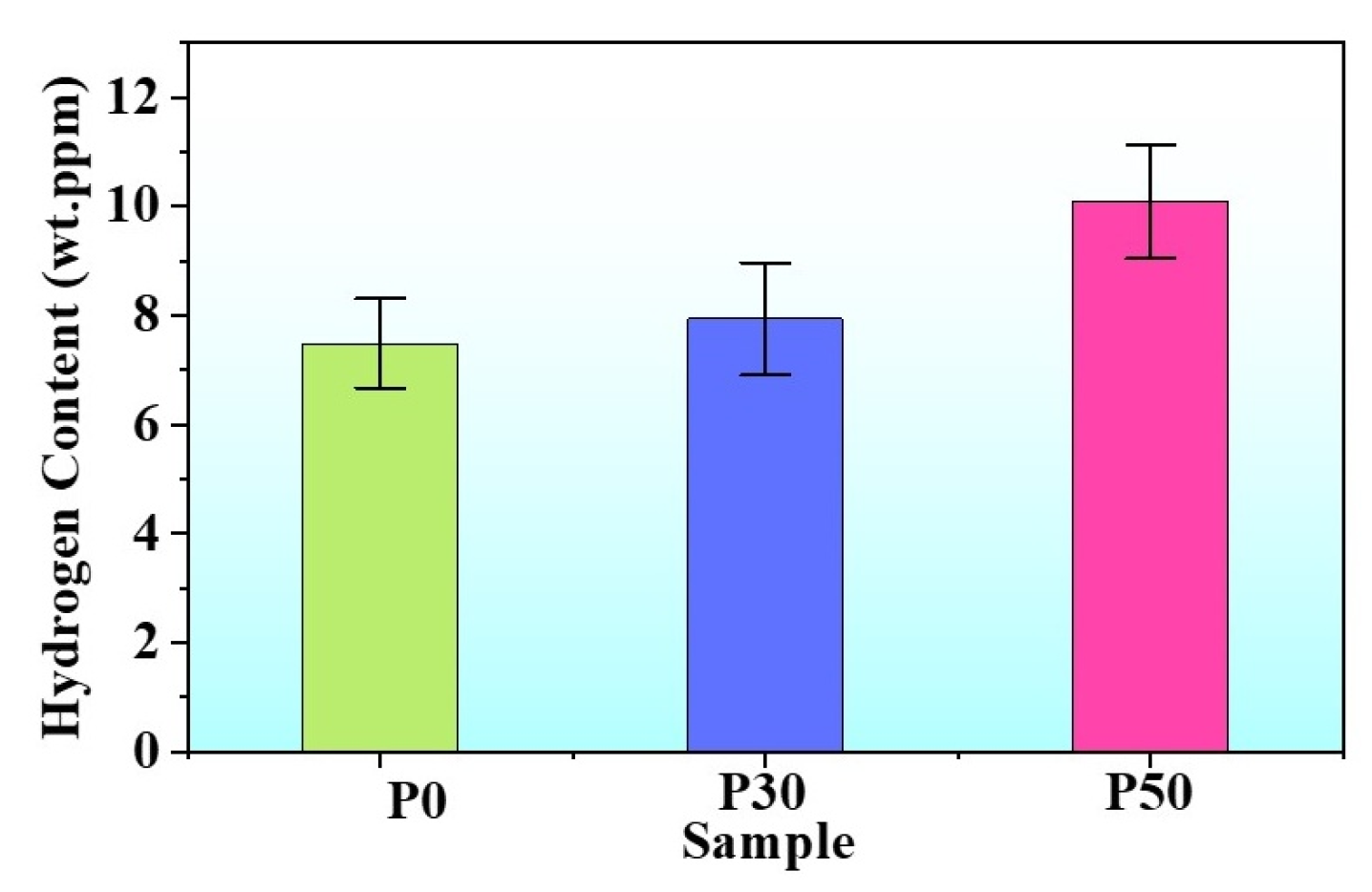
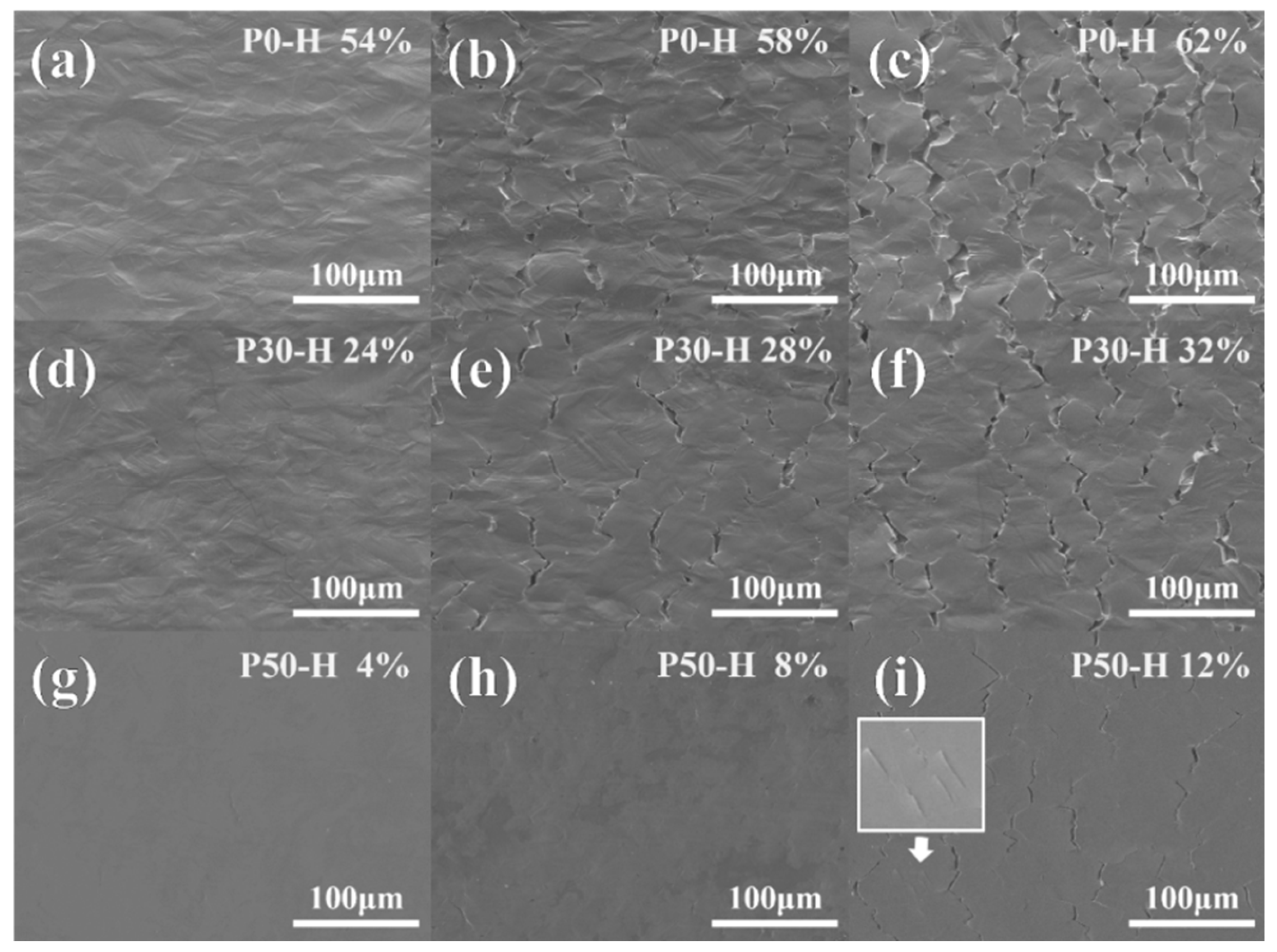
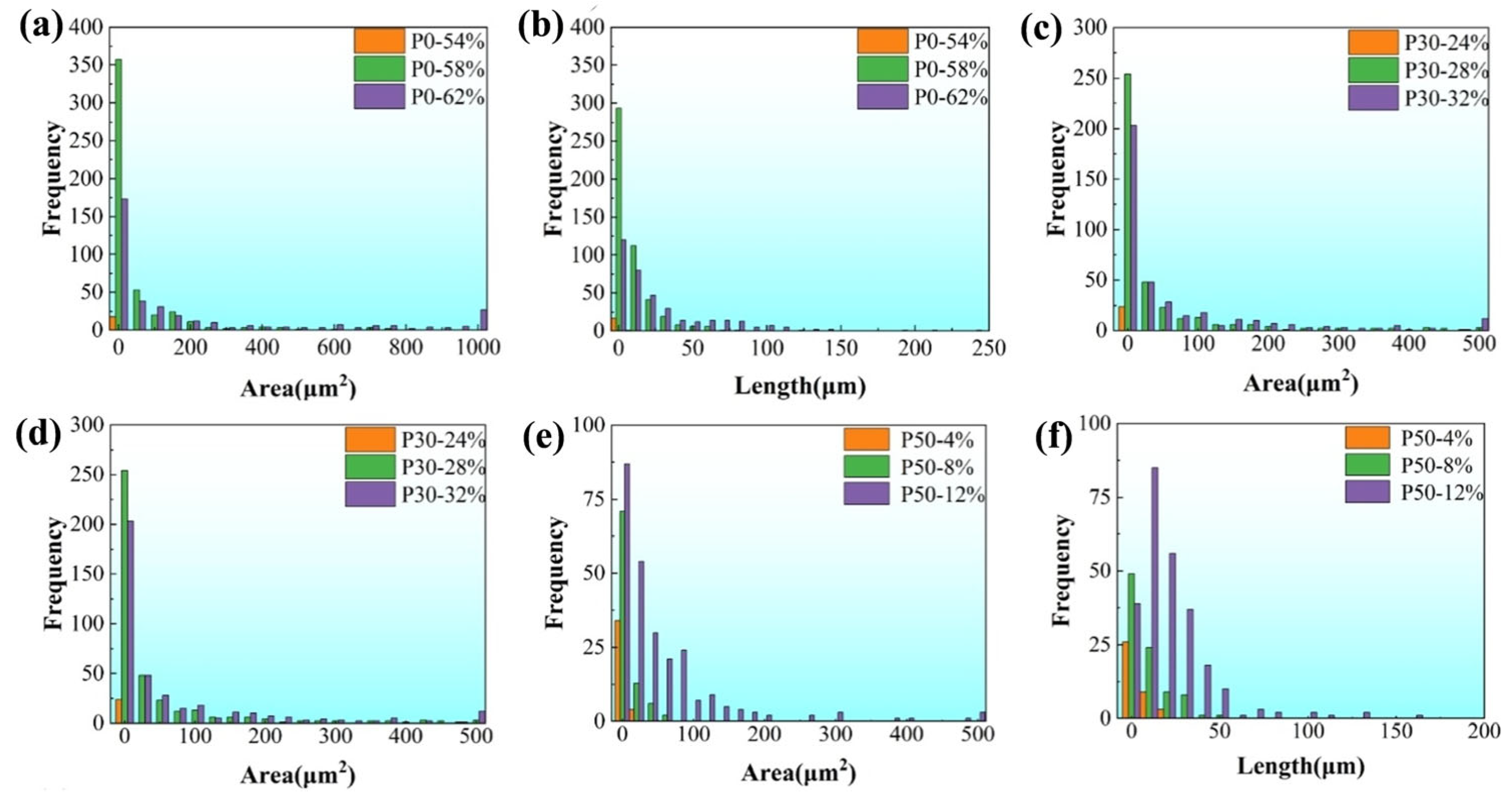
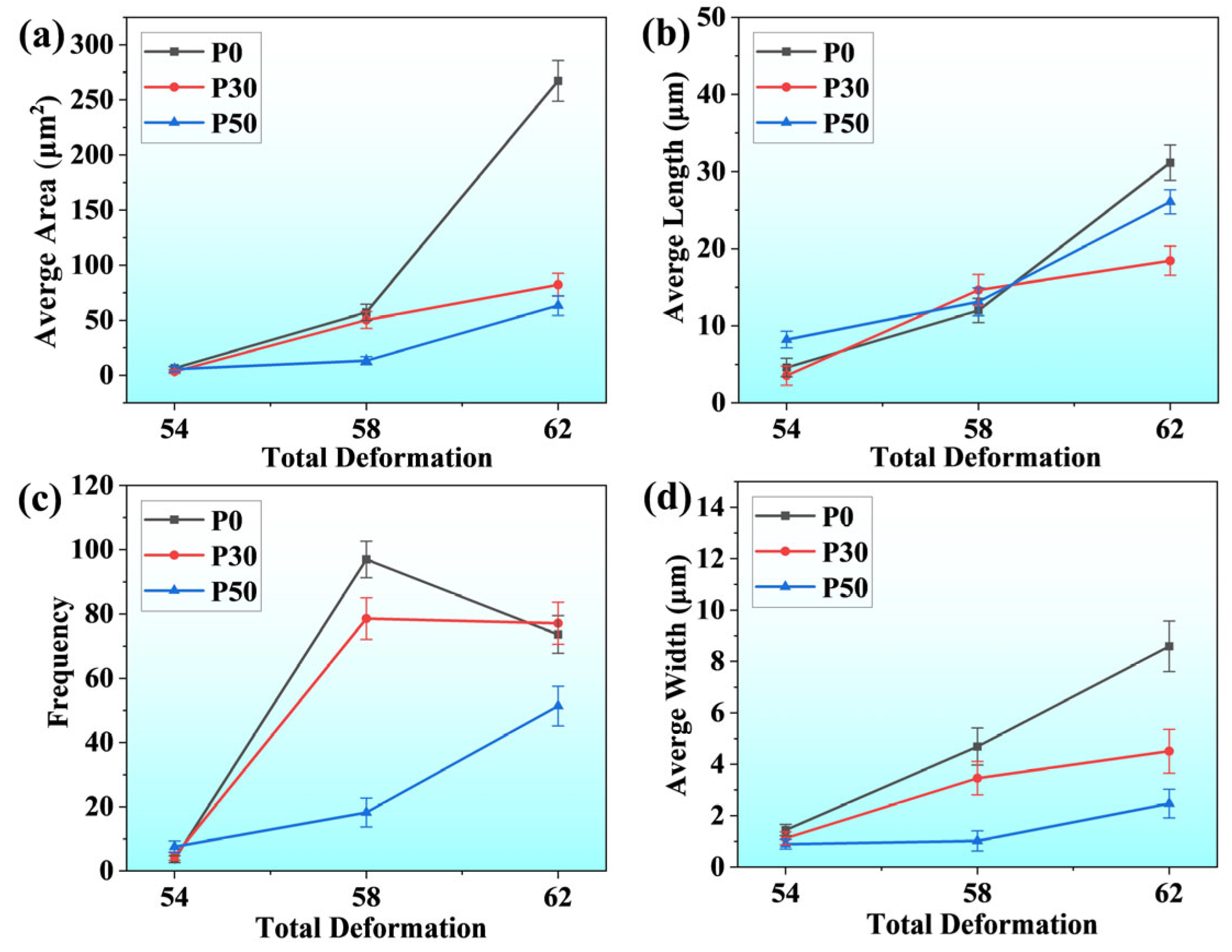
3.3. Fracture Surface and Gauge Surface Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Louthan, M., Jr.; Caskey, G., Jr.; Donovan, J.; Rawl, D., Jr. Hydrogen embrittlement of metals. Mater. Sci. Eng. 1972, 10, 357–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okonkwo, P.C.; Belgacem, I.B.; Mansir, I.B.; Aliyu, M.; Emori, W.; Uzoma, P.C.; Beitelmal, W.H.; Akyüz, E.; Radwan, A.B.; Shakoor, R. A focused review of the hydrogen storage tank embrittlement mechanism process. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2023, 48, 12935–12948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, X.; Xie, W.; Zeng, L.; Wei, H.; Zhang, X.; Wang, H. Achieving high strength and ductility in a heterogeneous-grain-structured CrCoNi al and subsequent short-annealing. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2021, 821, 141610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Yu, Q.; Kabra, S.; Jiang, M.; Forna-Kreutzer, P.; Zhang, R.; Payne, M.; Walsh, F.; Gludovatz, B.; Asta, M. Exceptional fracture toughness of CrCoNi-based medium-and high-entropy alloys at 20 kelvin. Science 2022, 378, 978–983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, L.; Hilhorst, A.; Idrissi, H.; Jacques, P.J. Potential TRIP/TWIP coupled effects in equiatomic CrCoNi medium-entropy alloy. Acta Mater. 2022, 234, 118049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, X.; Jiang, H.; Lv, Y.; Xie, W.; Lu, S.; Xu, D. Research Progress on the Hydrogen Embrittlement Resistance Performance of High-Entropy Alloys. Materials 2025, 18, 2862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nygren, K.E.; Wang, S.; Bertsch, K.M.; Bei, H.; Nagao, A.; Robertson, I.M. Hydrogen embrittlement of the equi-molar FeNiCoCr alloy. Acta Mater. 2018, 157, 218–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, D.; Wang, M.; Li, T.; Wei, X.; Lu, Y. A critical review of the mechanical properties of CoCrNi-based medium-entropy alloys. Microstructures 2022, 2, 2022001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agustianingrum, M.P.; Lee, U.; Park, N. High-temperature oxidation behaviour of CoCrNi medium-entropy alloy. Corros. Sci. 2020, 173, 108755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weng, F.; Chew, Y.; Ong, W.K.; Man, Y.; Sui, S.; Tan, C.; Ng, F.L.; Goh, M.H.; Bi, G. Enhanced corrosion resistance of laser aided additive manufactured CoCrNi medium entropy alloys with oxide inclusion. Corros. Sci. 2022, 195, 109965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Xu, Z.; Zhu, Y.; Shi, R.; Gao, K.; Pang, X. Superior hydrogen embrittlement resistance of CoCrNi-based medium-entropy alloy via coherent precipitation and grain boundary strengthening. Corros. Sci. 2024, 240, 112483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soundararajan, C.K.; Luo, H.; Raabe, D.; Li, Z. Hydrogen resistance of a 1 GPa strong equiatomic CoCrNi medium entropy alloy. Corros. Sci. 2020, 167, 108510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, H.; Sohn, S.S.; Lu, W.; Li, L.; Li, X.; Soundararajan, C.K.; Krieger, W.; Li, Z.; Raabe, D. A strong and ductile medium-entropy alloy resists hydrogen embrittlement and corrosion. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 3081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chung, D.H.; Kim, Y.K.; Kim, Y.K.; Song, S.Y.; Kwon, H.J.; Sohn, S.S.; Na, Y.S. Enhancing hydrogen embrittlement resistance of medium entropy alloys by forming dislocation cell walls. Corros. Sci. 2023, 215, 111023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, J.; Zhuang, X.; He, J.; He, M.; Liu, W.; Wang, S. Effect of Mo doping on the gaseous hydrogen embrittlement of a CoCrNi medium-entropy alloy. Corros. Sci. 2021, 189, 109628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Y.; Luo, H.; Pan, Z.; Wei, Y.; Gan, B.; Bi, Z.; Li, X. Hydrogen induced microstructure, mechanical properties and cracking evolution in a novel CoCrNiMo medium-entropy alloy. J. Alloys Compd. 2023, 939, 168790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, X.; Gong, J.; Shen, L.; Dong, W. Hydrogen embrittlement of catholically hydrogen-precharged 304L austenitic stainless steel: Effect of plastic pre-strain. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2014, 39, 13909–13918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, I.-J.; Jung, J.-G.; Jo, S.Y.; Lee, S.-M.; Lee, Y.-K. The effect of pre-strain on the resistance to hydrogen embrittlement in 316L austenitic stainless steel. Mater. Trans. 2014, 55, 964–970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Ma, L.; Zhou, C.; Hong, Y.; Tao, H.; Zheng, J.; Zhang, L. Improved resistance to hydrogen environment embrittlement of warm-deformed 304 austenitic stainless steel in high-pressure hydrogen atmosphere. Corros. Sci. 2019, 148, 159–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koyama, M.; Akiyama, E.; Tsuzaki, K.; Raabe, D. Hydrogen-assisted failure in a twinning-induced plasticity steel studied under in situ hydrogen charging by electron channeling contrast imaging. Acta Mater. 2013, 61, 4607–4618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, C.; Song, Y.; Shi, Q.; Hu, S.; Zheng, J.; Xu, P.; Zhang, L. Effect of pre-strain on hydrogen embrittlement of metastable austenitic stainless steel under different hydrogen conditions. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2019, 44, 26036–26048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Yu, H.; Zhi, H.; Antonov, S.; Su, Y. Twinning behavior and hydrogen embrittlement of a pre-strained twinning-induced plasticity (TWIP) steel. Corros. Sci. 2021, 192, 109791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Zhi, H.; Antonov, S.; He, J.; Guo, Z.; Su, Y. Effect of pre-strain on hydrogen embrittlement of high manganese steel. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2022, 834, 142596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.; Yin, S.; Liang, X.; Cao, F.; Yu, Q.; Zhang, R.; Dai, L.; Ruestes, C.J.; Ritchie, R.O.; Minor, A.M. Deformation and failure of the CrCoNi medium-entropy alloy subjected to extreme shock loading. Sci. Adv. 2023, 9, eadf8602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, J.; Slone, C.; Smith, T.; Niu, C.; Bei, H.; Ghazisaeidi, M.; Pharr, G.; Mills, M.J. The evolution of the deformation substructure in a Ni-Co-Cr equiatomic solid solution alloy. Acta Mater. 2017, 132, 35–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laplanche, G.; Kostka, A.; Reinhart, C.; Hunfeld, J.; Eggeler, G.; George, E. Reasons for the superior mechanical properties of medium-entropy CrCoNi compared to high-entropy CrMnFeCoNi. Acta Mater. 2017, 128, 292–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Z.; Xie, J.; Wang, C.; Wang, T.; Chen, A.; Wang, X.; Gan, B. Twin-induced transformation strengthening of CoCrNi-based medium-entropy alloy with a gradient nanostructure. J. Mater. Res. Technol.-JMRT 2023, 24, 3969–3976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, L.; Chen, X.; Huang, X.; Lu, K. Revealing the maximum strength in nanotwinned copper. Science 2009, 323, 607–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, P.; Li, B.; Song, X.; Chen, J. Effect of pre-strain on hydrogen embrittlement of high strength steels. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2014, 616, 116–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.W.; Park, T.M.; Kim, H.-J.; Han, J. Correlation between pre-strain and hydrogen embrittlement behavior in medium-Mn steel. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2025, 206, 62–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Z.; Yan, Y. The role of cryogenic pre-strain on the hydrogen embrittlement of FeNiCoCrMn high-entropy alloys. Corros. Sci. 2023, 218, 111197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Z.; Li, S.; Wang, Y.; Li, W.; Yan, Y. The role of ambient and cryogenic pre-strain on hydrogen embrittlement of a FeNiCoCr high-entropy alloy: A comparative study. Corros. Sci. 2025, 244, 112661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Han, K.; Liu, X.; Zhu, Y.; Yuan, S.; Zhao, L.; Liang, S.; Huang, M.; Li, Z. Effect of pre-strain on hydrogen embrittlement susceptibility of Fe40Mn40Co10Cr10 high-entropy alloy. Eng. Fail. Anal. 2025, 173, 109439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Feng, Z.; Song, X.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Y. Effect of hydrogen charging time on hydrogen embrittlement of CoCrFeMnNi high-entropy alloy. Corros. Sci. 2022, 198, 110073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lynch, S. Progression markings, striations, and crack-arrest markings on fracture surfaces. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2007, 468, 74–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Z.; Wu, P.; Zhu, S.; Gan, K.; Yan, D.; Li, Z. Effects of interstitial C and N on hydrogen embrittlement behavior of non-equiatomic metastable FeMnCoCr high-entropy alloys. Corros. Sci. 2022, 194, 109933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, H.; Park, I.-J.; Lee, S.-M.; Lee, Y.-K. The effect of pre-strain on hydrogen embrittlement in 310S stainless steel. J. Alloys Compd. 2014, 598, 205–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashimoto, M.; Latanision, R. Hydrogen Transport During Plastic Deformation. In Proceedings of the International Congress on Metallic Corrosion, Toronto, ON, Canada, 3–7 June 1984; pp. 427–436. [Google Scholar]
- Kacher, J.; Eftink, B.; Cui, B.; Robertson, I. Dislocation interactions with grain boundaries. Curr. Opin. Solid State Mater. Sci. 2014, 18, 227–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dadfarnia, M.; Nagao, A.; Wang, S.; Martin, M.L.; Somerday, B.P.; Sofronis, P. Recent advances on hydrogen embrittlement of structural materials. Int. J. Fract. 2015, 196, 223–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tehranchi, A.; Curtin, W. Atomistic study of hydrogen embrittlement of grain boundaries in nickel: I. Fracture. J. Mech. Phys. Solids 2017, 101, 150–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.; Lu, T.; Zhao, P.; Sun, B.; Yao, N.; Chen, X.; Tan, J.; Zhang, X.-C.; Tu, S.-T. Cryoforged nanotwinned CoCrNi medium-entropy alloy with exceptional fatigue property at cryogenic temperature. Scr. Mater. 2023, 237, 115718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sathiyamoorthi, P.; Moon, J.; Bae, J.W.; Asghari-Rad, P.; Kim, H.S. Superior cryogenic tensile properties of ultrafine-grained CoCrNi medium-entropy alloy produced by high-pressure torsion and annealing. Scr. Mater. 2019, 163, 152–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, J.; Li, F.; Gu, Z.; Jiang, M.; Liu, Y.; Wang, G.; Wu, X. Impact resistance and energy dissipation mechanism of nanocrystalline CoCrNi medium entropy alloy nanofilm under supersonic micro-ballistic impact. Int. J. Plast. 2023, 171, 103801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Sheng, H.; Wang, Z.; Gludovatz, B.; Zhang, Z.; George, E.P.; Yu, Q.; Mao, S.X.; Ritchie, R.O. Dislocation mechanisms and 3D twin architectures generate exceptional strength-ductility-toughness combination in CrCoNi medium-entropy alloy. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 14390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birnbaum, H.K.; Sofronis, P. Hydrogen-enhanced localized plasticity—A mechanism for hydrogen-related fracture. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 1994, 176, 191–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, Z.; Jing, S.; Yan, Y. Effect of Pre-Strain Induced Microstructure Evolution on Hydrogen Embrittlement Resistance of a CoCrNi Medium-Entropy Alloy. Materials 2025, 18, 4915. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18214915
Wang Z, Jing S, Yan Y. Effect of Pre-Strain Induced Microstructure Evolution on Hydrogen Embrittlement Resistance of a CoCrNi Medium-Entropy Alloy. Materials. 2025; 18(21):4915. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18214915
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Zening, Sirui Jing, and Yu Yan. 2025. "Effect of Pre-Strain Induced Microstructure Evolution on Hydrogen Embrittlement Resistance of a CoCrNi Medium-Entropy Alloy" Materials 18, no. 21: 4915. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18214915
APA StyleWang, Z., Jing, S., & Yan, Y. (2025). Effect of Pre-Strain Induced Microstructure Evolution on Hydrogen Embrittlement Resistance of a CoCrNi Medium-Entropy Alloy. Materials, 18(21), 4915. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18214915






