Hardness Characterization of Simultaneous Aging and Surface Treatment of 3D-Printed Maraging Steel
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Specimens
2.2. Technologies, Equipment, Parameters of Heat Treatments, and Testing
- -
- DLC: diamond-like hydrogenated amorphous carbon with a tungsten carbide base layer, with an expected hardness of 2500–4000 HV;
- -
- CrN: chromium nitride base layer, with an expected hardness of 1500–3000 HV;
- -
- TiN: titanium nitride base layer, with an expected hardness of 2000–3500 HV.
2.3. Characterization of the Surface Hardness of the Nitrided and Coated Samples Using the Modified ECM
3. Experimental Work
3.1. Pre-Tests to Investigate the Effect of the Direct Aging of Parts Produced by SLM
3.2. Designing the Target Test for the Simultaneous Heat Treatment of Parts Produced by SLM
3.3. The Industrial Complex Heat Treatment Target Test Procedure
3.3.1. Conditions of the Performed Industrial Treatment
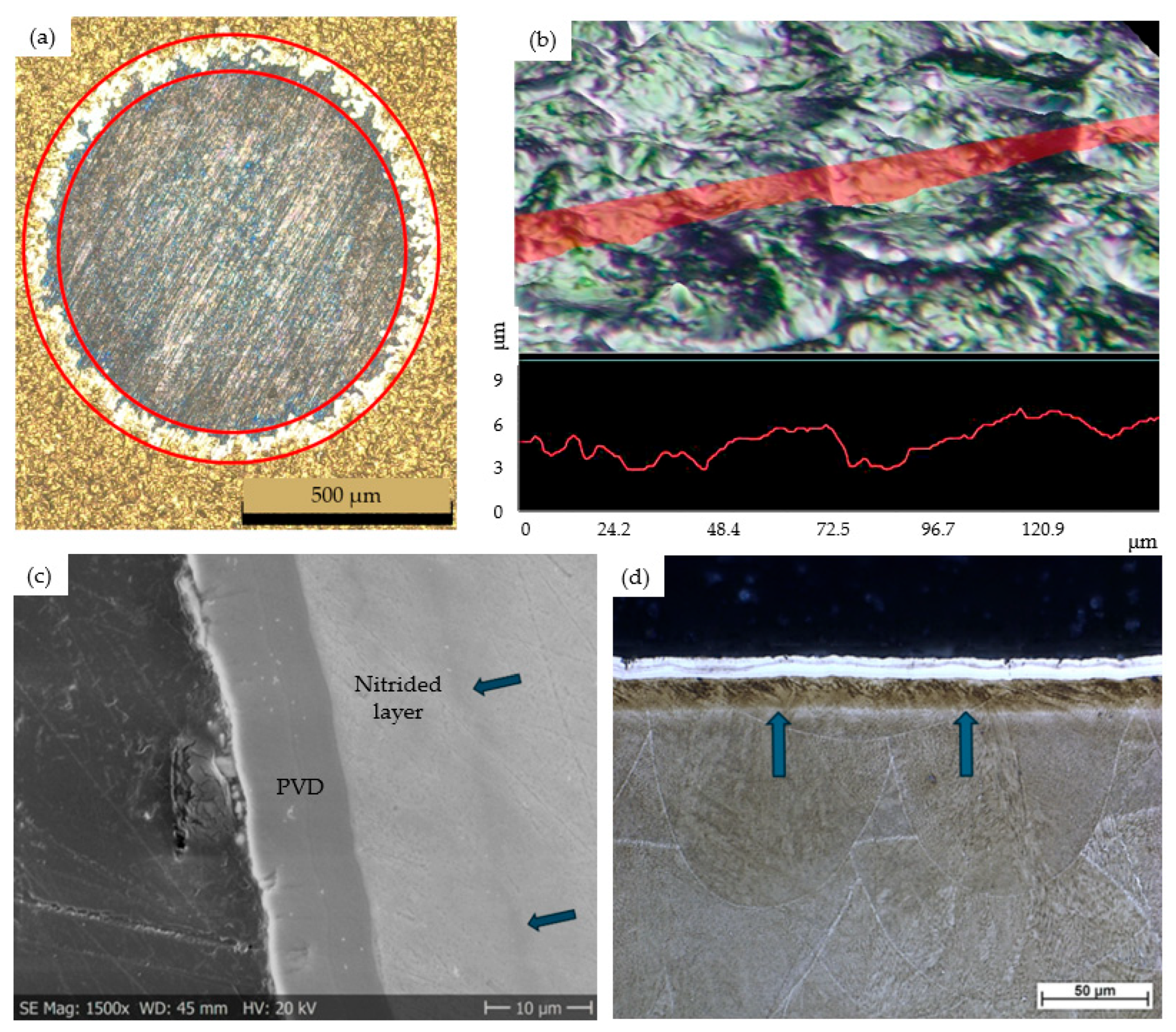
3.3.2. Characterizing the Architecture of the Duplex-Coated Samples
3.3.3. Determining the Case Depth of the Nitrided Layer of the Target Samples by Estimating the In-Depth Hardness Distribution
3.3.4. Estimating the Composite Hardness of the Duplex-Treated, i.e., the Nitrided and PVD-Coated Samples
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
- -
- The temperature and duration of the heat treatment steps can be optimized for simultaneous aging and surface treatment.
- -
- The optimal temperature for simultaneous aging is around 480 °C, while industrial salt bath nitriding requires a higher temperature, approximately 530 °C, at which the alloy would reach its maximum hardness in 20–25 min. However, this short holding time would only result in the formation of a very thin nitrided layer, approximately 10 µm thick.
- -
- The preheating step of heat treatment applied under industrial circumstances also has to be taken into account because it can strongly affect the aging process.
- -
- The samples after PVD coating can be characterized by a surface roughness of around Ra = 0.5 µm. The load applied during hardness testing must be adjusted to the surface roughness of the sample.
- -
- The in-depth hardness distribution of a very thin nitrided layer can be characterised by a set of surface hardness measurements combined with the application of a modified ECM.
- -
- The composite in-depth hardness distribution of a duplex-treated (nitrided + PVD-coated) layer can be characterised by a set of surface hardness measurements combined with the application of a modified ECM.
- -
- The evaluation and interpretation of the test results are effectively supported by the mathematical modeling of the relationship between surface and in-depth hardness functions using, e.g., the applied modified ECM or other appropriate model.
- -
- There is no significant difference between the surface composite hardness of 3D printed maraging steel (P series) and bulk annealed Böhler W720 (B series) samples.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| Test Phase | TEST | Sample ID | Sample Condition | Test Treatment | Test Objective | Observation | Conclusions/Decision |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PRE-TEST | Bulk heat treatment | PP_1 | as-built (3D printed) | no treatment | Comparing the effect of aging on the as-built and annealed 3D-printed steel | No significant difference in the bulk hardness of the annealed vs. as-built 3D printed samples after the same aging treatment. Also, the hardness of the as-printed sample is slightly higher than that of the annealed 3D-printed sample. | Utilize the 3D-printed samples in their as-built condition for the target heat treatment test to save time, energy, and costs. |
| PP_2 | as-built + aged | T = 480 °C; t = 2.5 h | |||||
| PP_3 | as-built + aged | T = 480 °C; t = 4.5 h | |||||
| PP_4 | solution annealed | T = 830 °C; t = 1 h | |||||
| PP_5 | solution annealed + aged | T = 830 °C; t = 1 h and T = 480 °C; t = 2.5 h | |||||
| PP_6 | solution annealed + aged | T = 830 °C; t = 1 h and T = 480 °C; t = 4.5 h | |||||
| DSC test (I) with continuous heating up to T = 600 °C | PP_1.1 | as-built (3D printed, untreated) | Continuous heating up to T = 600 °C with vh = 2, 5, and 10 K/min | Define the temperature range and activation energy of the precipitation-hardening | No significant difference in ΔT and Ea of the aging process for the as-built vs. solution annealed, 3D printed samples | Utilize the 3D-printed samples in their as-built condition for the target test to save time, energy, and costs. | |
| PP_4.1 | solution annealed (T = 830 °C; t = 1 h) (3D printed) | ||||||
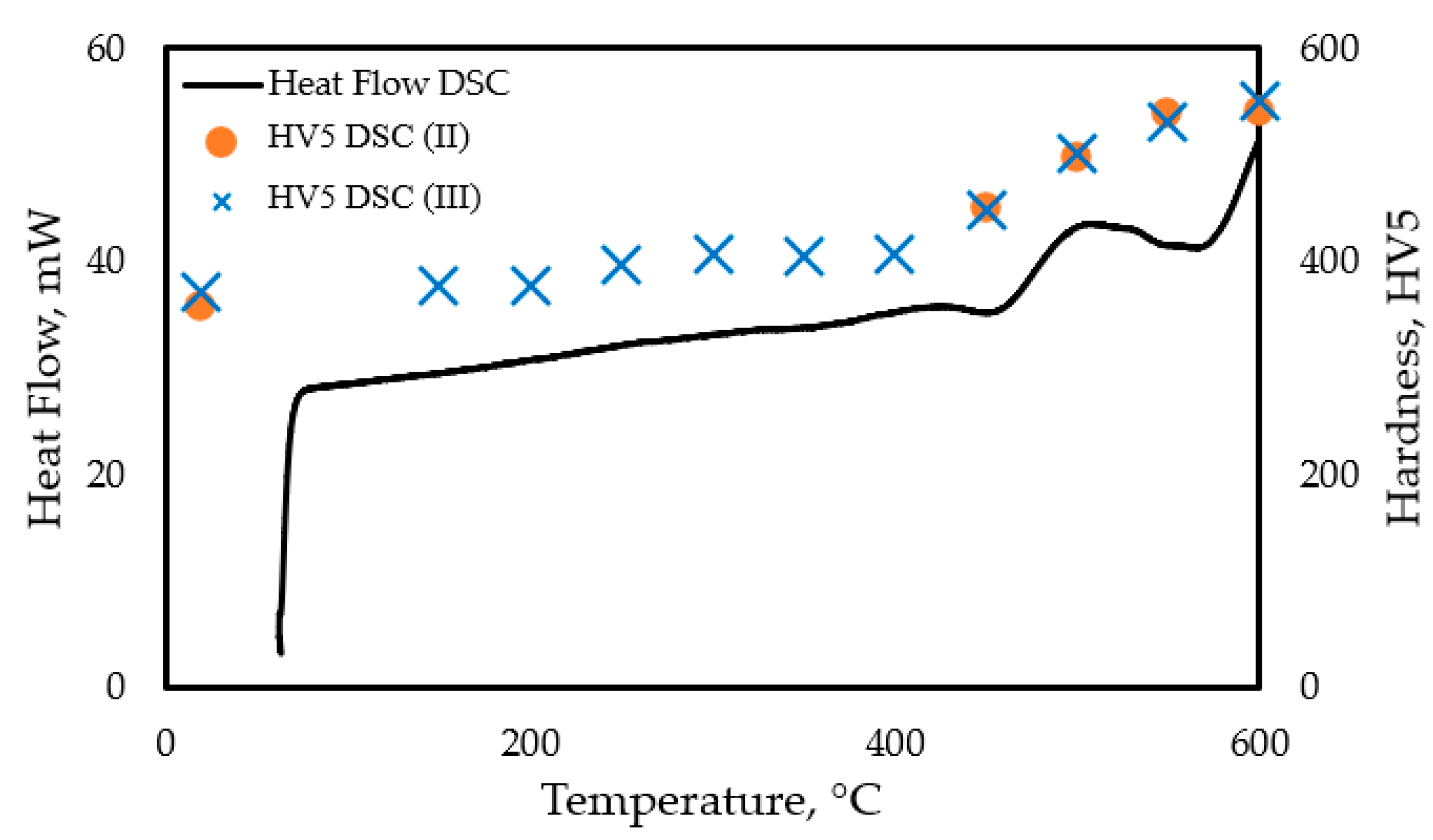
| DSC test (II) with interrupted heating. | PP_1.2 | as-built (3D printed) | Heating up to T = 600 °C, with vh = 10 K/min, interrup-ting (fast cooling + reheating) at 450, 500, and 550 °C | Determine the relationship between the thermal history and the change in hardness. | HV5 microhardness of the samples for the DSC I and DSC II tests is similar. Interruption does not influence the kinetics of the aging process. | The interrupted DSC test is a suitable measuring technique for modeling the kinetics and analyzing the thermodynamics of the precipitation hardening process of 3D printed samples. | |
| DSC test (III) with interrupted heating | PP_1.3 | as-built (3D printed) | Heating up to T = 600 °C, with vh = 10 K/min, interrupting (fast cooling + reheating) between 150 and 600 °C at every heat increment of 50 °C | ||||
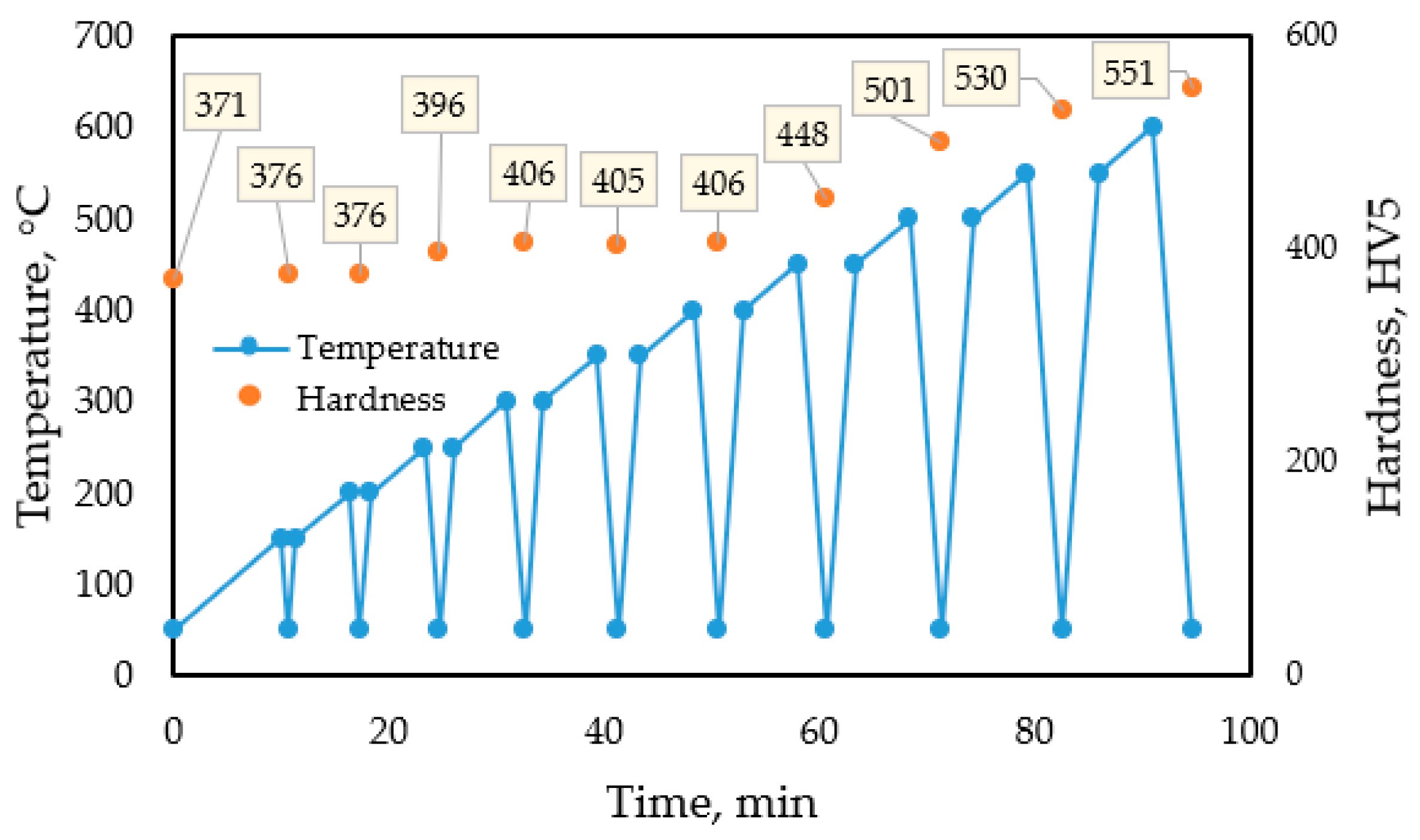
| DSC test (IV) with continuous heating. | PP_1.4 | as-built (3D printed) | Continuous heating up to T = 500 °C, vh = 10 K/min | Comparative analysis of the hardness evolution with no interruption of heating. Defining the heat flow. | HV5 microhardness obtained after aging with continuous heating up to different temperatures is identical to that obtained from the interrupted DSC tests. | ||
| PP_1.5 | as-built (3D printed) | Continuous heating up to T = 550 °C, vh = 10 K/min | |||||
| PP_1.6 | as-built (3D printed) | Continuous heating up to T = 600 °C, vh = 10 K/min | |||||
| DESIGNING THE TARGET-TEST | DSC test (V) at a constant temperature with interrupted holding | PP_1.7 | as-built (3D printed) | Fast heating (vh = 150 K/s) followed by isothermal holding at T = 530 °C and t = 200 min, and interruption at t = 5, 10, 15, 30, 60, 90, 120, 180 min for measuring HV. | Defining the optimal duration of simultaneous nitriding and aging at the designed temperature. | The optimal precipitation-hardened structure, with maximum hardness, forms at a holding time of t = 15–25 min at a temperature of T = 530 °C. The expected nitrided layer thickness, however, is thin: 10–15 µm. | Use a holding time of t = 15–25 min for simultaneous nitriding and aging to achieve maximum hardness. |
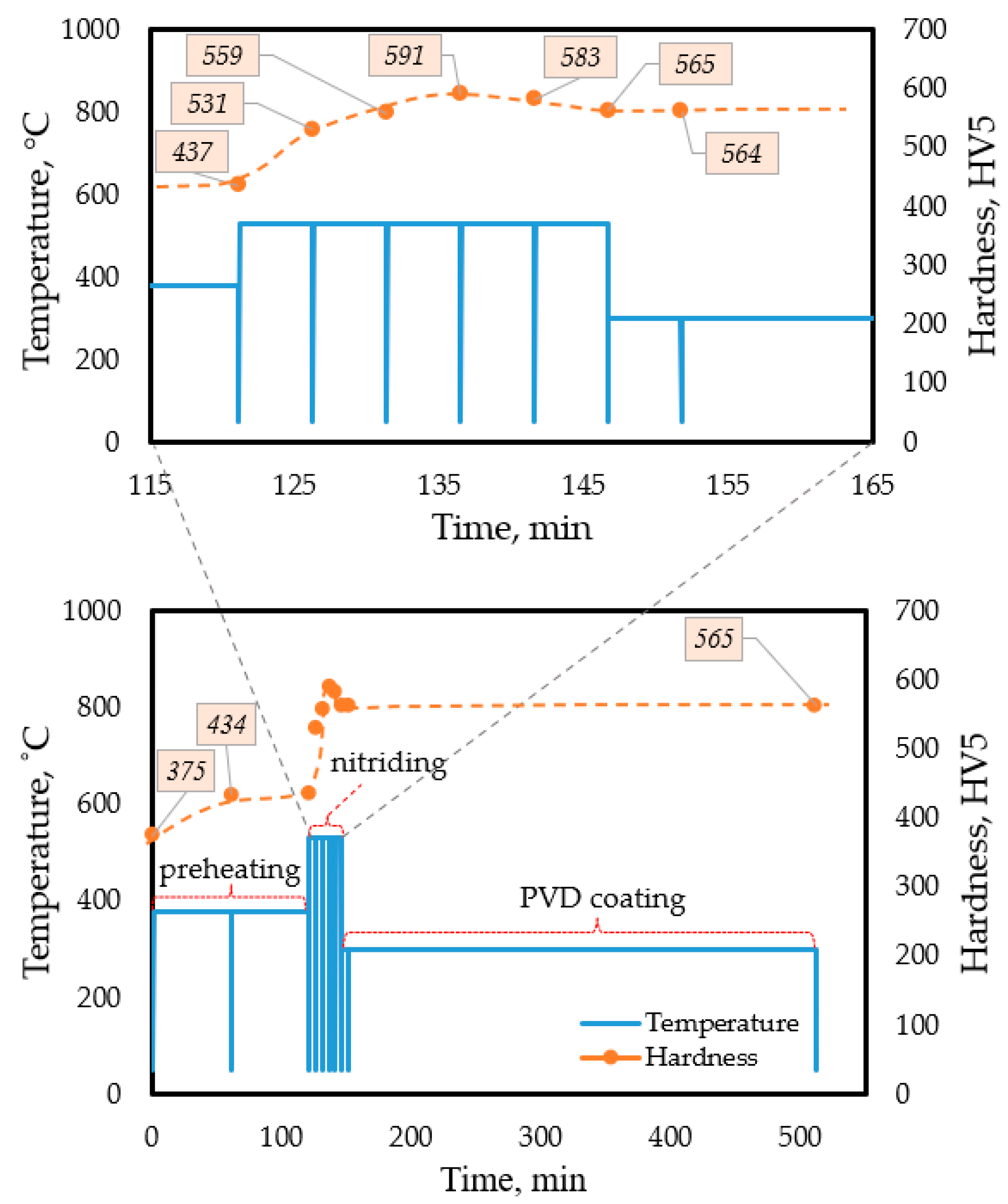
| DSC test (VI) modeling the target test with an interrupted preheating and nitriding cycle | PP_1.7 | as-built (3D printed) | Steps (as planned for the target test): (1) Preheat: T = 380 °C; t = 2 h (2) Nitriding+aging: T = 530 °C; t = 25 min PVD coating: T = 300 °C; t = 8 h | Modeling the complete industrial heat treatment and analyzing the hardness evolution to design the optimal technological parameters for the target test. | The achievable max. hardness is 590 HV reached in 10 min from starting the nitriding step. Due to overaging during the PVD step, the final hardness is approximately 560 HV. | Realize target tests by applying the technological parameters used in the DSC (VI) design test. | |
| TARGET-TEST | Complete industrial heat treatment to produce duplex-coated samples with a maraging steel substrate under different initial conditions. | PT_1 | as-built (3D printed) DLC coated | (1) Preheat: T = 380 °C; t = 1 h (2) Nitriding+aging: T = 530 °C; t = 25 min PVD coating: T = 300 °C; t = 8 h for DLC, TiN, and CrN. | Comparing the surface layer architecture and hardness distribution in duplex-coated samples with maraging steel substrates of different initial conditions. | The hardness distribution in the surface layer of the coated composite material systems is not influenced by the type of the applied substrate materials (bulk or 3D printed) or their heat treatment (whether it is a conventional, multi-step treatment or a simultaneous nitriding + aging process) | The industrial heat treatment process for producing wear-resistant, duplex-coated maraging steel components is suggested to be modified by applying simultaneous nitriding and aging treatments, as well as using 3D-printed components in their as-built condition, rather than the current practice of using bulk, annealed initial base material. |
| PT_2 | as-built (3D printed) CrN coated | ||||||
| PT_3 | as-built (3D printed) TiN coated | ||||||
| BT_1 | bulk, solution annealed (T = 830 °C; t = 1 h) DLC coated | ||||||
| BT_2 | bulk, solution annealed (T = 830 °C; t = 1 h) CrN coated | ||||||
| BT_3 | bulk, solution annealed (T = 830 °C; t = 1 h) TiN coated |
References
- Fonseca, D.P.M.D.; Feitosa, A.L.M.; Carvalho, L.G.D.; Plaut, R.L.; Padilha, A.F. A short review on ultra-high-strength maraging steels and future perspectives. Mater. Res. 2021, 24, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, J.R.; Mills, K.M.; Lampman, S.R. Lampman, Metals Handbook. Vol. 1. Properties and Selection: Irons, Steels, and High-Performance Alloys; ASM International: Materials Park, OH, USA, 1990; p. 1063. [Google Scholar]
- Cajner, F.; Landek, D.; Leskovsek, V. Surface modifications of maraging steels used in the manufacture of moulds and dies. Mater. Tehnol. 2010, 44, 85–91. [Google Scholar]
- Hatos, I.; Fekete, I.; Ibriksz, T.; Kovács, J.G.; Maros, M.B.; Hargitai, H. Surface modification and wear properties of direct metal laser sintered hybrid tools used in moulds. Stroj. Vestn. J. Mech. Eng. 2018, 64, 121–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kladaric, I.; Kozak, D.; Krumes, D. The Effect of Aging Parameters on Properties of Maraging Steel. Mater. Manuf. Process. 2009, 24, 747–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, S.; Li, X.; Liu, Y.; Geng, R.; Lei, S.; Li, Y.; Wang, C. Effect of Aging Treatment on the Microstructure and Properties of 2.2 GPa Tungsten-Containing Maraging Steel. Materials 2023, 16, 4918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Silva, J.J.M.; de Vasconcelos, I.F.; de Oliveira, C.A.S.; Souza, P.H.L.; Loureiro, R.D.C.P.; SLima, M.N.D.; Filgueiras Rodrigues, S.; Ferreira Gomes de Abreu, H. Exploring phase transformation mechanisms in maraging-300 steel during ageing beyond widely applied temperature parameters. Steel Res. Int. 2024, 95, 2300871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simm, T.H.; Sun, L.; Galvin, D.R.; Hill, P.; Rawson, M.; Birosca, S.; Gilbert, E.P.; Bhadeshia, H.; Perkins, K. The Effect of a Two-Stage Heat-Treatment on the Microstructural and Mechanical Properties of a Maraging Steel. Materials 2017, 10, 1346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ASM International Handbook Committee. ASM Handbook, Vol. 4: Heat Treating; ASM International: Metals Park, OH, USA, 1991; pp. 528–548. [Google Scholar]
- Carson, C. Heat Treating of Maraging Steels. In ASM Handbook, Vol. 4D: Heat Treating of Iron and Steels; Dossett, J.L., Totten, G.E., Eds.; ASM International: Metals Park, OH, USA, 2014; pp. 468–480. [Google Scholar]
- Bai, Y.; Wang, D.; Yang, Y.; Wang, H. Effect of heat treatment on the microstructure and mechanical properties of maraging steel by selective laser melting. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2019, 760, 105–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, J.; Tang, Q.; Feng, Q.; Ma, S.; Setchi, R.; Liu, Y.; Han, Q.; Fan, X.; Zhang, M. Effect of heat treatment on microstructure and mechanical behaviours of 18Ni-300 maraging steel manufactured by selective laser melting. Opt. Laser Technol. 2019, 120, 105725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monkova, K.; Zetkova, I.; Kučerová, L.; Zetek, M.; Monka, P.; Daňa, M. Study of 3D printing direction and effects of heat treatment on mechanical properties of MS1 maraging steel. Arch. Appl. Mech. 2019, 89, 791–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godec, M.; Podgornik, B.; Kocijan, A.; Donik, C.; Balantič, D.A.S. Use of plasma nitriding to improve the wear and corrosion resistance of 18Ni-300 maraging steel manufactured by selective laser melting. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 3277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godec, M.; Ruiz-Zepeda, F.; Podgornik, B.; Donik, C.; Kocijan, A.; Balantič, D.A.S. The influence of the plasma-nitriding temperature on the microstructure evolution and surface properties of additive-manufactured 18Ni300 maraging steel. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2022, 433, 128089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, Y.; Dong, D.D.; Lin, S.S.; Wang, W.; Tang, C.M.; Kuang, T.C.; Dai, M.J. Improving surface mechanical properties of the selective laser melted 18Ni300 maraging steel via plasma nitriding. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2021, 406, 126675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balantič, D.A.S.; Donik, C.; Podgornik, B.; Kocijan, A.; Godec, M. Improving the surface properties of additive-manufactured Inconel 625 by plasma nitriding. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2023, 452, 129130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, C.; Zhou, K.; Kuang, M.; Ma, W.; Kuang, T. Microstructural characterization and properties of selective laser melted maraging steel with different build directions. Sci. Technol. Adv. Mater. 2018, 19, 746–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Priyadarshi, A.; Shahrani, S.B.; Choma, T.; Zrodowski, L.; Qin, L.; Leung, C.L.A.; Tzanakis, I. New insights into the mechanism of ultrasonic atomization for the production of metal powders in additive manufacturing. Addit. Manuf. 2024, 83, 104033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koutny, D.; Pantelejev, L.; Tomes, J.; Palousek, D. Comparison of selective laser melting of 18NI maraging steel by PXL and M2 cusing. Laser 2016, 180, 220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mugwagwa, L.; Yadroitsev, I.; Matope, S. Effect of process parameters on residual stresses, distortions, and porosity in selective laser melting of maraging steel 300. Metals 2019, 9, 1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demir, A.G.; Previtali, B. Investigation of remelting and preheating in SLM of 18Ni300 maraging steel as corrective and preventive measures for porosity reduction. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2017, 93, 2697–2709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takata, N.; Nishida, R.; Suzuki, A.; Kobashi, M.; Kato, M. Crystallographic features of microstructure in maraging steel fabricated by selective laser melting. Metals 2018, 8, 440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, C.; Zhou, K.; Ma, W.; Zhang, P.; Liu, M.; Kuang, T. Microstructural evolution, nanoprecipitation behavior and mechanical properties of selective laser melted high-performance grade 300 maraging steel. Mater. Des. 2017, 134, 23–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jägle, E.A.; Sheng, Z.; Kürnsteiner, P.; Ocylok, S.; Weisheit, A.; Raabe, D. Comparison of maraging steel micro-and nanostructure produced conventionally and by laser additive manufacturing. Materials 2016, 10, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chadha, K.; Tian, Y.; Bocher, P.; Spray, J.G.; Aranas, C. Microstructure evolution; mechanical properties, and deformation behavior of an additively manufactured maraging steel. Materials 2020, 13, 2380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frandsen, R.B.; Christiansen, T.; Somers, M.A. Simultaneous surface engineering and bulk hardening of precipitation hardening stainless steel. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2006, 200, 5160–5169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selg, H.; Meka, S.R.; Kachel, M.; Schacherl, R.E.; Waldenmaier, T.; Mittemeijer, E.J. Nitriding behaviour of maraging steel: Experiments and modelling. J. Mater. Sci. 2013, 48, 4321–4335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, S.D.; Tschiptschin, A.P.; Pinedo, C.E. Simultaneous plasma nitriding and ageing treatments of precipitation hardenable plastic mould steel. Mater. Des. 2007, 28, 1714–1718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riazi, H.; Ashrafizadeh, F.; Hosseini, S.R.; Ghomashchi, R. Influence of simultaneous aging and plasma nitriding on fatigue performance of 17-4 PH stainless steel. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2017, 703, 262–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Ara, J.F.; Almandoz, E.; Palacio, J.F.; Fuentes, G.G. Simultaneous ageing and plasma nitriding of grade 300 maraging steel: How working pressure determines the effective nitrogen diffusion into narrow cavities. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2017, 317, 64–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Funch, C.V.; Christiansen, T.L.; Somers, M.A. Gaseous nitriding of additively manufactured maraging steel; nitriding kinetics and microstructure evolution. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2022, 432, 128055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Funatani, K. Low-temperature salt bath nitriding of steels. Met. Sci. Heat Treat. 2004, 46, 277–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeghni, A.E.; Hashmi, M.S.J. The effect of coating and nitriding on the wear behaviour of tool steels. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2004, 155, 1918–1922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polok-Rubiniec, M.; Dobrzański, L.A.; Adamiak, M. Comparison of the adhesion and wear resistance of the PVD coatings. J. Achiev. Mater. Manuf. Eng. 2007, 20, 87–90. [Google Scholar]
- Polok-Rubiniec, M.; Dobrzański, L.A.; Adamiak, M. The properties and wear resistance of the CrN PVD coatings. J. Achiev. Mater. Manuf. Eng. 2008, 30, 165–171. [Google Scholar]
- Maros, M.B.; Siddiqui, S.A. Tribological Study of Simply and Duplex-Coated CrN-X42Cr13 Tribosystems under Dry Sliding Wear and Progressive Loading Scratching. Ceramics 2022, 5, 1084–1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Felde, I. Artificial Intelligence Techniques and Biomimetic Methods Supporting Heat Treatment Processes. Acta Polytech. Hung. 2024, 21, 317–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gadelmawla, E.S.; Koura, M.M.; Maksoud, T.M.; Elewa, I.M.; Soliman, H.H. Roughness parameters. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2002, 123, 133–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burnett, P.; Rickerby, D. The mechanical properties of wear-resistant coatings: I: Modelling of hardness behaviour. Thin Solid Film. 1987, 148, 41–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mata, M.; Casals, O.; Alcalá, J. The plastic zone size in indentation experiments: The analogy with the expansion of a spherical cavity. Int. J. Solids Struct. 2006, 43, 5994–6013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ichimura, H.; Rodriguez, F.; Rodrigo, A. The composite and film hardness of TiN coatings prepared by cathodic arc evaporation. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2000, 127, 138–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ichimura, H.; Ishii, Y.; Rodrigo, A. Hardness analysis of duplex coating. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2003, 169, 735–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Réger, M.; Horváth, R.; Széll, A.; Réti, T.; Gonda, V.; Felde, I. The relationship between surface and in-depth hardness for the nitrocarburizing treatment process. Metals 2021, 11, 812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menczel, J.D.; Judovits, L.; Prime, R.B.; Bair, H.E.; Reading, M.; Swier, S. Differential scanning calorimetry (DSC). In Thermal Analysis of Polymers: Fundamentals and Applications; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2009; pp. 7–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Floreen, S. The physical metallurgy of maraging steels. Metall. Rev. 1968, 13, 115–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiss, B.Z. Maraging steels—Structure; properties; applications. In Specialty Steels and Hard Materials; Pergamon: Oxford, UK, 1983; pp. 35–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tewari, R.; Mazumder, S.; Batra, I.S.; Dey, G.K.; Banerjee, S. Precipitation in 18 wt% Ni maraging steel of grade 350. Acta Mater. 2000, 48, 1187–1200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masneri, C. Microstructural and Mechanical Properties of Maraging Steel Parts Produced by Selective Laser Melting. Master’s Thesis, Politecnico di Milano, Milan, Italy, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Kissinger, H.E. Reaction kinetics in differential thermal analysis. Anal. Chem. 1957, 29, 1702–1706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- SAE J423_202305; Methods of Measuring Case Depth (STABILIZED May 2023). SAE: Warrendale, PE, USA, 2023.
- Brautigam, A.; Szalai, S.; Légmán, N.; Fischer, S. Laboratory Investigation on Seams between Rails and Hardened Fine-grained, as well as Hadfield Steel Plates with Manual Arc Welding. Acta Polytech. Hung. 2025, 22, 83–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ISO 18203:2016; Steel—Determination of the Thickness of Surface-Hardened Layer. ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2016.
- Frank, H.; Ambos, M.; Lutze, S.; Scholz, M. Improvement of the properties of additively manufactured steel parts by combination of heat treatment and hard coatings. In IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering; IOP Publishing: Bristol, UK, 2021; Volume 1147, No. 1; p. 012001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casati, R.; Lemke, J.N.; Tuissi, A.; Vedani, M. Aging behaviour and mechanical performance of 18-Ni 300 steel processed by selective laser melting. Metals 2016, 6, 218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







| Maraging Steel Grade | Shape of the Raw Material | Element, wt% | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ni | Co | Ti | Mo | Al | Mn | C | Si | ||
| EOS MS1 | powder, grain size of d = 20–30 µm | 18.1 | 9 | 0.7 | 4.8 | 0.1 | ≤0.1 | ≤0.03 | ≤0.1 |
| Böhler W720 | hot rolled commercial rod, D = 30 mm | 18.5 | 9 | 0.7 | 5 | 0.1 | ≤0.1 | ≤0.03 | ≤0.1 |
| 3D Printed Sample | Treatment | Hardness, HV5 6 Measurements | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Solution Annealing | Aging | |||||||
| No | Condition | Temp., °C | Time, h | Temp., °C | Time, h | Average | St. dev. | Coeff. of var., % |
| PP1 | as-built | – | – | – | – | 340–375 | 13.7 | 3.8 |
| PP2 | as-built+aged | – | – | 480 | 2.5 | 570 | 9.0 | 1.6 |
| PP3 | as-built+aged | – | – | 480 | 4.5 | 601 | 11.3 | 1.9 |
| PP4 | annealed | 830 | 1 | – | – | 280 | 6.0 | 2.1 |
| PP5 | annealed+aged | 830 | 1 | 480 | 2.5 | 573 | 4.1 | 0.7 |
| PP6 | annealed+aged | 830 | 1 | 480 | 4.5 | 609 | 4.4 | 0.7 |
| Sample Condition | Temperature Range (°C) at a Heating Rate of 5 K/min | Activation Energy (kJ/mol) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Peak 1 | Peak 2 | Peak 1 | Peak 2 | |
| As built | 359.2–447.3 | 442.2–551.2 | 223.8 | 235.4 |
| Solution annealed | 356.7–440.6 | 438.1–549.3 | 324.2 | 258.1 |
| Samples | Base Material | EOS MS1 | Böhler W720 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Initial Condition | 3D Printed (No Annealing) | Bulk, Solution Annealed | |||||
| Designation | PT1 | PT2 | PT3 | BT1 | BT2 | BT3 | |
| Characteristics of the nitrided layer | Thickness by OM, µm | 9 | 10 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 10 |
| Thickness by SEM, µm | 9 | 10 | 10 | 9 | 10 | 10 | |
| Surface roughness, Ra, µm | 0.021 | 0.024 | 0.019 | 0.019 | 0.022 | 0.020 | |
| Rz, µm | 0.149 | 0.155 | 0.148 | 0.144 | 0.124 | 0.116 | |
| Characteristics of the PVD coating | Type of coating | DLC | CrN | TiN | DLC | CrN | TiN |
| Thickness by OM, µm | 2.1 | 7.1 | 1.6 | 1.9 | 7.4 | 1.8 | |
| Thickness by SEM, µm | 2.7 | 7.2 | 2.1 | 2.6 | 7.3 | 2 | |
| Thickness by Calotest, µm | 2.8 | 7.2 | 2.1 | 2.9 | 7.2 | 2.2 | |
| PVD thickness average, µm | 2.7 | 7.2 | 2.1 | 2.7 | 7.2 | 2.1 | |
| Surface roughness, Ra µm | 0.48 | 0.65 | 0.46 | 0.58 | 0.68 | 0.38 | |
| Rz, µm | 2.96 | 3.94 | 2.65 | 3.61 | 4.49 | 2.67 | |
| Substrate core hardness, HV5 | Average | 537 | 534 | 534 | 538 | 532 | 536 |
| St. Dev. | 7.4 | 7.2 | 6.2 | 5.6 | 4.2 | 5.8 | |
| Var. coeff., % | 1.4 | 1.3 | 1.2 | 1.0 | 0.8 | 1.1 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Olesnyovicsné, Z.S.; Széll, A.; Horváth, R.; Maros, M.B.; Réger, M. Hardness Characterization of Simultaneous Aging and Surface Treatment of 3D-Printed Maraging Steel. Materials 2025, 18, 4830. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18214830
Olesnyovicsné ZS, Széll A, Horváth R, Maros MB, Réger M. Hardness Characterization of Simultaneous Aging and Surface Treatment of 3D-Printed Maraging Steel. Materials. 2025; 18(21):4830. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18214830
Chicago/Turabian StyleOlesnyovicsné, Zsuzsa Szabadi, Attila Széll, Richárd Horváth, Mária Berkes Maros, and Mihály Réger. 2025. "Hardness Characterization of Simultaneous Aging and Surface Treatment of 3D-Printed Maraging Steel" Materials 18, no. 21: 4830. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18214830
APA StyleOlesnyovicsné, Z. S., Széll, A., Horváth, R., Maros, M. B., & Réger, M. (2025). Hardness Characterization of Simultaneous Aging and Surface Treatment of 3D-Printed Maraging Steel. Materials, 18(21), 4830. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18214830






